Submitted:
09 January 2024
Posted:
10 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Plant-Derived EVs
3. EVs as a Delivery System for Vaccines
4. Edible Plant-Derived EVs as a Platform for Mucosal Vaccine Delivery
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratajczak, J.; Wysoczynski, M.; Hayek, F.; Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia 2006, 20, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- György, B.; Szabó, T.G.; Pásztói, M.; Pál, Z.; Misják, P.; Aradi, B.; László, V.; Pállinger, E.; Pap, E.; Kittel, A.; Nagy, G.; Falus, A.; Buzás, E.I. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2667–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocucci, E.; Racchetti, G.; Meldolesi, J. Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2008; 19, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Yang, N.; Nadithe, V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 2016, 6, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Zheng, J.C. Exosome engineering: current progress in cargo loading and targeted delivery. NanoImpact. 2020, 20, 100261–100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Schwarz, H.; Nanda, HS.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Y. Exosomes, a new star for targeted delivery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 751079–751100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.M. Exosomes biological significance: a concise review. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2006, 36, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The regulation of exosome secretion: a novel function of the p53 protein. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4795–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Zhan, W.; Gao, Y.; Huang, L.; Gong, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Gao, S.; Kang, T. RAB31 marks and controls an ESCRT-independent exosome pathway. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schara, K.; Jansa, V.; Sustar, V.; Dolinar, D.; Pavlic, J.I.; Lokar, M.; Kralj-Iglic, V.; Veranic, P.; Iglic, A. Mechanisms for the formation of membranous nanostructures in cell-to-cell communication. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2009, 14, 636–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugel, B.; Martinez, M.C.; Kunzelmann, C.; Freyssinet, J.M. Membrane microparticles: two sides of the coin. Physiology 2005, 20, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Conde, I.; Shrimpton, C.N.; Thiagarajan, P.; López, J.A. Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipids rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood 2005, 106, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, E.; Pallinger, E.; Pasztoi, M.; Falus, A. Highlights of a new type of intercellular communication: microvesicle-based information transfer. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Abreu, R.C.; Fernandes, H.; da Costa Martins, P.A.; Sahoo, S.; Emanueli, C.; Ferreira, L. Native and bioengineered extracellular vesicles for cardiovascular therapeutics. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020, 17, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling, Cell Commun Signal 2021, 19, 47–65. 19. [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, J.; Miekus, K.; Kucia, M.; Zhang, J.; Reca, R.; Dvorak, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia 2006, 20, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deregibus, MC.; Cantaluppi, V.; Calogero, R.; Lo Iacono, M.; Tetta, C.; Biancone, L.; Bruno, S.; Bussolati, B.; Camussi, G. () Endothelial progenitor cell derived microvesicles activate an angiogenic program in endothelial cells by a horizontal transfer of mRNA. Blood 2007, 110, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nature Cell Biology 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guduric-Fuchs, J.; O'Connor, A.; Camp, B.; O'Neill, C.L.; Medina, R.J.; Simpson, D.A. Selective extracellular vesicle- mediated export of an overlapping set of microRNAs from multiple cell types. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Chen, M.; Greening, D.W.; Rai, A.; Zhang, W.; Simpson, R.J. Deep sequencing of RNA from three different extracellular vesicle (EV) subtypes re- leased from the human LIM1863 colon cancer cell line uncovers distinct miRNA-enrichment signatures. PloS One 2014, 9, e110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte-'t Hoen, E.N.; Buermans, H.P.; Waasdorp, M.; Stoorvogel, W.; Wauben, M.H.; 't Hoen, P.A. Deep sequencing of RNA from immune cell-derived vesicles uncovers the selective incorporation of small non-coding RNA biotypes with potential regulatory functions. Nucleic Acids Research 2012, 40, 9272–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Wu, G.; Jose, P.A.; Zeng, C. Functional transferred DNA within extracellular vesicles. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 349, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Visakorpi, T.; Escobedo-Lucea, C.; Siljander, P.; Ayuso-Sacido, A.; Yliperttula, M. Different gDNA content in the subpopulations of prostate cancer extracellular vesicles: apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes. Prostate 2014, 74, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Cornils, K.; Speiseder, T.; Badbaran, A.; Reimer, R.; Indenbirken, D.; Grundhoff, A.; Brunswig-Spickenheier, B.; Alawi, M.; Lange, C. Indication of horizontal DNA gene transfer by extracellular vesicles. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0163665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliotta, J.M.; Pereira, M.; Johnson, K.W.; de Paz, N.; Dooner, M.S.; Puente, N.; Ayala, C.; Brilliant, K.; Berz, D.; Lee, D.; Ramratnam, B.; McMillan, P.N.; Hixson, D.C.; Josic, D.; Quesenberry, P.J. Microvesicle entry into marrow cells mediates tissue-specific changes in mRNA by direct delivery of mRNA and induction of transcription. Exp. Hematol. 2010, 38, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butreddy, A.; Kommineni, N.; Dudhipala, N. Exosomes as naturally occurring vehicles for delivery of biopharmaceuticals: insights from drug delivery to clinical perspectives. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1481–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkasy, O.M.; Nordin, J.Z.; Hagey, D.W.; de Jong, O.G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Vader, P. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: why and how? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.; Yu, F.; Han, B.; Li, B.; Li, L. Therapeutic roles of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modani, S.; Tomar, D.; Tangirala, S.; Sriram, A.; Mehra, N.K.; Kumar, R.; Khatri, D.K.; Singh, P.K. An updated review on exosomes: biosynthesis to clinical applications. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einabadi, M.; Ai, J.; Kargar, M.; Kafilzadeh, F.; Taghdiri Nooshabadi, V.; Jamali, H. Mesenchymal cell-derived exosomes as novel useful candidates for drug delivery. Arch. Neurosci. 2020, 7, e98722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.; Almeida, F. Exosome-based vaccines: history, current state, and clinical trials. Front Immunol. 2021, 14, 12:711565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučuk, N.; Primožič, M.; Knez, Ž.; Leitgeb, M. Exosomes engineering and their roles as therapy delivery tools, therapeutic targets, and biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9543–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaner-Tarbes, S.; Fraile, L.; Montoya, M.; Del Portillo, H. Exosome-based vaccines: pros and cons in the world of animal health. Viruses 2021, 13, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, S.; Tehrani, F.R.; Tahmasebi, S.; Shafiee, A.; Hashemi, S.M. Exosome engineering in cell therapy and drug delivery. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 31,145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mo, H.; He, Z.; Chen, A.; Cheng, P. Extracellular vesicles as an emerging drug delivery system for cancer treatment: Current strategies and recent advances. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113480–113494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, A.; Jeong, G.B. A systematic review on the modifications of extracellular vesicles: a revolutionized tool of nano-biotechnology. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Shin, S.; Do, M.; Oh, B.H.; Song, Y.; Bui, V.D.; Lee, E.S.; Jo, D.G.; Cho, Y.W.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.H. Engineering approaches for effective therapeutic applications based on extracellular vesicles. J. Control Release 2021, 330, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, B.; Yuana, Y. Extracellular vesicles-based drug delivery system for cancer treatment. Cogent Med. 2019, 6, 1635806–1635829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.C.; Choi, C. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as therapeutics and as a drug delivery platform. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, W.J.; Zou, S.; Lee, C.K.; Ou, Y.H.; Wang, J.W.; Czarny, B.; Pastorin, G. EXOPLEXs: chimeric drug delivery platform from the fusion of cell-derived nanovesicles and liposomes. Biomacromol. 2018, 19, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiei, M.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Razak, S.I.A.; Khan, M.U.A. A comprehensive review on the applications of exosomes and liposomes in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Polymers 2021, 13, 2529–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosone, A.; Barbulova, A.; Cappetta, E.; Cillo, F.; De Palma, M.; Ruocco, M.; Pocsfalvi, G. Plant Extracellular Vesicles: Current Landscape and Future Directions. Plants 2023, 12, 4141–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, W.; Jensen, W.A. Ultrastructural Changes during Growth and Embryogenesis in Carrot Cell Cultures. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1967, 18, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Q.; Van Bel, A.J.E.; Hückelhoven, R. Do Plant Cells Secrete Exosomes Derived from Multivesicular Bodies? Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, V.; Hauser, M.T. Exploring the ESCRTing Machinery in Eukaryotes. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, A.; Oberkofler, L.; Robatzek, S.; Weiberg, A. Spotlight on Plant RNA-Containing Extracellular Vesicles. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 69, 102272–102280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Hillmer, S.; Miao, Y.; Lo, S.W.; Wang, X.; Robinson, D.G.; Jiang, L. EXPO, an Exocyst-Positive Organelle Distinct from Multivesicular Endosomes and Autophagosomes, Mediates Cytosol to Cell Wall Exocytosis in Arabidopsis and Tobacco Cells. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 4009–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Ho, J.; Lai, C.; Hoi, V.; Chan, L.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Tan, X.; Bao, Y.; Xia, J.; Robinson, D.G.; Jiang, L. Exo70E2 is essential for exocyst subunit recruitment and expo formation in both plants and animals. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woith, E.; Guerriero, G.; Hausman, J.F.; Renaut, J.; Leclercq, C.C.; Weise, C.; Legay, S.; Weng, A.; Melzig, M.F. Plant Extracellular Vesicles and Nanovesicles: Focus on Secondary Metabolites, Proteins and Lipids with Perspectives on Their Potential and Sources. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3719–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woith, E.; Fuhrmann, G.; Melzig, M.F. Extracellular Vesicles—Connecting Kingdoms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5695–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, N.; Cabanillas, D.G.; Wan, J.; Vali, H.; Laliberté, J.-F.F.; Zheng, H. Turnip Mosaic Virus Components Are Released into the Extracellular Space by Vesicles in Infected Leaves. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, B.D.; Innes, R.W. Extracellular Vesicles as Key Mediators of Plant-Microbe Interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 44, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Canal, L.; Pinedo, M. Extracellular Vesicles: A Missing Component in Plant Cell Wall Remodeling. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 4655–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berin, M.C.; Shreffler, W.G. Mechanisms underlying induction of tolerance to foods. Immunol Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2016, 36, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Deng, Z.B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Kakar, S.; Jun, Y.; Miller, D.; Zhang, H.G. Interspecies communication between plant and mouse gut host cells through edible plant derived exosome-like nanoparticles. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkryl, Y.; Tsydeneshieva, Z.; Degtyarenko, A.; Yugay, Y.; Balabanova, L.; Rusapetova, T.; Bulgakov, V. Plant Exosomal Vesicles: Perspective Information Nanocarriers in Biomedicine. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8262–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.A.; Khan, M.I.; Kameli, N.; Alsahafi, E.; Riza, Y.M. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Exciting Potential as the Future of Next-Generation Drug Delivery. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Teng, Y.; Samykutty, A.; Mu, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cao, P.; Rong, Y.; Yan, J.; Miller, D.; Zhang, H.G. Grapefruit-derived Nanovectors Delivering Therapeutic miR17 Through an Intranasal Route Inhibit Brain Tumor Progression. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Han, M.K.; Collins, J.F.; Merlin, D. Oral administration of ginger-derived nanolipids loaded with siRNA as a novel approach for efficient siRNA drug delivery to treat ulcerative colitis. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1927–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orefice, N.S. Development of New Strategies Using Extracellular Vesicles Loaded with Exogenous Nucleic Acid. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, C.; Sgueglia, G.; Frattolillo, V.; Baglio, S.R.; Altucci, L.; Dell’Aversana, C. Extracellular Vesicle-Based Nucleic Acid Delivery: Current Advances and Future Perspectives in Cancer Therapeutic Strategies. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 980–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- György, B.; Szabó, T.G.; Pásztói, M.; Pál, Z.; Misják, P.; Aradi, B.; László, V.; Pállinger, E.; Pap, E.; Kittel, A.; Nagy, G.; Falus, A.; Buzás, E.I. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: Emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol. Life Sci 2011, 68, 2667–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P.D.; Morelli, A.E. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfers, J.; Lozier, A.; Raposo, G.; Regnault, A.; Théry, C.; Masurier, C.; Flament, C.; Pouzieux, S.; Faure, F.; Tursz, T.; Angevin, E.; Amigorena, S.; Zitvogel, L. Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeelenberg, I.S.; Ostrowski, M.; Krumeich, S.; Bobrie, A.; Jancic, C.; Boissonnas, A.; Delcayre, A.; Le Pecq, J. B.; Combadière, B.; Amigorena, S.; Théry, C. Targeting tumor antigens to secreted membrane vesicles in vivo induces efficient antitumor immune responses. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A. Exosomes-based cell-free cancer therapy: a novel strategy for targeted therapy. Immunol. Med. 2020, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Panda, M.; Baral, B.; Varshney, N.; R, S.; Bhandari, V.; Parmar, H.S.; Prasad, A.; Jha, H.C. Outer Membrane Vesicles: An Emerging Vaccine Platform. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1578–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronopoulos, A.; Kalluri, R. Emerging role of bacterial extracellular vesicles in cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6951–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lei, Q.; Zou, X.; Ma, D. The role and mechanisms of gram-negative bacterial outer membrane vesicles in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1157813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.; Martin, D.; Arnold, R.; Huergo, C.C.; Oster, P.; O’Hallahan, J.; Rosenqvist, E. Properties and Clinical Performance of Vaccines Containing Outer Membrane Vesicles from Neisseria Meningitidis. Vaccine 2009, 27, B3–B12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Pol, L.; Stork, M.; van der Ley, P. Outer Membrane Vesicles as Platform Vaccine Technology. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 1689–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.M.; Fang, Y.; Fallon, J.K.; Yang, J.M.; Hildreth, J. E.; Gould, S. J. Exosomes and HIV Gag bud from endosome-like domains of the T cell plasma membrane. J. Cell Bio.l 2006, 172, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.D.; Maier, C.L.; Pober, J.S. Cytomegalovirus-infected human endothelial cells can stimulate allogeneic CD4+ memory T cells by releasing antigenic exosomes. J. Immunol. Baltim. 2009, Md 1950, 182, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tertel, T.; Tomic ́, S.; Ðokic ́, J.; Radojevic ́, D.; Stevanovic ́, D.; Ilic ́, N.; Giebel, B.; Kosanovic ́, M. Serum-derived extracellular vesicles: Novel biomarkers reflecting the disease severity of COVID-19 patients. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motallebnezhad, M.; Omraninava, M.; Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, H.; Jonaidi-Jafari, N.; Hazrati, A.; Malekpour, K.; Bagheri, Y.; Izadi, M.; Ahmadi, M. Potential therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles in the immunopathogenesis of COVID-19. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 241, 154280–154289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, P.; Astorgano, D.; Albericio, G.; Flores, S.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Luczkowiak, J.; Delgado, R.; Casasnovas, J.M.; Esteban, M.; García-Arriaza, J. Intranasal administration of a single dose of MVA-based vaccine candidates against COVID-19 induced local and systemic immune responses and protects mice from a lethal SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 995235–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuate, S.; Cinatl, J.; Doerr, H.W.; Uberla, K. Exosomal vaccines containing the S protein of the SARS coronavirus induce high levels of neutralizing antibodies. Virology 2007, 362, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrantelli, F.; Chiozzini, C.; Manfredi, F.; Giovannelli, A.; Leone, P.; Federico, M. Simultaneous CD8+ T-Cell Immune Response against SARS-Cov-2 S, M, and N Induced by Endogenously Engineered Extracellular Vesicles in Both Spleen and Lungs. Vaccines 2021, 9, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciottolo, M.; Nice, J.B.; Li, Y.; LeClaire, M.J.; Twaddle, R.; Mora, C.L.; Adachi, S.Y.; Chin, E.R.; Young, M.; Angeles, J.; Elliott, K.; Sun, M. Exosome-Based Multivalent Vaccine: Achieving Potent Immunization, Broadened Reactivity, and Strong T-Cell Responses with Nanograms of Proteins. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0050323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciottolo, M.; Li, Y.; Nice, J.B.; LeClaire, M.J.; Twaddle, R.; Mora, C.L.; Adachi, S.Y.; Young, M.; Angeles, J.; Elliott, K.; Sun, M. Nanograms of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein delivered by exosomes induce potent neutralization of both delta and omicron variants. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0290046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrantelli, F.; Chiozzini, C.; Manfredi, F.; Leone, P.; Spada, M.; Di Virgilio, A.; Giovannelli, A.; Sanchez, M.; Cara, A.; Michelini, Z.; Federico, M. Strong SARS-CoV-2 N-Specific CD8+ T Immunity Induced by Engineered Extracellular Vesicles Associates with Protection from Lethal Infection in Mice. Viruses 2022, 14, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Jong, W.S.P.; Dhakal, S.; Bart van den Berg van Saparoea, H.; Sitaras, I.; Zhou, R.; Caputo, C.; Littlefield, K.; Lowman, M.; Chen, M.; Lima, G.; Gololobova, O.; Smith, B.; Mahairaki, V.; Riley Richardson, M.; Mulka, K.R.; Lane, A.P.; Klein, S.L.; Pekosz, A.; Brayton, C.; Mankowski, J.L.; Luirink, J.; Villano, J.S.; Witwer, K.W. A bacterial extracellular vesicle-based intranasal vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 protects against disease and elicits neutralizing antibodies to wild-type and Delta variants. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12192, Erratum in: J Extracell Vesicles 2022 May;11(5), e12219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young Chung, J.; Thone, M.N.; Davies, J.E.; Gach, J.S.; Huw Davies, D.; Forthal, D.N.; Kwon, Y.J. Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 using extracellular blebs derived from spike protein expressing dendritic cells. Cell. Immunol. 2023, 386, 104691–104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Popowski, K.D.; Zhu, D.; de Juan Abad, B.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Lutz, H.; De Naeyer, N.; DeMarco, C.T.; Denny, T.N.; Dinh, P.C.; Li, Z.; Cheng, K. Exosomes decorated with a recombinant SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain as an inhalable COVID-19 vaccine. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popowski, K.D.; Moatti, A.; Scull, G.; Silkstone, D.; Lutz, H.; López de Juan Abad, B.; George, A.; Belcher, E.; Zhu, D.; Mei, X.; Cheng, X.; Cislo, M.; Ghodsi, A.; Cai, Y.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Brown, A.C.; Greenbaum, A.; Dinh, P.C.; Cheng, K. Inhalable dry powder mRNA vaccines based on extracellular vesicles. Matter 2022, 5, 2960–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popowski, K.D.; López de Juan Abad, B.; George, A.; Silkstone, D.; Belcher, E.; Chung, J.; Ghodsi, A.; Lutz, H.; Davenport, J.; Flanagan, M.; Piedrahita, J.; Dinh, P.C.; Cheng, K. Inhalable exosomes outperform liposomes as mRNA and protein drug carriers to the lung. Extracell Vesicle 2022, 1, 100002–100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.J.; Atai, N.A.; Cacciottolo, M.; Nice, J.; Salehi, A.; Guo, C.; Sedgwick, A.; Kanagavelu, S.; Gould, S.J. Exosome-mediated mRNA delivery in vivo is safe and can be used to induce SARS-CoV-2 immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101266–101285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.A.; Khan, M.I.; Kameli, N.; Alsahafi, E.; Riza, Y.M. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Exciting Potential as the Future of Next-Generation Drug Delivery. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, A.; Jeong, G.B. A systematic review on the modifications of extracellular vesicles: a revolutionized tool of nano-biotechnology. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
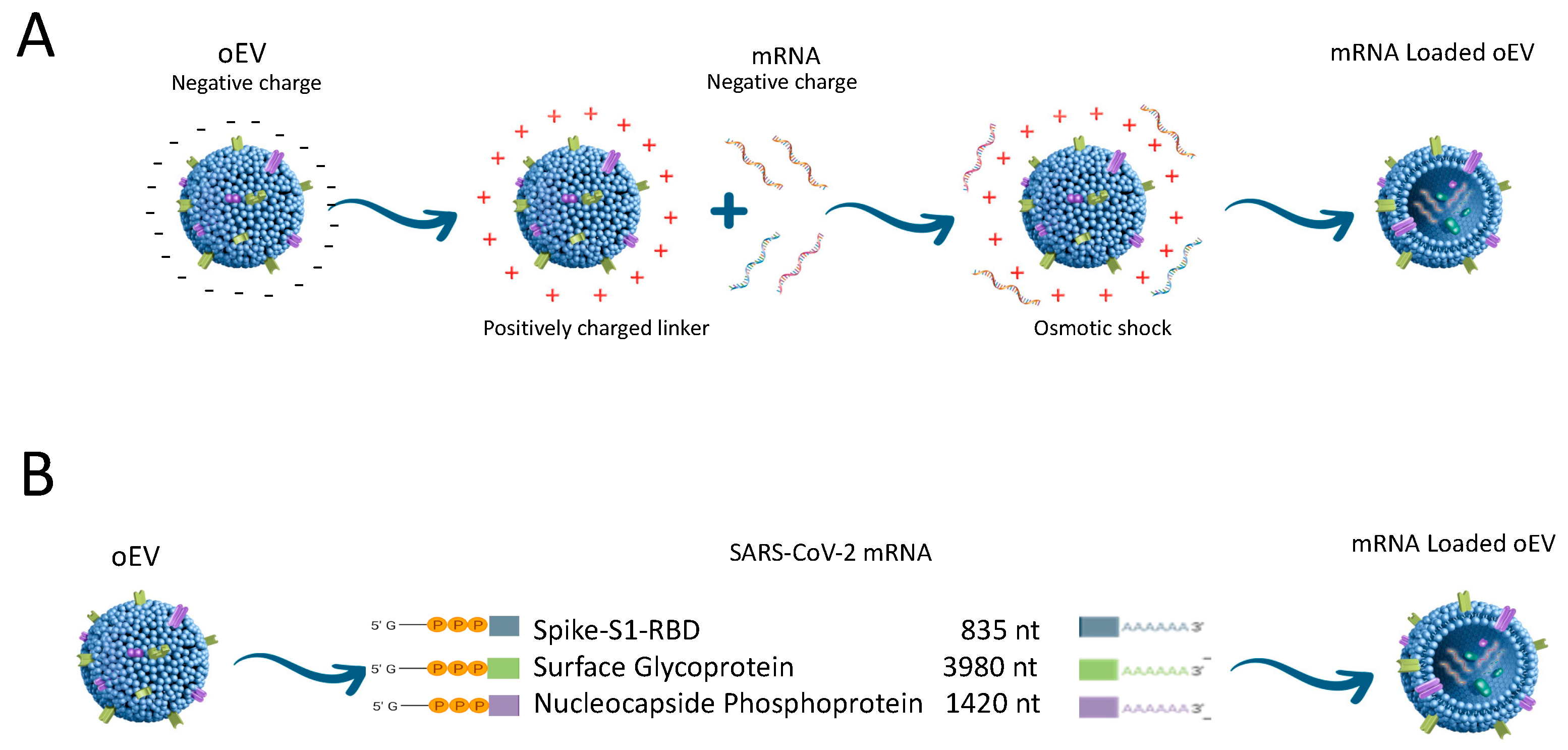
- Pomatto, M.A.C.; Gai, C.; Negro, F.; Massari, L.; Deregibus, M.C.; Grange, C.; De Rosa, F.G.; Camussi, G. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Delivery Platform for RNA-Based Vaccine: Feasibility Study of an Oral and Intranasal SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 974–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomatto, M.A.C.; Gai, C.; Negro, F.; Massari, L.; Deregibus, M.C.; De Rosa, F.G.; Camussi, G. Oral Delivery of mRNA Vaccine by Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Carriers. Cells 2023, 12, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knisely, J.M.; Buyon, L.E.; Mandt, R.; Farkas, R.; Balasingam, S.; Bok, K.; Buchholz, U.J.; D'Souza, M.P.; Gordon, J.L.; King, D.F.L.; Le, T.T.; Leitner, W.W.; Seder, R.A.; Togias, A.; Tollefsen, S.; Vaughn, D.W.; Wolfe, D.N.; Taylor, K.L.; Fauci, A.S. Mucosal vaccines for SARS-CoV-2: scientific gaps and opportunities-workshop report. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schäfer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neutra, M.R.; Kozlowski, P.A. Mucosal vaccines: The promise and the challenge. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.N.; Li, X.F.; Deng, Y.Q.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.J.; Yang, G.; Huang, W.J.; Gao, P.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, R.R.; Guo, Y.; Sun, S.H.; Fan, H.; Zu, S.L.; Chen, Q.; He, Q.; Cao, T.S.; Huang, X.Y.; Qiu, H.Y.; Nie, J.H.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, H.Y.; Ye, Q.; Zhong, X.; Xue, X.L.; Zha, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.C.; Ying, B.; Qin, C.F. A Thermostable mRNA Vaccine against COVID-19. Cell 2020, 182, 1271–1283.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PLOS BLOGS - Absolutely Maybe: Progress on Intranasal & Oral Covid Vaccines – Plus a US Government Funding Boost. Available online: URL (Last update: 21 April 2023, accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Miteva, D.; Peshevska-Sekulovska, M.; Snegarova, V.; Batselova, H.; Alexandrova, R.; Velikova, T. Mucosal COVID-19 vaccines: Risks, benefits and control of the pandemic. World.J Virol. 2022, 11, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
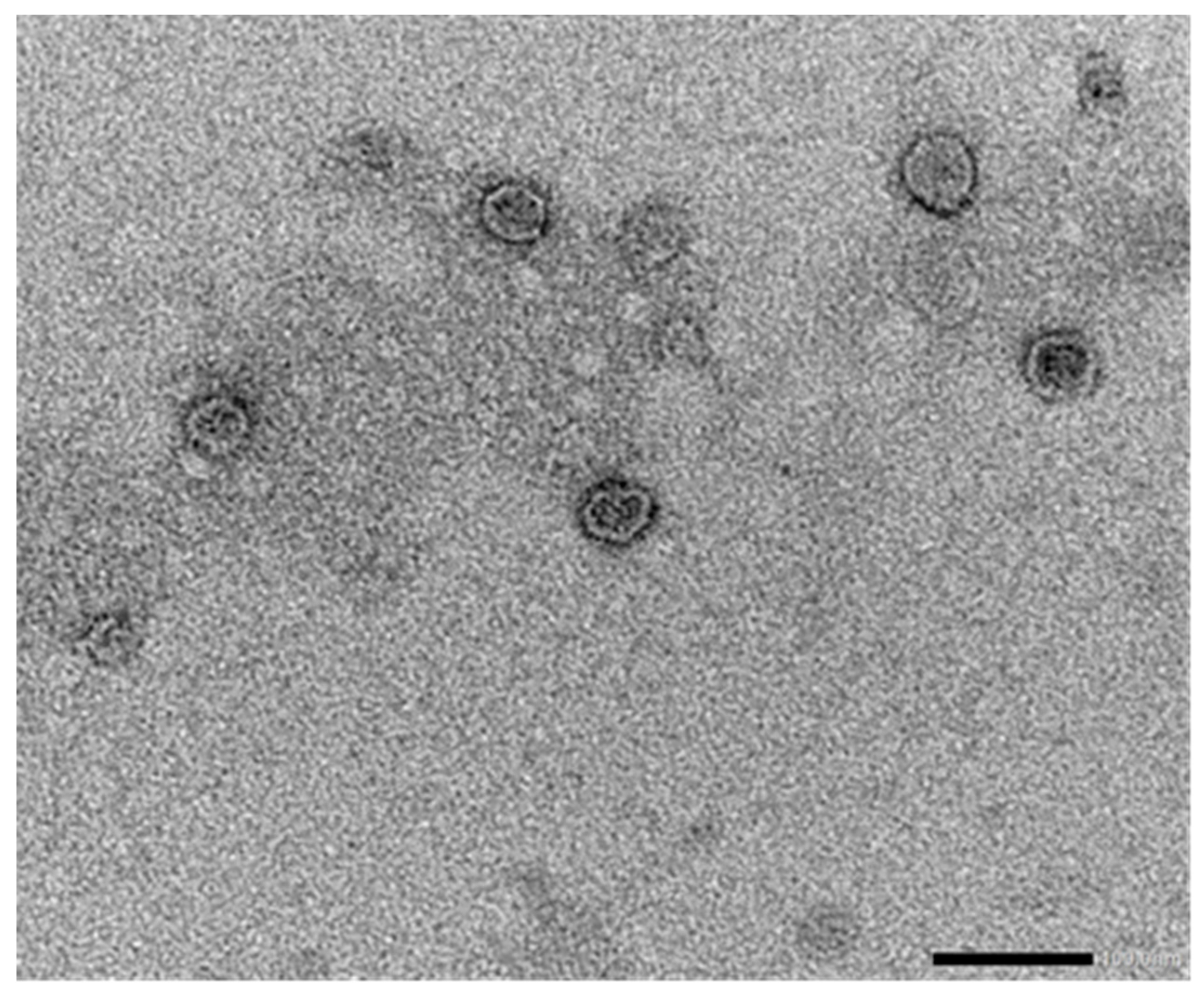
| Vaccine type | Administration route | Serum antibodies | Presence of Neutralizing antibodies | IFNγ secretion | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-S protein in EVs (compared to AAV) | Footpad injection | Presence of serum antibodies | Yes | / | 82 |
| SARS-CoV-2 S or N protein on the surface of EVs | i.m. | Presence of serum antibodies | Yes | Yes | 84, 85 |
| Endogenous engineered EVs expressing SARS-CoV-2 antigens | i.m. | Presence of serum antibodies | / | Yes | 83, 86 |
| EVs of Salmonella typhimurium decorated with SARS-CoV-2 S protein | i.n. | Presence of serum antibodies: IgG, IgM, IgA | Yes | / | 87 |
| EVs from engineered DCs | s.c. | Presence of serum antibodies: IgG | / | / | 88 |
| SARS-CoV-2 S mRNA in Lung-derived EVs (compared to LNPs) | i.n. | Presence of serum antibodies IgG, IgA | / | / | 89 |
| SARS-CoV-2 S and N mRNA in EVs (compared to LNPs) | i.m. | Presence of serum antibodies | / | / | 91 |
| SARS-CoV-2 S mRNA in oEV, liquid | i.m., i.n., oral | Presence of serum antibodies: IgG, IgM, IgA | Yes | Yes | 95 |
| SARS-CoV-2 S mRNA in oEV, lyophilized | oral | Presence of serum antibodies: IgG, IgM, IgA | Yes | Yes | 96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





