Submitted:
11 January 2024
Posted:
11 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- (1)
- They require a threshold, and selecting a suitable threshold can be challenging.
- (2)
- They primarily focus on spectral data while ignoring the potential of spatial features in improving HCD results, which has been proven by multiple studies.
- (3)
- Most HCD methods are complex to implement and require high-complexity computation.
- (4)
- Noise and atmospheric conditions can negatively affect the automatic generation of pseudo-sample data through simple predictors and thresholding methods.
- (5)
- Most HCD methods require additional pre-processing steps, such as highlighting changes (recognizing changes from no-changes) or dimensional reduction. The dependence of HCD results on the chosen method for conducting these pre-processing steps makes it difficult to obtain robust results in different study areas.
- (1)
- Proposing a double-stream deep feature extraction method for HCD using 3D/2D convolution layers.
- (2)
- Implementing the HCD-Net in an End-to-End manner without additional processing.
- (3)
- Taking advantage of the 3D/2D attention mechanism for informative deep feature extraction.
- (4)
- Evaluating the efficiency of HCD methods in different areas using both space-borne and airborne HIS.
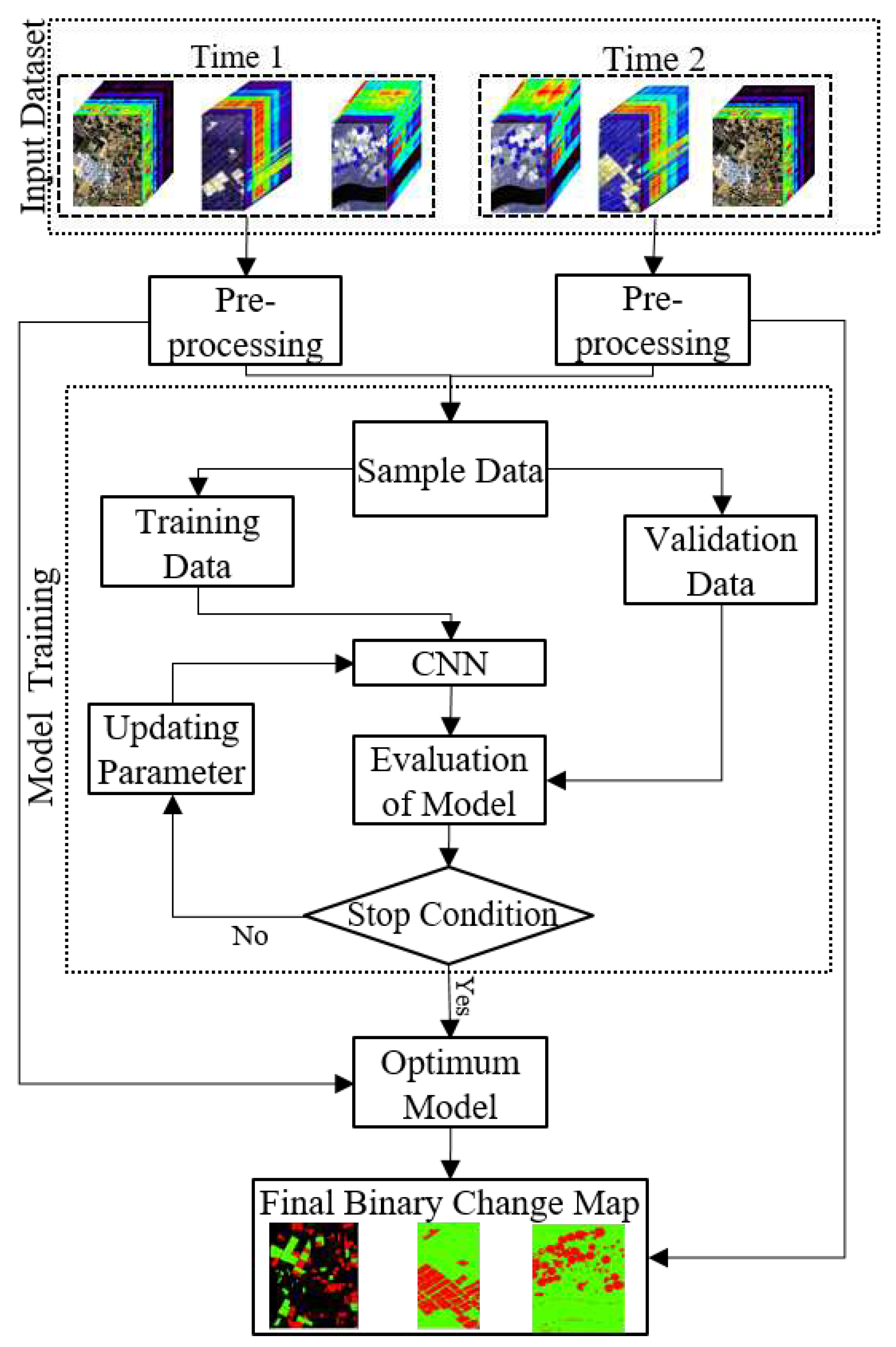
2. Methodology
2.1. Pre-Processing
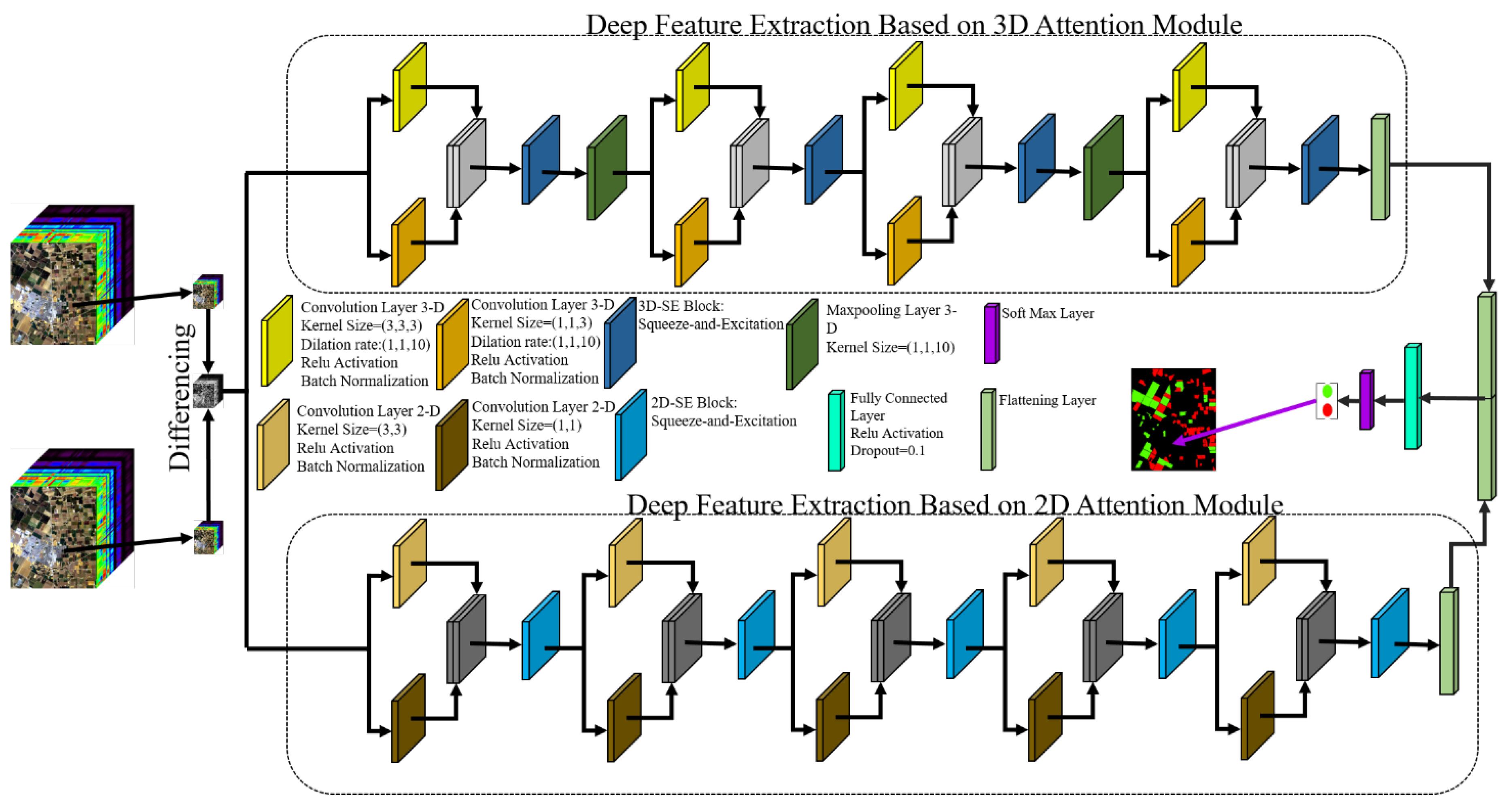
2.2. CNN-based HCD
- (1)
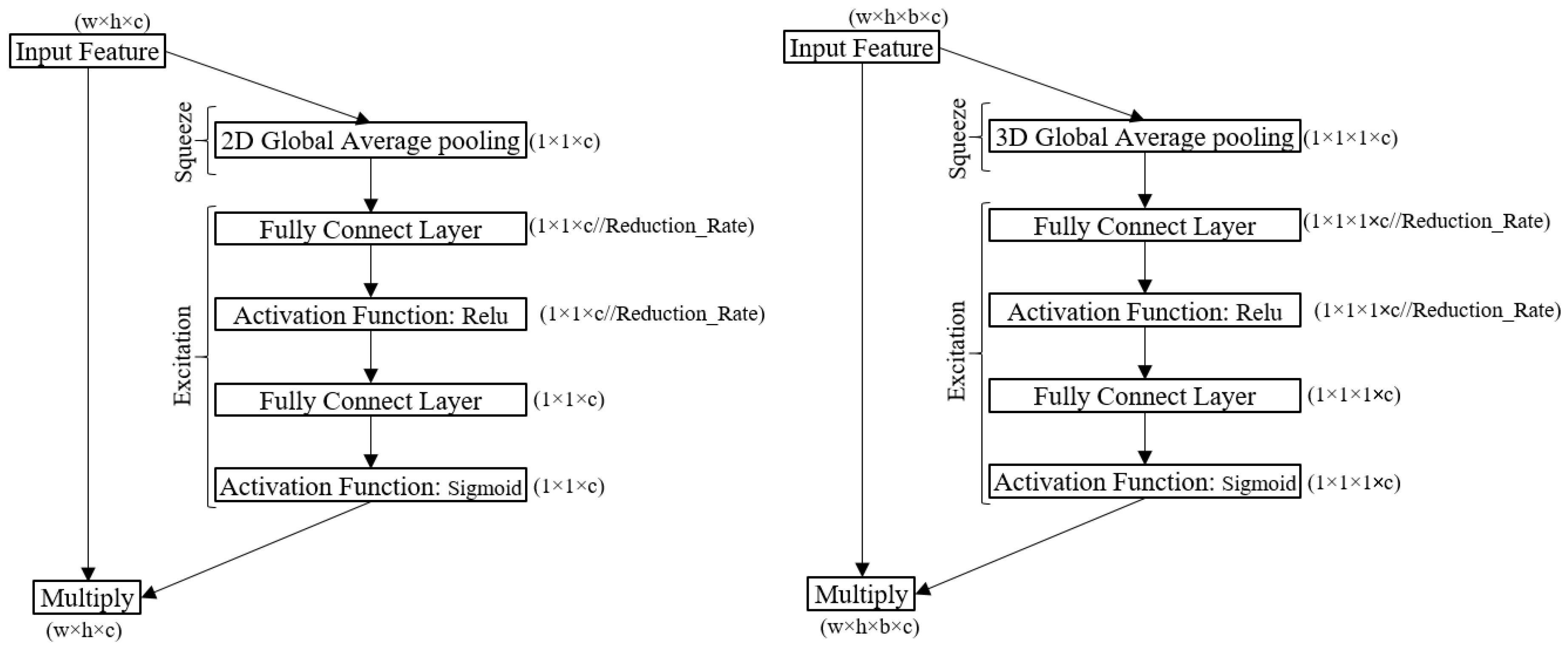
- Taking advantage of SE-bock in extracting informative deep features.
- (2)
- Utilizing the advantages of spectral information in the hyperspectral dataset through 3D convolution layers.
- (3)
- Combining 3D and 2D convolutions to explore high-level spectral and spatial information.
- (4)
- Utilizing a multiscale convolution block to increase the robustness of the network against different object sizes.
- (5)
- Employing a differencing algorithm to reduce computational and time costs instead of concatenating deep features in the first layers.
2.3. Squeeze and Excitation (SE) Blocks
2.4. Convolution Layers
2.5. Model Parameters Optimization
2.6. Accuracy Assessment and Comparison with Other Methods
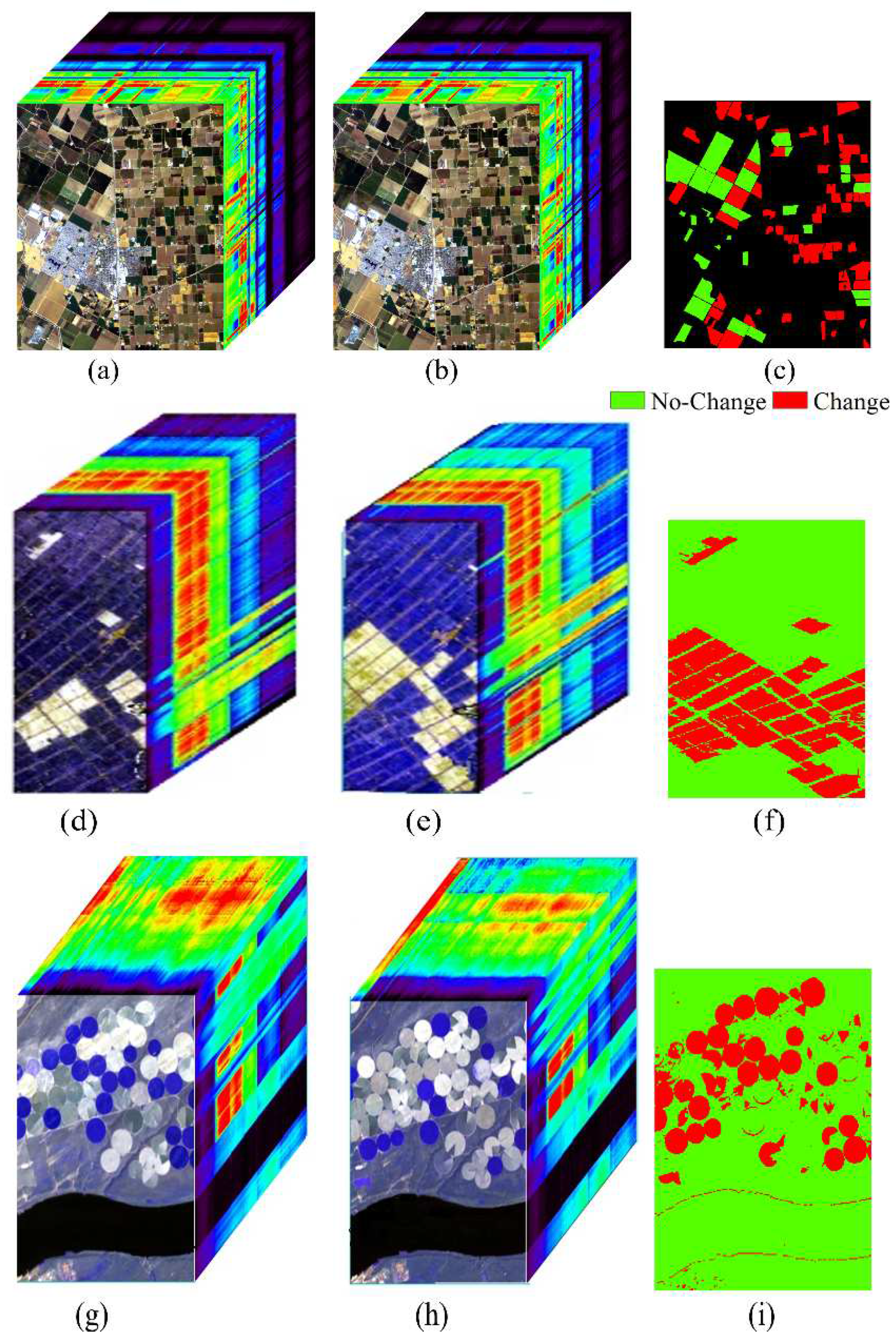
3. Case Study
4. Experiment and Results
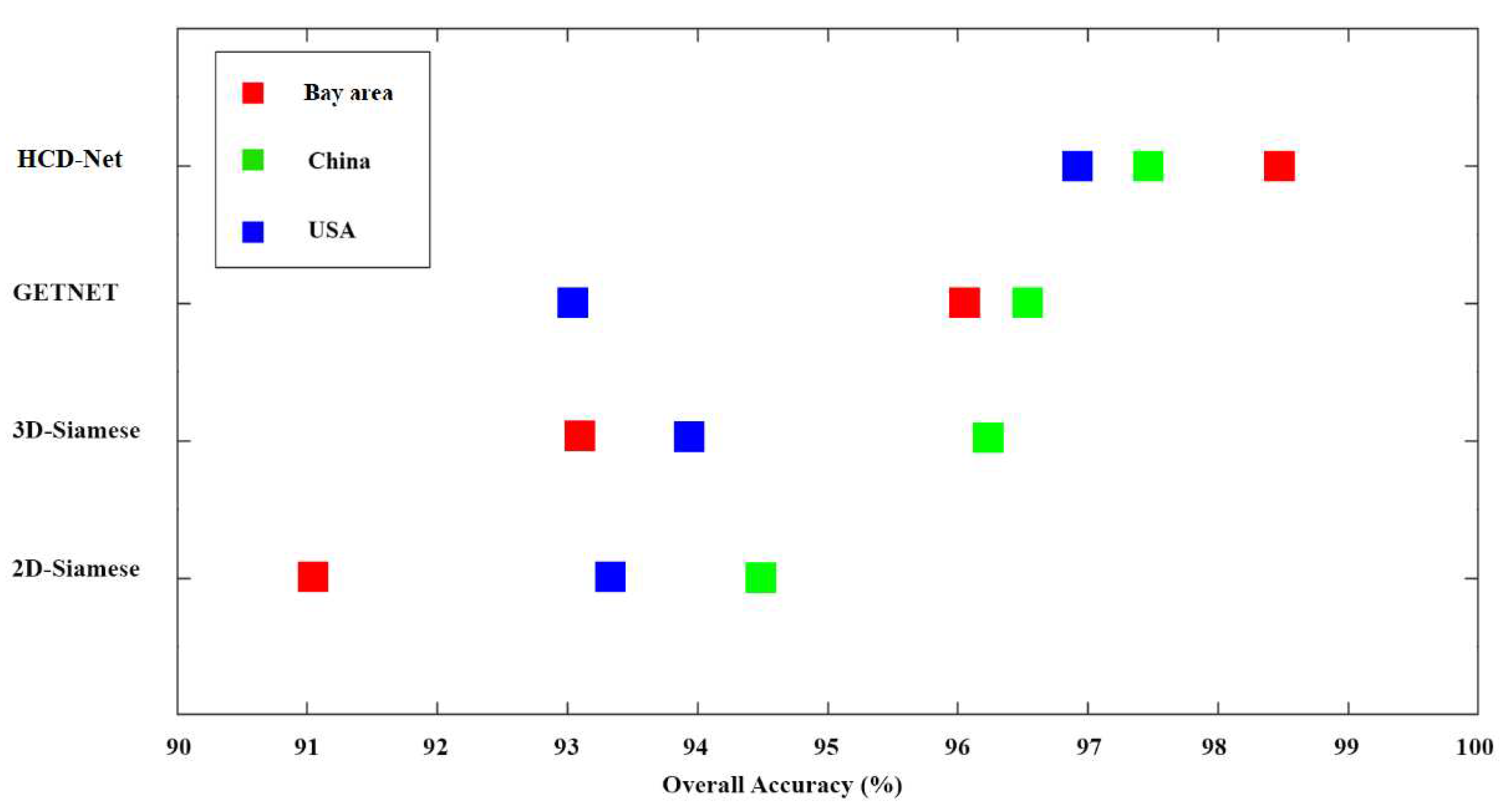
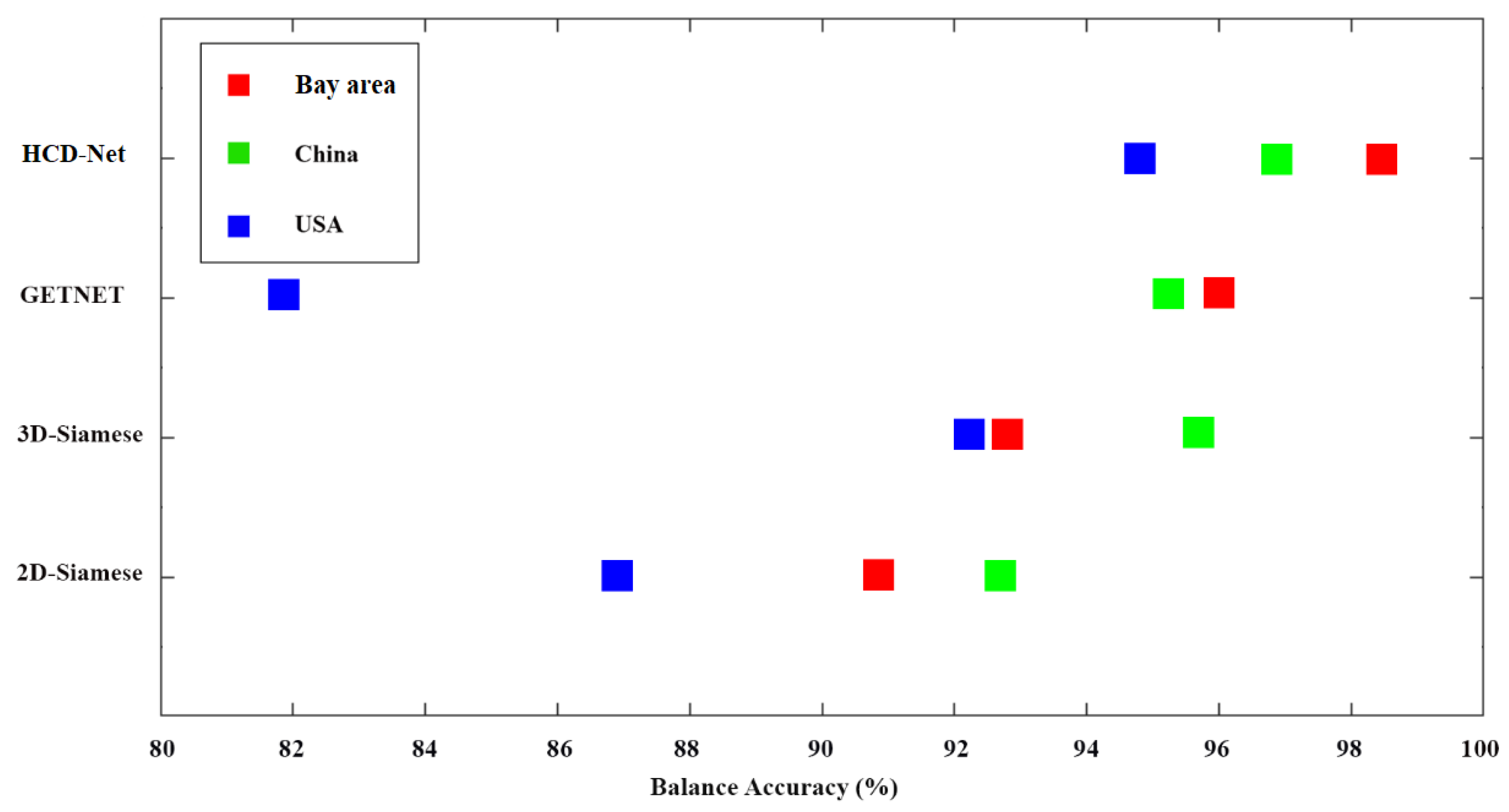
4.1. Results of HCD for the Bay Area Dataset
4.2. Results of HCD for the China Dataset
4.3. Results of HCD for the USA Dataset
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Auto-Encoder |
| AVIRIS | Airborne Visible InfraRed Imaging Spectrometer |
| BA | Balance Accuracy |
| CD | Change Detection |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CVA | Change Vector Analysis |
| DBN | Deep Belief Network |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| GAP | Global Average Pooling |
| GETNET | General End-to-end Two-dimensional CNN Framework |
| HCD-Net | Hyperspectral Change Detection |
| HIS | Hyperspectral RS Imagery |
| KC | Kappa Coefficient |
| MPL | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| OA | Overall Accuracy |
| PRISMA | Recursore IperSpettrale della Missione Applicativa |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| SAM | Spectral Angle Mapper |
| SVDD | Support Vector Domain Description |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
References
- Zhan, T.; Gong, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, M. Unsupervised scale-driven change detection with deep spatial–spectral features for VHR images. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2020, 58, 5653–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renza, D.; Martinez, E.; Molina, I.; others. Unsupervised change detection in a particular vegetation land cover type using spectral angle mapper. Advances in Space Research 2017, 59, 2019–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, D.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. A novel change detection method for multitemporal hyperspectral images based on binary hyperspectral change vectors. IEEE transactions on geoscience and remote sensing 2019, 57, 4913–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, D.; Cheng, A.; Wei, H.; Stanley, D. Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS Journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing 2013, 80, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydi, S.T.; Hasanlou, M. A new land-cover match-based change detection for hyperspectral imagery. European Journal of Remote Sensing 2017, 50, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmens, K.A.; Ramage, J. Investigating correlations between snowmelt and forest fires in a high latitude snowmelt dominated drainage basin. Hydrological Processes 2012, 26, 2608–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, W.M.; Freeborn, P.H.; Page, W.G.; Butler, B.W. Severe fire danger index: A forecastable metric to inform firefighter and community wildfire risk management. Fire 2019, 2, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gong, P.; Fu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Liang, S.; Xu, B.; Shi, J.; Dickinson, R. The role of satellite remote sensing in climate change studies. Nature climate change 2013, 3, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boueshagh, M.; Hasanlou, M. Estimating water level in the Urmia Lake using satellite data: a machine learning approach. The International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2019, 42, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, J.; Ahmadi, A.; Abbaspour, K. Runoff responses to human activities and climate change in an arid watershed of central Iran. Hydrological Sciences Journal 2021, 66, 2280–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Jalali, J.; Mohammadpour, A. Future runoff assessment under climate change and land-cover alteration scenarios: a case study of the Zayandeh-Roud dam upstream watershed. Hydrology Research 2022, 53, 1372–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, A.; Seydi, S.T.; Alipour-Fard, T.; Cao, G.; Yang, D. SSViT-HCD: A Spatial Spectral Convolutional Vision Transformer for Hyperspectral Change Detection. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol Sadrabadi, M.; Innocente, M.S. Vegetation Cover Type Classification Using Cartographic Data for Prediction of Wildfire Behaviour. Fire 2023, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, P.; Colombo, R.; Maggi, M.; Tomasoni, R. Integration of remote sensing data and GIS for accurate mapping of flooded areas. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2002, 23, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, H.S.; Hammad, A.W.; Waller, S.T. Remote sensing methods for flood prediction: A review. Sensors 2022, 22, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maymandi, N.; Hummel, M.A.; Zhang, Y. Compound coastal, fluvial, and pluvial flooding during historical hurricane events in the Sabine-Neches Estuary, Texas. Water Resources Research 2022, e2022WR033144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, K.; Hummel, M.A. A Bayesian copula-based nonstationary framework for compound flood risk assessment along US coastlines. Journal of Hydrology 2022, 610, 128005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanlou, M.; Seydi, S.T. Hyperspectral change detection: An experimental comparative study. International journal of remote sensing 2018, 39, 7029–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Xiao, S.; Liang, J.; Qu, J. Fusion of hyperspectral and panchromatic images using structure tensor and matting model. Neurocomputing 2020, 399, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chan, J.C.W. Collaborative learning of lightweight convolutional neural network and deep clustering for hyperspectral image semi-supervised classification with limited training samples. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2020, 161, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi, F.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive band selection for pan-sharpening of hyperspectral images. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2020, 41, 3924–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, M.; Ghassemian, H. An overview on spectral and spatial information fusion for hyperspectral image classification: Current trends and challenges. Information fusion 2020, 59, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi Miyoshi, G.; Imai, N.N.; Garcia Tommaselli, A.M.; Antunes de Moraes, M.V.; Honkavaara, E. Evaluation of hyperspectral multitemporal information to improve tree species identification in the highly diverse atlantic forest. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydi, S.T.; Hasanlou, M. A new structure for binary and multiple hyperspectral change detection based on spectral unmixing and convolutional neural network. Measurement 2021, 186, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Wu, X.; Ghamisi, P.; Chanussot, J.; Yokoya, N.; Zhu, X.X. Invariant attribute profiles: A spatial-frequency joint feature extractor for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2020, 58, 3791–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fandiño, J.B.; Heras, D.; Argüello, F.; Dalla Mura, M. GPU framework for change detection in multitemporal hyperspectral images. International Journal of Parallel Programming 2019, 47, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Liu, L.; Tan, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Tu, B. A Hyperspectral Image Change Detection Framework With Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning Pretrained Model. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2022, 15, 7724–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, L.; Liu, S.; Bovolo, F.; Du, P. Change detection in multitemporal hyperspectral images. Multitemporal Remote Sensing: Methods and Applications 2016, 63–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ertürk, A.; Iordache, M.D.; Plaza, A. Sparse unmixing-based change detection for multitemporal hyperspectral images. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2015, 9, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, S. Fuzzy fusion of change vector analysis and spectral angle mapper for hyperspectral change detection. IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE, 2018, pp. 5045–5048.
- Ghasemian, N.; Shah-Hosseini, R. Hyperspectral multiple-change detection framework based on sparse representation and support vector data description algorithms. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2020, 14, 014523–014523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Kondmann, L.; Zhu, X.X. Deep no learning approach for unsupervised change detection in hyperspectral images. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2021, 3, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Pan, H.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Luo, X.; Xie, H.; Xu, X. A novel approach for hyperspectral change detection based on uncertain area analysis and improved transfer learning. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2020, 13, 2056–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydi, S.; Hasanlou, M. Binary hyperspectral change detection based on 3D convolution deep learning. The International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2020, 43, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsoi, R.A.; Imbiriba, T.; Bermudez, J.C.M.; Richard, C. Fast unmixing and change detection in multitemporal hyperspectral data. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging 2021, 7, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Hasan, M.; Van Essen, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.; Asari, V.K. A state-of-the-art survey on deep learning theory and architectures. electronics 2019, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.E.; Anderson, D.T.; Chan, C.S. Comprehensive survey of deep learning in remote sensing: theories, tools, and challenges for the community. Journal of applied remote sensing 2017, 11, 042609–042609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Choo, K.K.R.; Huang, F. Spectral–spatial multi-feature-based deep learning for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. Soft Computing 2017, 21, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, H.; Hasanlou, M. An unsupervised binary and multiple change detection approach for hyperspectral imagery based on spectral unmixing. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2019, 12, 4888–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Advanced techniques for automatic change detection in multitemporal hyperspectral images. PhD thesis, University of Trento, 2015.
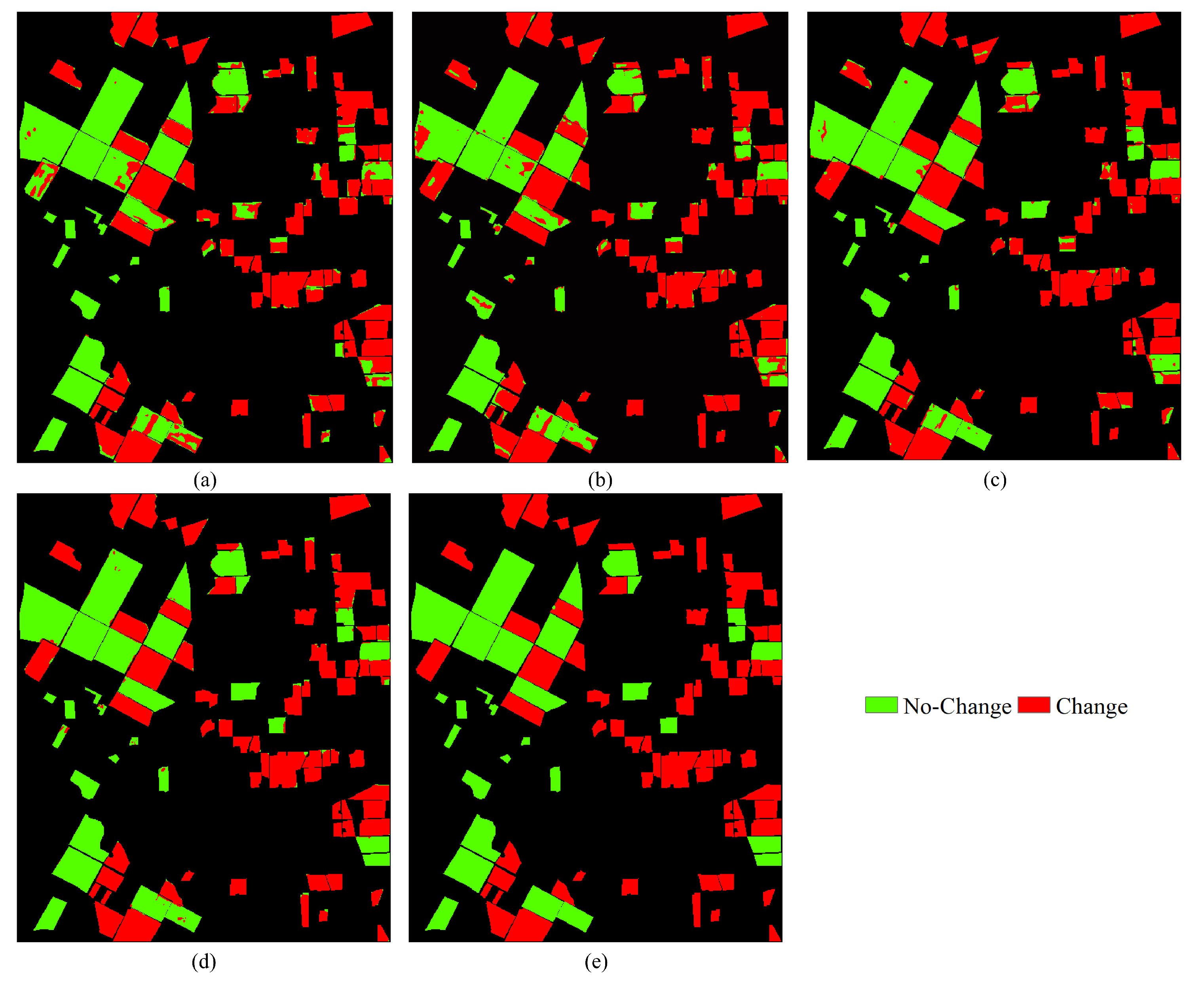
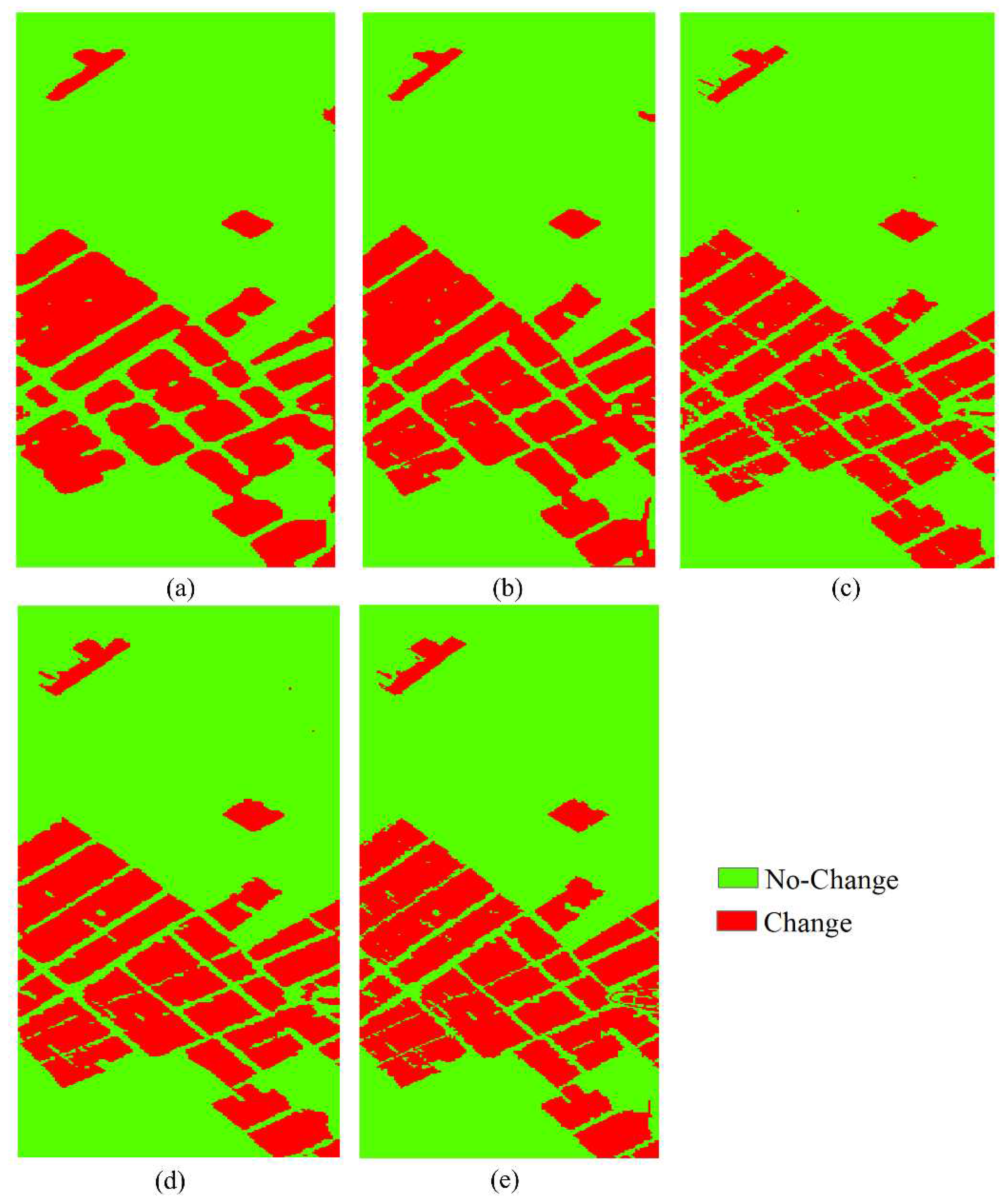
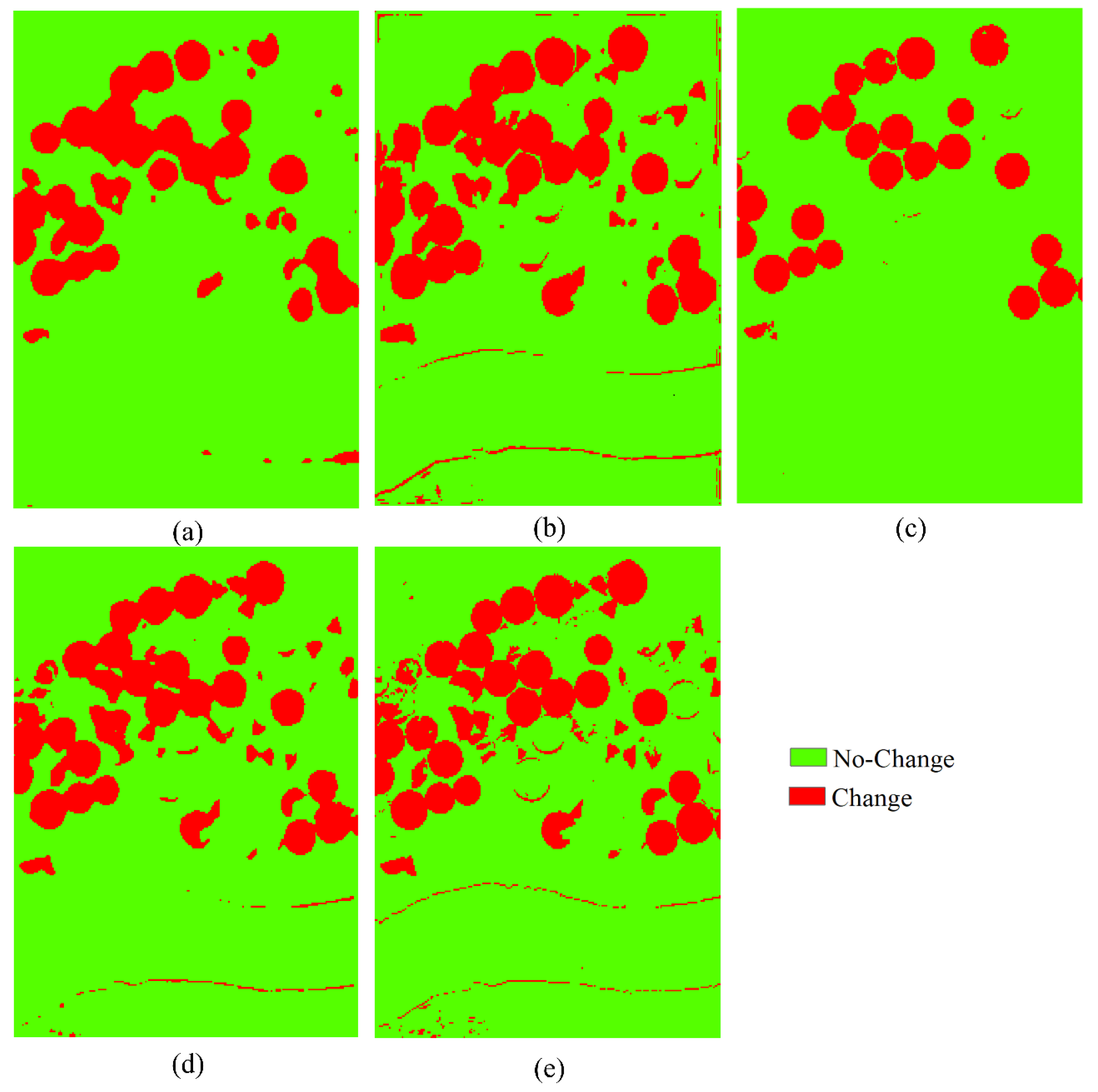
| Dataset | Size | Data | No-Change | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bay Area | 600×500 | 73,404 | 34,211 | 39,270 |
| China | 420×140 | 58,800 | 40,417 | 18,383 |
| USA | 307×241 | 74,987 | 59,688 | 14,299 |
| Index | 2D-Siamese | 3D-Siamese | GETNET | HCD-Net |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | 91.05 | 93.10 | 96.05 | 98.47 |
| Precision (%) | 90.57 | 91.19 | 95.64 | 98.58 |
| Recall (%) | 92.92 | 96.40 | 97.04 | 98.55 |
| F1-Score (%) | 91.73 | 93.73 | 96.33 | 98.56 |
| BA (%) | 90.91 | 92.86 | 95.98 | 98.46 |
| KC | 0.820 | 0.861 | 0.920 | 0.969 |
| Index | 2D-Siamese | 3D-Siamese | GETNET | HCD-Net |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | 94.49 | 96.25 | 96.53 | 97.46 |
| Precision (%) | 94.43 | 93.63 | 97.28 | 96.69 |
| Recall (%) | 87.53 | 94.44 | 91.46 | 95.15 |
| F1-Score (%) | 90.85 | 94.03 | 94.28 | 95.92 |
| BA (%) | 92.59 | 95.76 | 95.15 | 96.83 |
| KC | 0.869 | 0.913 | 0.892 | 0.941 |
| Index | 2D-Siamese | 3D-Siamese | GETNET | HCD-Net |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | 93.33 | 93.92 | 93.03 | 96.92 |
| Precision (%) | 87.13 | 81.18 | 100 | 92.53 |
| Recall (%) | 76.69 | 89.27 | 63.93 | 91.46 |
| F1-Score (%) | 81.58 | 85.03 | 78.00 | 91.99 |
| BA (%) | 86.98 | 92.15 | 81.96 | 94.85 |
| KC | 0.775 | 0.812 | 0.740 | 0.900 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





