1. Introduction
The human colon contains all sorts of gut microbiota, which plays a critical part in maintaining the development and balance of the body (Knight, Callewaert, Marotz, Hyde, Debelius, McDonald, et al., 2017). Gut microbiota can resolve indigestible nutrients into bioactive molecules, such as neurotransmitters, vitamins, and fatty acids, which protect the body from pathogens (Kamada, Kim, Sham, Vallance, Puente, Martens, et al., 2012). Furthermore, gut microbiota is susceptible to the influence of numerous factors, such as diet, living habits, and environment, and has a high degree of plasticity. Hence, modification of gut microbiota through diet has a great potential to promote human health and prevent and control diseases.
Shaping gut microbiota by carbohydrate has become one of the important ways to promote human health (Koropatkin, Cameron, & Martens, 2012). Such substances are capable of changing the gut microbiota and metabolites, which results in beneficial effects on the human body (Asadpoor, Peeters, Henricks, Varasteh, Pieters, Folkerts, et al., 2020). Sialic acid (SA) is a nine-carbon chain monosaccharide with various biological functions, such as neurotransmission, antiviral activity, promotion of gut health and nutrient absorption, and acceleration of cognitive development of the brain (Stencel-Baerenwald, 2014; Varki & Gagneux, 2012). In addition, SA can resist digestion and reach the colon for use by gut microbiota (Coker, Moyne, Rodionov, & Zengler, 2021). Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) containing SA can promote probiotic growth and inhibit pathogenic bacteria colonization and thus have a significant effect on infant health (Engfer, Stahl, Finke, Sawatzki, & Daniel, 2000; Newburg, Ruiz-Palacios, & Morrow, 2005). At present, studies on the effects of dietary SA on adult gut microbial ecosystem are still lacking (Coker, Moyne, Rodionov, & Zengler, 2021). In addition, countries, such as those belonging to the European Union, Japan, Singapore, and Malaysia, have approved the use of SA as food ingredients. The SA produced by our laboratory through hydrolytic polysialic acid (PSA) meets the basic requirements of food safety and has been approved as a novel food in China.
PSA is a polymer formed by SA, and it makes a critical difference in the maintenance of nervous system development, function, and health (Colley, Kitajima, & Sato, 2014; Sato & Kitajima, 2013). PSA has widespread applications in biomedicine, bio-binding materials, and materials for drug embedding and sustained release (Antony Constantinou, 2008; Jung, Shim, Park, Jang, Yoon, Kim, et al., 2017; Zhang, 2016). In addition, polysaccharides of different molecular weights have varied effects on gut microbiota (Deng, Zhong, Long, Zou, Wang, Song, et al., 2020; Mao, Xu, Li, Cao, Song, Zhao, et al., 2021). As a polymer of SA, PSA has not been reported to regulate gut microbiota in healthy people.
Under ideal conditions, the digestion of food and its influence on gut microbiota can be investigated scientifically and accurately through human experiments. However, high costs, technical limitations, and ethical constraints cause difficulties in human experiments. Therefore, more in vitro gastrointestinal models have been developed to evaluate the digestive properties and prebiotic functions of foods. In this study, a self-developed bionic gastrointestinal reactor (BGR) was used, and it can simulate the whole process of food fermentation in the colon after the action of the digestive system(Li, Zhu, Zhang, Zhan, & Gao, 2020). BGRs have been used to investigate the fate of food and polysaccharides during digestion and their effects on gut microbiota (Li, Hu, Zhu, Zhao, Jiang, Gao, et al., 2021; Sun, Xu, Yin, Li, Li, Zhu, et al., 2022).
According to existing studies, HMOs containing SA have a positive effect on infant gut microbiota, and dietary SA can change the community of adult gut microbiota. Meanwhile, differences in the molecular weights of polysaccharides may have various effects on gut microbiota. The difference between the effects of PSA and SA on the gut microbiota of healthy people are unknown and no relevant studies have been reported thus far. We hypothesized that PSA and SA have different effects on gut microbiota of healthy people. We predicted that (1) PSA and SA have different influences on gut microbial community composition and metabolites and (2) positive effects on gut microbiota. To verify our prediction, we prepared PSA with a molecular weight of 260 kDa by a specific fermentation process and obtained SA by acid hydrolysis. Subsequently, a BGR was used to explore the digestive processes of PSA and SA, and their effects on gut microbial community composition and metabolites of healthy people were explored by 16s rDNA high-throughput sequencing technology and non-targeted metabolomics technology. This study explored the different effects of PSA and SA on gut microbiota in healthy people for the first time and conducted comparative analysis to provide innovative theoretical foundation and feasible solutions for the application of PSA and SA in the regulation of gut microbiota.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemicals
Pepsin, α-amylase, gastric lipase, trypsin, bile salts, and vitamin K were from Sigma–Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Chlorine heme, NaCl, KCl, NaHCO3, HCl, MgSO4, CaCl2, CH3COONa, sorbitol, K2HPO4·3H2O, (NH4)2SO4, tryptone, FeCl3, MnCl2, ZnSO4, MgSO4, and oxalic acid were from China National Pharmaceutical Group Corporation (Beijing, China). The above reagents were of analytical grade.
Methanol, ammonium acetate, and formic acid were from Thermo-Fisher (Waltham, MA, USA), The above reagents were of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analytical grade.
2.2. Preparation and Extraction of PSA and SA
Fermentation preparation of PSA. This study is based on the research of Zheng et al., with minor modifications (Zheng, Wang, Li, Zhan, Lin, Wu, et al., 2013). PSA with a molecular weight of 260 kDa was prepared by fermentation of Escherichia coli K235 6E61 (CCTCC M208088) in a 7 L bioreactor. The fermentation medium consisted of (g·L-1) 60 sorbitol, 2.5 K2HPO4·3H2O, 4.94 (NH4)2SO4, 1.5 tryptone, 0.26 FeCl3, 0.11 MnCl2, 0.00051 ZnSO4, and 0.92 MgSO4. The culture conditions of fermentation were as follows: pH of 6.4 at 0–18 h and 7.4 at 18–36 h, mixing speeds of 250 r·min-1 at 0–12 h, 400 r·min-1 at 12–20 h, and 250 r·min-1 at 20–36 h; temperature of 37 ℃; air flow of 1.2 vvm.
Extraction and purification of PSA. A certain amount of fermentation liquid was centrifuged at 4 ℃ and 10000 r·min-1 for 10 min. Then, 95% ethanol at three times the volume was added into the supernatant and left for 2 h at 4 ℃. After centrifugation at 4 ℃ and 10000 r·min-1 for 5 min, the precipitation was collected and redissolved in water. Finally, the supernatant was obtained after centrifugation at 4 ℃ and 12000 r·min-1 for 5 min. In addition, purification was carried out through a procedure established in our laboratory (Liu, Zhan, Wu, Lin, & Yu, 2010).
Preparation of SA. SA was prepared by acid hydrolysis method, in accordance with Wu et al.’s research, and slightly modified (Wu, Chen, R., Sun, Yuan, & M., 2020). At 90 ℃, the PSA solution underwent hydrolysis for 3.5 h in the presence of a 0.1 mol·L-1 oxalic acid solution, followed by separation and purification of the resulting hydrolysate.
After purification, the purity of each sample was above 98%. The obtained samples were non-toxic and harmless, which meet the basic standards of food safety, and have been approved as a novel food in China.
2.3. Simulated Digestion Experiments
The configuration method of simulated saliva was as described by Shi et al., (Shi, Liu, Yan, You, Yang, & Jiang, 2018). The digestive stage of the mouth was carried out in a 37 ℃ constant-temperature water-bath magnetic stirrer. Exactly 5 mL simulated saliva was mixed with 5 mL 25 mg·mL-1 PSA solutions, and oral digestion was finished after 1 min reaction. The digestive stage of the gastric and small intestine occurred in the BGR, which consisted of the digestive (gastric and small intestine) and fermentation (colon) systems (Fig S1). The dynamic parameters of BGR were set as described by Li et al. and slightly modified (Li, et al., 2021). The simulated gastric fluid, which contained 0.1 M muriatic acid, 8 mg·mL-1 pepsase, and 20 U·mL-1 gastric lipase, had pH 2.0. The sample flow after oral digestion was added to the gastric reactor, and the gastric digestion phase began. After 2 h of digestion, the gastric digestion phase was completed. The simulated intestinal fluid contained fresh pig bile and pancreatic fluid (4% w/v, contains amylase, protease, and lipase), electrolyte solution, and 1 M supercarbonate, and the pH was 6.5. The digestive sample from the stomach reactor was transported to the small intestine, where pancreatic and intestinal fluids were secreted, and the intestinal digestion was initiated. After 4 h of intestinal digestion, the digestion liquid was freeze dried to make lyophilized powder, which was stored at -80 ℃ for subsequent fermentation experiment (SA freeze-dried powder was prepared through the same digestion process).
2.4. Preparation of Fecal Inoculum Solution
Fecal samples were collected from ten healthy volunteers (5 males and 5 females aged 21–28 years) who had no gastrointestinal diseases, followed a normal Chinese diet, had not taken probiotics or prebiotics for three months, and had not been treated with antibiotics. The subjects’ informed written consent was obtained for this experiment. On the day of sampling, we collected the fecal samples provided by volunteers during fasting in anaerobic tubes. The fecal dialysate was formulated as described by Aguirre et al., (Aguirre, Eck, Koenen, Savelkoul, Budding, & Venema, 2015). The fecal samples were mixed with an appropriate amount of dialysis solution, and impurities were removed with four layers of sterile gauze after homogenization. The filtrate was mixed with 30% glycerin at a ratio of 1:1 and then frozen in liquid nitrogen for subsequent in vitro fermentation experiment.
2.5. Fecal Fermentation in BGR
The experiment was conducted on three experimental groups: blank, SA, and PSA groups. The basic medium was formulated as described by sun et al., with slight modifications (Sun, et al., 2022). The composition of supplemental medium in the blank group was exactly the same as that in the basic medium, whereas the carbon sources (amylum) in the supplemental medium of SA and PSA groups were replaced by SA and PSA, respectively. The other components were the same as those in the basic medium. The prepared medium was sterilized at 121 ℃ for 15 min. The fecal inoculum solution preserved in liquid nitrogen was incubated at 37 ℃ for 30 min. After sterilization, the BGR was injected with 180 mL basic medium and 18 mL fecal inoculum solution (10% inoculum, v/v) in a super-clean workbench. After inoculation, the BGR was transferred to the worktable, and the 37 ℃ water circulation and peristalsis device were started. During fermentation, the pH sensor can dynamically add 0.5 mol·L-1 NaOH to the reactor to maintain pH stability (the pH was set to 5.8). N2 was injected into the BGR every 8 h to maintain an anaerobic environment. After 20 h fermentation, the fecal fermentation liquid reached a stable stage. And the fecal fermentation liquid was starved for 2 h to exhaust the carbon source. Then 40 mL fermentation liquid was discharged, and 40 mL supplementary medium was added to the BGR. At this point, the initial fermentation time (0 h) was recorded, and the experimental period was commenced. During the experimental period (48 h), 40 mL fermentation liquid was discharged every 12 h and sampled, and 40 mL supplementary medium was added to maintain the stable working volume of the experiment. The 10 mL samples were collected at 0, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h. After liquid nitrogen freezing, the samples were subsequently stored in a -80 ℃ refrigerator for future experiments and sample delivery.
2.6. Determination the Molecular Weight of PSA
The molecular weight change of PSA during digestion was measured by high-performance LC (HPLC; Waters 1525 HPLC, USA). The chromatographic parameters were as follows. Molecular weights were determined using an UltrahydrogelTM Linear 300 mm×7.8 mm column, with a mobile phase consisting of 0.1 N sodium nitrate at a flow rate of 0.5 mL·min-1. The column temperature was 40 ℃.
2.7. Determination of Short-Chain Fatty Acid (SCFAs)
An enhanced gas chromatography method was utilized to quantify the SCFA content (Gao, Yang, Wu, Li, Wu, Yin, et al., 2022). The supernatant was obtained by centrifuging 1 mL fecal fermentation liquid at 12000 r·min-1 for 5 min. Subsequently, 10 µL internal standard solution (100 mmol·L-1 of 2-ethylbutyric acid) and 250 µL HCl were added to supernatant. The desired product was then extracted using 1 mL anhydrous ether. The filtrate was obtained by the addition of anhydrous sodium sulfate to the separated the organic phase for dehydration, followed by filtration through a 0.22 µm organic filter membrane. Finally, 7890A gas chromatograph (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used for the determination of SCFAs. The chromatographic conditions were as follows: HP-INNOWax (Restek, Bellefonte, PA, USA) column with inlet and detector temperatures set at 220 ℃ and 250 ℃, respectively, flow rate of 1.5 mL·min-1, heating process from 60 ℃ to 190 ℃ for 4 min, and sample (5 µL) to N2 ratio of 1:20. The peaks of SCFAs were recorded, and their concentrations were calculated by an external standard method.
2.8. Determination of Gut Microbiota
The total genomic DNA of samples was extracted by the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide/sodium dodecyl sulphate method. The specific primers 338F (5’-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3’) and 806R (5’-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3’) were used to amplify the 16S rRNA gene in the V3–V4 region. The sequencing libraries were constructed using NEBNext® Ultra™ IIDNA Library Prep Kit (Cat No. E7645). The chimera sequences were detected using Vsearch (Version 2.15.0) to compare the clean tags with the SILVA database (
https://www.arbsilva.de/). Then, the effective tags were obtained by removing the chimera sequences (Haas, Gevers, Earl, Feldgarden, Ward, Giannoukos, et al., 2011). Multiple sequence alignment analysis was used to investigate the phylogenetic relationships among amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) and differences in dominant species between various samples or groups.
2.9. Determination of Metabolites
The metabolites of different experimental groups were determined by LC-tandem MS (MS/MS) technique. Statistical software R (R version r-3.4.3), Python (Python 2.7.6), and CentOS (CentOS 6.6) were used for statistical analysis. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database and Human Metabolome Database were used to annotate various metabolites. The metabolites with variable importance in projection (VIP) > 1, P-value < 0.05, and fold change ≥ 2 or ≤ 0.5 were classified as differential metabolites. Pheatmap package was used to draw the clustering heatmaps. Cor () and cor.mtest() were used to analyze the correlation and statistically significant between differential metabolites, respectively. The function and metabolic pathways of these metabolites were studied by comparison with the KEGG database.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Three biological replicates were performed for each experiment, and the results were presented as mean ± standard deviation. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan multiple test were used to explore the differences and significance between groups in SPSS software, respectively. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results and Discussion
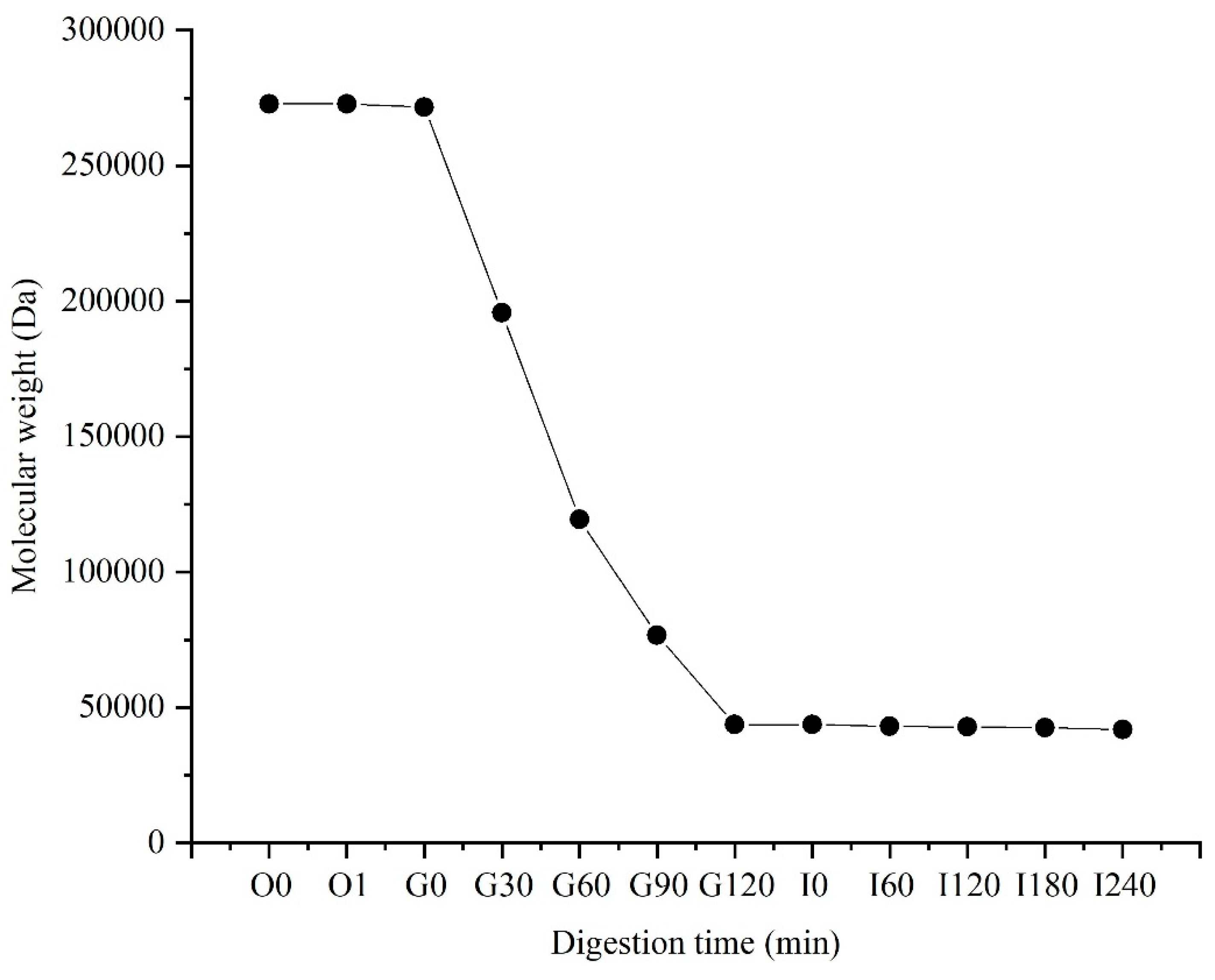
3.1. Molecular Weight Changes of PSA In Vitro Digestion
Digestive results showed that PSA was unaffected by oral digestion, and its molecular weight did not change significantly (
Figure 1). However, after 2 h of gastric digestion, the molecular weight decreased significantly from 260 kDa to about 40 kDa, and a mixed system of PSA and SA was formed. PSA was unstable in acidic environment, and the strong acidic environment of gastric fluid promoted the hydrolyzation of PSA, which resulted in a significant reduction in its molecular weight. The molecular weight of PSA did not change significantly after 4 h digestion in the small intestine, which indicates the relative stability of PSA in the small intestine fluid. The molecular weight of PSA remained at about 40 kDa after digestion. A mixed system of PSA and SA was formed, and it can reach the colon and be used by gut microbiota.
3.2. Consumption of PSA and SA in In Vitro Fermentation
At 0–12 h, the minimum consumption of PSA was 36.4 mg, which was significantly lower than that of SA (74.4 mg). Within 12–24 h, PSA consumption rapidly increased to 93.6 mg, which was slightly higher than SA consumption (90.0 mg). At 24–36 h, the consumption of PSA increased, but the value was lower than that of SA, and reached the maximum of 104.4 mg. Moreover, PSA consumption continuously increased and reached a maximum of 99.6 mg, which was comparable to the SA consumption at 36–48 h (Table S1). Before entering the experimental period, gut microbiota was in the hungry stage and used various nutrients in the medium. Given that SA is a small molecular-monomer compound, it can be quickly utilized by gut microbiota to promote bacterial growth. Therefore, the SA group showed a higher consumption in the early stage of fermentation. However, the PSA group was a mixture of SA and PSA with molecular weight of about 40 kDa. Gut microbiota may lack the enzyme to decompose large-molecular-weight PSA. SA was used for cell growth preferentially, which resulted in the low consumption of the PSA group. With the progress of fermentation, the bacteria grew vigorously, and the amount of enzyme that can secrete PSA for consumption increased. As a result, the consumption of PSA increased.
3.3. Effects of SA and PSA on SCFA Content
SCFAs are important metabolites of gut microbiota, and they play an irreplaceable role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis, immunoregulation, and energy supply. Compared with the blank group, the PSA and SA groups indicated significantly increased content of SCFAs at each fermentation time point (
Table 1). After fermentation for 12 h, the contents of SCFAs in the PSA and SA groups increased rapidly. The contents of total acid in the PSA and SA groups reached 77.59 ± 2.07 and 68.36 ± 0.97 mmol/L, respectively, which were significantly higher than that of the blank group (55.26 ± 0.51 mmol/L). After fermentation for 48 h, the content of total acid in the PSA group increased from 41.27 ± 0.65 mmol/L to 117.67 ± 0.57 mmol/L, and that in the SA group increased from 41.42 ± 0.76 mmol/L to 95.68 ± 0.29 mmol/L, which indicate increases in the content by 48% and 20% compared with the blank group, respectively.
The acetic acid content of the PSA group increased from 24.19 ± 0.18 mmol/L to 58.15 ± 0.09 mmol/L, that of the SA group increased from 24.38 ± 0.74 mmol/L to 51.91 ± 0.06 mmol/L, and these values were 27% and 13% higher than that of the blank group, respectively, after 48 h. Acetic acid is the most important substrate for cholesterol synthesis, and it can be ingested and utilized by numerous tissues and participate in the metabolism of muscles, spleen, heart, and the brain (Zhou, Yan, Mi, Zhang, Lu, Luo, et al., 2018). The butyric acid content of the PSA group significantly increased from 2.64 ± 0.26 mmol/L to 25.8 ± 0.86 mmol/L, that of the SA group significantly increased from 2.78 ± 0.24 mmol/L to 18.41 ± 0.13 mmol/L, and the values were 239% and 142% higher than that of the blank group, respectively. Butyric acid has a variety of physiological functions, and it can be absorbed and utilized by colon epithelial cells, regulate gene expression, and maintain the stability of intestinal environment (Lin, Frassetto, Kowalik, Nawrocki, Lu, Kosinski, et al., 2012). Notably, the PSA and SA groups showed different propionic acid contents. Propionic acid content increased significantly by 23% in the PSA group compared with the blank group. However, no significant increase in propionic acid production of SA group was observed compared with the blank group. Propionic acid is absorbed by the colon, can reduce cholesterol levels and fat storage, and has anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties. PSA and SA can significantly increase the content of SCFAs, which help in maintaining the homeostasis of intestinal environment and are beneficial to human health. Nevertheless, they showed different results in terms of propionic acid production. Thus, PSA and SA may have different effects on gut microbiota.
3.4. Effects of PSA and SA on Gut Microbiota In Vitro Fermentation
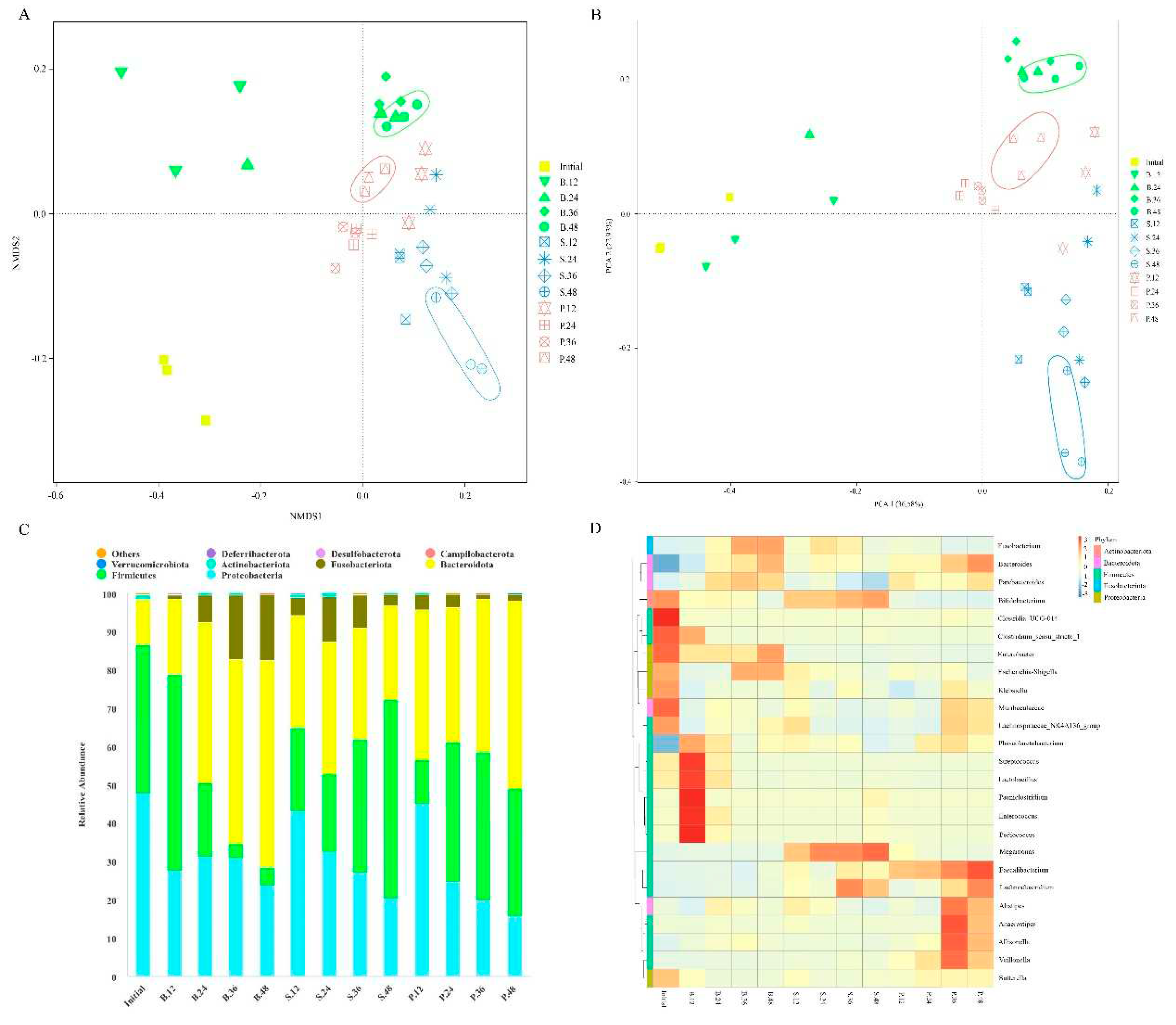
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis results indicated that the clustering trend of gut microbiota evidently differed among various groups (
Figure 2A). Furthermore, analysis of similarities indicated a statistical separation of intestinal microbial community composition among the groups (
P = 0.005). Similarly, principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) suggested different clustering of gut microbiota in the PSA, SA, and blank groups. The different groups of gut microbiota were classified, and samples from the same group were clustered together (
Figure 2B). Moreover, permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) suggested statistical differences between groups (
P = 0.001). The percentage variations of the first two components were 36.58% and 22.93%, which suggest that PSA and SA had different intestinal microbial community compositions, respectively.
At different classification levels, the intestinal microbial community composition was further analyzed. At the phylum level, the gut microbiota of each group mainly consisted of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Fusobacteria (
Figure 2C). After 12 h fermentation, the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes significantly increased, whereas that of Firmicutes significantly decreased in the SA and PSA groups. As fermentation progressed, the levels of Bacteroidetes in the PSA group and Firmicutes in the SA group gradually increased. After 48 h, the PSA group exhibited significantly decreased relative abundances of Proteobacteria and Fusobacteria and increased relative abundances of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes compared with the blank group. In the SA group, the levels of Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Fusobacteria significantly decreased, whereas that of Firmicutes increased. The results indicated that Bacteroidetes may be the dominant microbiota that can preferentially utilize SA. In general, PSA and SA enriched Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes, with the latter and former showing a higher relative abundance in the SA and PSA groups, respectively. Furthermore, PSA and SA can significantly reduce Proteobacteria and may have the ability to inhibit the propagation of harmful bacteria (Lange, Buerger, Stallmach, & Bruns, 2016).
At the genus level, the relative abundances of
Bacteroides,
Faecalibacterium, and
Anaerostipes in the PSA group increased significantly compared with the blank group after 48 h (
Figure 2D).
Faecalibacterium is one of the most crucial bacterial genera in human gut microbiota; it can produce butyric acid, maintains the balance of the gut microbiota, and protects the colon from intestinal pathogens (Lopez-Siles, Duncan, Garcia-Gil, & Martinez-Medina, 2017). In addition,
Anaerostipes is a common beneficial bacterium in intestinal tract; it can ferment polysaccharides and produce SCFAs and is an important member of bacteria that produce butyrate in the intestinal tract (Bui, Manneras-Holm, Puschmann, Wu, Troise, Nijsse, et al., 2021). The SA group showed significantly increased relative abundances of
Bifidobacterium,
Megamonas, and
Lachnoclostridium.
Bifidobacterium is an important beneficial gut microbiota with a series of physiological effects, such as synthesis of vitamins, stimulation of immune function, and improvement of host anti-infection and anti-tumor functions (Feng, Duan, Xu, Lyu, Liu, Liang, et al., 2019).
Megamonas can ferment various carbohydrates and produce SCFAs, lactic acid, and other beneficial organic acids, which can maintain the homeostasis of intestinal environment (Sakon, Nagai, Morotomi, & Tanaka, 2008). Moreover, PSA and SA can inhibit the colonization of potential pathogenic bacteria
Fusobacterium and
Escherichia-Shigella. These results suggest that PSA and SA can regulate the community composition of gut microbiota in different ways, such as by inhibiting the growth of harmful pathogens, promoting the proliferation of different kinds of probiotics, and enabling the gut microbiota to develop toward an orientation beneficial to the human body.
The results of spearman correlation analysis suggested that total SCFAs, acetic acid, and propionic acid were positively correlated with Bacteroidetes, whereas butyric acid was negatively correlated with Actinomyces at the phylum level. At the genus level, butyric acid, propionic acid, and acetic acid were positively correlated with Anaerostipes, Faecalibacterium, and Coprococcus but negatively correlated with Enterobacter and Streptococcus (Figure S2). In general, changes in microbial communities at the genus level can cause changes in SCFA concentrations in the fermentation broth.
3.5. Non-targeted metabolomics analysis of differential metabolites
When carbohydrates affect the composition of intestinal microbial community, the phenomenon will be accompanied by a series of changes of various metabolites. In this study, non-targeted metabolomics technique was used to investigate the initial point of fermentation and the changes in metabolites in each experimental group after 48 h fermentation. The results of principal component analysis (PCA) suggested that biological duplicate samples for each group were clustered together, and samples in different experimental groups were separated. Thus, each experimental group exhibited significant differences in their metabolites. The addition of PSA and SA changed the metabolic profile. Furthermore, quality control (QC) samples were gathered together, and they showed good data quality and high reliability of the results (Figure S3).
The results of differential metabolite screening showed that 403 metabolites with significant differences were screened in comparison with the blank group (207 in the SA group and 196 in the PSA group). Moreover, 128 differential metabolites were screened in the PSA group in comparison with the SA group. The differential metabolites were analyzed by hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA) to normalize and cluster relative quantitative values. The metabolites of the three experimental groups were significantly enriched at the initial point of fermentation but significantly decreased after 48 h. The concentrations of metabolites in the PSA, SA and blank groups were significantly different (Figure S4). The results suggest that PSA and SA had significant effects on the metabolism level of related metabolites to varying degrees.
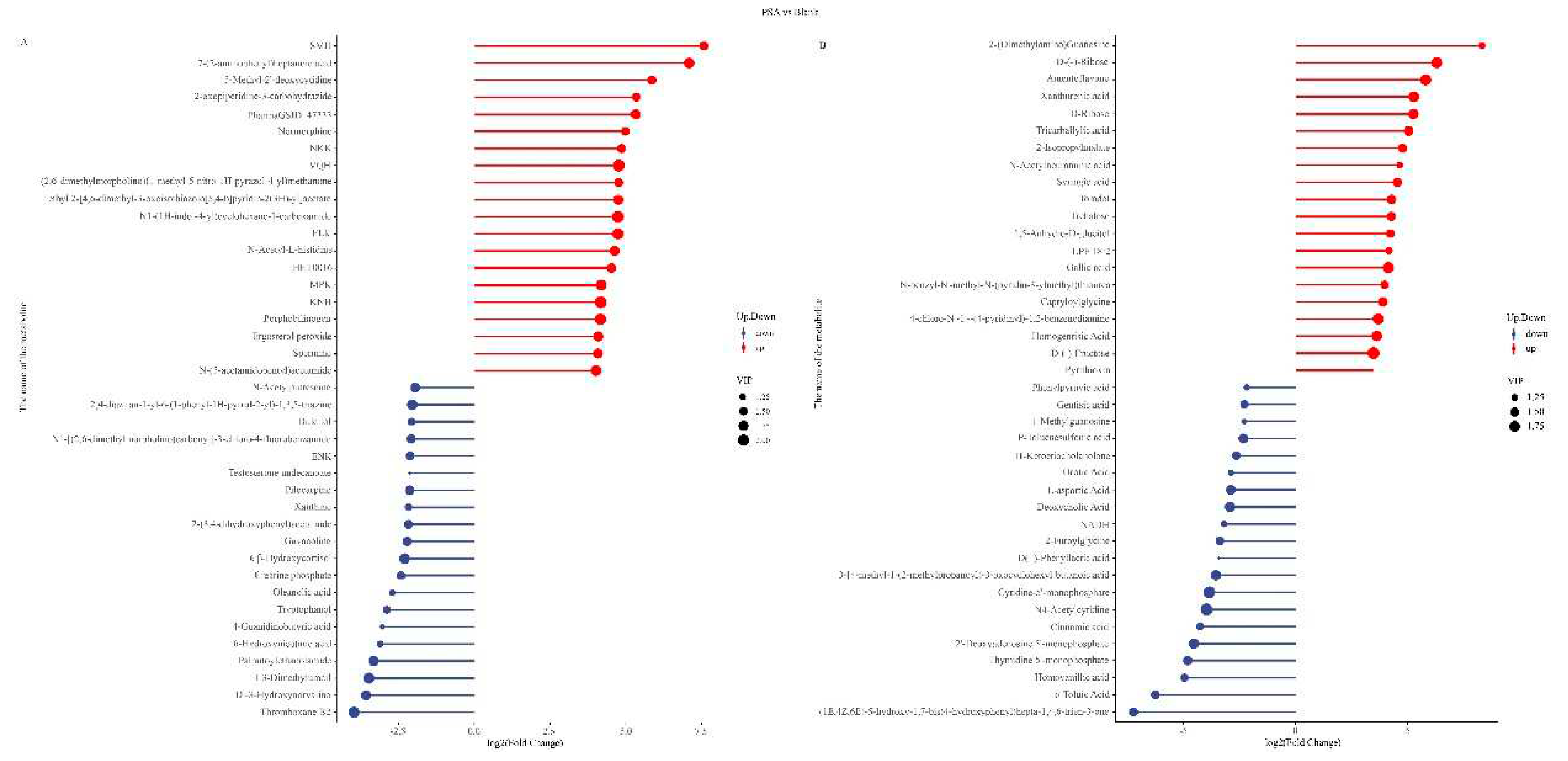
Based on the screening results of differential metabolites, matchstick charts were drawn for the top 20 differential metabolites. The results suggest that in the POS mode, in contrast to the blank group, the PSA group significantly upregulated metabolites, such as 7-(2-aminophenyl) heptanoic acid, ergosterol peroxide, and N-acetyl-L-histidine, and downregulated metabolites, such as N-acetylputrescine, thromboxane B2, and 1,3-dimethyluracil (
Figure 3A). In NEG mode, the significantly up-regulated metabolites included xanthurenic acid, tricarballylic acid, gallic acid, etc. The significantly down-regulated metabolites comprised o-toluic acid, phenylpyruvic acid, and cinnamic acid (
Figure 3B). Ergosterol peroxide is a steroid derivative that inhibits the inflammatory response of cells and the growth of cancer cells; it has various biological activities, such as anti-tumor, pro-apoptosis, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and anti-proliferation effects (Kobori, Yoshida, Ohnishi-Kameyama, & Shinmoto, 2007). Gallic acid has anti-inflammatory, anti-mutation, anti-oxidation and free radical, antiviral, and other biological activities and is beneficial to human health (Booth, Masri, Robbins, Emerson, Jones, & De Eds, 1959). In addition, putrescine is a kind of metabolite harmful to human body, can damage the intestinal epithelial cells and intestinal wall, and increase the intestinal permeability, which result in a series of physiological or pathological changes in the body. PSA can up-regulate beneficial metabolites, such as ergosterol peroxide and gallic acid, and down-regulate the harmful substance N-acetylputrescine, which may have a positive effect on human health.
The SA group showed significantly up-regulated levels of 5-methyl-2’-deoxycytidine, 4-pyridoxic acid, and normorphine and down-regulated levels of palmitoylethanolamide, 2-phenylethlamine, and tryptophanol compared with the blank group in the POS mode (Figure S5A). The significantly upregulated metabolites were amentoflavone, capryloylglycine, and lipoic acid, and the down-regulated ones included thymidine 5’-monophosphate, homovanillic acid, and cinnamic acid in NEG mode (Figure S5B). 4-Pyridoxic acid has a strong antioxidant capacity, can promote the synthesis of nucleic acid, prevent the aging of tissues and organs, and promote tryptophan conversion to niacin (Lewis & Nunn, 1977). Lipoic acid can be used as a coenzyme to participate in acyl transfer in the metabolism of substances in the body; it has significant electron affinity and the capability to react with free radicals. Lipoic acid with antioxidant properties can also eliminate free radicals that lead to accelerated aging and disease and thus has extremely high health function and medical value (Patel & Packer, 2008). SA significantly up-regulated beneficial metabolites, such as 4-pyridoxic acid and lipoic acid, which indicates that it can up-regulate metabolites with antioxidant function, maintain body balance, and delay aging.
Furthermore, compared with the SA group, the PSA group significantly up-regulated anandamide (AEA), methionine, and 16,16-dimethyl prostaglandin A1 and down-regulated flavanone, theobromine, and N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate in POS mode (Figure S6A). In the NEG mode, PSA can significantly up-regulate docosahexaenoic acid, docosatrienoic acid, and syringic acid and down-regulate phenylpyruvic acid, palmitoleic acid, and deoxycholic acid (Figure S6B). AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid that can regulate the functions of central and peripheral nervous and immune systems to maintain the physiological balance of the body (Deutsch, Goligorsky, Schmid, Krebsbach, Schmid, Das, et al., 1997). Methionine is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by the human body, but it has various physiological functions, such as liver protection, anti-depression, blood pressure reduction, and metabolism promotion (Aksnes & Njaa, 1983). Intestinal microbial metabolites have a wide range of effects on human health (Oliphant & Allen-Vercoe, 2019). The results showed that PSA and SA had different effects on intestinal microbial metabolites. Moreover, PSA and SA can positively regulate the intestinal microbial metabolites and may positively contribute to keeping human health.
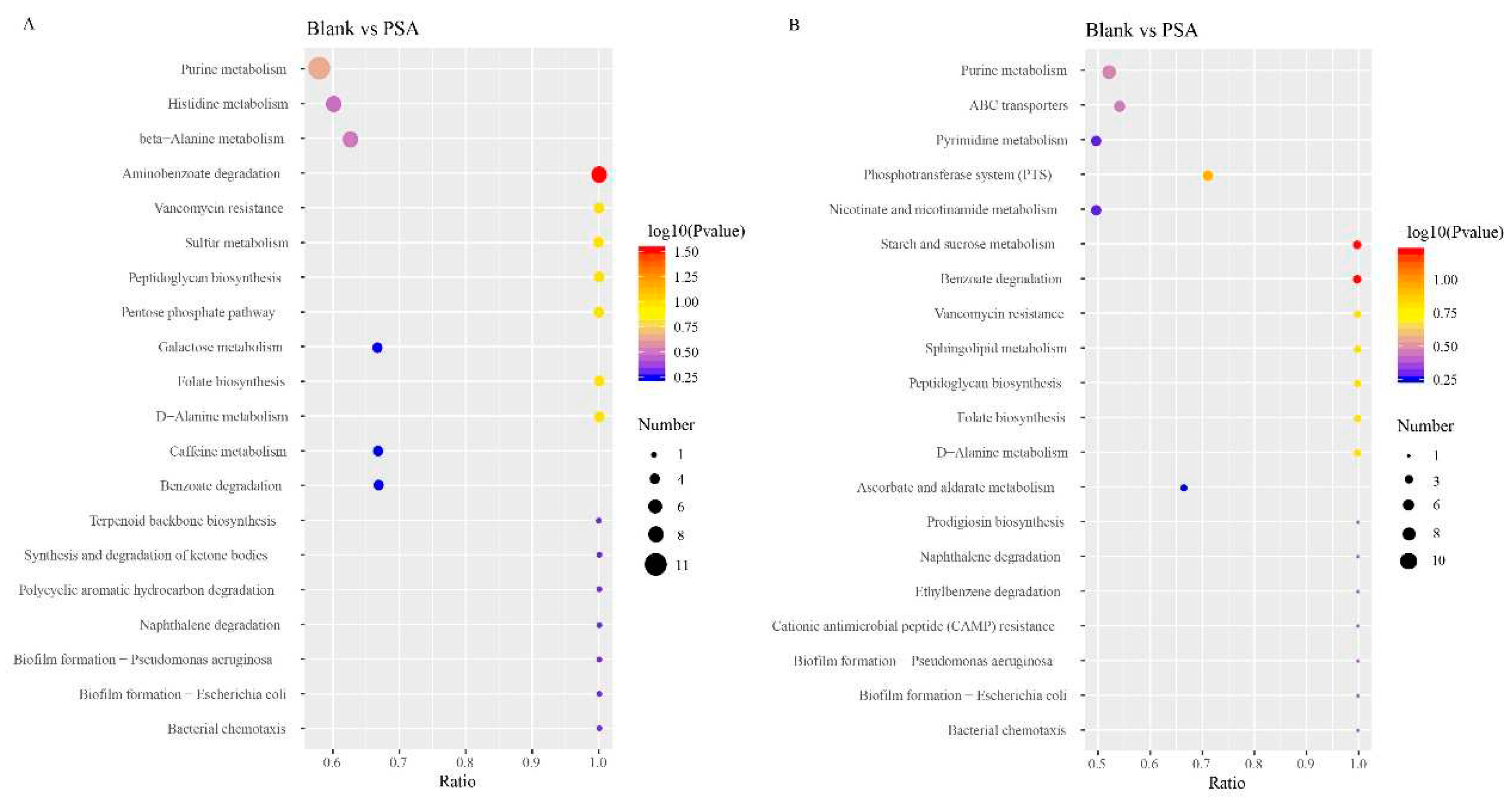
The results of KEGG enrichment analysis suggested that in contrast to those in the blank group, the main metabolic pathways in the PSA group were amino acid (histidine and alanine metabolism) and purine metabolisms (
Figure 4A). Histidine can help in the formation of healthy tissues in the body; it covers the myelin sheath of nerve cells and ensures the smooth transmission of information from the brain to all parts of the body. Although histidine can be synthesized in adult body, its deficiency easily occurs, which affects human health. Moreover, histidine produces histamine and can promote iron absorption, which has physiological functions such as prevention of anemia. PSA mainly affected histidine synthesis pathway in the histidine metabolism pathway. Specifically, PSA caused the up-regulation of carnosine by causing the downregulation of anserine and ultimately affected the synthesis of L-histidine, which resulted in the up-regulation of histidine (Figure S8). Amino acids are involved in numerous important physiological activities in the body and make an important contribution to keeping human health. PSA can promote the metabolism of amino acids and has a positive effect on promoting human health.
The main metabolic pathways enriched in the SA group were nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism, pyrimidine metabolism, and purine metabolism (
Figure 4B). Nicotinate and nicotinamide are one of the essential micronutrients in the body, and they have multiple physiological functions, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and nervous health maintenance. In the metabolic pathway of nicotinate and nicotinamide, SA can up-regulate trigonelline and succinate and down-regulate nicotinamide and nicotinurate, which affect the metabolism of niacinamide and niacinamide (Figure S9). SA can promote the metabolism of niacin and niacinamide, which may enhance the antioxidant-related effect and contribute to the promotion of human health.
Furthermore, compared with the SA group, the main metabolic pathways in the PSA group included tyrosine metabolism, biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, and glutathione metabolism (Figure S7). Tyrosine is a conditionally essential amino acid for the human body, and it can regulate mood, stimulate the nervous system, and help speed up the metabolism. PSA affected the metabolism of tyrosine by up-regulating L-DOPA (Levodopa) and fumarate and down-regulating L-tyrosine and acetoacetate (Figure S10). The enrichment results of the metabolic pathway showed that the addition of SA and PSA changed the metabolic pathway of gut microbiota.
In conclusion, the 16s rDNA and non-targeted metabolome results strongly support our hypothesis that PSA and SA affect gut microbiota and metabolites in different ways and contribute positively to the maintenance of human health.
3.6. Correlation Analysis between Differential Metabolites and Microbiota
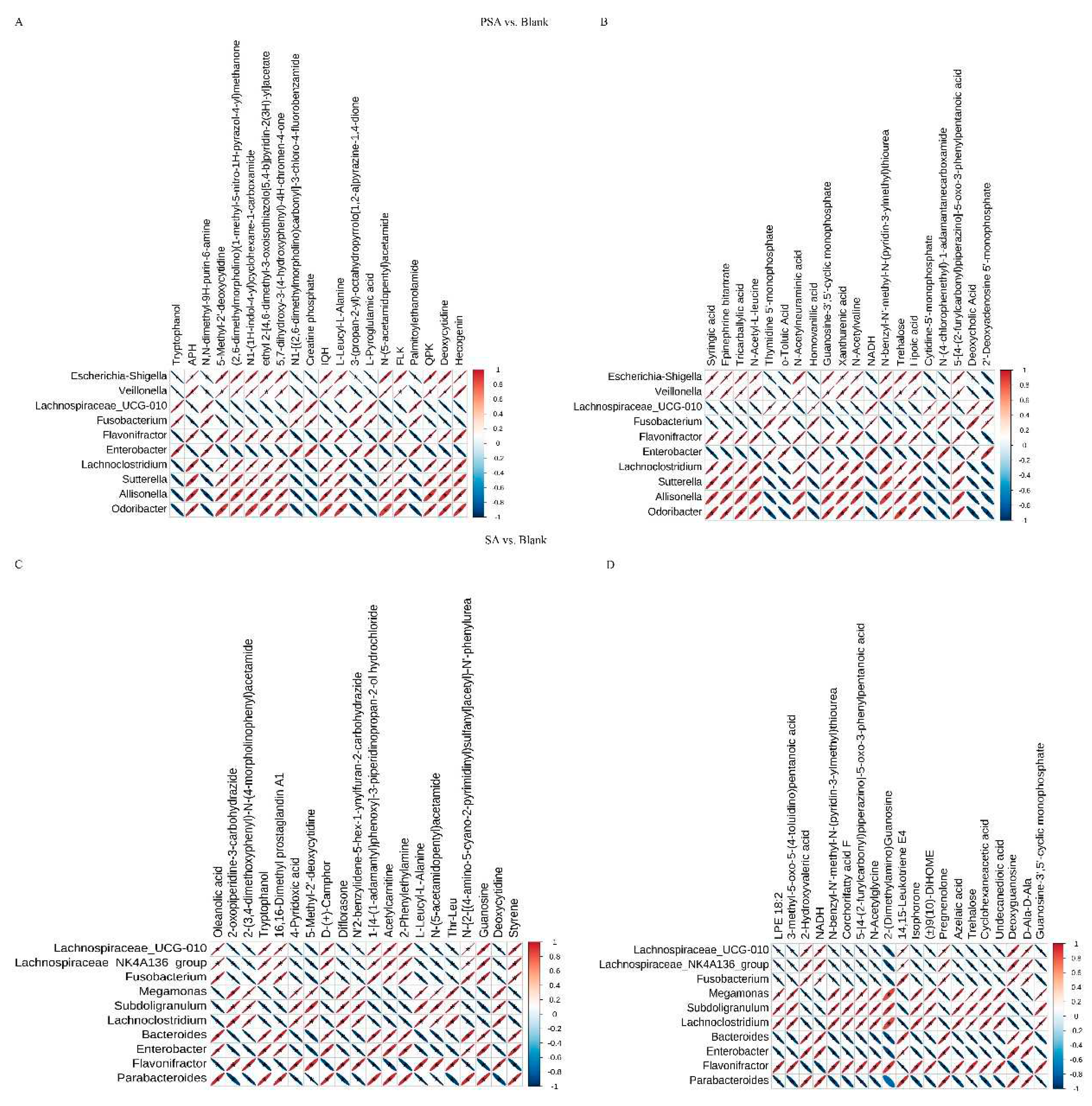
Correlation analysis of non-targeted metabolome and microbiome data was performed to investigate metabolite changes that might have been caused by changes in microbial community structure. Correlation analysis was conducted between the top 10 differential microbiota at the genus level and top 20 differential metabolites based on Pearson correlation coefficient, and a heat map was drawn to determinate the degree of correlation between microbiota diversity and metabolites. The results between the PSA and blank groups showed that
Enterobacter and
Fusobacterium were positively correlated with tryptophanol, 6-dimethyl-9H-purin-6-amine, and creatine phosphate and showed a significant negative correlation with 5-methyl-2’-deoxycytidine, 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, and L-leucyl-L-alanine in POS mode (
Figure 5A).
Enterobacter and
Fusobacterium were positively correlated with thymidine 5’-monophosphate, homovanillic acid, and lipoic acid and negatively correlated with syringic acid, tricarballylic acid, and N-acetyl-L-leucine in NEG mode (
Figure 5B). Nevertheless,
Escherichia-Shigella,
Veillonella,
Allisonella,
flavonifractor,
Lachnoclostridium,
Sutterella, and
Odoribacter showed opposite correlations with the above metabolites compared with
Enterobacter and
Fusobacterium.
The results between the SA and blank groups suggest that
Fusobacterium,
Bacteroides,
Enterobacter, and
Parabacteroides were positively correlated with oleanolic acid, tryptophanol, and acetylcarnitine and significantly negatively correlated with 4-pyridoxic acid, L-leucyl-L-alanine, and deoxycytidine in POS mode (
Figure 5C). In addition, in NEG mode, these bacteria were positively correlated with 2-hydroxyvaleric acid, pregnenolone, and deoxyguanosine and negatively correlated with LPE 18:2, 3-methyl-5-oxo-5-(4-toluidino) pentanoic acid, and N-acetylglycine (
Figure 5D). By contrast,
Megamonas,
Subdoligranulum,
Lachnoclostridium, and
Flavonifractor had completely opposite correlation with the above-mentioned metabolites.
Moreover, the results between PSA and SA groups showed that Veillonella, Allisonella, Flavonifracto, Parabacteroides, and Phascolarctobacterium had a significantly negative correlation with pantothenic acid, AEA, and linoleoyl ethanolamide and a negative correlation with 1,4-dihydroxyheptadec-16-en-2-ylacetate, 1,3-dimethyluric acid, and methyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside in POS mode (Figure S11A). In NEG mode, these bacteria were positively correlated with syringic acid, 2-hydroxy-2-methylbutanedioic acid, and uric acid and negatively correlated with corchorifatty acid F, palmitoleic acid, and cyclohexaneacetic acid (Figure S11B). However, Megamonas, Succinatimonas, and Dorea showed opposite correlations for the same metabolites compared with the above bacteria.
Altogether, these results reveal a potentially important relationship between significantly altered metabolites and microbial composition after the addition of PSA and SA and may lead to new research hypotheses regarding the existence of specific microchemical associations.