Submitted:
11 January 2024
Posted:
12 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Activated sludge characteristics
3.2. Performances of the SFD MBR tests
4. Discussion
4.1. Activated sludge characteristics
4.2. Permeate quality in the different SFD MBR tests
4.3. Effects of the mesh pore size and the AML on SFD MBR performances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friha, F. Karray, F. Feki, L. Jlaiel, e S. Sayadi, «Treatment of cosmetic industry wastewater by submerged membrane bioreactor with consideration of microbial community dynamics», Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., vol. 88, pp. 125–133, mar. 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. Hoinkis et al., «Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Treated Domestic Wastewater for Reuse in a Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS)», in Water-Energy-Nexus in the Ecological Transition: Natural-Based Solutions, Advanced Technologies and Best Practices for Environmental Sustainability, V. Naddeo, K.-H. Choo, e M. Ksibi, A c. di, in Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation. , Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022, pp. 153–155. [CrossRef]
- P. Vergine, S. Amalfitano, C. Salerno, G. Berardi, e A. Pollice, «Reuse of ultrafiltered effluents for crop irrigation: On-site flow cytometry unveiled microbial removal patterns across a full-scale tertiary treatment», Sci. Total Environ., vol. 718, p. 137298, mag. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. B. Asif et al., «Membrane Bioreactor for Wastewater Treatment: Current Status, Novel Configurations and Cost Analysis», in Cost-efficient Wastewater Treatment Technologies: Engineered Systems, M. Nasr e A. M. Negm, A c. di, in The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry. , Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023, pp. 147–167. [CrossRef]
- S. J. Judd, P. Le-Clech, T. Taha, e Z. F. Cui, «Theoretical and experimental representation of a submerged membrane bio-reactor system», Membr. Technol., vol. 2001, fasc. 135, pp. 4–9, lug. 2001. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wu, X. Huang, X. Wen, e F. Chen, «Function of dynamic membrane in self-forming dynamic membrane coupled bioreactor», Water Sci. Technol., vol. 51, fasc. 6–7, pp. 107–114, mar. 2005. [CrossRef]
- L. Borea, F. Castrogiovanni, G. Ferro, S. W. Hasan, V. Belgiorno, e V. Naddeo, «Hydrogen Production in Electro Membrane Bioreactors», in Frontiers in Water-Energy-Nexus—Nature-Based Solutions, Advanced Technologies and Best Practices for Environmental Sustainability, V. Naddeo, M. Balakrishnan, e K.-H. Choo, A c. di, in Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 85–87. [CrossRef]
- Pollice et al., «Removal of nalidixic acid and its degradation products by an integrated MBR-ozonation system», J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 203–204, pp. 46–52, feb. 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. W. Hasan, M. Elektorowicz, e J. A. Oleszkiewicz, «Correlations between trans-membrane pressure (TMP) and sludge properties in submerged membrane electro-bioreactor (SMEBR) and conventional membrane bioreactor (MBR)», Bioresour. Technol., vol. 120, pp. 199–205, set. 2012. [CrossRef]
- F. Meng, S.-R. Chae, A. Drews, M. Kraume, H.-S. Shin, e F. Yang, «Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material», Water Res., vol. 43, fasc. 6, pp. 1489–1512, apr. 2009. [CrossRef]
- P. Le-Clech, V. Chen, e T. A. G. Fane, «Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment», J. Membr. Sci., vol. 284, fasc. 1, pp. 17–53, nov. 2006. [CrossRef]
- S. Judd e C. Judd, A c. di, The MBR Book (Second Edition), 2nd ed. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2011. [CrossRef]
- R. W. Field e G. K. Pearce, «Critical, sustainable and threshold fluxes for membrane filtration with water industry applications», Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 164, fasc. 1, pp. 38–44, mag. 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Stoller, M. Bravi, e A. Chianese, «Threshold flux measurements of a nanofiltration membrane module by critical flux data conversion», Desalination, vol. 315, pp. 142–148, apr. 2013. [CrossRef]
- W. Xie, J. Li, F. Sun, W. Dong, e Z. Dong, «Strategy study of critical flux/threshold flux on alleviating protein fouling of PVDF-TiO2 modified membrane», J. Environ. Chem. Eng., vol. 9, fasc. 5, p. 106148, ott. 2021. [CrossRef]
- C.-H. Wei, X. Huang, R. Ben Aim, K. Yamamoto, e G. Amy, «Critical flux and chemical cleaning-in-place during the long-term operation of a pilot-scale submerged membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment», Water Res., vol. 45, fasc. 2, pp. 863–871, gen. 2011. [CrossRef]
- R. M. Moattari, T. Mohammadi, S. Rajabzadeh, H. Dabiryan, e H. Matsuyama, «Reinforced hollow fiber membranes: A comprehensive review», J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., vol. 122, pp. 284–310, mag. 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Salerno, P. Vergine, G. Berardi, e A. Pollice, «Influence of air scouring on the performance of a Self Forming Dynamic Membrane BioReactor (SFD MBR) for municipal wastewater treatment», Bioresour. Technol., vol. 223, pp. 301–306, gen. 2017. [CrossRef]
- P. Vergine, C. Salerno, G. Berardi, e A. Pollice, «Sludge cake and biofilm formation as valuable tools in wastewater treatment by coupling Integrated Fixed-film Activated Sludge (IFAS) with Self Forming Dynamic Membrane BioReactors (SFD-MBR)», Bioresour. Technol., vol. 268, pp. 121–127, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. E. Ersahin, H. Ozgun, R. K. Dereli, I. Ozturk, K. Roest, e J. B. van Lier, «A review on dynamic membrane filtration: Materials, applications and future perspectives», Bioresour. Technol., vol. 122, pp. 196–206, ott. 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Mohan e S. Nagalakshmi, «A review on aerobic self-forming dynamic membrane bioreactor: Formation, performance, fouling and cleaning», J. Water Process Eng., vol. 37, p. 101541, ott. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. Salerno, G. Berardi, B. Casale, e A. Pollice, «Comparison of fine bubble scouring, backwash, and mass air load supply for dynamic membrane maintenance and steady operation in SFD MBR for wastewater treatment», J. Water Process Eng., vol. 53, p. 103846, lug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Pollice e P. Vergine, «10 - Self-forming dynamic membrane bioreactors (SFD MBR) for wastewater treatment: Principles and applications», in Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering, G. Mannina, A. Pandey, C. Larroche, H. Y. Ng, e H. H. Ngo, A c. di, Elsevier, 2020, pp. 235–258. [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), e Water Environment Federation (WEF), Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 24th ed. Washington DC: APHA Press, 2023. Consultato: 16 novembre 2023. [Online]. Disponibile su: https://www.standardmethods.org/.
- Y. Kim, H. Yeom, S. Choi, H. Bae, e C. Kim, «Sludge settleability detection using automated SV30 measurement and comparisons of feature extraction methods», Korean J. Chem. Eng., vol. 27, fasc. 3, pp. 886–892, mag. 2010. [CrossRef]
- H. Han, X. Wu, L. Ge, e J. Qiao, «A sludge volume index (SVI) model based on the multivariate local quadratic polynomial regression method», Chin. J. Chem. Eng., vol. 26, fasc. 5, pp. 1071–1077, mag. 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. Jenkins, M. G. Richard, e G. T. Daigger, Manual on the Causes and Control of Activated Sludge Bulking, Foaming, and Other Solids Separation Problems, 3a ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2003. [CrossRef]
- X. Chen, F. Kong, Y. Fu, C. Si, e P. Fatehi, «Improvements on activated sludge settling and flocculation using biomass-based fly ash as activator», Sci. Rep., vol. 9, fasc. 1, Art. fasc. 1, ott. 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Maltos, R. W. Holloway, e T. Y. Cath, «Enhancement of activated sludge wastewater treatment with hydraulic selection», Sep. Purif. Technol., vol. 250, p. 117214, nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. Nittami e S. Batinovic, «Recent advances in understanding the ecology of the filamentous bacteria responsible for activated sludge bulking», Lett. Appl. Microbiol., vol. 75, fasc. 4, pp. 759–775, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Gerardi, «Appendix I: F/M, HRT, MCRT, MLVSS, Sludge Age, SVI», in Settleability Problems and Loss of Solids in the Activated Sludge Process, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2002, pp. 153–156. [CrossRef]
- W. Zhao, X. Bi, M. Bai, e Y. Wang, «Research advances of ammonia oxidation microorganisms in wastewater: metabolic characteristics, microbial community, influencing factors and process applications», Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng., vol. 46, fasc. 5, pp. 621–633, mag. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Vivar, M. Fuentes, J. Torres, e M. J. Rodrigo, «Solar disinfection as a direct tertiary treatment of a wastewater plant using a photochemical-photovoltaic hybrid system», J. Water Process Eng., vol. 42, p. 102196, ago. 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Vergine, C. Salerno, B. Casale, G. Berardi, e A. Pollice, «Role of Mesh Pore Size in Dynamic Membrane Bioreactors», Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health, vol. 18, fasc. 4, Art. fasc. 4, gen. 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. Cai, J. Huang, G. Liu, M. Li, Y. Yu, e F. Meng, «Effect of support material pore size on the filtration behavior of dynamic membrane bioreactor», Bioresour. Technol., vol. 255, pp. 359–363, mag. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Saleem, E. Masut, A. Spagni, e M. C. Lavagnolo, «Exploring dynamic membrane as an alternative for conventional membrane for the treatment of old landfill leachate», J. Environ. Manage., vol. 246, pp. 658–667, set. 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Sreeda, A. B. Sathya, e V. Sivasubramanian, «Novel application of high-density polyethylene mesh as self-forming dynamic membrane integrated into a bioreactor for wastewater treatment», Environ. Technol., vol. 39, fasc. 1, pp. 51–58, gen. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Z. Wang, J. Ma, C. Y. Tang, K. Kimura, Q. Wang, e X. Han, «Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review», Membr. Clean. Membr. Bioreact. Rev., vol. 468, pp. 276–307, ott. 2014. [CrossRef]
- D. Guan, J. Dai, M. Ahmar Siddiqui, e G. Chen, «Comparison of different chemical cleaning reagents on fouling recovery in a Self-Forming dynamic membrane bioreactor (SFDMBR)», Sep. Purif. Technol., vol. 206, pp. 158–165, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
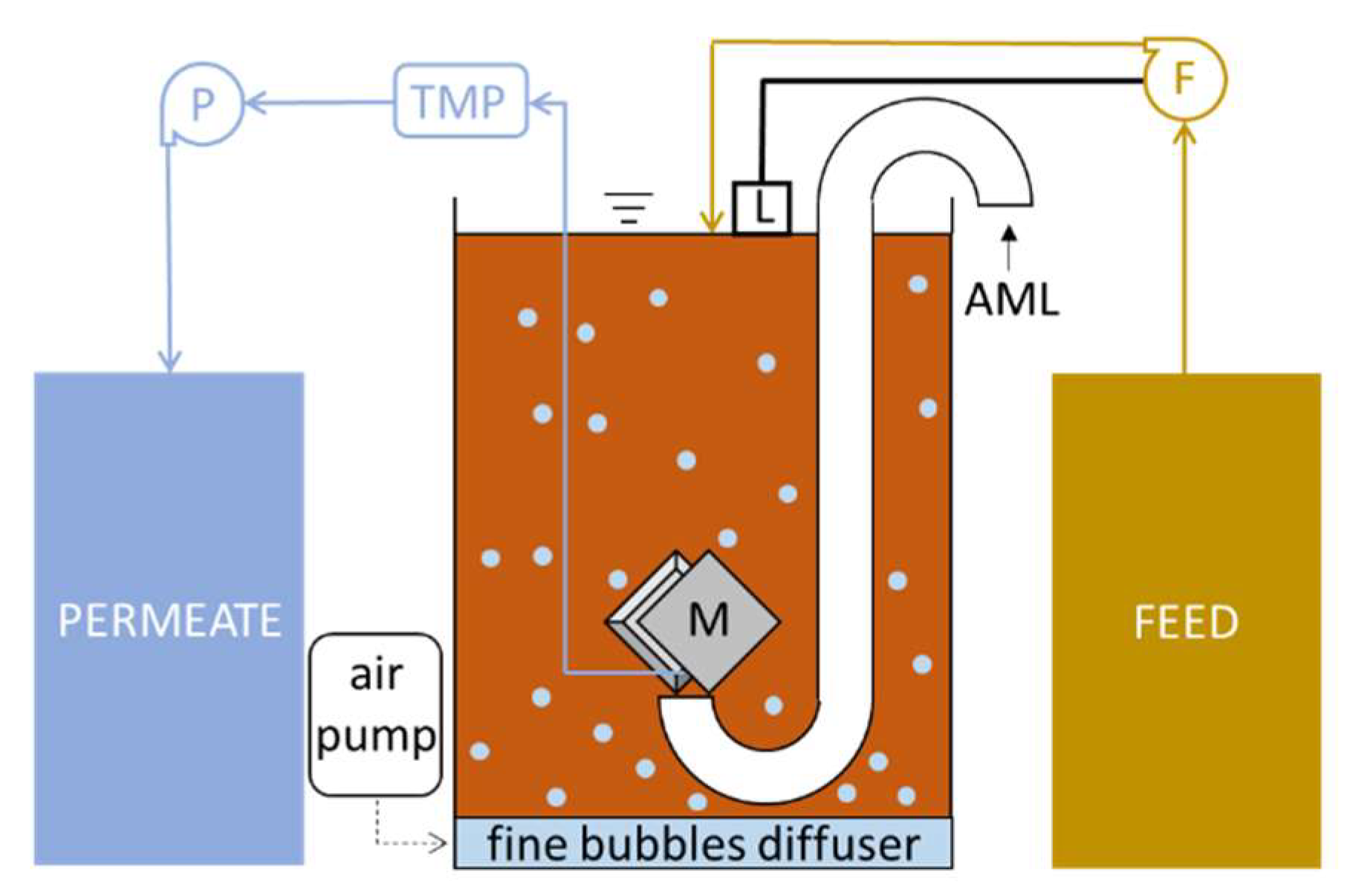
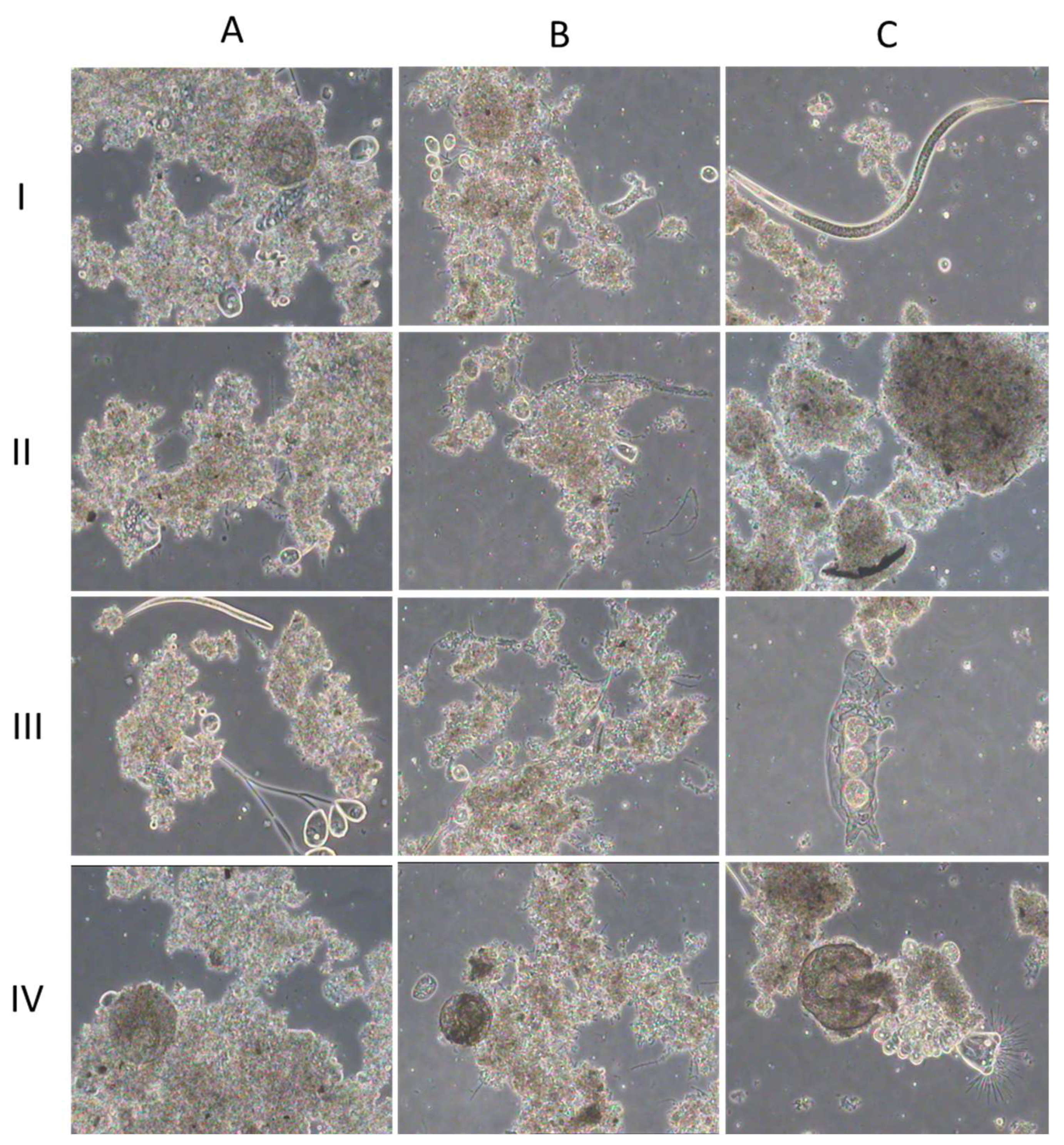
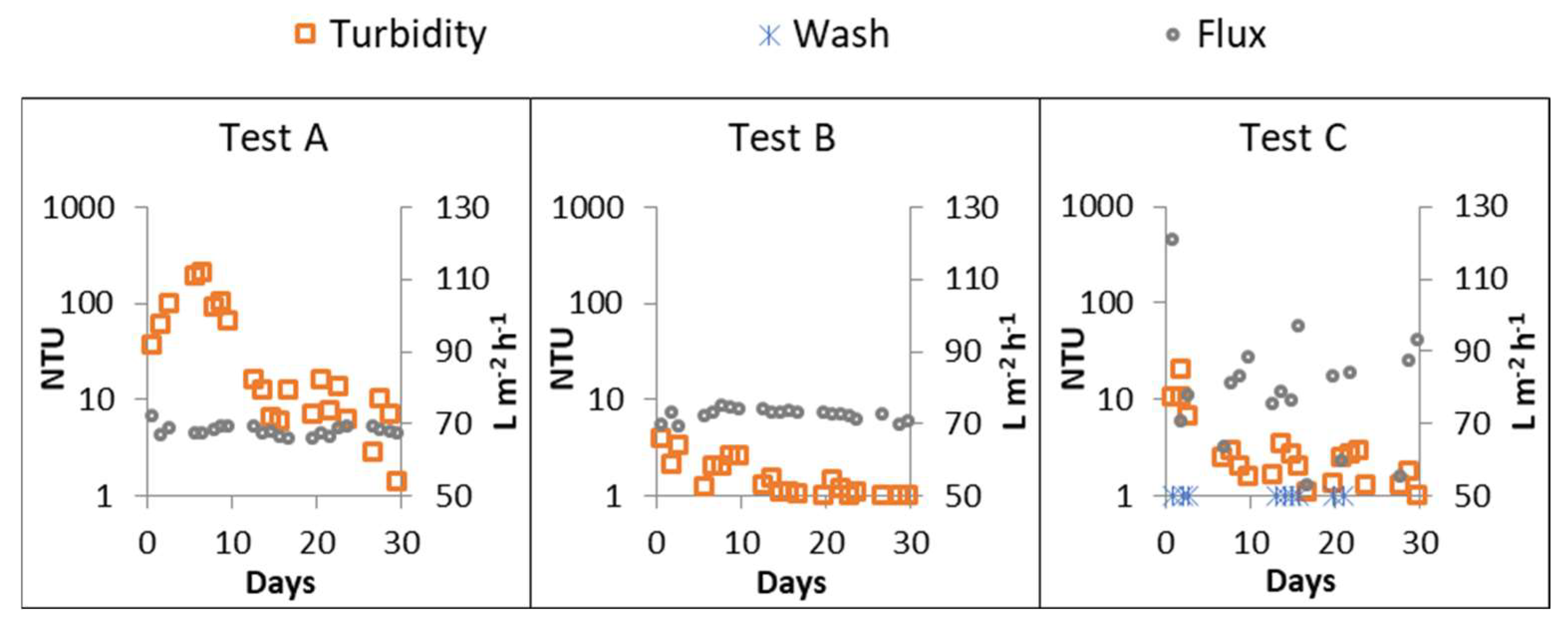
| Parameter | Test A | Test B | Test C |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRT | 30 days | 30 days | 30 days |
| Volume | 16.0 L | 16.0 L | 16.0 L |
| Filtering area | 0.0072 m2 | 0.0072 m2 | 0.0072 m2 |
| Target flux | 73 L m-2 h-1 | 73 L m-2 h-1 | 73 L m-2 h-1 |
| Mesh pore-size | 50 µm | 20 µm | 20 µm |
| Periodic maintenance* | AML | AML | relaxation |
| No-suction time distribution | 3’break + 5’AML + 3’break | 3’break + 5’AML + 3’break | 11’break |
| Parameter | unit | Average ± st.dev. |
|---|---|---|
| TSS | mg L-1 | 248.8 ± 103.6 |
| VSS | mg L-1 | 243.2 ± 95.9 |
| COD | mg L-1 | 460.0 ± 22.6 |
| soluble COD | mg L-1 | 112.3 ± 49.0 |
| TN | mg L-1 | 65.5 ± 17.3 |
| N-NH4+ | mg L-1 | 42.0 ± 11.1 |
| N-NO2- | mg L-1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 |
| N-NO3- | mg L-1 | 0.2 ± 0.2 |
| pH | - | 7.4 ± 0.2 |
| Electr. conductivity | mS cm-1 | 1.3 ± 0.5 |
| Tot. coliforms | MPN 100 mL-1 | 2.5E+07 (median); 2.0E+06 (min); 7.9E+07 (max) |
| E. coli | MPN 100 mL-1 | 7.9E+06 (median); 3.0E+05 (min); 2.9E+07 (max) |
| Parameter | Unit | Test A | Test B | Test C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLSS | g L-1 | 3.4 ± 1.2 | 4.4 ± 1.3 | 2.9 ± 1.6 |
| MLVSS | g L-1 | 3.0 ± 1.0 | 3.8 ± 1.1 | 2.6 ± 1.4 |
| SVI30 | mL g-1 | 64.3 ± 14.1 | 92.1 ± 8.6 | 43.9 ± 9.9 |
| Temperature | °C | 20.0 ± 0.6 | 20.2 ± 0.2 | 22.5 ± 0.8 |
| DO | mg L-1 | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 4.1 ± 1.2 | 6.2 ± 1.8 |
| ORP | mV | 305.5 ± 39.1 | 294.6 ± 6.2 | 314.8 ± 9.7 |
| pH | - | 6.8 ± 0.5 | 7.1 ± 0.5 | 7.0 ± 0.8 |
| Parameter | unit | Test A | Test B | Test C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSS | mg L-1 | 366.7 ± 78.5 | 4.7 ± 1.9 | 6.4 ± 6.2 |
| COD | mg L-1 | 103.0 ± 86.7 | 30.4 ± 5.0 | 32.8 ± 6.2 |
| TN | mg L-1 | 98.7 ± 52.1 | 55.1 ± 5.3 | 41.3 ± 8.8 |
| N-NH4+ | mg L-1 | 1.0 ± 2.3 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.3 |
| N-NO2- | mg L-1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 1.6 ± 0.9 |
| N-NO3- | mg L-1 | 24.7 ± 5.1 | 35.7 ± 6.7 | 27.1 ± 7.3 |
| Electr. conductivity | mS cm-1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.0 |
| pH | - | 7.1 ± 0.8 | 7.4 ± 0.3 | 7.3 ± 0.3 |
| Tot. coliforms | MPN 100 mL-1 | 1.6E+05 (median) | 4.4E+05 (median) | 1.6E+04 (median) |
| 1.3E+05 (min) | 5.0E+04 (min) | 1.0E+04 (min) | ||
| 1.9E+05 (max) | 4.6E+05 (max) | 2.2E+04 (max | ||
| E. coli | MPN 100 mL-1 | 6.0E+04 (median) | 1.0E+05 (median) | 8.2E+03 (median) |
| 5.8E+04 (min) | 2.0E+04 (min) | 6.3E+03 (min) | ||
| 6.3E+04 (max) | 2.2E+05 (max) | 1.0E+04 (max) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





