1. Introduction
Urothelial carcinomas are the 11th most common cancers in developed countries [
1,
2]. Upper tract urothelial carcinoma constitutes a relatively uncommon subset of urothelial carcinoma, making up 5-10% of all cases of urothelial carcinoma, and being three times more common in men compared to women. Among upper tract urothelial carcinoma, pyelocaliceal tumours are twice as prevalent as ureteral tumours. Concurrent bladder tumours are identified in 17% of individuals with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Notably, bladder recurrence after upper tract urothelial carcinoma is prevalent, manifesting in 22-47% of patients, while contralateral upper tract recurrence is less frequent, occurring in only 2-6% of cases [
3,
4,
5,
6]. The most common symptoms in patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma are haematuria (70-80%) followed by flank pain (20-30%) [
7,
8,
9], and rarely with presentation of a lumbar mass, occurring 10%-20% of patients. As such, approximately half of the patients are asymptomatic at presentation [
10] and may become only apparent in case of symptoms due to locally advanced disease symptoms such as malaise and fatigue [
10,
11,
12,
13].
On the other hand, upper tract recurrence following radical cystectomy for a primary bladder urothelial carcinoma is deemed rare, with an incidence ranging from 0.8% - 6.4% occurring 24-36 months postoperatively [
14,
15,
16]. Established risk factors are carcinoma in situ at radical cystectomy, tumour multifocality and history of multifocal bladder urothelial carcinoma, a prior history of upper tract urothelial carcinoma prior to radical cystectomy and a positive ureteral or urethral margin [
14,
15,
17].
Diagnosis of primary upper tract urothelial carcinoma is challenging and based on mainly invasive procedures. Bladder urinary cytology has a relatively low sensitivity for the diagnosis of upper tract urothelial carcinoma and has no role in the diagnosis of upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Invasive procedures such as selective cytology from the upper urinary tract show a sensitivity of 70-75% for high grade upper tract urothelial carcinoma [
18]. To date, numerous other molecular biomarkers in the setting of upper tract urothelial carcinoma are under investigation. Biomarkers currently being under investigation are circulating tumour cells, circulating tumour DNA and exfoliated cells in urine, as well as proteins, mRNAs, miR-NAs, long noncoding RNAs, and vesicles [
19]. Furthermore, single studies evaluated tumour-associated cellular antigens (ImmunoCyt/uCyt+) [
20], chromosomal anomalies (UroVysion) [
21], nuclear matrix protein-22 [
22], hCFHrp (BTA stat) [
23], DNA Analysis and genetic mutations (EpiCheckTM) [
24,
25,
26,
27]. Not surprisingly and in line with what has been observed for bladder tumours, performance of biomarkers seems to be improved by turbulence of liquids in the upper urinary tract. E-cadherin is a cell–cell adhesion transmembrane glycoprotein and is a core component of epithelial junctions. Loss of E-cadherin expression has been described as a prognostic factor and is associated with tumour aggressiveness in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. In this context, using a mechanical force to obtain a cytology in the upper urinary tract is critical to increase the diagnostic performance [
28]. In a prospective study, cytology of liquids obtained through barbotage demonstrated to outperform standard cytology of the upper urinary tract (sensitivity: 92% for high-grade, 87% for low-grade) [
29]. The drawback of urine cytology obtained by barbotage is the need for invasive intervention. Therefore, the generation of drug induced turbulences in the upper urinary tract and sampling of voided urine thereafter may be a promising approach to enhance biomarker performances.
The aim of this study was to evaluate urine cytology analysis of a pharmacologically forced diuresis in the diagnostic setting. We enrolled a cohort of patients with primary upper tract urothelial carcinoma to evaluate the performance of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis as diagnostic biomarker. In addition, we selected a separate cohort of patients that underwent radical cystectomy for urothelial cancer of the bladder to determine the value of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis as a follow-up method for cancer recurrence in the upper urinary tract.
2. Materials and Methods
Study Population
As the first cohort, we enrolled 77 consecutive patients from 2009-2022 with confirmed upper tract urothelial carcinoma treated with radical nephroureterectomy or segmental ureterectomy in a curative intent. Patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma who underwent endoscopic treatments as well as patients with previous radical cystectomy were excluded. Cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was performed in tumour-naive patients in case of radiological suspicion for upper tract urothelial carcinoma to support the diagnostic workup. In 25/77 (35%) patients, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was performed preoperatively. Postoperative follow-up was performed in accordance with the European guidelines [
30].
A declaration of consent of the University Hospital of Bern (Inselspital) for the use of biological material and health-related data for medical research was signed by each patient.
A second cohort (n=1250) of patients who underwent radical cystectomy (with or without neoadjuvant chemotherapy) in a curative intent due to urothelial cancer of the bladder from 2000 to 2020 was prospectively followed according to a standard protocol. Preoperative investigation, surgical technique for radical cystectomy, pelvic lymph node dissection and urinary diversion has been described previously [
31,
32,
33,
34,
35]. Bedside ultrasound, imaging of the upper urinary tract with CT- or MRI-urography was performed at 6, 12, 18 and 24 months after radical cystectomy. In addition, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis is performed as follow-up control to detect recurrence in the upper urinary tract at 6 months and yearly thereafter in case of tumour location close to or in the ureter, multifocal carcinoma in situ in the cystectomy specimen, histopathological confirmed lymph node metastasis at the time of radical cystectomy or on demand in case of suspicious upper urinary tract imaging.
Data collection of this second cohort is in accordance with the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE). Ethical approval for this study (Ethical Committee N° KEKBE 2016-00660) was provided by the Ethical Committee of Canton Bern, Switzerland (Chairperson Professor C. Seiler) on 2nd June 2016 and the need for informed consent was waived.
Cytology of Pharmacologically Forced Diuresis: Technique
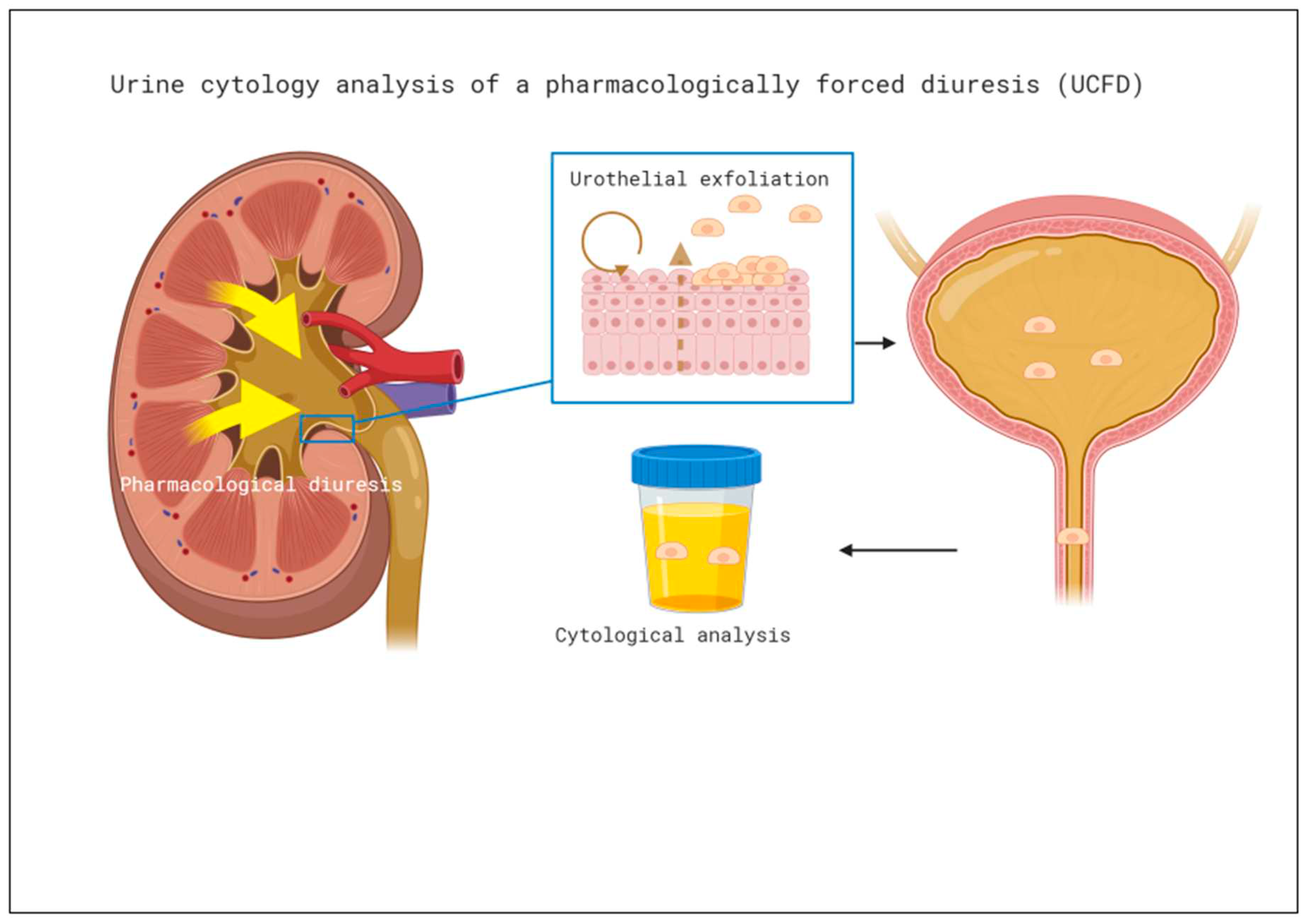
Cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was performed by collecting urine after a forced diuresis induced by oral furosemide 40mg and an oral fluid overload. In an outpatient setting, patients were asked to collect approximately 500 ml of spontaneously voided urine after taking the diuretic and an oral water intake of 1l (i.e., forced diuresis). Urine was then stored in a fridge (at 4° C) and processed at the Department of Pathology of the University Hospital Bern within 24 hours, see
Figure 1.
Pathologic and Cytological Analysis
All specimens after radical cystectomy and radical nephroureterectomy or segmental ureterectomy, respectively, as well as collected urine specimens were evaluated by specialised genitourinary pathologists. Cytology was classified as either
high-grade, atypical/suspicious/low-grade or negative according to the Paris System for reporting urinary cytology [
36]
. Pathology of the surgical specimens was analysed according to the histological classification published by WHO and the International Society of Urological Pathology in 2016 [
37].
Statistical Analysis
For both cohorts we used descriptive analysis. In the first cohort sensitivity of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was measured for the entire population as well as for subgroups (invasive and high-grade cancer, and concomitant carcinoma in situ). In the second cohort sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis were evaluated during the postoperative follow-up using descriptive analysis for the entire population as well as for subgroups (muscle invasive disease, non-muscle invasive disease, lymph node positive disease, and concomitant carcinoma in situ). Performance of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis between different subgroups was compared using Youden’s index, chi-squared test and Fisher’s Exact Test for categorical variables and a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS® v. 25 statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Definition of Positivity
We assessed the diagnostic value of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis and used two different criteria (“stringent” and “soft”) to define positive cytology (
Table 1). In the “stringent” criteria category, positivity was only defined in the presence of high-grade UC (HGUC) according to the Paris System [
36]. The other categories “atypical urothelial cells (AUC)”, “suspicious for high-grade UC (suspicious)”, and “low-grade urothelial neoplasia (LGUN)” were considered “negative” in the “stringent” criteria group but positive in the “soft” criteria group. Finally, “negative for high-grade UC (negative)” was considered negative for both criteria.
3. Results
First Cohort—Clinicopathological Characteristics
For clinicopathological characteristics of the first cohort (n=25) see
Table 2. Median age of patients (8 females, 17 males) at surgery was 66 years. History of tobacco consumption was noted in 13/25 (52%) patients. At first diagnosis, hydronephrosis was found in 13/25 (52%) of patients. Tumours were located in the pelvic-calyceal system in 15/25 (60%) patients and in the ureter in 7/25 (28%) patients. Multifocal upper tract urothelial carcinoma was diagnosed in 3/25 (12%) and concomitant carcinoma in situ in 8/25 (32%) patients. Ureteroscopic biopsy as an integral part of initial diagnosis was performed in 12/25 (48%) cases and local cytology (barbotage and non-barbotage) in 20/25 (80%) of cases of which high-grade, atypical/suspicious/low-grade and negative urothelial cells were present in 7/25 (28%), 9/25 (36%) and 4/25 (16%) of cases, respectively. Muscle-invasive upper tract urothelial carcinoma in the radical nephroureterectomy or segmental ureterectomy specimens was found in 17/25 (57%) patients.[
30]. Median follow-up was 24.5 months with extra-vesical recurrence occurring in 28% (42% local, 29% nodal and 29% distant) patients. Bladder recurrence during follow-up was diagnosed in 15/25 (60%) patients after a median of 6 months (range 3-53). Finally, 3-year overall and cancer-specific survival was 71% and 82%, respectively.
Diagnostics Value of Cytology of Pharmacologically Forced Diuresis
Cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was positive with high-grade urothelial carcinoma being found in 2/25 (8%) patients. Atypia/suspicious/low-grade and negative cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was diagnosed in 6/25 (24%) and 17/25 (68%) patients, see
Figure 2.
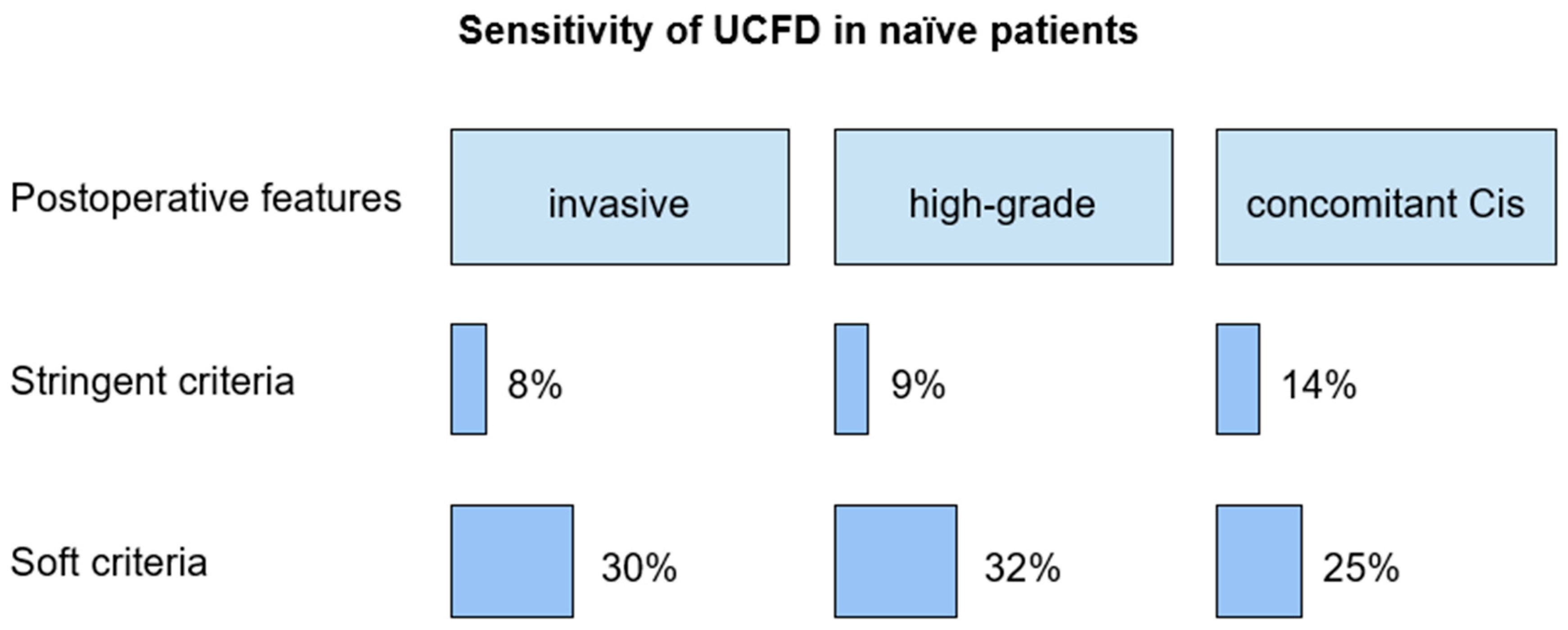
Sensitivity of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis according to the stringent criteria in patients with invasive upper tract urothelial carcinoma, high-grade, and low-grade UC, and concomitant carcinoma in situ was 8%, 9%, 0%, 14%, respectively.
According to the soft criteria, sensitivity in patients with invasive upper tract urothelial carcinoma, high-grade and low-grade upper tract urothelial carcinoma, and concomitant carcinoma in situ was 30%, 32%, 50%, 25%, respectively.
Interestingly, among the 23 patients with negative cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis, 12/23 (52%) had muscle invasive upper tract urothelial carcinoma (pT-stage ≥ 2), 7/23 (30%) had a concomitant carcinoma in situ, and 5/23 (22%) had a subsequent high-grade selective urine cytology. Of the two patients with low-grade urothelial carcinoma, one presented a cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis with atypia/suspicious/low-grade.
Second Cohort—Clinicopathological Characteristics
For clinicopathological characteristics of the second cohort (n=689), see
Table 3. Median age of patients (201 [29%] females, 488 [71%] males) at radical cystectomy was 68 years. History of tobacco consumption was noted in 405/689 (59%) patients. At diagnosis, hydronephrosis was found in 131/689 (19%) of patients. 41/689 (6%) of patients had upper tract urothelial carcinoma prior to or time (synchronous) of radical cystectomy. Muscle-invasive disease was diagnosed in 510/689 (74%) of radical cystectomy specimens. High-grade bladder urothelial carcinoma was found in 625/689 (91%) patients. During extended pelvic lymph node dissection, a median number of 33 lymph nodes was removed (IQR 24-43) with lymph node metastasis in 161/689 (23%) cases. Positive surgical margin rate was 2.8% (19/689). During follow-up local recurrence and distant metastasis occurred in 92/689 (13%) and and 177/689 (26%) patients.
Diagnostic Value of Cytology of Pharmacologically Forced Diuresis
In total 1431 cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis were analysed. Of them 3.4% (49/1431) contained urothelial cancer cells that were considered as ‘positive’ according to the stringent criteria (
Table 1). Cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was positive in 30/689 (4.3%) of patients. In those patients upper urinary tract and urethral recurrence occurred in 21/30 (70%) and 8/30 (26.7%), respectively. One patient (3.3%) had a false-positive cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis.
From another perspective, 46/1250 patients undergoing radical cystectomy (3.7%) patients had proven recurrence in the upper urinary tract. In 31/46 (67%) patients cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was analysed prior to treatment (of the upper urinary tract recurrence) while urothelial cancer cells (true positive) were found in 17/31 (55%) tests. In 2/46 (4%) patients cancer recurrence in the upper urinary tract was detected by cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis only, while upper urinary tract imaging was negative (
Table 4).
As such, when assessing diagnostic accuracy of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis according to the stringent criteria, sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value were 60% (42-76%), 99% (97-99%), 70% (50-85%) and 98% (96-99%) respectively, with a Youden’s index of 0.59 (0.42-0.75), see
Table 5.
Due to its nature, a high number of atypical findings in forced diuresis samples are found in patients with an ileal conduit. Therefore, diagnostic accuracy of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis according to the soft criteria has not been evaluated.
Clinical Parameters Associated with Higher Accuracy of Cytology of Pharmacologically Forced Diuresis in Both Cohorts
No perioperative factor was statistically significant in predicting a positive cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis in the primary diagnosis of upper tract urothelial carcinoma, but a trend was observed. Preoperative factors associated with a positive cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis were smoking history (p = 0.07), positive selective ureter cytology (p = 0.07) at time of initial diagnostic work-up, normal preoperative kidney function > 75ml/min/1.73m2 (p = 0.09), absence of hydronephrosis at diagnosis (p = 0.22), and variant histology (p = 0.08).
Similarly, in the second cohort no preoperative factor was significantly associated with a higher sensitivity and specificity for cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis, see
Table 6 and
Table 7.
4. Discussion
In this study, we evaluated diagnostic accuracy and clinical significance of drug induced turbulence in the upper urinary tract and subsequent urine sampling in the diagnosis of primary upper tract urothelial carcinoma and upper tract urothelial carcinoma recurrence during follow-up after radical cystectomy for primary bladder urothelial carcinoma.
Not surprisingly for primary upper tract urothelial carcinoma, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis performance was only adequate in case of invasive and high-grade pathology or concomitant carcinoma in situ.
Similarly, in the second cohort, precursor lesions of advanced tumours as non-muscle invasive disease and carcinoma in situ were associated with better sensitivity of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis. This notable difference between the two cohorts is partly attributable to upper urinary tract recurrence being detected at early stages in the second cohort due to intensive follow-up after radical cystectomy.
In fact, about 60% of patients with confirmed recurrence in the upper urinary tract had non-muscle invasive disease in the radical cystectomy specimens, while this was the case in less than 50% of the patients in the first cohort. In the second cohort negative predictive value as well as specificity were remarkably high, likely due to the relatively low rate of recurrence in the upper urinary tract after radical cystectomy. Some preoperative factors may interfere with the performance of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis (e.g., normal kidney function and smoking history). However, none of these parameters reached statistical significance. Interestingly, all patients with a positive cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis in primary upper tract urothelial carcinoma developed a bladder recurrence. Apparently, patients with desquamation of cancer cells are at risk for bladder recurrence which may support the hypothesis that tumour cells can spread from the upper urinary tract to the bladder [
38].
Overall performance of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis for the follow-up in the upper urinary tract after radical cystectomy (second cohort) was better than in the first cohort. Also, due to the relatively high rate of false negative results, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis cannot replace standard diagnostic techniques (i.e., CT- and MR-imaging or ureteroscopic biopsy). However, in few cases, it allowed the diagnosis of recurrence in the upper urinary tract despite negative imaging and in case of orthotopic bladder substitute, it could diagnose recurrence in the urethra during follow-up.
Cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis is a simple and non-invasive diagnostic tool. However, the current diagnostic gold standard for upper tract urothelial carcinoma is predominantly based on CT- and MR-imaging and invasive tumour biopsy or cytology. A major limitation of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis is that cytological results in patients with ureteral tumours obstructing the urine flow are associated with false-negative test results. This is not surprising given that the tumour cells are not washed out. As such, negative predicting factors (i.e., hydronephrosis) allows for negative selection of patients for testing.
To our knowledge, this is the first study to assess the diagnostic utility of drug induced turbulence in the upper urinary tract and urine cytology in the context of upper tract urothelial carcinoma. However, the use of urine-based biomarkers in the setting of urothelial carcinoma is a constantly evolving field. Several potential biomarkers have been investigated or are under investigation. Considering morbidity and limitations of the currently recommended diagnostic work-up, non-invasive tumour biomarkers are promising. To date, despite promising results, performance and accuracy varied significantly (sensitivity: 44-91%; specificity 67-100%) and have been analysed mostly in single studies with small populations [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
39].
Nevertheless, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis may have implication for clinical practice. As such, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis might be considered to support the diagnostic workup for upper tract urothelial carcinoma in well-selected patients (e.g., in the follow-up of patients with associated risk factor for recurrence in the upper urinary tract who underwent radical cystectomy for bladder urothelial carcinoma). Clearly, increased prevalence in a specified population increases the predictive positive value. However, the use of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis in the primary diagnosis of upper tract urothelial carcinoma seems limited by the low diagnostic performance and even in case of positive results it does not allow for avoidance of the standard diagnostic assessment. On the other hand, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis is useful in patients with contraindication for CT or MR urography (e.g., allergy to contrast agents, chronic renal insufficiency, claustrophobia), and difficult endoscopic access to the upper urinary tract. As such, a long ileal conduit or mucosal folds in the proximity of the neo-orifices may impede endoscopic investigation. In these situations, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis may add diagnostic information to other baseline investigations (i.e., clinical examination, non-contrast CT, ultrasound).
Also, it remains an open question whether the use of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis may reduce performance of invasive procedures or imaging. For these reasons, the need for more performing biomarkers remains.
Before implementation of biomarker testing, economic burden and benefit for the patients need to be balanced against the costs. We therefore evaluated the costs of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis in our department and weighed them against others. In comparison to other biomarkers, costs for cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis analysis in our institution are 87
$ in an outpatient setting. Costs from the currently available biomarkers are variable ranging between 25
$ and 800
$ [
19]. However, the value of new biomarkers for daily routine needs to be balanced against its costs as well and has to be validated in several datasets.
The results of this study must be interpreted in the context of its limitations. The retrospective nature of the study may introduce selection bias. The first cohort has a limited sample size that lowers statistical power of the study. Furthermore, despite processing the samples as early as possible, collection and processing of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was not controlled and errors and delay in both steps may be a potential source of bias. Also, predictive values in the first cohort have not been calculated due to the initial patient selection criteria.
5. Conclusions
Urine cytology obtained from forced diuresis is a simple and non-invasive diagnostic method.
When considering diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity of cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis is slightly better in patients with invasive upper tract urothelial carcinoma and concomitant carcinoma in situ. As follow-up method, positive cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis was strongly related to cancer recurrence and could even reveal cancer recurrence in the urethra in cases with an orthotopic bladder substitute. While cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis may add diagnostic value in a few cases with recurrence of carcinoma in situ, its diagnostic accuracy is not adequate as a standalone test for recurrence. Therefore, there is a need for more reliable biomarkers for the follow-up and diagnosis of the upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Furthermore, cytology of pharmacologically forced diuresis is useful in patients with contraindication for CT or MR urography and difficult endoscopic access to the upper urinary tract.
References
- Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JWW, Comber H, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 2013 Apr;49(6):1374–403. [CrossRef]
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019 Jan 8;69(1):7–34. [CrossRef]
- Cosentino M, Palou J, Gaya JM, Breda A, Rodriguez-Faba O, Villavicencio-Mavrich H. Upper urinary tract urothelial cell carcinoma: location as a predictive factor for concomitant bladder carcinoma. World J Urol. 2013 Feb;31(1):141–5. [CrossRef]
- Green DA, Rink M, Xylinas E, Matin SF, Stenzl A, Roupret M, et al. Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and the upper tract: disparate twins. J Urol. 2013 Apr;189(4):1214–21. [CrossRef]
- Schwartz CB, Bekirov H, Melman A. Urothelial tumours of upper tract following treatment of primary bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Urology. 1992 Dec;40(6):509–11. [CrossRef]
- Shariat SF, Favaretto RL, Gupta A, Fritsche H-M, Matsumoto K, Kassouf W, et al. Gender differences in radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma. World J Urol. 2011 Aug;29(4):481–6. [CrossRef]
- Inman BA, Tran V-T, Fradet Y, Lacombe L. Carcinoma of the upper urinary tract: predictors of survival and competing causes of mortality. Cancer. 2009 Jul 1;115(13):2853–62. [CrossRef]
- Yeh H-C, Jan H-C, Wu W-J, Li C-C, Li W-M, Ke H-L, et al. Concurrent preoperative presence of hydronephrosis and flank pain independently predicts worse outcome of upper tract urothelial carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2015 Oct 15;10(10):e0139624. [CrossRef]
- Qi N, Zhang J, Chen Y, Wen R, Li H. Microscopic hematuria predicts lower stage in patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Oct 24;10:4929–33. [CrossRef]
- Raman JD, Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Lotan Y, Sagalowsky AI, Roscigno M, et al. Does preoperative symptom classification impact prognosis in patients with clinically localized upper-tract urothelial carcinoma managed by radical nephroureterectomy? Urol Oncol. 2011 Dec;29(6):716–23. [CrossRef]
- Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Compérat E, Zigeuner R, Sylvester RJ, Burger M, et al. European association of urology guidelines on upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: 2017 update. Eur Urol. 2018 Jan;73(1):111–22. [CrossRef]
- Lughezzani G, Jeldres C, Isbarn H, Sun M, Shariat SF, Widmer H, et al. Temporal stage and grade migration in surgically treated patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. BJU Int. 2010 Mar;105(6):799–804. [CrossRef]
- Browne BM, Stensland KD, Moynihan MJ, Canes D. An analysis of staging and treatment trends for upper tract urothelial carcinoma in the national cancer database. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018 Feb 5;16(4):e743–50. [CrossRef]
- Gakis G, Black PC, Bochner BH, Boorjian SA, Stenzl A, Thalmann GN, et al. Systematic Review on the Fate of the Remnant Urothelium after Radical Cystectomy. Eur Urol. 2017;71(4):545–57. [CrossRef]
- Fahmy O, Khairul-Asri MG, Schubert T, Renninger M, Kübler H, Stenzl A, et al. Urethral recurrence after radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol Oncol. 2018;36(2):54–9. [CrossRef]
- Kiss B, Furrer MA, Wuethrich PY, Burkhard FC, Thalmann GN, Roth B. Stenting Prior to Cystectomy is an Independent Risk Factor for Upper Urinary Tract Recurrence. J Urol. 2017 Jun 8;198(6):1263–8. [CrossRef]
- Picozzi S, Ricci C, Gaeta M, Ratti D, Macchi A, Casellato S, et al. Upper urinary tract recurrence following radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a meta-analysis on 13,185 patients. J Urol. 2012 Dec;188(6):2046–54. [CrossRef]
- Messer J, Shariat SF, Brien JC, Herman MP, Ng CK, Scherr DS, et al. Urinary cytology has a poor performance for predicting invasive or high-grade upper-tract urothelial carcinoma. BJU Int. 2011 Sep;108(5):701–5. [CrossRef]
- Miyake M, Owari T, Hori S, Nakai Y, Fujimoto K. Emerging biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of urothelial carcinoma. Res Rep Urol. 2018 Dec 14;10:251–61. [CrossRef]
- Lodde M, Mian C, Wiener H, Haitel A, Pycha A, Marberger M. Detection of upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma with ImmunoCyt: a preliminary report. Urology. 2001 Sep;58(3):362–6. [CrossRef]
- Marín-Aguilera M, Mengual L, Ribal MJ, Musquera M, Ars E, Villavicencio H, et al. Utility of fluorescence in situ hybridization as a non-invasive technique in the diagnosis of upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2007 Feb;51(2):409–15; discussion 415. [CrossRef]
- Coskuner E, Cevik I, Ozkan A, Dillioglugil O, Akdas A. In the cystoscopic follow-up of non-muscle-invasive transitional cell carcinoma, NMP-22 works for high grades, but unreliable in low grades and upper urinary tract tumours. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012 Jun;44(3):793–8. [CrossRef]
- Walsh IK, Keane PF, Ishak LM, Flessland KA. The BTA stat test: a tumour marker for the detection of upper tract transitional cell carcinoma. Urology. 2001 Oct;58(4):532–5. [CrossRef]
- Lin H-H, Ke H-L, Hsiao K-H, Tsai C-W, Wu W-J, Bau D-T, et al. CCND1 1722 polymorphism and potential relevance to upper tract urothelial cancer. Anticancer Res. 2011 Mar;31(3):1043–7.
- Wang K, Liu T, Ge N, Liu L, Yuan X, Liu J, et al. TERT promoter mutations are associated with distant metastases in upper tract urothelial carcinomas and serve as urinary biomarkers detected by a sensitive castPCR. Oncotarget. 2014 Dec 15;5(23):12428–39. [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Reis S, Leça L, Almeida M, Antunes L, Monteiro P, Dias PC, et al. Accurate detection of upper tract urothelial carcinoma in tissue and urine by means of quantitative GDF15, TMEFF2 and VIM promoter methylation. Eur J Cancer. 2014 Jan;50(1):226–33. [CrossRef]
- Witjes JA, Morote J, Cornel EB, Gakis G, van Valenberg FJP, Lozano F, et al. Performance of the Bladder EpiCheckTM Methylation Test for Patients Under Surveillance for Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: Results of a Multicenter, Prospective, Blinded Clinical Trial. Eur Urol Oncol. 2018 Jul 17;1(4):307–13. [CrossRef]
- Fromont G, Rouprêt M, Amira N, Sibony M, Vallancien G, Validire P, et al. Tissue microarray analysis of the prognostic value of E-cadherin, Ki67, p53, p27, survivin and MSH2 expression in upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2005 Nov;48(5):764–70. [CrossRef]
- Malm C, Grahn A, Jaremko G, Tribukait B, Brehmer M. Diagnostic accuracy of upper tract urothelial carcinoma: how samples are collected matters. Scand J Urol. 2017 Apr 7;51(2):137–45. [CrossRef]
- Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Compérat E, Zigeuner R, Sylvester RJ, Burger M, et al. European association of urology guidelines on upper urinary tract urothelial cell carcinoma: 2015 update. Eur Urol. 2015 Nov;68(5):868–79. [CrossRef]
- Kessler TM, Burkhard FC, Studer UE. Clinical indications and outcomes with nerve-sparing cystectomy in patients with bladder cancer. Urol Clin North Am. 2005 May;32(2):165–75. [CrossRef]
- Furrer MA, Studer UE, Gross T, Burkhard FC, Thalmann GN, Nguyen DP. Nerve-sparing radical cystectomy has a beneficial impact on urinary continence after orthotopic bladder substitution, which becomes even more apparent over time. BJU Int. 2018 Feb 4;121(6):935–44. [CrossRef]
- Furrer MA, Papa N, Luetolf S, Roth B, Cumberbatch M, Dorin Vartolomei M, et al. A longitudinal study evaluating interim assessment of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2022 Sep;130(3):306–13. [CrossRef]
- Furrer MA, Grueter T, Bosshard P, Vartolomei MD, Kiss B, Thalmann GN, et al. Routine Preoperative Bone Scintigraphy Has Limited Impact on the Management of Patients with Invasive Bladder Cancer. Eur Urol Focus. 2021 Sep;7(5):1052–60. [CrossRef]
- Furrer MA, Abgottspon J, Huber M, Engel D, Löffel LM, Beilstein CM, et al. Perioperative continuation of aspirin, oral anticoagulants or bridging with therapeutic low-molecular-weight heparin does not increase intraoperative blood loss and blood transfusion rate in cystectomy patients: an observational cohort study. BJU Int. 2022 Apr;129(4):512–23. [CrossRef]
- Barkan GA, Wojcik EM, Nayar R, Savic-Prince S, Quek ML, Kurtycz DFI, et al. The paris system for reporting urinary cytology: the quest to develop a standardized terminology. Adv Anat Pathol. 2016 Jul;23(4):193–201. [CrossRef]
- Humphrey PA, Moch H, Cubilla AL, Ulbright TM, Reuter VE. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part B: Prostate and Bladder Tumours. Eur Urol. 2016 Jul;70(1):106–19. [CrossRef]
- Seisen T, Granger B, Colin P, Léon P, Utard G, Renard-Penna R, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinicopathologic Factors Linked to Intravesical Recurrence After Radical Nephroureterectomy to Treat Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2015 Jun;67(6):1122–33. [CrossRef]
- Smentkowski KE, Bagley DH, Hubosky SG. Ureteroscopic biopsy of upper tract urothelial carcinoma and role of urinary biomarkers. Transl Androl Urol. 2020 Aug;9(4):1809–14. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).