1. Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common tachyarrhythmia characterized by various symptoms such as chest pain, palpitation, and fatigue, with a prevalence of 3.2% in adults [
1,
2]. Worldwide, the number of people living with AF was approximately 33.5 million in 2010, and due to the increased prevalence of its risk factors, this number is projected to increase two-fold by 2060 [
3,
4]. Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of stroke [
5], with a rate of five-fold greater, compared to those without AF [
6]. Stroke risk in patients with AF ranges between 1% and 20% [
7]. In the United States, the number of annual ischemic strokes exceeds 70,000 accounting for 10% to 12% of all ischemic strokes [
7]. Anticoagulants such as warfarin are the most efficacious treatments for stroke related to AF [
6]. Even when other non-pharmacological interventions (such as ablation, cardioversion, and cardiac pacing) are present [
8], warfarin needs to be continued, to assist in reducing the incidence of thromboembolism and mortality in AF [
9].
Various demographic and clinical factors have been found to increase the stroke risk in patients with AF including age over 65 years, coronary heart disease, heart failure, hypertension, transient ischemic attack, previous stroke, and diabetes mellitus [
10]. Thus, risk stratification schemes have been developed to identify levels of stroke risk in patients with AF such as CHA2DS2-VASc score [
11].
The majority of patients with AF and those who have at least one risk factor are given warfarin based on the CHA2DS2-VASc score (heart failure or dysfunction, age between 65 to 74, hypertension, [1 point] or age over 75 years [2 points], stroke, thromboembolism, and diabetes [2 points] [
9]. Warfarin has a narrow therapeutic effect, which can increase the risk of hemorrhagic or embolic stroke [
5]. Hemorrhagic stroke is the outmost critical health complications resulted from the use of warfarin [
12]. Despite the low prevalence of hemorrhagic stroke in the world (nearly 15% of overall strokes), most of them are associated with AF and responsible for about 50% of mortalities as well as 42% of disabilities [
13,
14]. Thus, the anticoagulation effect of warfarin needs to be constantly monitored to ensure optimal therapeutic dose of anticoagulation, maximize the ration of risk–benefit, and ultimately prevent any potential health complications [
14].
Data on patients with AF are limited in Jordan. Therefore, this study aimed to provide in-depth analysis of a cohort of Jordanian patients with AF on warfarin regarding patients’ characteristics, AF related symptoms, interventions, comorbidities, and 12-months outcomes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
This is a quantitative analysis of data obtained from the Jordanian AF clinical trial. The Jordanian AF study is a multi-center prospective observational non-interventional study which assessed AF patients both in- and out-of-hospital. The original clinical trial enrolled 2160 participants aged 18 years and older, with data collection starting on May 25, 2019, and concluding on November 25, 2021. Participants in this study with AF were enrolled from 28 major hospitals and outpatient clinics in Jordan using a non-probability sampling method. The study focuses on assessing the morbidity and mortality associated with AF in this region, specifically in relation to the HAS BLED and CHADS VAC scores. The methods and procedures were previously mentioned in a previous study [
15].
2.2. Study Population and Data Source
This study enrolled 645 patients with atrial fibrillation on warfarin from the Jordan atrial fibrillation registry (JoFIB). Participants were consecutively and prospectively registered in 28 outpatient clinics and hospitals across Jordan between May 2019 and January 2021. To be eligible for inclusion, patients had to be diagnosed with AF and aged over 18 years, confirmed either by a 12-lead electrocardiogram (EKG) rhythm strip lasting >30 seconds or an ambulatory EKG monitor showing >1 episode of AF. Data were collected using a standardized clinical data form at the time of enrollment and at one, six, and twelve months after the initial assessment.
2.3. Clinical Data Collection
Baseline data encompassed demographic and clinical profiles, EKG readings, laboratory data, details about the use of oral anticoagulants and other medications, as well as transthoracic echocardiographic features. The study utilized standard definitions for classifying different AF types (e.g., persistent, permanent, paroxysmal, long-standing) [
16], and calculated the HAS-BLED scores [
17] and CHA2DS2-VASc scores [
18].
2.4. Oral Anticoagulant Eligibility
Oral anticoagulant eligibility was analyzed based on the 2019 focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for AF management [
16].
2.5. Assessment of INR Stability and Quality of Anticoagulation Control
Numerous measures and computations were used to evaluate the stability of the INR and the effectiveness of the anticoagulation management. INR readings below 2 for a target INR of 2-3 were defined as subtherapeutic INR measures. INR readings exceeding 3 for a target INR of 2-3 were defined as supratherapeutic INR measures. This assessment approach was previously adopted in a different study [
19].
2.6. Ethical Considerations
Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of the Jordan Ministry of Health, and all participants provided written informed consent. The study was registered on clinicaltrials.gov under the number NCT03917992. Patient or public involvement was not involved in the design, conduct, reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
2.7. Data Analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS version 28 (IBM SPSS). Data visualization was performed using GraphPad Prism version 9.3.1 for Windows, GraphPad Software, Boston, Massachusetts USA. Descriptive statistics, such as means and standard deviations for continuous variables, and percentages for categorical variables, were employed for data presentation and interpretation. All statistical tests were two-sided, with p values <0.05 considered to be statistically significant. All underlying assumptions were met unless otherwise indicated.
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ characteristics
This study included 645 patients with AF who were on warfarin therapy, 500 from outpatient departments and 145 from inpatient units. Of inpatients, 33 were admitted due to AF. The mean age of patients was 67.43 (SD 10.91) year, and more than half (57.2%) were females.
Table 1 shows the baseline demographic, clinical, and relevant characteristics of patients in this study. Of all patients, 76.9% had hypertension, 46.6% had diabetes mellitus, 43.1% had dyslipidemia and 11.0% were current smokers. More than one third of patients (38.8%) had a permanent AF, and 38.3% had left ventricular hypertrophy, with a mean ejection fraction of 50.95% (SD 12.09) for the left ventricle. The averages for the baseline parameter of international normalized ratio (INR), CHA2DS2VASC score, and HAS-BLED score were 2.49 (1.15), 3.70 (1.66), and 1.72 (1.16), respectively (
Table 1).
Table 1 also shows the participants' history concerning cerebrovascular accident (CVA) and systemic embolization. Almost 16.3% of patients experienced CVA (n=105) in the past, and 16 out of 105 had a recurrent CVA. The most commonly known type of CVA among participants was the embolic type (32.4%), followed by the thrombotic type (16.2%). In addition, 2.5% of the participants had a history of systemic embolization (16 out of 645), and one out of these 16 had recurrent systemic embolization (6.2%). The most commonly reported site of systemic embolization was in the lower limbs (9 out of 16).
Table 1.
Patient characteristics and embolization history (N=645).
Table 1.
Patient characteristics and embolization history (N=645).
| Variable |
Sub-Variable |
N (%) |
| Age (Mean ± SD) |
|
67.43 ± 10.91 |
| Sex |
Male |
276 (42.8) |
| Female |
369 (57.2) |
| Hypertension |
|
496 (76.9) |
| Diabetes Mellitus |
|
299 (46.4) |
| Dyslipidemia |
|
278 (43.1) |
| Current Smoker |
|
71 (11.0) |
| BMI, Mean ± SD |
|
29.65 ± 5.94 |
| INR, Mean ± SD |
|
2.49 ± 1.15 |
| CHA2DS2VASC score (Mean ± SD) |
|
3.70 ± 1.66 |
| HAS BLED score (Mean ± SD) |
|
1.72 ± 1.16 |
| First Time of AF Episode |
Yes |
127 (19.7) |
| No |
518 (80.3) |
| Type of AF |
Paroxysmal |
135 (20.9) |
| Persistent |
94 (14.6) |
| Long Standing |
166 (25.7) |
| Permanent |
250 (38.8) |
| Enrollment |
Outpatient |
500 (77.5) |
| Inpatient |
145 (22.5) |
| Reason of admission for inpatient |
AF |
33 (5.1) |
| CVS |
73 (11.4) |
| ACS Acute coronary syndrome |
23 (3.6) |
| Heart failure |
29 (4.5) |
| CVA |
10 (1.6) |
| Systemic embolization |
3 (0.5) |
| Bleeding |
8 (1.2) |
| Non- Cardiovascular system |
41 (6.4) |
| Echocardiogram findings |
LVEF (Mean ± SD) |
50.95 ± 12.09 |
| Left atrial size (Mean ± SD) |
4.51 ± 0.81 |
| Left ventricular hypertrophy |
247 (38.3) |
| Pulmonary hypertension |
221 (34.4) |
| Non rheumatic or metallic valve |
499 (77.4) |
| History of CVA (n=645) |
105 (16.3) |
| History of recurrent CVA (n=105) |
16 (15.2) |
| Type of CVA (n=105) |
Embolic |
34 (32.4) |
| Thrombotic |
17 (16.2) |
| Hemorrhagic |
7 (6.7) |
| Unknown |
47 (44.7) |
| History of systemic embolization (n=645) |
|
16 (2.5) |
| History of recurrent systemic embolization (n=16) |
|
1 (6.2) |
| Site of systemic embolization (n=16) |
Lower limbs |
9 (56.3) |
| Upper limbs |
2 (12.5) |
| Mesenteric |
2 (12.5) |
| Kidneys |
1 (6.25) |
| Ophthalmic |
1 (6.25) |
| Unknown site |
1 (6.25) |
Table 2 shows participants’ baseline AF-related symptoms, interventions, and other associated comorbidities. While 28.8% of participants remained asymptomatic, others reported several symptoms. The most commonly reported symptom was palpitation (41.4%), followed by shortness of breath (39.1%) and fatigue (26.2%). Electric cardioversion was the most frequent intervention (5.9%). In addition to AF, participants had many comorbidities. The most widely prevalent comorbidities were congestive heart failure (22.5%), valvular heart diseases (16.6%), and CVA (16.3%).
Table 2.
Participants’ AF related symptoms, interventions, and other comorbidities (N = 645).
Table 2.
Participants’ AF related symptoms, interventions, and other comorbidities (N = 645).
| Variable |
Sub-Variable |
N (%) |
| Symptoms related to AF |
Palpitation |
267 (41.4) |
| Shortness of breath |
252 (39.1) |
| Fatigue |
169 (26.2) |
| Dizziness |
81 (12.6) |
| Chest pain |
11 (1.7) |
| Syncope |
7 (1.1) |
| Asymptomatic |
186 (28.8) |
| AF related interventions |
History of ablation |
5 (0.8) |
| History of occluder device |
3 (0.5) |
| History of electric cardioversion |
38 (5.9) |
| History of permanent pacemaker/ICD/CRT |
7 (1.1) |
| Comorbidities |
Congestive heart failure |
145 (22.5) |
| Valvular disease (rheumatic and non-rheumatic) |
107 (16.6) |
| Cerebrovascular accident (old/new) |
105 (16.3) |
| Coronary artery disease |
33 (5.1) |
| Thyroid disease |
69 (10.7) |
| Chronic kidney disease |
52 (8.1) |
| Active cancer |
36 (6.6) |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary disease |
23 (3.6) |
| Sleep apnea |
17 (2.6) |
Table 3 shows AF related interventions after first month, 6 months, and 12 months. Electric cardioversion was the most commonly reported intervention during a 12-month follow-up period (7 cases out of 645).
Table 3.
AF related interventions after first month, 6 months, and 12 months.
Table 3.
AF related interventions after first month, 6 months, and 12 months.
| Variable |
1 month
(n = 631) |
6 months
(n = 607) |
12 months
(n = 557) |
total in 12 months |
| Electric cardioversions |
2 |
2 |
3 |
7 |
| Ablations |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Occluder device |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Permanent pacemaker/ICD/CRT |
0 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
| Remained on warfarin therapy |
600 |
579 |
539 |
- |
Table 4 provides detail on the death outcome of participants on warfarin therapy across the follow-up points of 12 months. There were 44 death cases (6.82%) in 12 months, where the highest frequency of death occurred after 12 months of follow-up (15 out of 44). A one-year survival rate for patients with AF and on warfarin therapy was 93.18%. Other health outcomes for participants on warfarin therapy across the three follow-up points (1, 6, and 12 months) were documented (
Table 4). The number of CVA cases occurred during the period of follow up was 21 (3.25%). Four cases (0.62%) of systemic embolization occurred in 12 months. A lower limb was the most frequent site of systemic embolization (3 out of 4). In addition, 24 cases of major bleeding (3.72%) occurred in 12 months. Major bleeding leading to hospitalization was the most frequent type of bleeding (10 out of 24). Only 8 cases of ACS (1.24%) occurred in the 12 months follow up period. A non-ST-segment-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) was the most common type of ACS (6 out of 8). Finally, the average of INR values at baseline were 2.49 ± 1.15, and after first month, 6 months, and 12 months were 2.60 ± 1.16, 1.00 ± 1.33, and 1.10 ± 1.48, respectively (data of INR were not reported in the tables) (
Table 4).
3.2. Response to warfarin treatment
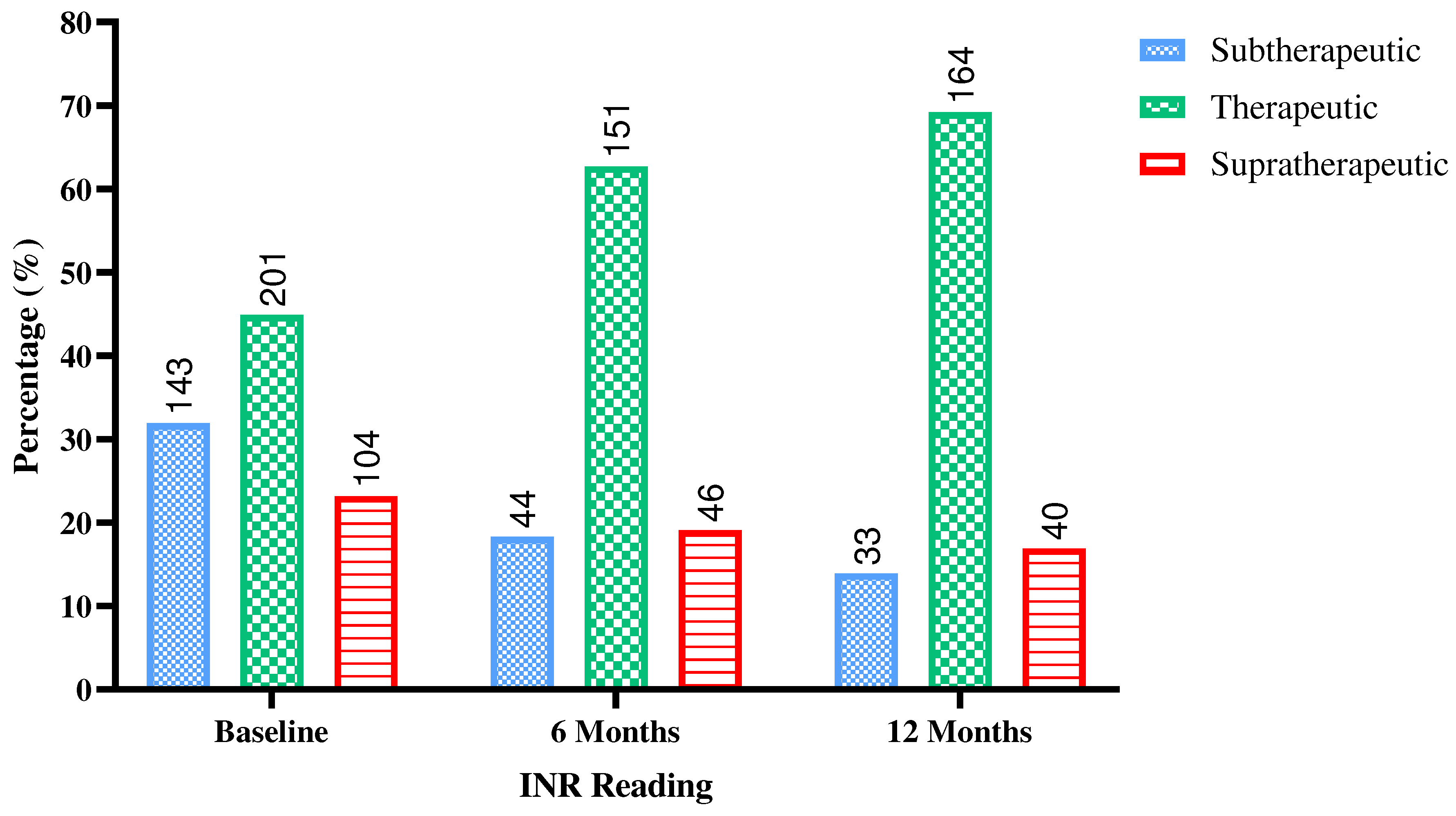
In response to warfarin treatment, INR readings were assessed at baseline, 6 months, and 12 months. At baseline, out of 448 readings, 143 (31.9%) were subtherapeutic, 201 (44.9%) were in the therapeutic range, and 104 (23.2%) were supratherapeutic. However, over the course of 6 months, among 241 readings, a noticeable shift occurred, with 44 (18.3%) of patients being subtherapeutic, 151 (62.7%) achieving therapeutic INR levels, and 46 (19.1%) remaining supratherapeutic. After 12 months, out of 237 readings, the trend continued as only 33 (13.9%) were subtherapeutic, 164 (69.2%) maintained therapeutic INR levels, and 40 (16.9%) remained supratherapeutic. These results suggest that warfarin treatment was effective in gradually shifting the majority of patients into the therapeutic INR range over the course of the study, indicating a positive response to the treatment regimen.
Figure 1.
Response to warfarin treatment among study participants. Subtherapeutic INR <2.0, Therapeutic INR 2.0 - <3.0, Supratherapeutic ≥3.0. INR: International Normalized Ratio. The figure was produced using GraphPad Prism version 9.3.1 for Windows, GraphPad Software, Boston, Massachusetts USA.
Figure 1.
Response to warfarin treatment among study participants. Subtherapeutic INR <2.0, Therapeutic INR 2.0 - <3.0, Supratherapeutic ≥3.0. INR: International Normalized Ratio. The figure was produced using GraphPad Prism version 9.3.1 for Windows, GraphPad Software, Boston, Massachusetts USA.
4. Discussion.
This study provides in-depth analysis of a cohort of patients with AF on warfarin therapy considering patients’ factors, such as the personal characteristics, AF related symptoms, interventions, comorbidities, and 12-months outcomes. Based on our findings, the majority of patients had hypertension and approximately half had diabetes mellitus. Previous studies showed that hypertension is the most frequent comorbidity in AF patients, an established risk factor of cardiovascular disease, and a leading worldwide disease burden [
20] [
21]. For example, ATRIA and AFFIRM studies reported that more than 50% of patients with AF had hypertension [
22,
23]. A Jordanian study indicated that the rate of hypertension was nearly 76.9% [
24].
Our study showed that 38.8% of the patients had permanent AF, 34.4% had pulmonary hypertension, and 38.3% had left ventricular hypertrophy, with an average left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 50.95 for the left ventricle. This finding is in line with a Jordanian study, which reported that 35.8% of patients with AF had left ventricular hypertrophy, and that the average LVEF was 53.7% with 59.9% of patients having normal ejection fraction [
24]. Previous studies indicated that the coexistence of AF with other associated risk factors such as ageing, congestive heart failure, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus increases the risk of developing CVA [
25,
26].
In the current study, the averages for the baseline parameter of INR, CHA2DS2VASc score, and HAS-BLED score were 2.49 (1.15), 3.70 (1.66), and 1.72 (1.16), respectively. Jarrah, Alrabadi, Alzoubi, Mhaidat and Hammoudeh [
24] compared 949 females and 874 males and reported that females (83.0%) had a significantly higher rate of a high CHA2DS2VASc score than males (77.9%) and a lower rate of patients with a low score (6.7 vs. 10.1%). Finding in the present study indicate a higher score for the CHA2DS2VASc, which has been recommended for the assessment of the risk of systemic emboli in patients with AF receiving oral anticoagulants [
27]. The components of the CHA2DS2VASc scale have been associated with increased incidences of systemic emboli and mortality in AF including CVA, hypertension, and DM history[
28,
29]. Additionally, A study by Kaplan
, et al. [
30] reported that stroke and systemic embolism rates were low in patients with a CHA2DS2VASc score of 0 to 1. The study also emphasized that stroke risk was heightened with a CHA2 DS2 -VASc score of 2 among patients experiencing AF for more than 23 hours.
Almost 16.3% (n=105) of patients experienced CVA in the past, and 16 out of them had a recurrent CVA. The most commonly known type of CVA among participants was the embolic type. In addition, 2.5% of the participants had a history of systemic embolization (16 out of 645), and one out of these 16 had recurrent systemic embolization (6.2%). The most commonly reported site of systemic embolization was in the lower limbs (9 out of 16). Jarrah M et. al. found that 83.0% of females and 77.9% of males had a high risk of stroke [
24].
In our study, we incorporated the HAS-BLED score to assess this risk of bleeding in patients with AF who recieve oral anticoagulants. HAS-BLED has been reported to have a clinically significant predictive performance for bleeding events [
31]. Almost half of the patients in our study had a low risk of bleeding, 31.5% had intermediate risk, and 19.6% had a high risk according to the HAS-BLED score. Previous reports emphasized the predictive clinical value of HAS-BLED to patient outcomes including the incidence of embolic events, death, in non-AF patient populations, such as patients with ischemic heart disease and congestive heart failure, DM, heart failure [
21,
32,
33].
Morrone D et al found that the average one-year mortality among AF was 3.1% with strong gradients between stroke-systemic embolic events, major bleeding and mortality for CHA2DS2VASc and HAS-BLED scores, with a statistically significant predictive value for mortality by combining both scores [
33]. According to Parsons P et al., the incidence of thromboembolic event and death was significant among patient who had CHA2DS2VASc scores greater than two [
34]. In our study, death rate over 12 month-period was 2.7%, which could be associated with the thromboembolic event [
35]. Although this association has been reported in literature [
34], this conclusion could not be established in this study. In addition, this percentage of asymptomatic AF indicates the possible presence of higher numbers of patients who could have variable CHA2DS2-VASc scores and go undiagnosed leading to limitations in this, or similar clinical studies.
One-third the participants remained asymptomatic in this study. According to the Asymptomatic AF and Stroke Evaluation in Pacemaker Patients and the AF Reduction Atrial Pacing Trial, device-detected AF that last longer than six minutes was associated with an increased risk of stroke and systemic embolism [
34].
The management scheme and decision of AF depends on the severity and frequency of symptoms. According to Potpara L et al, the clinical profile of the patients with AF determines the sequence of their management protocol [
36]. In that respect, the pattern of AF (e.g., paroxysmal, persistent, and long-standing), valvular condition, co-morbidity and severity of symptoms are the main determinants of management [
16,
37]. Electric cardioversion was the most frequent intervention (5.9%), and the most commonly reported symptom was palpitation, shortness of breath and fatigue. In addition to AF, participants had many comorbidities. The most widely prevalent comorbidities were congestive heart failure (22.5%), valvular heart diseases (16.6%), and CVA (16.3%).
Nursing interventions, including education and coordination of care, are crucial to improve management of patients with AF and those living with other associated comorbidities such as hypertension and heart failure. Studies showed that nursing education interventions have been found to be effective in reducing life-threatening complications, length of hospital stay, and hospital readmissions [
38,
39]. Additionally, nursing education can also assist with improving adherence to take anticoagulation medication, follow dietary restrictions, and seek medication attention when needed, and ultimately reduce the risk of worsening worse cardiovascular prognosis [
38,
39].
Our study has two main strengths. First, it’s the first contemporary Middle Eastern study on atrial fibrillation. Most of the previous atrial fibrillation studies were conducted at least five to ten years ago. Second, the study is the first multi-center study conducted in the region to investigate warfarin population.
The limitation of the study includes that observational studies can cause potential bias. Despite the emphasis on consecutive enrollment, participants might not have been enrolled consecutively. In our study, all participants received AF management at health centers by cardiologists, while other patients in the country might be managed by their family medicine physicians, internists, or general physicians.
5. Conclusions
Congestive heart failure and valvular heart diseases were the most prevalent AF-associated comorbidities. The mortality rate and incidence of CVA, systemic embolization, major bleeding, and ACS were the most frequently reported among participants on warfarin therapy after 6 months of follow-up. The highest incidence rate was for the major bleeding and CVA. Electric cardioversion was the most commonly reported intervention during a 12-month follow-up period. Medical and nursing interventions, considering the factors influencing AF course, are crucial to improve adherence to treatment regimen and clinical outcomes, and ultimately reduce as well as health-related complications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Tariq Al-Shatanawi, Osama Alkouri, Husam ALSalamat and Ayman Hammoudeh; Data curation, Tariq Al-Shatanawi, Osama Alkouri and Husam ALSalamat; Formal analysis, Tariq Al-Shatanawi, Osama Alkouri and Husam ALSalamat; Investigation, Ayman Hammoudeh; Methodology, Tariq Al-Shatanawi, Osama Alkouri, Husam ALSalamat, Omar Qaladi, Rasha Dabbour, Ahmad Al-Bashaireh, Aysam Hweidi, Lourance Al-Hadid and Ayman Hammoudeh; Project administration, Tariq Al-Shatanawi, Osama Alkouri, Husam ALSalamat and Ayman Hammoudeh; Resources, Tariq Al-Shatanawi, Osama Alkouri, Husam ALSalamat and Ayman Hammoudeh; Supervision, Tariq Al-Shatanawi and Osama Alkouri; Visualization, Husam ALSalamat; Writing – original draft, Tariq Al-Shatanawi, Osama Alkouri, Husam ALSalamat, Sameh Al-Zubiedi, Omar Qaladi, Rasha Dabbour, Ahmad Al-Bashaireh, Aysam Hweidi, Lourance Al-Hadid and Ayman Hammoudeh; Writing – review & editing, Tariq Al-Shatanawi, Osama Alkouri, Husam ALSalamat, Sameh Al-Zubiedi, Omar Qaladi, Rasha Dabbour, Ahmad Al-Bashaireh, Aysam Hweidi, Lourance Al-Hadid and Ayman Hammoudeh.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Jordan Ministry of Health (NCT03917992).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting the findings of this research are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge participants for their participation in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jonas, D.E.; Kahwati, L.C.; Yun, J.D.Y.; Middleton, J.C.; Coker-Schwimmer, M.; Asher, G.N. Screening for Atrial Fibrillation With Electrocardiography: Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2018, 320, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, R.; Cha, M.-J.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, J.M.; Park, J.; Park, H.W.; Kang, K.-W.; Shim, J.; Uhm, J.-S.; Kim, J. Characteristics of symptom burden in atrial fibrillation with concomitant heart failure. International Journal of Arrhythmia 2020, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.R.; Taylor, C.J.; Hobbs, F.D.R.; Bowman, L.; Casadei, B. Screening for atrial fibrillation: a call for evidence. Eur Heart J 2020, 41, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdahl, J.; Rosenqvist, M. Large-scale screening studies for atrial fibrillation - is it worth the effort? J Intern Med 2021, 289, 474–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, P.; Stancampiano, F.; Kurklinsky, A.; Nikpour, N.; McLeod, E.; Li, Z.; Oken, K.; Valery, J. Warfarin therapy in atrial fibrillation: assessment of patient knowledge of risks and benefits. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect 2020, 10, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, C.I.; Costa, O.S.; Brescia, C.W.; Vardar, B.; Abdelgawwad, K.; Sood, N. Thromboembolism, bleeding and vascular death in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients with type 2 diabetes receiving rivaroxaban or warfarin. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2021, 20, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, A.M. Stroke in atrial fibrillation: Review of risk stratification and preventive therapy. J Family Community Med 2019, 26, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Stecker, E.; B, A.W. Direct Oral Anticoagulant Use: A Practical Guide to Common Clinical Challenges. J Am Heart Assoc 2020, 9, e017559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.B.; Larsen, T.B.; Skjoth, F.; Lip, G.Y. Outcomes Associated With Resuming Warfarin Treatment After Hemorrhagic Stroke or Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Intern Med 2017, 177, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wańkowicz, P.; Nowacki, P.; Gołąb-Janowska, M. Atrial fibrillation risk factors in patients with ischemic stroke. Archives of Medical Science: AMS 2021, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohtung, R.B.; Rich, M.W. Identification of patients at risk of stroke from atrial fibrillation. Risk 2016, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.; Goldstein, J.N. Anticoagulant-associated intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Hemorrhages 2020, 1, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, A.; Olie, V.; Bejot, Y. Atrial Fibrillation in Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Dijon Stroke Registry (2006-2017). J Am Heart Assoc 2021, 10, e020040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.S.; Lai, N.M.; Nathisuwan, S.; Jahan, N.K.; Dilokthornsakul, P.; Kongpakwattana, K.; Hollingworth, W.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Comparative efficacy and safety of warfarin care bundles and novel oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoudeh, A.J.; Khader, Y.; Kadri, N.; Al-Mousa, E.; Badaineh, Y.; Habahbeh, L.; Tabbalat, R.; Janabi, H.; Alhaddad, I.A. Adherence to the 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline on the Use of Oral Anticoagulant Agents in Middle Eastern Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: The Jordan Atrial Fibrillation (JoFib) Study. Int J Vasc Med 2021, 2021, 5515089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2019, 74, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Nieuwlaat, R.; de Vos, C.B.; Crijns, H.J.; Lip, G.Y. A novel user-friendly score (HAS-BLED) to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation: the Euro Heart Survey. Chest 2010, 138, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, G.Y.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: the euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, B.; Alsalamat, H.; Krishan, M.; Al-Zubiedi, S. Predictors of Anticoagulant Treatment Control in New Warfarin Patients in Jordan. Authorea Preprints 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alhaddad, Z.; Hammoudeh, A.; Khader, Y.; Alhaddad, I.A. Demographics and Risk Profile of Elderly Middle Eastern Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: The Jordan Atrial Fibrillation (JoFib) Study. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2022, 18, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgaard, L.; Gorst-Rasmussen, A.; Lane, D.A.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Larsen, T.B.; Lip, G.Y. Assessment of the CHA2DS2-VASc score in predicting ischemic stroke, thromboembolism, and death in patients with heart failure with and without atrial fibrillation. Jama 2015, 314, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, D.E.; Chang, Y.; Borowsky, L.H.; Fang, M.C.; Pomernacki, N.K.; Udaltsova, N.; Reynolds, K.; Go, A.S. A new risk scheme to predict ischemic stroke and other thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation: the ATRIA study stroke risk score. J Am Heart Assoc 2013, 2, e000250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyse, D. Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) Investigators: A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2002, 347, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrah, M.I.; Alrabadi, N.; Alzoubi, K.; Mhaidat, Q.N.; Hammoudeh, A. Is there a Concordance between CHA2DS2 VASc and HAS-BLED Scores in Middle Eastern Patients with Nonvalvular AF? Analysis of the Jordan Atrial Fibrillation (JoFib) Study. The Open Cardiovascular Medicine Journal 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Doblas, J.J.; Muniz, J.; Martin, J.J.; Rodriguez-Roca, G.; Lobos, J.M.; Awamleh, P.; Permanyer-Miralda, G.; Chorro, F.J.; Anguita, M.; Roig, E.; et al. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in Spain. OFRECE study results. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) 2014, 67, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J.B.; Lip, G.Y.; Hansen, M.L.; Hansen, P.R.; Tolstrup, J.S.; Lindhardsen, J.; Selmer, C.; Ahlehoff, O.; Olsen, A.M.; Gislason, G.H.; et al. Validation of risk stratification schemes for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in patients with atrial fibrillation: nationwide cohort study. BMJ 2011, 342, d124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Alpert, J.S.; Calkins, H.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C.; Conti, J.B.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2014, 64, e1–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, K.M.; Farahmand, B.; Johansson, S.; Asberg, S.; Terent, A.; Edvardsson, N. Survival after stroke--the impact of CHADS2 score and atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol 2010, 141, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemmos, K.; Ntaios, G.; Savvari, P.; Vemmou, A.M.; Koroboki, E.; Manios, E.; Kounali, A.; Lip, G.Y. Stroke aetiology and predictors of outcome in patients with heart failure and acute stroke: a 10-year follow-up study. Eur J Heart Fail 2012, 14, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.M.; Koehler, J.; Ziegler, P.D.; Sarkar, S.; Zweibel, S.; Passman, R.S. Stroke risk as a function of atrial fibrillation duration and CHA2DS2-VASc score. Circulation 2019, 140, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Gersh, B.J.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Kent, D.M.; Shah, N.D.; Abraham, N.S.; Noseworthy, P.A. Comparison of the CHA2DS2-VASc, CHADS2, HAS-BLED, ORBIT, and ATRIA risk scores in predicting non–vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants-associated bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation. The American Journal of Cardiology 2017, 120, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolillo, D.J.; Patti, G.; Chan, K.T.; Han, Y.; Huang, W.C.; Yakovlev, A.; Paek, D.; Del Aguila, M.; Girotra, S.; Sibbing, D. De-escalation from ticagrelor to clopidogrel in acute coronary syndrome patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2019, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrone, D.; Kroep, S.; Ricci, F.; Renda, G.; Patti, G.; Kirchhof, P.; Chuang, L.-H.; van Hout, B.; De Caterina, R. Mortality prediction of the CHA2DS2-VASc score, the HAS-BLED score, and their combination in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. Journal of clinical medicine 2020, 9, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, C.; Patel, S.I.; Cha, S.; Shen, W.K.; Desai, S.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Luis, S.A.; Aguilar, M.I.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Mookadam, F.; et al. CHA(2)DS(2)-VASc Score: A Predictor of Thromboembolic Events and Mortality in Patients With an Implantable Monitoring Device Without Atrial Fibrillation. Mayo Clin Proc 2017, 92, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambatti, M.; Connolly, S.J.; Gold, M.R.; Morillo, C.A.; Capucci, A.; Muto, C.; Lau, C.P.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Carlson, M. Temporal relationship between subclinical atrial fibrillation and embolic events. Circulation 2014, 129, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potpara, T.S.; Lip, G.Y.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hindricks, G.; Camm, A.J. The 4S-AF scheme (stroke risk; symptoms; severity of burden; substrate): a novel approach to in-depth characterization (rather than classification) of atrial fibrillation. Thrombosis and haemostasis 2021, 121, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, G.; Freedman, B.; De Caterina, R.; Potpara, T.S. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: Past, present and future. Comparing the guidelines and practical decision-making. Thromb Haemost 2017, 117, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutugno, C.L. CE: Atrial Fibrillation: Updated Management Guidelines and Nursing Implications. Am J Nurs 2015, 115, 26–38, quiz 39, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesheiwat, Z.; Goyal, A.; Jagtap, M.; Shammas, A. Atrial Fibrillation (Nursing). In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing, 2021. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).