Submitted:
09 January 2024
Posted:
09 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol
2.2. Search strategies
- (“Bunyavir*” OR “orthobunyavirus*”) AND (“Shamonda*” OR “Simbu*”)
- (“Bunyavir*” OR “orthobunyavirus” OR “Akabane” OR “Tinaroo” OR “Yaba-7” OR “Jatobal” OR “Buttonwillow” OR “Cat Que” OR “Ingwavuma” OR “Inini” OR “Manzanilla” OR “Mermet” OR “Facey's paddock” OR “Iquitos” OR “Madre de Dios” OR “Oropouche” OR “Perdoes” OR “Pintupo” OR “Utinga” OR “Utive” OR “Douglas” OR “Sango” OR “Sathuperi” OR “Peaton” OR “Schmallenberg” OR “Shamonda” OR “Sabo” OR “Aino” OR “Kaikalur” OR “Shuni” OR “Oya” OR “Para” OR “Simbu” OR “Thimiri”) AND (“bovine” OR “cattle” OR “cow” OR “calf” OR “calves” OR “dairy” OR “beef” OR “ovine” OR “sheep” OR “caprine” OR “goat” OR “equine” OR “horse” OR “porcine” OR “pig” or “pork”)
2.3. Eligibility criteria
2.4. Data collection and analysis
| Variable | Description | Unit/Levels |
|---|---|---|
| Authors | The names of the authors listed on the publication | Free text list |
| Publication Date | The date for which the publication was published | Date/Month/Year format |
| Publication Year | The year for which the publication was published | Date/Month/Year format |
| Country | A list of the country affiliations of the authors | Free text list |
| Continent | The continent in which the study was conducted | Americas Africa Asia Australia/Oceania Europe |
| Title | The title of the publication | Free text list |
| Journal | The name of the journal of publication | Free text list |
| Virus name | The Simbu group virus/es investigated | see Supplementary Table S1 for the 33 viruses included in the serogroup |
| Theme: The veterinary important SGVs and the associated animal disease presentation | ||
| Study type | Study type/design | Descriptive Observational Experimental Theoretical |
| Infection type | Natural exposure or experimental challenge | Natural Experimental |
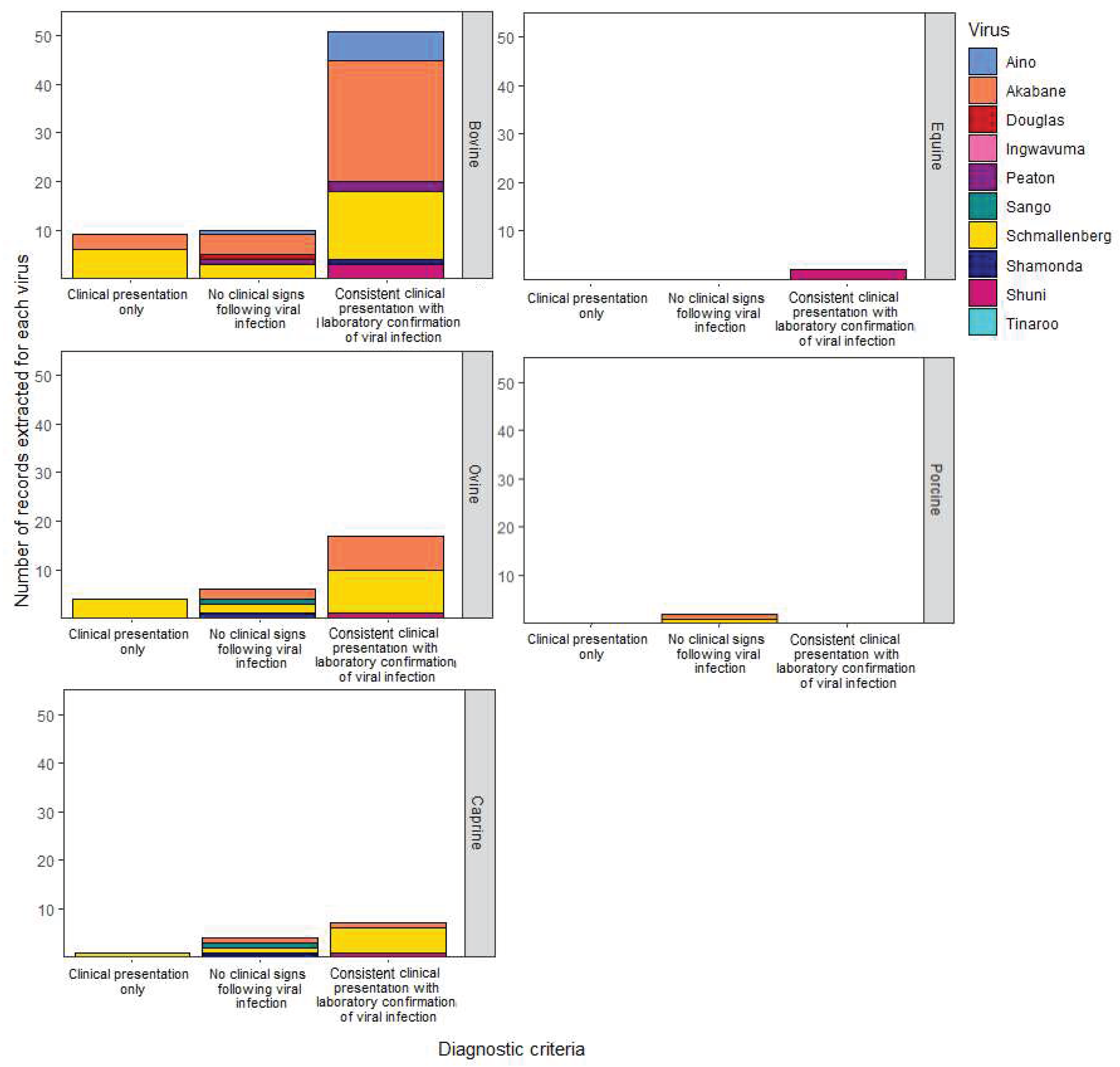
| Case definition1 | Diagnostic criterion applied to recruit cases into this review to provide a systematic description of disease presentations associated with SGV infection |
Clinical presentation only Antibody detection only Agent detection only Consistent clinical presentation with confirmation of viral infection with a SGV |
| Diagnostic test | Test type(s) utilized for confirmation of disease due to the virus of interest | Free text list |
| Start | The start date of the period of observation | Date/Month/Year format |
| End | The end date of the period of observation | Date/Month/Year format |
| Season | The season in which the observations of animal disease occurred. The date of disease report was used to determine the season based on the period and location of the observation. |
Summer Autumn Spring Winter |
| Host species | Species of animal host with disease | Bovine Ovine Caprine Porcine Equine |
| Host age group2 | Age group of the animal host with disease |
Foetal: unborn Juvenile: born to <12 months of age Adult: 12 months of age |
| Disease system2 | The organ system involved | Circulatory Respiratory Gastrointestinal Musculoskeletal Nervous Urinary Reproductive Congenital Non-specific |
| Clinical signs2 | A list of all clinical signs reported | Free text list |
| Frequency of clinical signs listed | The count of the observations of clinical signs by the number of cases | Numeric |
| Differentials considered | What other diseases were considered | Free text list |
| Diagnostic tests | Assay types used to diagnose the virus of interest | Free text list |
| Histopathological description | The inclusion of histopathological description of disease | Yes No |
| Economic losses estimated | The inclusion of an estimate or economic assessment of the impact of associated disease | Yes, with information collected in a free text list No |
|
1 This assessment was completed to ensure that cases of clinical disease described was confirmed to be a result of infection with the virus of interest. The four diagnostic criteria are based on the unified case definitions proposed by European agencies during data collection for the Schmallenberg virus epidemic [21]. The diagnostic challenge in identifying a SGV as a cause of disease were exemplified by the different and varying case definitions used by affected countries during the outbreak in Europe. In January 2012, different countries had varying criteria for what constituted a confirmed case following Schmallenberg virus infection. These criteria depended on factors such as the age of the host (offspring or adult) or the location of the infection (within or outside the known range). Additionally, laboratory confirmation of the viral infection was achieved through a variety of agent and/or antibody tests. 2 To provide a distinction between maternal and foetal outcomes of infection, clinical signs relating to reproductive and neurological disease were categorised given the context provided from the host age group. This allowed for congenital disease to be considered as a foetal outcome and reproductive disease to be measured as a maternal effect. Theme: Diagnostic tests – development and validation studies | ||
| Test scenario | Reason for testing | Monitoring populations for infection/exposure Diagnosis in animals where disease is suspected |
| Sample types | List of the samples utilized in test development or validation | Free text list |
| Test types | List of the test types investigated | Free text list |
| Test level | Test is designed to detect SGVs either at a group level or to differentiate a specific named virus | Group Virus |
| Test target | Test designed for serology or agent detection | Serology Agent |
| Test details | Details such as the test manufacturer, reagents, primer, and probe sequences | Free text list |
| Test validation | If the assay has undergone validation and if so, to which stage along the validation pathway as defined by WOAH guidelines [22] | None: No validation data provided Stage 1: Analytical characteristics Stage 2: Diagnostic characteristics and cut-off values Stage 3: Reproducibility Stage 4: Implementation |
|
Theme: Monitoring methods | ||
| Virus | Simbu group virus of interest for the activity | Free text list |
| Survey Area | Area of interest for the study | Local region (intra-country) Country Multinational Continent |
| Survey location | Details of the country and region where the activity occurred | Free text list |
| Survey period | Length of time over the course of the study | Numeric (months) |
| Sample collection | The type sample collection used in the study: Active if the samples were primarily collected for the surveillance activity. Passive if the samples were collected for another purpose (diagnostic investigation or a non-SGV surveillance program) |
Active Passive |
| Survey test | Test type(s) utilized in the monitoring activity | Free text list |
| Animal | Animal species from where samples were collected from | Free text list |
| Sample frequency | Frequency of sampling used for the study | Single Serial – repeated/ daily/ weekly/ monthly/ quarterly/ Yearly Paired |
| Sample size calculation | - If sample size calculations were considered and the details of the:
|
Yes/No Numeric for the information on the sample size calculation |
| Sample size | Sample size | Numeric |
| Seroprevalence3 | Reported seroprevalence in each study was charted by:
|
Numeric |
| 3 A quantitative summary of seroprevalence by country, animal species, and Simbu group virus was prepared using R with data extracted (Supplementary Figure S1). | ||
3. Results
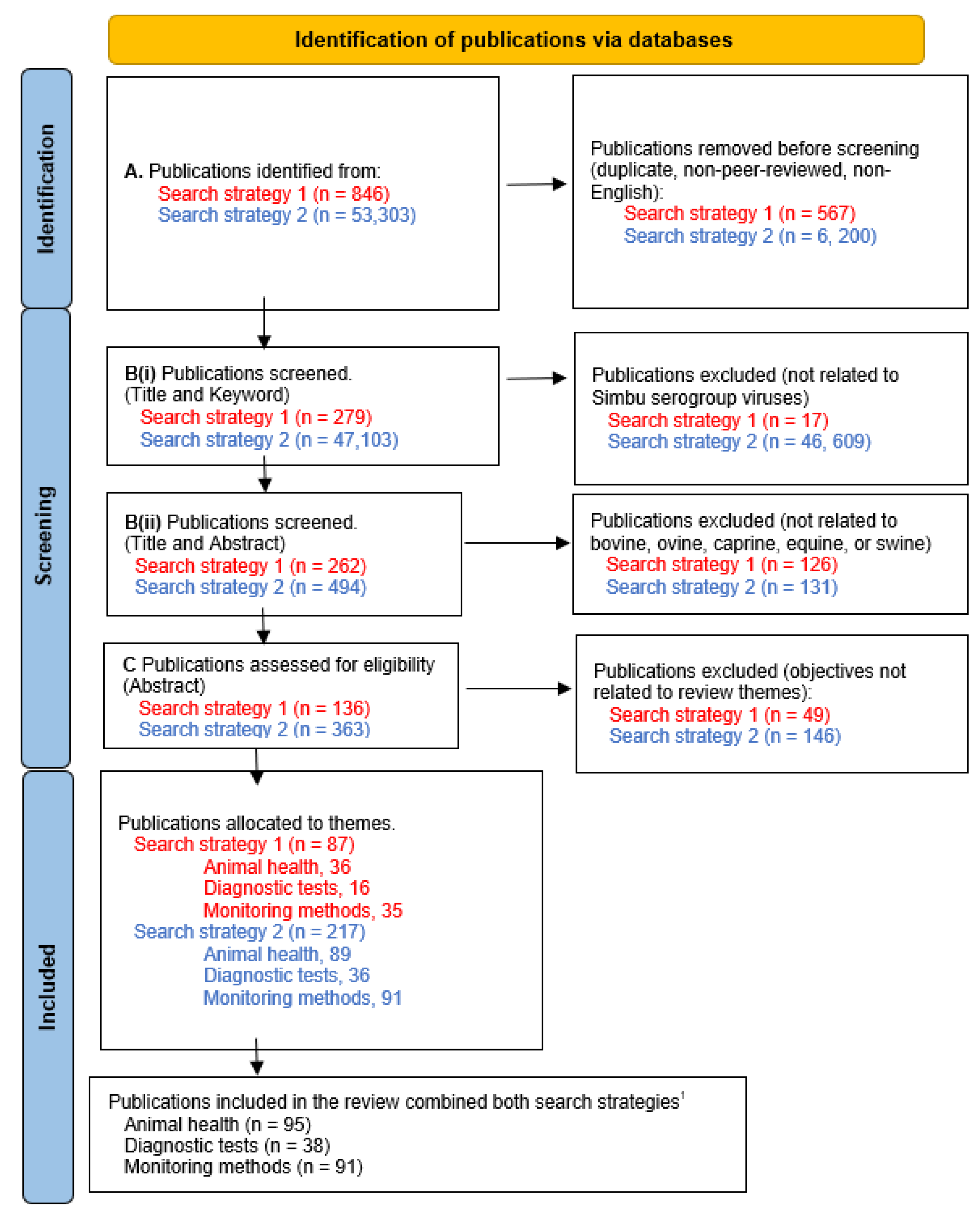
3.1. Selection of sources of evidence
3.2. Characteristics of sources of evidence
3.3. Animal health impacts associated with Simbu group viruses
3.3.1. Clinical presentation of livestock disease
3.3.2. The Simbu group viruses associated with livestock disease
3.4. Test development and validation studies for assays to detect viruses in the Simbu group
3.4.1. Agent detection
3.4.2. Antibody detection
3.5. Monitoring the distribution of viruses in the Simbu group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
- Supplementary Table S1: The distribution, insect vector, host range, and disease observations for the 33 viruses within the Simbu serogroup as arranged by their species designation;
- Supplementary Table S2: Histopathological details extracted from publications describing the animal health outcomes following natural or experimental infection of a Simbu group virus in livestock;
- Supplementary Table S3: PCR details extracted from publications describing the molecular assays developed and validated for the detection of Simbu group viruses
- Supplementary Figure S1: Mean seroprevalence extracted from the seroprevalence studies describing the distribution and diversity of SGVs by A) country, B) host species , and C) virus.
- RepRows function to match variables entered as a comma-separated list and extract the details into multiple records for the same publication.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Girard M, Nelson CB, Picot V, Gubler DJ. Arboviruses: A global public health threat. Vaccine. 2020;38(24):3989-94. Epub 2020/04/24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, RM. Orthobunyaviruses: recent genetic and structural insights. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2014;12(10):673-85. [CrossRef]
- Hughes HR, Adkins S, Alkhovskiy S, Beer M, Blair C, Calisher CH, et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Peribunyaviridae. Journal of General Virology. 2020;101(1):1-2. [CrossRef]
- Vasilakis N, Tesh RB, Popov VL, Widen SG, Wood TG, Forrester NL, et al. Exploiting the Legacy of the Arbovirus Hunters. Viruses. 2019;11(5). Epub 2019/05/28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, CH. History, Classification, and Taxonomy of Viruses in the Family Bunyaviridae. In: Elliott RM, editor. The Bunyaviridae. Boston, MA: Springer US; 1996. p. 1-17.
- Walter CT, Barr JN. Recent advances in the molecular and cellular biology of bunyaviruses. Journal of General Virology. 2011;92(11):2467-84. [CrossRef]
- Briese T, Calisher CH, Higgs S. Viruses of the family Bunyaviridae: Are all available isolates reassortants? Virology. 2013;446(1-2):207-16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abudurexiti A, Adkins S, Alioto D, Alkhovsky SV, Avšič-Županc T, Ballinger MJ, et al. Taxonomy of the order Bunyavirales: update 2019. Archives of Virology. 2019;164(7):1949-65. Epub 2019/05/09. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds P, Adriaenssens EM, Zerbini FM, Abrescia NGA, Aiewsakun P, Alfenas-Zerbini P, et al. Four principles to establish a universal virus taxonomy. PLOS Biology. 2023;21(2):e3001922. [CrossRef]
- Jin H, Elliott RM. Mutagenesis of the L protein encoded by Bunyamwera virus and production of monospecific antibodies. Journal of General Virology. 1992;73(9):2235-44. [CrossRef]
- Kinney RM, Calisher CH. Antigenic Relationships among Simbu Serogroup (Bunyaviridae) Viruses. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 1981;30(6):1307-18. [CrossRef]
- Yanase T, Murota K, Suda Y. Whole-genome sequence analysis of a novel orthobunyavirus isolated in Japan in the 1980s. Archives of Virology. 2023;168(2):67. [CrossRef]
- Ladner JT, Savji N, Lofts L, Travassos da Rosa A, Wiley MR, Gestole MC, et al. Genomic and phylogenetic characterization of viruses included in the Manzanilla and Oropouche species complexes of the genus Orthobunyavirus, family Bunyaviridae. Journal of General Virology. 2014;95(5):1055-66. [CrossRef]
- Miura Y, Hayashi S, Ishihara T, Inaba Y, Omori T. Neutralizing antibody against akabane virus in precolostral sera from calves with congenital arthrogryposis hydranencephaly syndrome. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;46(3-4):377-80. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann B, Scheuch M, Höper D, Jungblut R, Holsteg M, Schirrmeier H, et al. Novel orthobunyavirus in cattle, Europe, 2011. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2012;18(3):469-72. [CrossRef]
- van Eeden C, Williams JH, Gerdes TGH, van Wilpe E, Viljoen A, Swanepoel R, et al. Shuni virus as cause of neurologic disease in horses. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2012;18(2):318-21. [CrossRef]
- De Regge, N. Akabane, Aino and Schmallenberg virus—where do we stand and what do we know about the role of domestic ruminant hosts and Culicoides vectors in virus transmission and overwintering? Current Opinion in Virology. 2017;27:15-30. [CrossRef]
- Murray, MD. Akabane epizootics in New South Wales: evidence for long-distance dispersal of the biting midge Culicoides brevitarsis. Australian Veterinary Journal. 1987;64(10):305-8. [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan JL, Walker PJ, Duchemin J-B, Jeanne I, Holmes EC. Seasonal Drivers of the Epidemiology of Arthropod-Borne Viruses in Australia. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2014;8(11):e3325. [CrossRef]
- Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O'Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Annals of internal medicine. 2018;169(7):467-73. [CrossRef]
- Afonso A, Abrahantes JC, Conraths F, Veldhuis A, Elbers A, Roberts H, et al. The Schmallenberg virus epidemic in Europe-2011-2013. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2014;116(4):391-403. [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health. Chapter 1.1.6. Principles and Methods of Validation of Diagnostic Assays for Infectious Diseases. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals 20222018.
- Kurogi H, Inaba Y, Takahashi E, Sato K, Omori T, Miura Y, et al. Epizootic congenital arthrogryposis-hydranencephaly syndrome in cattle: Isolation of Akabane virus from affected fetuses. Archives of Virology. 1976;51(1-2):67-74. [CrossRef]
- Kirkland PD, Barry RD, Harper PA, Zelski RZ. The development of Akabane virus-induced congenital abnormalities in cattle. The Veterinary Record. 1988;122(24):582-6. [CrossRef]
- Gibney EH, Kipar A, Rosbottom A, Guy CS, Smith RF, Hetzel U, et al. The extent of parasite-associated necrosis in the placenta and foetal tissues of cattle following Neospora caninum infection in early and late gestation correlates with foetal death. International Journal for Parasitology. 2008;38(5):579-88. [CrossRef]
- Osburn, B. Ontogeny of immune responses in cattle. In: Morrison WI, editor. Ruminant immune system in health and disease. 1986.
- Bayrou C, Garigliany M-M, Sarlet M, Sartelet A, Cassart D, Desmecht D. Natural Intrauterine Infection with Schmallenberg Virus in Malformed Newborn Calves. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2014;20(8):1327-30. [CrossRef]
- Hirashima Y, Kitahara S, Kato T, Shirafuji H, Tanaka S, Yanase T. Congenital malformations of calves infected with Shamonda virus, southern Japan. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2017;23(6):993-6. [CrossRef]
- Parsonson IM, Della-Porta AJ, Snowdon WA. Congenital abnormalities in newborn lambs after infection of pregnant sheep with Akabane virus. Infection and Immunity. 1977;15(1):254-62. [CrossRef]
- Parsonson IM, Della-Porta AJ, Snowdon WA. Akabane virus infection in the pregnant ewe. 2. Pathology of the foetus. Veterinary Microbiology. 1981;6(3):209-24. [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P. Interception of the development of self tolerance in fetal lambs. European Journal of Immunology. 1989;19(8):1387-92. Epub 1989/08/01. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashiguchi Y, Nanba K, Kumagai T. Congenital abnormalities in newborn lambs following Akabane virus infection in pregnant ewes. National Institute of Animal Health Quarterly. 1979;19(1-2):1-11. PubMed PMID: WOS:A1979HN75400001.
- Laloy E, Bréard E, Trapp S, Pozzi N, Riou M, Barc C, et al. Fetopathic effects of experimental Schmallenberg virus infection in pregnant goats. Veterinary Microbiology. 2017;211:141-9. [CrossRef]
- Porto WJN, Horcajo P, Kim PdCP, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Romão EA, Álvarez-García G, et al. Peripheral and placental immune responses in goats after primoinfection with Neospora caninum at early, mid and late gestation. Veterinary Parasitology. 2017;242:38-43. [CrossRef]
- Golender N, Bumbarov V, Assis I, Beer M, Khinich Y, Koren O, et al. Shuni virus in Israel: Neurological disease and fatalities in cattle. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases. 2019;66(3):1126-31. [CrossRef]
- Golender N, Brenner J, Valdman M, Khinich Y, Bumbarov V, Panshin A, et al. Malformations Caused by Shuni Virus in Ruminants, Israel, 2014-2015. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2015;21(12):2267-8. [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki M, Miura Y, Hayashi S, Ishitani R. Histopathological findings of calves infected experimentally with Aino virus. National Institute of Animal Health quarterly. 1977;17(3):95-106. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC917129.
- Coverdale OR, Cybinski DH, St George TD. Congenital abnormalites in calves associated with Akabane virus and Aino virus. Australian Veterinary Journal. 1978;54(3):151-2. [CrossRef]
- Behar A, Leibovich BB, Edery N, Yanase T, Brenner J. First genomic detection of Peaton virus in a calf with hydranencephaly in Israel. Veterinary Medicine and Science. 2019;5(1):87-92. [CrossRef]
- Garigliany M-M, Hoffmann B, Dive M, Sartelet A, Bayrou C, Cassart D, et al. Schmallenberg Virus in Calf Born at Term with Porencephaly, Belgium. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2012;18(6):1005-6. [CrossRef]
- Parsonson IM, McPhee DA, Della-Porta AJ, McClure S, McCullagh P. Transmission of Akabane virus from the ewe to the early fetus (32 to 53 days). Journal of Comparative Pathology. 1988;99(2):215-27. [CrossRef]
- Haughey KG, Hartley WJ, Della-Porta AJ, Murray MD. Akabane disease in sheep. Australian Veterinary Journal. 1988;65(5):136-40. [CrossRef]
- Saegerman C, Martinelle L, Dal Pozzo F, Kirschvink N. Preliminary survey on the impact of Schmallenberg virus on sheep flocks in South of Belgium. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases. 2014;61(5):469-72. [CrossRef]
- Liao YK, Lu YS, Goto Y, Inaba Y. The isolation of Akabane virus (Iriki strain) from calves in Taiwan. Journal of Basic Microbiology. 1996;36(1):33-9. [CrossRef]
- Motlou TP, Williams J, Venter M. Epidemiology of Shuni Virus in Horses in South Africa. Viruses. 2021;13(5). [CrossRef]
- Oem JK, Lee KH, Kim HR, Bae YC, Chung JY, Lee OS, et al. Bovine Epizootic Encephalomyelitis caused by Akabane Virus Infection in Korea. Journal of Comparative Pathology. 2012;147(2-3):101-5. [CrossRef]
- Lee JK, Park JS, Choi JH, Park BK, Lee BC, Hwang WS, et al. Encephalomyelitis Associated with Akabane Virus Infection in Adult Cows. Veterinary Pathology. 2002;39(2):269-73. [CrossRef]
- Lechner I, Wüthrich M, Meylan M, van den Borne BHP, Schüpbach-Regula G. Association of clinical signs after acute Schmallenberg virus infection with milk production and fertility in Swiss dairy cows. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2017;146:121-9. [CrossRef]
- Shaw AE, Mellor DJ, Purse BV, Shaw PE, McCorkell BF, Palmarini M. Transmission of Schmallenberg virus in a housed dairy herd in the UK. Veterinary Record. 2013;173(24):609. [CrossRef]
- Laloy E, Riou M, Barc C, Belbis G, Breard E, Breton S, et al. Schmallenberg virus: experimental infection in goats and bucks. BMC Veterinary Research. 2015;11. [CrossRef]
- Miyazato S, Miura Y, Hase M, Kubo M, Goto Y, Kono Y. Encephalitis of cattle caused by Iriki isolate, a new strain belonging to Akabane virus. Nippon juigaku zasshi The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Science. 1989;51(1):128-36. [CrossRef]
- Barrett D, O'Neill R, Sammin D, Clegg TA, More SJ. The impact of infection with Schmallenberg virus on weaning rate in Irish sheep flocks. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2015;122(3):332-8. [CrossRef]
- Martinelle L, Dal Pozzo F, Gauthier B, Kirschvink N, Saegerman C. Field veterinary survey on clinical and economic impact of schmallenberg virus in Belgium. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases. 2014;61(3):285-8. [CrossRef]
- Horikita T, Yoshinaga S, Okatani AT, Yamane I, Honda E, Hayashidani H. Loss of milk yield due to Akabane disease in dairy cows. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science. 2005;67(3):287-90. [CrossRef]
- Häsler B, Alarcon P, Raboisson D, Waret-Szkuta A, Rushton J. Integration of production and financial models to analyse the financial impact of livestock diseases: A case study of Schmallenberg virus disease on British and French dairy farms. Veterinary Record. 2015;2(1). [CrossRef]
- Waret-Szkuta A, Alarconl P, Häsler B, Rushton J, Corbière F, Raboisson D. Economic assessment of an emerging disease: The case of Schmallenberg virus in France. OIE Revue Scientifique et Technique. 2017;36(1):265-77. [CrossRef]
- Shirafuji H, Yazaki R, Shuto Y, Yanase T, Kato T, Ishikura Y, et al. Broad-range detection of arboviruses belonging to Simbu serogroup lineage 1 and specific detection of Akabane, Aino and Peaton viruses by newly developed multiple TaqMan assays. Journal of Virological Methods. 2015;225:9-15. [CrossRef]
- Fischer M, Schirrmeier H, Wernike K, Wegelt A, Beer M, Hoffmann B. Development of a pan-Simbu real-time reverse transcriptase PCR for the detection of Simbu serogroup viruses and comparison with SBV diagnostic PCR systems. Virology Journal. 2013;10. [CrossRef]
- De Regge N, Madder M, Deblauwe I, Losson B, Fassotte C, Demeulemeester J, et al. Schmallenberg virus circulation in Culicoides in Belgium in 2012: Field validation of a real time RT-PCR approach to assess virus replication and dissemination in midges. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(1). [CrossRef]
- De Regge N, Van Den Berg T, Georges L, Cay B. Diagnosis of Schmallenberg virus infection in malformed lambs and calves and first indications for virus clearance in the fetus. Veterinary Microbiology. 2013;162(2-4):595-600. [CrossRef]
- Camarão AAR, Swanepoel R, Boinas F, Quan M. Development and analytical validation of a group-specific RT-qPCR assay for the detection of the Simbu serogroup orthobunyaviruses. Journal of Virological Methods. 2019;271. [CrossRef]
- Golender N, Bumbarov VY, Erster O, Beer M, Khinich Y, Wernike K. Development and validation of a universal S-segment-based real-time RT-PCR assay for the detection of Simbu serogroup viruses. Journal of Virological Methods. 2018;261:80-5. [CrossRef]
- Gurau MR, Baraitareanu S, Manescu MA, Popp MC, Danes D. Studies concerning the optimisation of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction technique of pan-Simbu virus group. Scientific Bulletin Series F Biotechnologies. 2016;20:329-32. PubMed PMID: CABI:20173026101.
- Wernike K, Beer M. International proficiency trial demonstrates reliable Schmallenberg virus infection diagnosis in endemic and non-affected countries. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(6). [CrossRef]
- Aebischer A, Wernike K, Hoffmann B, Beer M. Rapid genome detection of Schmallenberg virus and bovine viral diarrhea virus by use of isothermal amplification methods and high-speed real-time reverse transcriptase PCR. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2014;52(6):1883-92. [CrossRef]
- Wernike K, Aebischer A, Sick F, Szillat KP, Beer M. Differentiation of antibodies against selected Simbu serogroup viruses by a glycoprotein Gc-based triplex ELISA. Veterinary Sciences. 2021;8(1):1-14. [CrossRef]
- Tsuda T, Yoshida K, Yanase T, Ohashi S, Yamakawa M. Competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of the antibodies specific to Akabane virus. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 2004;16(6):571-6. [CrossRef]
- Blacksell SD, Lunt RA, White JR. Rapid identification of Australian bunyavirus isolates belonging to the Simbu serogroup using indirect ELISA formats. Journal of Virological Methods. 1997;66(1):123-33. [CrossRef]
- Näslund K, Blomqvist G, Vernersson C, Zientara S, Bréard E, Valarcher JF. Development and evaluation of an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological detection of Schmallenberg virus antibodies in ruminants using whole virus antigen. Acta veterinaria Scandinavica. 2014;56:71. [CrossRef]
- Ungar-Waron H, Gluckman A, Trainin Z. ELISA test for the serodiagnosis of Akabane virus infection in cattle. Tropical Animal Health and Production. 1989;21(3):205-10. [CrossRef]
- Kittelberger R, McFadden AMJ, Kirkland PD, Hannah MJ, Orr D, Bueno R, et al. Evaluation of two commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for the detection of serum antibodies against Akabane virus in cattle. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 2013;25(5):645-8. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Jing H, Liu X, Wang Q, Qiu S, Liu D, et al. Comparative evaluation of two commercial ELISA kits for detection of antibodies against Akabane virus in cattle serum. BMC Veterinary Research. 2019;15(1). [CrossRef]
- Pejaković S, Wiggers L, Coupeau D, Kirschvink N, Mason J, Muylkens B. Test selection for antibody detection according to the seroprevalence level of Schmallenberg virus in sheep. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(4). [CrossRef]
- Bréard E, Lara E, Comtet L, Viarouge C, Doceul V, Desprat A, et al. Validation of a Commercially Available Indirect Elisa Using a Nucleocapside Recombinant Protein for Detection of Schmallenberg Virus Antibodies. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(1). [CrossRef]
- Daly JM, King B, Tarlinton R, Gough KC, Maddison BC, Blowey R. Comparison of Schmallenberg virus antibody levels detected in milk and serum from individual cows. BMC Veterinary Research. 2015;11(56):(11 March 2015)-(11 March ). PubMed PMID: CABI:20153115888.
- Douglass AP, O'Grady L, McGrath G, Tratalos J, Mee JF, Barrett D, et al. Development of a syndromic surveillance system for Irish dairy cattle using milk recording data. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2022;204. [CrossRef]
- Causey OR, Kemp GE, Causey CE, Lee VH. Isolations of Simbu-group viruses in Ibadan, Nigeria 1964–69, including the new types Sango, Shamonda, Sabo and Shuni. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology. 1972;66(3):357-62. [CrossRef]
- St George TD, Cybinski DH, Filippich C, Carley JG. Isolation of three Simbu group viruses new to Australia. Australian Journal of Experimental Biology and Medical Science. 1979;57(6):581-2. PubMed PMID: BIOSIS:PREV198019052059.
- Matsumori Y, Aizawa M, Sakai Y, Inoue D, Kodani M, Tsuha O, et al. Congenital abnormalities in calves associated with Peaton virus infection in Japan. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 2018;30(6):855-61. Epub 2018/09/12. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase T, Maeda K, Kato T, Nyuta S, Kamata H, Yamakawa M, et al. The resurgence of Shamonda virus, an African Simbu group virus of the genus Orthobunyavirus, in Japan. Archives of Virology. 2005;150(2):361-9. [CrossRef]
- Hirashima Y, Sakaguchi Z, Okada D, Fujioka M, Kitahara S, Iwamoto J, et al. Retrospective survey of shamonda virus infection in sentinel and breeding cattle and in malformed calves in Kagoshima Prefecture. Journal of the Japan Veterinary Medical Association. 2017;70(11):729-34. [CrossRef]
- Walt Mvd, Rakaki ME, MacIntyre C, Mendes A, Junglen S, Theron C, et al. Identification and Molecular Characterization of Shamonda Virus in an Aborted Goat Fetus in South Africa. Pathogens. 2023;12(9):1100. PubMed PMID:. [CrossRef]
- Konno S, Moriwaki M, Nakagawa M. Akabane Disease in Cattle: Congenital Abnormalities caused by Viral Infection. Spontaneous Disease. Veterinary Pathology. 1982;19(3):246-66. [CrossRef]
- Hartley WJ, Desaram WG, Della-Porta AJ, Snowdon WA, Shepherd NC. Pathology of congenital bovine episootic arthrogryposis and hydranenecphaly and its relationship to Akabane virus. Australian Veterinary Journal. 1977;53(7):319-25. [CrossRef]
- Herder V, Wohlsein P, Peters M, Hansmann F, Baumgaertner W. Salient Lesions in Domestic Ruminants Infected With the Emerging So-called Schmallenberg Virus in Germany. Veterinary Pathology. 2012;49(4):588-91. [CrossRef]
- König P, Wernike K, Hechinger S, Tauscher K, Breithaupt A, Beer M. Fetal infection with Schmallenberg virus — An experimental pathogenesis study in pregnant cows. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases. 2019;66(1):454-62. [CrossRef]
- Steinrigl A, Schiefer P, Schleicher C, Peinhopf W, Wodak E, Bago Z, et al. Rapid spread and association of Schmallenberg virus with ruminant abortions and foetal death in Austria in 2012/2013. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2014;116(4):350-9. [CrossRef]
- Noda Y, Yokoyama H, Katsuki T, Kurashige S, Uchinuno Y, Narita M. Demonstration of Akabane virus antigen using immunohistochemistry in naturally infected newborn calves. Veterinary Pathology. 2001;38(2):216-8. [CrossRef]
- Murata Y, Uchida K, Shioda C, Uema A, Bangphoomi N, Chambers JK, et al. Histopathological Studies on the Neuropathogenicity of the Iriki and OBE-1 Strains of Akabane Virus in BALB/cAJcl Mice. Journal of Comparative Pathology. 2015;153(2-3):140-9. [CrossRef]
- Park B-K, Chang C-H, Lyoo Y-S, Son S-W, Lee P-S, Rhee J-C, et al. Studies on an attenuated live Akabane virus vaccine against Akabane disease. Research Reports of the Rural Development Administration (Suweon). 1992;34(2 VET.):20-6. PubMed PMID: BIOSIS:PREV199395108926.
- Kurogi H, Inaba Y, Takahashi E, Sato K, Akashi H, Satoda K, et al. An attenuated strain of Akabane virus: a candidate for live virus vaccine. National Institute of Animal Health Quarterly. 1979;19(1-2):12-22.
- Kraatz F, Wernike K, Hechinger S, Koenig P, Granzow H, Reimann I, et al. Deletion Mutants of Schmallenberg Virus Are Avirulent and Protect from Virus Challenge. Journal of Virology. 2015;89(3):1825-37. [CrossRef]
- Sick F, Breithaupt A, Golender N, Bumbarov V, Beer M, Wernike K. Shuni virus-induced meningoencephalitis after experimental infection of cattle. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases. 2021;68(3):1531-40. [CrossRef]
- Yang D-K, Kim H-H, Nah J-J, Choi S-S, Seok K-O, Kim S-Y, et al. Evaluation of Akabane vaccine strains based on molecular characterization. Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2012;36(4):180-5. PubMed PMID: KJD:ART001754575.
- McPhee DA, Parsonson IM, Della Porta AJ, Jarrett RG. Teratogenicity of Australian Simbu serogroup and some other Bunyaviridae viruses: The embryonated chicken egg as a model. Infection and Immunity. 1984;43(1):413-20. [CrossRef]
- Kurogi H, Inaba Y, Akashi H, Takahashi E, Sato K, Satoda K, et al. Immune response of various animals to Akabane disease live virus vaccine. National Institute of Animal Health Quarterly. 1979;19(1-2):23-31. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC537650.
- Poskin A, Verite S, Comtet L, Van Der Stede Y, Cay B, De Regge N. Persistence of the protective immunity and kinetics of the isotype specific antibody response against the viral nucleocapsid protein after experimental Schmallenberg virus infection of sheep. Veterinary Research. 2015;46(1). [CrossRef]
- McClure S, McCullagh P, Parsonson IM, McPhee DA, Della-Porta AJ, Orsini A. Maturation of immunological reactivity in the fetal lamb infected with Akabane virus. Journal of Comparative Pathology. 1988;99(2):133-43. [CrossRef]
- Collins ÁB, Mee JF, Kirkland PD. Pathogenicity and teratogenicity of Schmallenberg virus and Akabane virus in experimentally infected chicken embryos. Veterinary Microbiology. 2018;216:31-7. [CrossRef]
- Parsonson IM, Della-Porta AJ, Snowdon WA. Developmental disorders of the fetus in some arthropod-borne virus infections. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 1981;30(3):660-73. [CrossRef]
- Kurogi H, Inaba Y, Takahashi E, Sato K, Satoda K, Goto Y, et al. Congenital abnormalities in newborn calves after inoculation of pregnant cows with Akabane virus. Infection and Immunity. 1977;17(2):338-43. [CrossRef]
- St George TD, Standfast HA, Cybinski DH. Isolations of Akabane virus from sentinel cattle and Culicoides brevitarsis. Australian Veterinary Journal. 1978;54(12):558-61. [CrossRef]
- Wernike K, Eschbaumer M, Breithaupt A, Hoffmann B, Beer M. Schmallenberg virus challenge models in cattle: infectious serum or culture-grown virus? Veterinary Research. 2012;43(1):84. [CrossRef]
- Wernike K, Holsteg M, Sasserath M, Beer M. Schmallenberg virus antibody development and decline in a naturally infected dairy cattle herd in Germany, 2011-2014. Veterinary Microbiology. 2015;181(3-4):294-7. Epub 2015/11/01. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernike K, Aebischer A, Sick F, Szillat KP, Beer M. Differentiation of Antibodies against Selected Simbu Serogroup Viruses by a Glycoprotein Gc-Based Triplex ELISA. Veterinary Sciences. 2021;8(1):12. PubMed PMID:. [CrossRef]
- Hoste ACR, Ruiz T, Fernández-Pacheco P, Jiménez-Clavero MÁ, Djadjovski I, Moreno S, et al. Development of a multiplex assay for antibody detection in serum against pathogens affecting ruminants. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases. 2021;68(3):1229-39. [CrossRef]
- Varol, K. Investigation of Schmallenberg virus seroprevalence in Honamli goats from Burdur region. Kocatepe Veterinary Journal. 2022;15(1):115-9. [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ruiz S, Risalde MA, Acevedo P, Arnal MC, Gómez-Guillamón F, Prieto P, et al. Serosurveillance of Schmallenberg virus in wild ruminants in Spain. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases. 2021;68(2):347-54. [CrossRef]
- Yang D-K, Hwang I-J, Kim B-H, Kweon C-H, Lee K-W, Kang M-I, et al. Serosurveillance of Viral Diseases in Korean Native Goats (Capra hircus). Journal of Veterinary Medical Science. 2008;70(9):977-9. [CrossRef]
- de Souza Nunes Martins M, Pituco EM, Taniwaki SA, Okuda LH, Richtzenhain LJ. Schmallenberg virus: research on viral circulation in Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. 2022;53(1):377-83. [CrossRef]
- St. George TD. A sentinel herd system for the study of arbovirus infections in Australia and Papua-New Guinea. Veterinary Science Communications. 1980;4(1):39-51. PubMed PMID: CABI:19800577999.
- Behar A, Friedgut O, Rotenberg D, Zalesky O, Izhaki O, Yulzary A, et al. Insights on Transmission, Spread, and Possible Endemization of Selected Arboviruses in Israel—Interim Results from Five-Year Surveillance. Veterinary Sciences. 2022;9(2). [CrossRef]
- Shin YK, Oem JK, Yoon S, Hyun BH, Cho IS, Yoon SS, et al. Monitoring of five bovine arboviral diseases transmitted by arthropod vectors in Korea. Journal of Bacteriology and Virology. 2009;39(4):353-62. [CrossRef]
- Abu Elzein EME, Al-Afaleq AI, Mellor PS, El-Bashir AM, Hassanein MM. Study of Akabane infection in Saudi Arabia by the use of sentinel ruminants. Journal of Comparative Pathology. 1998;119(4):473-8. [CrossRef]
- Jesse FFA, Paul BT, Hashi HA, Chung ELT, Sedek NIHBM, Lila MAM. Schmallenberg Virus (SBV) Infection Among Small Ruminants in Selected States of Peninsular Malaysia. Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research. 2022;12(1):62-7.
- Waddell L, Pachal N, Mascarenhas M, Greig J, Harding S, Young I, et al. Cache Valley virus: A scoping review of the global evidence. Zoonoses Public Health. 2019;66(7):739-58. Epub 2019/06/30. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama S, Maruyama F, Tanaka Y, Itoh H, Uematsu N. Experimental infection of pigs with Akabane virus. Uirusu Journal of Virology. 1983;33(2):131-3. [CrossRef]
- Zimmer J-Y, Saegerman C, Martinelle L, Losson B, Leroy P, Haubruge E, et al. Pig farms: reservoirs of vectors of Bluetongue and Schmallenberg viruses? Biotechnologie Agronomie Societe Et Environnement. 2014;18(4):480-7. PubMed PMID: WOS:000346244100002.
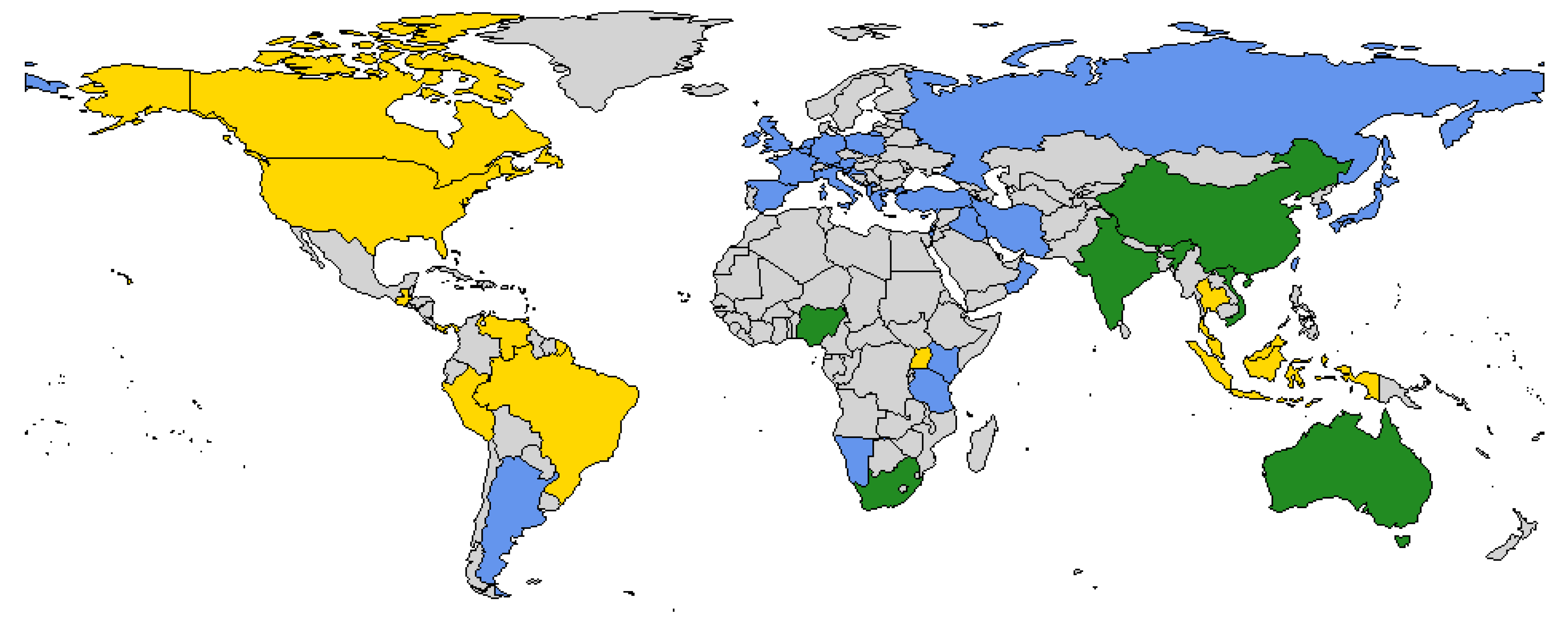
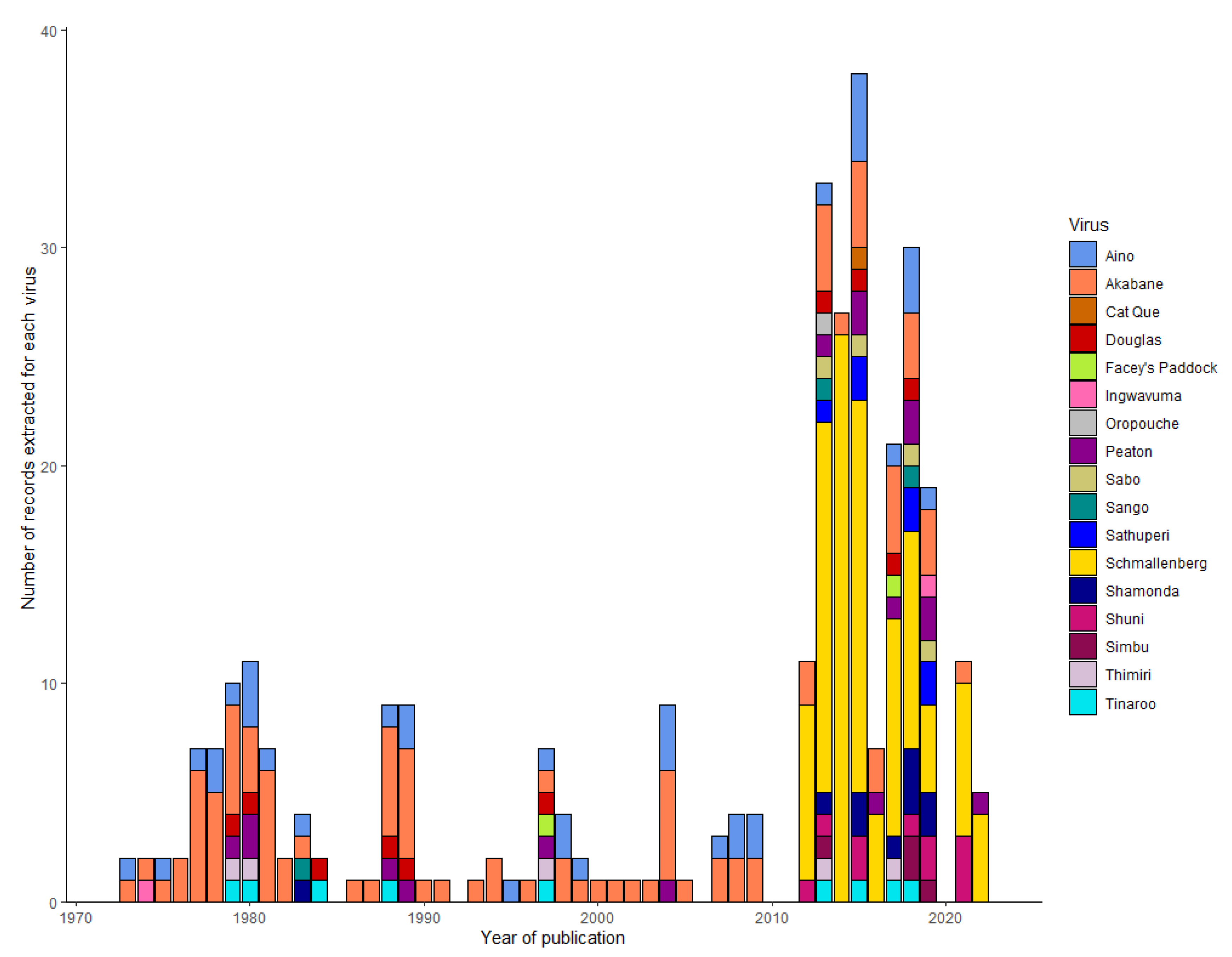
| Clade | Virus species | Virus names | Animal Health | Diagnostic Tests | Distribution | Total records by virus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of records | Species | Key disease syndrome | No. of records | Highest level of WOAH validation | Validated assay types | No. of records | Mean seroprevalence | 95% CI | ||||
| A | Orthobunyavirus buttonwillowense | Buttonwillow virus | ||||||||||
| A | Orthobunyavirus catqueense | Cat Que virus | 1 | 60 | 50-70 | 1 | ||||||
| Oya virus | ||||||||||||
| A | Orthobunyavirus faceyense | Facey's paddock virus | 1 | No validation | 1 | - | - | 2 | ||||
| A | Orthobunyavirus ingwavumaense | Ingwavuma virus | 1 | Porcine | No disease | 1 | Stage 1 | PCR | 2 | |||
| A | Orthobunyavirus jatobalense | Jatobal virus | ||||||||||
| A | Orthobunyavirus manzanillaense | Manzanilla virus | ||||||||||
| Inini virus | ||||||||||||
| A | Orthobunyavirus mermetense | Mermet virus | ||||||||||
| A | Orthobunyavirus oropoucheense | Oropouche virus | 1 | Stage 1 | PCR | 1 | ||||||
| Iquitos virus | ||||||||||||
| Madre de Dios virus | ||||||||||||
| Perdoes virus | ||||||||||||
| Pintupo virus | ||||||||||||
| A | Orthobunyavirus thimiriense | Thimiri virus | 2 | Stage 1 | PCR | 3 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |||
| A | Orthobunyavirus utingaense | Utinga virus | ||||||||||
| Utive virus | ||||||||||||
| N/A | Orthobunyavirus oyoense | Oyo virus | ||||||||||
| B | Orthobunyavirus ainoense | Aino virus | 8 | Bovine | Congenital malformations, Neurological syndrome, Reproductive disease |
8 | Stage 1 | ELISA, PCR | 21 | 27.9 | 20.4-35.5 | 37 |
| B | Orthobunyavirus akabaneense | Akabane virus | 43 | Bovine, Ovine, Caprine Porcine |
Congenital malformations, Neurological syndrome, Reproductive disease No disease |
20 | Stage 2 | ELISA, PCR | 32 | 23.5 | 14.6-32.4 | 95 |
| Tinaroo virus | 1 | Bovine | No disease | 3 | Stage 1 | PCR | 5 | 24.6 | 20.9-28.3 | 9 | ||
| Yaba-7 virus | ||||||||||||
| B |
Orthobunyavirus schmallenbergense | Schmallenberg virus | 36 | Bovine, Ovine, Caprine Porcine |
Reproductive disease, Congenital malformations, Non-specific & Gastrointestinal No disease |
21 | Stage 2 | ELISA, PCR, VNT, LAMP, RPA, IFA | 51 | 34.9 | 27.0-42.8 | 108 |
| Shamonda virus | 2 | Bovine, Ovine, Caprine | Congenital malformations | 4 | Stage 1 | PCR | 4 | 34.1 | 3.1-65.1 | 10 | ||
| Douglas virus | 2 | Bovine | No disease | 3 | Stage 1 | PCR | 5 | 14.0 | 8.8-19.3 | 10 | ||
| Sathuperi virus | 4 | 3 | 34.9 | 8.2-61.5 | 7 | |||||||
| B | Orthobunyavirus peachesterense | Peaton virus | 3 | Bovine | Congenital malformations, Reproductive disease |
5 | Stage 1 | PCR | 9 | 21.6 | 15.7-27.5 | 17 |
| B | Orthobunyavirus saboense | Sabo virus | 3 | Stage 1 | PCR | 1 | 6.6 | 0-13.9 | 4 | |||
| B | Orthobunyavirus saboense | Sango virus | 1 | Ovine, Caprine | No disease | 2 | Stage 1 | PCR | 3 | |||
| B | Orthobunyavirus shuniense | Shuni virus | 6 | Bovine, Equine | Neurological, Congenital malformations, Reproductive |
4 | Stage 2 | ELISA, PCR | 10 | |||
| Kaikalur virus | ||||||||||||
| B | Orthobunyavirus simbuense | Simbu virus | 3 | Stage 1 | PCR | 1 | 9.5 | 1.9-17.1 | 4 | |||
| Para virus | ||||||||||||
| Gestational age at infection (days) | Species | ||
|
Bovine Endometrium attachment: 35 days Foetal immunocompetence: ≥120-150days Full term: 279–292days |
Ovine Endometrium attachment: 21 days Foetal immunocompetence: ≥64-87days Full term: 144-151days |
Caprine Endometrium attachment: 19 days Foetal immunocompetence: ≥40days Full term: 145-155 days |
|
| 0-28 | Embryonic death (day 28) | ||
| 29-59 |
At gestational age 30-36 days: Arthrogryposis Brachygnathism Brain agenesis or hydranencephaly Lung hypoplasia Microencephaly Muscle neuronal atrophy and degeneration Porencephaly Scoliosis Spinal cord agenesis or hypoplasia |
Foetal death (day 42) | |
| 60-90 | Hydranencephaly Porencephaly Myositis of skeletal muscles |
||
| 91-120 | Arthrogryposis Hydranencephaly Porencephaly Stillborn |
||
| 121-150 | Arthrogryposis | ||
| 151-180 | Arthrogryposis Stillborn |
||
| 181-210 | |||
| 211-240 | Degenerative encephalopathy | ||
| 241-270 | Clinical encephalopathy Stillborn |
||
| References | [23,24,25,26,27,28] | [29,30,31,32] | [33,34] |
| Akabane virus | Schmallenberg virus | Shuni virus | Aino virus | Shamonda virus | Peaton virus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cases | 1675 | 553 | 48 | 17 | 15 | 2 |
| Clinical signs |
Congenital malformations: Unable to suckle, 140 Arthrogryposis, 118 Blind, 109 Scoliosis/ Vertebral deformities, 51 Brachgnathia inferior/ prognathism, 45 Torticollis, 37 Skeletal muscle atrophy, 19 Lameness, 13 Leg extension, 11 Weak, 9 Deaf, 7 Cleft palate, 3 Dwarf, 2 Cryptorchid, 1 Neurological Astasia/Dysstasia, 90 Dull, 47 Recumbency, 31 Convulsions/tremors, 24 Circling, 15 Nystagmus, 15 Hypersensitivity, 14 Collison with barrier, 9 Paralysis. 8 Pupillary contraction, 4 Altered consciousness, 2 Reproductive: Abortion, 76 Dystocia, 33 Perinatal mortality, 4 Mummified/autolyzed foetus, 2 Stillborn, 2 Non-specific: Tachypnoea,47 Pyreixa,46 Ataxia, 44 Tachycardia, 42 Salivation, 25 Reduced appetite, 13 Hypothermia, 4 Jaundice, 1 Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, 3 |
Non-specific: Temporary decrease in milk yield, 350 Pyrexia, 227 Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, 323 Congenital malformations: Arthrogryposis, 109 Scoliosis/ Vertebral deformities, 82 Brachgnathia inferior/ prognathism, 63 Torticollis, 46 Skeletal muscle atrophy, 1 Blind, 1 Cleft palate, 1 Neurological (only in animals surviving in-utero infection): Dull, 1 Proprioception deficits, 1, Strabismus, 1 Reproductive: Abortion, 50 Mummified/autolyzed foetus, 16 Perinatal mortality, 10 Stillborn, 2 |
Non-specific: Found dead, 12 Pyrexia, 9 Reduced appetite, 5 Anemia, 2 Leukopenia, 2 Neurological: Ataxia, 10 Recumbency, 7 Paralysis, 5 Convulsions/tremors, 2 Hypersensitivity, 1 Circling, 1 Weak, 1 Reproductive: Abortion, 3 Congenital malformations: Arthrogryposis, 1 Torticollis, 1 |
Congenital malformations: Arthrogryposis, 13 Torticollis, 1 Leg extension, 7 Neurological (only in animals surviving in-utero infection): Ataxia, 8 Astasia/Dysstasia, 8 Recumbency, 7 Hypersensitivity, 7 Circling, 7 Nystagmus, 1 Non-specific: Pyrexia, 7 Reduced appetite, 7 Reproductive Mummified/autolyzed foetus, 7 Stillborn, 4 Abortion, 1 |
Congenital malformations: Arthrogryposis, 12 Scoliosis/ Vertebral deformities, 11 Torticollis, 10 |
Congenital malformations: Arthrogryposis, 1 Scoliosis/ Vertebral deformities, 1 Blind, 1 Reproductive: Stillborn, 1 |
| Necropsy findings |
Congenital malformations: Micro-/hydranencephaly, 190 Hydrocephalus/ porencephaly, 90 Hypoplasia of the cerebellum, 56 Hypoplasia of the spinal cord, 55 Vestigial lungs/pulmonary hypoplasia, 25 Hypoplasia of the cerebrum, 3 |
Congenital malformations: Hypoplasia of the cerebellum, 86 Hypoplasia of the spinal cord, 67 Hydrocephalus/ porencephaly, 45 Micro-/hydranencephaly, 41 Hypoplasia of the cerebrum, 12 Cardiac ventricular septal defect, 3 Vestigial lungs/pulmonary hypoplasia, 1 Colonic atresia, 1 Ectopic cordis, 1 Unilateral hydronephrosis, 1 |
No reports |
Congenital malformations: Micro-/hydranencephaly, 6 Hypoplasia of the cerebellum, 3 |
Congenital malformations: Micro-/hydranencephaly, 2 Hypoplasia of the cerebrum, 1 |
Congenital malformations: Hydrocephalus/ porencephaly, 2 Hypoplasia of the cerebellum, 1 |
| ELISA | Format | Target (virus) | Sample | Sample status and size | Positive agreement (%) | Negative agreement (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID-Screen Akabane ELISA (Innovative Diagnostics, Grabels, France) |
Competition | Whole virus (Akabane virus) | Serum | Positive (n = 378) Negative (n=334) |
96.0-98.9 | 99.7 | [71] |
| Serum | Positive (n = 153) Negative (n = 537) |
93.5 | 82.3 | [72] | |||
| Akabane ELISA kit (Chisso Corp, Yokohama) |
Competition | Gc glycoprotein (Akabane virus) | Serum | Positive (n = 378) Negative (n=334) |
78.0 | 100 | [71] |
| ID-Screen Schmallenberg virus Multi-species ELISA (Innovative Diagnostics, Grabels, France) | Competition | Nucleoprotein (Schmallenberg virus) | Serum | Positive (n = 45) Negative (n = 45) |
96-100 | 100 | [73] |
| ID-Screen Schmallenberg virus Indirect Multi-species ELISA (Innovative Diagnostics, Grabels, France) |
Indirect | Nucleoprotein (Schmallenberg virus) | Serum | Positive (n = 180) Negative (n = 1364) |
97.2 | 99.8 | [74] |
| IDEXX Schmallenberg virus Antibody Test Kit (IDEXX, Hoofddorp, Netherlands) |
Indirect | Nucleoprotein (Schmallenberg virus) | Serum | Positive (n = 45) Negative (n = 45) |
78-93 | 93-98 | [73] |
| Serum | Positive (n = 153) Negative (n = 537) |
80.4 | 93.5 | [72] | |||
| Svanovir Schmallenberg antibody ELISA (Svanova, Uppsala, Sweden) |
Indirect | Whole virus (Schmallenberg virus) |
Serum Bulk milk |
Positive (n = 82) Negative (n = 6) Positive (n = 82) Negative ( n = 6) |
94 98 |
50 100 |
[75] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





