Submitted:
12 January 2024
Posted:
15 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
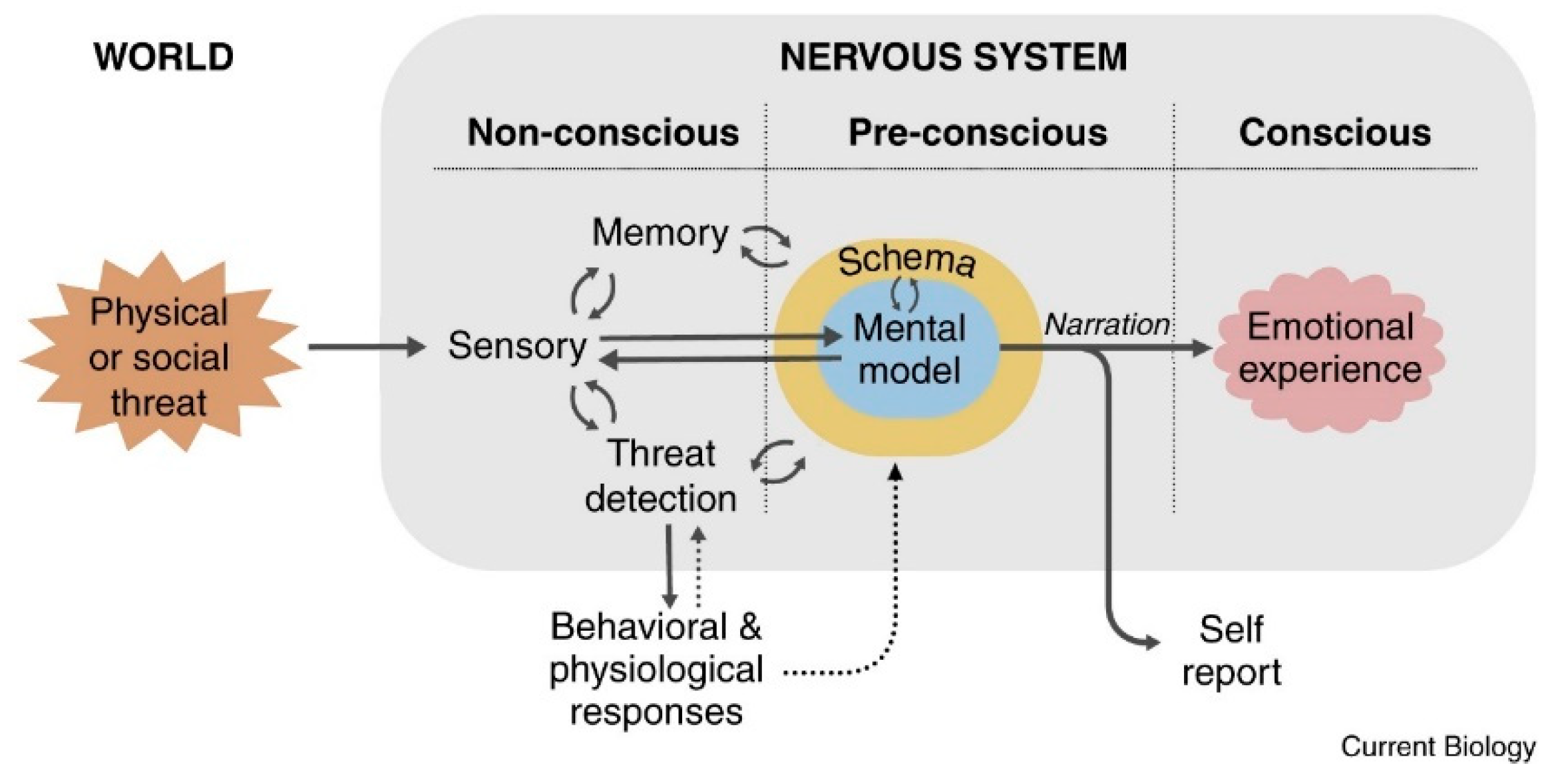
1. The LeDoux Proposal (2021)
2. Theory of Constructed Emotion
3. Polyvagal Theory
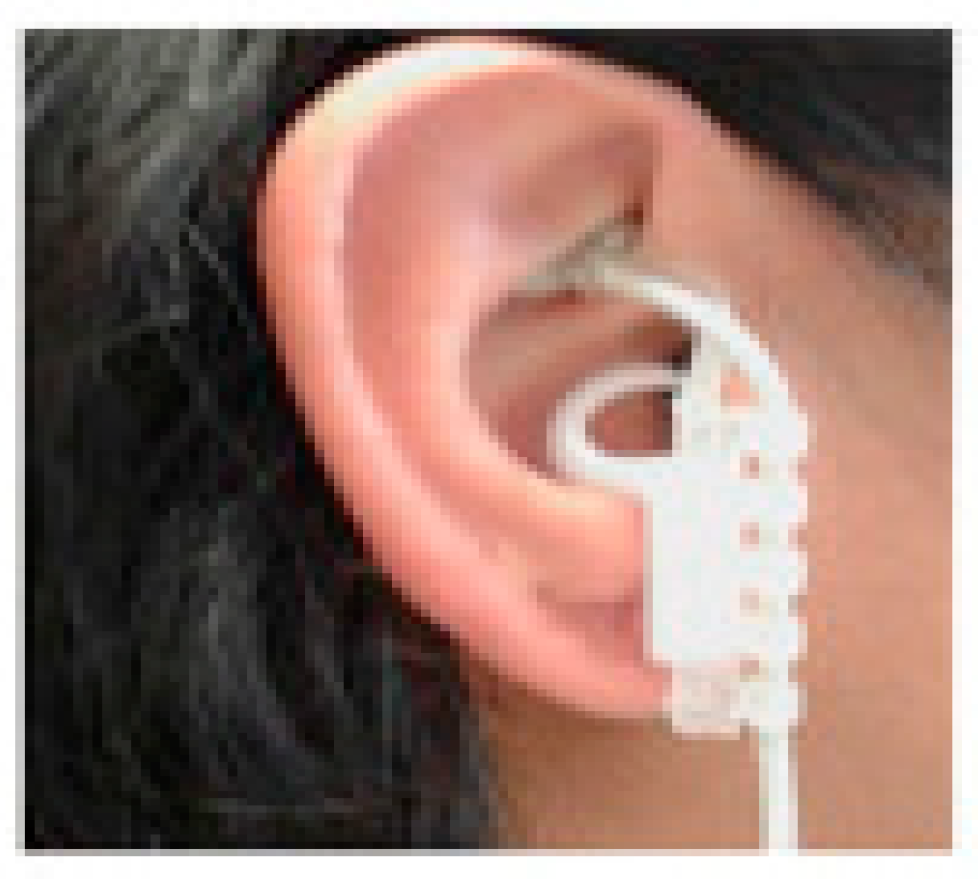
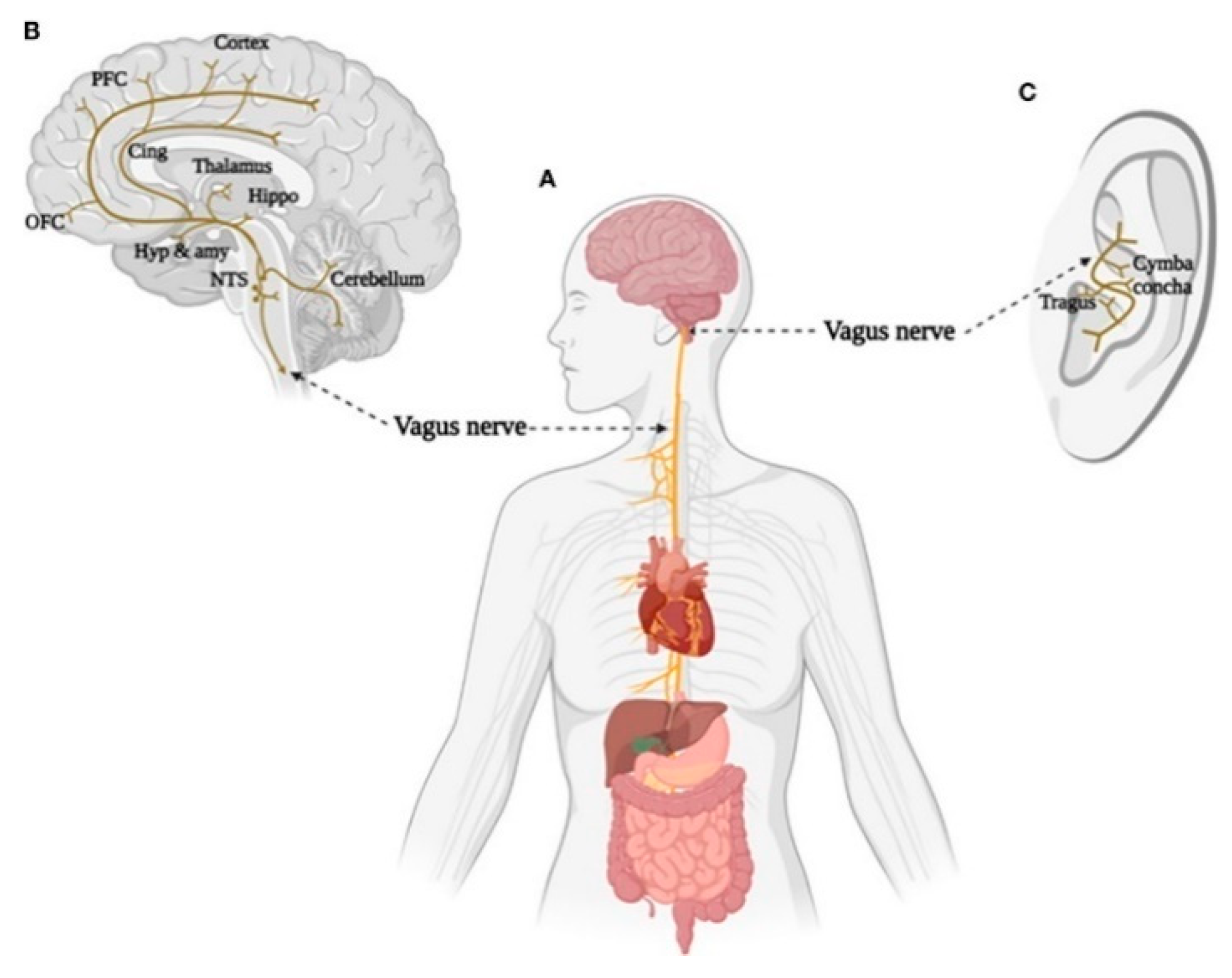
4. Transauricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation
5. Discussion and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019, Disease and Injuries Collaborators (2022). Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019, The Lancet Psychiatry, 9(2), 137-150. 1016. [CrossRef]
- Arias, D., Saxena, S., & Verguet, S. (2022). Quantifying the global burden of mental disorders and their economic value. Eclinicalmedicine, 54. [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, K. M. , Bukalo, O., Zeller, M., Aksoy-Aksel, A., Karalis, N., Limoges, A., Rigg, T., Campbell, T., Mendez, A., Weinholtz, C., Mahn, M., Zweifel, L. S., Palmiter, R. D., Ehrlich, I., Lüthi Andreas, & Holmes, A. (2021). Intercalated amygdala clusters orchestrate a switch in fear state. Nature: International Weekly Journal of Science, 594(7863), 403–407. [CrossRef]
- Kenwood, M. M. , Kalin, N. H., & Barbas, H. (2021). The prefrontal cortex, pathological anxiety, and anxiety disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology : At the Intersection of Brain, Behavior, and Therapeutics, 47(1), 260–275. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A., Yang, C., Li, G., Wang, Y., Liu, P. H., Liu, Z., Sun, N., & Zhang, K. (2020). Functional connectivity of the prefrontal cortex and amygdala is related to depression status in major depressive disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 274, 897–902. 274, 897–902. [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A., Murray, G., & Ray, S. (2023). Circadian biology to advance therapeutics for mood disorders. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 44(10), 689–704. [CrossRef]
- Clark, J. E. , Watson, S., & Friston, K. J. (2018). What is mood? a computational perspective. Psychological Medicine, 48(14), 2277–2284. [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P., Kaltenboeck, A., & Harmer, C. J. (2019). Cognitive emotional processing across mood disorders. Cns Spectrums, 24(1), 54–63. [CrossRef]
- Aranberri Ruiz, A. (2023). Emotional experience and its biological underpinnings: improving emotional well-being through vagal tone. Papeles Del Psicólogo - Psychologist Papers, 44(2), 95–95. [CrossRef]
- Cloninger, C. R., & Zwir, I.(2022) Genetics of human character and temperament. eLS, 3, 1-20. [CrossRef]
- LeDoux, J. E. (2021). What emotions might be like in other animals. Current Biology : Cb, 31(13), 829. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L. F. (2017). The theory of constructed emotion: an active inference account of interoception and categorization. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 12(1), 1–23. [CrossRef]
- Porges, S.W. (2001). The polyvagal theory: phylogenetic substrates of a social nervous system. Int J Psychophysiol.;42:123–146.
- Porges, S. W. (2023). The vagal paradox: a polyvagal solution. Comprehensive Psychoneuroendocrinology, 16. [CrossRef]
- LeDoux, J. (2012). Rethinking the emotional brain. Neuron, 73(4), 653–676. [CrossRef]
- LeDoux, J. E. (2000). Emotion circuits in the brain. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 23, 155–184. [CrossRef]
- Chin, R. , Chang, S. W. C., & Holmes, A. J. (2023). cortex: The evolution of the human brain. Psychological Review, 130(2), 285–307. [CrossRef]
- Brabec, J. , Rulseh, A., Hoyt, B., Vizek, M., Horinek, D., Hort, J., & Petrovicky, P. (2010). Volumetry of the human amygdala—An anatomical study. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 182(1), 67–72. 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, H.-C. , & Pare, D. (2010). Plastic synaptic networks of the amygdala for the acquisition, expression, and extinction of conditioned fear. Physiological Reviews, 90(2), 419–419. [CrossRef]
- Tyszka, J. M. , & Pauli, W. M. (2016). In vivo delineation of subdivisions of the human amygdaloid complex in a high-resolution group template. Human Brain Mapping, 37(11), 3979–3998. [CrossRef]
- Janak, P. H., & Tye, K. M. (2015). From circuits to behaviour in the amygdala. Nature, 517(7534), 284–292. [CrossRef]
- Milad, M. R. , & Quirk, G. J. (2012). Fear extinction as a model for translational neuroscience: Ten years of progress. Annual Review of Psychology, 63, 129–151. [CrossRef]
- LeDoux, J. E. (2014). Coming to terms with fear. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(8), 2871–2878. [CrossRef]
- Barger, N. , Hanson, K. L., Teffer, K., Schenker-Ahmed, N. M., & Semendeferi, K. (2014). Evidence for evolutionary specialization in human limbic structures. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, Article 277. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z., Jian, L., Qiu, H., Zhang, C., Cheng, S., Ji, J., Li, T., Wang, Y., Li, J., & Li, K. (2021). Understanding complex functional wiring patterns in major depressive disorder through brain functional connectome. Translational Psychiatry, 11(1), 526–526. [CrossRef]
- Haris, E. M. , Bryant, R. A., Williamson, T., & Korgaonkar, M. S. (2023). Functional connectivity of amygdala subnuclei in ptsd: a narrative review. Molecular Psychiatry, 28(9), 3581–3594. [CrossRef]
- Henigsberg, N. , Kalember, P., Petrović, Z. K., & Šečić, A. (2019). Neuroimaging research in posttraumatic stress disorder - focus on amygdala, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 90, 37–42. [CrossRef]
- Millan, M. J. (2022). Agomelatine for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: focus on its distinctive mechanism of action. Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology, 12. [CrossRef]
- Hohwy, J. (2020). New directions in predictive processing. Mind & Language, 35(2), 209–223. [CrossRef]
- Shipp, S. , Adams, R. A., & Friston, K. J. (2013). Reflections on agranular architecture: predictive coding in the motor cortex. Trends in Neurosciences, 36(12), 706–706. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L. F. (2019). In search of emotions. Current Biology, 29(5), 142. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L. F. (2022). Context reconsidered: complex signal ensembles, relational meaning, and population thinking in psychological science. The American Psychologist, 77(8), 894–894. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.F. , & Finlay, B. L. (2018). Concepts, goals and the control of survival-related behaviors. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 24, 172–179. [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.D. (2015). How Do You Feel?: an Interoceptive Moment with Your Neurobiological Self. Princeton University Press.
- Kurtin, D. L. , Giunchiglia, V., Vohryzek, J., Cabral, J., Skeldon, A. C., & Violante, I. R. (2023). Moving from phenomenological to predictive modelling: progress and pitfalls of modelling brain stimulation in-silico. Neuroimage, 272. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L. F., & Simmons, W. K. (2015). Interoceptive predictions in the brain. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 16(7), 419–29. [CrossRef]
- Kleckner, I. R. , Zhang, J., Touroutoglou, A., Chanes, L., Xia, C., Simmons, W. K.,... & Feldman Barrett, L. (2017). Evidence for a large-scale brain system supporting allostasis and interoception in humans. Nature human behaviour, 1(5), 0069.
- Ventura-Bort, C. , Wendt, J., & Weymar, M. (2021). The role of interoceptive sensibility and emotional conceptualization for the experience of emotions. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. [CrossRef]
- Kuppens, P., Tuerlinckx, F., Russell, J. A., & Barrett, L. F. (2013). The relation between valence and arousal in subjective experience. Psychological Bulletin, 139(4), 917–940. [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, Y. , Kamona, N., Zhang, J., Bunce, J. G., Hutchinson, J. B., Yarossi, M., & Barrett, L. F. (2021). Functional connectivity gradients as a common neural architecture for predictive processing in the human brain. BioRxiv, 2021-09. [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, Y., Theriault, J. E., Quigley, K. S., & Barrett, L. F. (2022). Allostasis as a core feature of hierarchical gradients in the human brain. Network Neuroscience, 6(4), 1010–1031. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L. F. , & Satpute, A. B. (2013). Large-scale brain networks in affective and social neuroscience: towards an integrative functional architecture of the brain. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 23(3), 361–72. [CrossRef]
- Press, C., Kok, P., & Yon, D. (2020). The perceptual prediction paradox. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 24(1), 13–24. [CrossRef]
- Touroutoglou, A., Bliss-Moreau, E., Zhang, J., Mantini, D., Vanduffel, W., Dickerson, B. C., & Barrett, L. F. (2016). A ventral salience network in the macaque brain. Neuroimage, 132, 190–197. [CrossRef]
- Wager, T. D. , Kang, J., Johnson, T. D., Nichols, T. E., Satpute, A. B., Barrett, L. F., & Diedrichsen, J. (2015). A bayesian model of category-specific emotional brain responses. Plos Computational Biology, 11(4). [CrossRef]
- Porges, S. W. (2007). The polyvagal perspective. Biological Psychology, 74(2), 116–143. [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H. R. , & Neuhuber, W. L. (2000). Functional and chemical anatomy of the afferent vagal system. Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic & Clinicall, 85(1–3), 1–17.
- Neuhuber, W. L. , & Berthoud, H.-R. (2021). Functional anatomy of the vagus system - emphasis on the somato-visceral interface. Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical, 236. [CrossRef]
- Gourine, A. V. , Machhada, A., Trapp, S., & Spyer, K. M. (2016). Cardiac vagal preganglionic neurones: an update. Autonomic Neuroscience : Basic & Clinical, 199, 24–8. [CrossRef]
- Porges, S. W. (1997). Emotion: an evolutionary by-product of the neural regulation of the autonomic nervous system. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 807, 62–77.
- Arnsten, A. F. T. (2015). Stress weakens prefrontal networks: molecular insults to higher cognition. Nature Neuroscience, 18(10), 1376–1385. [CrossRef]
- Ruffoli, R., Giorgi, F. S., Pizzanelli, C., Murri, L., Paparelli, A., & Fornai, F. (2011). The chemical neuroanatomy of vagus nerve stimulation. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy, 42(4), 288–296. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H., & Silberstein, S. D. (2018). Histamine and migraine. Headache, 58(1), 184–193. [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.F. , Albusoda, A., Farmer, A.D. & Aziz, Q. (2020), The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. J. Anat, 236: 588-611. [CrossRef]
- Stegeman, I. , Velde, H. M., Robe, P. A. J. T., Stokroos, R. J., & Smit, A. L. (2021). Tinnitus treatment by vagus nerve stimulation: a systematic review. Plos One 16(3), 0247221. [CrossRef]
- Mather, M., & Thayer, J. F. (2018). How heart rate variability affects emotion regulation brain networks. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 19, 98–104. [CrossRef]
- De Smet, S. , Ottaviani, C., Verkuil, B., Kappen, M., & Baeken, C. (2023). Effects of non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation on cognitive and autonomic correlates of perseverative cognition. Psychophysiology, 60(6). [CrossRef]
- Goggins, E. , Mitani, S., & Tanaka, S. (2022). Clinical perspectives on vagus nerve stimulation: present and future. Clinical Science, 136(9), 695–709. [CrossRef]
- Warren, C.M. , Tona, K.D., Ouwerkerk, L., van Paridon, J., Poletiek, F., van Steenbergen, H., Bosch, J.A., Nieuwenhuis, S., (2019). The neuromodulatory and hormonal effects of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation as evidenced by salivary alpha amylase, salivary cortisol, pupil diameter, and the P3 event-related potential. Brain Stimul 12, 635–642. [CrossRef]
- Assenza, G. , Campana, C., Colicchio, G., Tombini, M., Assenza, F., Di Pino, G., & Di Lazzaro, V. (2017). Transcutaneous and invasive vagal nerve stimulations engage the same neural pathways: In-vivo human evidence. Brain Stimulation, 10(4), 853–854. [CrossRef]
- Peuker, E. T., & Filler, T. J. (2002). The nerve supply of the human auricle. Clinical Anatomy, 15(1), 35–37. [CrossRef]
- Kiyokawa, J. , Yamaguchi, K., Okada, R., Maehara, T. & Akita, K. (2014) Origin, course and distribution of the nerves to the posterosuperior wall of the external acoustic meatus. Anat Sci Int. Sep;89(4):238-45. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K. , Tubbs, R. S., Satoh, S., Zomorodi, A. R., Liedtke, W., Labidi, M., Friedman, A. H., & Fukushima, T. (2016). Isolated Deep Ear Canal Pain: Possible Role of Auricular Branch of Vagus Nerve-Case Illustrations with Cadaveric Correlation. World neurosurgery, 96, 293–301. [CrossRef]
- Farmer, A. D., Strzelczyk, A., Finisguerra, A., Gourine, A. V., Gharabaghi, A., Hasan, A., Burger, A. M., Jaramillo, A. M., Mertens, A., Majid, A., Verkuil, B., Badran, B. W., Ventura-Bort, C., Gaul, C., Beste, C., Warren, C. M., Quintana, D. S., Hämmerer, D., Freri, E., … Weymar, M. (2021). International consensus based review and recommendations for minimum reporting standards in research on transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (version 2020). Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 14. [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, P. , Silva, M. E. D., Carvalho, T. C. D., Cordeiro, Q., Brunoni, A. R., & Fregni, F. (2014). Transcutaneous vagus and trigeminal nerve stimulation for neuropsychiatric disorders: A systematic review. Arquivos de Neuro-psiquiatria, 72(7), 542e547.
- Sellaro, R., de Gelder, B., Finisguerra, A., & Colzato, L. S. (2018). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tvns) enhances recognition of emotions in faces but not bodies. Cortex, 99, 213–223. [CrossRef]
- Vonck, K. , Raedt, R., Naulaerts, J., De, V. F., Thiery, E., Van, R. D., Miatton, M., Boon, P., & Aldenkamp, B. (2014). Vagus nerve stimulation...25 years later! what do we know about the effects on cognition?. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 45, 63–71. [CrossRef]
- Tan, C. , Yan, Q., Ma, Y., Fang, J., & Yang, Y. (2022). Recognizing the role of the vagus nerve in depression from microbiota-gut brain axis. Frontiers in Neurology, 13, 1015175–1015175. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. , Li, S.-Y., Wang, D., Wu, M.-Z., He, J.-K., Zhang, J.-L., Zhao, B., Hou, L.-W., Wang, J.-Y., Wang, L., Wang, Y.-F., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z.-X., & Rong, P.-J. (2020). Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation: from concept to application. Neuroscience Bulletin, 37(6), 853–862. [CrossRef]
- Pu-Wei, H. , Hsin-Cheng, H., Yi-Wen, L., Nou-Ying, T., Chin-Yi, C., & Ching-Liang, H. (2015). The history, mechanism, and clinical application of auricular therapy in traditional chinese medicine. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Kong, J. , Fang, J., Park, J., Li, S., & Rong, P. (2018). Treating depression with transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation: state of the art and future perspectives. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9. [CrossRef]
- Ferstl, M. , Teckentrup, V., Lin, W. M., Kräutlein, F., Kühnel, A., Klaus, J., Martin, W., & Kroemer, N. B. (2022). Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation boosts mood recovery after effort exertion. Psychological Medicine, 52(14), 3029–3039. [CrossRef]
- Ventureyra, E. C. G. (2000). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation for partial onset seizure therapy. Childs Nerv. Syst. 16, 101–102. [CrossRef]
- Yap, J. Y. Y. , Keatch, C., Lambert, E., Woods, W., Stoddart, P. R., & Kameneva, T. (2020). Critical review of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation: challenges for translation to clinical practice. Frontiers in Neuroscience, N/a. [CrossRef]
- Carreno, F. R., & Frazer, A. (2016). The allure of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation as a novel therapeutic modality. Biological Psychiatry, 79(4), 260–1. [CrossRef]
- Daban, C. , Martinez-Aran, A., Cruz, N., & Vieta, E. (2008). Safety and efficacy of vagus nerve stimulation in treatment-resistant depression. a systematic review. Journal of Affective Disorders, 110(1–2), 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Diedrich, A. , Urechie, V., Shiffer, D., Rigo, S., Minonzio, M., Cairo, B., Smith, E. C., Okamoto, L. E., Barbic, F., Bisoglio, A., Porta, A., Biaggioni, I., & Furlan, R. (2021). Transdermal auricular vagus stimulation for the treatment of postural tachycardia syndrome. Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical, 236. [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, W. C. , Kempf, M.-C., Moneyham, L., & Vance, D. E. (2017). The potential role of vagus-nerve stimulation in the treatment of hiv-associated depression: a review of literature. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 13, 1677–1689. [CrossRef]
- Barbella, G. , Cocco, I., Freri, E., Marotta, G., Visani, E., Franceschetti, S., & Casazza, M. (2018). Transcutaneous vagal nerve stimulatio (t-vns): an adjunctive treatment option for refractory epilepsy. Seizure: European Journal of Epilepsy, 60, 115–119. [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S. , Baier, H., Baumgartner, C., Bohlmann, K., Fauser, S., Graf, W., Hillenbrand, B., Hirsch, M., Last, C., Lerche, H., Mayer, T., Schulze-Bonhage, A., Steinhoff, B. J., Weber, Y., Hartlep, A., Rosenow, F., & Hamer, H. M. (2016). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tvns) for treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial (cmpse02). Brain Stimulation, 9(3), 356–363. [CrossRef]
- Badran, B. W. , Mithoefer, O. J., Summer, C. E., LaBate, N. T., Glusman, C. E., Badran, A. W., DeVries, W. H., Summers, P. M., Austelle, C. W., McTeague, L. M., Borckardt, J. J., & George, M. S. (2018). Short trains of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tavns) have parameter-specific effects on heart rate. Brain Stimulation, 11(4), 699–708. [CrossRef]
- Kim, A. Y. , Marduy, A., de Melo, P. S., Gianlorenco, A. C., Kim, C. K., Choi, H., Song, J.-J., & Fregni, F. (2022). Safety of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tavns): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 22055–22055. 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A. M. , D’Agostini, M., Verkuil, B., & Van Diest, I. (2020). Moving beyond belief: a narrative review of potential biomarkers for transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. Psychophysiology, 57(6). [CrossRef]
- Redgrave, J. , Day, D., Leung, H., Laud, P. J., Ali, A., Lindert, R., & Majid, A. (2018). Safety and tolerability of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation in humans; a systematic review. Brain Stimulation, 11(6), 1225–105 1238. [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B. , Picq, C., Sinniger, V., Mayol, J. F. & Clarençon, D. (2013).Vagus nerve stimulation: From epilepsy to the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25, 208–221. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S., Zhang, X., Zhou, M., Kendrick, K. M., & Zhao, W. (2022). Therapeutic applications of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation with potential for application in neurodevelopmental or other pediatric disorders. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 13, 1000758–1000758. [CrossRef]
- Frangos, E. , Ellrich, J., & Komisaruk, B. R. (2015). Non-invasive access to the vagus nerve central projections via electrical stimulation of the external ear: fmri evidence in humans. Brain Stimulation, 8(3), 624–36. [CrossRef]
- Komisaruk, B. R. , & Frangos, E. (2022). Vagus nerve afferent stimulation: projection into the brain, reflexive physiological, perceptual, and behavioral responses, and clinical relevance. Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical, 237. [CrossRef]
- Banks, S. J. , Eddy, K. T., Angstadt, M., Nathan, P. J., & Phan, K. L. (2007). Amygdala-frontal connectivity during emotion regulation. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 2(4), 303–12. [CrossRef]
- Berboth, S. , & Morawetz, C. (2021). Amygdala-prefrontal connectivity during emotion regulation: a meta-analysis of psychophysiological interactions. Neuropsychologia, 153. [CrossRef]
- Kohn, N. , Eickhoff, S. B., Scheller, M., Laird, A. R., Fox, P. T., & Habel, U. (2014). Neural network of cognitive emotion regulation — an ale meta-analysis and macm analysis. Neuroimage, 87, 345–355. [CrossRef]
- Vanderhasselt, M.-A. , Baeken, C., Van Schuerbeek, P., Luypaert, R., & De Raedt, R. (2013). Inter-individual differences in the habitual use of cognitive reappraisal and expressive suppression are associated with variations in prefrontal cognitive control for emotional information: an event related fmri study. Biological Psychology, 92(3), 433–439. [CrossRef]
- Messina, I. , Grecucci, A., & Viviani, R. (2021). Neurobiological models of emotion regulation: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies of acceptance as an emotion regulation strategy. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 16(3), 257–267. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. , & Zhen, R. (2022). How do physical and emotional abuse affect depression and problematic behaviors in adolescents? the roles of emotional regulation and anger. Child Abuse & Neglect, 129. [CrossRef]
- Fornai, F., Ruffoli, R., Giorgi, F. S., & Paparelli, A. (2011). The role of locus coeruleus in the antiepileptic activity induced by vagus nerve stimulation. European Journal of Neuroscience, 33(12), 2169–2178. [CrossRef]
- Panaro, M. A. , Benameur, T., & Porro, C. (2020). Hypothalamic neuropeptide brain protection: focus on oxytocin. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5). [CrossRef]
- D’Agostini, M., Burger, A. M., Franssen, M., Perkovic, A., Claes, S., von Leupoldt, A., Murphy, P. R., & Van Diest, I. (2023). Short bursts of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation enhance evoked pupil dilation as a function of stimulation parameters. Cortex, 159, 233–253. [CrossRef]
- Manta, S. , Dong, J., Debonnel, G., & Blier, P. (2009). Enhancement of the function of rat serotonin and norepinephrine neurons by sustained vagus nerve stimulation. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience : Jpn, 34(4), 272–80.
- Wienke, C. , Grueschow, M., Haghikia, A., & Zaehle, T. (2023). Phasic, Event-Related Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Modifies Behavioral, Pupillary, and Low-Frequency Oscillatory Power Responses. Journal of Neuroscience. 6319. [Google Scholar]
- Giraudier, M. , Ventura-Bort, C., Burger, A. M., Claes, N., D’Agostini, M., Fischer, R., Franssen, M., Kaess, M., Koenig, J., Liepelt, R., Nieuwenhuis, S., Sommer, A., Usichenko, T., Van Diest, I., von Leupoldt, A., Warren, C. M., & Weymar, M. (2022). Evidence for a modulating effect of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tavns) on salivary alpha-amylase as indirect noradrenergic marker: a pooled mega-analysis. Brain Stimulation, 15(6), 1378–1388. [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, B., Wurm, F., de Kleijn, R., &; Nieuwenhuis, S. (2023). Short-term transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation increases pupil size but does not affect eeg alpha power: a replication of sharon et al. (2021, journal of neuroscience). Brain Stimulation, 16(4), 1001–1008. [CrossRef]
- Ventura-Bort, C. , Wirkner, J., Genheimer, H., Wendt, J., Hamm, A. O., & Weymar, M. (2018). Effects of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tvns) on the p300 and alpha-amylase level: a pilot study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12. [CrossRef]
- Burger, A. M. , Van der Does, W., Brosschot, J. F., & Verkuil, B. (2020). From ear to eye? No effect of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation on human pupil dilation: a report of three studies. Biological psychology, 152, 107863. [CrossRef]
- Keute, M. , Demirezen, M., Graf, A., Mueller, N. G., & Zaehle, T. (2019). No modulation of pupil size and event-related pupil response by transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tavns). Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Long-Smith, C. , O’Riordan, K. J., Clarke, G., Stanton, C., Dinan, T. G., & Cryan, J. F. (2020). Microbiota-gut-brain axis: new therapeutic opportunities. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 60, 477–502. [CrossRef]
- Fülling, C. , Dinan, T. G., & Cryan, J. F. (2019). Gut microbe to brain signaling: what happens in vagus…. Neuron, 101(6), 998–1002. [CrossRef]
- Han, W. , Tellez, L. A., Perkins, M. H., Perez, I. O., Qu, T., Ferreira, J., Ferreira, T. L., Quinn, D., Liu, Z.-W., Gao, X.-B., Kaelberer, M. M., Bohórquez, D. V., Shammah-Lagnado, S. J., de Lartigue, G., & de Araujo, I. E. (2018). A neural circuit for gut-induced reward. Cell, 175(3), 665–678. [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, K. L. , Klein, M. E., Barth, B. B., Montoya, M. M., & Bohórquez, D. V. (2018). A gut-brain neural circuit for nutrient sensory transduction. Science, 361(6408). [CrossRef]
- Bellono, N. W., Bayrer, J. R., Leitch, D. B., Castro, J., Zhang, C., O’Donnell, T. A., Brierley, S. M., Ingraham, H. A., & Julius, D. (2017). Enterochromaffin cells are gut chemosensors that couple to sensory neural pathways. Cell, 170(1), 185–198. [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. , Salinas, E., Ortiz, G. G., Ramirez-Jirano, L., Morales, J. A., & Bitzer-Quintero, O. (2019). From Probiotics to Psychobiotics: Live Beneficial Bacteria Which Act on the Brain-Gut Axis. Nutrients, 11(4), 890. [CrossRef]
- Morais, L. H. , Schreiber, Henry L., & Mazmanian, S. K. (2021). The gut microbiota–brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nature Reviews.Microbiology, 19(4), 241-255. [CrossRef]
- Bany Bakar, R. , Reimann, F., & Gribble, F. M. (2023). The intestine as an endocrine organ and the role of gut hormones in metabolic regulation. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 20(12), 784–796. [CrossRef]
- Venegas, D. P. , De, L. F. M. K., Landskron, G., Hermoso, M. A., Dijkstra, G., Faber, K. N., Gonzalez, M. J., Quera, R., & Harmsen, H. J. M. (2019). Short chain fatty acids (scfas)mediated gut epithelial and immune regulation and its relevance for inflammatory bowel diseases. Frontiers in Immunology, 10(Mar). [CrossRef]
- Agirman, G. , Yu, K. B., & Hsiao, E. Y. (2021). Signaling inflammation across the gut-brain axis. Science, 374(6571), 1087–1092. 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J. A. , Rinaman, L., & Cryan, J. F. (2017). Stress & the gut-brain axis: regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiology of Stress, 7, 124–136. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C. A. , Diaz-Arteche, C., Eliby, D., Schwartz, O. S., Simmons, J. G., & Cowan, C. S. M. (2021). The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression - a systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 83, 101943–101943. 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. , Zhan, G., Cai, Z., Jiao, B., Zhao, Y., Li, S., & Luo, A. (2021). Vagus nerve stimulation in brain diseases: therapeutic applications and biological mechanisms. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 127, 37-53. [CrossRef]
- Fang, J., Egorova, N., Rong, P., Liu, J., Hong, Y., Fan, Y., Wang, X., Wang, H., Yu, Y., Ma, Y., Xu, C., Li, S., Zhao, J., Luo, M., Zhu, B., & Kong, J. (2017). Early cortical biomarkers of longitudinal transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation treatment success in depression. Neuroimage. Clinical, 14, 105–111. [CrossRef]
- Hein, E. , Nowak, M., Kiess, O., Biermann, T., Bayerlein, K., Kornhuber, J., & Kraus, T. (2013). Auricular transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in depressed patients: a randomized controlled pilot study. Journal of Neural Transmission, 120(5), 821–7. [CrossRef]
- Rong, P.-J. , Fang, J.-L., Wang, L.-P., Meng, H., Liu, J., Ma, Y., Ben, H., Li, L., Liu, R.-P., Huang, Z.-X., Zhao, Y.-F., Li, X., Zhu, B., & Kong, J. (2012). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of depression: a study protocol for a double blinded randomized clinical trial. Bmc Complementary and Alternative Medicine : The Official Journal of the International Society for Complementary Medicine Research(Iscmr), 12(1), 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Lamb, D. G. , Porges, E. C., Lewis, G. F., & Williamson, J. B. (2017). Non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation effects on hyperarousal and autonomic state in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder and history of mild traumatic brain injury: preliminary evidence. Frontiers in Medicine, 4. [CrossRef]
- Bottari, S. A. , Lamb, D. G., Porges, E. C., Murphy, A. J., Tran, A. B., Ferri, R., Jaffee, M. S., Davila, M. I., Hartmann, S., Baumert, M., & Williamson, J. B. (2023). Preliminary evidence of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation effects on sleep in veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder. Journal of Sleep Research, E13891, 13891. [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R. M. , Shaam, P., Williams, M. S., McCann-Pineo, M., Ryniker, L., Debnath, S., & Zanos, T. P. (2022). Understanding mental health needs and gathering feedback on transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation as a potential PTSD treatment among 9/11 responders living with PTSD symptoms 20 years later: A qualitative approach. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(8), 4847. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Perez, J. A. , Gazi, A. H., Rahman, F. N., Seith, A., Saks, G., Sundararaj, S., Erbrick, R., Harrison, A. B., Nichols, C. J., Modak, M., Chalumuri, Y. R., Snow, T. K., Hahn, J.-O., & Inan, O. T. (2023). Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation and median nerve stimulation reduce acute stress in young healthy adults: a single-blind sham-controlled crossover study. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 17. [CrossRef]
- Borgmann, D. , Rigoux, L., Kuzmanovic, B., Edwin Thanarajah, S., Münte, T. F., Fenselau, H., & Tittgemeyer, M. (2021). Technical note: modulation of fmri brainstem responses by transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. Neuroimage, 244. [CrossRef]
- Colzato, L. S., Ritter, S. M., & Steenbergen, L. (2018). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tvns) enhances divergent thinking. Neuropsychologia, 111, 72–76. [CrossRef]
- Jongkees, B. J., Immink, M. A., Finisguerra, A., & Colzato, L. S. (2018). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tvns) enhances response selection during sequential action. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 1159–1159. [CrossRef]
- Szeska, C. , Richter, J., Wendt, J., Weymar, M., & Hamm, A. O. (2020). Promoting long-term inhibition of human fear responses by non-invasive transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation during extinction training. Scientific Reports, 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., Fang, J., Wang, Z., Rong, P., Hong, Y., Fan, Y., & Kong, J. (2016). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation modulates amygdala functional connectivity in patients with depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 205, 319–326. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. , Liu, P., Fu, H., Chen, W., Cui, S., Lu, L., & Tang, C. (2018). Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation in treating major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine, 97(52), e13845. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



