1. Introduction
The depletion of monocytes or macrophages abrogates the immunomodulatory and regenerative activities of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) in multiple disease models, pointing to the crucial role of innate immune cells as essential mediators of MSC action [
1,
2]. A number of studies have elucidated the actions and mechanisms of MSCs, revealing their capacity to suppress pro-inflammatory immune cells and induce immunosuppressive cells. Notably, among the suppressive immune cells induced by MSCs are myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs).
MDSCs constitute a heterogeneous group of myeloid cells with potent immunosuppressive activity. Recent data uncover that the development of MDSCs occurs in two partially overlapping phases [
3,
4]: One is the expansion and conditioning of myeloid cells in the bone marrow (BM) and spleen, and the other is the conversion of neutrophils and monocytes into pathologically activated MDSCs in peripheral tissues. MDSCs accumulate in tissues in various pathologic conditions, including cancer, infection, acute and chronic inflammation, and autoimmunity, and play an important role in regulating immune responses. The immunoregulatory activity of MDSCs can be detrimental or beneficial [
3,
4]. For instance, in cancer, MDSCs exacerbate the disease and are generally associated with poor clinical outcome. In contrast, in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, the immunosuppressive functions of MDSCs contribute to limiting disease severity.
Although emerging data have elucidated the genomic, proteomic and metabolic characteristics of MDSCs [3-5], the precise mechanisms that drive neutrophils and monocytes to differentiate into MDSCs remain unclear. Several molecular pathways that regulate the suppressive functions of MDSCs have been suggested, but they largely vary depending on the factors and tissue microenvironments inducing MDSC development [
4,
5,
6,
7]. Identifying the specific pathways leading to MDSC differentiation and activation would provide valuable information for potential clinical targeting of MDSCs for the treatment of various diseases.
In a previous study, our group demonstrated that MSCs directed the differentiation of BM cells from pro-inflammatory CD11b
hiLy6C
hiLy6G
lo monocytes to CD11b
midLy6C
midLy6G
lo MDSCs in granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) stimulation and in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis [
8]. In the present study, we explore the signaling pathway in BM cells through which MSCs induce MDSC differentiation and regulate their suppressive functions.
2. Results
2.1. MAPK-related genes are upregulated in MSC-induced MDSCs
In our prior study [
8], MSCs were found to induce the expression of
Arg1 and
Nos2, hallmark MDSC genes encoding the immunosuppressive enzymes arginase and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), respectively [
3,
4], in GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells. Also, MSCs elevated the production of immunosuppressive cytokines, such as IL-10, TGF-β1 and TGF-β2, in GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells, while suppressing TNF-α secretion [
8]. Notably, the MSC-induced MDSCs exhibited a CD11b
midLy6C
midLy6G
lo phenotype, distinct from the pro-inflammatory CD11b
hiLy6C
hiLy6G
lo monocytes differentiated from GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells [
8].
Building upon these findings, we conducted a screening for the signaling pathway involved in MSC-induced MDSC differentiation. We analyzed RNA-seq data from CD11b
midLy6C
midLy6G
lo MDSCs derived from MSC-cocultured BM cells under GM-CSF stimulation and compared them with those of CD11b
hiLy6C
hiLy6G
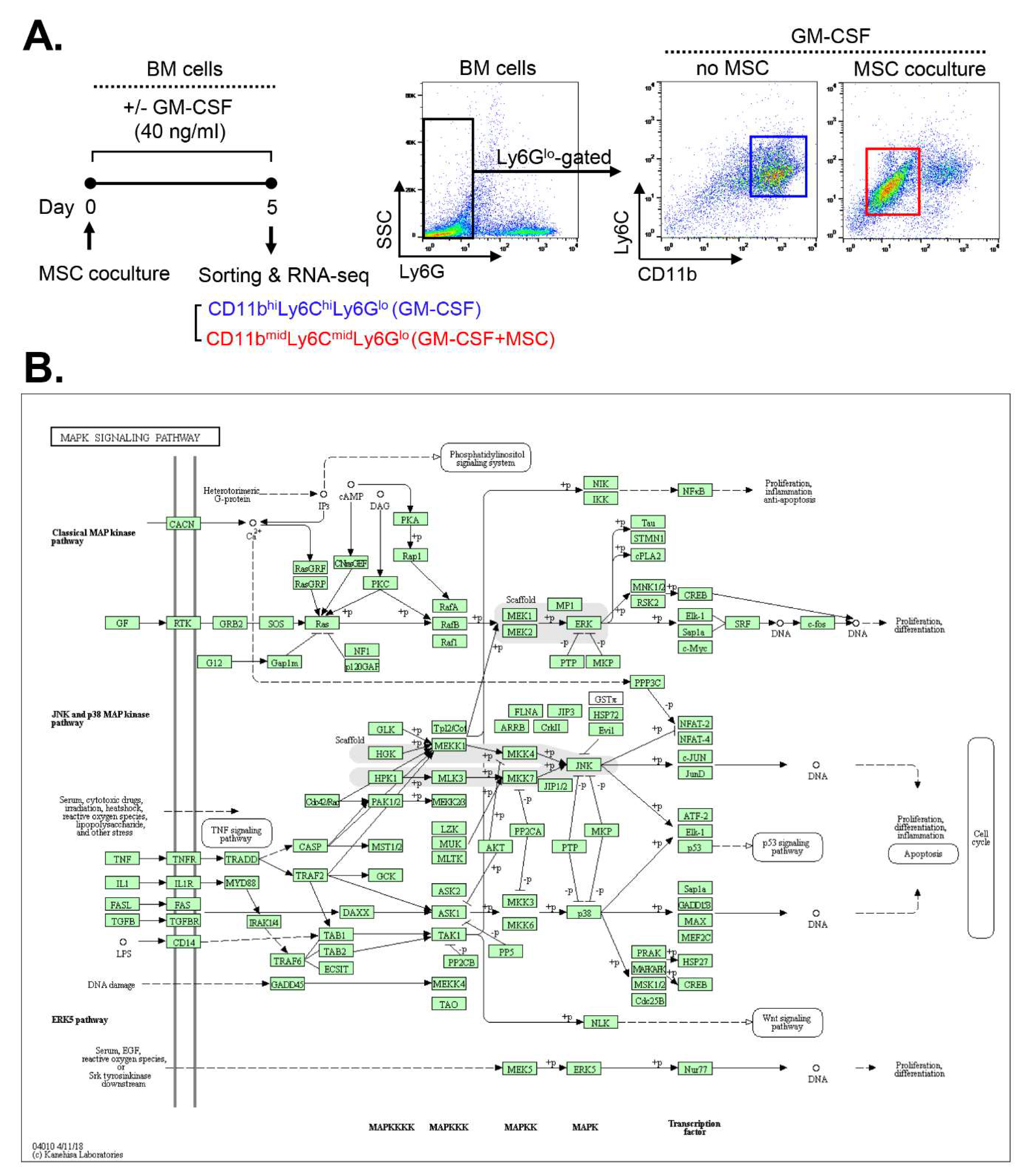
lo monocytes sorted from GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells without MSC coculture (ArrayExpress accession E-MTAB-8975) (
Figure 1A).
A comparative Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis using the DAVID database revealed that the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways exhibited the highest number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) enriched in MSC-induced MDSCs compared to BM cells without MSC coculture. The identified target genes are listed in
Table 1, and the pathways in which they are involved are illustrated in
Figure 1B.
Figure 1.
RNA-seq reveals up-regulation of MAPK pathway-related genes in MSC-induced MDSCs. (A) Experimental design. CD11bhiLy6ChiLy6Glo cells were isolated from BM cells cultured for 5 d under GM-CSF stimulation (40 ng/mL) without MSC coculture. CD11bmidLy6CmidLy6Glo cells were sorted from GM-CSF–stimulated BM cells with MSC coculture. Both cell populations were comparatively analyzed by RNA-seq. (B) The KEGG pathway analysis by the DAVID tool. The highest number of DEGs upregulated in MSC-induced MDSCs was associated with the MAPK signaling pathway.
Figure 1.
RNA-seq reveals up-regulation of MAPK pathway-related genes in MSC-induced MDSCs. (A) Experimental design. CD11bhiLy6ChiLy6Glo cells were isolated from BM cells cultured for 5 d under GM-CSF stimulation (40 ng/mL) without MSC coculture. CD11bmidLy6CmidLy6Glo cells were sorted from GM-CSF–stimulated BM cells with MSC coculture. Both cell populations were comparatively analyzed by RNA-seq. (B) The KEGG pathway analysis by the DAVID tool. The highest number of DEGs upregulated in MSC-induced MDSCs was associated with the MAPK signaling pathway.
2.2. MSCs activate the JNK pathway in BM cells
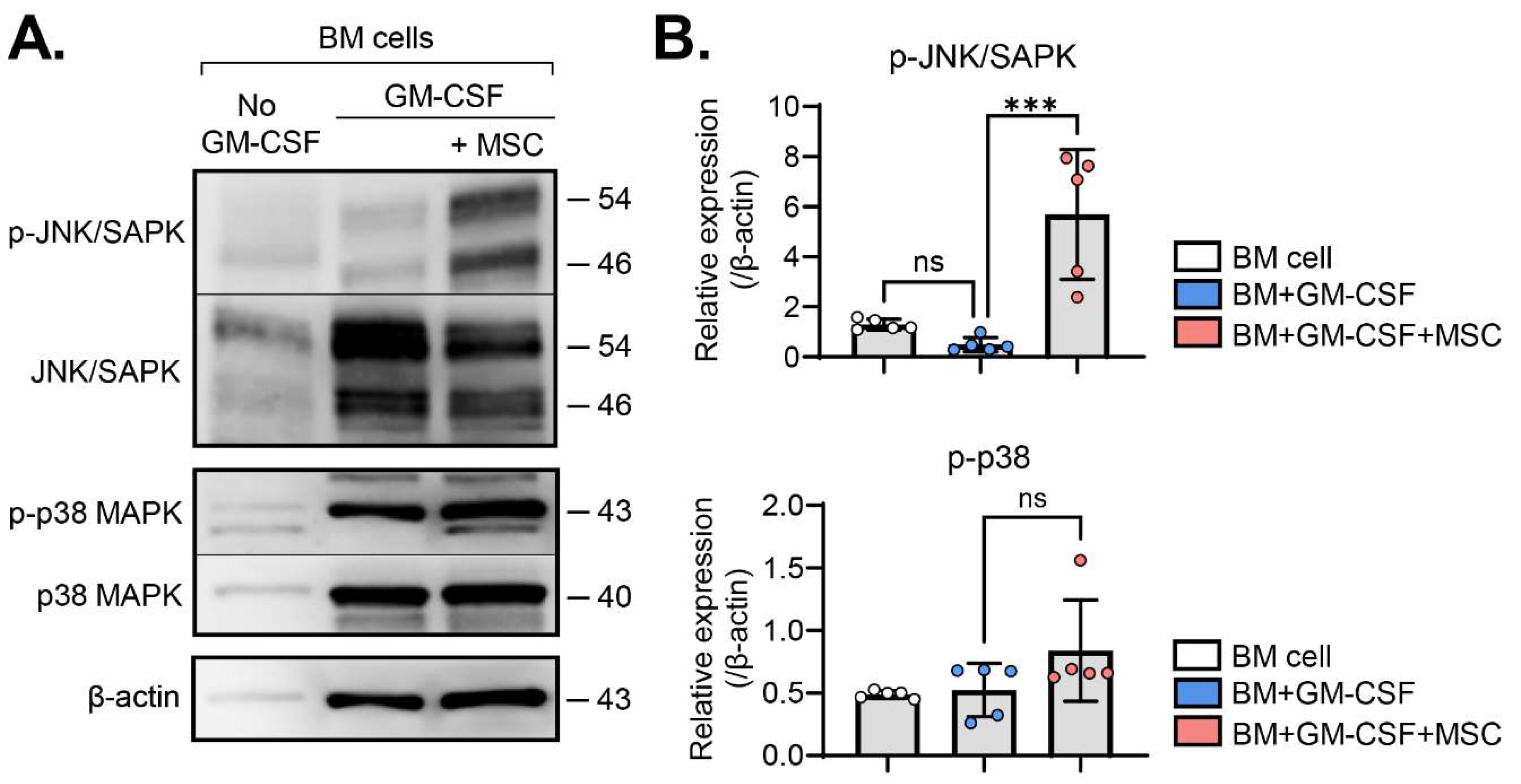
Based on the observed upregulation of MAPK-related genes in MSC-induced MDSCs (
Figure 1), we next investigated the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, the members of MAPK families [
9], in BM cells with and without MSC coculture in the presence or absence of GM-CSF. Western blot analysis showed that GM-CSF did not significantly influence JNK or p38 phosphorylation in BM cells. Remarkably, MSC coculture induced robust phosphorylation of JNK in GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells (
Figure 2A,B). In contrast, while JNK activation was prominent, p38 phosphorylation showed no significant increase in BM cells with MSC coculture (
Figure 2A,B).
These findings indicate that, among biochemical pathways, MSCs specifically activate the JNK MAPK signaling pathway in GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells.
Figure 2.
MSCs induce JNK activation in GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells. (A) Representative western blot images. BM cells were subjected to western blot analysis to assess total and phosphorylated forms of JNK/SAPK and p38 proteins under the indicated treatments. (B) Densitometric analysis of western blot images. The relative amounts of phosphorylated forms of specified proteins were quantitated as a ratio of each protein band relative to β-actin. Mean values ± SD are shown. ***p < 0.001, ns: not significant by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (p-JNK/SAPK) or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (p-p38).
Figure 2.
MSCs induce JNK activation in GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells. (A) Representative western blot images. BM cells were subjected to western blot analysis to assess total and phosphorylated forms of JNK/SAPK and p38 proteins under the indicated treatments. (B) Densitometric analysis of western blot images. The relative amounts of phosphorylated forms of specified proteins were quantitated as a ratio of each protein band relative to β-actin. Mean values ± SD are shown. ***p < 0.001, ns: not significant by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (p-JNK/SAPK) or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (p-p38).
2.3. JNK inhibition abrogates MSC effects on MDSC induction
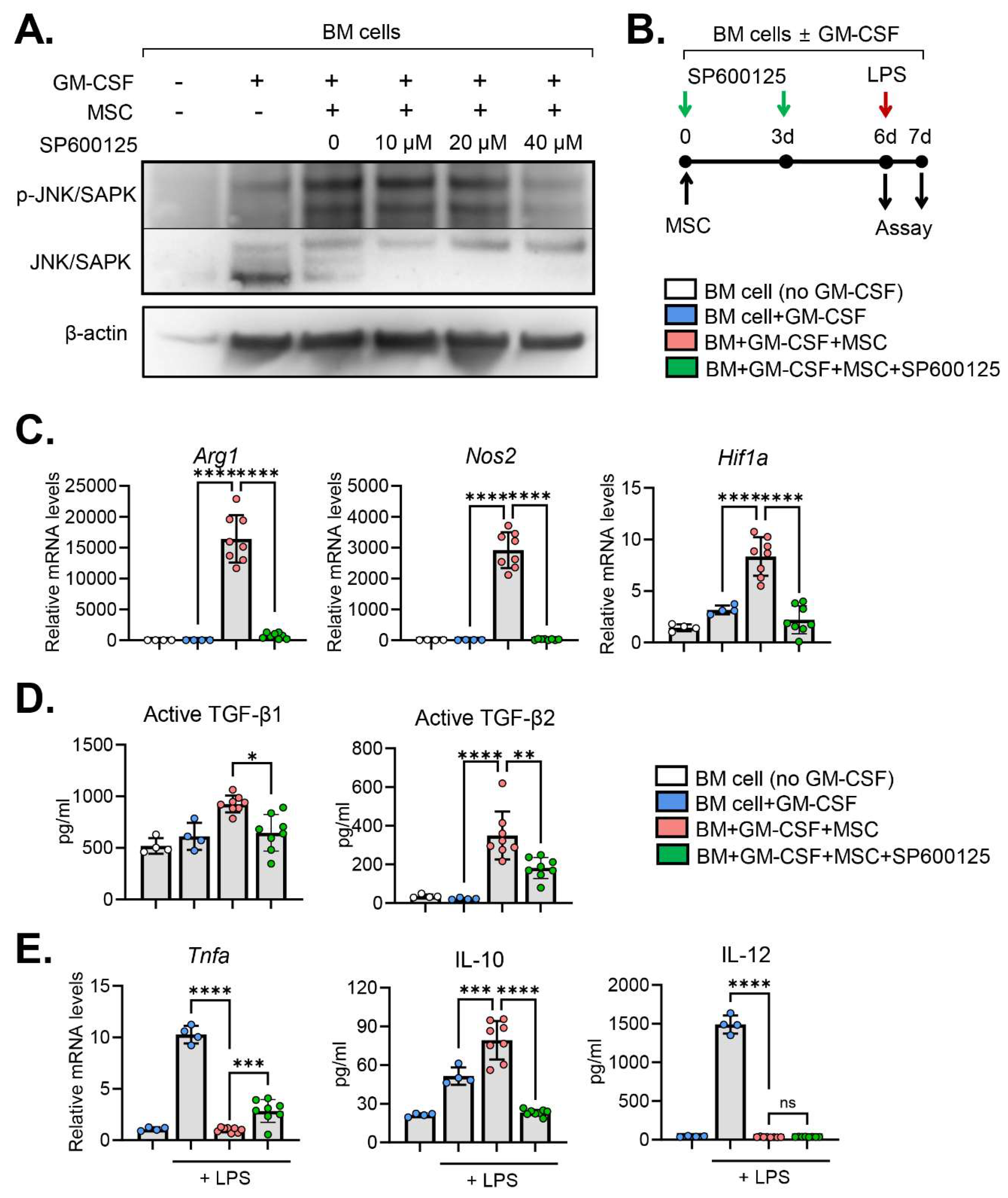
To assess the specific contribution of JNK in the MSC-induced differentiation of BM cells, we utilized the anthrapyrazolone inhibitor SP600125 as a JNK inhibitor [
10]. Initially, we confirmed the efficacy of SP600125 in inhibiting JNK phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment of BM cells with 40 μM SP600125 for 3 d negated the effect of MSCs on JNK activation in BM cells (
Figure 3A).
Subsequently, we examined the impact of JNK inhibition on the expression of molecules mediating the immunosuppressive functions of MDSCs in BM cells cocultured with MSCs (
Figure 3B). Results revealed that MSCs highly induced the expression of
Arg1,
Nos2 and
Hif1a in BM cells (
Figure 3C).
Arg1 and
Nos2 are hallmark MDSC genes encoding the immunosuppressive enzymes, arginase and iNOS, respectively [
3,
4].
Hif1a encodes hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α that has been shown to mediate the functional re-programming of monocytes into suppressive phenotype [
11]. Interestingly, JNK inhibition by SP600125 significantly downregulated the expression of
Arg1, Nos2 and
Hif1a (
Figure 3C). Similar results were observed with the production of immunoregulatory cytokines. BM cells cocultured with MSCs exhibited elevated levels of immunosuppressive cytokines TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 compared to those without MSC coculture (
Figure 3D). However, JNK inhibition by SP600125 significantly reduced the secretion of TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 in BM cells cocultured with MSCs (
Figure 3D).
We furthermore investigated the response of BM cells to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) stimulation (
Figure 3B). As expected, LPS treatment markedly upregulated the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-12 in BM cells (
Figure 3E). MSCs almost completely suppressed the upregulation of TNF-α and IL-12 in BM cells in response to LPS (
Figure 3E). SP600125 treatment significantly reversed the effects of MSCs on TNF-α downregulation in BM cells, while the secretion of IL-12 remained unaffected by SP600125 (
Figure 3E). In addition, MSCs induced IL-10 secretion in BM cells in response to LPS stimulation, which effect was significantly attenuated by SP600125 (
Figure 3E).
Collectively, these results demonstrate that MSCs induce MDSC genes and immunosuppressive molecules in BM cells under GM-CSF stimulation and mitigate their pro-inflammatory activation in response to LPS. Inhibition of the JNK pathway in BM cells reverses these effects of MSCs on BM cells.
Figure 3.
JNK inhibition reverses MSC effects on immunoregulatory molecules in BM cells. (A) Representative western blot images. BM cells were subjected to western blot analysis for total and phosphorylated forms of JNK/SAPK in BM cells under the indicated treatments. The cells were treated with incremental doses (10 ~ 40 μM) of SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, for 3 d. (B) Experimental scheme. For JNK inhibition, GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells were treated with 40 μM SP600125 every 3 d. For LPS stimulation assay, the cells were exposed to 100 ng/mL LPS for 18 h. (C) qRT-qPCR for MDSC hallmark and immunoregulatory genes Arg1, Nos2 and Hif1a in BM cells. The mRNA levels are presented as fold changes relative to the levels in GM-CSF-untreated and MSC-uncocultured cells. (D) ELISA for secreted levels of immunoregulatory cytokines TFG-β1 and TGF- β2 in the supernatant of BM cell culture. (E) qRT-qPCR for Tnfa and ELISA for IL-10 and IL-12 in BM cells in response to LPS stimulation. Mean values ± SD are shown. p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns: not significant by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (active TFG-β1).
Figure 3.
JNK inhibition reverses MSC effects on immunoregulatory molecules in BM cells. (A) Representative western blot images. BM cells were subjected to western blot analysis for total and phosphorylated forms of JNK/SAPK in BM cells under the indicated treatments. The cells were treated with incremental doses (10 ~ 40 μM) of SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, for 3 d. (B) Experimental scheme. For JNK inhibition, GM-CSF-stimulated BM cells were treated with 40 μM SP600125 every 3 d. For LPS stimulation assay, the cells were exposed to 100 ng/mL LPS for 18 h. (C) qRT-qPCR for MDSC hallmark and immunoregulatory genes Arg1, Nos2 and Hif1a in BM cells. The mRNA levels are presented as fold changes relative to the levels in GM-CSF-untreated and MSC-uncocultured cells. (D) ELISA for secreted levels of immunoregulatory cytokines TFG-β1 and TGF- β2 in the supernatant of BM cell culture. (E) qRT-qPCR for Tnfa and ELISA for IL-10 and IL-12 in BM cells in response to LPS stimulation. Mean values ± SD are shown. p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns: not significant by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (active TFG-β1).
3. Discussion
Our results demonstrated that a significant number of genes related to MAPK pathways were upregulated in MDSCs induced by MSCs in the BM. Specifically, the JNK pathway shows prominent activation in MSC-cocultured BM cells. Blockade of JNK activation in BM cells abolished the effects of MSCs on the induction of hallmark MDSC genes and immunosuppressive molecules mediating the MDSC function. Also, JNK inhibition abrogated the suppressive action of MSCs on the inflammatory activation of BM cells in response to LPS. Therefore, the results suggest that the JNK MAPK signaling pathway is crucial for MSCs’ action to promote immunosuppressive molecules and induce MDSC differentiation in BM cells during inflammation.
The JNK signaling pathway is a member of the MAPK signal transduction pathways, which relay, amplify and integrate signals from a range of extracellular stimuli and elicit multiple physiological processes in mammalian cells, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and inflammatory response [
9]. The JNK pathway has been implicated in diverse innate immune responses. For example, JNK inhibition was reported to decrease IL-10 expression in stimulated human monocytes [
12]. Also, JNK inhibition significantly reduced Pam3CSK4 (PAM3)-dependent generation of immunosuppressive macrophages in human monocytes [
13]. Moreover, JNK inhibition was shown to increase the apoptosis of both granulocytic and monocytic MDSCs [
14]. In our study, MSCs induced JNK activation in BM cells, thereby leading to the induction of immunoregulatory molecules (
Arg1,
Nos2,
Hif1α, TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and IL-10) mediating the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs. These results indicate that JNK activation contributes to the action, survival and differentiation of MDSCs and immunosuppressive macrophages. Given that MDSCs and monocytes/marophages are highly heterogeneous and context-dependent [
7], it can be suggested that other signaling pathways, in addition to JNK pathway, are also involved in MDSC differentiation and functions. In our study, JNK inhibition did not influence the effect of MSCs on IL-12 expression in BM cells, while it significantly abrogated the effect on TNF-α and IL-10 levels, pointing to the involvement of other pathway in MSC-mediated IL-12 downregulation in BM cells. In a study by Bayik et al., JNK contributed to PAM3-driven generation of suppressive macrophages, but it was not involved in M-CSF-dependent suppressive macrophage polarization [
13]. In fact, various pathways, including PI3K, Ras, Jak/Stat and TGF-β, have been demonstrated to play a role in the generation of MDSCs from myeloid precursors in various disease conditions [
5].
Conflicting results on the role of JNK in innate immune responses have also been reported. A study by Deng et al. demonstrated that JNK activation by synthetic bacterial lipoprotein, a TLR1/2 agonist, redirected differentiation of monocytic MDSC towards M1 pro-inflammatory macrophages [
15]. Also, a study by Liu et al. reported that TNF-α–stimulated gene/protein 6 secreted by human umbilical cord-derived MSCs inhibited activation of both p38 and JNK MAPK pathways in peritoneal macrophages, and thus attenuated inflammation in the skin wound after burned injury [
16]. These discrepancies suggest that the signaling pathways involved in the polarization of monocytes/macrophages and MDSC differentiation depend on the cell type and extracellular stimuli [
13,
17], and that JNK activation can be pro-inflammatory or immunosuppressive according to cell types and tissue microenvironments. As such, the identification of specific signals and pathways that direct MDSC differentiation and lead to suppressive modes in myeloid populations in different disease settings would be important for improving clinical outcomes of MDSC-based therapies.
The exogenous administration of MSCs has proven beneficial in ameliorating acute inflammatory pathology or autoimmune diseases, making MSC-based therapies the subject of extensive clinical trials [
18]. One of key mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of MSCs is their ability to generate suppressive macrophages or MDSCs. However, the immunosuppressive environment created by MSCs raises concerns about potential tumor promotion in hosts receiving MSC therapy [
19,
20]. Therefore, unraveling the molecular pathways involved in MSC-induced immunosuppressive actions, including generation of MDSCs and suppressive macrophages, would be essential for designing safe and effective regimens for the treatment of immune-related diseases and cancers. Our study reveals the JNK pathway as one such mechanism mediating MSC-induced MDSC differentiation in the BM. As mimetics and inhibitors targeting the JNK pathway become available, their combination with MSC therapy hold promise for enhancing therapeutic efficacy and mitigating side effects in patients.
In summary, our data demonstrate that MSCs activate the JNK MAPK pathway in BM cells under GM-CSF stimulation to induce the expression of immunosuppressive molecules, promote MDSC differentiation, and repress pro-inflammatory activation.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell culture
The experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Seoul National University Biomedical Research Institute (Seoul, Korea).
Single cell suspensions of BM cells were prepared by flushing the femur of 7-week C57BL/6 mice (Orient Bio, Seongnam, Korea). The cells were then filtered through a 70-μM cell strainer (# 352350, Corning incorporation, Corning, NY) and collected through centrifugation. After red blood cell lysis, the resulting cells were cultured in RPMI1640 media (Welgene, Daegu, Korea) with 10% (vol/vol) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, Waltham, MA) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (PS) (Lonza, Walkersville, MD) at 37°C in 5% CO2. For differentiation induction, the cells were treated with GM-CSF (40 ng/ml, GenScript, Piscataway, NJ) for 5 d.
In the LPS stimulation assay, GM-CSF-treated cells were exposed to 100 ng/mL LPS (InvivoGen, San Diego, CA) for 18 h.
For JNK inhibition, SP600125 (0, 10, 20 and 40 μM) (#tlrl-sp60, InvivoGen) was added to BM cells for 3 d.
Human BM-derived MSCs were provided by the Center for the Preparation and Distribution of Adult Stem Cells (
http://medicine.tamhsc.edu/irm/msc-distribution.html) and cultured according to the instructions. Briefly, passage 2 MSCs were cultured at 37°C in 5% CO
2 until reaching 70–80% confluency (approximately 7 d). The culture medium consisted of α-minimal essential medium (Gibco), 17% FBS (Gibco), 1% PS (Lonza) and 2 mM L-glutamine (Lonza), and was changed every two days during culture. MSCs were harvested by incubating in 0.25% trypsin/1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) at 37°C for 2 min and cocultured with BM cells at a ratio of 1:5 (MSCs:BM cell) in the BM cell culture media.
4.2. RNA sequencing
CD11bhiLy6Chi monocytes were isolated from GM-CSF-stimulated, MSC-uncocultured BM cells. CD11bmidLy6Cmid MDSCs were sorted from GM-CSF-stimulated, MSC-cocultured BM cells. For FACS-sorting, the BM cells were stained with anti-CD11b (clone M1/70, eBioscience, San Diego, CA) and anti-Ly6C (clone HK1.4, eBioscience) antibodies (Abs) and sorted using BD FACSAria™ III cell sorter (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA).
For RNA-seq with the sorted BM cells, 500 ng of total RNA was extracted, and library construction was performed with the QuantSeq 3’ mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit (Lexogen, Vienna, Austria). High-throughput sequencing was conducted as single-end 75 sequencing using NextSeq 500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). QuantSeq 3’ mRNA-Seq reads were aligned using Bowtie2, and DEGs were determined based on counts from unique and multiple alignments using coverage in Bedtools. Gene classification was based on searches conducted by DAVID (
http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/) and Medline databases (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The data were deposited at ArrayExpress accession E-MTAB-8975.
4.3. Western blot assays
BM cells were lysed in RIPA Buffer (Biosesang, Seongnam, Korea) including protease inhibitor and phosphatase inhibitor (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) and sonicated on ice. After centrifugation, clear cell lysates were acquired and assayed for protein concentration. Following denaturation, 40 µg protein was separated on a 4–12% SDS-PAGE gel (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA) at 150 V for 90 min and transferred to a methanol-soaked PVDF membrane (Invitrogen) at 40 V for 100 min. The membranes were blocked with 3% bovine serum albumin for 1 h and then incubated at 4ºC overnight with anti-phopho-SAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) (#9255, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), anti-phopho-p38 MAPK (Thr180/Tyr185) (#9216, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-SAPK/JNK (#9252, Cell Signaling Technology) and anti-p38 MAPK (#9212, Cell Signaling Technology) Abs. The membranes were then incubated with anti-mouse or anti-rabbit IgG Abs conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (HRP) at room temperature for 1 h. After stripping at 55ºC for 30 min, they were incubated at room temperature for 1 h with anti-β-actin Ab (Santa cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX) and subsequently with anti-mouse HRP Ab (Cell Signaling Technology). The protein expression levels were normalized to the corresponding β–actin levels.
4.4. Quantitative real-time reverse-transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
BM cells were lysed in RNA isolation reagent (RNA Bee, Tel-Test, Friendswood, TX) and homogenized with an ultrasound sonicator (Ultrasonic Processor, Cole Parmer Instruments, Vernon Hills, IL). Total RNA was extracted using RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), and double-stranded cDNA were synthesized by reverse transcription (High Capacity RNA-to-cDNATM Kit, Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA). Real-time PCR amplification was performed using TaqMan® Universal PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) in an automated instrument (ABI 7500 Real Time PCR System, Applied Biosystems). Data were normalized to Gapdh and expressed as fold changes relative to controls. All PCR probe and primer sets were mouse-specific (TaqMan® Gene Expression Assay, Applied Biosystems).
4.5. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
The cell-free supernatants were collected by centrifugation and analyzed for concentrations of mouse-specific IL-10, active TGF-β1 and active TGF-β2 (DuoSet® ELISA, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.6. Statistical analysis
After a normality test, data were analyzed either by one-way ANOVA followed by Tuckey’s Honestly Significant Difference test or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism Software, San Diego, CA). Data were presented as mean ± SD, and differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Y.O.; Methodology, H.J.L. and J.Y.O.; Formal Analysis, H.J.L. and J.Y.O.; Investigation, H.J.L. and J.Y.O.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, H.J.L. and J.Y.O.; Writing – Review & Editing, H.J.L. and J.Y.O.; Visualization, J.Y.O.; Supervision, J.Y.O.; Project Administration, J.Y.O.; Funding Acquisition, J.Y.O.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2021R1A2C3004532).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2021R1A2C3004532).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Galipeau, J. Macrophages at the nexus of mesenchymal stromal cell potency: The emerging role of chemokine cooperativity. Stem Cells. 2021, 39, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh JY, Lee RH. Mesenchymal stromal cells for the treatment of ocular autoimmune diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021, 85, 100967. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veglia, F.; Perego, M.; Gabrilovich, D. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells coming of age. Nat Immunol 2018, 19, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veglia F, Sanseviero E, Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the era of increasing myeloid cell diversity. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 485–498. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikha P, Carson WE 3rd. Signaling pathways involved in MDSC regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014, 1846, 55–65. [CrossRef]
- Condamine T, Mastio J, Gabrilovich DI. Transcriptional regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Leukoc Biol 2015, 98, 913–933. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde S, Leader AM, Merad M. MDSC: Markers, development, states, and unaddressed complexity. Immunity 2021, 54, 875–884. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee HJ, Ko JH, Kim HJ, Jeong HJ, Oh JY. Mesenchymal stromal cells induce distinct myeloid-derived suppressor cells in inflammation. JCI Insight 2020, 18, e136059. [CrossRef]
- Zhang W, Liu HT. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O'Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y, Bhagwat SS, Manning AM, Anderson DW. SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, 13681–13686. [CrossRef]
- Shalova IN, Lim JY, Chittezhath M, Zinkernagel AS, Beasley F, Hernández-Jiménez E, Toledano V, Cubillos-Zapata C, Rapisarda A, Chen J, Duan K, Yang H, Poidinger M, Melillo G, Nizet V, Arnalich F, López-Collazo E, Biswas SK. Human monocytes undergo functional re-programming during sepsis mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Immunity 2015, 42, 484–498. [CrossRef]
- Dobreva ZG, Miteva LD, Stanilova SA. The inhibition of JNK and p38 MAPKs downregulates IL-10 and differentially affects c-Jun gene expression in human monocytes. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2009, 31, 195–201. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayik D, Tross D, Haile LA, Verthelyi D, Klinman DM. Regulation of the maturation of human monocytes into immunosuppressive macrophages. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 2510–2519. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TYu J, Li H, Zhang Z, Lin W, Wei X, Shao B. Targeting the MDSCs of Tumors In Situ With Inhibitors of the MAPK Signaling Pathway to Promote Tumor Regression. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 647312. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng Y, Yang J, Qian J, Liu R, Huang E, Wang Y, Luo F, Chu Y. TLR1/TLR2 signaling blocks the suppression of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell by promoting its differentiation into M1-type macrophage. Mol Immunol. 2019, 112, 266–273. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu L, Song H, Duan H, Chai J, Yang J, Li X, Yu Y, Zhang X, Hu X, Xiao M, Feng R, Yin H, Hu Q, Yang L, Du J, Li T. TSG-6 secreted by human umbilical cord-MSCs attenuates severe burn-induced excessive inflammation via inhibiting activations of P38 and JNK signaling. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 30121. [CrossRef]
- Valledor AF, Sánchez-Tilló E, Arpa L, Park JM, Caelles C, Lloberas J, Celada A. Selective roles of MAPKs during the macrophage response to IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 2008, 180, 4523–4529. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galipeau J, Sensébé L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. 2018, 22, 824–833. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee MJ, Park SY, Ko JH, Lee HJ, Ryu JS, Park JW, Khwarg SI, Yoon SO, Oh JY. Mesenchymal stromal cells promote B-cell lymphoma in lacrimal glands by inducing immunosuppressive microenvironment. Oncotarget. 2017, 8, 66281–66292. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren G, Zhao X, Wang Y, Zhang X, Chen X, Xu C, Yuan ZR, Roberts AI, Zhang L, Zheng B, Wen T, Han Y, Rabson AB, Tischfield JA, Shao C, Shi Y. CCR2-dependent recruitment of macrophages by tumor-educated mesenchymal stromal cells promotes tumor development and is mimicked by TNFα. Cell Stem Cell. 2012, 11, 812–824. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).