1. Introduction
Local population have knowledge of the benefits of plants which span forests, natural pastures, human nutrition and medicinal plants, enjoyment and well-being of natural life, and landscape culture. Town mayors and a significant group of residents, livestock farmers, and tourism entrepreneurs have a crucial importance to acquire direct information on ecosystem services and well-being, and to set strategies for environmental conservation and sustainable development [
1].
1.1. Biodiversity and the Preservation of the Balance between Conservation and Profit
On public and protected areas, resident communities have the difficult challenging task of balancing the business activities to avoid the risk of declining genetic richness, currently under more and more uncertain conditions due to varying rainfall patterns and rising temperatures. Management requires community participation and awareness. It entails the overcoming of purely utilitarian perception, which affects the balance between profit and conservation, leading to increased animal reared and loss of biodiversity through overgrazing. The presence of livestock farmers in conditions of equilibrium, without exceeding the carrying capacity of ecosystems [
2], as a matter of fact, provides the opportunity to maintain the richness of biodiversity [
3]. For the past few decades, integration with hospitality and experiential tourism [
4] has taken place, largely thanks to the younger generations and to environmental protection education, crucial elements for the perception shift regarding forests which affect regulations, well-being and the aesthetic value of the landscape.
1.2. Mediterranaean Holm Oak Forests and the Content of Acorns as a Benefit of Ecosystem Services
Forests of
Quercus ilex and
rotundifolia habitat are the most extensive in the Mediterranean countries of Europe and northern Africa, covering more than 700.000 km
2, predominantly in the Iberian Peninsula, in Italy, and in Greece [
5]. The rural communities have always considered the content of acorns to be a benefit of ecosystem services for human nutrition [
6,
7] for the properties due to the high amount of antioxidant polyphenols and complex sugars. Therefore, such content has been explored as a functional food of medical interest [
8], as well as a pig food with positive effects on meat and fat quality, richer in mono - and polyunsaturated acids [
9].
1.3. Plants Eaten by Grazing Animals and the Conservation of Biodiversity
Mediterranean pastures of goats and pigs raised in the semi-wild state have been the focus of many studies in relation to farmers’ actions to preserve plant biodiversity or to the risks of loss [
10]. The list of plants eaten by animals shifts from those with the greatest appeal to them to others they eat whenever they are compelled by a shortage of reproducing plant species or by overgrazing. Collaborative monitoring with livestock farmers is useful to update the list of edible species and to achieve greater awareness toward endemic species conservation and sustainability.
1.4. Plant Biodiversity in Human Nutrition and Folk Medicine
Plants as primary producers and animals reared on semi-wild pasture provided most of the food of rural people in the past. Wild plants formed a part of the human diet, and many species are still favored and spread through seed collection and exchange [
11]. The variety of secondary metabolites produced by wild plants used as dietary sources of compounds with antioxidant and biological activity [
12] and treating diseases is reported in many scientific studies. Most often, research has focused on the presence of active biomolecules with high phenolic contents as well as antioxidant and anti-free radical effects. Several studies have highlighted the importance of diet as one of the epigenetic factors influencing health conditions. According to research, the Mediterranean diet appears to be a nutritional pattern capable of promoting health [
13]. The marked biodiversity of plant species has been one of the major contributors to the consolidation of the diet-health pair in the population, in line with the conceptual model proposed by Marselle, [
14]. which precisely views the strengthening of biodiversity as the most powerful tool to counter the increase in chronic noncommunicable diseases. Over the past decade, further studies on healthy human longevity have been highlighting the importance of diet in addition to population genetic factors [
15,
16].
1.5. Plant Biodiversity and the Aesthetic Enjoyment and Well-Being
Plant biodiversity has aesthetic value of landscapes that contributes to human well-being [
17]. This has been highlighted in a number of urban planning [
18]. Local stakeholders benefit through the cultivation of plants with richly colored and fragrant blooms and through the use of shrubs and trees in the shaping of home gardens and parks, contributing to enhance cultural identity and the development of sense of place, [
19].
1.6. Conceptual Outline of the Research and Purpose
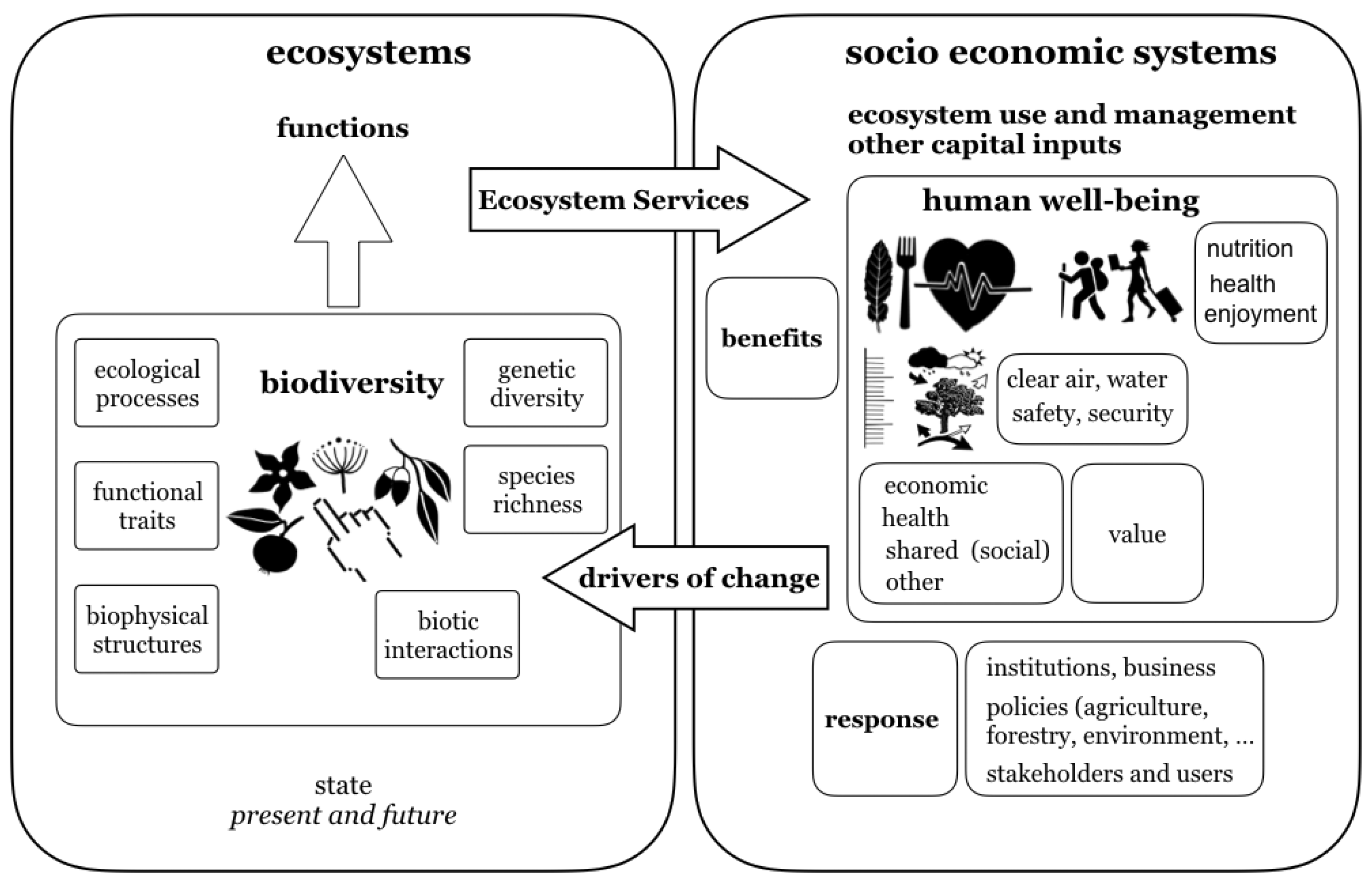
The conceptual framework of our research is based on the interrelationships between plant biodiversity and socioeconomic and well-being benefits (
Figure 1). Our goals have been to test the collaborative method seen as shared paths of knowledge of biodiversity functions so as to obtain measurable scientific data over the years, which will be useful for sustainable management policies and to strengthen the link between natural and human capital.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
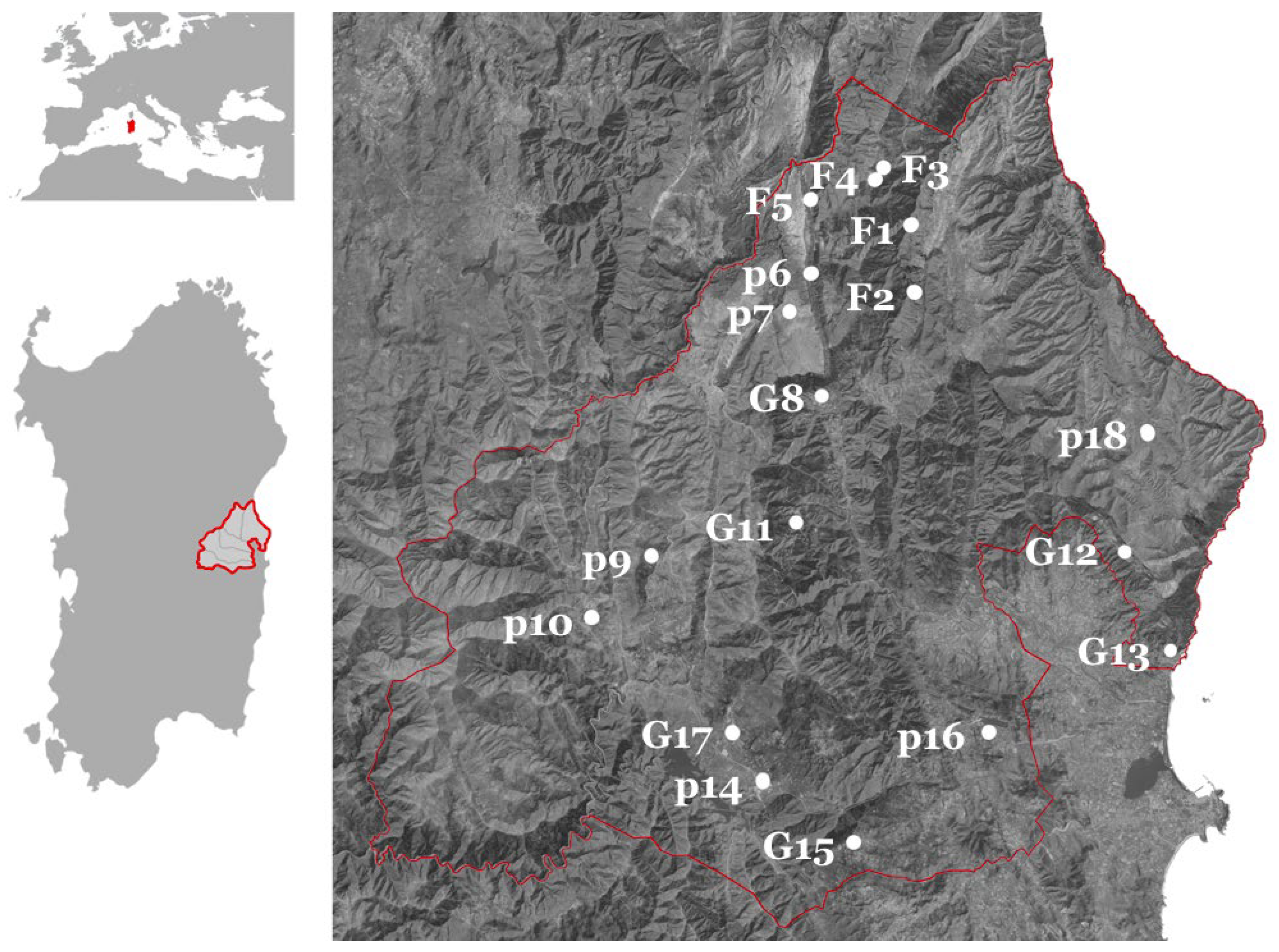
The monitored area covers more than 800 km
2 in east-central Sardinia (
Figure 2) and is about 85 % publicly owned and protected area. Genetic richness characterizes the area, featuring 19 habitats marked with Natura 2000 and EUNIS codes (
Figure 3) to summarize landscape traits and protection measures. For the purposes of communicating the benefits of biodiversity to the local communities, we have named the study area Terre dell‘Aquilegia: this helps emphasize how the genetic richness goes beyond the administrative limits of municipalities and has proven effective in encouraging the cooperation of mayors in its implementation. A further peculiarity of the monitored area is that it overlaps with one of the areas of the planet in which the phenomenon of human longevity has been evidenced by the presence – greater than demographic average – of healthy ultra-centenarians. Research has highlighted many epigenetic factors related to lifestyles and particularly to Mediterranean nutrition and diet in these areas, called Blue Zones [
21].
2.2. Pathways for Monitoring Plant Biodiversity
The 18 monitoring pathways were in forest habitats (F1, F2, F3, F4, F5) with a predominance of holm oak [
22], on public land granted by municipalities for local goat and pig farming and for hospitality and trekking tourism (p6, p7, p9, p10, p14), and in family gardens (G8, G11, G12, G13, G15, G17). The monitoring pathways were carried out in different seasons, from 2019 until September 2023. The length of each monitoring pathway was about 5 km, while for family gardens, the survey of edible wildlife species was located on areas less than one hectare.
2.3. Accessing the Habitats
The surveys are reported as supplementary material in a file named:
Table S1 – Ecosystem biodiversity and socioeconomic and well-being benefits report.docx. The four chart columns report: 1) plant name and family; 2) habitat, 3) biodiversity in ecosystems, in relation to genetic richness, especially endemism; 4) benefits and knowledge which farmers have of the plants, whether palatable by grazing goats and pigs, or eaten in the absence of anything else or when they are dry, as well as plants discarded by the animals because they are unpalatable or toxic. We have included information on medicinal and healing plants in folk medicine as well as on the wild plants of the Mediterranean diet found in family gardens and collected for local recipes in the rural surroundings of villages. We have also added information about the plants which characterize the landscape and are grown in the gardens. The habitats in the study area are: 9340
Quercus ilex and
Quercus rotundifolia forests, 6310 Dehesas with evergreen
Quercus sp. pl., 92D0 Southern riparian galleries and thickets (Nerio – Tamaricetea and Securinegion tinctoriae), 5320 Low formations of Euphorbia close to cliffs Sclerophyllous scrub (matorral), 6220 Pseudo-steppe with grasses and annuals of the Thero-Brachypodietea natural and semi-natural grass-land formations, 5330 Thermo-Mediterranean and pre-desert scrub - Sclerophyllous scrub (matorral), 91E0 Alluvial forests with
Alnus glutinosa and
Fraxinus excelsior, 9560 Endemic forests with
Juniperus sp.pl., 1210 Annual vegetation of drift lines, 9320 Olea and Ceratonia forests, 8210 Calcareous rocky slopes with chasmophytic vegetation, 8130 Western Mediterranean and thermophilous scree Rocky habitats and caves, 8130 Western Mediterranean and thermophilous scree, 5210 Arborescent matorral with
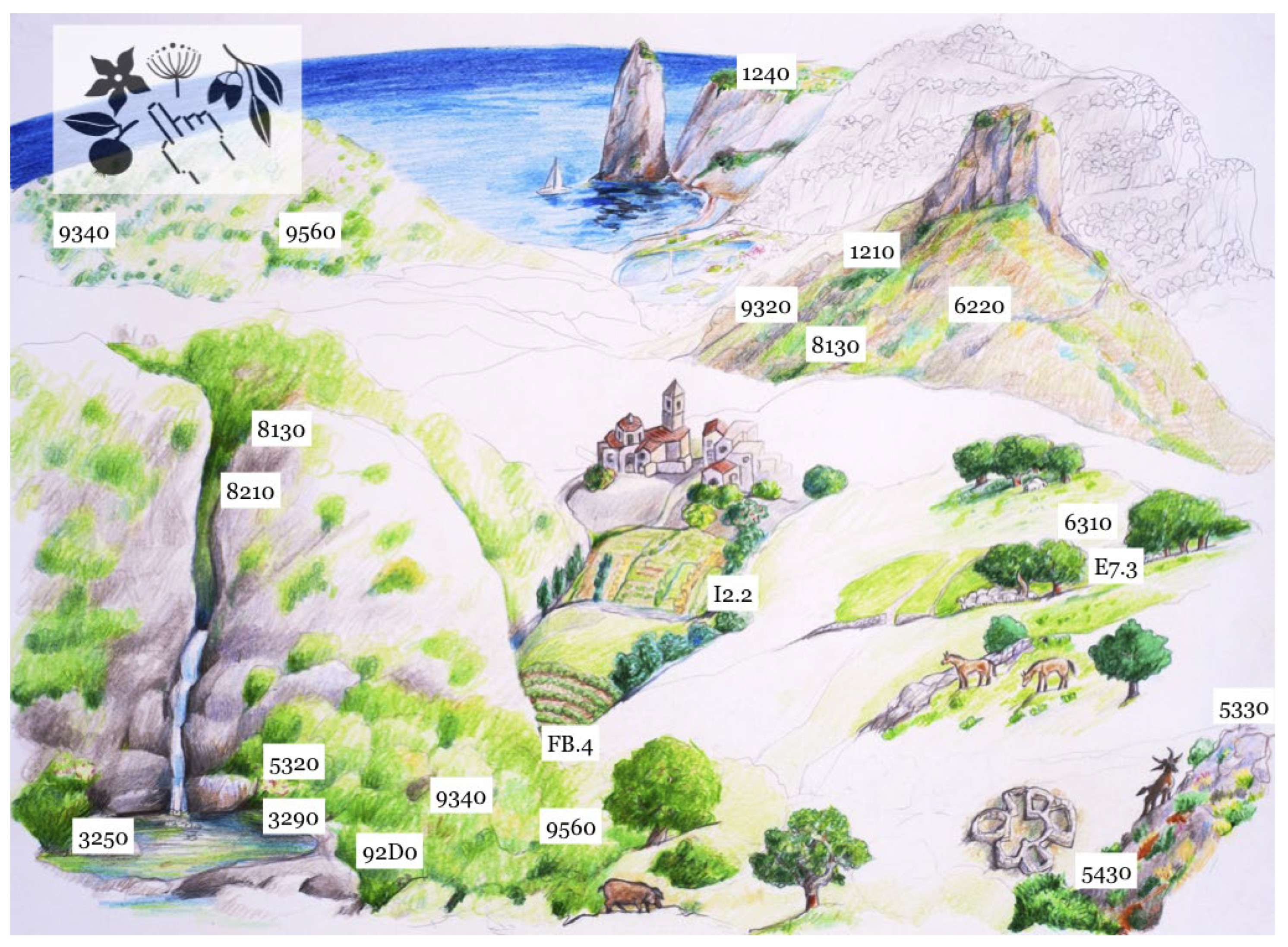
Juniperus sp. pl., 3170 Mediterranean tempo-rary ponds, 3290 Intermittently flowing Mediterranean rivers of the Paspalo-Agrostidion Freshwater habitats, 5430 Endemic phryganas of the Euphorbio-Verbascion Sclerophyllous scrub (matorral), I2.2 Small-scale or-namental and domestic garden areas, FB.4 Vineyards.
2.4. Criteria for Collaboration with the Local Communities
The collaboration with the local communities had two aims: on the one hand, it could help raise awareness and education about conservation and sustainable management of biodiversity; on the other hand, we would learn firsthand knowledge and understand the difficulties in the relationships between natural and human capital to minimize possible conflicts. Four groups were considered: the mayors of the five municipalities in the area; farmers who had been given the land in concession; owners of family gardens and elderly people who had knowledge of edible and healing plants; and a sample of more than 1,000 tourists over the 5-year monitoring period.
2.5. Searching Ancient Ecosystem Services of Holm Oak (Quercus ilex L.) with Sweet Acorns
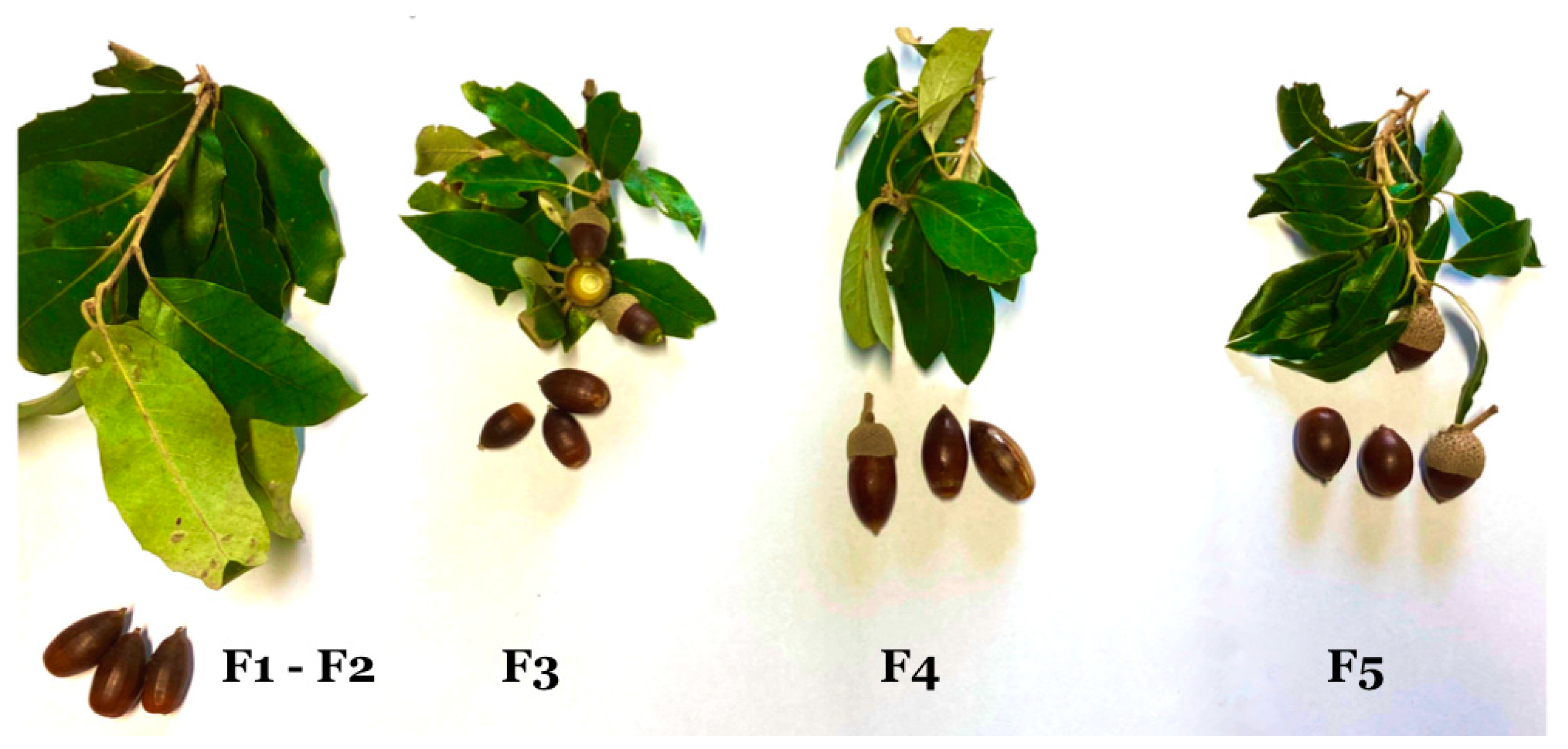
In this case study, forest cover is about 50% with holm oak, Quercus ilex L.; as prevailing species. Significant intraspecific genetic variability has been favored by local people for the ecosystem services provided by acorns in human nutrition and as food for pigs farmed in the semi-wild state. Biodiversity surveys in forest areas aimed at identifying holm oak trees thought by residents and pig farmers to have different features than other holm oaks. The alleged difference by farmers referred to holm oaks with sweeter acorns in cenoses consisting of multiple trees being chosen primarily by wild boars and pigs in semi-wild grazing. Five forest stations were identified and are indicated as F1, F2, F3, F4, and F5 in the map. Station F1 is the control with holm oaks standard features in the study area, i.e., having contents presumably not different with respect to the chemical composition of acorns. In November 2021 and 2022, 20 acorn samples of approximately 700 g each were collected and taken to the chemical laboratory for immediate analysis in sugar and total polyphenol contents. Macroelements, trace elements, and heavy metals were also examined, sup-posing that any differences could serve for further studies of plant physiology and nutrient uptake from the soil.
2.6. Chemical Analysis of Acorns
Each of the 20 samples was tested in a double analysis at the Agris agricultural chemistry laboratory. Laboratory results were analyzed with Statgraphics Centurion 18 software, with analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s test with 95% confidence level. The method used for the detection of total sugars was developed in accordance with Ministerial Decree No. 168 dated 03/02/1989 Official Methods of Analysis for Vegetable Preserves, Title II, Paragraph 18 Measurement of Sugars and with the report of the Italian Health Authority ISTISAN 96/34 [
23], Methods of analysis for chemical control of food. For total polyphenols, the method used was extraction of the lyophilized sample with a mixture of methanol and water and instrumental measurement after coloration with Folin-Ciocâlteau reagent as indicated by Dewanto et al. [
24]. For the detection of macro -, micro-elements and heavy metals, the analysis was based on the guidelines of the Italian Agency for Environment Protection APAT CNR IRSA Section 3020 Issue 29/2003, performing instrumental measurements using ICP-OES after microwave - assisted wet mineralization of the lyophilized samples.
2.7. Analysis of Weather and Climate Data
Data of rainfall and average maximum temperatures were considered to get useful indications for agroforestry purposes. Data for the years 2019 - 2023 were obtained from the daily records of 5 meteo stations in the given area. The stations are operated by the Meteo-climatic Department of the Region of Sardinia, which also provided climate data for the 30-year period 1981 - 2010. Daily rainfall and maximum temperature averages in different months from 2019 to 2023 were compared with climate data from the 30-year period 1981 - 2010 from the same area.
3. Results
3.1. Finding of the Mother Plants of Holm Oak with Sweet Acorns and Richer in Polyphenols
Chemical analysis confirmed a higher content of sugars and polyphenols in the mother plants of holm oak indicated by local people and considered to be a precious legacy of the past.
Table 1 shows the laboratory data expressed in g/100 g for sugars, and mg/100 g for polyphenols. The monitoring forest station F1 accounts for the generality of ordinary holm oaks spread throughout the territory. Stations F3, F4, F5, differ from F1 in higher contents of sugars and polyphenols, apart from F2, which does not confirm the expected significant differences.
Figure 4 shows a photograph of leaf and acorn samples, which allows us to observe how the leaves are smaller and slightly rounded. Smaller leaves in trees producing acorns with higher sugar and polyphenol contents seem a contradiction. This fact, however, can partly be interpreted with the observation of these plants having denser leaf systems with favorable exposure to sunlight. Confirmation of the sweet and polyphenol-rich feature helps understand why local people have considered it functional in human nutrition for centuries; in times of poverty after World War II it was appreciated as ingredient for acorn bread, and it is currently used for the fattening of pigs.
3.2. Results of Plant Biodiversity Monitoring in the Pathways of Farmers and Tourists
The biodiversity of plants surveyed in the monitoring pathways is shown in the supplementary file named
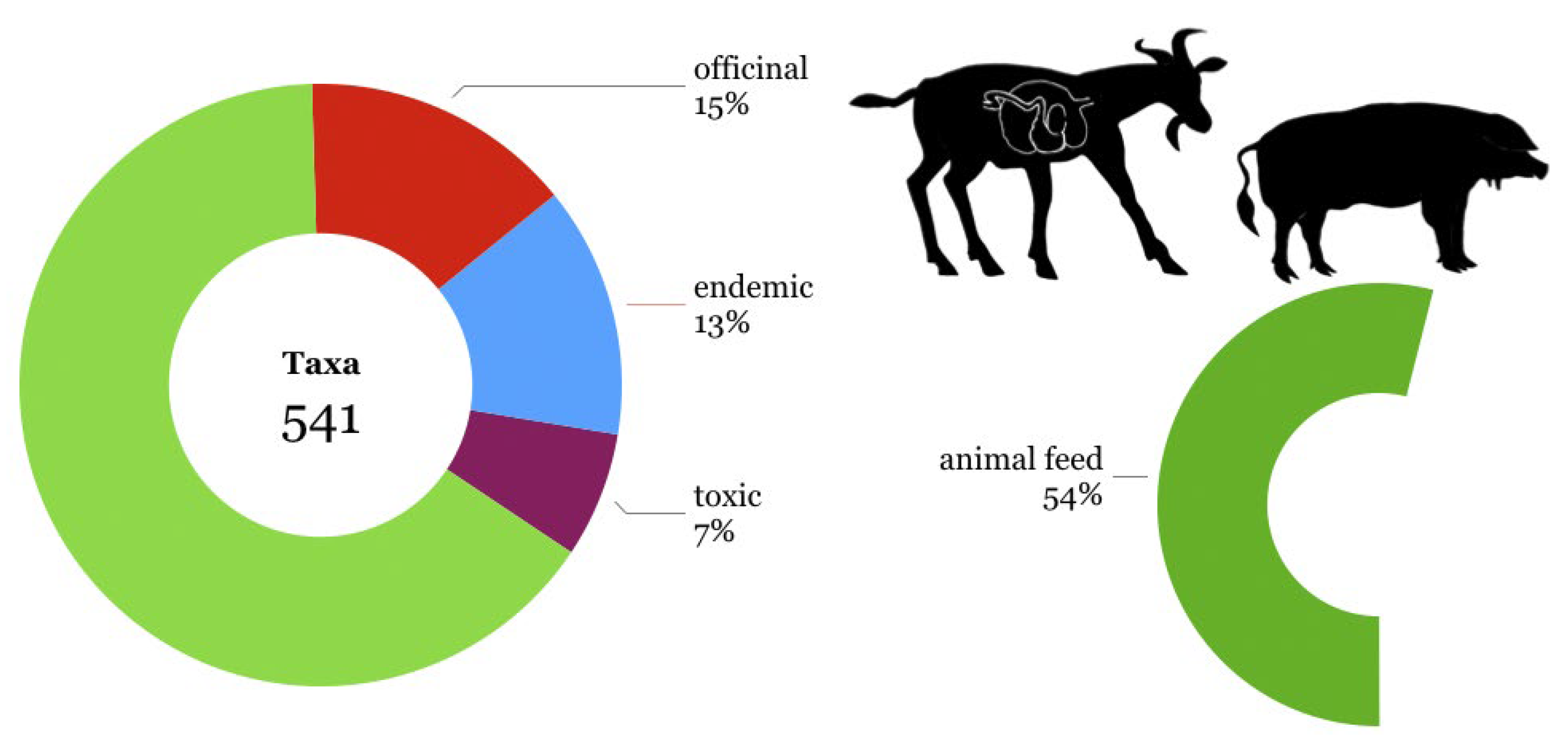
Table S1 – Ecosystem biodiversity and socioeconomic and well-being benefits report.docx and in graphic form in
Figure 5: we identified 541 taxa, 15% of which are medicinal plants, 13% endemics and 7% toxic. The graph on the right summarizes the report compiled with the cooperation of farmers in the pathways. It shows that 54% of the plants are also eaten by goats and pigs of local breeds when grazing, ranging from the most palatable plants – which are mainly of Poaceae and Fabaceae families – to shrubby and tree-like plants of the Mediterranean shrub, to non-palatable species which are only eaten under extreme conditions of need or overgrazing. The eating preferences of local grazing breeds are most significant when they are particularly hungry. The example of ferula (
Ferula communis L.) is worth mentioning here: this plant is toxic in all its green parts and is therefore avoided by goats, a behavior they’ve learned from their mothers. In summer, however, when the plants are dry and lignified, hungry goats strike them with their horns to drop and eat the seeds, the only non-toxic part of the plant. Livestock farmers’ pathways run throughout the entire area of this study: from the plateaus (Supramonte and the Tacchi) to the sea, through deep gorges (canyons) to the sheepfolds, a cultural and socioeconomic poor heritage recently repurposed by young people into hospitality and tourism.
3.3. Wild Edible Plants Used in Nutrition and Medicine Polyphenols
In family gardens, we have found 15 species of wild plants used in the Mediterranean diet, and 68 species with medicinal uses, as shown in the file attached to this paper. This case study provides an opportunity to further investigate the epigenetic factors of nutrition in relation to the phenomenon of longevity and good health in the population of this geographical area. The number of plants with medicinal applications observed in this study is remarkable: this testifies to their near-routine use, albeit entrusted to the competent management of particularly skilled individuals; although they were used for simple pathologies, elaborate preparations and uses seem to have existed against some pathologies of non-trivial etiology. Locally there is a marked technocratic consciousness of the function of the natural principle intended in its terminological fullness and not as a means through which some supernatural intercession takes place, as is the case of other non-European countries. The presence of such a large portion is also undoubtedly favored by ideal microclimatic conditions of speciation, particularly for the more polymorphic plants, as well as by of the heterogeneity of environments which can unequivocally influence the formation of the phenotype and secondary metabolites [
25]. This contingent consists of species with high pharmaceutical value from which molecules of wide therapeutic use and, consequently, of extreme commercial interest are still being extracted. Specific targeted phytochemical and pharmacological studies have also highlighted the different action, the heterogeneous pharmacokinetic diversification, of the same or new metabolites, present in wild plant species. The number of aromatic and essential plants commonly used in daily nutrition as well as of essences with cosmetic and herbal interest is significant.
3.4. Biodiversity of Plants for Landscape Enjoyment and Gardens
The landscape of this research is summarized by the illustration in
Figure 3, created during the monitoring, showing distinctive geomorphological features and habitat codes. The analysis of Mediterranean plants in this study provides a better understanding of the aesthetic value and of the enjoyment of shapes, colors, and scents. The sense of well-being experienced in nature, hiking trails admiring the naturalness of the elements, and forest bathing are aspects of the landscape which produce enjoyment. Plants observed in the monitoring pathways were reported in the biodiversity plant file as they also reveal the effects of interaction with human activities during the path of knowledge with the local communities. The euphorbias (
Euphorbia sp. pl.), asphodels (
Asphodelus microcarpus), brooms (
Genista corsica,
Cytisus sp. pl.), oleanders (
Nerium oleander), cysts (Cistus sp. pl.) hellebore (
Helleborus argutifolius Viv.), which tinge the valleys and impervious walls of the area of this case study, are toxic plants to animals and exhibit ecological forms of greater fire resistance.
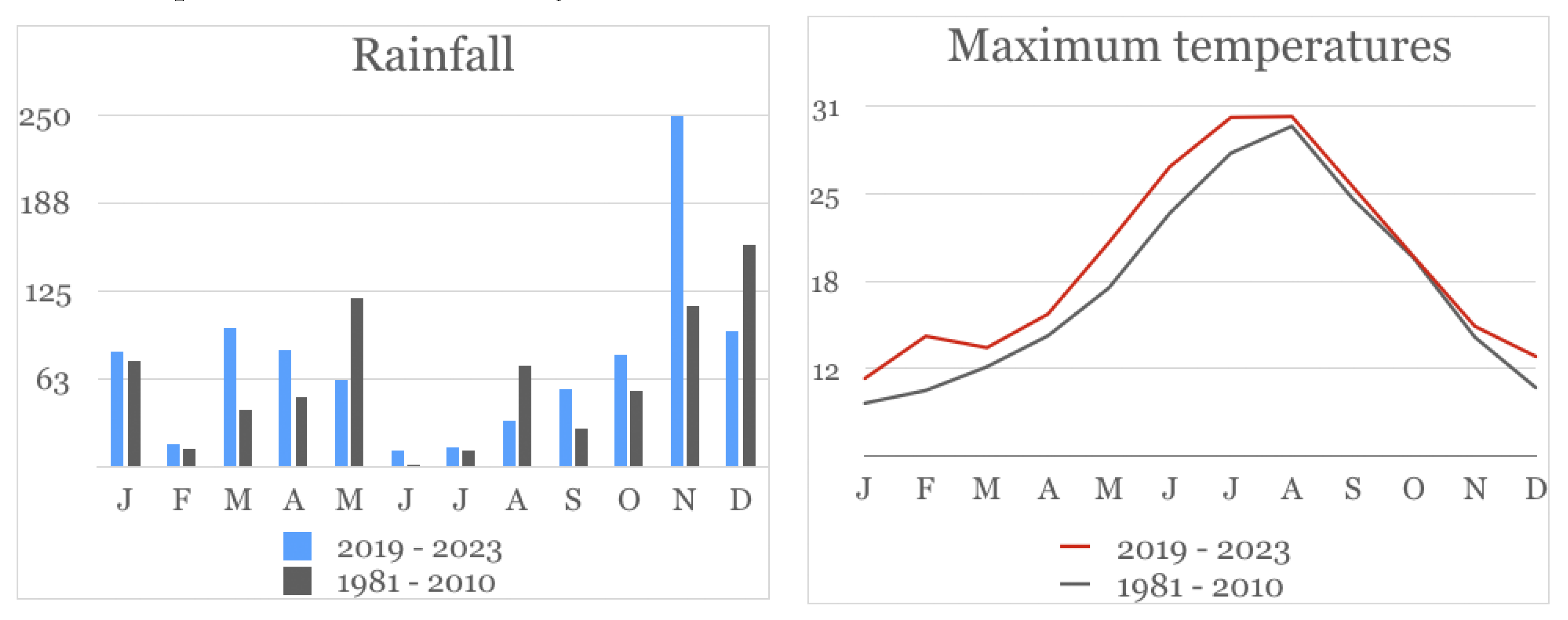
3.5. Climate Variability Measurement Data
The rainfall and maximum temperatures recorded from 2019 to 2023, compared with the 30-year climate series (1981 - 2010), can be seen in the graphs in
Figure 6. The histograms of rainfall distribution show differences in November (with rainfall being recorded at agro-meteorological stations with higher intensity and increasingly flooding character), and especially a clear increase in maximum temperatures, indicated by the red dashed line.
4. Discussion
This work is inspired by the classic Western culture idea of pathways involving in-progress knowledge of reality, comparing different points of view and different tools, i.e., scientific rigor and the knowledge of the local communities who use natural resources, shape the landscape, and have the difficult task of maintaining a balance between conservation and profit. In the forest pathways, the confirmation of the discovery of the mother plants of holm oak with sweet acorns highlights the ancient forest culture of the Mediterranean people, as well as the selection of a feature useful for human and animal nutrition, which, for selected plants, was prioritized over timber supply. This feature has been discussed in two aspects: the pig breeding management policy and the sanitary measures to contain the African swine fever virus. One additional aspect noted in this collaborative monitoring work is the favorable attitude of the local community toward the conservation of mother plants and regarding the protection of forest habitats when the scientific aspects of biodiversity are recognized in them, which strengthen the connection of the natural capital with the human capital. Forests are not places for livestock farming, but they have ecological importance in the biosphere and for multiple ecosystem services. The presence of the inhabitants of rural communities in fact amplifies plant genetic variability and enjoyment, but it can also restrict it through overgrazing and fires, or through excessive mass tourism on fragile ecosystems. On the one hand, the number of 541 taxa along the monitoring pathways expresses the factual objectivity of a territory providing many benefits and allows us to understand the value it provides under specific climatic, ecological, geographic, and socioeconomic conditions; on the other hand, it has limitations and serves, critically and educationally, as an indicator of the health of ecosystems for sustainable management policies. Identifying the number of taxa with the percentage of plants eaten by goats and pigs does not give this study zoo technical purposes. Rather, it is intended to focus attention on the ecosystem benefits of biodiversity functions seen as genetic richness to-ward animal nutrition on natural pastures, and therefore foster a deeper understanding of how many plants are likely to be lost under conditions of excessive grazing pressures. One weakness which has emerged was communicating the multiple functions of plant biodiversity to older farmers who are prone to exploitation of pastures with excesses of bred animals or replacing local breeds of goats and pigs with cattle unfit for maintaining the balance between profit and preservation of local genetic diversity. A key strength has been the ecosystem services of human well-being, produced by plant biodiversity through nutrition via the Mediterranean diet, as well as the enjoyment of the landscape. Poor pastoral farming, which, mainly thanks to young people, is evolving toward the experiential tourism of hospitality and nature trekking, has been prioritizing environmental protection and sustainable management. This Terre dell ’Aquilegia case study, over-laying a Blue Zone, could lend opportunity for further scientific research on the Mediterranean diet and well-being conditions. A significant element of surprise and discussion was how much landscape is directly related to plant biodiversity. Many but not all plants distinctive of the landscape have been found in family gardens. The lack of aesthetic appreciation for cultivating some of them in home gardens can perhaps be explained by the habit of considering them already as part of the landscape, which local people see as a natural garden; or it could depend on the fact that their presence is seen as weed of pastures, as for example in the case of hellebore, cistus, asphodel, broom, or euphorbias. Finally, the rise in maximum temperatures and the change in rainfall distribution, which was shared with local communities, warns of the in-creased and accelerated risks of loss of biodiversity and landscape quality in extreme cases of overgrazing and wildfires.
5. Conclusions
The analysis of the data collected and the experience of interacting with stakeholders have taught us how to improve collaboration. Therefore, we suggest the collaborative monitoring within path of knowledge to be used as an effective method which extends beyond this specific case and could prove useful in many other cases in which complexity requires participation. We have seen how the conceptual scheme (
Figure 1) of biodiversity and ecosystem services has been appreciated as a clear starting point which helps to communicate effectively and leads to collaboration and increased sense of ownership of the area as well as to trust toward scientific approach. We have offered an interpretation of biodiversity in numerical terms, complementing it with the detail of individual species shown in the attached file
Table S2 – Ecosystem biodiversity and socioeconomic and well-being benefits report, which reveal the almost hidden richness, as was the case with the mother plants of holm oak with sweet acorns. Particularly, the discovery of mother plants has strengthened the affective connection with the past and the vision of forests not only as a source of timber, but more importantly as a habitat for health and well-being and for connection with nature as well as for resilience and adaptation under changing climate conditions. During the pathways we have noted our limited knowledge of the stages of habitat depletion in some extreme cases, but we have also gained profound understanding of the benefits of human and animal food plants which have got a name in the local language. It was also interesting to find a high number of plants used in folk medicine, a clear positive sign for improving scientific studies and collaborative approach. Regarding the pathways, we had favoured freedom of choice within all habitats in this case study in order to obtain robust biodiversity estimation data. We would like to emphasize how the collaborative monitoring brought along that positive approach of feeling at home and of knowledge exchange. It also fostered involvement in sustainable management and a comprehensive view of ecosystem services and well-being, bringing back the centrality of biodiversity conservation and contributing at regional scale.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to this work; Conceptualization, A.S.P. and M.P.; methodology, M.B.; software, A.S.P.; validation, M.P.; B.P.; M.B.; formal analysis, M.B.; investigation, A.S.P.; M.P.; F.S.; G.S.; resources, A.S.P.; data curation, A.S.P.; M.P.; M.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.P.; writing—review and editing, A.S.P.; M.P.; M.B.; visualization, M.B.; M.P.; supervision, M.B.; A.S.P.; project administration, A.S.P.; funding acquisition, A.S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
data and material are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the majors of the municipalities and the population of the study area.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Qiu, J.; Yu, D.; Huang, T. Influential paths of ecosystem services on human well-being in the context of the sustainable development goals. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 852, 158443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graymore, M.L.M.; Sipe, N.G.; Rickson, R.E. Sustaining Human Carrying Capacity: A tool for regional sustainability assessment. Ecological Economics 2010, 69, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, D.; Vrahnakis, M.; Yiakoulaki, M.; Xanthopoulos, G.; Kazoglou, Y. (2023). Grazing as a Management Tool in Mediterranean Pastures: A Meta-Analysis Based on A Literature Review. In Land (Vol. 12, Issue 7). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI). [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeong, M. Research on hospitality and tourism education: Now and future. Tourism Management Perspectives 2018, 25, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rigo, D.; Caudullo, G. “Quercus ilex in Europe: Distribution, habitat, usage and threats.” European Atlas of Forest Tree Species; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; de Rigo, D.; Caudullo, G.; Houston Durrant, T.; Mauri, A.; Eds (2016): 152-153.
- Claudia, P. Acorn bread: A traditional food of the past in Sardinia (Italy). Journal of Cultural Heritage 2013, 14, S71–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, D.M.; Bondioli, C.; Hamzeh Hosseini, S.; Miara, M.D.; Musarella, C.M.; Mohammadi, D.; Khan Manduzai, A.; Dilawer Issa, K.; Sulaiman, N.; Khatib, C.; et al. Food Security beyond Cereals: A Cross-Geographical Comparative Study on Acorn Bread Heritage in the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Foods 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakić, S.; Povrenović, D.; Tešević, V.; Simić, M.; Maletić, R. Oak acorn, polyphenols and antioxidant activity in functional food. Journal of Food Engineering 2006, 74, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejerina, D.; García-Torres, S.; Cabeza de Vaca, M.; Vázquez, F.M.; Cava, R. Acorns (Quercus rotundifolia Lam.) and grass as natural sources of antioxidants and fatty acids in the “montanera” feeding of Iberian pig: Intra- and inter-annual variations. Food Chemistry 2011, 124, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risch, D.R.; Ringma, J.; Price, M.R. The global impact of wild pigs (Sus scrofa) on terrestrial biodiversity. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pautasso, M.; Aistara, G.; Barnaud, A.; et al. Seed exchange networks for agrobiodiversity conservation. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Carvalho, A.M.; Sánchez-Mata, M.C.; Cámara, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Pardo-de-Santayana, M.; Tardío, J. Mediterranean non-cultivated vegetables as dietary sources of compounds with antioxidant and biological activity. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2014, 55, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A. Mediterranean diet as intangible heritage of humanity: 10 years on. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2021, 31, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marselle, M.R.; Hartig, T.; Cox, D.T.C.; de Bell, S.; Knapp, S.; Lindley, S.; Triguero-Mas, M.; Böhning-Gaese, K.; Braubach, M.; Cook, P.A.; et al. Pathways linking biodiversity to human health: A conceptual framework. Environment International 2021, 150, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pes, G.; Tolu, F.; Dore, M.; et al. Male longevity in Sardinia, a review of historical sources supporting a causal link with dietary factors. Eur J Clin Nutr 2015, 69, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pes, G.M.; Poulain, M.; Errigo, A.; Dore, M.P. Evolution of the Dietary Patterns across Nutrition Transition in the Sardinian Longevity Blue Zone and Association with Health Indicators in the Oldest Old. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribot, Anne-Sophie, Julie Deter, and Nicolas Mouquet. “Integrating the aesthetic value of landscapes and biological diversity.”. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2018, 285, 20180971. [CrossRef]
- Wolch, J.R.; Byrne, J.; Newell, J.P. Urban green space, public health, and environmental justice: The challenge of making cities ‘just green enough’. Landscape and Urban Planning 2014, 125, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet-Mir, L.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Reyes-García, V. Beyond food production: Ecosystem services provided by home gardens. A case study in Vall Fosca, Catalan Pyrenees, Northeastern Spain. Ecological Economics 2012, 74, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Liquete, C.; Teller, A.; Erhard, M.; Paracchini, M.L.; Barredo, J.I.; Grizzetti, B.; Cardoso, A.; Somma, F.; Petersen, J.-E.; et al. An indicator framework for assessing ecosystem services in support of the EU Biodiversity Strategy to 2020. Ecosystem Services 2016, 17, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, Michel, Anne Herm, and Gianni Pes. “The Blue Zones: areas of exceptional longevity around the world.” Vienna yearbook of population research 2013, 87–108.
- Puxeddu, M.; Cuccuru, F.; Fais, S.; Casula, G.; Bianchi, M.G. 3D Imaging of CRP and Ultrasonic Tomography to Detect Decay in a Living Adult Holm Oak (Quercus ilex L.) in Sardinia (Italy). Applied Sciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onori, Roberta, Leucio Orefice, and Angelo Stacchini. “Massimo Baldini, Fabio Fabietti, Stefania Giammarioli.”. Rapporti ISTISAN 1996, 96, 34.
- Dewanto, Veronica, Xianzhong Wu, and Rui Hai Liu. “Processed sweet corn has higher antioxidant activity.”. Journal of Agricultural and food Chemistry 2002, 50, 4959–4964. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballero, M.; Loi, M.C.; Van Rozendaal, E.L.M.; Van Beek, T.A.; Van De Haar, C.; Poli, F.; Appendino, G. Analysis of pharmaceutically relevant taxoids in wild yew trees from Sardinia. Fitoterapia 2003, 74, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).