Submitted:
10 January 2024
Posted:
10 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Study Protocol
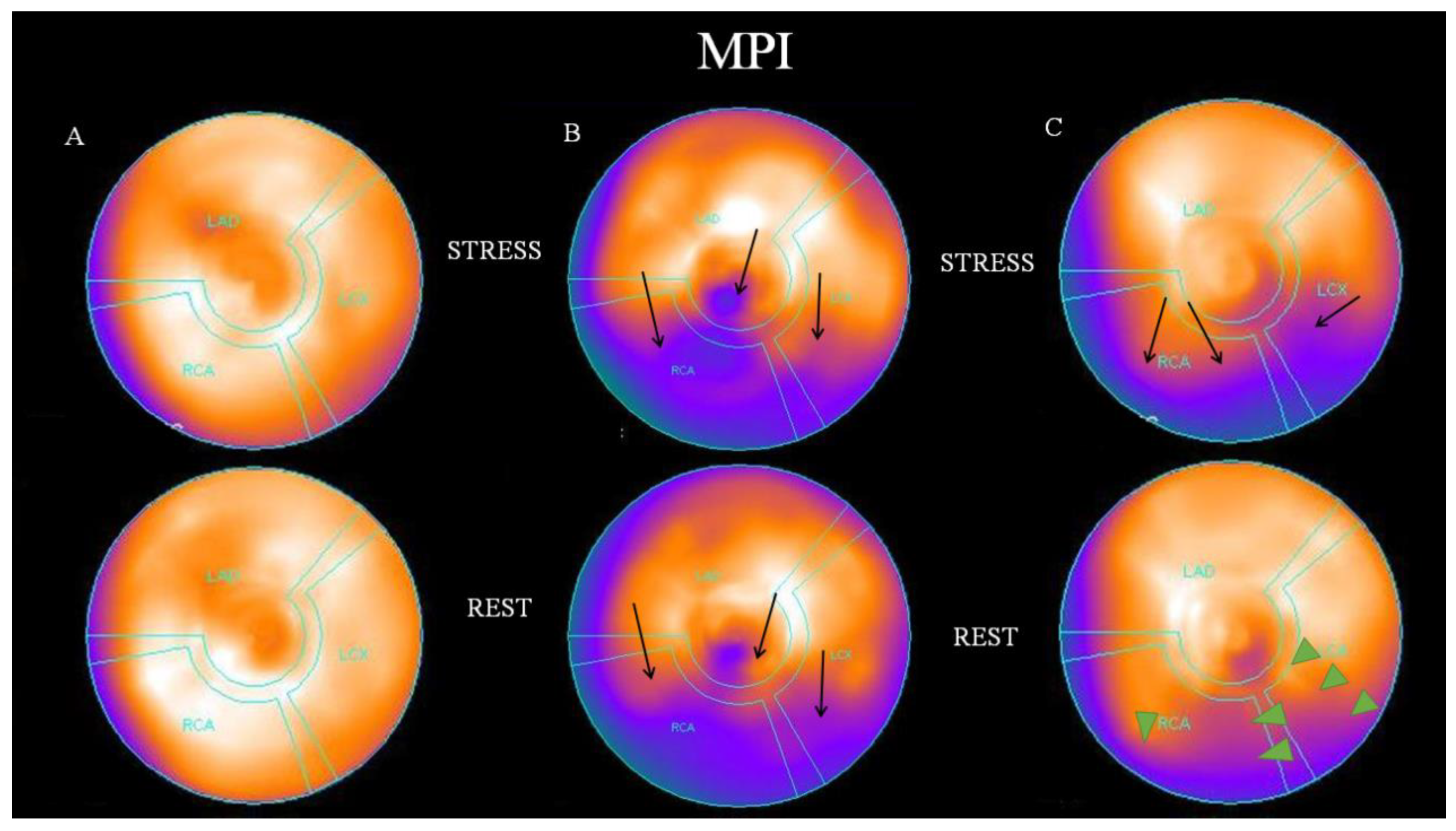
2.4. Visual Analysis of Myocardial Perfusion SPECT
2.5. CRP Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; Isasi, C.R.; Jiménez, M.C.; Jordan, L.C.; Judd, S.E.; Lackland, D.; Lichtman, J.H.; Lisabeth, L.; Liu, S.; Longenecker, C.T.; Mackey, R.H.; Matsushita, K.; Mozaffarian, D.; Mussolino, M.E.; Nasir, K.; Neumar, R.W.; Palaniappan, L.; Pandey, D.K.; Thiagarajan, R.R.; Reeves, M.J.; Ritchey, M.; Rodriguez, C.J.; Roth, G.A.; Rosamond, W.D.; Sasson, C.; Towfighi, A.; Tsao, C.W.; Turner, M.B.; Virani, S.S.; Voeks, J.H.; Willey, J.Z.; Wilkins, J.T.; Wu, J.H.; Alger, H.M.; Wong, S.S.; Muntner, P. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146-e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis — An Inflammatory Disease. N. Eng. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stary, H.C.; Chandler, A.B.; Glagov, S.; Guyton, J.R.; Insull, W.; Rosenfeld, M.E.; Schaffer, S.A.; Schwartz, C.J.; Wagner, W.D.; Wissler, R.W. A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Circulation 1994, 89, 2462–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Eng. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapic, I.; Padoan, A.; Bozzato, D.; Plebani, M. Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-Reactive Protein in Acute Inflammation. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020, 153, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Cornel, J.H.; Pais, P.; Pella, D.; Genest, J., Cifkova; Lorenzatti, A.; Forster, T.; Kobalava, Z.; Vida-Simiti, L.; Flather, M.; Shimokawa, H.; Ogawa, H.; Dellborg, M.; Rossi, P.R.F.; Troquay, R.P.T.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J.; CANTOS Trial Group. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, D.A.; Eranki, A.P. StatPearls [Internet]; Stat Pearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jungen, M.J.; Ter Meulen, B.C.; van Osch, T.; Weinstein, H.C.; Ostelo, R.W.J.G. Inflammatory biomarkers in patients with sciatica: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019, 20, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, N.E.; Cosgrove, V.E.; Dunlap, K.; Subramaniapillai, M.; McIntyre, R.S.; Suppes, T. A clinical model for identifying an inflammatory phenotype in mood disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 113, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madjid, M.; Willerson, J.T. Inflammatory markers in coronary heart disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2011, 100, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschborn, S.; Weitkamp, J.H. Procalcitonin versus C-reactive protein: review of kinetics and performance for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. J. Perinatol. 2019, 39, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darooghegi Mofrad, M.; Milajerdi, A.; Koohdani, F.; Surkan, P.J.; Azadbakht, L. Garlic Supplementation Reduces Circulating C-reactive Protein, Tumor Necrosis Factor, and Interleukin-6 in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, A.G.; Magill, N.; White, T.C.H.; Kokkinakis, M.; Norman-Taylor, F. C-reactive protein: what to expect after bony hip surgery for nonambulatory children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B. 2019, 28, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabro, P.; Golia, E.; Yeh, E.T. Role of C-reactive protein in acute myocardial infarction and stroke: possible therapeutic approaches. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, S.; Kushner, I.; Samols, D. C-reactive Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48487–48490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Lowe, G.; Pepys, M.B.; Thompson, S.G.; Collins, R.; Danesh, J. C-reactive protein concentration and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and mortality: an individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 375–140. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, M.I.; Khan, R.A.; Fozia, Ahmad, I.; Khan, N.; Urooj, K.; Shah, A.U.H.A.; Khan, A.U.; Ali, T.; Ishtiaq, A.; Shah, M.; Ullah, A.; Murtaza, I.; Ullah, R.; Alotaibi, A.; Murthy, H.C.A. C-Reactive Protein and High-Sensitive Cardiac Troponins Correlate with Oxidative Stress in Valvular Heart Disease Patients. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 5029853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, J.P.; Shah, T.; Hingorani, A.D.; Danesh, J.; Pepys, M.B. C-reactive protein and coronary heart disease: a critical review. J. Intern. Med. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, O.; Mohanty, B.D.; Martin, S.S.; Joshi, P.H.; Blaha, M.J.; Nasir, K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Budoff, M.J. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and cardiovascular disease: a resolute belief or an elusive link? J. Am. Coll Cardiol. 2013, 62, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Morrow, D.A.; Jablonski, K.A.; Rice, M.M.; Warnica, J.W.; Domanski, M.J.; Hsia, J.; Gersh, B.J.; Rifai, N.; Ridker, P.M.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Braunwald, E.; PEACE Investigators. Prognostic significance of the Centers for Disease Control/American Heart Association high-sensitivity C-reactive protein cut points for cardiovascular and other outcomes in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Circulation 2007, 115, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younan, H.; Al-Khashab, K. Correlation of high sensitivity C-reactive protein to presence, extent and severity of angiographic coronary artery disease in patients with chronic stable angina. Egypt Heart J. 2008, 60, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Razban, M.M.; Eslami, M.; Bagherzadeh, A. The relationship between serum levels of hs-CRP and coronary lesion severity. Clujul Med. 2016, 89, 322–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.J.; Alzahrani, T. Myocardial Perfusion Scan. In: StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL), 2023, StatPearls Publishing 2023.
- Sioka, C.; Nikas, D.; Tsoumani, A.; Kiortsis, D.N.; Fotopoulos, A.; Kostadima, V. Transient myocardial ischemia due to corticosteroid use in a patient with multiple sclerosis diagnosed with myocardial perfusion imaging. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 1805–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsalou, I.; Georgoulias, P.; Karydas, I.; Fourlis, S.; Sioka, C.; Zoumboulidis, A.; Demakopoulos, N. A rare case of myocardial infarction and ischemia in a cannabis-addicted patient. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2007, 32, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioka, C.; Papadimitropoulos, K.; Michalis, L.; Pappas, K.; Lakkas, L.; Fotopoulos, A.; Dounousi, E. Myocardial ischemia with normal coronary angiography in a chronic kidney disease patient. Cardiol. J. 2019, 26, 620–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, F.; Tundo, F.; Terranova, P.; Battezzati, P.M.; Ramella, M.; Bestetti, A.; Tagliabue, L. Prognostic value of C-reactive protein in patients with stress induced myocardial ischemia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 98, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtdas, M.; Yaylali, Y.T.; Kaya, Y.; Ozdemir, M. Increased plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and myeloperoxidase levels may predict ischemia during myocardial perfusion imaging in slow coronary flow. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, R.M.; Harrington, G.M. What is the relationship between myocardial perfusion imaging and coronary artery disease risk factors and markers of inflammation? Angiology 2008, 59, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitevska, I.; Srbinovska, E.; Stojanovska, L.; Antova, E.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Bosevski, M. Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Myocardial Ischemia Detection in High-Risk Asymptomatic Patients: Correlation with Coronary Calcium Score and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein. Indian J. Nuc. Med. 2019, 34, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verberne, H.J.; Acampa, W.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Ballinger, J.; Bengel, F.; De Bondt, P.; Buechel, R.R.; Cuocolo, A.; van Eck-Smit, B.L.; Flotats, A.; Hacker, M.; Hindorf, C.; Kaufmann, P.A.; Lindner, O.; Ljungberg, M.; Lonsdale, M.; Manrique, A.; Minarik, D.; Scholte, A.J.; Slart, R.H.; Trägårdh, E.; de Wit, T.C.; Hesse, B.; European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). EANM procedural guidelines for radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging with SPECT and SPECT/CT: 2015 revision. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging, 2015; 42, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Sioka, C.; Moulias, C.; Voulgari, P.V.; Fotopoulos, A.; Bassukas, I.D. Single photon emission computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Nucl. Med. Rev. Cent. East Eur. 2021, 24, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulos, A.; Papadimitropoulos, K.; Papadopoulos, A.; Lakkas, L.; Spiliotopoulou, M.; Kotrotsios, T.D., Pappas; Notopoulos, A.; Sioka, C. Myocardial ischemia in female patients with rheumatoid arthritis assessed with single photon emission tomography-myocardial perfusion imaging. Nucl. Med. Rev. Cent. East Eur. 2019, 22, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fotopoulos, A.; Petrikis, P.; Iakovou, I.; Papadopoulos, A.; Sakelariou, K.; Gkika, E.; Lakkas, L.; Touzios, C. The impact of depression and anxiety in prognosis of patients undergoing myocardial perfusion imaging with 99mTc tetrofosmin SPECT for evaluation of possible myocardial ischemia. Nucl. Med. Rev. Cent. East Eur. 2020, 23, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsi, C.; Gkika, E.; Astrakas, L.; Papadopoulos, A.; Iakovou, I.; Dogoritis, A.; Fotopoulos, A.; Sioka, C. Vitamin D Deficiency as a Risk Factor for Myocardial Ischemia. Medicina 2021, 57, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioka, C.; Zotou, P.; Papafaklis, M.I.; Bechlioulis, A.; Sakellariou, K.; Rammos, A.; Gkika, E.; Lakkas, L.; Alexiou, S.; Kekiopoulos, P.; Naka, K.K.; Katsouras, C. Body Mass Index Is Independently Associated with the Presence of Ischemia in Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. Medicina 2022, 58, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bairactaris, C.; Demakopoulos, N.; Tripsianis, G.; Sioka, C.; Farmakiotis, D.; Vadikolias, K.; Heliopoulos, I.; Georgoulias, P.; Tsougos, I.; Papanastasiou, I.; Piperidou, C. Impact of dopamine transporter single photon emission computed tomography imaging using I-123 ioflupane on diagnoses of patients with parkinsonian syndromes. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 16, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioka, C.; Assimakopoulos, A.; Fotopoulos, A. The diagnostic role of (18)F fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with fever of unknown origin. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 45, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioka, C.; Fotopoulos, A.; Kyritsis, A.P. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes and the role of PET imaging. Oncology 2010, 78, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiambas, E.; Fotiades, P.P.; Sioka, C.; Kotrotsios, D.; Gkika, E.; Fotopoulos, A.; Mastronikolis, S.N.; Armata, I.E.; Giotakis, E.; Ragos, V. Novel molecular and metabolic aspects in osteosarcoma. J. BUON. 2017, 22, 1595–1598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lakkas, L.; Serim, B.D.; Fotopoulos, A.; Iakovou, I.; Doumas, A.; Korkmaz, U.; Michalis, L.K.; Sioka, C. Infection of cardiac prosthetic valves and implantable electronic devices: early diagnosis and treatment. Acta. Cardiol. 2021, 76, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, A.; Gupta, S.; Olson, E.; Sepulveda, K.; Lenchik, L.; Ivanidze, J.; Rakow-Penner, R.; Patel, M.J.; Subramaniam, R.M.; Ganeshan, D. Role of imaging in the era of precision medicine. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A. Evolution of Quantification in clinical nuclear medicine: A brief overview of salient uses and upcoming trends. J. Nucl. Med. Radiat. Ther. 2018, 9, 05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markoula, S.; Tsoumani, A.; Votti, C.A.; Beltsiou, M.; Lakkas, L.; Pappas, K.; Iakovou, I.; Fotopoulos, A.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Sioka, C. Myocardial perfusion imaging single photon emission computed tomography may detect silent myocardial ischemia in patient with epilepsy. Nucl. Med. Rev. Cent. East Eur. 2022, 25, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioka, C.; Georgiou, G.; Katsouras, C.; Pappas, K.; Kiortsis, D.N.; Fotopoulos, A.; Petrikis, P. Silent severe myocardial ischemia in a past illicit drug user imaged with myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Perfusion 2022, 37, 863–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, S.; Kushner, I.; Samols, D. C-reactive Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48487–48490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.; Agrawal, A. Evolution of C-Reactive Protein. Front. Immunol. 2019, 30, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriya, J. Critical roles of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzknecht, M.; Tiller, C.; Reindl, M.; Lechner, I.; Troger, F.; Hosp, M.; Mayr, A.; Brenner, C.; Klug, G.; Bauer, A.; Metzler, B.; Reinstadler, S.J. C-reactive protein velocity predicts microvascular pathology after acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol 2021, 1, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, W.; Sund, M.; Frohlich, M.; Fischer, H.G.; Lowel, H.; Döring, A.; Hutchinson, W.L.; Pepys, M.B. C-Reactive protein, a sensitive marker of inflammation, predicts future risk of coronary heart disease in initially healthy middle-aged men: results from the MONICA (Monitoring Trends and Determinants in Cardiovascular Disease) Augsburg Cohort Study, 1984 to 1992. Circulation 1999, 99, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.K.; Lecis, D. Inflammation in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. F1000Res. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, P.P. Subclinical atherosclerosis: what it is, what it means and what we can do about it. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2008, 62, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.; Burg, M.M.; Vashist, A.; Collins, D.; Liu, J.; Jadbabaie, F.; Graeber, B.; Earley, C.; Lampert, R.; Soufer, R. C-reactive protein and vulnerability to mental stress-induced myocardial ischemia. Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.; Niedzwiedz, C.L. The association of anxiety and stress-related disorders with C-reactive protein (CRP) within UK Biobank. Brain Behav. Immun. Health. 2012, 19, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Fang, F.; Arnberg, F.K.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Fernández de la Cruz, L.; Almqvist, C.; Fall, K.; Lichtenstein, P.; Thorgeirsson, G.; Valdimarsdóttir, U.A. Stress related disorders and risk of cardiovascular disease: population based, sibling controlled cohort study. BMJ 2019, 365, l1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.B.; Lee, S.K.; Park, J.S.; Moon, D.H. Prevalence of coronary artery disease using thallium-201 single photon emission computed tomography among patients newly undergoing chronic peritoneal dialysis and its association with mortality. Ame J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Kawano, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Hase, H.; Joki, N.; Hatta, T.; Nishimura, S.; Moroi, M.; Nakagawa, S.; Kasai, T.; Kusuoka, H.; Takeishi, Y.; Momose, M.; Takehana, K.; Nanasato, M.; Yoda, S.; Nishina, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Nishimura, T. Prognostic study of cardiac events in Japanese patients with chronic kidney disease using ECG-gated myocardial Perfusion imaging: Final 3-year report of the J-ACCESS 3 study. J. Nuc. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.B.; Min, W.K.; Lee, S.K.; Park, J.S.; Hong, C.D.; Yang, W.S. Persistent elevation of C-reactive protein and ischemic heart disease in patients with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majstorov, V.; Pop Gjorceva, D.; Vaskova, O.; Vavlukis, M.; Peovska, I.; Maksimovic, J.; Kuzmanovska, S.; Zdraveska-Kocovska, M. C-reactive protein in patients with normal perfusion and mild to moderate perfusion defects who have undergone myocardial perfusion imaging with 99m-Tc sestamibi gated spect. Prilozi 2008, 29, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rathcke, C.N.; Kjøller, E.; Fogh-Andersen, N.; Zerahn, B.; Vestergaard, H. NT-proBNP and circulating inflammation markers in prediction of a normal myocardial scintigraphy in patients with symptoms of coronary artery disease. PLoS One. 2010, 5, e14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, S.Ç.; Özdemir Candan, Ö.; Gündoğan, C.; Öz, A.; Yüksel, Y.; Ayca, B.; Çermik, T.F. Value of C-reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio for Predicting Ischemia in Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy. Mol. Imaging Radionucl. Ther. 2020, 29, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjort, M.; Eggers, K.M.; Lakic, T.G.; Lindbäck, J.; Budaj, A.; Cornel, J.H.; Giannitsis, E.; Katus, H.A.; Siegbahn, A.; Storey, R.F.; Becker, R.C.; Wallentin, L.; Lindahl, B. Biomarker Concentrations and Their Temporal Changes in Patients with Myocardial Infarction and Nonobstructive Compared With Obstructive Coronary Arteries: Results From the PLATO Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc, 2023; 12, e027466. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, J.L.; Jones, J.; Bolleddu, S.I.; Vanthenapalli, S.; Rodgers, L.E.; Shah, K.; Karia, K.; Panguluri, S.K. Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Gender and Aging. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Baker, W.L.; Parker, M.W.; Heller, G.V. Meta-analysis of optimal risk stratification in patients >65 years of age. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Newman, A.B. Inflammatory markers in population studies of aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2011, 10, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fung, E.; Xu, A.; Lan, H.Y. C-reactive protein and ageing. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44 (Suppl. 1), 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liang, P.; Chen, J.; Fu, S.; Liu, B.; Feng, M.; Lin, B.; Lee, B.; Xu, A.; Lan, H.Y. The baseline levels and risk factors for high-sensitive C-reactive protein in Chinese healthy population. Immun. Ageing 2018, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida Roediger, M.; de Fátima Nunes Marucci, M.; Duim, E.L.; Santos, J.L.F.; de Oliveira Duarte, Y.A.; de Oliveira, C. Inflammation and quality of life in later life: findings from the health, well-being and aging study (SABE). Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2019, 17, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio-Mayoral, A.; Rimoldi, O.E.; Camici, P.G.; Kaski, J.C. Inflammation and microvascular dysfunction in cardiac syndrome X patients without conventional risk factors for coronary artery disease. JACC Cardiovasc. Iimaging 2013, 6, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wöhrle, J.; Nusser, T.; Merkle, N.; Kestler, H.A.; Grebe, O.C.; Marx, N.; Höher, M.; Kochs, M.; Hombach, V. Myocardial perfusion reserve in cardiovascular magnetic resonance: Correlation to coronary microvascular dysfunction. J. Cardiovasc. Magn Reson. 2006, 8, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, E.; Wiener, S.; Underwood, S.R.; European Council of Nuclear Cardiology. Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in Europe 2007: a survey of the European Council of Nuclear Cardiology. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging, 2012; 39, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.; Walker, A.; Hügli, O.; Togni, M.; Meier, B. Percutaneous coronary interventions in Europe: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections based on data up to 2004. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2007, 96, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechel, R.R.; Kaufmann, B.A.; Tobler, D.; Wild, D.; Zellweger, M.J. Non-invasive nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging improves the diagnostic yield of invasive coronary angiography. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; Agewall, S.; Dickstein, K.; Edvardsen, T.; Escaned, J.; Gersh, B.J.; Svitil, P.; Gilard, M.; Hasdai, D.; Hatala, R.; Mahfoud, F.; Masip, J.; Muneretto, C.; Valgimigli, M.; Achenbach, S.; Bax, J.J.; ESC Scientific Document Group. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, G.; Johnson, G.; Wijns, N.P.; Toth, B.; Achim, A.; Fournier, S.; Barbato, E. Revascularization decisions in patients with chronic coronary syndromes: Results of the second International Survey on Interventional Strategy (ISIS-2). Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 336, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achim, A.; Leibundgut, G. FAME 3 fails to defame coronary artery bypass grafting: what went wrong in the percutaneous coronary intervention arm? Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 62, ezac036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Chu, Z.; Li, Z. CRP as a potential predictor of outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Biomed. Rep. 2023, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total populationN=102 | CRP ≤ 6 mg/LN=63 | CRP > 6 mg/LN=39 | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yrs | 71±11 | 69±11 | 72±11 | 0.189 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 69 (68) | 40 (64) | 29 (74) | 0.254 |
| CAD Hx, n (%) | 33 (32) | 21 (33) | 12 (31) | 0.788 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 78 (77) | 50 (79) | 28 (72) | 0.381 |
| DM, (%) | 40 (39) | 24 (38) | 16 (41) | 0.768 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 65 (64) | 42 (67) | 23 (59) | 0.432 |
| Obesity, (%) | 26 (26) | 16 (25) | 10 (26) | 0.978 |
| Smoking (%) | 26 (26) | 16 (25) | 10 (26) | 0.978 |
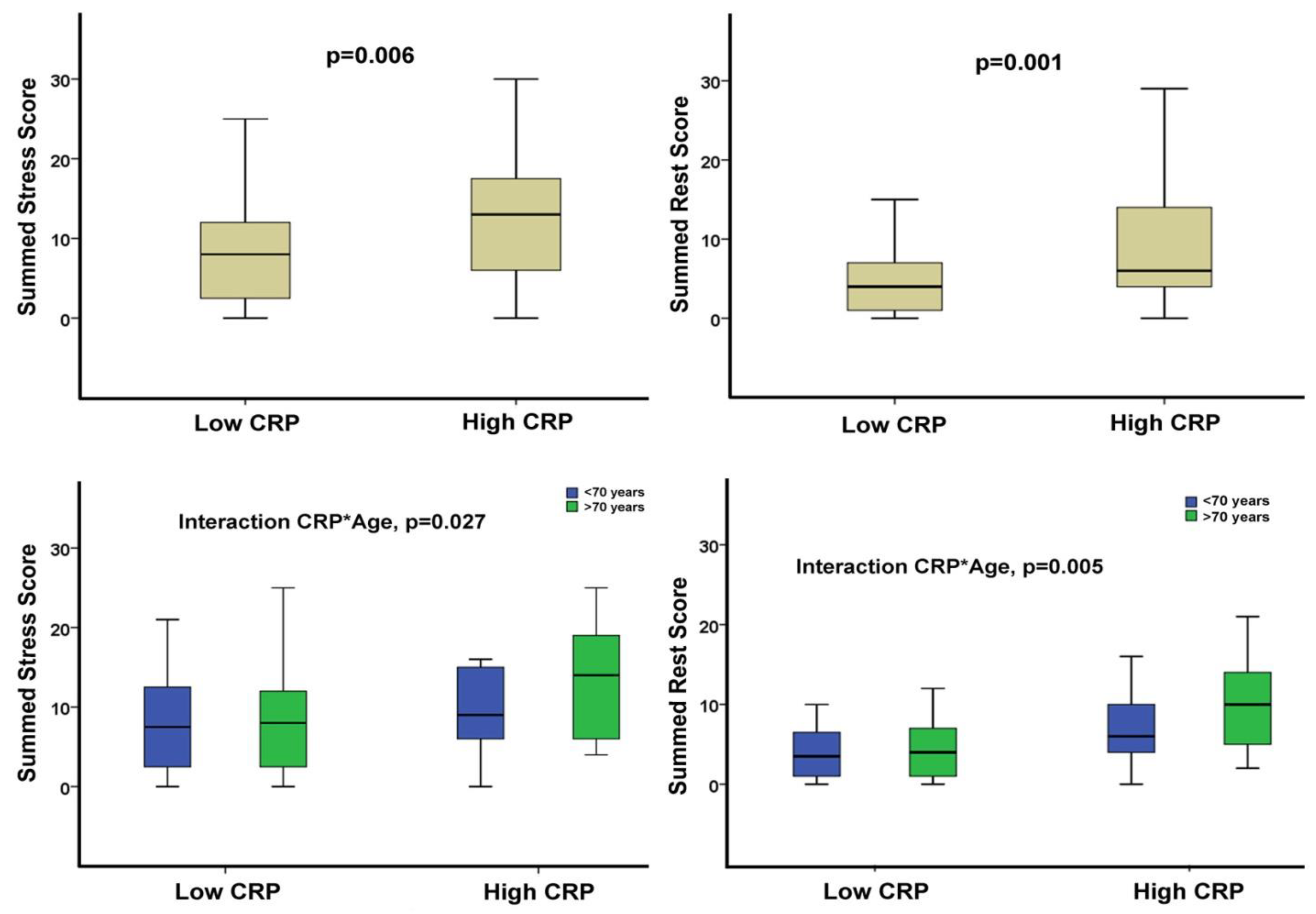
| SSS | 8 (4, 15) | 8 (2, 12) | 13 (6, 18) | 0.006 |
| SRS | 5 (2, 9) | 4 (1, 7) | 6 (4, 14) | 0.001 |
| SDS | 2 (1, 6) | 2 (0, 5) | 3 (1, 6) | 0.703 |
| SSS>3 | 79 (78) | 42 (67) | 37 (95) | 0.001 |
| SDS>1 | 61 (60) | 37 (59) | 24 (62) | 0.779 |
| CRP, mg/L | 4 (2, 10) | 2 (2, 3) | 12 (9, 23) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





