Submitted:
09 January 2024
Posted:
10 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. INTRODUCTION
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. STUDY OF INDIVIDUAL AND MIXTURE PERMEANCE
2.2. Membrane Separation Unit Simulation
2.3. Gas separation experiment
2.4. Materials screening
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1. Gas transport characteristics study by individual components
3.2. Mixture permeance study
3.3. Comparison of study methods for gas transport characteristics
4. CONCLUSION
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
References
- Kianfar, E.; Cao, V. Polymeric Membranes on Base of PolyMethyl Methacrylate for Air Separation: A Review. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2021, 10, 1437–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, J.-Y.; Tan, J.-Y.-L.; Chong, Q.-Y.; Ooi, J.-W.; Chemmangattuvalappil, J.; Design, N.G.; Cheun, J.-Y.; Liew, J.-Y.-L.; Tan, Q.-Y.; Chong, J.-W.; et al. Design of Polymeric Membranes for Air Separation by Combining Machine Learning Tools with Computer Aided Molecular Design. Processes 2023, Vol. 11, Page 2004 2023, 11, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzystowczyk, E.; Haribal, V.; Dou, J.; Li, F. Chemical Looping Air Separation Using a Perovskite-Based Oxygen Sorbent: System Design and Process Analysis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2021, 9, 12185–12195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckinghausen, A.; Odlare, M.; Thorin, E.; Schwede, S. From Removal to Recovery: An Evaluation of Nitrogen Recovery Techniques from Wastewater. Appl Energy 2020, 263, 114616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, Q.; Ho, T.C. Eco-Friendly Natural Gas Monetization Complex for Simultaneous Power Generation and Nitrogen-Based Fertilizer Production. Ind Eng Chem Res 2023, 62, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley, M.W. Medical Oxygen Concentrators: A Review of Progress in Air Separation Technology. Adsorption 2019, 25, 1437–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Rong, Y.; Fang, S.; Wang, K.; Zhi, X.; Qiu, L.; Chi, X. Thermodynamic Analysis of an Organic Rankine–Vapor Compression Cycle (ORVC) Assisted Air Compression System for Cryogenic Air Separation Units. Appl Therm Eng 2021, 189, 116678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.F.; Villardi, H.G.D.; Araujo, L.S.; Raptopoulos, L.S.C.; Dutra, M.S. Detailed Design and Economic Evaluation of a Cryogenic Air Separation Unit with Recent Literature Solutions. Ind Eng Chem Res 2021, 60, 14830–14844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Verma, P.; Yang, Z.; Axelbaum, R.L. Single-Column Cryogenic Air Separation: Enabling Efficient Oxygen Production with Rapid Startup and Low Capital Costs—Application to Low-Carbon Fossil-Fuel Plants. Energy Convers Manag 2021, 248, 114773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamin, Z.; Bahrun, M.H.V.; Bono, A. A Short Review on Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) Technology for Nitrogen Generation from Air. AIP Conf Proc 2022, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Ding, Z.; Xu, X.; Shi, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Simulation and Experiment of Six-Bed PSA Process for Air Separation with Rotating Distribution Valve. Chin J Chem Eng 2022, 42, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Zeng, Y. Experimental Study on the Performance of an Onboard Hollow-Fiber-Membrane Air Separation Module. Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2021, 18, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.G.; Bigdeli, F.; Panjehpour, A.; Hwa Jhung, S.; Al Lawati, H.A.J.; Morsali, A. Potential Applications of MOF Composites as Selective Membranes for Separation of Gases. Coord Chem Rev 2023, 496, 215413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, S.; Selyanchyn, R.; Kunitake, T. A New Strategy for Membrane-Based Direct Air Capture. Polymer Journal 2020 53:1 2020, 53, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, C.Y.; Goh, K.; Bae, T.H. Enhanced Performance of Carbon Molecular Sieve Membranes Incorporating Zeolite Nanocrystals for Air Separation. Membranes (Basel) 2021, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petukhov, A.N.; Shablykin, D.N.; Trubyanov, M.M.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Zarubin, D.M.; Vorotyntsev, A. V.; Stepanova, E.A.; Smorodin, K.A.; Kazarina, O. V.; Petukhova, A.N.; et al. A Hybrid Batch Distillation/Membrane Process for High Purification Part 2: Removing of Heavy Impurities from Xenon Extracted from Natural Gas. Sep Purif Technol 2022, 294, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.P.; Godhaniya, M.; Kothari, C. Emerging and Advanced Membrane Technology for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. J Basic Microbiol 2022, 62, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petukhov, A.N.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Kryuchkov, S.S.; Smorodin, K.A.; Zarubin, D.M.; Petukhova, A.N.; Atlaskina, M.E.; Nyuchev, A. V.; Vorotyntsev, A. V.; Trubyanov, M.M.; et al. A Highly-Efficient Hybrid Technique – Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption for Ammonia Recovery after the Haber-Bosch Process. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 421, 127726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhikku Kandath Valappil, R.; Ghasem, N.; Al-Marzouqi, M. Current and Future Trends in Polymer Membrane-Based Gas Separation Technology: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2021, 98, 103–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, I. V.; Murav’Ev, D. V. Fine Gas Purification to Remove Slightly Penetrating Impurities Using a Membrane Module with a Feed Reservoir. Doklady Chemistry 2006, 411, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlaskin, A.A.; Trubyanov, M.M.; Yanbikov, N.R.; Kryuchkov, S.S.; Chadov, A.A.; Smorodin, K.A.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Vorotyntsev, I. V. Experimental Evaluation of the Efficiency of Membrane Cascades Type of “Continuous Membrane Column” in the Carbon Dioxide Capture Applications. Membranes and Membrane Technologies 2020, 2, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlaskin, A.A.; Trubyanov, M.M.; Yanbikov, N.R.; Vorotyntsev, A. V.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Vorotyntsev, I. V. Comprehensive Experimental Study of Membrane Cascades Type of “Continuous Membrane Column” for Gases High-Purification. J Memb Sci 2019, 572, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushin, Y.V.; Kapostey, E.I. Developing a Comprehensive Mathematical Model for Aluminium Production in a Soderberg Electrolyser. Energies 2023, Vol. 16, Page 6313 2023, 16, 6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, K.; Margaritis, N.; Schulze-Küppers, F.; Wolters, J.; Natour, G. A Mathematical Model for Initial Design Iterations and Feasibility Studies of Oxygen Membrane Reactors by Minimizing Gibbs Free Energy. J Memb Sci 2023, 685, 121955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubyanov, M.M.; Kirillov, S.Y.; Vorotyntsev, A. V.; Sazanova, T.S.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Petukhov, A.N.; Kirillov, Y.P.; Vorotyntsev, I. V. Dynamic Behavior of Unsteady-State Membrane Gas Separation: Modelling of a Closed-Mode Operation for a Membrane Module. J Memb Sci 2019, 587, 117173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.J.; Gróf, G. Techno-Economic Optimization of Grid-Connected, Ground-Mounted Photovoltaic Power Plants by Genetic Algorithm Based on a Comprehensive Mathematical Model. Solar Energy 2020, 202, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub—CCSI-Toolset/Membrane_Model: Membrane Separation Model: Updated Hollow Fiber Membrane Model And System Example For Carbon Capture. Available online: Https://Github.Com/CCSI-Toolset/Membrane_model (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Pfromm, P.H.; Pinnau, I.; Koros, W.J. Gas Transport through Integral-Asymmetric Membranes: A Comparison to Isotropic Film Transport Properties. J Appl Polym Sci 1993, 48, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, B.D.; Ruiz-Trevino, A.; Musselman, I.H.; Balkus, K.J.; Ferraris, J.P. Gas Permeability Properties of Polysulfone Membranes Containing the Mesoporous Molecular Sieve MCM-41. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, B.C.; Ismail, A.F.; W Abdul Rahman, W.A.; Hasbullah, H.; Abdullah, M.S.; Hassan, A.R. FORMATION OF ASYMMETRIC POLYSULFONE FLAT SHEET MEMBRANE 73 FORMATION OF ASYMMETRIC POLYSULFONE FLAT SHEET MEMBRANE FOR GAS SEPARATION: RHEOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT. J Teknol 2004, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnau, I.; Koros, W.J. Structures and Gas Separation Properties of Asymmetric Polysulfone Membranes Made by Dry, Wet, and Dry/Wet Phase Inversion. J Appl Polym Sci 1991, 43, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbari, T.A.; Koros, W.J.; Paul, D.R. Polymeric Membranes Based on Bisphenol-A for Gas Separations. J Memb Sci 1989, 42, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.T.; Paul, D.R. Gas Sorption and Transport in UV-Irradiated Poly(2,6-Dimethyl-1,4-Phenylene Oxide) Films. J Appl Polym Sci 1998, 67, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotskaya, C.A.; Agranova, S.A.; Gazdina, N. V; Kuznetsov, Y.P.; Nesterov, V. V Effect of Molecular Weight Parameters on Gas Transport Properties of Poly(2,6-Dimethyl-1,4-Phenylene Oxide). [CrossRef]
- Polotskaya, G.A.; Penkova, A. V.; Toikka, A.M.; Pientka, Z.; Brozova, L.; Bleha, M. Transport of Small Molecules through Polyphenylene Oxide Membranes Modified by Fullerene. Sep Sci Technol 2007, 42, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checchetto, R.; Scarpa, M.; De Angelis, M.G.; Minelli, M. Mixed Gas Diffusion and Permeation of Ternary and Quaternary CO2/CO/N2/O2 Gas Mixtures in Matrimid®, Polyetherimide and Poly(Lactic Acid) Membranes for CO2/CO Separation. J Memb Sci 2022, 659, 120768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Li, P.; Chung, T.S. PIM-1 as an Organic Filler to Enhance the Gas Separation Performance of Ultem Polyetherimide. J Memb Sci 2014, 453, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Kaliaguine, S.; Rodrigue, D. Polymer Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation: A Comparison between Three Commercial Resins. AIP Conf Proc 2019, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenar, M.P.; Soltanieh, M.; Matsuura, T.; Tabe-Mohammadi, A.; Feng, C. Gas Permeation Properties of Commercial Polyphenylene Oxide and Cardo-Type Polyimide Hollow Fiber Membranes. Sep Purif Technol 2006, 51, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, T.; Masetto, N.; Wessling, M. Materials Dependence of Mixed Gas Plasticization Behavior in Asymmetric Membranes. J Memb Sci 2007, 306, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiner, O.M.; Kulkami, S.S. Process for Making Hollow Fiber Mixed Matrix Membranes 2003.
- Saimani, S.; Kumar, A.; Dal-Cin, M.M.; Robertson, G. Synthesis and Characterization of Bis (4-Maleimidophenyl) Fluorene and Its Semi Interpenetrating Network Membranes with Polyether Imide (Ultem® 1000). J Memb Sci 2011, 374, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, N.; Robertson, G.P.; Dal-Cin, M.M.; Scoles, L.; Guiver, M.D. Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity (PIMs) Substituted with Methyl Tetrazole. Polymer (Guildf) 2012, 53, 4367–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Pinnau, I.; Du, N.; Guiver, M.D. Hydrocarbon/Hydrogen Mixed-Gas Permeation Properties of PIM-1, an Amorphous Microporous Spirobisindane Polymer. J Memb Sci 2009, 338, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
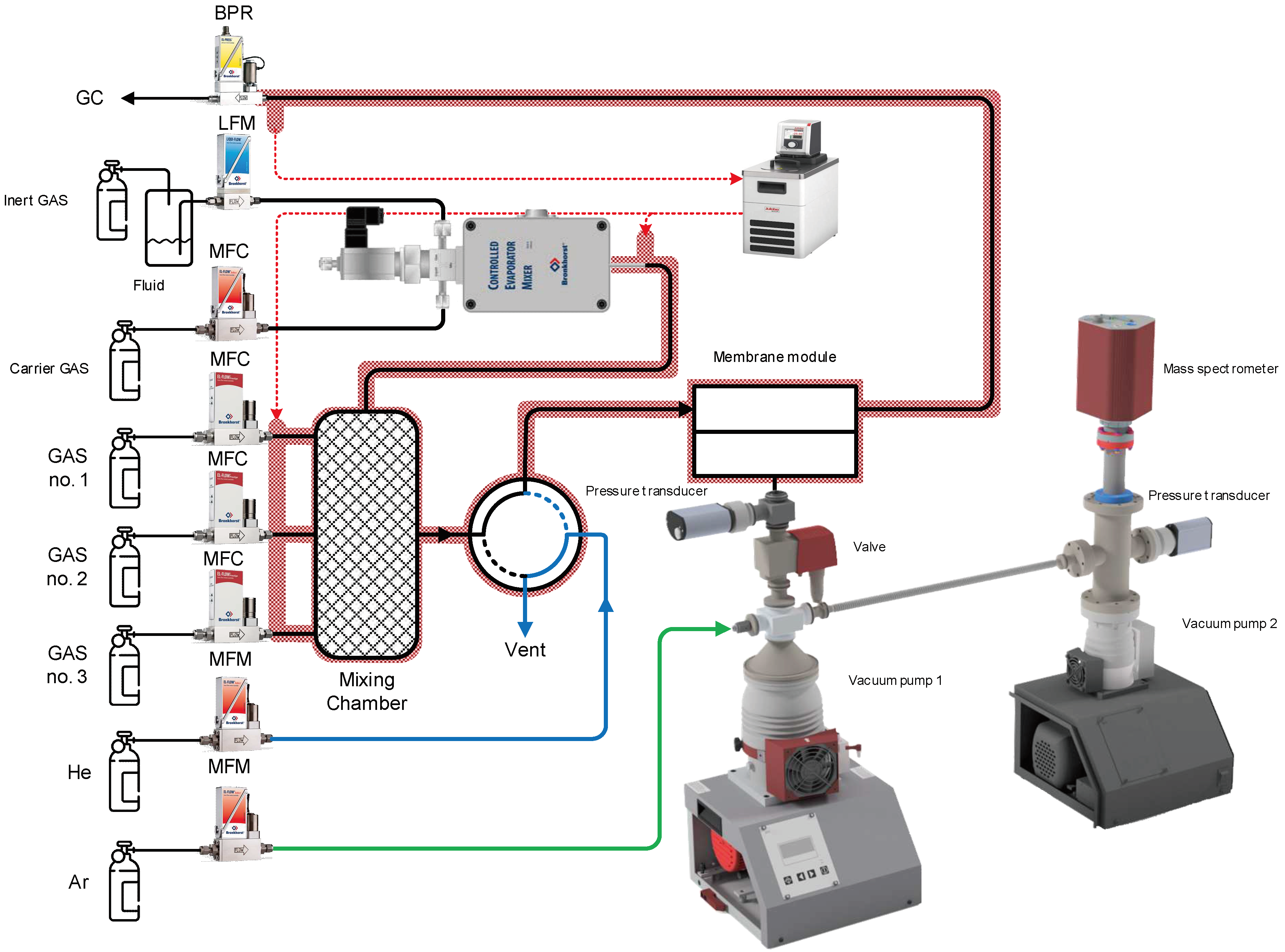
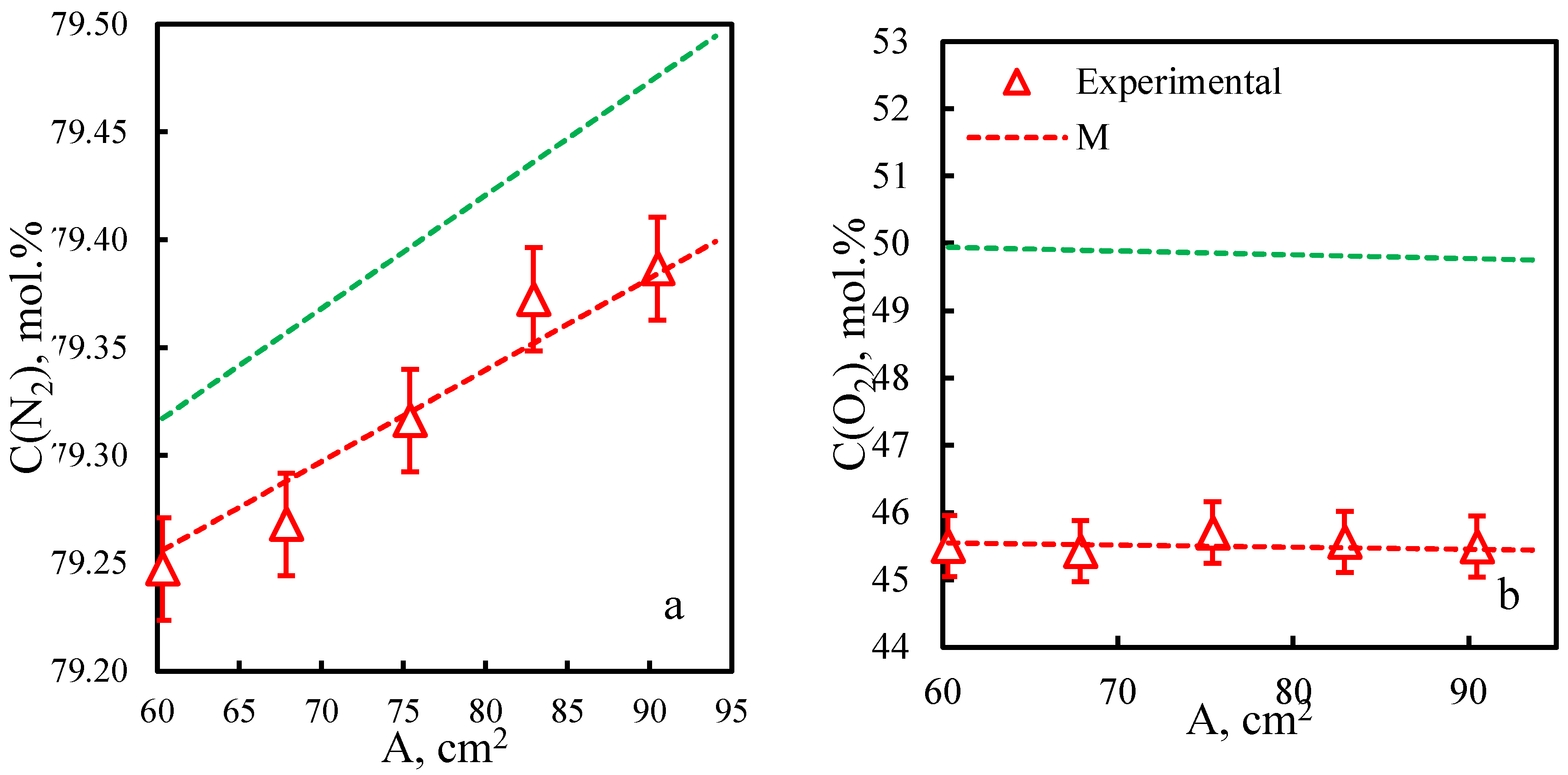
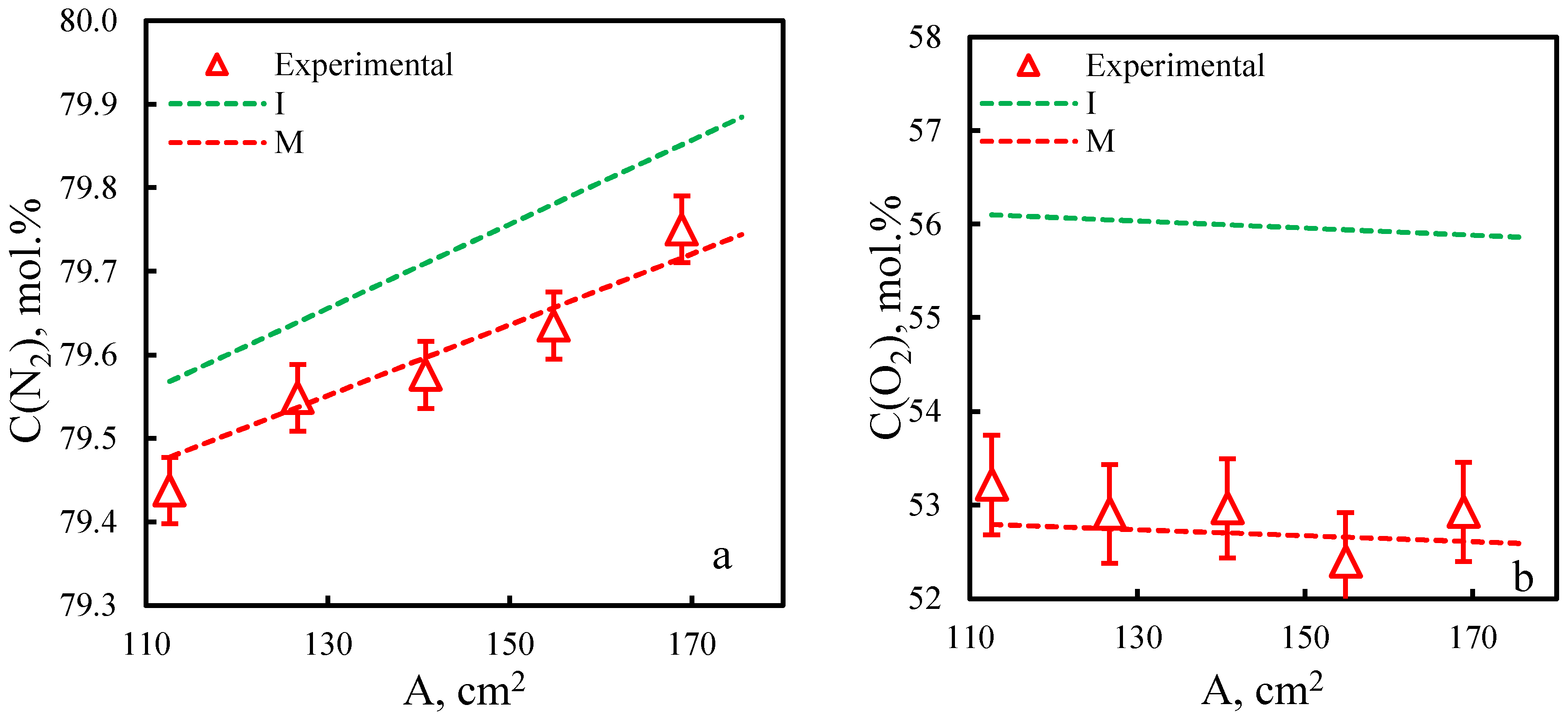
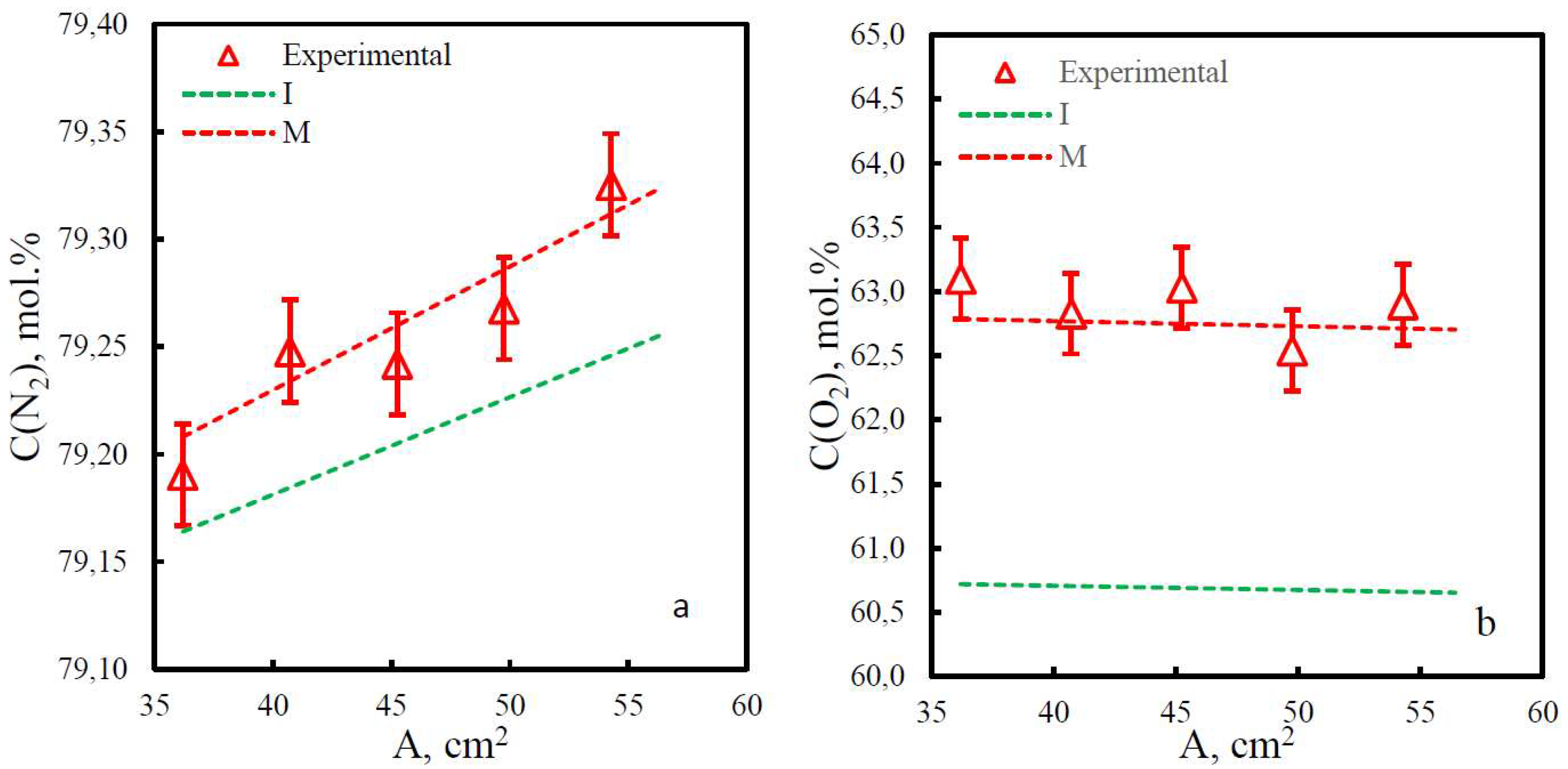
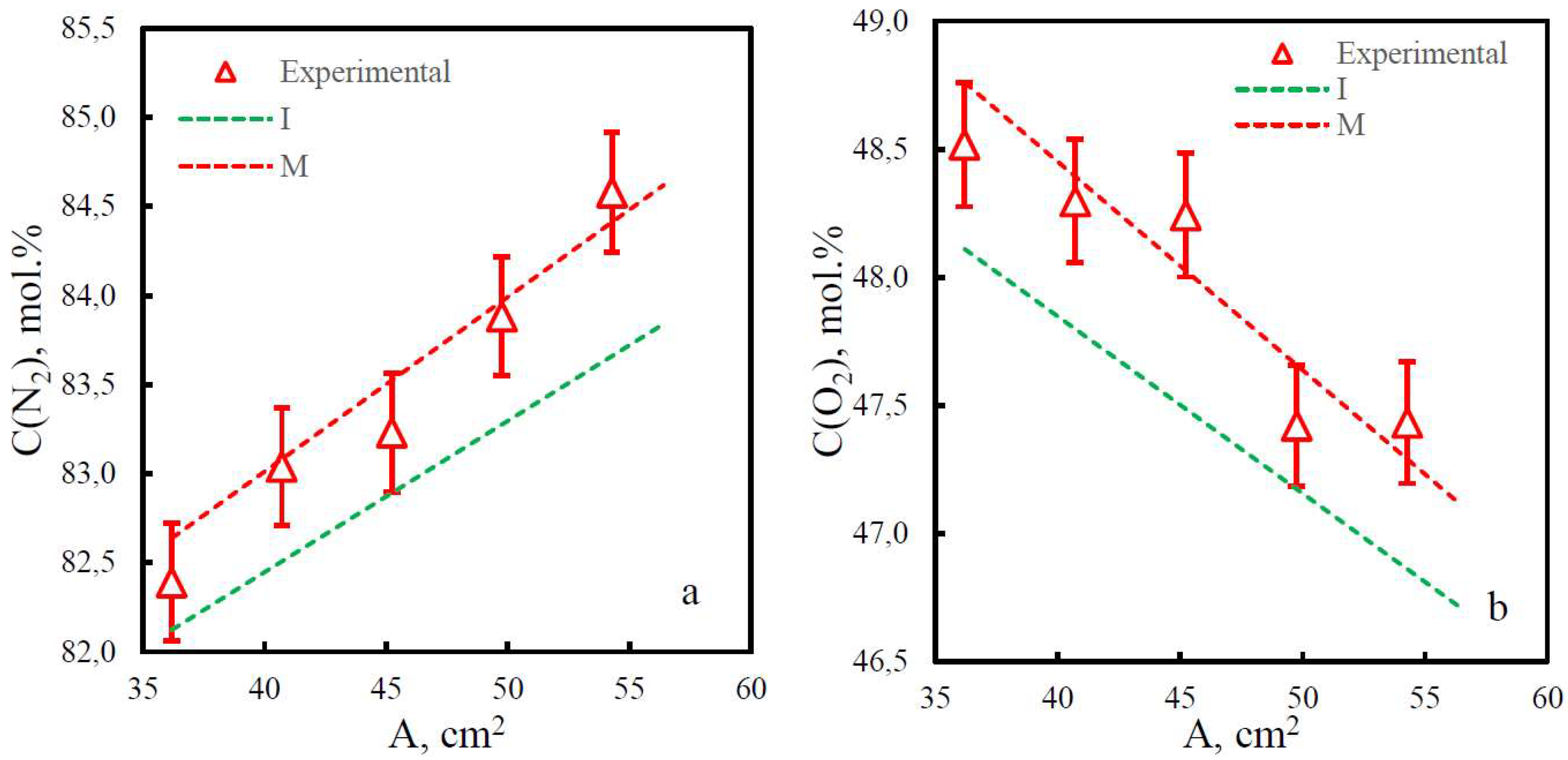
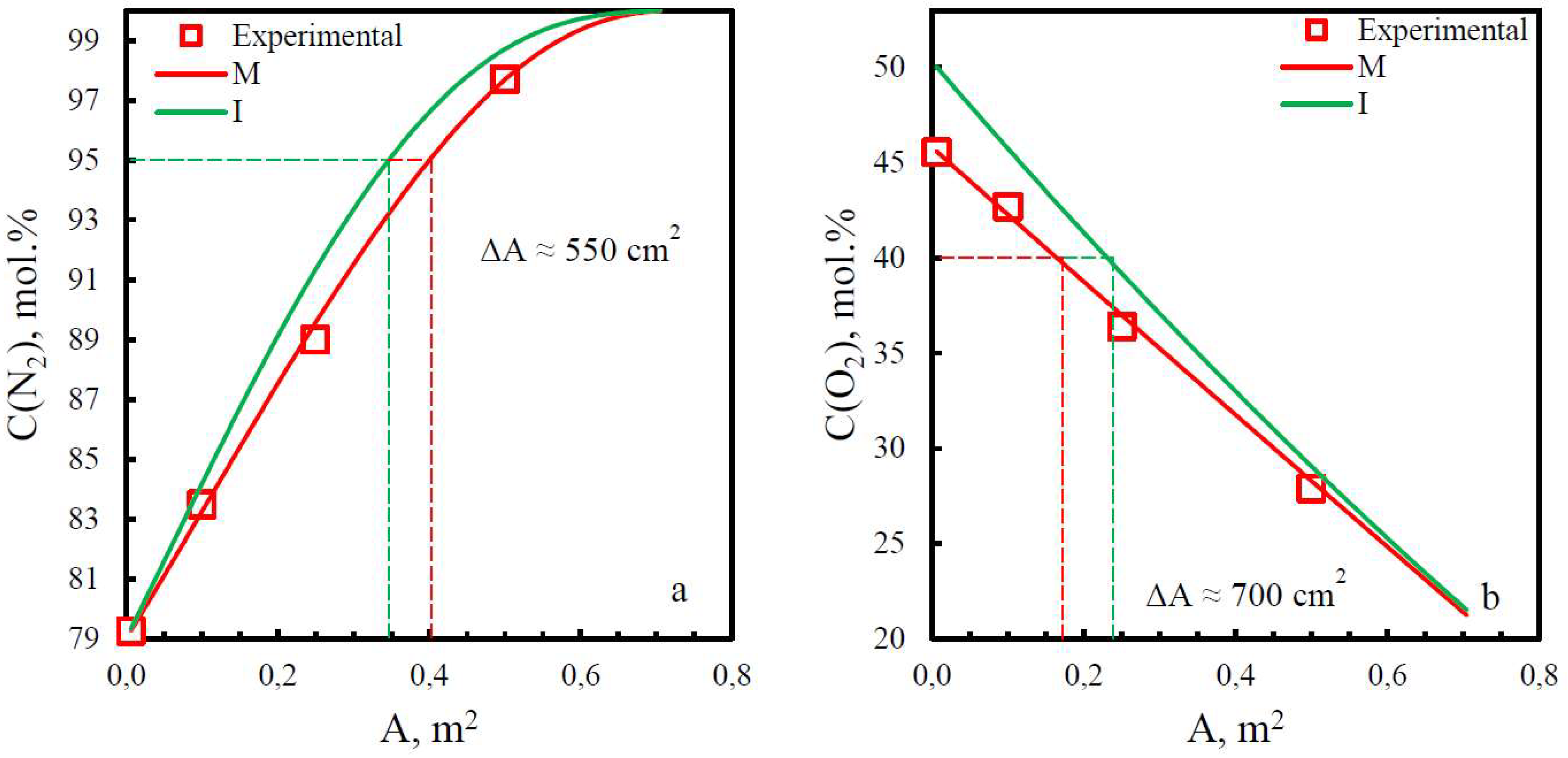
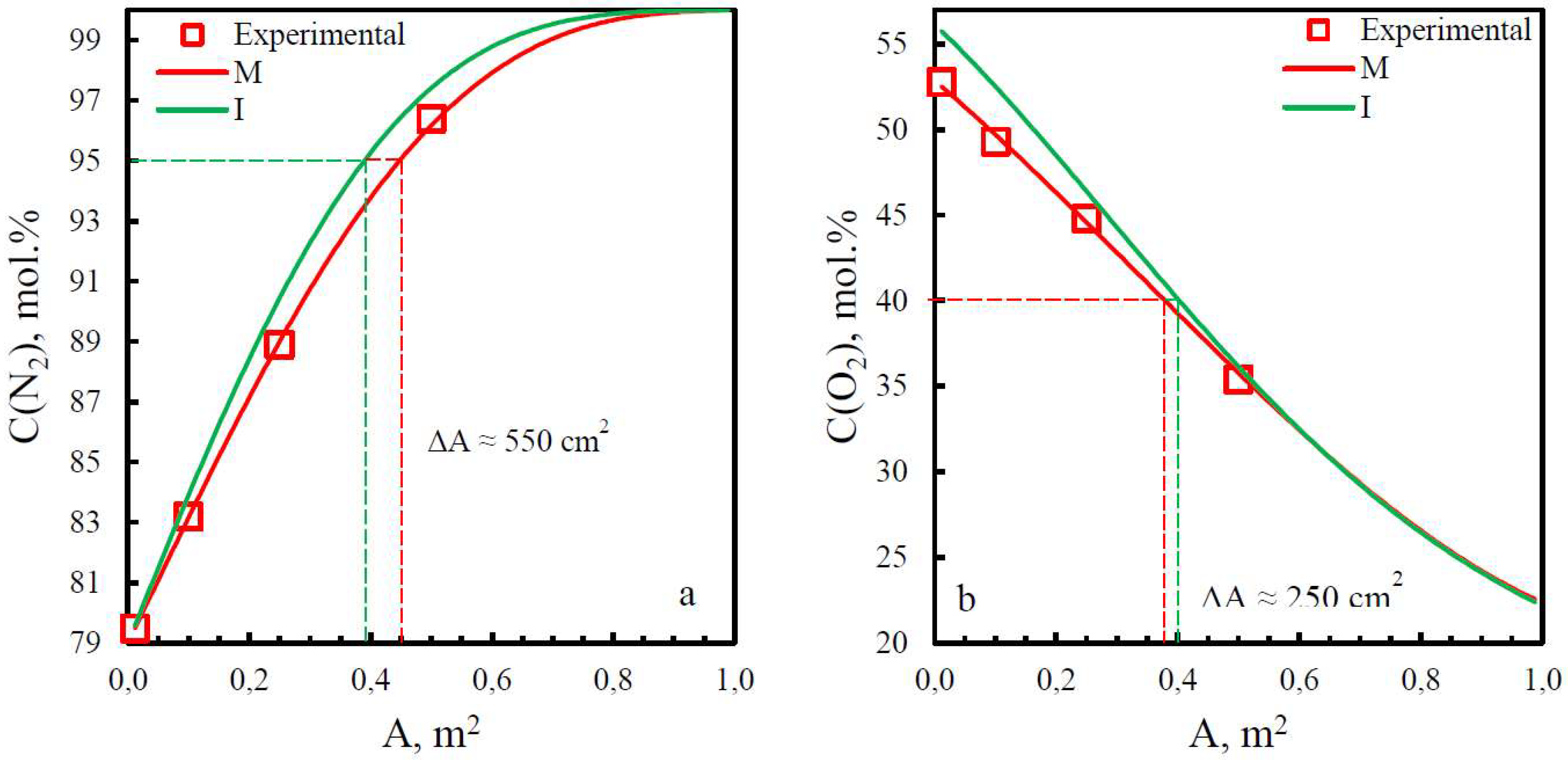
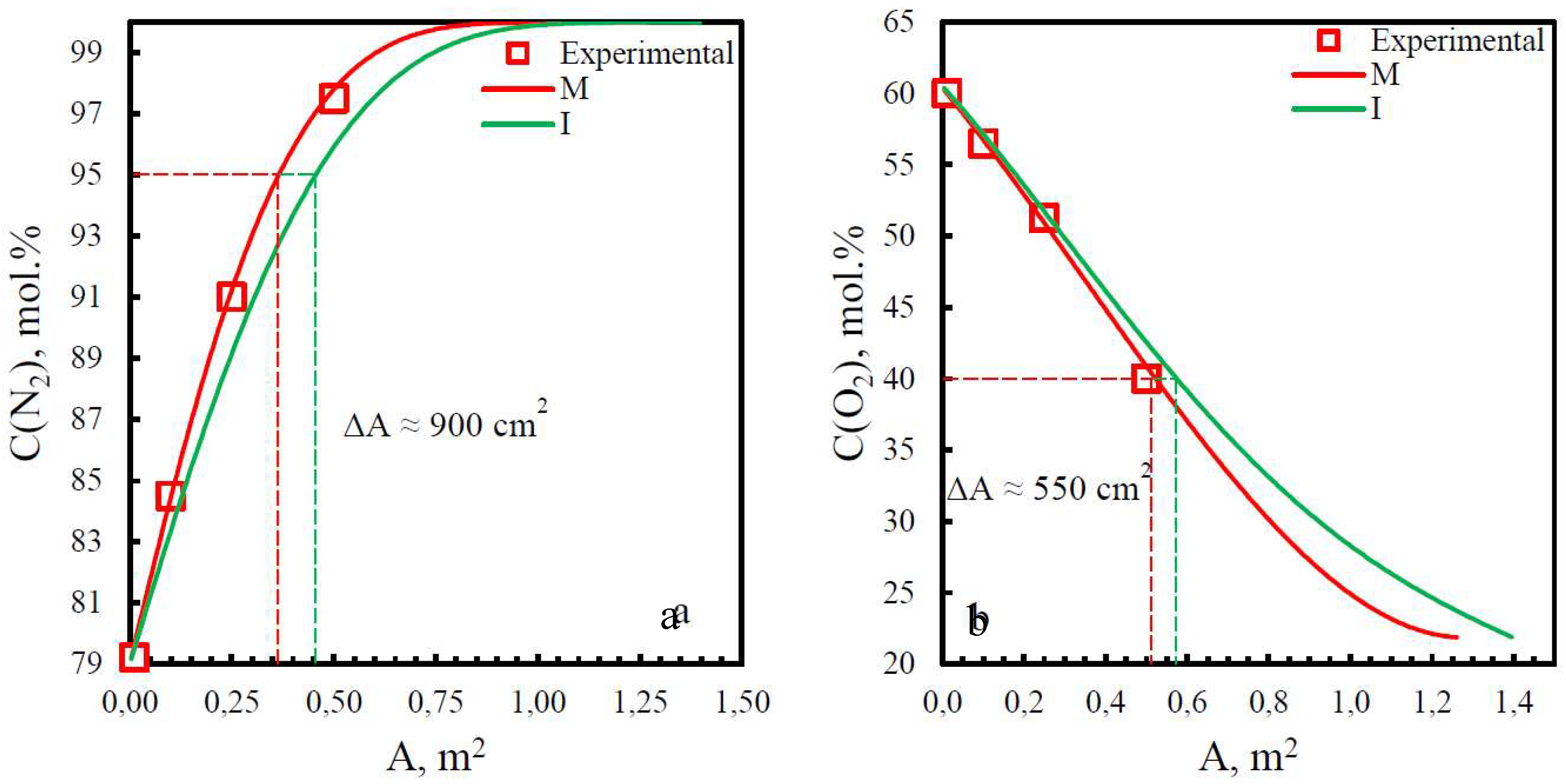
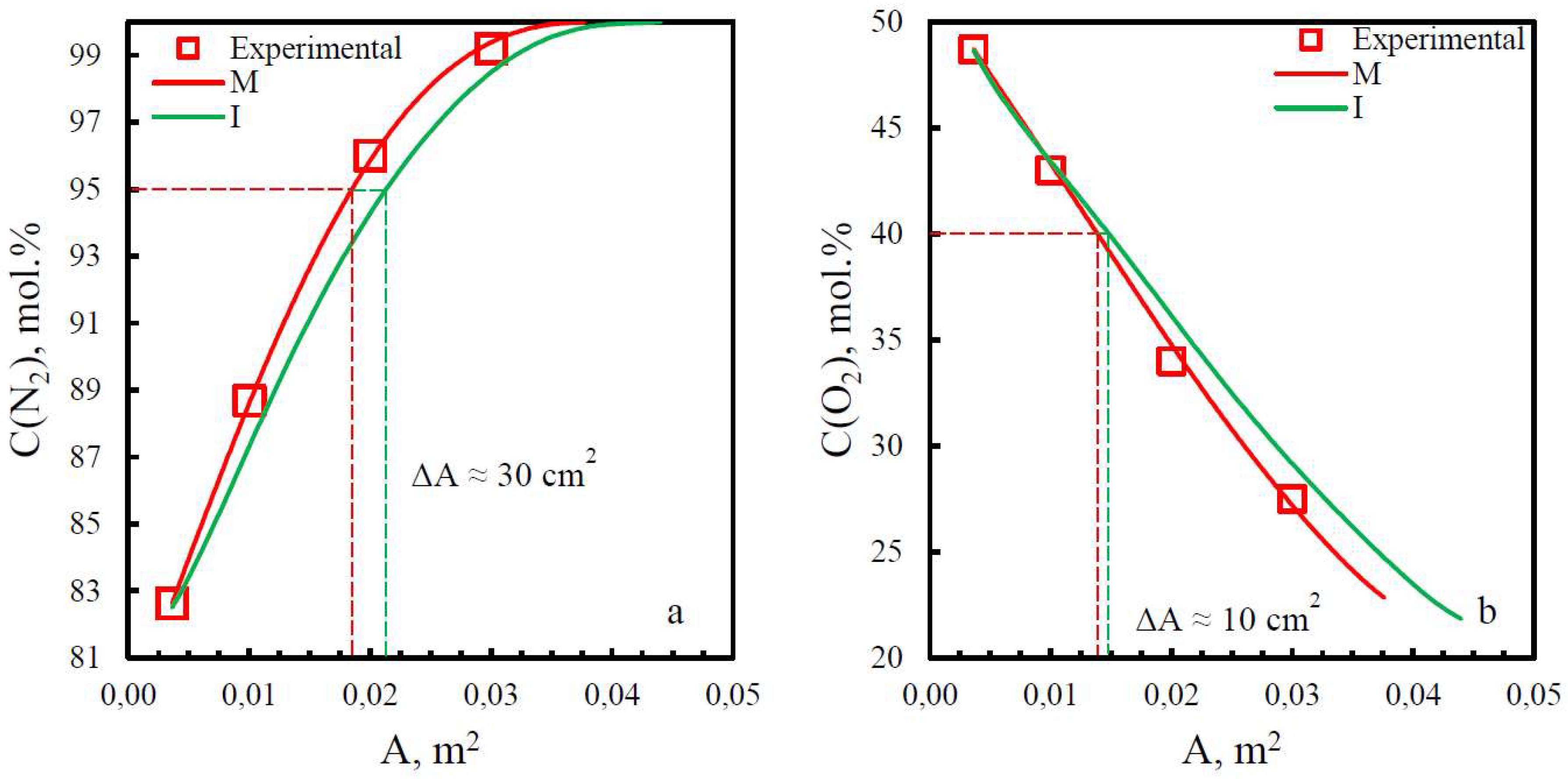
| Membrane | PO2, barrera | PN2, barrera | Selectivity, α(O2/N2) | T, ˚C | Pressure Difference, bar | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSF | 1.05 | 0.165 | 6.4 | 24 | 3.5 | [28] |
| 1.29 | 0.22 | 5.9 | 35 | 10 | ||
| 1.5 | 0.26 | 5.8 | 35 | 2 | [29] | |
| 1.1 | 0.23 | 4.8 | 30 | 1 | [30] | |
| 1.06 | 0.171 | 6.2 | 25 | 3.5 | [31] | |
| 1.2 | 0.2 | 6 | 35 | 5 | [32] | |
| PPO | 17 | 3.62 | 4.7 | 35 | 2 | [33] |
| 17 | 4.47 | 3.8 | 30 | 1 | [34] | |
| 19.08 | 4.65 | 4.1 | 30 | 1 | [35] | |
| PEI | 0.32 | 0.05 | 6.4 | 22 | 0.2-0.9 | [36] |
| 0.4 | 0.05 | 7.6 | 35 | 5 | [32] | |
| 0.38 | 0.054 | 7.1 | 35 | 3.5 | [37] | |
| 0.4 | 0.05 | 8 | 35 | 10 | [38] | |
| Membrane | QO2, GPUb | QN2, GPUb | Selectivity, α(O2/N2) | T, ˚C | Pressure Difference, bar | Ref. |
| PSF | 27.5 | 4 | 6.9 | 24 | 3.5 | [28] |
| 13.6 | 2.88 | 4.8 | 30 | 1 | [30] | |
| 39.3 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 25 | 3.5 | [31] | |
| PPO | 40 | 10 | 4 | 22.5 | 5 | [39] |
| 20 | 4.8 | 4.1 | 35 | 4 | [40] | |
| PEI | 2.89 | 0.33 | 8.8 | 30 | 2 | [38] |
| 11.5 | 1.77 | 6.5 | 27 | 6 | [41] | |
| 2.6 | 0.63 | 4.1 | 22 | 6.9 | [42] | |
|
a1 Barrer = 1 × 10–10 cm3(STP) · cm · cm-2 · s-1 · cmHg-1 b1 GPU = 1 × 10–6 cm3(STP) · cm-2 · s-1 · cmHg-1 | ||||||
| Membrane | Q, GPU* | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| O2 | N2 | ||
| PSF | 51.4 | 12.8 | 4.02 |
| PPO | 47.9 | 9.40 | 5.1 |
| PEI | 3.45 | 0.58 | 6.0 |
| PEI+PI | 6.65 | 1.68 | 3.96 |
| Membrane | Q, GPU* | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| O2 | N2 | ||
| PSF | 44.12 | 13.25 | 3.33 |
| PPO | 41.53 | 9.40 | 4.42 |
| PEI | 4.33 | 0.66 | 6.59 |
| PEI+PI | 7.69 | 1.86 | 4.15 |
| Membrane | Adif, % (N2) | Adif, % (O2) |
|---|---|---|
| PSF | 15.8 | 29.2 |
| PPO | 13.9 | 6.25 |
| PEI | 19.8 | 9.7 |
| PEI+PI | 15.9 | 6.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





