Submitted:
09 January 2024
Posted:
09 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and reagents
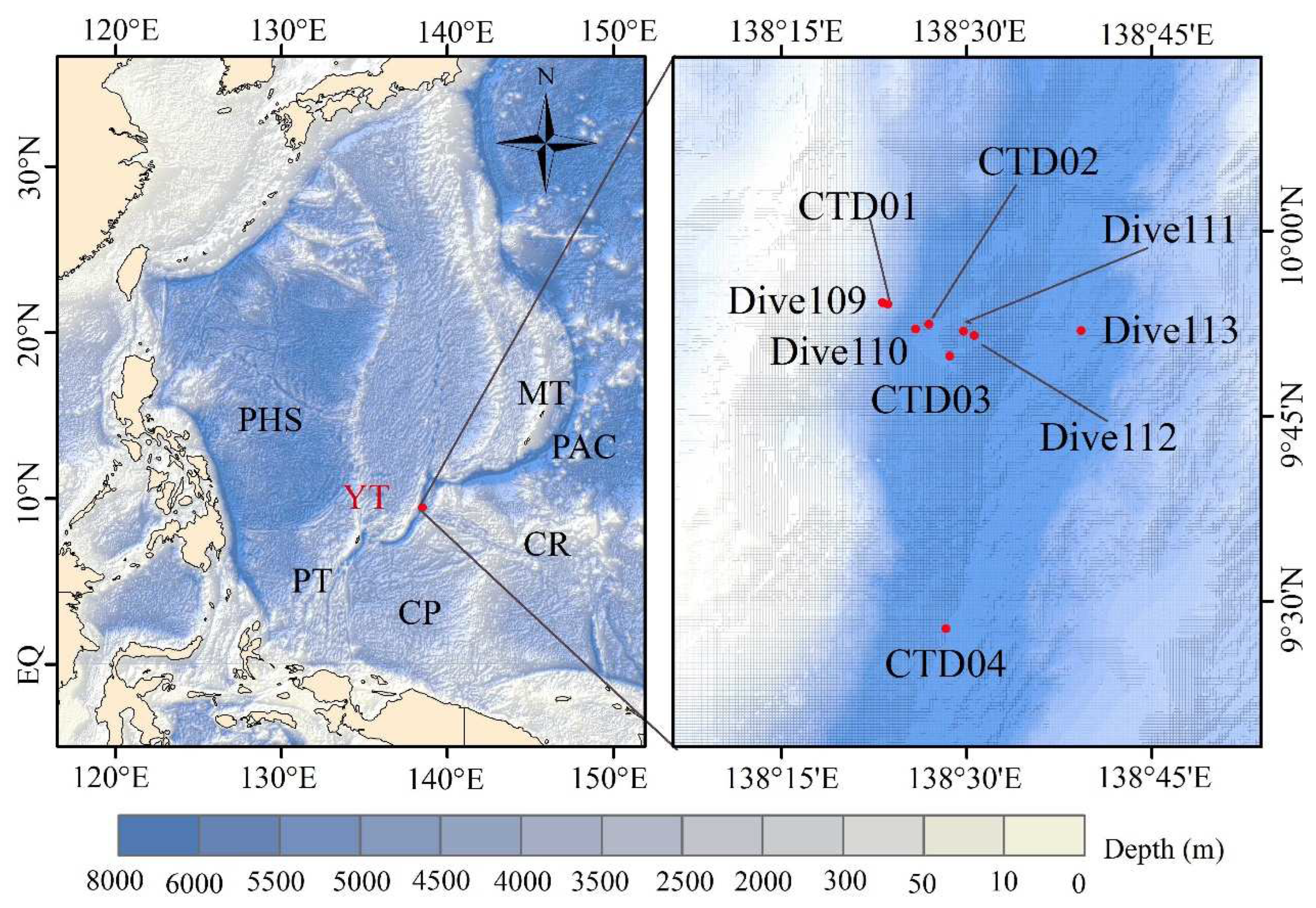
2.2. Sampling stations
2.3. Pretreatment and analysis of seawater samples
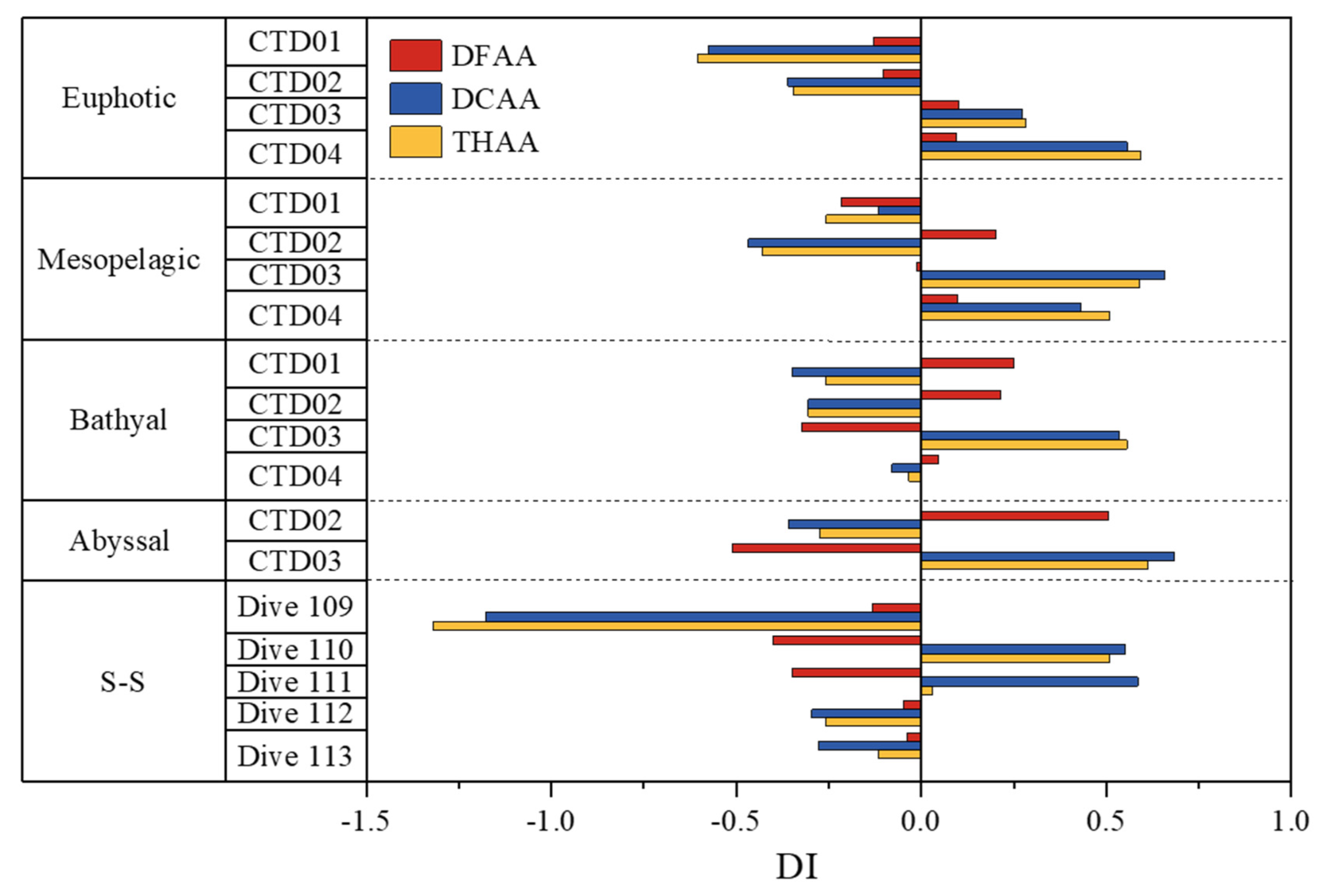
2.4. Diagenetic indicator
2.5. Quality assurance and control
2.6. Statistical analysis
3. Results and discussion
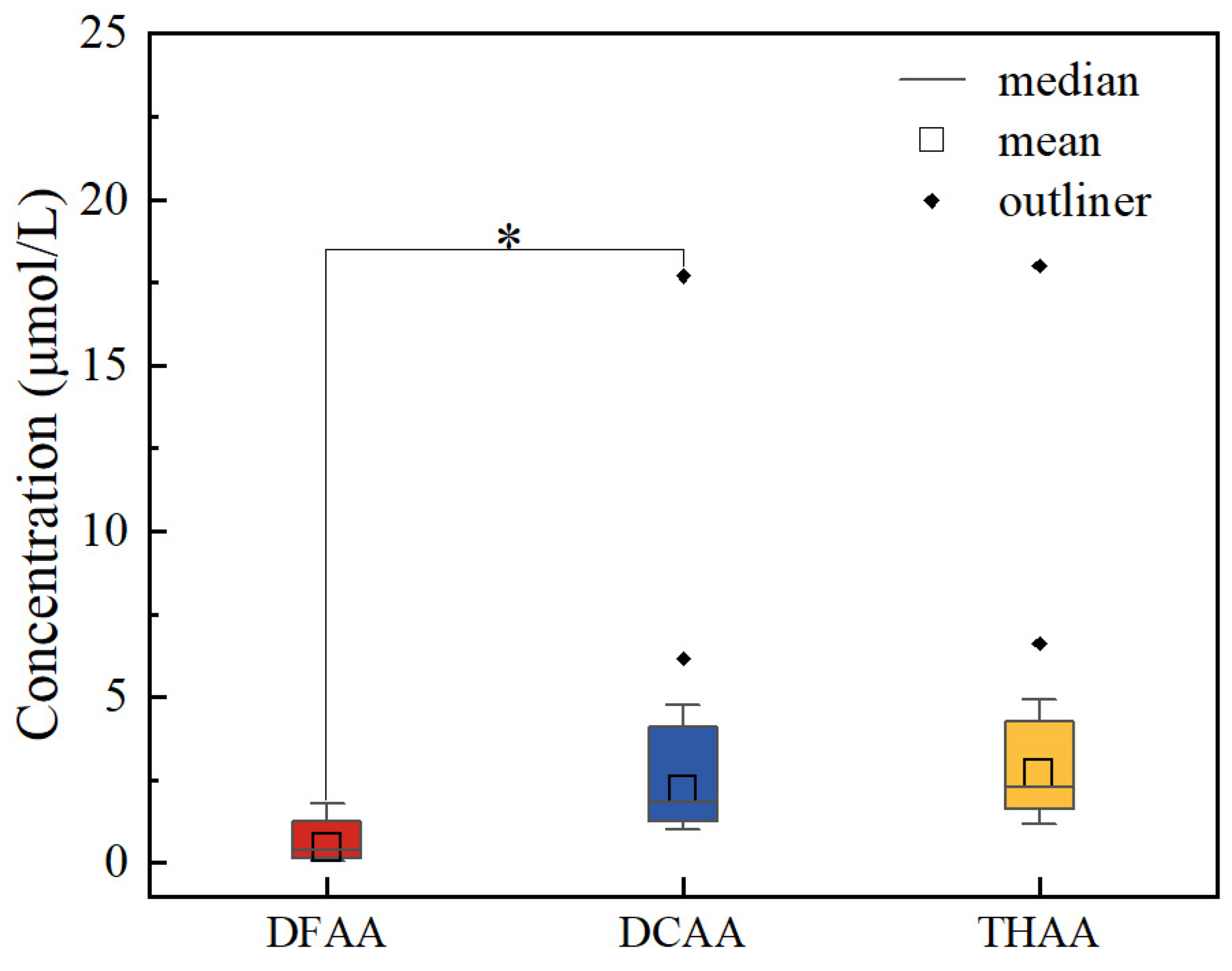
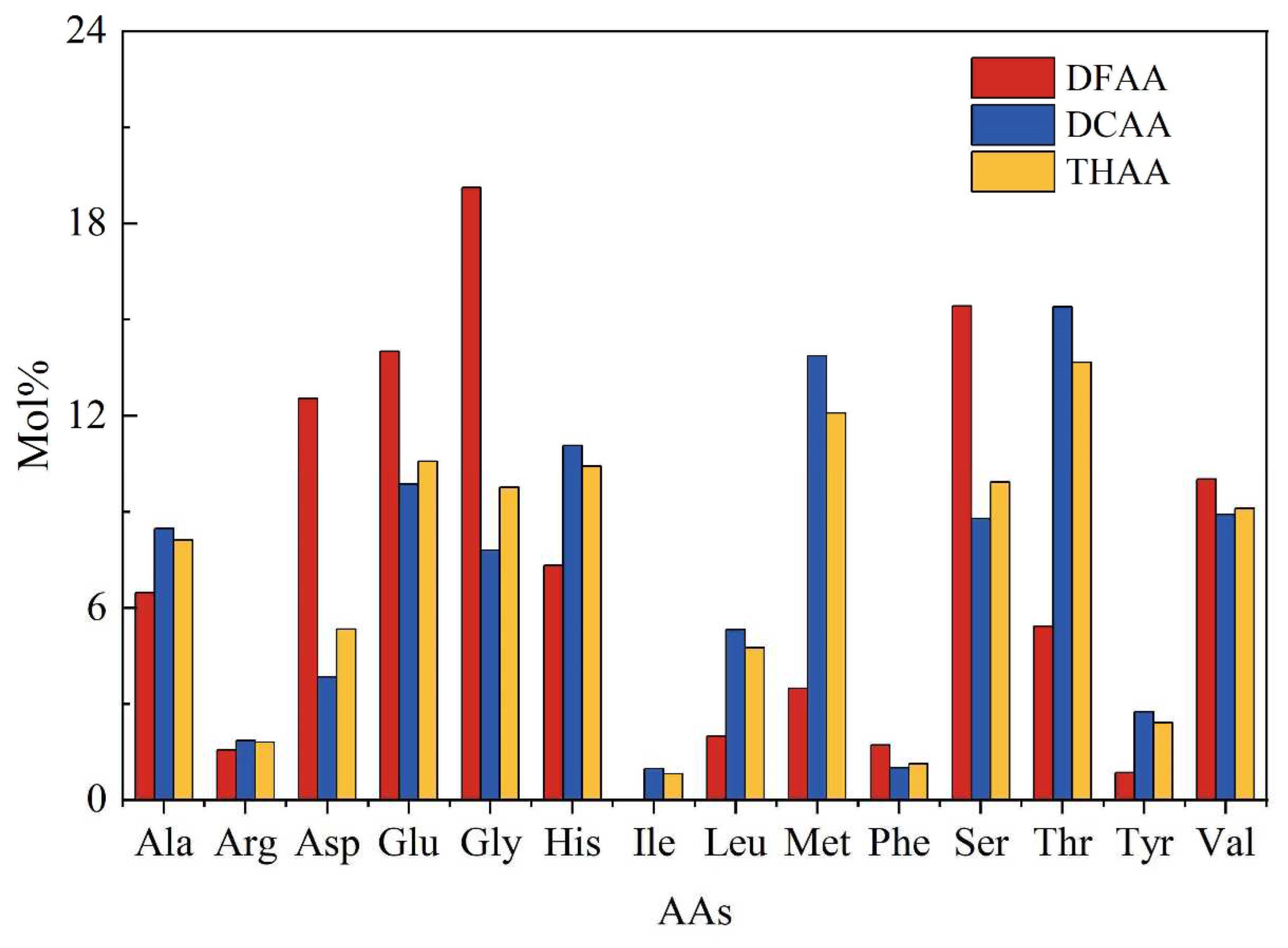
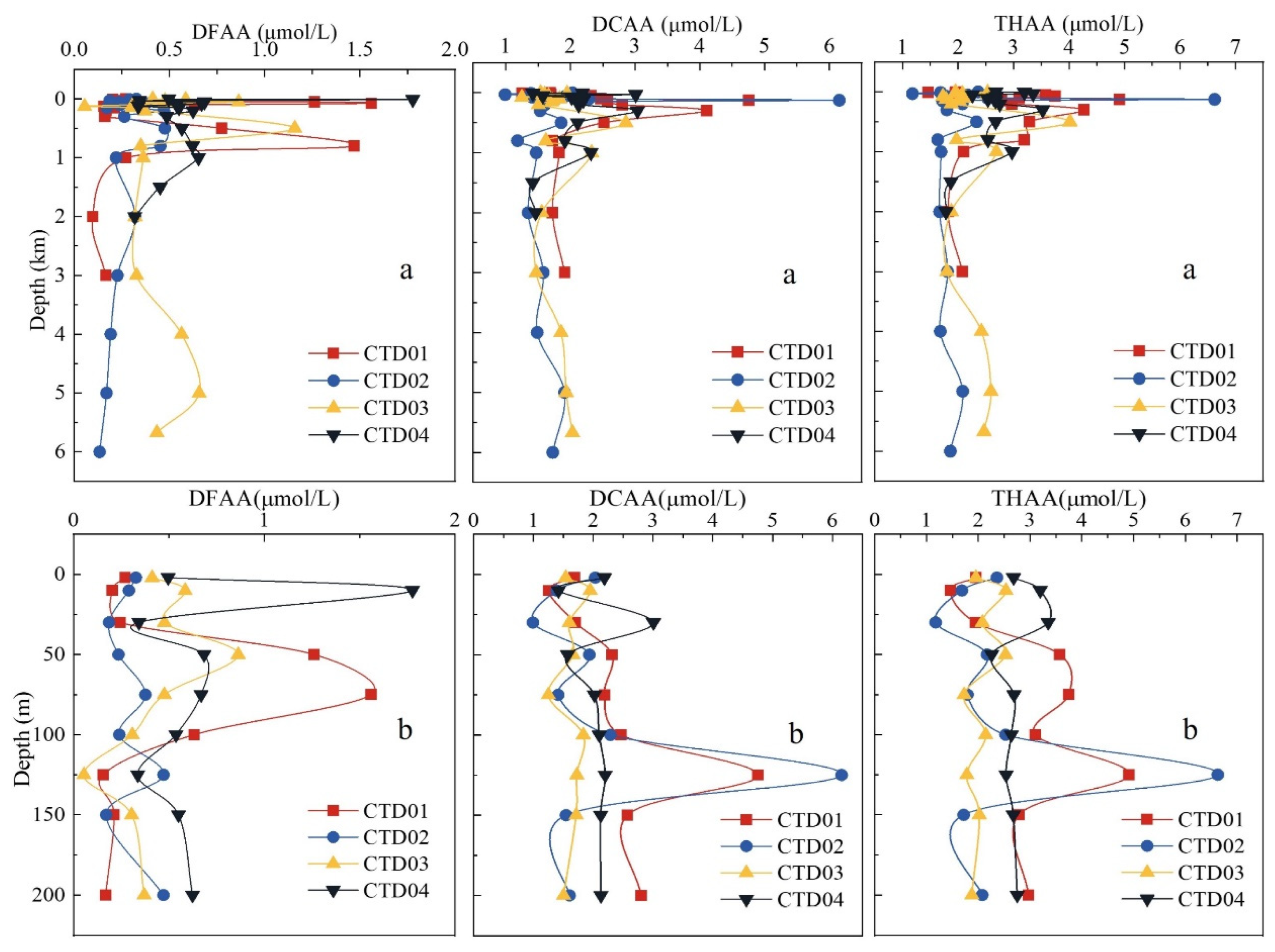
3.1. Compositions and concentrations of amino acids
3.2. Vertical variations of amino acids
3.2.1. Amino acids in euphotic layer
3.2.2. Amino acids in the mesopelagic to abyssal layer
3.2.3. Amino acids in the sediment-seawater interface
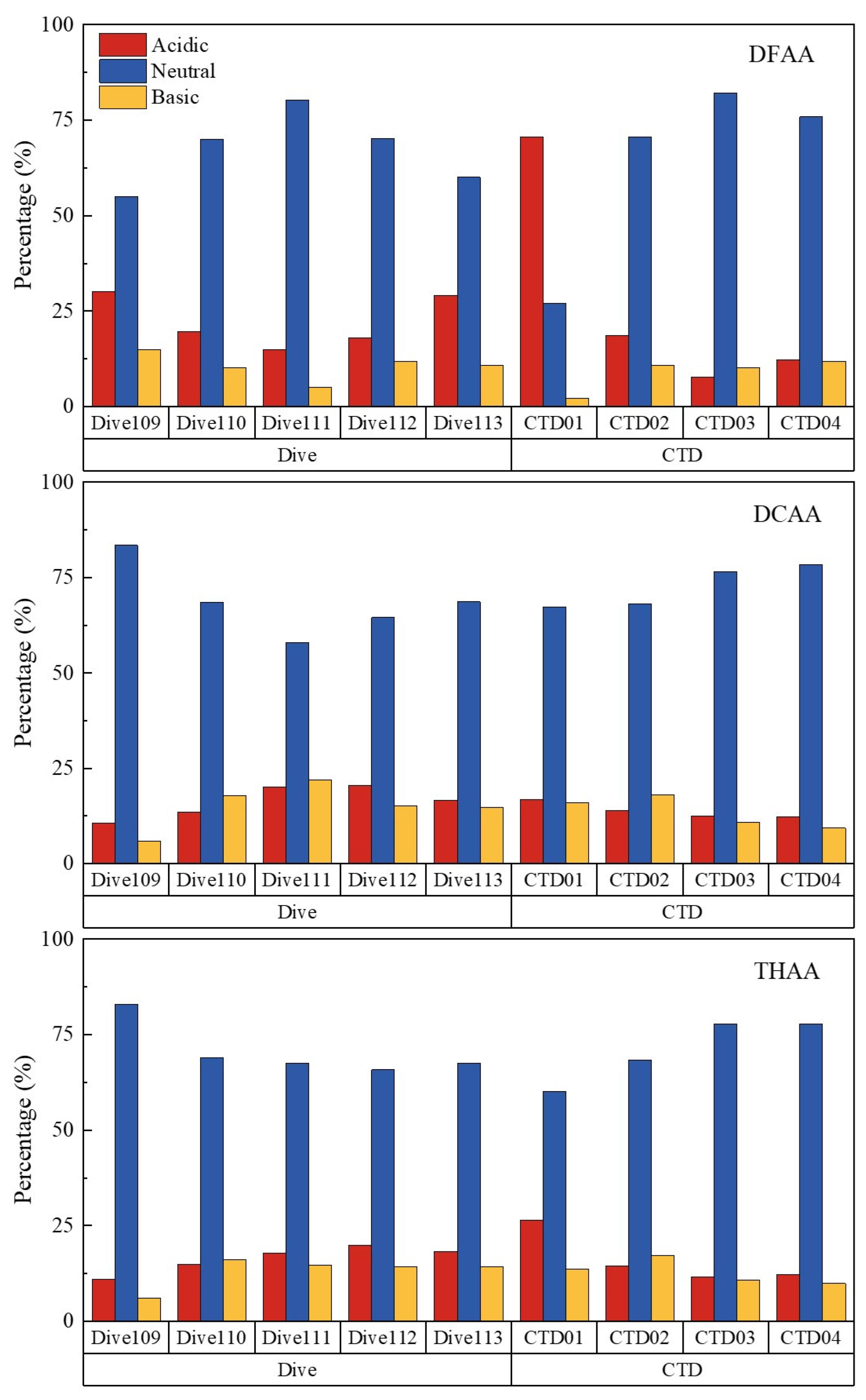
3.3. Sources and degradation of amino acids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgements
References
- Yang, G.P.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X.C. Distribution of Dissolved Free Amino Acids, Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen and Chlorophyll a in the Surface Microlayer and Subsurface Water of the Yellow Sea, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1737–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Yang, G.P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Dissolved Amino Acids in the Surface Microlayer and Subsurface Water of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2021, 219, 103543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Leng, W.; Ji, C. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Particulate and Dissolved Amino Acids in the East China Sea. Mar. Chem. 2016, 186, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, T.S.; Grace, B.L.; Carman, K.R.; Maulana, I. Amino Acid Cycling in the Mississippi River Plume and Effects from the Passage of Hurricanes Isadore and Lili. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 136, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Shi, D.; Ji, C.X.; Chen, R.; Gao, X.C.; Yang, G.P. Distribution and Bioavailability of Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter in Different Water Masses of the Southern Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2021, 222, 103596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.E.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, S.B.; Zhang, H.H.; Yang, G.P. Amino Acids and Amino Sugars as Indicators of the Source and Degradation State of Sedimentary Organic Matter. Mar. Chem. 2021, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, G.P.; Liu, L.; Zhang, P.Y.; Leng, W.S. Sources, Behaviors and Degradation of Dissolved Organic Matter in the East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 155, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niggemann, J.; Schubert, C.J. Sources and Fate of Amino Sugars in Coastal Peruvian Sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyuruk, H.; Kontas, A. Dissolved Free, Total and Particulate Enantiomeric Amino Acid Levels in Eutrophic and Oligotrophic Parts of a Semi-Enclosed Bay (İzmir, Aegean Sea). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Yang, G.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Pang, B. Distribution and Composition of Dissolved Amino Acids in Surface Water of Northern South China Sea. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2011, 30, 774–779. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Fichot, C.G.; Liang, S.K.; Benner, R. Biological Hot Spots and the Accumulation of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter in a Highly Productive Ocean Margin. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrichs, S.M.; Farrington, J.W.; Lee, C. Peru Upwelling Region Sediments near 15°S. 2. Dissolved Free and Total Hydrolyzable Amino Acids. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1984, 29, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landén, A.; Hall, P.O.J. Benthic Fluxes and Pore Water Distributions of Dissolved Free Amino Acids in the Open Skagerrak. Mar. Chem. 2000, 71, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Sun, C.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Jiang, F.; Cao, W.; Chen, Y.; Ding, H.; Huang, Y.; Gao, X. Vertical Variations and Composition of Dissolved Free Amino Acid in the Seawater of the Yap Trench in the Western Pacific Ocean. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, G.P.; Ji, C.X.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, P.Y. Sources and Degradation of Sedimentary Organic Matter in the Mud Belt of the East China Sea: Implications from the Enantiomers of Amino Acids. Org. Geochem. 2018, 116, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.P.; Kawahata, H. Amino Acids and Hexosamines in the Hess Rise Core during the Past 220,000 Years. Quat. Res. 2003, 60, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, R.B. Bacterial Uptake of Dissolved Free and Combined Amino Acids in Estuarine Waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1989, 34, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, B.; Simon, M. Use of Dissolved Combined and Free Amino Acids by Planktonic Bacteria in Lake Constance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, G.; Shen, Y.; Benner, R. Strong Linkages between Surface and Deep-Water Dissolved Organic Matter in the East/Japan Sea. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2561–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.E.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yang, J.Q.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.H.; Yang, G.P. Variability and Composition of Amino Acids and Amino Sugars in Sediment Cores of the Changjiang Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2022, 163, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Yao, P.; Liu, C.; Sun, C.; Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Han, Z.; Hu, J. Spatial Heterogeneity of Organic Carbon Cycling in Sediments of the Northern Yap Trench: Implications for Organic Carbon Burial. Mar. Chem. 2020, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Sun, C. Towards the Understanding from Sea Surface to Hadal Zone—A Multidisciplinary Study of the Yap Trench. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, G. Geochemical and Chronological Evidence for Collision of Proto-Yap Arc/Caroline Plateau and Rejuvenated Plate Subduction at Yap Trench. Lithos 2020, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M. Deformation from the Convergence of Oceanic Lithosphere into Yap Trench and Its Implications for Early-Stage Subduction. J. Geodyn. 2004, 37, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wu, C.; Han, P.; Liu, Z.; Liang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, G.; He, X.; Pang, J.; et al. The Microbiome and Its Association with Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Hadal Biosphere at the Yap Trench. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, X.; Cao, W.; Sun, C.; Lu, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, B.; Yang, J. Watermass Properties and Deep Currents in the Northern Yap Trench Observed by the Submersible Jiaolong System. Deep. Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2018, 139, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Cai, M.; Luo, Z.; Li, M. Metagenomics Reveals Microbial Diversity and Metabolic Potentials of Seawater and Surface Sediment from a Hadal Biosphere at the Yap Trench. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, E.I. A Manual of Chemical & Btologwal Methods for 5eawater Analysts T R Parsons, Y Malta & C M Lalll Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1984 184 Pp, 7 Illustrations and 120 Literature References Hard-Backed £1225 ISBN 0 08 030288 2 Soft-Backed £5 50 ISBN 0 08 030287 4. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1984, 15, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.; Sabine, C.; Christian, J. Guide to Best Practices for Ocean C02 Measurments; 2007; Vol. 3; ISBN 1897176074.
- Lindroth, P.; Mopper, K. High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Subpicomole Amounts of Amino Acids by Precolumn Fluorescence Derivatization with O-Phthaldialdehyde. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwe, B.; Middelburg, J.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Heip, C.H.R. Linking Diagenetic Alteration of Amino Acids and Bulk Organic Matter Reactivity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Bada, J.L. Amino Acids in Equatorial Pacific Ocean Water. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1975, 26, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelboe, M.; Borch, N.H.; Kirchman, D.L. Bacterial Utilization of Dissolved Free Amino Acids, Dissolved Combined Amino Acids and Ammonium in the Delaware Bay Estuary: Effects of Carbon and Nitrogen Limitation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 128, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, E.; Skoog, A.; Amend, J.P. Concentration and Distribution of Dissolved Amino Acids in a Shallow Hydrothermal System, Vulcano Island (Italy). Org. Geochem. 2004, 35, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.X.; Yang, G.P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.Y. Distribution, Degradation and Bioavailability of Dissolved Organic Matter in the East China Sea. Biogeochemistry 2019, 142, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zou, L.; Clevinger, C.; Liu, Q.; Hollibaugh, J.T.; Mou, X. Temporal Dynamics and Depth Variations of Dissolved Free Amino Acids and Polyamines in Coastal Seawater Determined by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Mar. Chem. 2014, 163, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogren, W.L.; Chollet, R. Photorespiration; 1982; ISBN 0122943023.
- Webb, L.; Johannes, R.E. Studies of the Release of Dissolved Free Amino Acids by Marine Zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1967, 12, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, G.L.; Hedges, J.I. Digestion and Alteration of the Biochemical Constituents of a Diatom (Thalassiosira Weissflogii) Ingested by an Herbivorous Zooplankton (Calanus Pacificus). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, R.T.; Harvey, H.R. Protein and Amino Acid Cycling during Phytoplankton Decomposition in Oxic and Anoxic Waters. Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, T.; Fitznar, H.P.; Kattner, G. Origin and Biogeochemical Cycling of Organic Nitrogen in the Eastern Arctic Ocean as Evident from D- and L-Amino Acids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 4103–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, G.P.; Wu, G.W.; Gao, X.C.; Xia, Q.Y. Concentration and Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter in the Surface Microlayer and Subsurface Water of the Bohai Sea, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 52, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecky, R.E.; Mopper, K.; Kilham, P.; Degens, E.T. The Amino Acid and Sugar Composition of Diatom Cell-Walls. Mar. Biol. 1973, 19, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, G.P.; Xia, Q.Y.; Wu, G.W. Enrichment and Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter in the Surface Microlayer and Subsurface Water of the South Yellow Sea. Mar. Chem. 2016, 182, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedyan, M.A.; Preston, M.R. The Coupling of Surface Seawater Organic Nitrogen and the Marine Aerosol as Inferred from Enantiomer-Specific Amino Acid Analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8698–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingalls, A.E.; Lee, C.; Wakeham, S.G.; Hedges, J.I. The Role of Biominerals in the Sinking Flux and Preservation of Amino Acids in the Southern Ocean along 170°W. Deep. Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 713–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.P. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Particulate and Dissolved Amino Acids in the East China Sea. Mar. Chem. 2015, 46, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Benner, R. Organic Matter Transformations in the Upper Mesopelagic Zone of the North Pacific: Chemical Composition and Linkages to Microbial Community Structure. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, G.L.; Hedges, J.I. Sources and Reactivities of Amino Acids in a Coastal Marine Environment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 703–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meon, B.; Kirchman, D.L. Dynamics and Molecular Composition of Dissolved Organic Material during Experimental Phytoplankton Blooms. Mar. Chem. 2001, 75, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabadel, A.J.M.; Browning, T.J.; Kruimer, D.; Airs, R.L.; Woodward, E.M.S.; Van Hale, R.; Frew, R.D. Determination of Picomolar Dissolved Free Amino Acids along a South Atlantic Transect Using Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Mar. Chem. 2017, 196, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wakeham, S.G.; I. Hedges, J. Composition and Flux of Particulate Amino Acids and Chloropigments in Equatorial Pacific Seawater and Sediments; 2000; Vol. 47; ISBN 0015166328820. 0015.
- Lee, C.; Bada, J.L. Dissolved Amino Acids in the Equatorial Pacific, the Sargasso Sea, and Biscayne Bay. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrends, B.; Liebezeit, G. Particulate Amino Acids in Wadden Sea Waters — Seasonal and Tidal Variations. J. Sea Res. 1999, 41, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrin, R.; Imazawa, M.; Fukuda, H.; Suzuki, Y. Full-Depth Profiles of Prokaryotes, Heterotrophic Nanoflagellates, and Ciliates along a Transect from the Equatorial to the Subarctic Central Pacific Ocean. Deep. Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veuger, B.; Middelburg, J.J.; Boschker, H.T.S.; Nieuwenhuize, J.; Van Rijswijk, P.; Rochelle-Newall, E.J.; Navarro, N. Microbial Uptake of Dissolved Organic and Inorganic Nitrogen in Randers Fjord. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnewitsch, R.; Falahat, S.; Stehlikova, J.; Oguri, K.; Glud, R.N.; Middelboe, M.; Kitazato, H.; Wenzhöfer, F.; Ando, K.; Fujio, S.; et al. Recent Sediment Dynamics in Hadal Trenches: Evidence for the Influence of Higher-Frequency (Tidal, near-Inertial) Fluid Dynamics. Deep. Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2014, 90, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; Gao, J.; Tian, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y. Geology of the Yap Trench: New Observations from a Transect near 10°N from Manned Submersible Jiaolong. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, I.; Takatsuki, Y.; Kamiya, H.; Kawae, S. Water Property and Current Distributions along the WHP-P9 Section (137°-142°E) in the Western North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 12959–12984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiri, H.L.; McCarthy, M.D. Compound Specific Δ15N Analysis of Amino Acids Reveals Unique Sources and Differential Cycling of High and Low Molecular Weight Marine Dissolved Organic Nitrogen. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 344, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glud, R.N.; Wenzhöfer, F.; Middelboe, M.; Oguri, K.; Turnewitsch, R.; Canfield, D.E.; Kitazato, H. High Rates of Microbial Carbon Turnover in Sediments in the Deepest Oceanic Trench on Earth. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, A.; Grémare, A.; Escoubeyrou, K.; Amouroux, J.M.; Fiordelmondo, C.; Danovaro, R. Impact of Natural (Storm) and Anthropogenic (Trawling) Sediment Resuspension on Particulate Organic Matter in Coastal Environments. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 2506–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappin, A.D.; Millward, G.E.; Fitzsimons, M.F. Distributions, Cycling and Recovery of Amino Acids in Estuarine Waters and Sediments. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2007, 5, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejjar, S.; Melanson, A.; Tremblay, L. Pore Waters as a Contributor to Deep-Water Amino Acids and to Deep-Water Dissolved Organic Matter Concentration and Composition in Estuarine and Marine Waters. Mar. Chem. 2021, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macko, S.A.; Estep, M.L.F. Microbial Alteration of Stable Nitrogen and Carbon Isotopic Compositions of Organic Matter. Org. Geochem. 1984, 6, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Cronin, C. Particulate Amino Acids in the Sea: Effects of Primary Productivity and Biological Decomposition. J. Mar. Res. 1984, 42, 1075–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwe, B.; Middelburg, J.J. Amino Acids and Hexosamines as Indicators of Organic Matter Degradation State in North Sea Sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 782–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medernach, L.; Grémare, A.; Amoureux, J.M.; Colomines, J.C.; Vétion, G. Temporal Changes in the Amino Acid Contents of Particulate Organic Matter Sedimenting in the Bay of Banyuls-Sur-Mer (Northwestern Mediterranean). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 214, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, J.C.; Silverberg, N.; Gearing, J.N. Amino Acid Biogeochemistry in the Laurentian Trough: Vertical Fluxes and Individual Reactivity during Early Diagenesis. Org. Geochem. 1998, 29, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobel, K.D.; West, J.K.; Hench, L.L. Computational Model for Protein-Mediated Biomineralization of the Diatom Frustule. Mar. Biol. 1996, 126, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, M.; Voigt, K.; Schuster, S. The Tip and Hidden Part of the Iceberg: Proteinogenic and Non-Proteinogenic Aliphatic Amino Acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 3258–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, T.M.; Nunes Nesi, A.; Araújo, W.L.; Braun, H.P. Amino Acid Catabolism in Plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinthaler, T.; Sintes, E.; Herndl, G.J. Dissolved Organic Matter and Bacterial Production and Respiration in the Sea-Surface Microlayer of the Open Atlantic and the Western Mediterranean Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Tanoue, E. Distribution and Alteration of Amino Acids in Bulk DOM along a Transect from Bay to Oceanic Waters. Mar. Chem. 2003, 82, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slocum, R.D. Genes, Enzymes and Regulation of Arginine Biosynthesis in Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 43, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, A. England: Cambridge University Press. 2015, pp. 1–372.
- Wu, B.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, C.; Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Han, Z.-B.; Hu, J. Vertical Distribution of Sedimentary Organic Carbon in the Yap Trench and Its Implications. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 3502–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.C.; Toole, J.M. Flow of Deep and Bottom Waters in the Pacific at 10°N. Deep. Res. Part I 1993, 40, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




