1. Introduction
Neuropathic pain consists in one of the most incapacitating pains representing a significant non met medical need [
1]. There are several conditions that can cause neuropathic pain such as traumatic and metabolic nerve lesions, infections, discal disease, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, head trauma or stroke [
1].
There have been several challenges in the definition of neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain was defined as “pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction of the nervous system” [
2] in 1994 and in 2008 the definition was modified to “pain arising as a direct consequence of a lesion or disease affecting the somatosensory system” [
2]. In 2011, a novel definition of neuropathic pain emerged as “pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory system” [
3]. Absent from the definition is the term “dysfunction” because some chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia or complex regional pain syndrome, are central nervous system related dysfunction without evidence of nerve lesion or without evidence of injury in the tissue. The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) proposed, in 2017, a new classification for chronic pains [
4] which includes the neuropathic pain [
5], and this condition is nowadays integrated into the International Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-11) of the World Health Organization (WHO) [
6]. The neuropathic pain classification differentiates pain with peripheral origin and pain with central origin and encompasses nine conditions, such as postherpetic neuralgia, painful nerve lesion or painful neuropathies [
5]. Each condition is part of detailed models, that describes investigations supporting a definitive diagnosis and that contains codes for temporal aspects, psychosocial factors and severity associated with pain. Interestingly, there is no requirement for chronicity to meet the nowadays definition of neuropathic pain. However, chronicity is often assumed. In fact, the update of the definition wants to show that this pain may occur acutely [
3]. Post-surgical pain, acute sciatica or Guillain-Barré syndrome, are some examples of conditions that can induce acute neuropathic pain.
The management of neuropathic pain stays a really challenge despite some promising results of drugs acting on novel targets [
7,
8]. In fact, some recent meta-analysis evaluations highlighted that just about 30% to 40% of patients with neuropathic pain have an appropriate response when compared with placebo and that the efficacy of drugs has become even poorer [
9,
10]. Despite some exciting results with several targets and classes of drugs different therapeutic strategies are required, namely in intractable neuropathic pain. These strategies include rational combination therapy, repositioning of drugs, individualised pain management, including cognitive-behavioral approaches, along with neurostimulation techniques.
Included in the group of the neurostimulation techniques, a non-invasive brain stimulation technique emerged in the last decades, namely the transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). TMS uses a transient magnetic field to produce electrical currents over the cortex [
11] and neuropathic pain seems to be shooted by the use of high-frequency (about 5Hz to 20Hz) stimulation of the contralateral primary motor cortex and using stimulation of high intensity (about 1500 to 2000 pulses per session) [
12,
13]. Two recent studies with placebo control using robotised neuronavigation and double-blind design confirmed the efficacy of sessions of TMS on the primary motor cortex in patients with peripheral [
14] and with central neuropathic pain [
15]. Safety was excellent with transient headache being the main side-effect. According to Lefaucheur et al. level A evidence is proposed for the use of high frequency TMS over the primary motor cortex contralateral to pain side in the management of neuropathic pain [
11]. Level A evidence means definite efficacy [
11].
Based on the challenges in neuropathic pain management and on the putative role of TMS, we performed an analysis of the literature using a bibliometric approach. This approach has been used recently to provide a general overview of the trend of publication in a certain field of research and has considerable advantages over narrative reviews, namely its higher objectivity and intuitive analysis [
16]. Interestingly, a group of authors recently carried out a bibliometric analysis that aim to provide a bibliometric perspective regarding articles on pain and transcranial direct current stimulation (TDCS) [
17]. TDCS is different of TMS because TDCS works by using a low voltage source of electricity that delivers a fixed current of low intensity between two electrodes placed on the scalp of the patient [
18]. Although being different approaches, that study along with the present one, shows the utility of bibliometric analysis. To our knowledge, however, there are no bibliometric analysis that focus specifically on the role of TMS to treat neuropathic pain, so it is relevant to perform such a study. The primary objective of this study was to identify the scientific production linked to the use of TMS to treat neuropathic pain and to provide an overview of the research developments in this field.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
A bibliometric analysis was carried out to evaluate the research on the use of TMS to treat neuropathic pain, from inception to July 6, 2023. The search had no restrictions.
2.2. Bibliographic database and journal impact factor value source
The bibliographic database used in this study took into consideration the broadest possible coverage regarding publications that address the subject under study. We opted for Scopus, a peer-reviewed database that is a generalized and broader database that allows us to use several tools for data extraction and aggregation in different formats, providing a detailed information for the analysis. Furthermore, Scopus is the largest abstract and citation database. The value of each journal impact factor (JIF) was obtained from the Journal Citation Reports.
2.3. Search expression
Firstly, we defined a search term using terms found in relevant articles or documents and then we calibrated the search [
19] through testing attempts considering combined and separate terms. The final search expression was obtained with the TITLE-ABS-KEY filter as follow:
2.4. Software and data analysis
All articles were analyzed by index and author keywords, document by source, publication year, type, country, top-cited articles and authors. Index keywords and author keywords were analyzed by frequency. We performed a ranking of publication sources by relevance. The total and the average number of citations were analyzed by country. By computing the number of multi-authored and the number of single publications we performed the co-authorship and the authorship analysis. In the analysis we used the VOSviewer [
20], a software program specifically designed for this type of analysis. VOSviewer allows the visualization of similarities and allows to build a similarity matrix from a co-occurrence matrix using association strength [
21]. The result is a two-dimensional map where similarity is reflected by the distance between elements [
21]. Microsoft Excel supported the preparation of the data exported from Scopus to perform the analysis.
3. Results
A search on Scopus was performed on July 6, 2023. A total of 474 documents were obtained.
3.1. Keywords
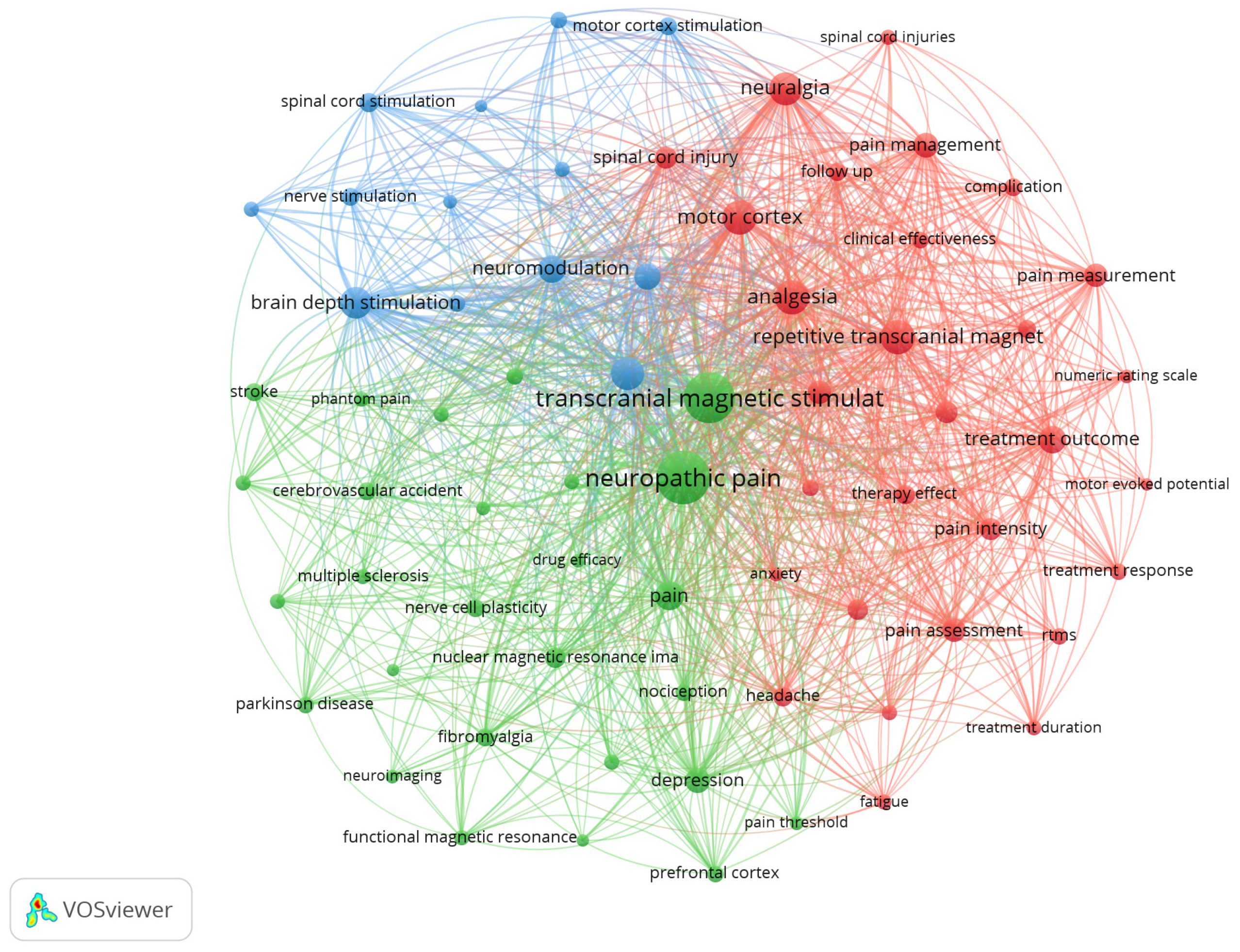
The minimum number of occurrences of a keyword was set at 25. Of 4470 keywords, 119 meet this minimum threshold (25 occurrences). For each of 119 keywords, total strength of the co-occurrence links with other keywords was calculated and the keywords with the highest total link strength were selected. More general terms such as “human” (423 occurrences), “humans” (312 occurrences), “article” (199 occurrences), “review” (183 occurrences), “female” (155 occurrences) or “male” (152 occurrences) were not considered for the analysis.
The Top 10 most relevant index or author keywords and their frequencies were “neuropathic pain” (401 occurrences; total link strength of 3894), “transcranial magnetic stimulation” (377 occurrences; total link strength of 3707), “analgesia” (173 occurrences; total link strength of 2075), “repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation” (166 occurrences; total link strength of 1783), “motor cortex” (164 occurrences; total link strength of 1770), “neuralgia” (159 occurrences; total link strength of 1720), “chronic pain” (153 occurrences; total link strength of 1649), “brain depth stimulation” (139 occurrences; total link strength of 1580), “pain” (125 occurrences; total link strength of 1330) and “treatment outcome” (108 occurrences; total link strength of 1205).
The co-occurrence of terms and words related to the study shows that the chosen search expression was relevant. This analysis was performed using the VOSviewer wich allows us to construct
Figure 1. The highest co-occurrence appears between “neuropathic pain” and “transcranial magnetic stimulation”.
3.2. Publication year
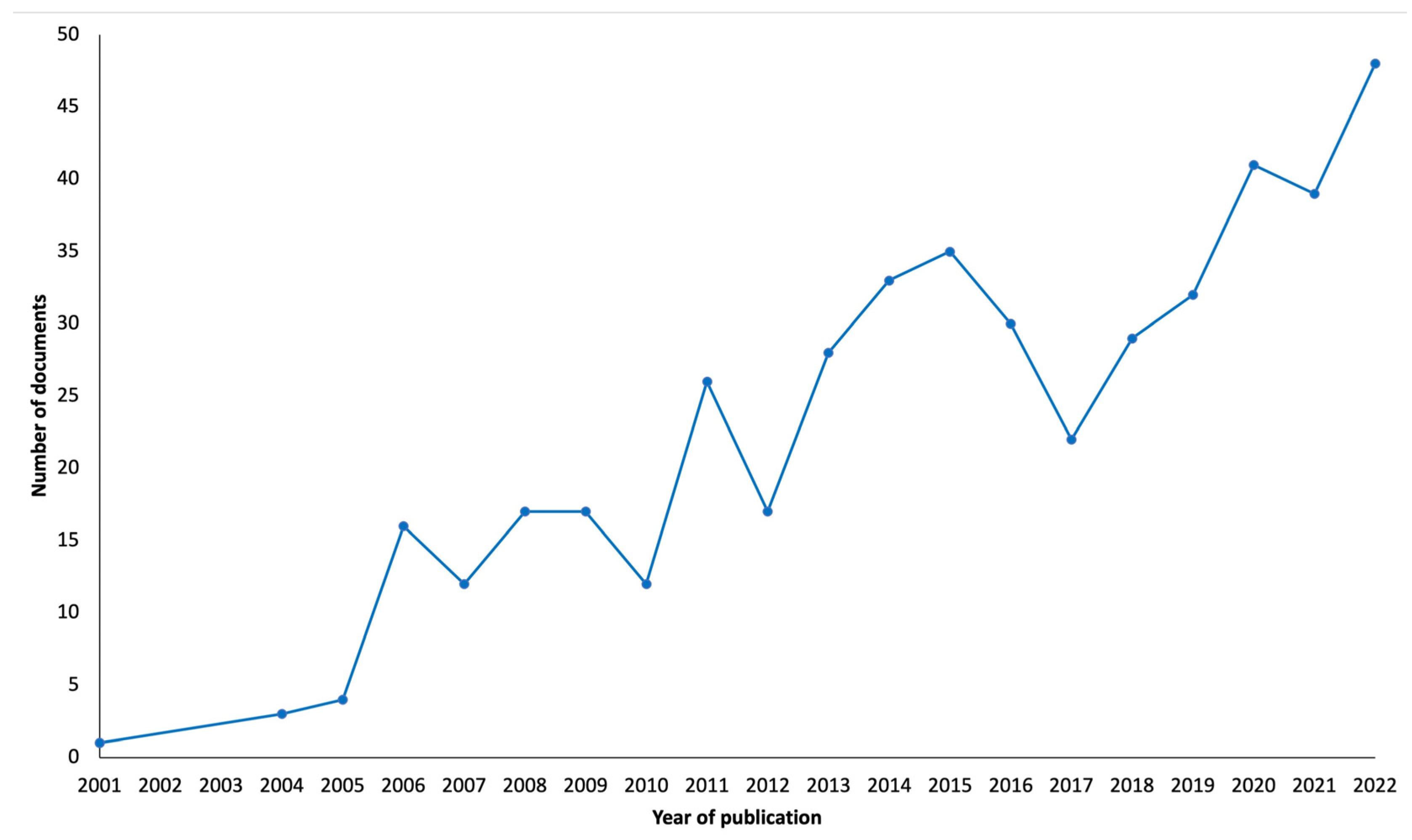
The results in
Figure 2 show that the interest in the use of TMS to treat neuropathic pain begun in the start of the twenty-first century, with the first publication about this theme in 2001 [
22]. More precisely, the first results in this domain were reported at the First International Symposium on Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, held in Göttingen, Germany, in October 1998 and published as an abstract in Clinical Neurophysiology [
23]. By the following years more publications in this area begun to appear and in 2013 this topic started to have a greater appearance on literature. In the past recent years, namely 2020, 2021 and 2022 this topic has obtained even more attention from investigators with 2022 being the year with more publications ever (n=48). The largest increment of publications happened between 2010 and 2011 (from 12 to 26 documents).
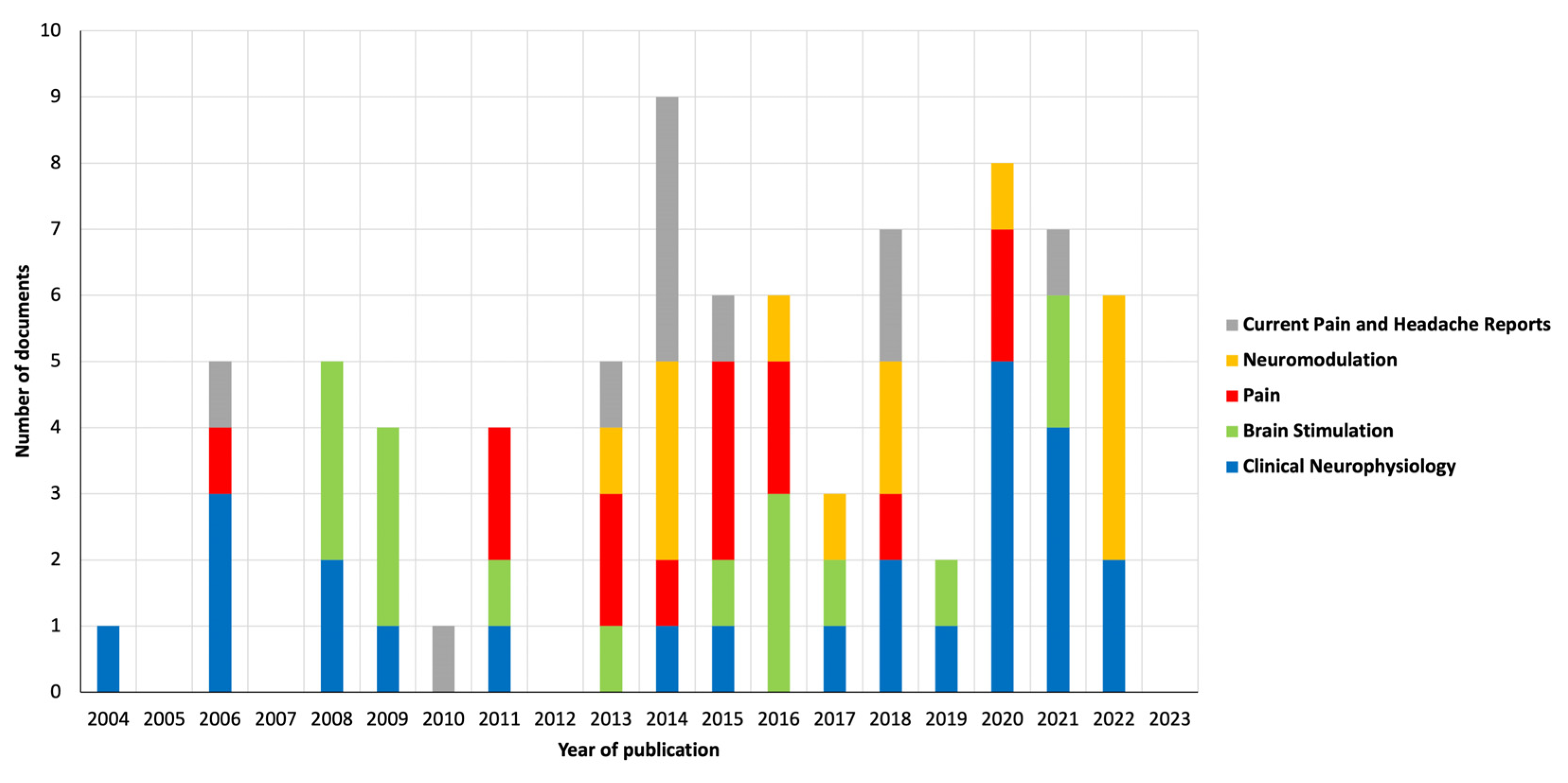
3.3. Source
Figure 3 shows the number of publications by the five most productive sources along the years. The source with the highest number of publications was the journal “Clinical Neurophysiology” (2022 JIF of 4.7), with a total of 25 publications (n=25) since 2004. The Top 10 most productive sources also included “Brain Stimulation” (2022 JIF of 7.7; n=16), “Pain” (2022 JIF of 7.4; n=14), “Neuromodulation” (2022 JIF of 2.8; n=13), “Current Pain and Headache Reports” (2022 JIF of 3.7; n=11), “Brain Sciences” (2022 JIF of 3.3; n=8), “European Journal of Pain” (2022 JIF of 3.6; n=8), “Pain Physician” (2022 JIF of 3.7; n=8), “Journal of Pain” (2022 JIF of 4.0; n=7) and “Frontiers in Human Neuroscience” (2022 JIF of 2.9; n=6). In 2022 the source of the Top 10 most productive sources with more publications was the “Neuromodulation” with a total of 4 documents.
3.4. Study type
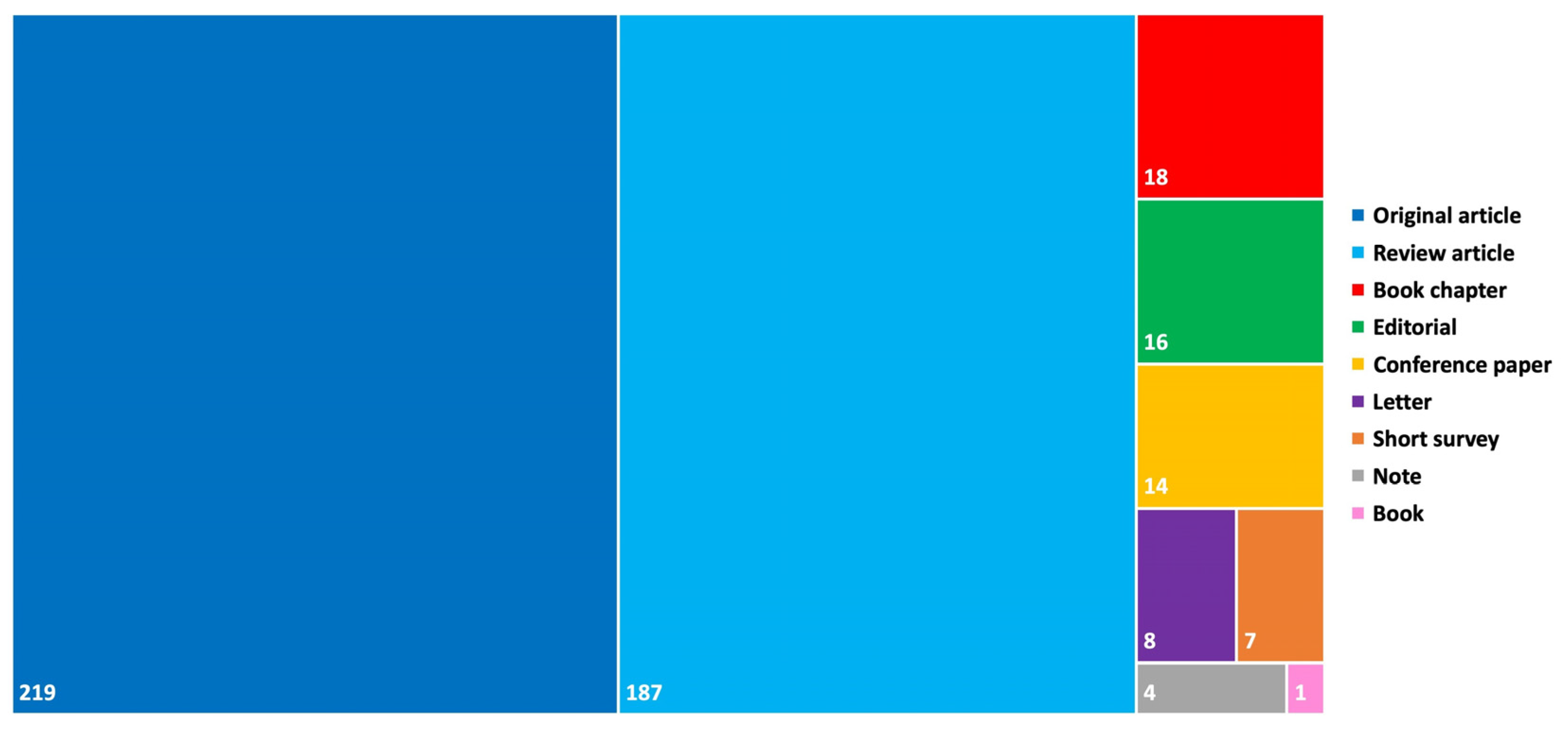
As shown in
Figure 4, the three most frequent types of documents in the results were “original article” (n=219, 46.2%), “review article” (n=187, 39.5%) and “book chapter” (n=18, 3.8%). Other publication types include “editorial” (n=16), “conference paper” (n=14), “letter” (n=8), “short survey” (n=7), “note” (n=4) and “book” (n=1). Regarding the “original article” type, two periods had the highest number of publications: 2013 to 2016 (n=62) and 2018 to 2021 (n=79). On another way, the highest number of publications from the type “review article” occurred in two periods: 2014 to 2017 (n=41) and 2020 to 2022 (n=60). The year with the higher number of publications was 2019 (n=20) for “original article” type and 2022 (n=27) for “review article” type.
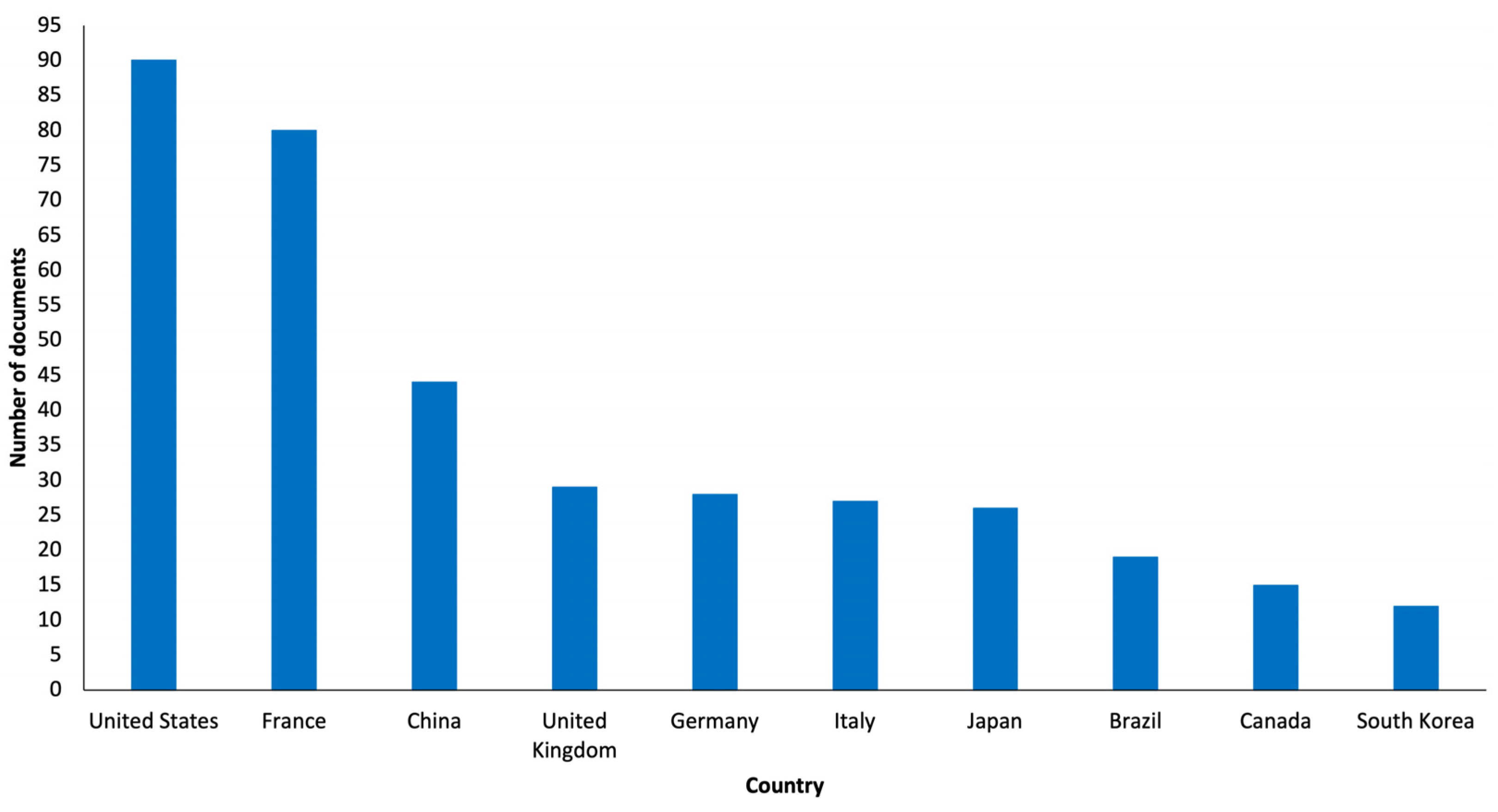
3.5. Country
The country assessment took into account the country of affiliation of the first author of the articles as unit of analysis. Notably, as shown in
Figure 5, most of the documents were originated in the United States (n=90, 19.0%), with the highest number of publications in 2014 (n=14). Top 10 most productive countries also included France (n=80, 16.9%), China (n=44, 9.3%), United Kingdom (n=29, 6.1%), Germany (n=28, 5.9%), Italy (n=27, 5.7%), Japan (n=26, 5.5%), Brazil (n=19, 4%), Canada (n=15, 3.2%) and South Korea (n=12, 2.5%). Interestingly in the United States around 50.0% of the documents were “review articles” (n=45) and around 34.4% of the documents were “original articles” (n=31) and in France around 56.3% of the documents were “original articles” (n=45) and around 23.8% of the documents were “review articles” (n=19).
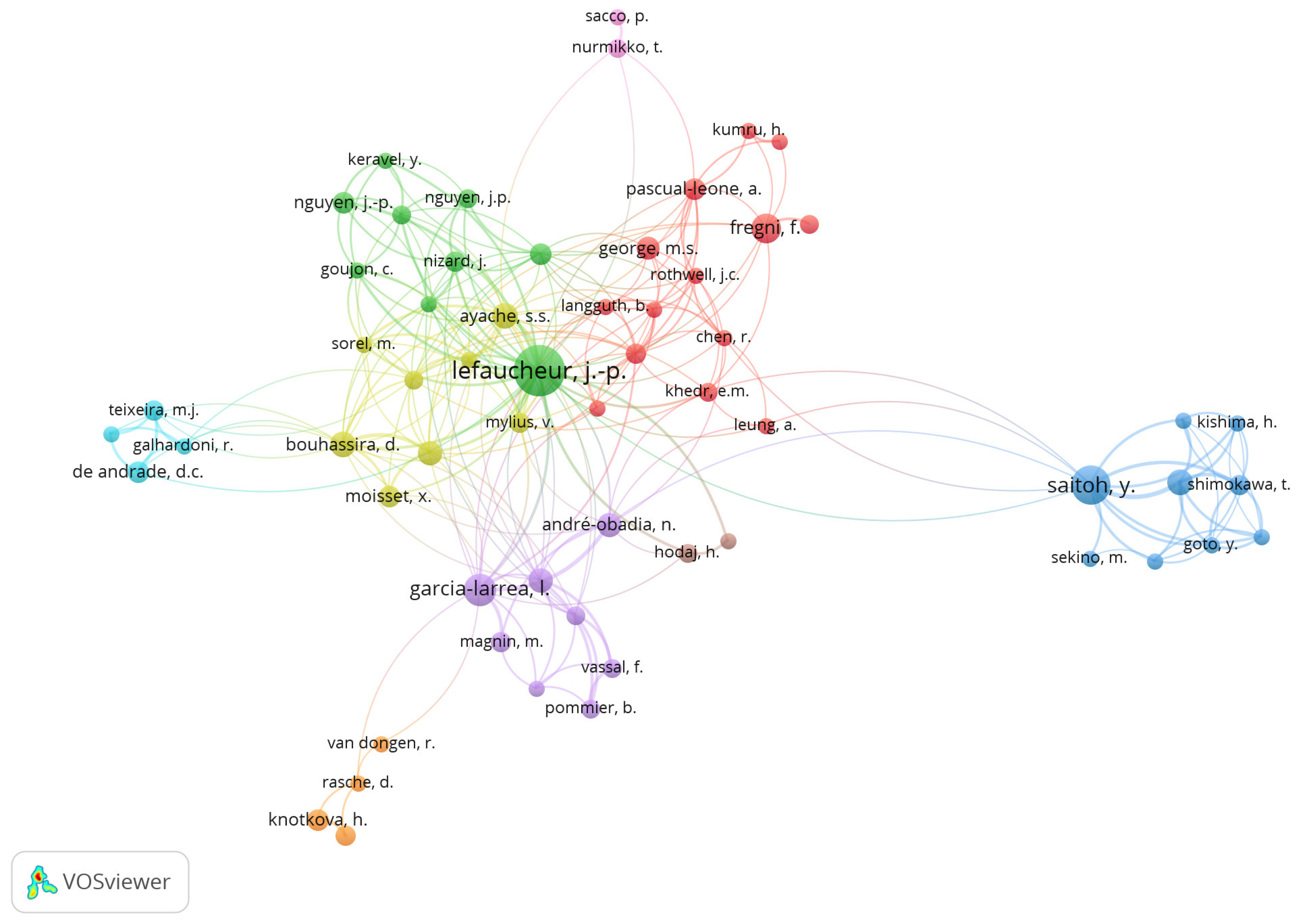
3.6. Authors and co-authorship
The authors with the most considerable number of publications were Lefaucheur, JP (n=48), Saitoh, Y (n=23) and Garcia-Larrea, L (n=16). In the Top 10 of authors in this field we can also see Fregni, F and Nguyen, JP (both with n=13), Ayache, SS and Bouhassira, D (both with n=12), André-Obadia, N and Hosomi, K (both with n=10) and Attal, N (n=9).
In the co-authorship evaluation, we used the VOSviewer to analyze the association strength and a maximum number of 25 authors per document and a minimum number of 4 documents by author was considered. As shown in
Figure 6 nine co-authorship interconnected clusters were obtained from the analysis. The authors with the highest strength link were Lefaucheur, JP and Saitoh, Y.
3.7. Top-cited publications
It is important to say that some documents in the first places of the Top of most-cited publications are not directly related to the primary subject of this article (transcranial magnetic stimulation to treat neuropathic pain). Because of that we highlighted here only the 3 most-cited “original articles” and the 3 most-cited “review articles” directly related to the primary subject of this study.
The 3 most-cited “original articles” were: in first place “Longlasting antalgic effects of daily sessions of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in central and peripheral neuropathic pain” [
24], published on 2005 at “Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry” with a total of 350 citations so far and a 2023 field-weighted citation impact (FWCI), that indicates the number of citations received by an article compares to the average or expected number of citations received by other similar publications, of 7.64; in second place “Motor cortex rTMS restores defective intracortical inhibition in chronic neuropathic pain” [
25], published on 2006 at “Neurology” with a total of 309 citations and a 2023 FWCI of 3.13; in third place “Transcranial magnetic stimulation for pain control. Double-blind study of different frequencies against placebo, and correlation with motor cortex stimulation efficacy” [
26], published on 2006 at “Clinical Neurophysiology” with a 2023 FWCI of 3.76 and a total of 208 citations.
The 3 most-cited “review articles” were: in first place “Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS)” [
27] published on 2014 at “Clinical Neurophysiology” with 1396 citations and a 2023 FWCI of 20.81; in second place “Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): An update (2014–2018)” [
11] published on 2020 at “Clinical Neurophysiology” with 767 citations and a 2023 FWCI of 33.42; in third place “rTMS for Suppressing Neuropathic Pain: A Meta-Analysis” [
28] published on 2009 at “Journal of Pain” with a 2023 FWCI of 2.46 and a total of 178 citations so far.
4. Discussion
The presented study analyzed a total of 474 publications during 22 years (from the inception of research in the field and until July 6, 2023) about the use of TMS to treat neuropathic pain. To our knowledge this is the first bibliometric analysis that focus on the existing research about the use of TMS in neuropathic pain. It seems clear the increase of literature on this subject, namely in the past recent years (2020, 2021 and 2022), with 2022 being the year with more publications ever. It is important to note that the year 2023 has less articles published on this topic than the year 2022 because the bibliometric analysis was conducted until 6 July 2023. The continuous increase of publications highlights the increase of research and the interest in the application of TMS for neuropathic pain. Herein, our bibliometric analysis indicates that new data will probably emerge soon about neuropathic pain and TMS. This comes in line with the need for research addressing nonpharmacological measures to treat neuropathic pain with cost-effective solutions and minimal side effects, which has been emphasized by some authors [
29,
30].
A large co-occurrence between the terms “neuropathic pain” and “transcranial magnetic stimulation” was detected in our analysis since, from the 474 documents analyzed, 451 mentioned at least one of these terms as keywords. This shows that inside this topic the relation between neuropathic pain and TMS is considerable visible. The keywords less mentioned but also with an important link strength were “neuralgia” and “treatment outcome”. This probably shows that some investigators devote their work in understanding the impact of using TMS in the treatment of neuropathic pain evaluating the resulting outcomes and even in understanding the impact of using TMS in the treatment of different types of neuropathic pain, namely neuralgia [
31]. In fact, there are studies which refer that TMS is a reasonable and well-tolerated add-on treatment in neuropathic pain [
32,
33,
34,
35].
Regarding the source of the publications, we listed and characterized the Top 10 most productive sources in this field. Interestingly, in the total of 12 publications published in 2023 none were published by the five most productive sources, until the moment of analysis (6 July, 2023). Instead of that the source with more publications in 2023 so far was “Brain Sciences” (sixth place in the Top 10 most productive sources). The journal “Clinical Neurophysiology”, the most productive source, is the journal responsible for the publication of the third [
26] most-cited “original article” and for the publication of the first [
27] and second [
11] most-cited “review articles”. It is important to highlight that the number of publications by source is relatively sparse and that The Top 10 most productive sources account for 24.5% of the total of publications. This shows that it is difficult to find a dominant source in this topic. The conclusion regarding the most productive countries is different, since the presented Top 10 most productive countries contributes to a total of 78.1% of published publications. The American continent and the European continent are the most productive continents, however, research in this area in other continents is increasing with a good contribution from Asian countries such as China or South Korea. From the author and co-authorship analysis it can be concluded that cooperation between different authors from different countries is a reality in this topic with Lefaucheur, JP and Saitoh, Y being the two most influents authors in this area. A strong co-authorship association was observed between Lefaucheur, JP and Nguyen, JP and between Saitoh, Y and Shimokawa, T.
The continuous growth of publications along 22 years in the use of TMS to manage neuropathic pain highlight the investment in researcher about the efficacy, benefits and risks of TMS. In fact, most of the articles published in the early years were proof-of-concept studies, based on single sessions, in particular for the purpose of predicting the efficacy of subsequent surgically-implanted epidural cortical stimulation [
36,
37] and the first articles mentioning the use of repeated sessions for a truly therapeutic purpose were published in 2004/2005 with a short-term evaluation for a series of patients [
23] or with a long-term evaluation for a single case [
38]. The bibliometric analysis in this study shows that there are lots of publications in this topic that are “original articles” but if we add up publications of other types it can be seen that these other types constitute the majority of publications. Nowadays, all original articles published relate only to protocols using repeated TMS sessions for several weeks with a more or less long-term evaluation. More clinical studies can be carried out to strengthen the evidence for using TMS to treat neuropathic pain. It may also be important to investigate the mechanisms subserving the TMS interventions in neuropathic pain, even using translations approaches. TMS is already recommended in the treatment of resistant psychiatric pathology, namely depression disorder [
39] or obsessive-compulsive disorder [
40] but the mechanisms behind TMS and the neuropathic pain complexity rise specific challenges that are not fully understood [
24] and clinical studies may be considered heterogeneous [
41]. In fact, a main problem in the use of repetitive TMS for a therapeutic purpose in chronic pain patients is the heterogeneity of the proposed protocols, particularly in terms of the definition of the stimulation target and session rhythm. Furthermore, a precise algorithm must be validated, namely the one proposed by Lefaucheur and Nguyen [
42]. Future high-quality studies in this topic are definitely awaited and we hope that this bibliometric analysis can help targeting the direction of the future research.
Regarding the limitations of this study, we highlighted that other scientific databases that were not investigated might have presented relevant publications within the scope of this analysis. However, since Scopus has a broader coverage, we elected this scientific base, in a manner similar to other authors [
43,
44]. We recognize that bibliometric data from Scopus are not produced exclusively for bibliometric analysis and therefore can contain imprecisions errors wich are not, however, likely to affect the main results of the current bibliometric analysis. In fact, this bibliometric analysis brings a considerable volume of publications resulted from research with no restrictions and consists in a useful representation of the most up-to-date knowledge on the subject. Furthermore, the analysis of the results was conducted critically and carefully to avoid errors that could arise from the direct analysis of the results obtained from Scopus.
5. Conclusions
According to the results of this bibliometric analysis and according to its scope, scientific community should know that the treatment of neuropathic pain may include TMS. The still weak scientific evidence for the use of TMS in the treatment of neuropathic pain should motivate more research in this area to improve the quality of life of patients.
This study offers a contextual outline that may be useful for leading and propose new studies with more homogeneous methods and offers some clues about the TMS role in the treatment of neuropathic pain and about what and how research has been carried out in this area. The results obtained allows to make some suggestions for future research, namely adding more scientific databases to find more relevant and current publications, perform large scale meta-analysis to obtain more evidence in this field and to promote the conduct of clinical trials that evaluate the role of TMS in the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Author Contributions
BDC and IT conceived the study. BDC and IT analyzed the data and drafted the initial manuscript. BDC created the figures and graphs. BDC and IT drafted the final manuscript. The two authors read and approved the final manuscript. IT guaranteed the funds.
Funding
The research was performed within the aims of the grant "Cátedra de Medicina da Dor" from Fundação Grunenthal.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Colloca L, Ludman T, Bouhassira D, et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17002. [CrossRef]
- Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, et al. Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology. 2008;70(18):1630-1635. [CrossRef]
- Finnerup NB, Haroutounian S, Kamerman P, et al. Neuropathic pain: an updated grading system for research and clinical practice. Pain. 2016;157(8):1599-1606. [CrossRef]
- Treede RD, Rief W, Barke A, et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: the IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain. 2019;160(1):19-27. [CrossRef]
- Scholz J, Finnerup NB, Attal N, et al. The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: chronic neuropathic pain. Pain. 2019;160(1):53-59. [CrossRef]
- Barke A, Korwisi B, Jakob R, Konstanjsek N, Rief W, Treede RD. Classification of chronic pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11): results of the 2017 international World Health Organization field testing. Pain. 2022;163(2):e310-e318. [CrossRef]
- Attal N, Bouhassira D, Colvin L. Advances and challenges in neuropathic pain: a narrative review and future directions. Br J Anaesth. 2023;131(1):79-92. [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska JM, Palmer J, Morisset V, et al. Safety and efficacy of a Nav1.7 selective sodium channel blocker in patients with trigeminal neuralgia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised withdrawal phase 2a trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(4):291-300. [CrossRef]
- Finnerup NB, Haroutounian S, Baron R, et al. Neuropathic pain clinical trials: factors associated with decreases in estimated drug efficacy. Pain. 2018;159(11):2339-2346. [CrossRef]
- Moisset X, Pereira B, Bouhassira D, Attal N. Pregabalin: a better neuropathic pain treatment in rodents than in humans. Pain. 2020;161(10):2425-2427. [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur JP, Aleman A, Baeken C, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): An update (2014-2018) [published correction appears in Clin Neurophysiol. 2020 May;131(5):1168-1169]. Clin Neurophysiol. 2020;131(2):474-528. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Larrea L, Quesada C. Cortical stimulation for chronic pain: from anecdote to evidence. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022;58(2):290-305. [CrossRef]
- Bouhassira D, Attal N. Emerging therapies for neuropathic pain: new molecules or new indications for old treatments?. Pain. 2018;159(3):576-582. [CrossRef]
- Attal N, Poindessous-Jazat F, De Chauvigny E, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for neuropathic pain: a randomized multicentre sham-controlled trial. Brain. 2021;144(11):3328-3339. [CrossRef]
- Quesada C, Pommier B, Fauchon C, et al. New procedure of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for central neuropathic pain: a placebo-controlled randomized crossover study. Pain. 2020;161(4):718-728. [CrossRef]
- Fu Y, Mao Y, Jiang S, Luo S, Chen X, Xiao W. A bibliometric analysis of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in ophthalmology. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1135592. [CrossRef]
- Chiriac VF, Leucuța DC, Moșoiu DV. Pain and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: A Bibliometric Analysis. J Pain Res. 2023 Nov 1;16:3655-3671. [CrossRef]
- DaSilva AF, Volz MS, Bikson M, Fregni F. Electrode positioning and montage in transcranial direct current stimulation. J Vis Exp. 2011 May 23; (51):2744. [CrossRef]
- Hutson, M. AI Glossary: Artificial intelligence, in so many words. Science. 2017;357(6346):19. [CrossRef]
- van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538. [CrossRef]
- Moghul M, Mahendran S., Lakshmi P, Arunachalam H, Suryakala S, Sudhagar R. Directions in Self Consolidating Concrete Research – Mapping using VOSviewer. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Keravel Y, et al. Pain relief induced by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of precentral cortex. Neuroreport. 2001;12(13):2963-2965. [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur JP, Nguyen JP, Drouot X, Pollin B, Keravel Y, Harf A. Chronic pain treated by rTMS of motor cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1998;107:92. [CrossRef]
- Khedr EM, Kotb H, Kamel NF, Ahmed MA, Sadek R, Rothwell JC. Longlasting antalgic effects of daily sessions of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in central and peripheral neuropathic pain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76(6):833-838. [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Ménard-Lefaucheur I, Keravel Y, Nguyen JP. Motor cortex rTMS restores defective intracortical inhibition in chronic neuropathic pain. Neurology. 2006;67(9):1568-1574. [CrossRef]
- André-Obadia N, Peyron R, Mertens P, Mauguière F, Laurent B, Garcia-Larrea L. Transcranial magnetic stimulation for pain control. Double-blind study of different frequencies against placebo, and correlation with motor cortex stimulation efficacy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;117(7):1536-1544. [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur JP, André-Obadia N, Antal A, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(11):2150-2206. [CrossRef]
- Leung A, Donohue M, Xu R, et al. rTMS for suppressing neuropathic pain: a meta-analysis. J Pain. 2009;10(12):1205-1216. [CrossRef]
- Hange N, Poudel S, Ozair S, et al. Managing Chronic Neuropathic Pain: Recent Advances and New Challenges. Neurol Res Int. 2022;2022:8336561. [CrossRef]
- Xu L, Zhang Y, Huang Y. Advances in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;904:117-129. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Hu Y, Deng J, et al. A randomised sham-controlled study evaluating rTMS analgesic efficacy for postherpetic neuralgia. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1158737. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes AM, Graven-Nielsen T, de Andrade DC. New updates on transcranial magnetic stimulation in chronic pain. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2022;16(2):65-70. [CrossRef]
- Rossi S, Antal A, Bestmann S, et al. Safety and recommendations for TMS use in healthy subjects and patient populations, with updates on training, ethical and regulatory issues: Expert Guidelines. Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;132(1):269-306. [CrossRef]
- Iriarte IG, George MS. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) in the Elderly. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2018;20(1):6. [CrossRef]
- Young NA, Sharma M, Deogaonkar M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation for chronic pain. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2014;25(4):819-832. [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur JP, Ménard-Lefaucheur I, Goujon C, et al. Predictive value of rTMS in the identification of responders to epidural motor cortex stimulation therapy for pain. J Pain. 2011;12(10):1102-1111. [CrossRef]
- André-Obadia N, Mertens P, Lelekov-Boissard T, et al. Is Life better after motor cortex stimulation for pain control? Results at long-term and their prediction by preoperative rTMS. Pain Physician. 2014;17(1):53-62.
- Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Ménard-Lefaucheur I, Nguyen JP. Neuropathic pain controlled for more than a year by monthly sessions of repetitive transcranial magnetic cortical stimulation, Neurophysiol Clin 2004;34:91-95. [CrossRef]
- Sonmez AI, Camsari DD, Nandakumar AL, et al. Accelerated TMS for Depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2019;273:770-781. [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini L, Garg K, Enara A, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (r-TMS) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor-resistance in obsessive-compulsive disorder: A meta-analysis and clinical implications. Compr Psychiatry. 2022;118:152-339. [CrossRef]
- Tsai YY, Wu WT, Han DS, et al. Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review. Life (Basel). 2023;13(2):258. [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur JP, Nguyen JP. A practical algorithm for using rTMS to treat patients with chronic pain. Neurophysiol Clin 2019;49:301-309. [CrossRef]
- da Costa BFC, Ramalho A, Gonçalves-Pinho M, Freitas A. Suicide Mortality Rate as a Sustainable Development Goal (SDG): A Bibliometric Analysis. Psychiatr Q. 2022;93(1):15-26. [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, A., Souza, J., Freitas, A. (2021). The Use of Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Coding Automation: A Bibliometric Analysis. In: Dong, Y., Herrera-Viedma, E., Matsui, K., Omatsu, S., González Briones, A., Rodríguez González, S. (eds) Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, 17th International Conference. DCAI 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1237. Springer, Cham.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).