Submitted:
27 December 2023
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
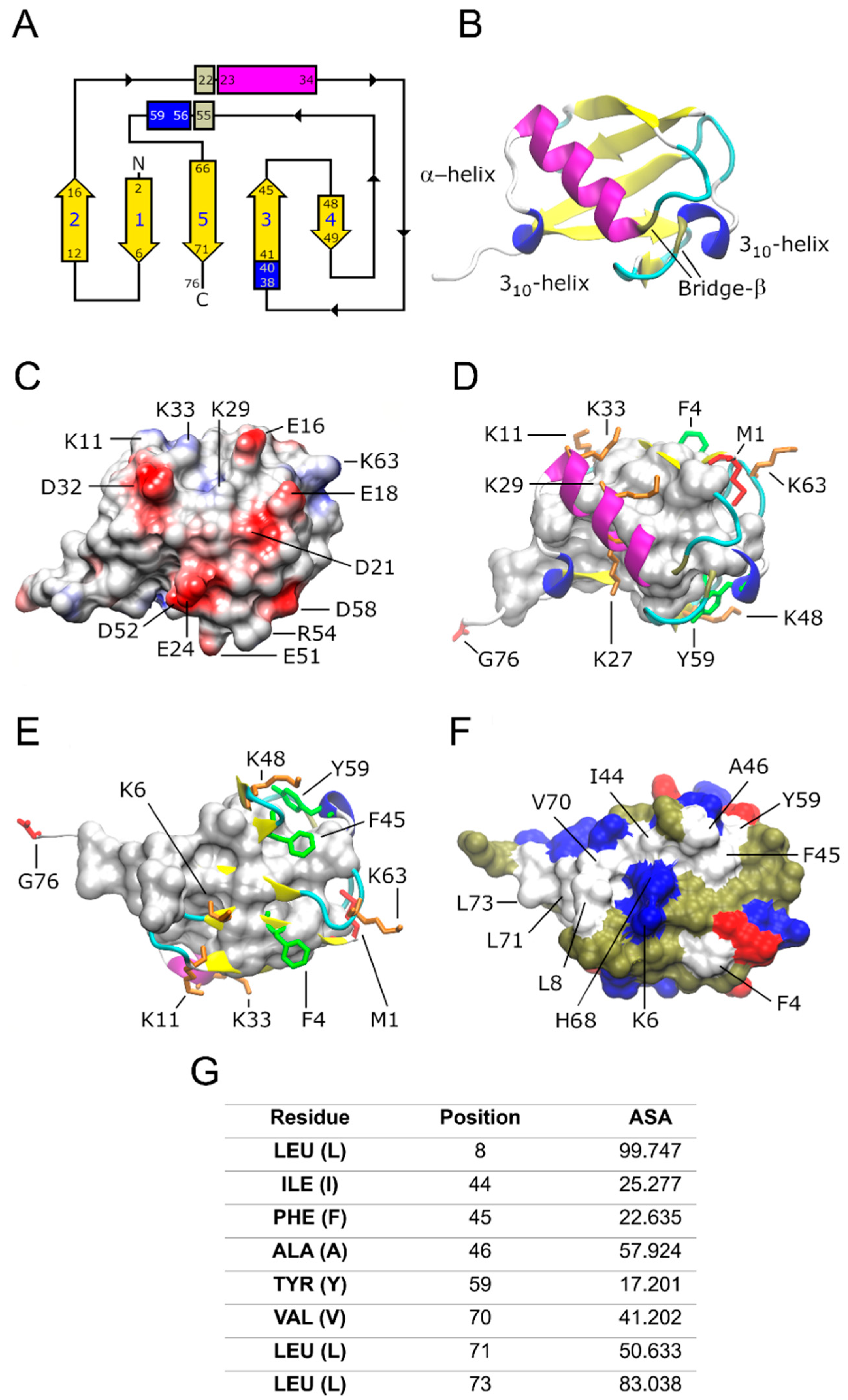
2. Ub structure at a glimpse
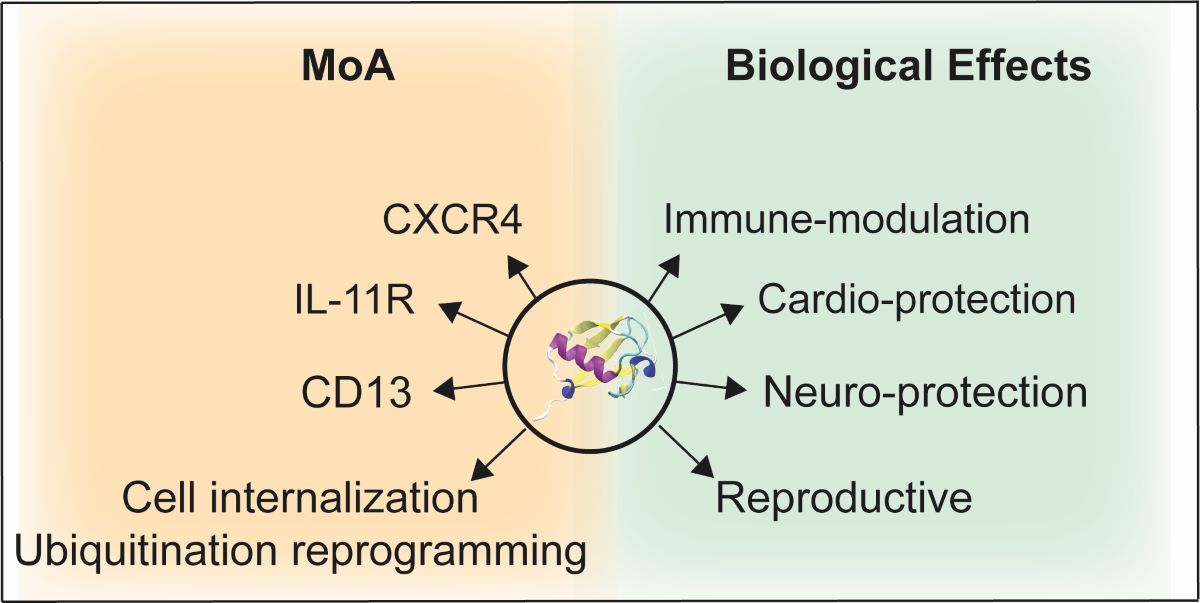
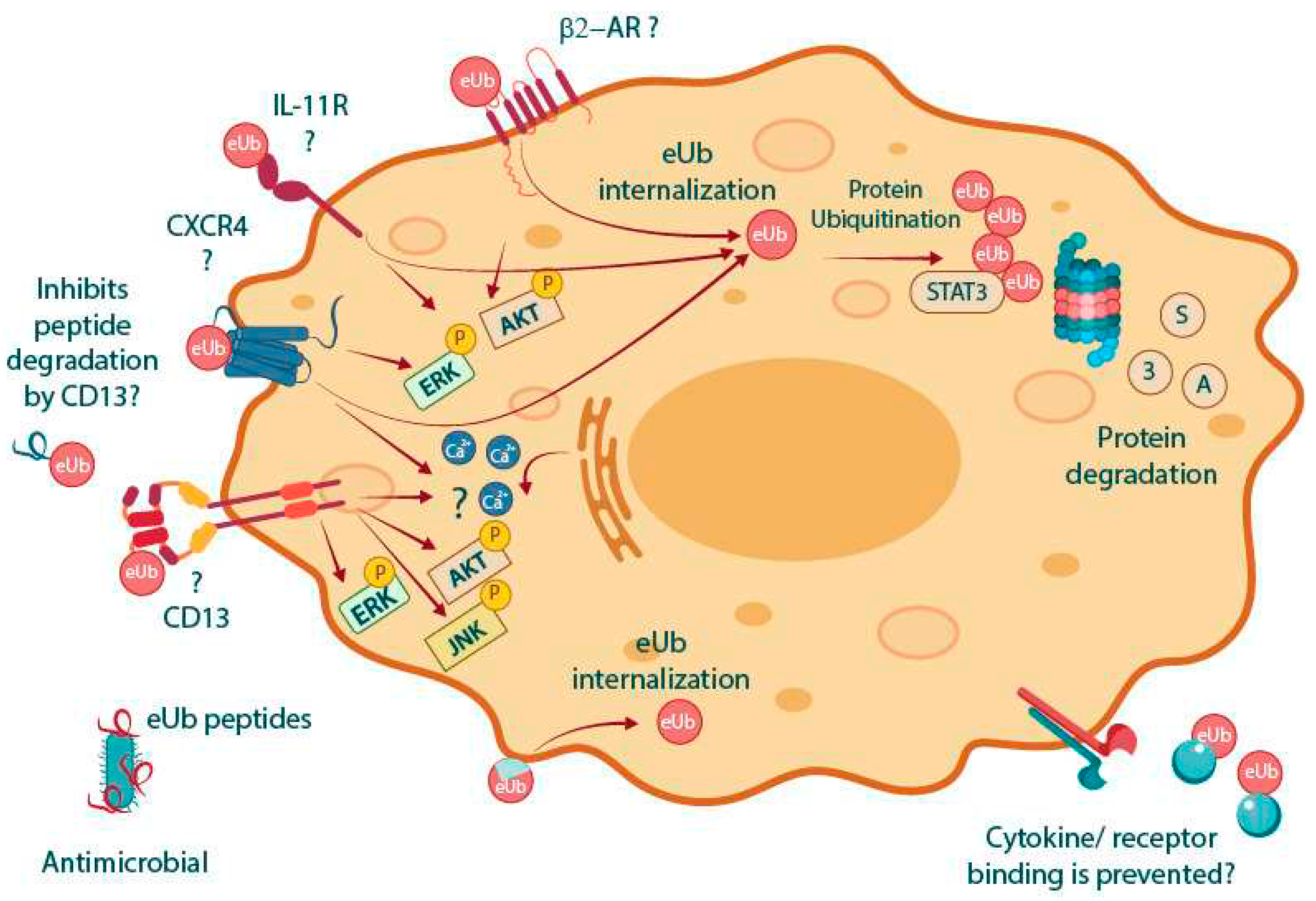
3. Potential MoAs of eUb
4. Biologic effects of eUb
4.1. Immune system
4.2. Nervous system
4.3. Cardiovascular system
5. Antibiotic effects of Ub
6. Effects of eUb in reproduction
7. Biopharmaceutical use of Ub
7.1. Development of Ub-based biotherapeutic
7.2. eUb as a component of Dialyzable Leukocyte Extracts (DLE)
7.3. Use of ubiquitin as scaffolds
8. Concluding remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, G.; Scheid, M.; Hammerling, U.; Schlesinger, D.H.; Niall, H.D.; Boyse, E.A. Isolation of a polypeptide that has lymphocyte-differentiating properties and is probably represented universally in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1975, 72, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Villanueva, S.; Gutierrez, G.; Kressler, D.; de la Cruz, J. Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-Like Proteins and Domains in Ribosome Production and Function: Chance or Necessity? Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikic, I.; Wakatsuki, S.; Walters, K.J. Ubiquitin-binding domains - from structures to functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009, 10, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.H.; Lee, S.; Prag, G. Ubiquitin-binding domains. Biochem J 2006, 399, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonico, E. Old and New Concepts in Ubiquitin and NEDD8 Recognition. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.L.; Meller, A.; Samandi, S.; Brunelle, M.; Frion, J.; Brunet, M.A.; Toupin, A.; Beaudoin, M.C.; Jacques, J.F.; Levesque, D.; et al. UBB pseudogene 4 encodes functional ubiquitin variants. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radici, L. , Bianchi, M., Crinelli, R. and Magnani, M. Ubiquitin C gene: Structure, function, and transcriptional regulation. Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology 2013, 4, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grou, C.P.; Pinto, M.P.; Mendes, A.V.; Domingues, P.; Azevedo, J.E. The de novo synthesis of ubiquitin: identification of deubiquitinases acting on ubiquitin precursors. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.S.; Baek, K.H. Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Related Proteins Modified by Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-like Proteins. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barandun, J.; Damberger, F.F.; Delley, C.L.; Laederach, J.; Allain, F.H.; Weber-Ban, E. Prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein remains intrinsically disordered when covalently attached to proteasomal target proteins. BMC Struct Biol 2017, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.J.; Mintseris, J.; Ferreyra, J.; Gygi, S.P.; Darwin, K.H. Ubiquitin-like protein involved in the proteasome pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 2008, 322, 1104–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, S.; Jobling, K.L.; O'Connor, D.; Thacker, Z.; Dryden, D.T.F.; Blakely, G.W. A unique homologue of the eukaryotic protein-modifier ubiquitin present in the bacterium Bacteroides fragilis, a predominant resident of the human gastrointestinal tract. Microbiology (Reading) 2011, 157, 3071–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.M.; LaPorte, H.M.; Albee, L.J.; Baker, T.A.; Bach, H.H.t.; Vana, P.G.; Evans, A.E.; Gamelli, R.L.; Majetschak, M. Ubiquitin Urine Levels in Burn Patients. J Burn Care Res 2017, 38, e133–e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I. Elevated levels of tau and ubiquitin in brain and cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer's disease. Int Psychogeriatr 1997, 9 Suppl 1, 289-296; discussion 317-221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandimalla, R.J.; Anand, R.; Veeramanikandan, R.; Wani, W.Y.; Prabhakar, S.; Grover, V.K.; Bharadwaj, N.; Jain, K.; Gill, K.D. CSF ubiquitin as a specific biomarker in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2014, 11, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majetschak, M.; Krehmeier, U.; Bardenheuer, M.; Denz, C.; Quintel, M.; Voggenreiter, G.; Obertacke, U. Extracellular ubiquitin inhibits the TNF-alpha response to endotoxin in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and regulates endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in critical illness. Blood 2003, 101, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagar, A.; Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Alexander, J.S.; Gonzalez-Toledo, E.; Albitar, M. Plasma ubiquitin-proteasome system profile in patients with multiple sclerosis: correlation with clinical features, neuroimaging, and treatment with interferon-beta-1b. Neurol Res 2012, 34, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjodin, S.; Hansson, O.; Ohrfelt, A.; Brinkmalm, G.; Zetterberg, H.; Brinkmalm, A.; Blennow, K. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Ubiquitin in Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinsonian Disorders. Proteomics Clin Appl 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, V.; Marchese, A.; Majetschak, M. CXC chemokine receptor 4 is a cell surface receptor for extracellular ubiquitin. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 15566–15576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; Marchese, A.; Tang, W.J.; Majetschak, M. Structural determinants of ubiquitin-CXC chemokine receptor 4 interaction. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 44145–44152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; Staren, D.M.; Ziarek, J.J.; Nashaat, Z.N.; Campbell, E.M.; Volkman, B.F.; Marchese, A.; Majetschak, M. The CXC chemokine receptor 4 ligands ubiquitin and stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha function through distinct receptor interactions. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 33466–33477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Xu, J.; Song, B.; Wu, A.; Pan, L.; Xu, Y.; Geng, F.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Hong, M.; et al. Interferon regulatory factor 1-triggered free ubiquitin protects the intestines against radiation-induced injury via CXCR4/FGF2 signaling. MedComm (2020) 2022, 3, e168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majetschak, M.; Ponelies, N.; Hirsch, T. Targeting the monocytic ubiquitin system with extracellular ubiquitin. Immunol Cell Biol 2006, 84, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppidi, A.; Doi, K.; Edwardraja, S.; Pulavarti, S.V.; Szyperski, T.; Wang, H.G.; Lin, Q. Targeted delivery of ubiquitin-conjugated BH3 peptide-based Mcl-1 inhibitors into cancer cells. Bioconjug Chem 2014, 25, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, D.S.; Sapmaz, A.; Gjonaj, L.; Merkx, R.; Ovaa, H. Enhanced Delivery of Synthetic Labelled Ubiquitin into Live Cells by Using Next-Generation Ub-TAT Conjugates. Chembiochem 2018, 19, 2553–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, O.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Wojciechowska, M.; Kedziora-Kornatowska, K. Ubiquitin Is Not a Blood Biomarker of an Early Cognitive Decline in the Polish Elderly. Curr Issues Mol Biol 2023, 45, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, M. Protein breakdown in muscle wasting: role of autophagy-lysosome and ubiquitin-proteasome. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2013, 45, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay-Kumar, S.; Bugg, C.E.; Cook, W.J. Structure of ubiquitin refined at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol 1987, 194, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, M.S.; Roder, H. Early hydrogen-bonding events in the folding reaction of ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992, 89, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.T.; Makhatadze, G.I. Contribution of the 30/36 hydrophobic contact at the C-terminus of the alpha-helix to the stability of the ubiquitin molecule. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 10275–10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, F. Branched ubiquitin code: from basic biology to targeted protein degradation. J Biochem 2022, 171, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Qi, F.; Fan, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; He, Y.; Gao, X.; Zeng, H.; et al. Multiomics approach reveals the ubiquitination-specific processes hijacked by SARS-CoV-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOVIA, D.S. Discovery Studio Visualizer; V19.1.0.18287; San Diego, CA, USA.
- Nguyen, T.; Ho, M.; Kim, K.; Yun, S.I.; Mizar, P.; Easton, J.W.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, K.K. Suppression of the Ubiquitin Pathway by Small Molecule Binding to Ubiquitin Enhances Doxorubicin Sensitivity of the Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappadocia, L.; Lima, C.D. Ubiquitin-like Protein Conjugation: Structures, Chemistry, and Mechanism. Chem Rev 2018, 118, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikic, I.; Schulman, B.A. An expanded lexicon for the ubiquitin code. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2023, 24, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, L.M.; Rahighi, S.; Ikeda, F. Linear ubiquitin chain-binding domains. FEBS J 2018, 285, 2746–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GIMP GNU IMAGE MANIPULATION PROGRAM. Available online: https://www.gimp.org/ (accessed on December 15th, 2023).
- Swatek, K.N.; Komander, D. Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res 2016, 26, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacoursiere, R.E.; Hadi, D.; Shaw, G.S. Acetylation, Phosphorylation, Ubiquitination (Oh My!): Following Post-Translational Modifications on the Ubiquitin Road. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 1996, 14, 33–38, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Davis, J.D.; Staren, D.M.; Volkman, B.F.; Majetschak, M. CXC chemokine receptor 4 signaling upon co-activation with stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha and ubiquitin. Cytokine 2014, 65, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Ho, M.; Ghosh, A.; Kim, T.; Yun, S.I.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, K.K. An ubiquitin-binding molecule can work as an inhibitor of ubiquitin processing enzymes and ubiquitin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 479, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eby, J.M.; Abdelkarim, H.; Albee, L.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gao, X.; Volkman, B.F.; Gaponenko, V.; Majetschak, M. Functional and structural consequences of chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 activation with cognate and non-cognate agonists. Mol Cell Biochem 2017, 434, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Job, F.; Settele, F.; Lorey, S.; Rundfeldt, C.; Baumann, L.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Haupts, U.; Lilie, H.; Bosse-Doenecke, E. Ubiquitin is a versatile scaffold protein for the generation of molecules with de novo binding and advantageous drug-like properties. FEBS Open Bio 2015, 5, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera-Vargas, A.; Gomez-Martin, D.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Merayo-Chalico, J.; Torres-Ruiz, J.; Manna, Z.; Hasni, S.; Alcocer-Varela, J.; Kaplan, M.J. Differential ubiquitination in NETs regulates macrophage responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 2018, 77, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiburghaus, C.; Welinder, C.; Tjornstad, U.; Lindmark-Mansson, H.; Paulsson, M.; Oredsson, S. Identification of ubiquitin in bovine milk and its growth inhibitory effects on human cancer cell lines. J Dairy Sci 2010, 93, 3442–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daino, H.; Matsumura, I.; Takada, K.; Odajima, J.; Tanaka, H.; Ueda, S.; Shibayama, H.; Ikeda, H.; Hibi, M.; Machii, T.; et al. Induction of apoptosis by extracellular ubiquitin in human hematopoietic cells: possible involvement of STAT3 degradation by proteasome pathway in interleukin 6-dependent hematopoietic cells. Blood 2000, 95, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, N.; Seno, H.; Konda, Y.; Marusawa, H.; Kanai, M.; Nakajima, T.; Kawashima, T.; Nanakin, A.; Sawabu, T.; Uenoyama, Y.; et al. STAT3 is constitutively activated and supports cell survival in association with survivin expression in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4921–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponelies, N.; Hirsch, T.; Krehmeier, U.; Denz, C.; Patel, M.B.; Majetschak, M. Cytosolic ubiquitin and ubiquitylation rates in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells during sepsis. Shock 2005, 24, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, M.E.; Passalacqua, K.D.; Hagen, S.E.; Showalter, H.D.; Wobus, C.E.; O'Riordan, M.X.D. Perturbation of ubiquitin homeostasis promotes macrophage oxidative defenses. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Roginskaya, M.; Dalal, S.; Menon, B.; Kaverina, E.; Boluyt, M.O.; Singh, K. Extracellular ubiquitin inhibits beta-AR-stimulated apoptosis in cardiac myocytes: role of GSK-3beta and mitochondrial pathways. Cardiovasc Res 2010, 86, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRocca, T.J.; Schwarzkopf, M.; Altman, P.; Zhang, S.; Gupta, A.; Gomes, I.; Alvin, Z.; Champion, H.C.; Haddad, G.; Hajjar, R.J.; et al. beta2-Adrenergic receptor signaling in the cardiac myocyte is modulated by interactions with CXCR4. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2010, 56, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafilou, M.; Brandenburg, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Fukase, K.; Mackie, A.; Seydel, U.; Triantafilou, K. Combinational clustering of receptors following stimulation by bacterial products determines lipopolysaccharide responses. Biochem J 2004, 381, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafilou, M.; Lepper, P.M.; Briault, C.D.; Ahmed, M.A.; Dmochowski, J.M.; Schumann, C.; Triantafilou, K. Chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) is part of the lipopolysaccharide "sensing apparatus". Eur J Immunol 2008, 38, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, K.P.; Tsai, S.; Aldakkak, M.; Gironda, S.; Adams, D.L. CXCR4 expression in tumor associated cells in blood is prognostic for progression and survival in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0264763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, N.; Saitoh, S.; Matsumoto, F.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Miyake, K. Roles for LPS-dependent interaction and relocation of TLR4 and TRAM in TRIF-signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008, 368, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoscato, A.A.; Prenovitz, D.A.; Lotze, M.T. Rapid extracellular degradation of synthetic class I peptides by human dendritic cells. J Immunol 1998, 161, 4023–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaber, J.; Baj, Z.; Pasnik, J.; Chmielewski, H.; Tchorzewski, H. Expression of aminopeptidase N (APN) on peripheral blood mononuclear cells' surface as a marker of these cells' transendothelial migration properties in the course of multiple sclerosis. Mediators Inflamm 2000, 9, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamysz, E.; Salaga, M.; Sobocinska, M.; Gieldon, A.; Fichna, J. Anti-inflammatory effect of novel analogs of natural enkephalinase inhibitors in a mouse model of experimental colitis. Future Med Chem 2016, 8, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, U.; Heimburg, A.; Helmuth, M.; Stefin, S.; Lendeckel, U.; Reinhold, D.; Faust, J.; Fuchs, P.; Sens, B.; Neubert, K.; et al. Triggering endogenous immunosuppressive mechanisms by combined targeting of Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPIV/CD26) and Aminopeptidase N (APN/ CD13)--a novel approach for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Int Immunopharmacol 2006, 6, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.N.; Langner, J.; Herrmann, M.; Riemann, D. Aminopeptidase N/CD13 is directly linked to signal transduction pathways in monocytes. Cell Immunol 2000, 201, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, J.; Ghosh, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Caromile, L.A.; Gerber, C.; Rezaul, K.; Han, D.K.; Shapiro, L.H. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CD13 regulates inflammatory cell-cell adhesion and monocyte trafficking. J Immunol 2013, 191, 3905–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellia, F.; Lanza, V.; Garcia-Vinuales, S.; Ahmed, I.M.M.; Pietropaolo, A.; Iacobucci, C.; Malgieri, G.; D'Abrosca, G.; Fattorusso, R.; Nicoletti, V.G.; et al. Ubiquitin binds the amyloid beta peptide and interferes with its clearance pathways. Chem Sci 2019, 10, 2732–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, J.E.; Prestel, A.; Martins, J.M.; Brondum, S.S.; Nielsen, O.; Garbers, A.E.; Suga, H.; Boomsma, W.; Rogers, J.M.; Hartmann-Petersen, R.; et al. A context-dependent and disordered ubiquitin-binding motif. Cell Mol Life Sci 2022, 79, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.; Freund, S.; Mohrle, B.; Wollner, K.; Brunjes, J.; Gauglitz, G.; Wiesmuller, K.H.; Jung, G. Ubiquitin binds to a short peptide segment of hydrolase UCH-L3: a study by FCS, RIfS, ITC and NMR. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michiels, L.; Van der Rauwelaert, E.; Van Hasselt, F.; Kas, K.; Merregaert, J. fau cDNA encodes a ubiquitin-like-S30 fusion protein and is expressed as an antisense sequence in the Finkel-Biskis-Reilly murine sarcoma virus. Oncogene 1993, 8, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van den Heuvel, J.; Ashiono, C.; Gillet, L.C.; Dorner, K.; Wyler, E.; Zemp, I.; Kutay, U. Processing of the ribosomal ubiquitin-like fusion protein FUBI-eS30/FAU is required for 40S maturation and depends on USP36. Elife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins in protein regulation. Circ Res 2007, 100, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Tanigawa, Y. Biochemical analysis of the receptor for ubiquitin-like polypeptide. J Biol Chem 1999, 274, 18026–18032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airapetov, M.I.; Eresko, S.O.; Ignatova, P.D.; Lebedev, A.A.; Bychkov, E.R.; Shabanov, P.D. Interleukin-11 in Pathologies of the Nervous System. Mol Biol 2023, 57, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedsadr, M.; Wang, Y.; Elzoheiry, M.; Shree Gopal, S.; Jang, S.; Duran, G.; Chervoneva, I.; Kasimoglou, E.; Wrobel, J.A.; Hwang, D.; et al. IL-11 induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation in monocytes and inflammatory cell migration to the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2221007120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, V.A.; Smith, H.T.; Hildebrandt, E.; Weiner, K. Ubiquitin has intrinsic proteolytic activity: implications for cellular regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1987, 84, 3685–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parakh, K.A.; Kannan, K. Ubiquitin with a non-ATP-dependent slow intrinsic proteolytic activity: a mild and rapid purification procedure. Indian J Biochem Biophys 1992, 29, 303–305. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; De, D.; Bhattacharyya, D. Degradation of fibrin-beta amyloid co-aggregate: A novel function attributed to ubiquitin. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2018, 1865, 1465–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, D.; Datta Chakraborty, P.; Mitra, J.; Sharma, K.; Mandal, S.; Das, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Bhattacharyya, D. Ubiquitin-like protein from human placental extract exhibits collagenase activity. PLoS One 2013, 8, e59585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiblein, M.; Ponelies, N.; Johnson, T.; Marzi, J.; Kontradowitz, K.; Geiger, E.; Marzi, I.; Henrich, D. Increased extracellular ubiquitin in surgical wound fluid provides a chemotactic signal for myeloid dendritic cells. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2020, 46, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majetschak, M.; Cohn, S.M.; Obertacke, U.; Proctor, K.G. Therapeutic potential of exogenous ubiquitin during resuscitation from severe trauma. J Trauma 2004, 56, 991–999; discussion 999–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majetschak, M.; Cohn, S.M.; Nelson, J.A.; Burton, E.H.; Obertacke, U.; Proctor, K.G. Effects of exogenous ubiquitin in lethal endotoxemia. Surgery 2004, 135, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.A.; Romero, J.; Bach, H.H.t.; Strom, J.A.; Gamelli, R.L.; Majetschak, M. Effects of exogenous ubiquitin in a polytrauma model with blunt chest trauma. Crit Care Med 2012, 40, 2376–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Covarrubias, L.; Manning, E.W., 3rd; Sorell, L.T.; Pham, S.M.; Majetschak, M. Ubiquitin enhances the Th2 cytokine response and attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury in the lung. Crit Care Med 2008, 36, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, S.L.C.; Dalal, S.; Lim, K.A.; Thrasher, P.R.; Daniels, C.R.; Peterson, J.M.; Singh, M.; Singh, K. Exogenous ubiquitin reduces inflammatory response and preserves myocardial function 3 days post-ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2019, 316, H617–H628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, B.; You, P.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, L.; Xia, R. Ubiquitin released in the plasma of whole blood during storage promotes mRNA expression of Th2 cytokines and Th2-inducing transcription factors. Transfus Apher Sci 2012, 47, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabika, T.; Terashima, M.; Momose, I.; Hosokawa, Y.; Nagasue, N.; Tanigawa, Y. Synergistic effect of ubiquitin on lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha production in murine macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999, 1450, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M.; Pasikowski, P.; Cebrat, M.; Stefanowicz, P.; Lisowski, M.; Artym, J.; Zimecki, M.; Zhukov, I.; Szewczuk, Z. The immunosuppressive activity and solution structures of ubiquitin fragments. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczuk, Z.; Stefanowicz, P.; Wilczynski, A.; Staszewska, A.; Siemion, I.Z.; Zimecki, M.; Wieczorek, Z. Immunosuppressory activity of ubiquitin fragments containing retro-RGD sequence. Biopolymers 2004, 74, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, S.A.; El-Haddad, A.; Patel, M.B.; Ruiz, P.; Pham, S.M.; Majetschak, M. Prolongation of skin graft survival by exogenous ubiquitin. Transplantation 2006, 82, 1544–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, X.; Li, J.; Qi, Q.; Sun, R.; Han, J.; Zhu, X.; Xie, M.; Guo, X.; et al. Extracellular ubiquitin promotes hepatoma metastasis by mediating M2 macrophage polarization via the activation of the CXCR4/ERK signaling pathway. Ann Transl Med 2020, 8, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Qian, X.; Qi, Q.; Han, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, R. Extracellular ubiquitin inhibits the apoptosis of hepatoma cells via the involvement of macrophages. Transl Cancer Res 2020, 9, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalatskaya, I.; Berchiche, Y.A.; Gravel, S.; Limberg, B.J.; Rosenbaum, J.S.; Heveker, N. AMD3100 is a CXCR7 ligand with allosteric agonist properties. Mol Pharmacol 2009, 75, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, R. Extracellular Ubiquitin is the Causal Link between Stored Blood Transfusion Therapy and Tumor Progression in a Melanoma Mouse Model. J Cancer 2019, 10, 2822–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujashvili, R.; Ioramashvili, I.; Mazmishvili, K.; Tsitsilashvili, S.; Gamkrelidze, M. Moderation of Quantitative Changes of Regenerating Erythropoietic Cells by Extracellular Ubiquitin. Georgian Med News 2019, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Cai, Q.; Xu, Y. The ubiquitin-CXCR4 axis plays an important role in acute lung infection-enhanced lung tumor metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 2013, 19, 4706–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.M.; West, C.M.; Chau, V. Antibodies directed against ubiquitin inhibit high affinity [3H]choline uptake in rat cerebral cortical synaptosomes. J Biol Chem 1986, 261, 14365–14368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.M.; West, C.M.; Stevens, B.R.; Chau, V.; Nguyen, M.T.; Judkins, J.H. Ubiquitin-directed antibodies inhibit neuronal transporters in rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem 1987, 49, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earle, S.A.; Proctor, K.G.; Patel, M.B.; Majetschak, M. Ubiquitin reduces fluid shifts after traumatic brain injury. Surgery 2005, 138, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griebenow, M.; Casalis, P.; Woiciechowsky, C.; Majetschak, M.; Thomale, U.W. Ubiquitin reduces contusion volume after controlled cortical impact injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goelz, L.; Casalis, P.A.; Thomale, U.W.; Misch, M. The effect of ubiquitin on immune response after controlled cortical impact injury. J Trauma 2011, 70, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarca-Castro, E.A.; Talavera-Pena, A.K.; Reyes-Lagos, J.J.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Perez-Sanchez, G.; de la Pena, F.R.; Maldonado-Garcia, J.L.; Pavon, L. Modulation of vagal activity may help reduce neurodevelopmental damage in the offspring of mothers with pre-eclampsia. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1280334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.Z.; Moster, D.; Harmon, Q.E.; Wilcox, A.J. Association of Preeclampsia in Term Births With Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Offspring. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzoni, L.; Faure, C.; Frasch, M.G. Fetal cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and necrotizing enterocolitis: the brain-gut connection begins in utero. Front Integr Neurosci 2013, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhimschi, I.A.; Nayeri, U.A.; Zhao, G.; Shook, L.L.; Pensalfini, A.; Funai, E.F.; Bernstein, I.M.; Glabe, C.G.; Buhimschi, C.S. Protein misfolding, congophilia, oligomerization, and defective amyloid processing in preeclampsia. Sci Transl Med 2014, 6, 245ra292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cater, J.H.; Kumita, J.R.; Zeineddine Abdallah, R.; Zhao, G.; Bernardo-Gancedo, A.; Henry, A.; Winata, W.; Chi, M.; Grenyer, B.S.F.; Townsend, M.L.; et al. Human pregnancy zone protein stabilizes misfolded proteins including preeclampsia- and Alzheimer's-associated amyloid beta peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 6101–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiber, A.; Andreadou, I.; Oelze, M.; Davidson, S.M.; Hausenloy, D.J. Discovery of new therapeutic redox targets for cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury and heart failure. Free Radic Biol Med 2021, 163, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Hashim, M.J.; Mustafa, H.; Baniyas, M.Y.; Al Suwaidi, S.; AlKatheeri, R.; Alblooshi, F.M.K.; Almatrooshi, M.; Alzaabi, M.E.H.; Al Darmaki, R.S.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Ischemic Heart Disease: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Cureus 2020, 12, e9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J.; Weng, Z.; He, Y. Extracellular ubiquitin levels are increased in coronary heart disease and associated with the severity of the disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 2020, 80, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrello, E.R.; Mahmoud, A.I.; Simpson, E.; Hill, J.A.; Richardson, J.A.; Olson, E.N.; Sadek, H.A. Transient regenerative potential of the neonatal mouse heart. Science 2011, 331, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, B.; Johnson, J.N.; Ross, R.S.; Singh, M.; Singh, K. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta plays a pro-apoptotic role in beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulated apoptosis in adult rat ventricular myocytes: Role of beta1 integrins. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2007, 42, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, C.R.; Foster, C.R.; Yakoob, S.; Dalal, S.; Joyner, W.L.; Singh, M.; Singh, K. Exogenous ubiquitin modulates chronic beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulated myocardial remodeling: role in Akt activity and matrix metalloproteinase expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2012, 303, H1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, S.; Daniels, C.R.; Li, Y.; Wright, G.L.; Singh, M.; Singh, K. Exogenous ubiquitin attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiac myocyte apoptosis via the involvement of CXCR4 and modulation of mitochondrial homeostasis. Biochem Cell Biol 2020, 98, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, P.R.; Nascimento, L.D.; Gerlach, R.F.; Rodrigues, K.E.; Prado, A.F. Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 as a Pharmacological Target in Heart Failure. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, G.; Locquet, F.; Kociszewska, J.; Osygus, Y.; Heger, J.; Schreckenberg, R.; Schluter, K.D.; Kenyeres, E.; Szabados, T.; Bencsik, P.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinases Repress Hypertrophic Growth in Cardiac Myocytes. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2021, 35, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Berry, E.; Hernandez-Anzaldo, S.; Takawale, A.; Kassiri, Z.; Fernandez-Patron, C. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 mediates a mechanism of metabolic cardioprotection consisting of negative regulation of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2/3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase pathway in the heart. Hypertension 2015, 65, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, W. Targeting angiogenesis in myocardial infarction: Novel therapeutics (Review). Exp Ther Med 2022, 23, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braile, M.; Marcella, S.; Cristinziano, L.; Galdiero, M.R.; Modestino, L.; Ferrara, A.L.; Varricchi, G.; Marone, G.; Loffredo, S. VEGF-A in Cardiomyocytes and Heart Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steagall, R.J.; Daniels, C.R.; Dalal, S.; Joyner, W.L.; Singh, M.; Singh, K. Extracellular ubiquitin increases expression of angiogenic molecules and stimulates angiogenesis in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells. Microcirculation 2014, 21, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, S.; Schenke-Layland, K. Cardiac fibrosis - A short review of causes and therapeutic strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2019, 146, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Takawale, A.; Lee, J.; Kassiri, Z. Cardiac fibroblasts, fibrosis and extracellular matrix remodeling in heart disease. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2012, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Bian, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. Cardiac Fibroblasts and Myocardial Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2021, 9, 599928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, S.L.C.; Daniels, C.R.; Dalal, S.; Millard, J.A.; Singh, M.; Singh, K. Extracellular ubiquitin modulates cardiac fibroblast phenotype and function via its interaction with CXCR4. Life Sci 2018, 211, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.K.; Mi, E.; Ritov, V.B.; Gillespie, D.G. Extracellular Ubiquitin(1-76) and Ubiquitin(1-74) Regulate Cardiac Fibroblast Proliferation. Hypertension 2018, 72, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.K.; Zhang, Y.; Gillespie, D.D.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, D.; Jackson, T.C. SDF-1alpha (Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1alpha) Induces Cardiac Fibroblasts, Renal Microvascular Smooth Muscle Cells, and Glomerular Mesangial Cells to Proliferate, Cause Hypertrophy, and Produce Collagen. J Am Heart Assoc 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralat, L.A.; Kalas, V.; Zheng, Z.; Goldman, R.D.; Sosnick, T.R.; Tang, W.J. Ubiquitin is a novel substrate for human insulin-degrading enzyme. J Mol Biol 2011, 406, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Stepien-Pysniak, D.; Wieczorek, K.; Dec, M.; Nowaczek, A.; Osek, J. Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria-A Review. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, S.; Zhu, C.; Li, P.; He, J.; Mackey, V.; Coy, D.H.; He, Q. The antimicrobial peptides and their potential clinical applications. Am J Transl Res 2019, 11, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kieffer, A.E.; Goumon, Y.; Ruh, O.; Chasserot-Golaz, S.; Nullans, G.; Gasnier, C.; Aunis, D.; Metz-Boutigue, M.H. The N- and C-terminal fragments of ubiquitin are important for the antimicrobial activities. FASEB J 2003, 17, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, S.; Pethe, K.; Russell, D.G.; Purdy, G.E. Lysosomal killing of Mycobacterium mediated by ubiquitin-derived peptides is enhanced by autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 6031–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.C.; Shin, S.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Park, Y.; Hahm, K.S. Purification and antimicrobial activity studies of the N-terminal fragment of ubiquitin from human amniotic fluid. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007, 1774, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.K.; Lee, M.J.; Go, H.J.; Kim, G.D.; Jeong, H.D.; Nam, B.H.; Park, N.G. Purification and antimicrobial function of ubiquitin isolated from the gill of Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Mol Immunol 2013, 53, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majetschak, M. Extracellular ubiquitin: immune modulator and endogenous opponent of damage-associated molecular pattern molecules. J Leukoc Biol 2011, 89, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, G.E.; Russell, D.G. Lysosomal ubiquitin and the demise of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell Microbiol 2007, 9, 2768–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, B.C.; Pasupathy, K.; Mishra, K.P. Effects of exogenous ubiquitin on cell division cycle mutants of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2005, 244, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, H.; Mino, M.; Akasaka, M. Sperm proteases and extracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system involved in fertilization of ascidians and sea urchins. Adv Exp Med Biol 2014, 759, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujino, J.; Flores, S.Y.; Yokosawa, H. Localization and roles in fertilization of sperm proteasomes in the ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. Mol Reprod Dev 2002, 62, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petelak, A.; Krylov, V. Surface sperm cell ubiquitination directly impaired blastocyst formation rate after intracytoplasmic sperm injection in pig. Theriogenology 2019, 135, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.M.; Zhang, X.; Qian, D.; Lin, H.Y.; Li, Q.L.; Liu, D.L.; Liu, G.Y.; Yu, X.D.; Zhu, C. Effect of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway on mouse blastocyst implantation and expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9. Biol Reprod 2004, 70, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz-Jaffe, M.G.; Schoolcraft, W.B.; Gardner, D.K. Analysis of protein expression (secretome) by human and mouse preimplantation embryos. Fertil Steril 2006, 86, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.T.; Zhang, K.; Dong, J.; Lord, E.M. Exogenous free ubiquitin enhances lily pollen tube adhesion to an in vitro stylar matrix and may facilitate endocytosis of SCA. Plant Physiol 2006, 142, 1397–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biotherapeutic products by Word Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/health-product-policy-and-standards/standards-and-specifications/biotherapeutic-products (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Apostolopoulos, V.; Bojarska, J.; Chai, T.T.; Elnagdy, S.; Kaczmarek, K.; Matsoukas, J.; New, R.; Parang, K.; Lopez, O.P.; Parhiz, H.; et al. A Global Review on Short Peptides: Frontiers and Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, S.; Tagliazucchi, D. Bioactive Peptides in Human Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morio, K.A.; Sternowski, R.H.; Brogden, K.A. Induction of Endogenous Antimicrobial Peptides to Prevent or Treat Oral Infection and Inflammation. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.; Delgado, M. Endogenous anti-inflammatory neuropeptides and pro-resolving lipid mediators: a new therapeutic approach for immune disorders. J Cell Mol Med 2008, 12, 1830–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem Biol Drug Des 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuin, A.; Isasa, M.; Crosas, B. Ubiquitin signaling: extreme conservation as a source of diversity. Cells 2014, 3, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surana, P.; Das, R. Observing a late folding intermediate of Ubiquitin at atomic resolution by NMR. Protein Sci 2016, 25, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DrugBank. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/ (accessed on 16 December 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 16 December 2023).
- Cortellis Drug Discovery Intelligence. Available online: https://www.cortellis.com/marketing/drugdiscovery/ (accessed on 16 December 2023).
- Medina-Rivero, E.; Merchand-Reyes, G.; Pavon, L.; Vazquez-Leyva, S.; Perez-Sanchez, G.; Salinas-Jazmin, N.; Estrada-Parra, S.; Velasco-Velazquez, M.; Perez-Tapia, S.M. Batch-to-batch reproducibility of Transferon. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2014, 88, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, A.E.; Guani-Guerra, E. Transfer Factor: Myths and Facts. Arch Med Res 2020, 51, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Parra, S.; Nagaya, A.; Serrano, E.; Rodriguez, O.; Santamaria, V.; Ondarza, R.; Chavez, R.; Correa, B.; Monges, A.; Cabezas, R.; et al. Comparative study of transfer factor and acyclovir in the treatment of herpes zoster. Int J Immunopharmacol 1998, 20, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Jazmin, N.; Estrada-Parra, S.; Becerril-Garcia, M.A.; Limon-Flores, A.Y.; Vazquez-Leyva, S.; Medina-Rivero, E.; Pavon, L.; Velasco-Velazquez, M.A.; Perez-Tapia, S.M. Herpes murine model as a biological assay to test dialyzable leukocyte extracts activity. J Immunol Res 2015, 2015, 146305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, A.I.; Vallejo-Castillo, L.; Fragozo, A.; Vazquez-Leyva, S.; Pavon, L.; Perez-Sanchez, G.; Soria-Castro, R.; Mellado-Sanchez, G.; Cobos-Marin, L.; Perez-Tapia, S.M. Increased survival in puppies affected by Canine Parvovirus type II using an immunomodulator as a therapeutic aid. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 19864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Castillo, L.; Favari, L.; Vazquez-Leyva, S.; Mellado-Sanchez, G.; Macias-Palacios, Z.; Lopez-Juarez, L.E.; Valencia-Flores, L.; Medina-Rivero, E.; Chacon-Salinas, R.; Pavon, L.; et al. Sequencing Analysis and Identification of the Primary Peptide Component of the Dialyzable Leukocyte Extract "Transferon Oral": The Starting Point to Understand Its Mechanism of Action. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 569039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonini, H.; Goncalves, A.; Dijkers, E.; Ferreira, A.O. Characterization and Safety Profile of Transfer Factors Peptides, a Nutritional Supplement for Immune System Regulation. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersbach, H.; Fiedler, E.; Scheuermann, T.; Fiedler, M.; Stubbs, M.T.; Reimann, C.; Proetzel, G.; Rudolph, R.; Fiedler, U. Affilin-novel binding molecules based on human gamma-B-crystallin, an all beta-sheet protein. J Mol Biol 2007, 372, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirecka, E.A.; Hey, T.; Fiedler, U.; Rudolph, R.; Hatzfeld, M. Affilin molecules selected against the human papillomavirus E7 protein inhibit the proliferation of target cells. J Mol Biol 2009, 390, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settele, F.; Zwarg, M.; Fiedler, S.; Koscheinz, D.; Bosse-Doenecke, E. Construction and Selection of Affilin((R)) Phage Display Libraries. Methods Mol Biol 2018, 1701, 205–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorey, S.; Fiedler, E.; Kunert, A.; Nerkamp, J.; Lange, C.; Fiedler, M.; Bosse-Doenecke, E.; Meysing, M.; Gloser, M.; Rundfeldt, C.; et al. Novel ubiquitin-derived high affinity binding proteins with tumor targeting properties. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 8493–8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, M.; Settele, F.; Knick, P.; Haupts, U.; Bosse-Doenecke, E. Mabfilin and Fabfilin - New antibody-scaffold fusion formats for multispecific targeting concepts. Protein Expr Purif 2018, 149, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienen, F.; Nilson, R.; Allmendinger, E.; Graumann, D.; Fiedler, E.; Bosse-Doenecke, E.; Kochanek, S.; Krutzke, L. Affilin-based retargeting of adenoviral vectors to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Biomater Adv 2023, 144, 213208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Yao, J.; He, Y. Extracellular ubiquitin protects cardiomyocytes during ischemia/hypoxia by inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis pathway through CXCR4. Biomed Pharmacother 2020, 131, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujashvili, R.; Ioramashvili, I.; Aptsiauri, K.; Gvinadze, N. Regulation of leucogenesis by extracellular ubiquitin in rodents after chemically induced inhibition. Tsitol Genet 2016, 50, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| REFERENCES [127] [127] [127] |
[129] |
[130] |
|||
| Pathogen/ MIC (μM)1 | Ub1-76 | Ub65-76 | Ub65-76 + 10 µM Ub1-34 | AFP-1 | cgUbiquitin |
|
Gram-positive bacteria |
|||||
| Micrococcus luteus | 60 | 5 | 5 | ND | ND |
| Bacillus megaterium | 60 | 4 | 3 | ND | ND |
| Bacillus subtilis | ND | NA | ND | ND | 0.4 |
| Listeria monocytogenes | ND | NA | ND | 8 | ND |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ND | NA | ND | 8 | 4.7 |
|
Gram-negative bacteria |
|||||
| Escherichia coli | ND | 20 | 20 | 32 | 0.2 |
| Salmonella typhimurium | ND | NA | ND | 32 | ND |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ND | NA | ND | ND | 0.6 |
| Shigella flexneri | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.7 |
| Filamentous fungi | |||||
| Neurospora crassa | 60 | 10 | 4 | 32 | ND |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | ND | 30 | 15 | 64 | ND |
| Tricophyton mentagrophytes | ND | 20 | 7 | ND | ND |
| Trichoderma viride | ND | 10 | 7 | ND | ND |
| Botrytis cinerea | ND | ND | ND | 16 | ND |
| Fusarium oxysporum | ND | 4 | ND | 16 | ND |
| Yeast | |||||
| Candida albicans | ND | 15 | 7 | 8 | 9.4 |
| Candida tropicalis | ND | 15 | 7 | ND | ND |
| Candida glabrata | ND | 20 | 10 | ND | ND |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | ND | 15 | 7 | 8 | ND |
| Cell line (Source) |
Dose and time of treatment | Observed effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Colon carcinoma cell line (CaCo; ATCC) |
0.02 - 2.0 µM 7 days |
Decrease in cell proliferation | [48] |
| Human PBMNCs | 865 ng/ mL 0.1-1 µg/mL |
Decreases TNF-α production induced by LPS | [16,84] |
|
Mouse macrophages (RAW 263) (RCB cell bank) |
0.1 -10 µM 24 h |
Synergizes with LPS to induce TNF-α production (100 ng/mL). | [85] |
| Mouse splenocytes | 1-100 µg/mL | Suppresses the Humoral immune response to SRBC. Inhibits mixed leukocyte reaction. |
[86,97] |
|
THP-1 macrophages (Shangai Biology Institute) |
10 µg /mL 72 h |
Induces M2 macrophage polarization with a decrease in secreted TGF-β and increased IL10. | [89] |
|
Murine melanoma B16 (Shangai Research Center for Southern Model Organisms) |
200 – 800 ng/mL 24-96h |
Decreases apoptosis and promotes invasion by inducing MMP9 and VEGF production. | [92] |
|
Blood cells: - Myeloid cells (HL-60 and U937) - B cells (Daudi) - T cells (KT3, MT4, YTC-3 and MOLT4) (Nakarai Tesque, Kyoto) |
100 µg/mL 48h |
Decreases cell viability and induces apoptosis | [49] |
| Neuroblastoma cells (SH-Sy5y)(Not stated) | 1,0–5,0 μg | Prevents amyloid-β1-42 and prevent aggregate cytotoxicity | [76] |
| Cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (CMEC) (Not stated) | 20 μg/ml | Promotes VEGF-A expression | [117] |
|
Mouse tumor cell lines (B16-F10 and 4T1) (ATCC) |
10 μg/ml | Promotes cell migration. | [94] |
|
Alveolar Ventricular Rat Myocytes (AVRM). (Freshly obtained from hearts of adult male Sprague-Dawley rats) |
10 μg/ml 30 min prior ISO |
Protects AVRRM from ISO-induced apoptosis via blockade of GSK-3β and JNK activation. Protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in ARVMs |
[53,110,111] |
|
Adult rat cardiac Fibroblast (Freshly obtained) |
10 μg/ml |
Reduced fibroblast migration and proliferation. Promotes differentiation to myofibroblasts | [121] |
|
Cardiac fibroblasts (Isolated from SHT and WKY rats) |
1-10 µM | Decreases SDF-1-induced cardiac fibroblast proliferation | [122] |
|
H9C2 rat cardiac myoblast (Cell line bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, China) |
0.1-1000 µg/mL 15 min prior 2h hypoxia |
Prevents apoptosis | [164] |
| Saccharomyces pombe | 25-100 μg/mL Early log phase addition |
Reduced cell growth | [133] |
| Animal (Source) |
Dose and time of treatment | Observed effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skin graft in mice | 3.125, 12.5 or 25 μg of ubiquitin/h 14 days | Decreases the leukocyte reaction of the host vs graft response Decreases skin graft rejection. | [88] |
| ISO-induced cardiomyopathy in mice | 1 μg/g 1 h before ISO infusion |
Prevents myocyte apoptosis (decreases cytosolic release of cytochrome C). | [110] |
| Mouse head trauma | 1.5mg/kg | Promotes the recruitment of activated macrophages around areas of brain injury and improves recovery markers after mechanical damage to the brain. | [97] |
| Irradiated mice | 100 µg/ml at 72 hours after irradiation | Regulation of stem cell activity. | [165] |
| HSV-1 infection in mice | 12.5 ng, 0.125 μg, 0.25 μg, 0.5 μg, 0.75 μg, 1.0 μg, or 1.50 μg of eUb in mixture. | Regulation of the production of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ. | [154] |
| Lilium longiflorum | Bovine eUb 150 and 200 ng per matrix | Promotion of pollen adhesion to the stigma (pollen tube adhesion enhancer) | [139] |
| Source | Dose and time of treatment | Observed effect | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolated hearts | 10 μg/L5 min post-ischemia 1μg/g/h |
Reduced apoptosis, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial fission, but increased mitochondrial biogenesis in a CXCR4-dependent manner. Reduced the inflammatory response in the heart by reducing the infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages. |
[83,111] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





