1. Introduction
Bone is a continuously renewed tissue that undergoes a dynamic remodeling throughout the life course. Bone homeostasis is maintained by the balance between osteoblast-mediated bone formation and osteoclast-mediated bone resorption [
1]. Osteoclasts are large multinucleated cells that are differentiated from hematopoietic myeloid precursors and exhibit bone-resorbing activity via degradation of the bone matrix [
2]. Osteoblasts stemming from the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and located in the bone remodeling units are responsible for the formation of bone extracellular matrix by producing bone matrix components, such as collagen type 1, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), osteopontin (OPG), osteocalcin, osteomodulin, and osteonectin [
3,
4]. An imbalance between bone formation and resorption due to reduced proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of bone marrow-derived stromal cells results in reduced bone regeneration.
Osteoporosis is one of the most common age-related bone diseases characterized by a reduction of bone mass, deterioration of bone tissues, and disruption of bone microstructure, leading to increased risk of fractures [
5]. The imbalance between bone anabolic and catabolic processes, which often leads to enhanced bone lysis, is the main reason for primary osteoporosis. Accordingly, inhibition of osteoclastic activity and/or stimulation of osteoblast differentiation is one of the most common and effective strategies for developing novel osteoporosis medications [
2].
Recent studies have reported that various factors originating from the nervous system can directly and/or indirectly regulate bone metabolism, homeostasis, and remodeling [
6,
7,
8]. Neurotransmitters released from the nervous system, such as substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and neuropeptide Y, play an important role in regulating regeneration, motility, proliferation, and differentiation of bone marrow cells [
9,
10,
11,
12]. In particular, increased release of bone injury-induced neurotransmitters vitally contributes to bone healing [
13,
14]. Pre-clinical and clinical studies have observed that brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level is enhanced following traumatic brain injury, possibly involving in fracture healing [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19].
BDNF, belonging to the family of neurotrophins, is often released from the central and peripheral neuronal tissues and essentially functions in the nervous systems, such as neuronal development, survival and differentiation, neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and cognitive function [
20,
21]. Recent studies have shown that BDNF has positive effects bone formation by enhancing osteoblast differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells [
22]. In addition, BDNF also stimulates MC3T3-E1 cell differentiation and promote new bone formation and maturation [
18]. Furthermore, suppression of BDNF expression by using long-coding RNA BDNF-antisense inhibited osteogenesis differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, possibly through inverse regulation of BDNF and osteogenic signaling pathway [
23].
Although several reports evaluated the effect of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation, the molecular mechanism of its action, aiming at essential components of the signal transduction machinery that plays a central role in the differentiation process, has not been fully investigated. In particular, the protective effect of BDNF against osteoporosis in estrogen-deficient rat models remains unknown. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the osteogenic potential and underlying mechanism of BDNF on bone marrow-derived stromal cells. The effect of BDNF on bone remodeling was also examined in an ovariectomized-induced osteoporosis rat model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
BDNF was purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA). Ascorbic acid, β-glycerophosphate, and neutral formalin were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Anti-ALP, OPN, BMP2/4, Osterix/Sp7, β-actin, and HRP-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Anti-Runx2, p-ERK, ERK, p-JNK, JNK, p-p38, p38, TrkB, and HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibodies were acquired from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA). Anti-p-TrkB antibody was obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, UK).
2.2. Cell Culture
MC3T3-E1 subclone 4, a mouse preosteoblast cell line, was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA) and cultured in α-Minimum Essential Medium without ascorbic acid (α-MEM, Gibco, Gaithersbug, MD, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco) and 1% antibiotic (100 µg/mL penicillin and 100 U/mL streptomycin, Gibco) in a humidified CO2 incubator at 37 °C. ST-2, a mouse bone marrow stromal cell, was obtained from RIKEN Cell Bank (Tsukuba Scientific City, Ibaraki, Japan) and maintained in RPMI-1640 medium (Gibco) supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% antibiotic (100 µg/mL penicillin and 100 U/mL streptomycin) in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air with 5% CO2 at 37 °C. During culture, fresh media were replaced every three days. For osteogenic differentiation, the cells were incubated in the osteogenic induction medium (OIM), including α-MEM medium plus 10% FBS, 1% antibiotics, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, and 50 µg/mL ascorbic acid. For co-culture, a direct 2D co-culture system of MC3T3-E1 and ST-2 was maintained in α-MEM medium containing 10% FBS and 1% antibiotics in a humidified incubator under 5% CO2 balanced air at 37˚C.
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
To evaluate the effects of BDNF on cell proliferation, the cells were seeded in 96-well plates and treated with various concentrations of BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days. The cell proliferation was then determined by the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay kit (Sigma-Aldrich) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The absorbance of the resulting solution was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA).
2.4. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Activity and Staining
The ALP activity was detected by a colorimetric assay using p-nitrophenyl phosphate as substrate. Briefly, the cells were seeded in 6-well plates and treated with different concentrations of BDNF for 3, 5, or 7 days. After treatment, the cells were lysed with assay buffer, and the total protein contents of the supernatants were measured by a PierceTM BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The ALP activity was determined by an ALP assay kit (Biovision, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and normalized to the protein content.
ALP staining was performed to confirm the results of ALP activity by using 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-phosphate (BCIP)/nitro-blue tetrazolium (NBT) solution (Sigma). After treatment, the medium was discarded, and the cells were washed twice with phosphate buffer saline (PBS, Sigma). The cells were fixed with 10% neutral formalin for 10 min at room temperature. The cells were then stained with BCIP/BNT solution for 30 min at 37 °C in the dark. Representative images were captured by a digital microscope camera (Paxcam, Iowa, IL, USA).
2.5. Mineralization Assay
Calcium accumulation was determined by an Alizarin Red S (Cell Biologics Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) staining. In brief, the cells were cultured in 12-well plates and then treated with various concentrations of BDNF for 14 or 21 days. After removing medium, the cells were fixed with 10% neutral formalin for 10 min and rinsed with distilled water. The cells were then stained with 2% Alizarin Red S for 30 min at room temperature and followed by washing five times with distilled water. The representative images were captured using a digital microscope camera (Paxcam).
2.6. Western Blot
The cells were cultured in 6-well plates and treated with various concentrations of BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) for 3, 5, or 7 days. After washing twice with ice-cold PBS, the cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (Cell Signaling) containing fresh protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Sigma). Cell homogenates were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C, and the protein concentration of resulting supernatants was quantified using a PierceTM BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Equal amounts of proteins were separated in SDS-PAGE gels and then transferred to Immobilon®-P PVDF membranes (Merck Millipore). After blocking with 5% skin milk in TBST (0.1% Tween 20 in Tris-buffered saline) overnight, the membranes were hybridized with indicated primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C and followed by incubation with proper horseradish-conjugated secondary anti-mouse or anti-rabbit antibody for 3 h at 4 °C. The protein bands were visualized with EzWestLumi plus reagent (Atto, Tokyo, Japan) using a LuminiGraph II system (Atto).
2.7. Animal Experiment
Twelve-week-old female Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were purchased and housed in individual cages under specific pathogen-free conditions at 22 ±2°C and a relative humidity of 55 ±5% with a 12/12 h light-dark cycle. Throughout the experiment, rats were allowed free access to standard chow and water ad libitum. All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Kyungpook National University (Protocol No. KNU 2022-0154, approved on May 3rd, 2022). Ovariectomized (OVX) rats were prepared by removing both ovaries to produce an osteoporosis model. We divided the rats into two groups; the control group was injected with normal saline, BDNF group was injected with BDNF. BDNF was intraperitoneally injected twice a week starting from twenty-eight days after ovariectomy. The initial rat weight range was 210~250g. The average weight was 200g due to weight loss during the four weeks after ovariectomy. We administered BDNF 10μg in the peritoneum weekly, in line with our preliminary previous experiment concentration (5μg/100g) for 12 weeks. After the 4 weeks of injection, due to weight gain (280~300g), we have increased BDNF dosage to 15μg for the next 8 weeks. At the end of the experiment, the rats were euthanized, and the bone structure was sectioned and stored for micro-CT and histological analysis.
2.7.1. Micro-Computed Tomography
Specimens were scanned using a micro-computed tomography system (SkyScan 1173; Bruker Micro-CT, Kontich, Belgium). Scanning was made at 130KV and a 1.0mm aluminum filter was used. The image resolution was 19.97 micrometers. The images were reconstructed using NRecon software (Ver. 1.7.4.6, Bruker-microCT, Kartuizersweg 3B 2550, Kontich, Belgium). Acquired reconstructed images were sorted using Dataviewer (Ver. 1.5.6.2, Bruker-microCT, Kartuizersweg 3B 2550 Kontich, Belgium) and parameters were calculated using CtAn Software (Ver. 1.19.4.0, Bruker-microCT, Kartuizersweg 3B 2550 Kontich, Belgium) Bone mineral density was used for bone structure evaluation [
24].
2.7.2. Histomorphometry Analysis
Samples were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. After dehydration, Microtome (Leica RM2255 Fully Automated Rotary Microtome, Leica Biosystems Division of Leica Microsystems Inc. 1700 Leider Lane Buffalo Grove, IL, United States) was used for 3 micrometer slicing. We performed hematoxylin (dako hemaoxylin) & eosin (BBC Biocehmical) and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) (Sigma-Aldrich) staining to evaluate the osteoblast and osteoclast activity in both control and BDNF group. Microscopic analysis was performed using Olympus BX51 (Olympus, Tokyo). Digital slide scanner (PANNORAMIC 250 Flash III, 3DHISTECH, Budapest, Hungary) was used to obtain images and analyzed using an exclusive viewing program (Caseviewer, 3DHISTECH, Budapest, Hungary).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of at least three independent experiments and analyzed using GraphPad Prism 10 software (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). Statistically significant differences were examined using Mann-Whitney test, and one-way or two-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P<0.001 values were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of BDNF on the Proliferation of ST-2 Cells
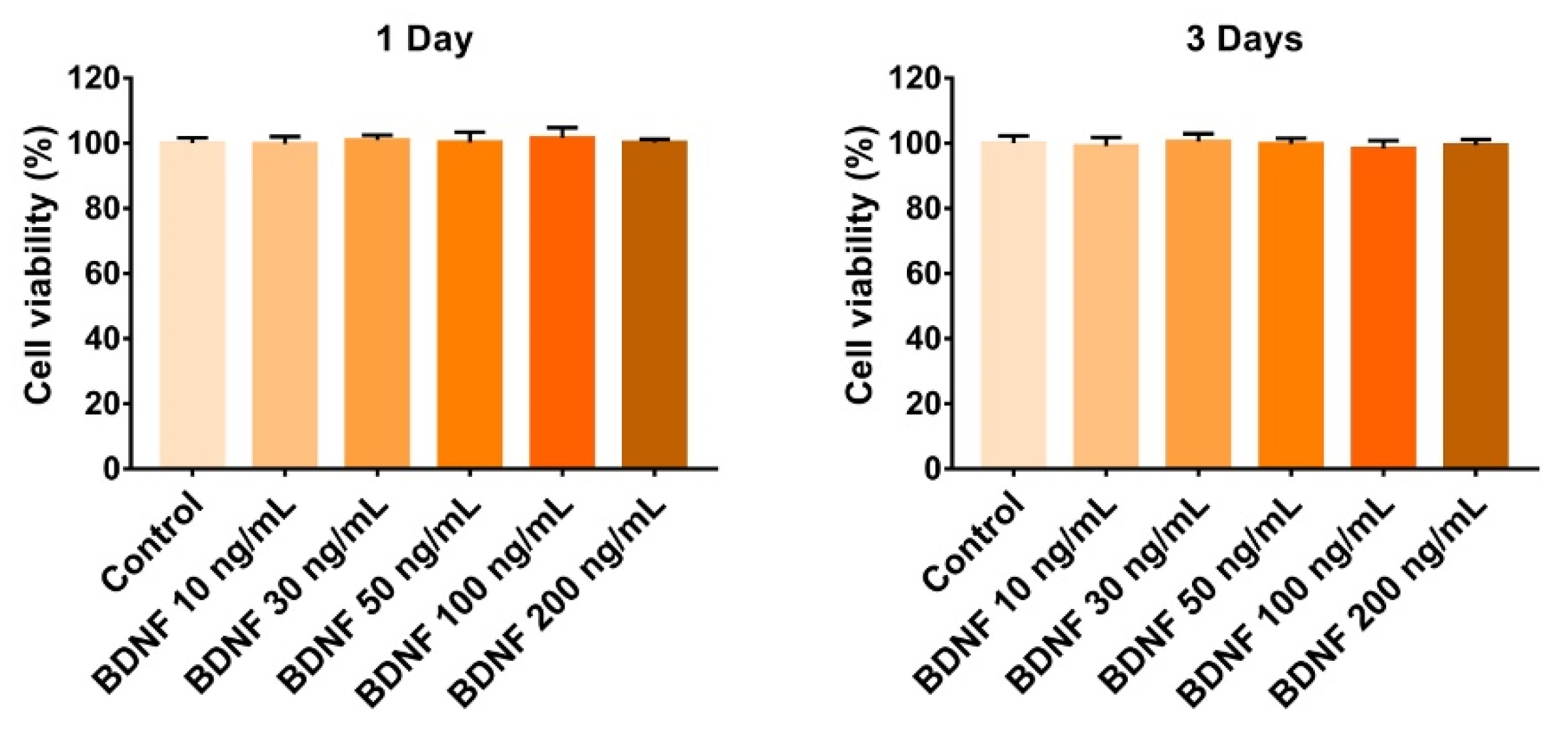
To investigate the proliferative effect of BDNF on bone marrow stromal cells, ST-2 cells were treated with various concentrations of BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) for up to 3 days, and cell proliferation was examined using a CCK-8 assay kit. Compared to the control group, BDNF did not significantly affect cell proliferation after 1 and 3 days of treatment (
Figure 1).
3.2. Effect of BDNF on the Osteoblast Differentiation of ST-2 Cells
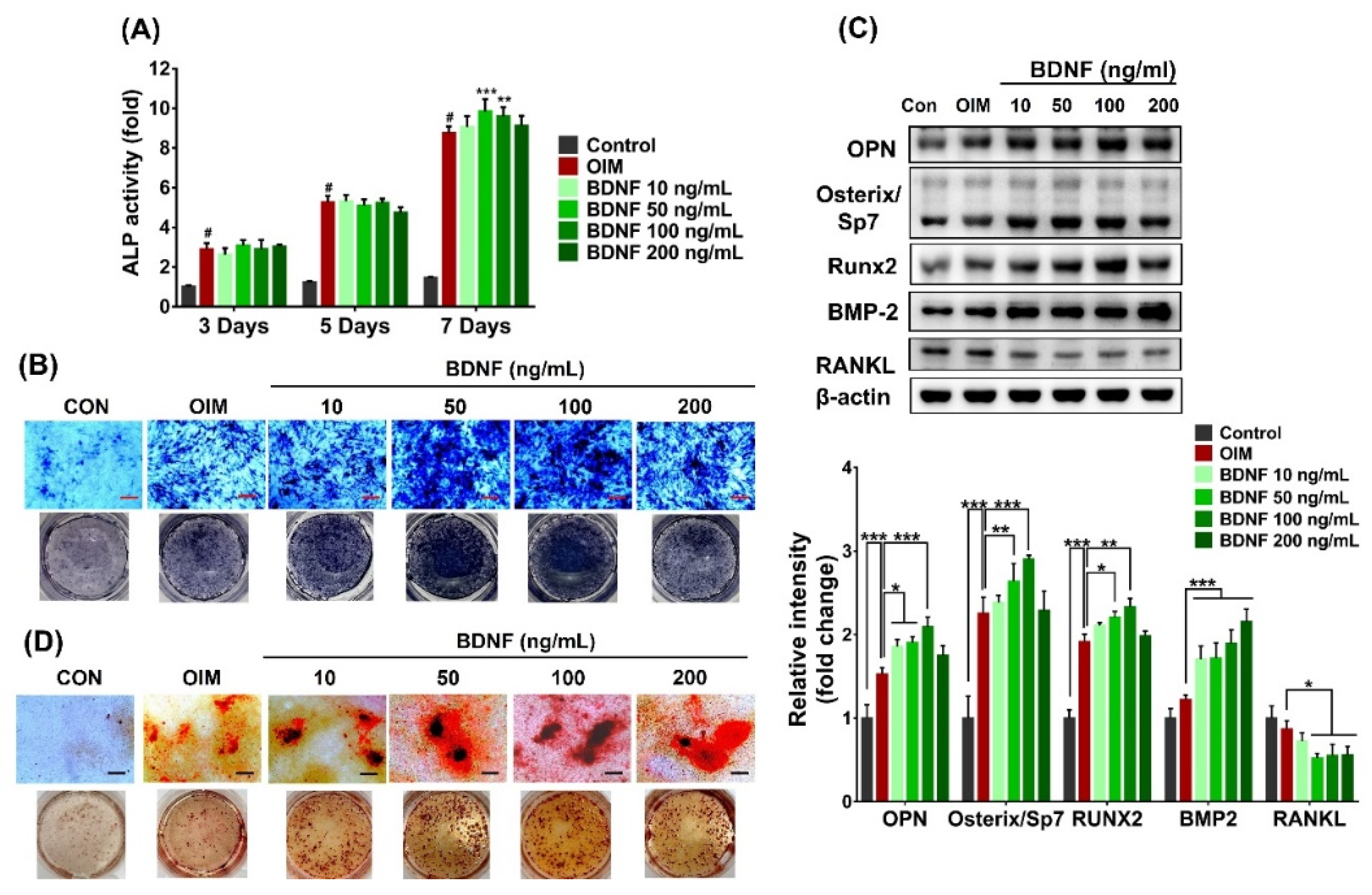
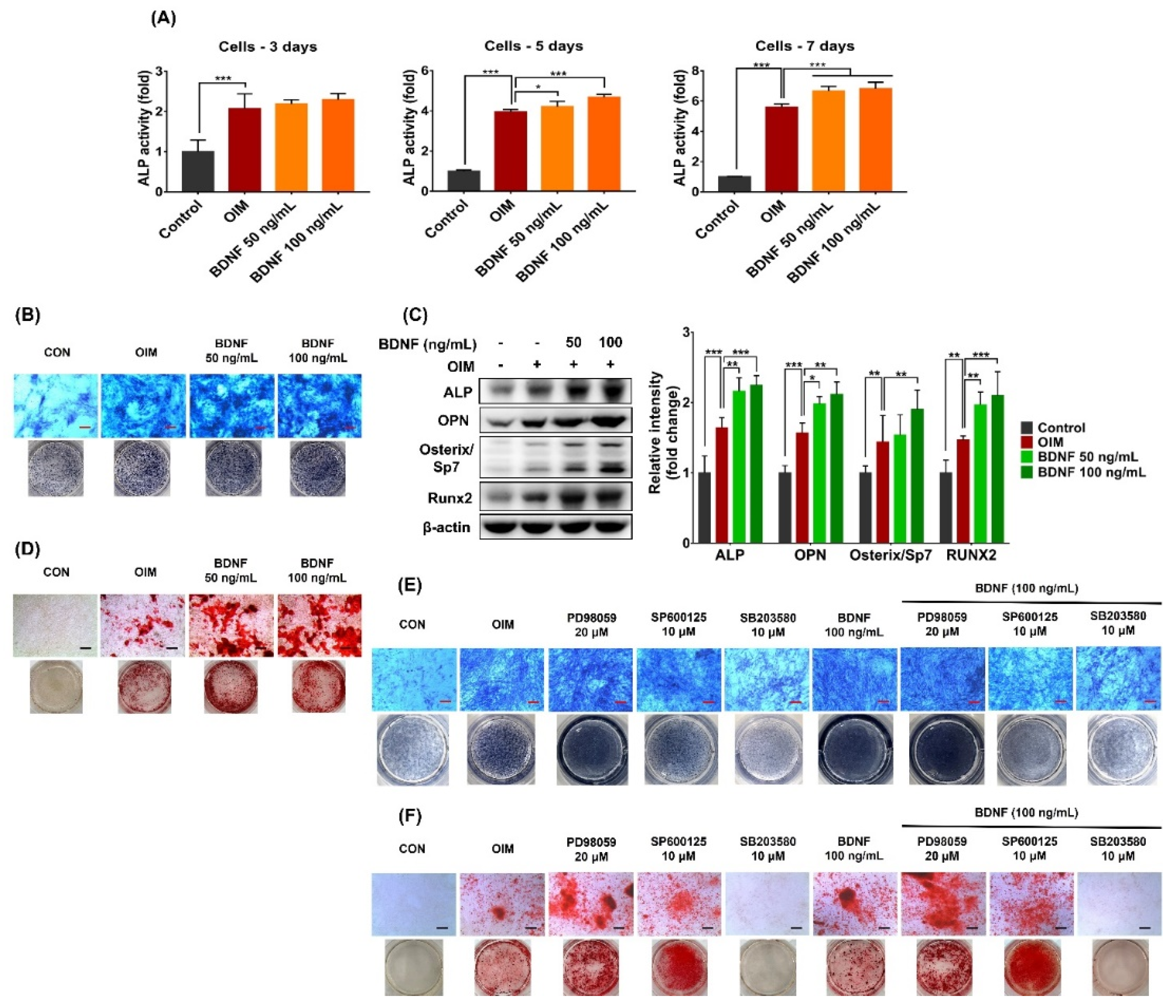
ALP plays an important role in the mineralization of newly formed bone and increases during cell proliferation and differentiation. Thus, ALP assay is widely used to screen bioactive compounds on bone formation. Firstly, the effect of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells was analyzed by measuring ALP activity, which is a marker for the early and middle stages of osteoblastic differentiation. Results showed that BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) did not produce a significant effect on ALP activity after 3 and 5 days of treatment. However, when compared to OIM group, BDNF significantly increased the ALP level at day 7. Of the tested concentrations, the highest effect on ALP activity was observed following the 50 and 100 ng/mL of BDNF treatment, whereas ALP activity was reduced at 200 ng/mL BDNF (
Figure 2A). These results were confirmed by ALP staining, which showed high ALP-stained levels in BDNF-treated groups (
Figure 2B). In addition, BDNF treatment also increased the expression of osteogenesis-related markers, such as osteopontin (OPN), osterix/Sp7, bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2), and runt-related protein 2 (Runx2), but reduced the level of RANKL (
Figure 2C).
Calcium deposition in the extracellular matrix is a phenotypic marker of the final stages of osteoblast differentiation. Therefore, to evaluate whether BDNF induces calcium accumulation, ST-2 cells were incubated with various concentrations of BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) for 21 days and subjected to Alizarin red S staining assay. Results showed that calcium accumulation was considerably increased by BDNF treatment at concentrations ranging from 10-200 ng/mL. Treatment with 100 ng/mL BDNF showed the highest calcium accumulation was observed in 100 ng/mL BDNF, while calcium deposition was slightly reduced by the treatment of 200 ng/mL BDNF (
Figure 2D).
3.3. Effect of BDNF on the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signaling Pathways in ST-2 Cells
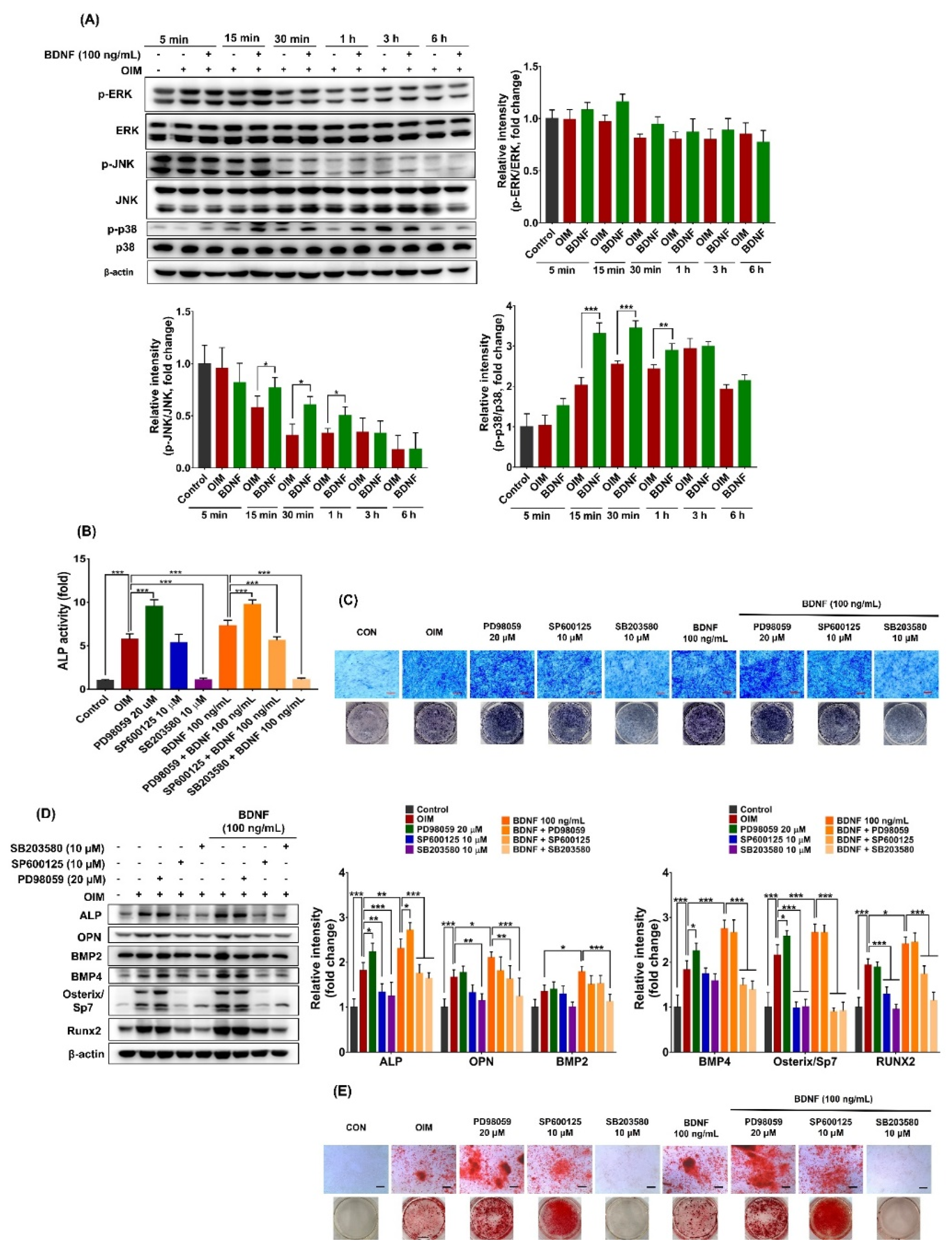
To investigate the effect of BDNF on MAPK signaling pathways in bone marrow stromal cells, the activation of MAPKs, including extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK, was examined. As shown in
Figure 3A, BDNF (100 ng/mL) treatment significantly activated JNK and p38 MAPK, and slightly induced ERK from 15 min to 1 h, as evidenced by increased their phosphorylation. The phosphorylated levels of ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK did not change after 3-6 h of BDNF treatment.
To further investigate whether MAPKs are involved in BDNF-induced osteoblast differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells, the effects of specific MAPK inhibitors, including PD98059 (ERK inhibitor), SP600125 (JNK inhibitor), and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor), in the presence and absence of BDNF (100 ng/mL) on osteoblast differentiation in ST-2 cells were examined. As shown in
Figure 3B,C, the ERK inhibitor (PD98059) highly increased ALP activity, whereas the p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) remarkably reduced ALP activity both in OIM- and in BDNF-treated ST-2 cells. Additionally, the JNK inhibitor (SP600125) was unlikely to affect ALP activity in OIM-treated ST-2 cells but partially reversed the effect of BDNF. Furthermore, BDNF-induced increases in ALP, OPN, BMP2, BMP4, Osterix/Sp7, and Runx2 protein expression were obviously decreased by the JNK and p38 MAPK inhibitors. The effect of the p38 MAPK inhibitor was greater than that of the JNK inhibitor. In contrast, the ERK inhibitor did not affect BDNF-induced gene expression (
Figure 3D). Moreover, BDNF-induced calcium deposition was strongly inhibited by the p38 MAPK inhibitor, whereas the JNK inhibitor did not affect the matrix mineralization (
Figure 3E). These findings suggest that BDNF stimulates osteoblast differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells mainly through p38 MAPK and at least in part via JNK signaling pathways.
3.4. TrkB Suppression Reduces BDNF-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation
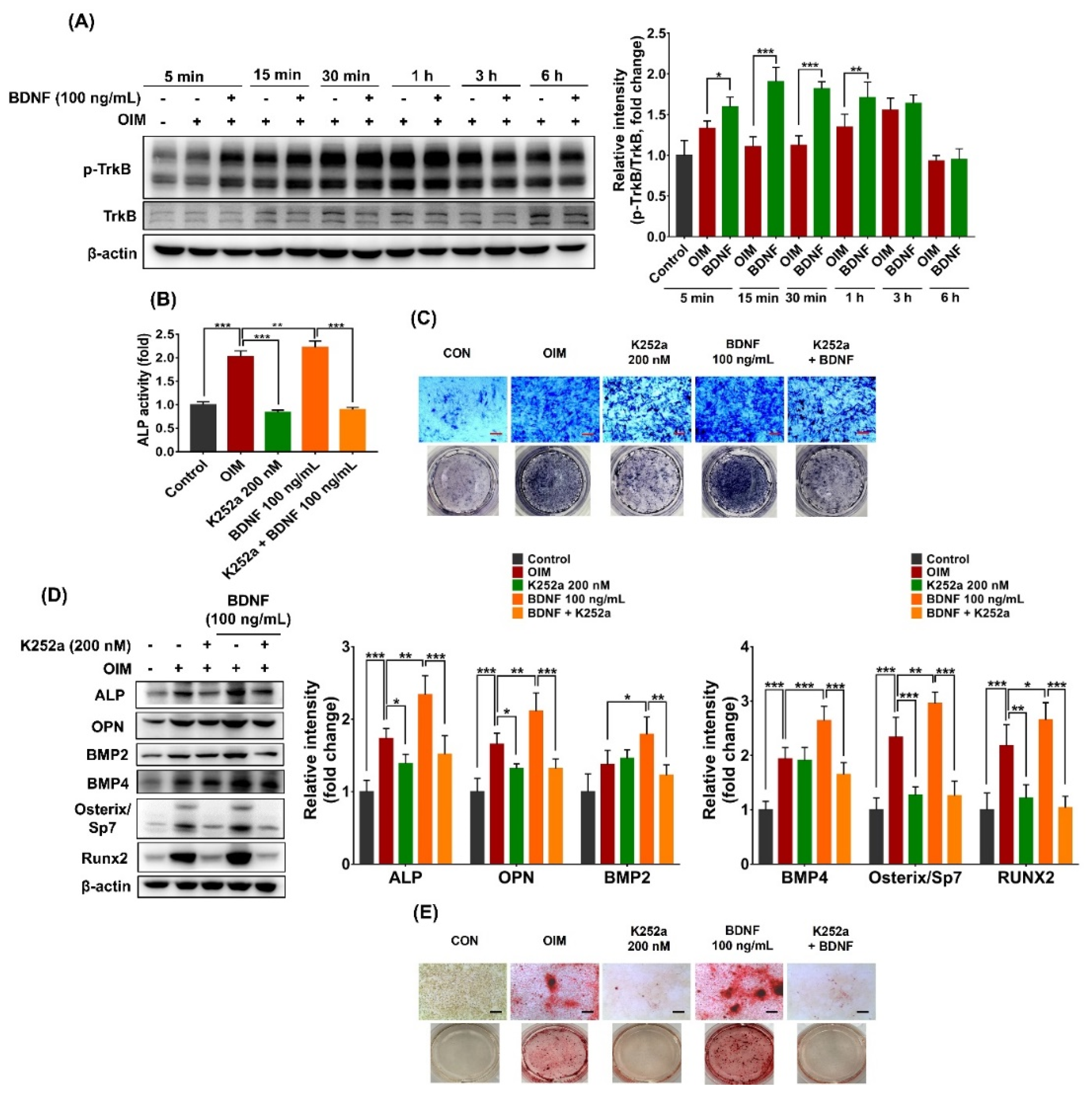
To examine whether BDNF could activate TrkB receptor in bone marrow stromal cells, ST-2 cells were treated with BDNF (100 ng/mL), and the phosphorylation of TrkB was determined at various indicated times. As shown in
Figure 4A, BDNF rapidly activated TrkB receptor in bone marrow stromal cell, as indicated by increased protein phosphorylation after 5 min of treatment. The activation of the TrkB receptor continuously remained until 1 h and gradually reduced after 3 h of BDNF treatment.
To understand the role of TrkB receptor in BDNF-induced osteogenesis, the effects of TrkB receptor inhibitor (K252a) in the presence and absence of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation of ST-2 cells were examined. Results showed that the TrkB receptor inhibitor (K252a) significantly reversed the effect of BDNF on ALP activity (
Figure 4B,C). In addition, K252a considerably reduced the expression of osteogenic markers, such as ALP, OPN, BMP2, BMP4, Osterix/Sp7, and Runx2, in the BDNF-treated ST-2 cells (
Figure 4D). Furthermore, BDNF-promoted calcium accumulation was remarkably inhibited in the presence of TrkB receptor inhibitor (
Figure 4E). These results suggest that BDNF promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through TrkB receptor activation.
3.5. Effect of BDNF on the Osteogenic Differentiation in the Co-Culture System of Osteoblasts and Bone Marrow Stromal Cells
Bone modeling is regulated by the interaction of various cell types, among them, osteoblasts and bone marrow stromal cells can communicate with each other during bone formation. Thus, the effect of BDNF on osteogenic differentiation under the more closely physiological conditions of MC3T3-E1 and ST-2 co-culture system was examined. BDNF (50 and 100 ng/mL) significantly increased the ALP activity in co-culture system after 5 and 7 days of treatment (
Figure 5A,B). In addition, the protein expressions of osteogenic markers, including ALP, OPN, osterix/Sp7, and Runx2 were upregulated by BDNF treatment (
Figure 5C). Furthermore, BDNF enhanced matrix mineralization in co-culture system, as indicated by increased levels of calcium deposition (
Figure 5D)
To further evaluate whether MAPKs plays a role in BDNF-induced osteogenic differentiation in co-culture system, the effects of PD98059 (ERK inhibitor), SP600125 (JNK inhibitor), and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) in the presence and absence of BDNF (100 ng/mL) on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 and ST2 co-culture system were examined. ALP staining showed that ERK inhibitor strongly enhanced ALP levels both in OIM- and in BDNF-treated groups after 5 days of treatment. In contrast, BDNF-induced ALP levels in co-culture system were attenuated by the JNK and p38 MAPK inhibitors (
Figure 5E). Similarly, p38 MAPK inhibitor strongly inhibited BDNF-induced calcium deposition, whereas ERK inhibitor enhanced this event in co-culture system. BDNF-induced calcium accumulation was partially prevented following treatment with JNK inhibitor (
Figure 5F). These findings support the above observations that BDNF promotes osteoblast differentiation mainly through p38 MAPK and partially via JNK signaling pathway.
3.6. BDNF Prevents Bone Loss in OVX-Induced Rats
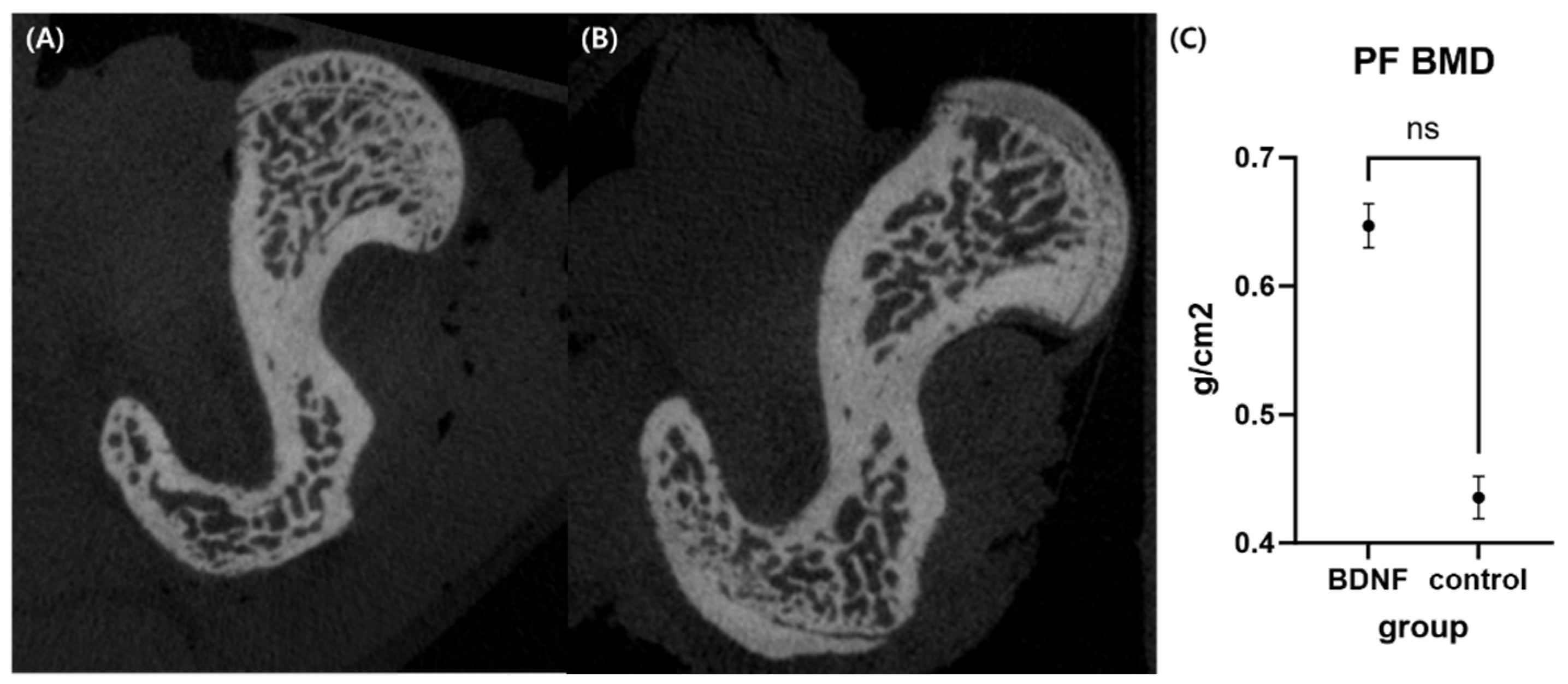
3.6.1. Micro-Computed Tomography
Micro-CT analysis showed that BMD of the BDNF group was higher compared to control group but statistically not significant. (
Figure 6)
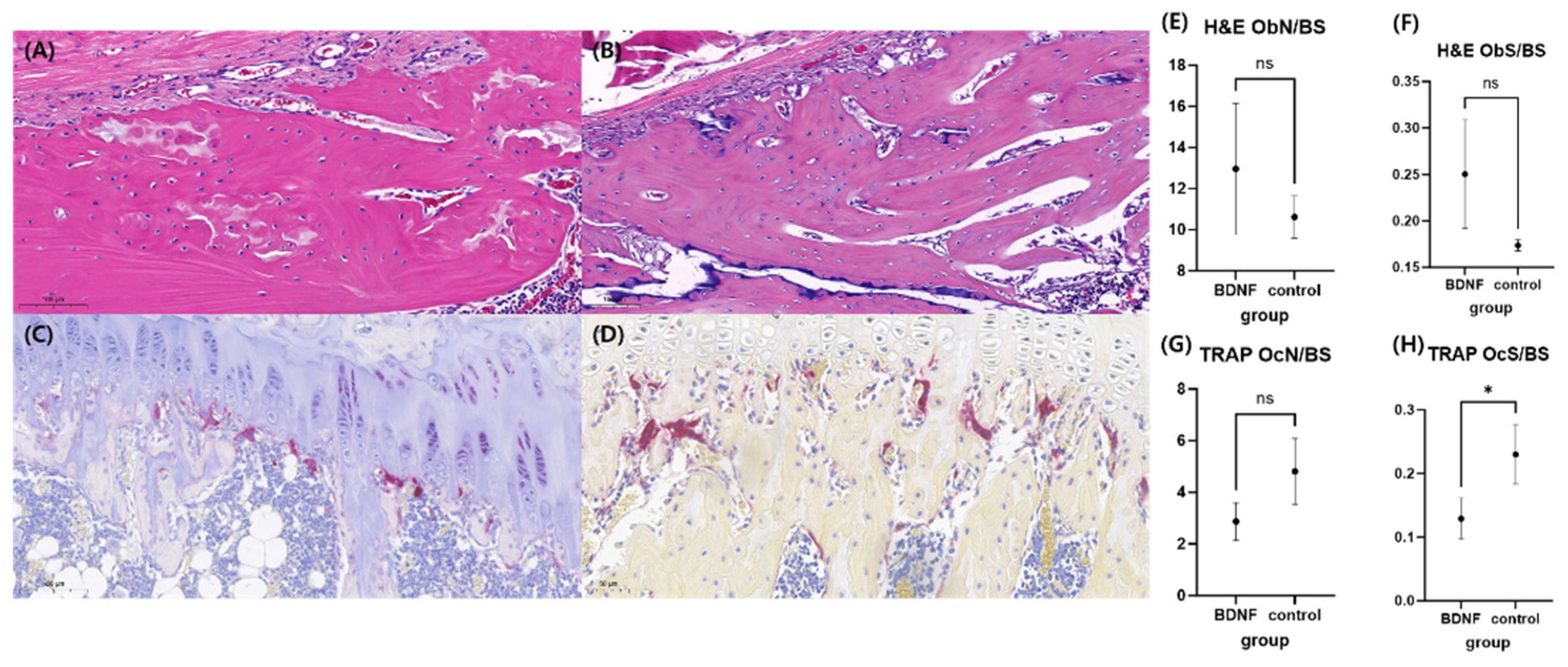
3.6.2. Histomorphometry Analysis
In HE stain, the osteoblast surface/bone surface ratio was higher in BDNF compared to control group, however, did not show statistical significance. In TRAP stain, BDNF showed significant lower osteoclast surface/bone surface ratio compared to control group. (
Figure 7)
4. Discussion
Due to the rapid aging population worldwide, osteoporosis has become a critical public health issue, affecting millions of people, especially the elderly and postmenopausal women.5 Its pathological process is complex and current mainstream treatment options have limitations. Thus, an urgent need is to identify safe anabolic agents that can effectively promote bone formation on a long-term basis to compensate for increased bone resorption and to improve bone mass in patients of osteoporosis. Recent studies have showed that numerous neurotransmitters, such as substance P, nerve growth factor, BDNF, neurotrophin 3 (NT-3), neurotrophin 4 (NT-4) are implicated in bone formation and fracture healing.24-26 Among them, BDNF, belonging to the family of neurotrophins, has attracted great attention due to its extensive bioactivity.15,16,18,19
Recently, BDNF have been reported to stimulate osteoblast differentiation of osteoblast-linage cell MC3T3-E1 and human bone mesenchymal stem cells, and enhance the expression of osteogenesis-related markers, such as ALP and osteocalcin.18,27 BDNF also upregulates the expression of bone/cementum-related proteins, including ALP, OPN, and BMP-2 in cementoblasts.28 However, the effects of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells and osteoporotic conditions, as well as its detailed mechanisms have not been fully investigated. In this study, we focused on the investigating effects of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation in stromal cells and co-culture system and associated bone formation signaling via MAPKs and TrkB receptor. We found that BDNF promoted osteoblast differentiation via the activation of TrkB receptor along with the JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Moreover, BDNF provided a protective effect against bone loss by enhancing bone mineral density, bone microarchitecture, and osteoblast number, as well as improving bone turnover rate in ovariectomized rats.
Bone marrow stromal cells, non-hematopoietic multipotent cells capable of differentiating into mesodermal cell types such as osteoblast and adipocytes, plays an important role in the normal development of bone.29 Osteoporosis occurrence may be associated with the imbalance of bone marrow stromal cells, which differentiate toward adipocytes instead of osteoblastic fate.30 Osteoblasts stemmed from bone marrow stromal cells experience a precise program of gene expression to regulate physiological processes, including osteoblastic commitment, proliferation, and terminal differentiation.31 In this study, BDNF did not affect the proliferation of ST-2 cell. This finding is in the line with previous studies that BDNF had no proliferative effect of human bone mesenchymal stem cells,27 as well as MC3T3-E1 osteoblast.18 In contrast, BDNF has been found to enhance the proliferation of MLO-Y4 osteocytes.32 Taken together, these observations reveal that the effects of BDNF on proliferation vary with the tested cell line.
Although BDNF did not change ST-2 cell proliferation, it obviously induced the osteoblast differentiation and maturation processes. BDNF treatment significantly increased ALP activity, a marker of early phase of osteoblast differentiation.31 Moreover, BDNF considerably increased the matrix mineralization, as indicated by increased level of calcium deposition. These findings suggest that BDNF has positive effects on osteoblast differentiation through enhanced cellular differentiation and mineralization in bone marrow-derived stromal cells, without affecting cell proliferation.
During the osteoblast differentiation and mineralization of bone marrow-derived stromal cells, these cells drive a program of gene expression governed by various transcription factors.33 Runx2 is regarded as the master transcription factor that promotes differentiation of mesenchymal progenitors into osteoblasts by regulating the expression of osteogenesis-related genes at the early stage of osteoblastic differentiation, such as ALP, collagen alpha 1 type I, and osteocalcin.31,34 Osterix/Sp7 plays a crucial role at the later step in the osteoblast differentiation process, that is, the differentiation of pre-osteoblast into mature osteoblast and osteocytes.1 In this study, BDNF significantly increased Runx2 and Osterix/Sp7 expression in ST-2 cells and co-culture system, implying that BDNF is able to promote osteogenesis in bone marrow stromal cells throughout all phases of osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Bone morphogenetic proteins, multi-functional factors that belong to the transforming growth factor beta superfamily, also plays important role in the osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and bone formation by targeting Runx2 expression.35 BMP2 expression was enhanced by BDNF treatment in ST-2 cells and co-culture system. In addition, BDNF simultaneously increased OPG expression and reduced RANKL level, suggesting that BDNF promotes osteogenic bone formation via elevating OPG/RANKL ratio. OPG, produced by osteoblasts as well as osteocytes, play a suppressive role in RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis.36 Thus, the OPG/RANKL ratio may be considered as an ultimate determinant of bone integrity and reflect the balance between bone formation and resorption.37
To gain further insights into the mechanisms of BDNF in promoting osteogenic differentiation, we first examined the MAPK signaling molecules. The ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways are believed to be associated with osteoblast differentiation.38-40 It has been reported that ERK signaling is required for osteoblast differentiation and osteogenic marker genes induction in human bone mesenchymal stem cells.27 In addition, ERK is involved in BDNF-induced vascular endothelial growth factor in rat osteoblasts.41 In contrast, BDNF was found to induce Akt signal but did not affect ERK signal during mouse MC3T3-E1 osteoblast differentiation.18 This study observed that BDNF activated JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, but not ERK, during osteoblast differentiation in ST-2 cells. Discrepancy of these results may be due to the different cell lines used in the experiment, and effect of BDNF varies with tested cell line. Furthermore, JNK and p38 MAPK inhibitors diminished BDNF-induced osteoblast differentiation both in ST-2 cells and co-culture system. Our results demonstrated that JNK and p38 MAPK inhibitors, but not ERK inhibitor, abolished the effects of BDNF on ALP activity and expression of osteogenesis-related markers, such as ALP, OPN, BMP2/4, Runx2, and Osterix/Sp7. The p38 MAPK inhibitor appeared to be more effective in suppressing BDNF-induced osteoblast differentiation and matrix mineralization than JNK inhibitors. Taken together, these findings indicate that BDNF-induced osteogenesis is mediated mainly by p38 MAPK and partially via JNK signaling pathways.
Accumulating evidence has indicated that effect of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation may be related to its receptor TrkB.19,27,29,41 Both BDNF and its TrkB receptor are required at various stages of the bone formation process and associated with fracture healing.19,29 In this study, we found that BDNF treatment early activated TrkB receptor in bone marrow-derived stomal cells. Furthermore, osteoblast differentiation was significantly reduced in the presence of TrkB inhibitor. The suppression of TrkB receptor significantly reduced BDNF-induced ALP activity as well as expression of osteogenesis-related markers, such as ALP, OPN, BMP2/4, Runx2, Osterix/Sp7. In addition, BDNF-induced matrix mineralization was prevented by TrkB inhibitor. These findings suggest that TrkB receptor is required for BDNF-mediated osteogenesis in bone marrow-derived stromal cells.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that BDNF promotes osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in bone marrow-derived stromal cells. BDNF-induced osteogenesis is mediated mostly by TrkB receptor via JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Moreover, BDNF also provides an effectively protective effect against ovariectomy-induced bone loss. The positive influence of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells may, at least in part, contribute to its protective effect on bone loss in ovariectomized rats. These results provide evidence to extend and complement many of existing information for the therapeutic potential of BDNF for prevention and/or treatment of osteoporosis in estrogen-deficient conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.M and W.J.; methodology, V.T., W.J., and W.M.; software, V.T. and E.J.P; validation, E.J.P., W.M., and W.J.; formal analysis, V.T. and E.J.P.; investigation, E.J.P., V.T., W.J., and W.M.; resources, X.X.; data curation, E.J.P. and V.T.; writing—original draft preparation, V.T.; writing—review and editing, E.J.P. and V.T.; visualization, V.T.; supervision, W.J. and W.M.; project administration, W.J. and W.M.; funding acquisition, W.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and APC were funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea. (Grant number 2021R1A2C2012475).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Kyungpook National University (Protocol No. KNU 2022-0154, approved May 30th, 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to privacy/ethical restriction.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Hye-Bin Yeo, RN, for the organization and preparation of the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xue, F.; Zhao, Z.; Gu, Y.; Han, J.; Ye, K.; Zhang, Y. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone modulates bone formation and resorption and ameliorates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. eLife 2021, 10, e64872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Peng, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.C.; Wang, H.B. Anemonin Attenuates RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis and Ameliorates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Bone Loss in Mice via Modulation of NFATc1. Front Pharmacol 2020, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.Z.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.C.; Chen, T.P. Pentraxin 3 promotes the osteoblastic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biosci Rep 2020, 40, BSR20201165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Xiao, D.; Weng, J.; Xiong, A.; Kang, B.; Zeng, H. Berberine promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett 2016, 240, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sözen, T.; Özışık, L.; Başaran, N. An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol 2017, 4, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerosa, L.; Lombardi, G. Bone-to-Brain: A Round Trip in the Adaptation to Mechanical Stimuli. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 623893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.Q.; Qin, W.P.; Ma, Y.X.; Shen, M.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.B.; Chen, J.H.; Tay, F.R.; Niu, L.N.; Jiao, K. Crosstalk between Bone and Nerves within Bone. Adv Sci 2021, 8, 2003390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elefteriou, F. Regulation of bone remodeling by the central and peripheral nervous system. Arch Biochem Biophys 2008, 473, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Jin, D.; Wu, J.Q.; Xu, Z.Y.; Fu, S.; Mei, G.; Zou, Z.L.; Ma, S.H. Neuropeptide Y stimulates osteoblastic differentiation and VEGF expression of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells related to canonical Wnt signaling activating in vitro. Neuropeptides 2016, 56, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; Jin, H.K.; Min, W.K.; Lee, W.W.; Lee, J.E.; Akiyama, H.; Herzog, H.; Enikolopov, G.N.; Schuchman, E.H.; Bae, J.S. Neuropeptide Y regulates the hematopoietic stem cell microenvironment and prevents nerve injury in the bone marrow. EMBO J 2015, 34, 1648–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Chai, J.; Zhang, S.; Ding, L.; Yan, P.; Du, W.; Yang, Z. CGRP may regulate bone metabolism through stimulating osteoblast differentiation and inhibiting osteoclast formation. Mol Med Rep 2016, 13, 3977–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Mei, G.; Wang, Z.; Zou, Z.L.; Liu, S.; Pei, G.X.; Bi, L.; Jin, D. Neuropeptide Substance P Improves Osteoblastic and Angiogenic Differentiation Capacity of Bone Marrow Stem Cells In Vitro. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014, 596023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelt, J.; Baranowsky, A.; Jahn, D.; Yorgan, T.; Köhli, P.; Otto, E.; Farahani, S.K.; Graef, F.; Fuchs, M.; Herrera, A.; et al. The neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide alpha is essential for bone healing. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaumi, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Asahara, H.; Inoue, H.; Takigawa, M. Expression of neurotrophins and their receptors (TRK) during fracture healing. Bone 2000, 26, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, D.; Klang, A.; Thams, S.; Rostami, E. The Role of BDNF in Experimental and Clinical Traumatic Brain Injury. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliciano, D.P.; Sahbaie, P.; Shi, X.; Klukinov, M.; Clark, J.D.; Yeomans, D.C. Nociceptive sensitization and BDNF up-regulation in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Neurosci Lett 2014, 583, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failla, M.D.; Conley, Y.P.; Wagner, A.K. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Traumatic Brain Injury–Related Mortality: Interrelationships Between Genetics and Acute Systemic and Central Nervous System BDNF Profiles. Neurorehabilit Neural Repair 2015, 30, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida-Yonemochi, H.; Yamada, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Seo, K. Locally Produced BDNF Promotes Sclerotic Change in Alveolar Bone after Nerve Injury. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0169201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, O.; Hartmann, S.; Dongowski, N.; Karnati, S.; Baumgart-Vogt, E.; Härtel, F.V.; Noll, T.; Schnettler, R.; Lips, K.S. BDNF and its TrkB receptor in human fracture healing. Ann Anat 2014, 196, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, F.; Qin, D.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Song, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. The role of brain derived neurotrophic factor in central nervous system. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 986443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front Cell Neurosci 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauschke, V.; Gebert, A.; Calin, M.; Eckert, J.; Scheich, S.; Heiss, C.; Lips, K.S. Effects of new beta-type Ti-40Nb implant materials, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, acetylcholine and nicotine on human mesenchymal stem cells of osteoporotic and non osteoporotic donors. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0193468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Lin, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, S.; Fu, D. Long non-coding RNA BDNF-AS modulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem 2018, 445, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouxsein, M.L.; Boyd, S.K.; Christiansen, B.A.; Guldberg, R.E.; Jepsen, K.J.; Muller, R. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res 2010, 25, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, J.; Park, J.S.; Hwang, D.Y.; Son, Y.; Hong, H.S. Substance P blocks ovariectomy-induced bone loss by modulating inflammation and potentiating stem cell function. Aging 2020, 12, 20753–20777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Kuo, L.T.; Luh, H.T. The Roles of Neurotrophins in Traumatic Brain Injury. Life 2022, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.W.; Zhou, X.F.; Foster, B.K.; Grills, B.L.; Xu, J.; Xian, C.J. Roles of neurotrophins in skeletal tissue formation and healing. J Cell Physiol 2018, 233, 2133–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lei, L.; Yu, T.; Jiang, T.; Kang, Y. Effect of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor on the Neurogenesis and Osteogenesis in Bone Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A 2018, 24, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiya, M.; Shiba, H.; Fujita, T.; Ouhara, K.; Takeda, K.; Mizuno, N.; Kawaguchi, H.; Kitagawa, M.; Takata, T.; Tsuji, K.; Kurihara, H. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Stimulates Bone/Cementum-related Protein Gene Expression in Cementoblasts. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 16259–16267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Adams, J.; Pacifici, R.; Ye, K. A TrkB agonist prodrug prevents bone loss via inhibiting asparagine endopeptidase and increasing osteoprotegerin. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tencerova, M.; Kassem, M. The Bone Marrow-Derived Stromal Cells: Commitment and Regulation of Adipogenesis. Front Endocrinol 2016, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantikanlayaporn, D.; Wichit, P.; Suksen, K.; Suksamrarn, A.; Piyachaturawat, P. Andrographolide modulates OPG/RANKL axis to promote osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells and protects bone loss during estrogen deficiency in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2020, 131, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loy, T.L.; Vehlow, D.; Kauschke, V.; Muller, M.; Heiss, C.; Lips, K.S. Effects of BDNF and PEC Nanoparticles on Osteocytes. Molecules 2020, 25, 4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.D.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Westendorf, J.J. Regulation of gene expression in osteoblasts. BioFactors 2010, 36, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Yoon, D.S.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.W. Zinc Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Via Activation of the cAMP-PKA-CREB Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells Dev 2018, 27, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Qin, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhou, L.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.; Ye, L.; Yue, S.; Zheng, Q.; Li, D. Astragalin Promotes Osteoblastic Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells and Bone Formation in vivo. Front Endocrinol 2019, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, B.F.; Xing, L. Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys 2008, 473, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcadet, L.; Bouredji, Z.; Argaw, A.; Frenette, J. The Roles of RANK/RANKL/OPG in Cardiac, Skeletal, and Smooth Muscles in Health and Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 903657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, M.B.; Shim, J.H.; Glimcher, L.H. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways in Osteoblasts. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2013, 29, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Kang, H.J.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, J. Fucoidan promotes osteoblast differentiation via JNK- and ERK-dependent BMP2–Smad 1/5/8 signaling in human mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Mol Med 2015, 47, e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carballo, E.; Gámez, B.; Ventura, F. p38 MAPK Signaling in Osteoblast Differentiation. Front Cell Dev Biol 2016, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, H.; Qiu, X.; Xiong, J.; Chen, Y. BDNF regulates the expression and secretion of VEGF from osteoblasts via the TrkB/ERK1/2 signaling pathway during fracture healing. Mol Med Rep 2017, 15, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Effect of BDNF on proliferation of bone marrow-derived stromal ST-2 cells. The cells were treated with various concentrations of BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) for 1 and 3 days. The cell proliferation was measured using the CCK-8 assay kit. Results are presented as percentage of the control. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments.
Figure 1.
Effect of BDNF on proliferation of bone marrow-derived stromal ST-2 cells. The cells were treated with various concentrations of BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) for 1 and 3 days. The cell proliferation was measured using the CCK-8 assay kit. Results are presented as percentage of the control. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments.
Figure 2.
Effect of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation in ST-2 cell. The cells were treated with BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) in osteogenic induction medium (OIM) for 3, 5, 7, or 21 days. (A) ALP activity on days 3, 5, and 7. (B) ALP staining on day 7. (C) Protein expressions of OPN, Osterix/Sp7, Runx2, BMP-2, and RANKL on day 7. (D) Calcium deposition on day 21. Scale bar = 400 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. The values of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant differences.
Figure 2.
Effect of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation in ST-2 cell. The cells were treated with BDNF (10-200 ng/mL) in osteogenic induction medium (OIM) for 3, 5, 7, or 21 days. (A) ALP activity on days 3, 5, and 7. (B) ALP staining on day 7. (C) Protein expressions of OPN, Osterix/Sp7, Runx2, BMP-2, and RANKL on day 7. (D) Calcium deposition on day 21. Scale bar = 400 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. The values of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant differences.
Figure 3.
Involvement of MAPK signaling pathways in BDNF-induced osteoblast differentiation in ST-2 cells. (A) The cells were treated with BDNF (100 ng/mL) in OIM for 5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 3 h, and 6 h and protein expressions of p-ERK, ERK, p-JNK, JNK, p-p38 MAPK, and MAPK were determined by western blot. (B-D) The cells were treated with PD98059 (ERK inhibitor, 20 µM), SP600125 (JNK inhibitor, 10 µM), and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor, 10 µM) in the presence and absence of BDNF (100 ng/mL) for 7 or 21 days. (B) ALP activity on day 7. (C) ALP staining on day 7. (D) Protein expressions of osteogenic markers, including ALP, OPN, BMP2, BMP4, Osterix/Sp7, and Runx2 on day 7. (E) Calcium deposition on day 21. Scale bar = 400 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. The values of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant differences.
Figure 3.
Involvement of MAPK signaling pathways in BDNF-induced osteoblast differentiation in ST-2 cells. (A) The cells were treated with BDNF (100 ng/mL) in OIM for 5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 3 h, and 6 h and protein expressions of p-ERK, ERK, p-JNK, JNK, p-p38 MAPK, and MAPK were determined by western blot. (B-D) The cells were treated with PD98059 (ERK inhibitor, 20 µM), SP600125 (JNK inhibitor, 10 µM), and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor, 10 µM) in the presence and absence of BDNF (100 ng/mL) for 7 or 21 days. (B) ALP activity on day 7. (C) ALP staining on day 7. (D) Protein expressions of osteogenic markers, including ALP, OPN, BMP2, BMP4, Osterix/Sp7, and Runx2 on day 7. (E) Calcium deposition on day 21. Scale bar = 400 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. The values of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant differences.
Figure 4.
Involvement of TrkB receptor in BDNF-induced osteoblast differentiation in ST-2 cells. (A) The cells were treated with BDNF (100 ng/mL) in OIM for 5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 3 h, and 6 h and protein expressions of p-TrkB and TrkB were determined by western blot. (B-D) The cells were treated with K252a (TrkB inhibitor, 200 nM) in the presence and absence of BDNF (100 ng/mL) for 3, 5, 7 or 21 days. (B) ALP activity on day 3, 5, and 7. (C) ALP staining on day 7. (D) Protein expressions of osteogenic markers, including ALP, OPN, BMP2, BMP4, Osterix/Sp7, and Runx2 on day 7. (E) Calcium deposition on day 21. Scale bar = 400 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. The values of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant differences.
Figure 4.
Involvement of TrkB receptor in BDNF-induced osteoblast differentiation in ST-2 cells. (A) The cells were treated with BDNF (100 ng/mL) in OIM for 5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 3 h, and 6 h and protein expressions of p-TrkB and TrkB were determined by western blot. (B-D) The cells were treated with K252a (TrkB inhibitor, 200 nM) in the presence and absence of BDNF (100 ng/mL) for 3, 5, 7 or 21 days. (B) ALP activity on day 3, 5, and 7. (C) ALP staining on day 7. (D) Protein expressions of osteogenic markers, including ALP, OPN, BMP2, BMP4, Osterix/Sp7, and Runx2 on day 7. (E) Calcium deposition on day 21. Scale bar = 400 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. The values of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant differences.
Figure 5.
Effect of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation in co-culture system of ST-2 and MC3T3-E1 cells. (A-D) The co-culture systems were treated BDNF (50 or 100 ng/mL) for 3, 5, 7, or 21 days. (A) ALP activity on day 3, 5, and 7. (B) ALP staining on day 5. (C) Protein expressions of ALP, OPN, BMP2, and Runx2 on day 5. (D) Calcium deposition on day 21. (E-F) The co-culture systems were treated with PD98059 (ERK inhibitor, 20 µM), SP600125 (JNK inhibitor, 10 µM), and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor, 10 µM) in the presence and absence of BDNF (100 ng/mL) for 5 or 21 days. (E) ALP staining on day 5. (F) Calcium deposition on day 21. Scale bar = 400 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. The values of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant differences.
Figure 5.
Effect of BDNF on osteoblast differentiation in co-culture system of ST-2 and MC3T3-E1 cells. (A-D) The co-culture systems were treated BDNF (50 or 100 ng/mL) for 3, 5, 7, or 21 days. (A) ALP activity on day 3, 5, and 7. (B) ALP staining on day 5. (C) Protein expressions of ALP, OPN, BMP2, and Runx2 on day 5. (D) Calcium deposition on day 21. (E-F) The co-culture systems were treated with PD98059 (ERK inhibitor, 20 µM), SP600125 (JNK inhibitor, 10 µM), and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor, 10 µM) in the presence and absence of BDNF (100 ng/mL) for 5 or 21 days. (E) ALP staining on day 5. (F) Calcium deposition on day 21. Scale bar = 400 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. The values of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 are considered as statistically significant differences.
Figure 6.
Micro-CT analysis. (A-B) axial cut of proximal femur of BDNF and control group. (C) Comparison of bone mineral density between BDNF and control group.
Figure 6.
Micro-CT analysis. (A-B) axial cut of proximal femur of BDNF and control group. (C) Comparison of bone mineral density between BDNF and control group.
Figure 7.
Histologic analysis. (A) HE stain in BDNF group. (B) HE stain in control group. (C) TRAP stain in BDNF group. (D) TRAP stain in control group. (E-F) Comparison of osteoblast number/bone surface ratio and osteoblast surface/bone surface ratio between BDNF and control group. (G-H) Comparison of osteoclast number/bone surface ratio and osteoclast surface/bone surface ratio between BDNF and control group.
Figure 7.
Histologic analysis. (A) HE stain in BDNF group. (B) HE stain in control group. (C) TRAP stain in BDNF group. (D) TRAP stain in control group. (E-F) Comparison of osteoblast number/bone surface ratio and osteoblast surface/bone surface ratio between BDNF and control group. (G-H) Comparison of osteoclast number/bone surface ratio and osteoclast surface/bone surface ratio between BDNF and control group.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).