Reading the abovementioned article
1, I was disappointed by the idea (which is shared by most researchers) that
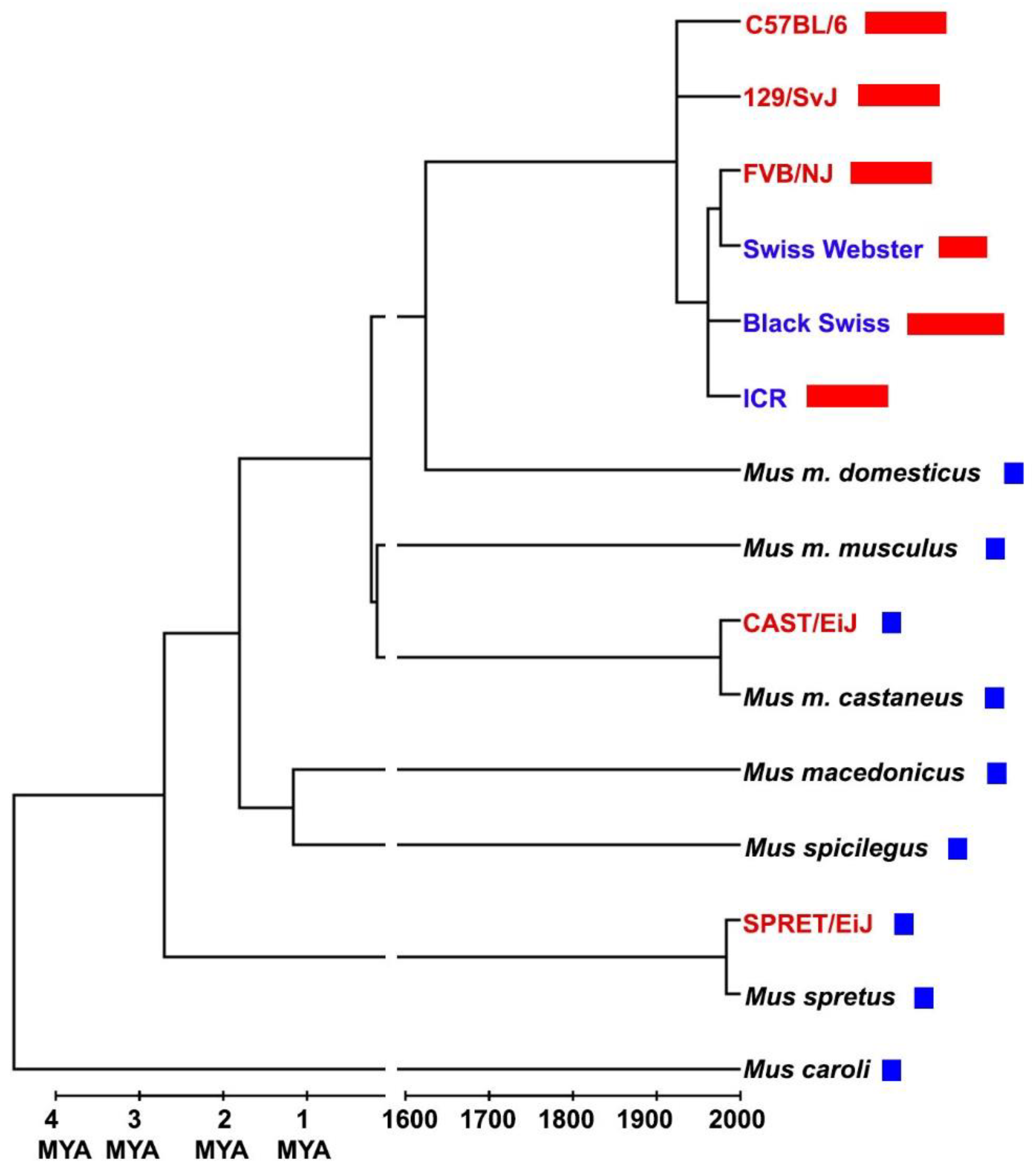
Mus musculus has very long telomeres. In reality, this a characteristic of “classical” laboratory strains (
Figure 1). Nonetheless, since the authors successfully reached their aim, I was surprised by the following contradiction: laboratory mice show the conserved character of having methionine 492 (M492) in RTEL1, but have not the conserved character of “short” (15-20 kb) telomeres, while
Mus spretus has not the conserved M492, but has the conserved character of short telomeres. So, I checked for RTEL1 in all other
Mus species and subspecies (identifying new orthologs in species for which only genome assemblies are available) and found that M492 is conserved in all species (
Figure S1 in Supplementary material). Finally, I used
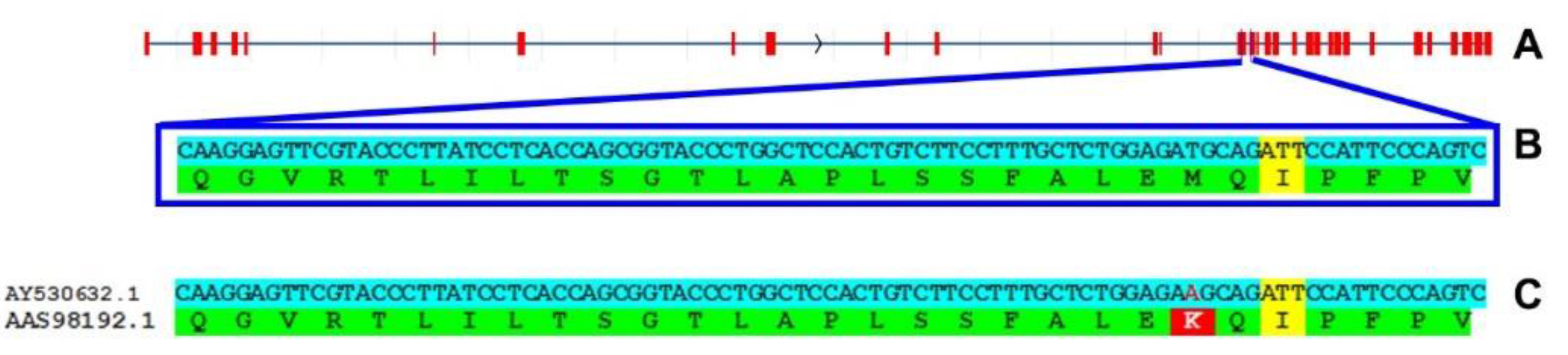
Mus spretus genome assemblies to predict
de novo the protein sequence and I found a surprise: RTEL1 in
Mus spretus has M492 (
Figure 2). Then I found that also the sequence present in the Ensembl genome database (
www.ensembl.org) is identical to the one predicted by me (
Figure S1 in Supplementary material). Because of all these findings, it can be said that
Mus spretus protein sequence of RTEL1 (deposited by Ding et al.
2 and used by Smoom et al. in their article
1) in the GenBank database shows a wrong amino acid in position 492. Thus, the amino acid 492 of RTEL1 is not responsible for the difference in telomere length between laboratory mice and
Mus spretus (as well as between laboratory mice and all other mice).
Because of a false premise (i.e., K492 in Mus spretus), the Telomouse does not mimic the condition in the Algerian mouse. Nonetheless, it is a useful inbred strain (congenic with the popular C57BL/6) with human-like telomere length. Moreover, it could recapitulate the RTEL1-related Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome (HHS), since many patients with this disease show the M492I variation3. Someone could object that Telomouse is a bad model for recapitulating HHS, because mice have telomerase activity and humans have not. However, this is an over-simplification (although very popular): in reality, many human cells (especially, but not limited to, hematopoietic stem cells) show telomerase activity4.
Beside the potential use of Telomouse, the results obtained by Smoom et al. open up new intriguing questions. How much the telomeres of Telomouse fibroblasts would shorten in vitro if grown at physiological oxygen levels (i.e., 5% instead of the usually employed atmospheric 20%). Is the telomere shortening observed in vitro and between generations of Telomouse ascribable only to a decrease in telomerase activity at telomeres? Or the reduced activity of RTEL1 has consequences also on Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres (ALT)? The authors found no differences in telomeric recombination (indicative of ALT) in vitro, but this does not exclude differences, for example, in oocytes and cleavage stage embryos. In these, in fact, telomere elongation has been observed also in telomerase-null mice and ALT activity has been reported5.
Another important question, not strictly related to Telomuse, is the link between RTEL1 and the presence of very long telomeres in laboratory mice. Smoom et al. already indicated that M492 is present in rodent species (excluding
Mus spretus, according to them) with short telomeres and thus cannot explain telomere length differences between these and laboratory mice
1. Here I demonstrated that this is valid also for
Mus spretus. Moreover, I found that there is no amino acid that is conserved in short-telomeres
Mus species and is modified in long-telomeres strains (
Figure S2 in Supplementary material). Therefore, differences in telomere length cannot be ascribed to differences in RTEL1 protein sequence. Nonetheless, the
Rtel1 gene was at first discovered as a chromosome locus responsible for telomere length differences between
Mus spretus and BALB/c
6 mice and a subsequent study showed that in crosses between
Rtel1+/- laboratory mice and
Mus spretus, the ones with
Rtel1+ allele had long telomeres and the ones with
Rtel1- had short telomeres
2. Different explanations can be proposed: 1) the study of Ding et al.
2 had some unidentified error and RTEL1 is not responsible at all for differences in telomere length; 2) differences between
Mus species/strains are due to differences in the relative abundance of RTEL1 isoforms; 3) differences in telomere length are due to the
Rtel1 gene, but the variations are in the promoter (causing different levels of transcription) and not in the coding sequence. I found that among the conserved (in wild species) nucleotides in the promoter, only two are modified in laboratory strains: one of the two is a C>T modification, changing a -CAAC- into a -CAAT-. However, although attractive, it does not really resemble a CCAAT box and seems to far from the transcription start site. In any case, these hypotheses can be easily tested by quantitative PCR and Western blot, in order to assess relative abundance of variant transcripts and protein isoforms.
The last issue (which in my personal opinion is the most important) regards telomere length in
Mus musculus. The mystery of how and why long telomeres appeared in laboratory strains has not been solved: it seems like it is not due to inbreeding (
Figure 1) and many hypotheses can be raised on domestication of mice and increase of mating period, ALT and telomerase activity in germ cells, epigenetics and so on. But beside these questions, one thing should be clarified:
Mus musculus (and even
Mus musculus domesticus) has NOT long telomeres. This is a characteristic of laboratory strains (for the history of their ancestry, see
7) and not of the species (or subspecies). Not grasping this aspect can lead to errors and false conclusions in studies on inter-species comparison or when physiological and life history traits are regressed against telomere length. For example, because of the plausible link between telomeres and aging, many researchers have regressed telomere length
8-9 (or telomere shortening rate
10-11) against maximum lifespan. However, the telomere length used for
Mus musculus is always the one of laboratory strains (40-100 kbp, heavily influencing every regression) and the maximum lifespan is the one of wild mice (4 years
12). Similar considerations can be made on studies on the evolution of telomeres in mammals
9. In conclusion, when dealing with telomere length, attention should be paid to the differences between
Mus musculus as a species and laboratory strains.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the published article and in the Supplementary material. RTEL1 sequences have been deposited in GenBank with accession number XXXXX.
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
References
- Smoom, R. , May, C.L., Ortiz, V. et al. Telomouse—A mouse model with human-length telomeres generated by a single amino acid change in RTEL1. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 6708. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; et al. Regulation of murine telomere length by Rtel: An essential gene encoding a helicase-like protein. Cell 2004, 117, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; et al. Inherited mutations in the helicase RTEL1 cause telomere dysfunction and Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013, 110, E3408–E3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udroiu, I. , Marinaccio, J., Sgura, A. Many functions of telomerase components: Certainties, doubts, and inconsistencies. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 15189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; et al. Telomere lengthening early in development. Nat Cell Biol 2007, 9, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L. , Hathcock, K.S., Hande, P., Lansdorp, P.M., Seldin, M.F., Hodes, R.J. Telomere length regulation in mice is linked to a novel chromosome locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998, 95, 8648–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; et al. A sequence-based variation map of 8.27 million SNPs in inbred mouse strains. Nature 2007, 448, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seluanov, A.; et al. Telomerase activity coevolves with body mass not lifespan. Aging Cell 2007, 6, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.M.; et al. Comparative biology of mammalian telomeres: Hypotheses on ancestral states and the roles of telomeres in longevity determination. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittemore, K. , Vera, E., Martínez-Nevado, E., Sanpera, C., Blasco, M.A. Telomere shortening rate predicts species life span. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2019, 116, 15122–15127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udroiu, I. On the correlation between telomere shortening rate and life span. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2020, 117, 2248–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.A. , Harper, J.M., Dysko, R.C., Durkee, S.J., Austad, S.N. Longer life spans and delayed maturation in wild-derived mice. Exp Biol Med 2002, 227, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).