1. Introduction
As a leading contributor to dementia, Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition. The most common presentation of AD is with insidious, progressive problems centered around the episodic memory of elderly individuals, which may meet the requirements of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) at this stage. Challenges with navigation as well as multitasking and confidence issues frequently surface. A patient can be diagnosed with AD dementia when cognitive impairments develop, becoming more severe and pervasive, and begin to interfere with daily activities. As the condition progresses, increasing reliance is typical, and subsequent behavioral changes, decreased mobility, hallucinations, and seizures may appear. The average time to death after presentation is 8.5 years (1). According to the Alzheimer's Association, 60–80 percent of dementia cases globally are caused by AD. In the United States, it is estimated that 6.7 million people aged 65 or older will be diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease in 2023 (2). According to recent estimates, 44 million individuals worldwide currently have dementia. As the population ages, this is anticipated to more than triple by 2050, when the yearly cost of dementia in the USA alone may surpass USD 600 billion (3).
There is currently a lack of knowledge on the precise pathophysiological pathways underlying AD. From a neuropathological standpoint, AD is characterized by the following: (1) extracellular neuritic plaques, which are extracellular deposits of β-amyloid (Aβ); (2) neurofibrillary tangles (NTFs), which are neuronal aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau; and (3) neuronal loss, particularly in the medial temporal lobe structures and the temporo-parietal association cortex (4). Along with aberrant protein deposition, various biochemical processes such as inflammation, oxidative damage, and lysosomal dysfunction occur, supporting the hypothesis that the etiological factors contributing to the disease process are heterogeneous and interact until the full disease pathway is established (5).
A diagnosis of dementia is typically determined by the patient's medical history, a pattern of cognitive deficits, and other factors evaluated through clinical investigations, such as blood testing and structural imaging of the brain, to rule out nondegenerative causes of the symptoms. The early-stage clinical diagnosis of AD is still challenging and requires a thorough medical history as well as a battery of neuropsychological tests to establish a diagnosis of dementia and to distinguish AD from other types like vascular dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and Lewy body dementia (6). The remaining functioning neurons in the AD brain cannot currently be directly measured in vivo; instead, postmortem pathological examination is used to determine the disease's definitive diagnosis (7). The amyloid cascade hypothesis states that amyloid production occurs 10 years or more before the start of clinical symptoms (8). Thus, investigating new techniques for the early and precise identification of AD in vivo is crucial for treatments to be effective.
Research on brain imaging and its application in the study of AD has advanced extraordinarily over the past 30 years (9). Currently, a number of imaging techniques have been utilized to clinically diagnose AD. Computed tomography (CT), nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and different derivative technologies may be utilized, and these technologies can be classified in general terms. However, widely used imaging methods are only capable of identifying structural or metabolic alterations at the anatomical level in the brain, and can only be utilized for drawing inferential distinctions. As a disease with a complex pathophysiological mechanism, AD has many different molecular pathological features and molecular biomarkers. Therefore, molecular imaging for AD pathology indicators provides a practical method for the early diagnosis and impartial assessment of AD (10).
Functional neuroimaging using positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) has been used to study various metabolic and biochemical alterations in the brain in vivo, contributing to the early diagnosis and differential diagnosis of AD and providing essential data for the understanding of the underlying pathology. Different molecular radiotracers have been employed to estimate impairments in neurotransmitters, regional blood flow, and glucose metabolism, among other aspects of brain function (11). These molecular imaging approaches will be essential for accurate patient selection and the assessment of therapeutic response in light of new medicines. The imaging of aberrant protein deposits was made possible by recent developments in technology and radiopharmacology (12), while targeting new biochemical and molecular processes with the use of novel probes is a growing aspect of nuclear medicine imaging in the field of AD (13). Herein, we review the pathogenesis of AD, as well as the detection methods and principles of molecular imaging, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) techniques. Meanwhile, various tracers and probes applied in molecular imaging that detect Aβ deposits, tau protein accumulation, and neurotransmitters are also reviewed.
2. Pathogenesis of AD
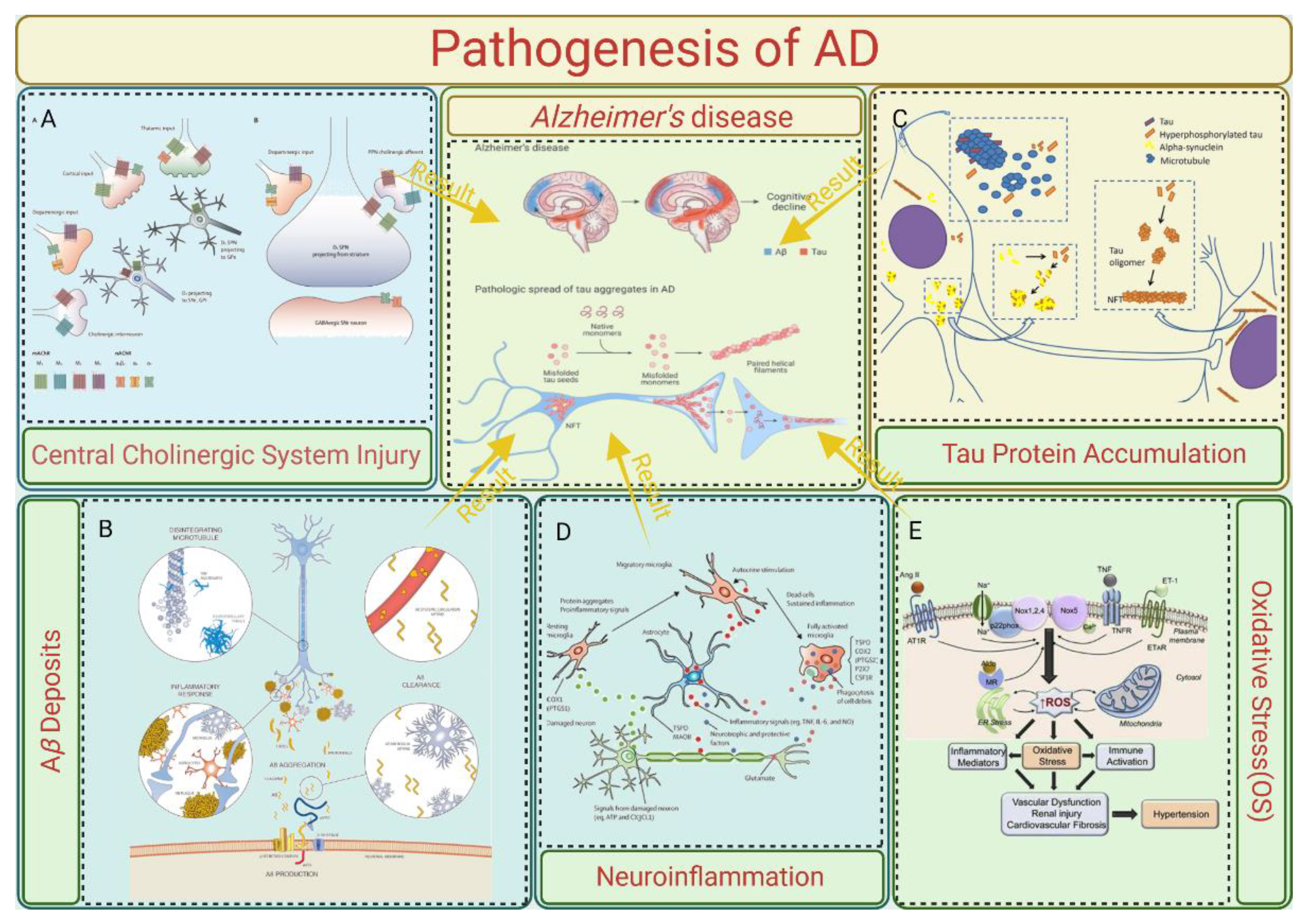
The pathological phenomenon of AD is complex. Brain tissue examination results have shown that senile plaques (SPs) formed by β-amyloid (Aβ) plaques outside of brain nerve cells were common in patients with AD. Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), neuron loss, neurodystrophy, synaptic loss, and other pathological phenomena are formed by SPs and the abnormal phosphorylation of tau proteins [3]. However, the relevant pathogenesis is still unclear. The following section covers the pathogenesis of AD, which is summarized in
Figure 1.
2.1. Central Cholinergic System Injury
The cholinergic system injury theory is the earliest theory about AD. Acetylcholine (ACh) is an important central excitatory neurotransmitter, which is related to a variety of advanced behaviors such as learning and memory. The central cholinergic nervous system affects the level of central acetylcholine by regulating the synthesis and release of acetylcholine (14). Early studies showed that severe neurodegeneration occurs in the basal nucleus of Meynert (mainly composed of cholinergic neurons), which is located in the basal forebrain, in patients with AD. At the same time, the presynaptic cholinergic transmitters in the cerebral cortex were severely depleted and the activity of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) was significantly decreased (15). The above two points indicate that severe cholinergic system damage occurs in the brains of patients with AD.
Studies have shown that a cholinergic nerve imbalance can accelerate the deposition of A β, and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) can directly bind to presenilin-1 (PS-1), a key enzyme in the production of A β, to significantly enhance its expression, thus increasing the level of A β and accelerating cognitive impairment (16). In addition, abnormal central cholinergic changes can also induce the abnormal phosphorylation of tau proteins, neuronal inflammation, apoptosis, and an imbalance in neurotransmitters and the neurohormone system (16).
2.2. Aβ Deposits
Aβ is a peptide produced by the cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), which is mediated by β-secretase and γ-secretase. It has 37043 amino acid residues (17). Toxic oligopeptides generated by disrupting the assembly of APP fragments comprise 39–43 fragments, including protofibrils or fibrils. These then result in deposits that become apparent under a microscope. BACE 1 cleaves APP at β-sites Asp1 and Glu11. γ-secretase further cleaves the 99 amino acid residues that are linked to the C-terminal membrane, resulting in the production of the isoforms Aβ1-42 and Aβ1-40. Presenilin 1 (PS1) or presenilin 2 (PS2) are the primary forms of γ-secretase. The typical soluble isoform is Aβ1-40, but if the cleavage pattern is altered, it could result in Aβ1-42, which aggregates readily and forms plaque because it contains two extra amino acids: alanine and isoleucine (18). Mutations in the APP, the presenilin 1 and presenilin 2 genes, or the apolipoprotein E (APOE4) gene cause this shift in the cleavage pattern. In addition to genetic mutations, a multitude of neuropeptides may play a role in the development of plaque. For instance, low levels of somatostatin, neuropeptide Y, and corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) may be linked to plaque formation, while higher levels of angiotensin II may contribute to irregular APP cleavage or poor removal of the Aβ1-42 fragment (19). Different parts of the brain experience the formation and deposition of Aβ plaques. The brain recognizes these plaques as foreign material, which triggers an immunological and inflammatory response due to the triggering of microglia and releasing of cytokines. This ultimately results in cell death and dementia (20).
A total of 26 A β protein forms were identified from the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with AD, among which A β 1-40 and A β 1-42 with 40 and 42 amino acid residues were the main components of accumulated A β. A β 1mur42 is more hydrophobic and easier to gather (21), and it is believed to be the main culprit for the initiation of senile plaques in the brain. An increase in the level or proportion of A β 1mur42 can induce the formation of A β amyloid fibers, which develop into senile plaques in the brain and lead to neurotoxicity (22). The A β aggregate can activate cysteine protease, which can cleave tau proteins and change the conformation of normal tau proteins so that the tau proteins cannot bind to microtubules and aggregate, which induces the pathology of the tau proteins and leads to AD.
2.3. Tau Protein Accumulation
Microtubular neuronal proteins are called tau proteins. The microtubule binding domain of tau proteins is important in the stabilization and polymerization of the microtubule assembly, hence preserving the cytoskeleton's integrity. Numerous kinases, including the Fyn kinase, glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β), and cyclin-dependent kinase-5 (CDK5), phosphorylate the serine and/or threonine residues to control this interaction. CDK5 may be involved in the development of neurofibrillary tangles. Calpain is activated by Aβ, and p35, an activator of CDK5, is deregulated. Phosphorylated tau is hyperphosphorylated as a result of p35 splitting into p25 in response to an excess of cytosolic calcium. This hyperactivates CDK5 (23). The hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins causes a reduction in their affinity for microtubules. The hyperphosphorylated tau loses its ability to preserve the cell's structure when it produces NFTs and is deposited in the cytoplasm. Additionally, typical cellular functions like synaptic transmission, axonal transport, signal transduction, and progressive cell degeneration are impacted by this deposition.
The Tau protein is another element involved in the process of plaque formation. It is a factor that facilitates the tubulin protein's particular assembly process. In contrast, tubulin polymerizes and forms microtubules that form the intracellular pathway that the cell's motor proteins travel along or use as a dividing spindle during cell division. The hyperphosphorylation of the Tau protein results in the formation and deposition of neurofibrillary fibers in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease (24). The loss of physiological function by a normal Tau protein, which results in the instability of microtubules, or the increase in function that is toxic to neurons, which causes apoptosis, are the two main mechanisms by which the Tau protein causes neurotoxicity (25). Numerous researchers have also demonstrated a link between the accumulation of β-amyloid and the Tau protein's aggregation, which is the last stage in the pathophysiology of illness (26).
2.4. Neuroinflammation
Microglia are the most important immune cells in the central nervous system that can recognize and remove damaged nerves, plaques, and infectious substances in the central nervous system, which is of great significance to maintain the homeostasis of the central nervous system. Microglia surface receptors can recognize damaged cells and heterogenous substances in the brain, cause microglia activation, produce a series of downstream effects, and play an immune role. However, the long-term excessive activation of microglia will release too many inflammatory factors and oxidizing substances, leading to an inflammatory reaction, nerve cell damage, and neurotoxicity (27). Bambergei et al. found that A β can bind and activate receptors on the surface of microglia, and activated microglia release cytokines, chemokines, reactive oxygen species, and other neurotoxic substances (such as NO, tumor necrosis factor, superoxide, etc.), leading to inflammation, which proves that neuroinflammation in the brain of patients with AD is closely related to A β-induced microglial activation (28).
A key factor in the pathophysiology of AD is neuroinflammation. Acute inflammation serves as a barrier to prevent brain damage caused by conditions like Aβ plaque buildup. The microglia's ability to release proinflammatory cytokines is maintained despite their inability to remove plaque due to chronic activation, which leads to an imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Aβ deposits trigger the activation of many Toll-like receptors (TLR2, TLR4, and TLR6) and their co-receptors, which include the microglia-expressed CD36, CD14, and CD47. The immune system produces proinflammatory cytokines of the IL-1β family, such as IL-1β and IL-18, upon the identification of microorganisms. Upon activation, caspase-1 or caspase-8 expresses these cytokines. The activation of caspase-1 is aided by inflammatory proteins such as the PYHIN (pyrin and HIN domain-containing) and NLR (Nod-like receptor) family. The main inflammasome that is capable of detecting Ab clumps is NLRP3. These proinflammatory cytokines can interfere with the microglial clearance of Aβ and damage dendritic spines. Nitric oxide (NO) generation is enhanced by the neuronal and glial cell expression of inducible isoforms of NO synthase in response to proinflammatory cytokines. As a result, the peptide's capacity to aggregate is enhanced, and its ability to inhibit synaptic plasticity is strengthened (29). As previously mentioned, these cytokines cause CDKs to become activated, which increases tau hyperphosphorylation and Aβ plaque formation (20).
2.5. Oxidative Stress (OS)
The functional imaging of the brains of patients with AD precursors revealed the hyperactivation of neurons in the hippocampus and neocortex regions of the brain (30). Mitochondria are the energy factories of cells, and abnormal neuron excitation indicates increased mitochondrial activity. Mitochondria are the main sites for the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Under normal circumstances, ROS are produced in a small amount and can function as the second messenger in cells. When neurons are abnormally excited, mitochondrial activity is enhanced and ROS production increases, and the antioxidant defense system cannot clear them in time. Excessive ROS will damage mitochondria and then damage nerve cells, resulting in abnormal neuronal death and promotion of the pathological process of AD (31). Mitochondrial defects exist in the brain tissue of AD patients. Pathological phenomena of abnormal mitochondrial function have been found through detection utilizing brain tissue samples of AD patients, experiments using AD transgenic mice, and studies on the expression of mutant APP- or Aβ-treated cells (32).
Mitochondrial dysfunction may result from cytochrome c oxidase levels that are too low. Furthermore, OS-induced hyperexcitation of glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3) can change the permeability of mitochondria. This might cause ROS to be produced in excess (33). ROS can be produced by metal ions, particularly copper and zinc, binding to the Aβ plaque. The resulting ROS oxidize the Aβ peptide, making it difficult to remove, and oxidize the cell membrane's lipid and protein membrane, making it permeable and therefore prone to degeneration (34).
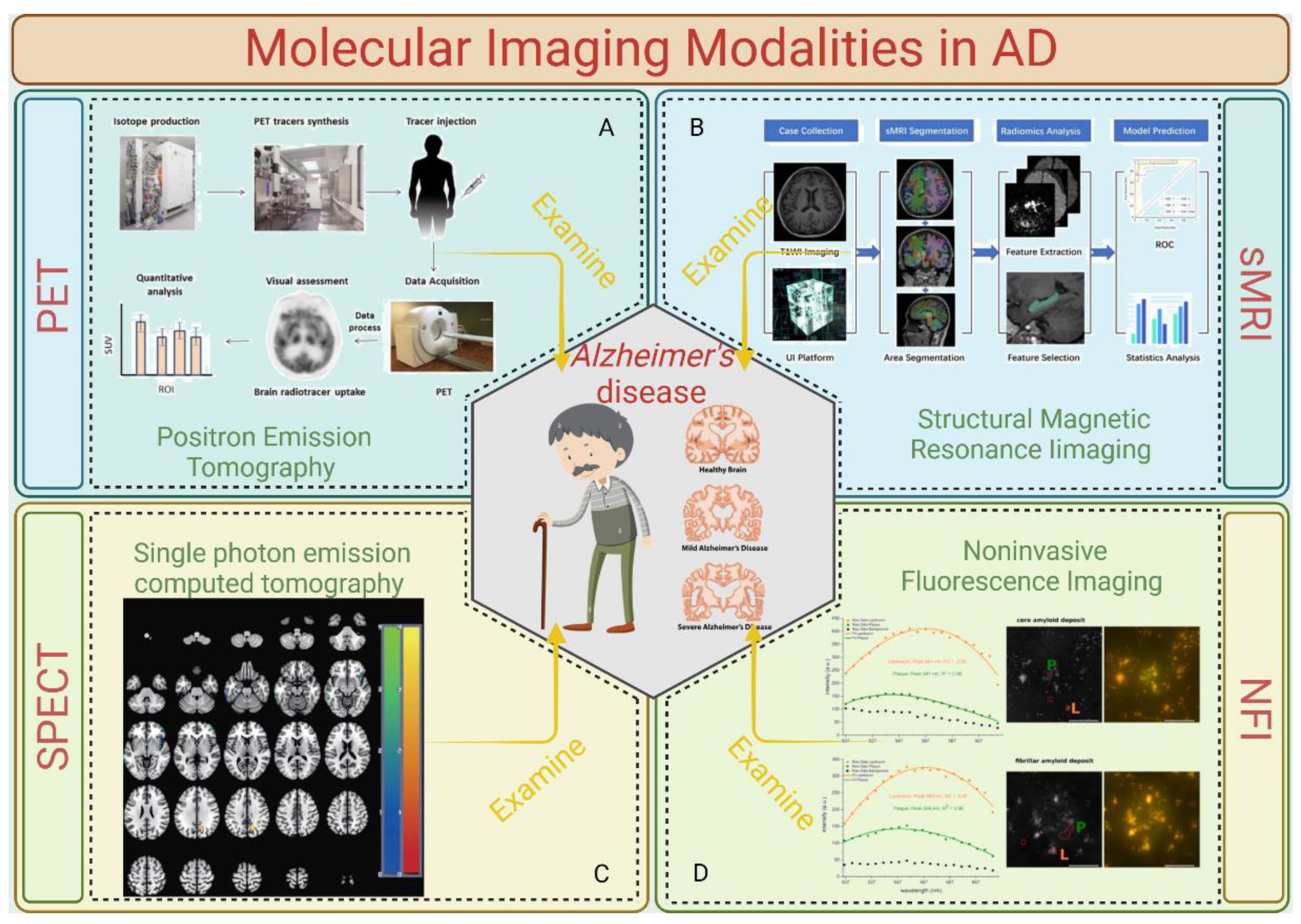
3. Molecular Imaging Modalities in AD
At present, there are great differences in neuroimaging results and interpretations, which are not enough to meet the needs for the early detection, disease classification, treatment evaluation, and accurate prognosis of AD. Initial factors such as pathological changes at the cellular level occur much earlier than the appearance of clinical symptoms and changes in the anatomical structure. In view of the fact that the epidemiological characteristics of AD have not been elucidated and there is a lack of disease reversal drugs, the need for early detection of molecular level changes through molecular imaging is quite urgent. Several molecular imaging modalities for detecting AD are summed up in
Figure 2.
3.1. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Various radioactive tracers are used depending on the intended target. Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging analyzes changes in metabolism (39). PET imaging is the simultaneous detection of gamma rays emitted by positron annihilation events from a radiotracer. Since a radioisotope is utilized to replace one of the tracer's atoms, the radioactive tracers in this case are comparable to common biological compounds like glucose, peptides, and proteins (40). After being injected into the patient, a radioactive tracer enters the targeted organs or tissues through the circulatory system and takes part in metabolic activities there (39). Due to their instability, the radioisotopes in the tracer decay. During this decay, positrons are released and collide with the electrons of nearby atoms, causing an annihilation reaction (41). Two 511 keV gamma rays, separated by around 180 degrees, are produced by the annihilation and are absorbed by scintillation crystals, where they are transformed into low-energy visible photons (41). The light impulses are subsequently translated into electrical signals by a photosensor. Scintillators, detectors, and readout electronics are combined to make a detector that measures three parameters: the energy of the gamma ray, its position upon impact, and the moment the ray strikes the detector (42). After that, these electronic signals are processed using reconstruction and correction techniques to create an image. The capacity of PET imaging to map various signals, such as brain metabolic activity, amyloid load, or tau-tracer retention, differs depending on the radiotracer used. PET scans of AD patient and non-patient groups can be compared as a diagnostic technique to observe variations in uptake patterns.
3.2. Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging (sMRI)
The most widely utilized brain imaging technique in the research of AD has been structural MRI. Clinically affected patients have increased ventricular and sulcal volumes; reduced gray matter or cortical thickness in other cerebral regions, such as the precuneus and posterior cingulate, parietal, and temporal cortex; and accelerated rates of decline in these and whole brain measurements over time. They also have significantly reduced hippocampal and entorhinal cortex volumes, gray matter, and cortical thicknesses (8). Hippocampal and entorhinal cortex size reductions seem to be associated with early memory decline and can be used to predict the development of more severe clinical stages, such as Alzheimer's dementia and moderate cognitive impairment (MCI) (43). In the clinical setting, structural MRI is often recommended to help rule out potentially reversible conditions.
3.3. Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
PET and SPECT are quite comparable. When used to measure cerebral perfusion in dementia patients, SPECT produces results that are similar to those from the clinical diagnostic PET scanning of glucose metabolism. SPECT research has demonstrated the ability to forecast MCI deterioration (44) and has led to similar results as those from autopsies (45). For a long time, the scarcity of PET led to a significant reliance on SPECT scanning. Nevertheless, with the increasing number of PET scanners and their usage in clinical settings for oncological purposes, PET's availability and potential for use in dementia research and care have grown.
3.4. Noninvasive Fluorescence Imaging
By verifying the fluorescence of Aβ, tau, and other AD-associated proteins, optical fluorescence imaging has been established as the most effective technique for diagnosing AD pathology and neural networking. Endogenous and/or exogenous fluorophores that emit light in response to laser excitation are used in fluorescence imaging. In particular, because of low light scattering, low light absorption in surrounding tissues, and negligible autofluorescence, NIR fluorescence imaging (650–1000 nm for NIR-I and 1000–1700 nm for NIR-II) can provide great sensitivity and specificity for the real-time imaging of biological systems (46). To facilitate the noninvasive imaging of AD, fluorescence imaging probes must meet three requirements: (1) they must be (pseudo)permeable to cross the pathologically vulnerable blood–brain barrier (BBB); (2) they must bind to AD-specific cells and proteins, such as tau proteins in the brain; and (3) they must have absorbance and fluorescence emission spectra in the NIR window (650–1700 nm) (46).
By verifying the fluorescence of Aβ, tau, and other AD-associated proteins, optical fluorescence imaging has been established as the most effective technique for diagnosing AD pathology and neural networking. Endogenous and/or exogenous fluorophores that emit light in response to laser excitation are used in fluorescence imaging. In particular, because of low light scattering, low light absorption in surrounding tissues, and negligible autofluorescence, NIR fluorescence imaging (650–1000 nm for NIR-I and 1000–1700 nm for NIR-II) can provide great sensitivity and specificity for the real-time imaging of biological systems (46). To facilitate the noninvasive imaging of AD, fluorescence imaging probes must meet three requirements: (1) they must be (pseudo)permeable to cross the pathologically vulnerable blood–brain barrier (BBB); (2) they must bind to AD-specific cells and proteins, such as tau proteins in the brain; and (3) they must have absorbance and fluorescence emission spectra in the NIR window (650–1700 nm) (46).
4. Radioactive Tracers/Fluorescence Imaging Probes in Molecular Imaging
AD molecular imaging is used to design molecular probes or imaging agents based on indicative molecular targets. The commonly used criteria for testing and evaluating the performance of the designed tracers are high affinity, high binding specificity, high specific activity, high blood–brain barrier penetration, and low side effects. Before achieving these goals, the metabolism and mechanisms of the peripheral and central nervous systems need to be fully studied. Their emission energy and half-life should be consistent with the target application. In addition, tracers need to maintain the same biological properties after positron or single-photon isotope labeling. The application of tracers and fluorescence imaging probes to diagnose AD is summarized in
Table 1.
4.1. Targeted β-amyloid traces/Probes
In in vitro experiments, Congo red and sulfur T were the first compounds found to bind to β-fiber cross-structures, but their ionic charges prevented them from crossing the blood–brain barrier (59). Based on the structures of these two compounds, many PET tracers with 11C or 18F as radioisotopes have been developed to directly visualize A β and its distribution in vivo to evaluate neuroinflammatory plaques.
The first compound used in vivo to recognize the β-amyloid protein was BSB, which has good blood–brain barrier penetration and plaque-specific binding power. Marie L. et al. compared the results of using BSB with those using standard histochemical dyes like thioflavin S and immunohistochemical stains specifically meant for use on the same lesions in postmortem tissues from patients with a variety of neurodegenerative diseases. The diagnostic lesions were characterized by fibrillar intra- or extracellular lesions. These findings indicate that BSB binds not only to the external amyloid beta protein but also to a variety of intracellular lesions made up of aberrant tau and synuclein proteins. This suggests that derivatives of radioiodinated BSB or comparable ligands could be helpful imaging agents to track various amyloids in vivo (47).
After testing synthetic Aβ fibers from AD patients and cadaveric AD specimens, 6-OH-BAT-1, or PIB, stood out among more than 100 chemicals. During the prodromal phase of AD, PIB binding increases, showing bimodal behavior, and approximately 50% of positive individuals subsequently progress to AD. In prospective studies, increased PIB ligand retention was able to identify 82% of AD patients at follow-up, with only one prediction failure, demonstrating its high sensitivity and specificity. In addition, both amygdala and hippocampus atrophy were found to be positively correlated with PIB binding, suggesting differences in susceptibility to Aβ toxicity in different brain regions. Although this tracer seems promising for showing an increase in Aβ deposits before the clinical onset of AD, there is a ceiling effect, and large multicenter studies are still needed to develop objective evaluation criteria (48).
Based on sensitivity and specificity, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved three radiopharmaceuticals that bind to the fiber-aggregating form of beta-amyloid. Flutimol, as a benzothiazole derivative, can estimate plaque density with a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity greater than 80%, and no adverse reactions were observed in the phase III clinical trials (49).
Osama et al. compared in vivo PET imaging with postmortem histopathology in an open-label, nonrandomized, multicenter, phase 3 research study to validate the (18)F-labeled β-amyloid tracer florbetaben. Flubetaben demonstrated a 97.9% sensitivity and an 88.9% specificity in identifying Aβ plaque, as validated by histology. As a result, florbetaben PET may be a useful addition for clinical diagnosis, and especially for the exclusion of AD, as the results revealed good sensitivity and specificity for the detection of neuritic β-amyloid plaques as verified by histology (50).
Viola et al. attached oligomer-specific antibodies to magnetic nanostructures to construct a stable compound which can enter the central nervous system through intranasal administration and combine with A β oligomers to produce detectable MRI signals. Targeting neurotoxic Aβ oligomers, these nanostructures have the potential to be valuable in assessing the effectiveness of novel medications and, eventually, in diagnosing and treating Alzheimer's disease in its early stages (51).
4.2. Targeted Phosphorylated Tau Protein Tracers/Probes
Fluorine-containing radioactive tracers have been developed to bind tau fibers with high precision. Watanabe [
11] constructed a compound called BIP-Nme2. As a tau imaging probe, BIP-NMe2 demonstrated a strong and specific affinity for tau aggregation in brain slices from AD patients. Furthermore, BIP-NMe2 showed a strong initial uptake into the normal mouse brain and a rapid washout from it, indicating that its pharmacokinetics are advantageous for identifying tau aggregation through in vivo imaging (52).
The tracers labeled with 11C are 11C-THK5351 and 11C-PPB. Konstantinos evaluated the binding of two chemically different tau-specific PET tracers (11C-THK5351 and 11C-PBB3) in a head-to-head, in vivo, multimodal design. It was found that the former signal is more closely related to the pre-determined distribution of tau proteins, while the latter is more closely related to the co-deposition of β-amyloid and tau proteins (53).
A PET radiotracer called 18F-T807 was created to image tau protein aggregates, which have been linked to neurologic conditions like Alzheimer's disease and traumatic brain injury (TBI). Dustin et al. used metabolite-corrected arterial input functions and dynamic PET imaging to describe the pharmacokinetics of 18F-T807 in human participants. The results indicated that 18F-T807 can detect tau proteins quantitatively and the plasma clearance rate is high (54).
Though their value in early diagnosis or detection is inferior to that of A β-targeted tracers, the pathology of tau proteins is more closely linked to the clinical symptoms of AD and appears relatively late in the disease's progression, making this imaging more commonly used in clinical trials to assess how well drugs delay the disease's progression.
4.3. Targeted Neurotransmitter Tracers/Probes
The most important energy consumption site of neurons is the synapse, that is, it is the place where active electrical activity and material exchange take place (60). Neuronal dysfunction and loss of function are usually reflected in the reduction in neurotransmitters or their receptors that are produced and released (61). Neurotransmitters and their receptors are generally considered to be markers of specific types of neurons (61).
Weinberger et al. found that when 123I-4-IQNB was used in SPECT, the brain region with strong binding to the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor was not correlated with the glucose metabolism intensity measured by FDG-PET, and the defect range was larger in AD patients. In patients with AD, the signal of the tracer showed differences in the expression of receptors in different brain regions (55).
Drugs targeting vesicular ACh transporters are also under development; it has been found that the signal intensity of 123I-IBVM, as a representative, is inversely proportional to age and symptom severity. In addition, the decrease in affinity was limited to the parietal lobe and occipital lobe in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD), but decreased in the whole cortex in patients with PD and AD. Therefore, this compound is also considered to be used to detect cholinergic neuronal degeneration, but its specificity and sensitivity for the diagnosis of AD need to be determined (56).
Dopaminergic neurons are widely studied in diseases such as PD, schizophrenia, and drug abuse. Tracers targeting dopamine transporters, such as 123i-fluoropropyl carboxyl-methoxydeoxane (123I-FP-CIT), help to distinguish between PD dementia, Lewy body dementia, and AD dementia. Niels advocated for the use of 123I-FP-CIT SPECT as a supplemental diagnostic technique to enhance the identification of prodromal DLB and probable dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) in a group of individuals with concurrent mental health symptoms. When DLB patients arrive with nigrostriatal dysfunction, psychiatric onset is more common than MCI onset. This suggests the value of extensive clinical phenotyping in memory clinics, which includes psychopathology assessment (57).
Higuchi et al. developed 11C-doxepin, a radioligand for H(1) receptors, and using positron emission tomography, assessed cerebral histamine H(1) receptor binding in vivo in ten individuals with Alzheimer's disease and eleven without (five elderly and six young). The results showed a low signal intensity in the frontal and parietal lobes in patients with AD. More importantly, the expression concentration of the corresponding receptors represented by the signal in specific brain regions is closely related to the severity of the disease (58).
5. Summary and Conclusions
Molecular pathological tracers provide a possibility to accurately quantify brain changes through molecular imaging. The absence of diagnostic criteria to detect AD early is the main obstacle to theranostics in this field. As evidenced by our explanation of the pathophysiology of AD, various brain imaging modalities, and radioactive tracers/fluorescence probes, molecular imaging enhances our understanding of AD by establishing more crucial links between various patient groups at different stages of the disease. Typically, at least one type of imaging technique can lead to an AD diagnosis or the exclusion of dementia through the identification of intracranial causes that demonstrate structural alterations in the brain. Subjective vision is dependent on technology and software and has limitations when used to assess hippocampus volume or medial temporal lobe atrophy. In the future, the issues with conventional imaging techniques may be resolved by fusing automatic computer-aided techniques with different tracers or multimodal imaging.
Author Contributions
L.X. collected the literature, performed the analysis and interpretation, and wrote the manuscript. X.L. and Y.G. contributed to the literature collection and the analysis of the results. D.Q., H.S. and X.L. contributed to the literature collection and analysis and revised the manuscript interpretation of the results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31960178, 82160923, 82374425); Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Yunnan Province (202301AS070053); Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Yunnan Provincial Department of Education; Scientific Research Projects for High-level Talents of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine (2019YZG01); Young Top-Notch Talent in 10,000 Talent Program of Yunnan Province (YNWR-QNBJ-2019-235).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jost, B.C.; Grossberg, G.T. The Natural History of Alzheimer's Disease: A Brain Bank Study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1995, 43, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2023 Alzheimer's Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer's Disease. European journal of neurology 2018, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; de Leon, M.J.; Zetterberg, H. Alzheimer's Disease. Lancet (London, England) 2006, 368, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G. Research Progress in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. Chinese medical journal 2018, 131, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Hampel, H.; Feldman, H.H.; Scheltens, P.; Aisen, P.; Andrieu, S.; et al. Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease: Definition, Natural History, and Diagnostic Criteria. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2016, 12, 292–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.; Baxter, B.; Campbell, B.C.V.; Carpenter, J.S.; Cognard, C.; Dippel, D.; et al. Multisociety Consensus Quality Improvement Revised Consensus Statement for Endovascular Therapy of Acute Ischemic Stroke. International journal of stroke : official journal of the International Stroke Society 2018, 13, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Jr Knopman, D.S.; Jagust, W.J.; Shaw, L.M.; Aisen, P.S.; Weiner, M.W.; et al. Hypothetical Model of Dynamic Biomarkers of the Alzheimer's Pathological Cascade. The Lancet Neurology 2010, 9, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valotassiou, V.; Malamitsi, J.; Papatriantafyllou, J.; Dardiotis, E.; Tsougos, I.; Psimadas, D.; et al. Spect and Pet Imaging in Alzheimer's Disease. Annals of nuclear medicine 2018, 32, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, M.; Stiles, W.R.; Choi, H.S. Neuroimaging Modalities in Alzheimer's Disease: Diagnosis and Clinical Features. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valotassiou, V.; Wozniak, G.; Sifakis, N.; Demakopoulos, N.; Georgoulias, P. Radiopharmaceuticals in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Current clinical pharmacology 2008, 3, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valotassiou, V.; Archimandritis, S.; Sifakis, N.; Papatriantafyllou, J.; Georgoulias, P. Alzheimer's Disease: Spect and Pet Tracers for Beta-Amyloid Imaging. Current Alzheimer research 2010, 7, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mier, W.; Mier, D. Advantages in Functional Imaging of the Brain. Frontiers in human neuroscience 2015, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Reconsideration of Anticholinesterase Therapeutic Strategies against Alzheimer's Disease. ACS chemical neuroscience 2019, 10, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehouse, P.J.; Price, D.L.; Struble, R.G.; Clark, A.W.; Coyle, J.T.; Delon, M.R. Alzheimer's Disease and Senile Dementia: Loss of Neurons in the Basal Forebrain. Science (New York, NY) 1982, 215, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanari, M.L.; García-Ayllón, M.S.; Belbin, O.; Galcerán, J.; Lleó, A.; Sáez-Valero, J. Acetylcholinesterase Modulates Presenilin-1 Levels and Γ-Secretase Activity. Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 2014, 41, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Xu, J.; Cardoso Dos Santos, M.; Hildebrandt, N. Multiplexed Biosensing and Bioimaging Using Lanthanide-Based Time-Gated Förster Resonance Energy Transfer. Accounts of chemical research 2022, 55, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begcevic, I.; Brinc, D.; Brown, M.; Martinez-Morillo, E.; Goldhardt, O.; Grimmer, T.; et al. Brain-Related Proteins as Potential Csf Biomarkers of Alzheimer's Disease: A Targeted Mass Spectrometry Approach. Journal of proteomics 2018, 182, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, D.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, T.Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Underlying the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. Molecular neurodegeneration 2020, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Barve, K.H.; Kumar, M.S. Recent Advancements in Pathogenesis, Diagnostics and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. Current neuropharmacology 2020, 18, 1106–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalto, M.C.; Farrar, G.; Hehir, C.T. Fibrillar and Oligomeric Beta-Amyloid as Distinct Local Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2007, 1097, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kametani, F.; Hasegawa, M. Reconsideration of Amyloid Hypothesis and Tau Hypothesis in Alzheimer's Disease. Frontiers in neuroscience 2018, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, L.; Masliah, E. Molecular Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's Disease. Human molecular genetics 2010, 19, R12–R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.P.; Cao, L.L.; Wang, P. Elevating the Levels of Calcium Ions Exacerbate Alzheimer's Disease Via Inducing the Production and Aggregation of Β-Amyloid Protein and Phosphorylated Tau. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián-Serrano, Á.; de Diego-García, L.; Díaz-Hernández, M. The Neurotoxic Role of Extracellular Tau Protein. International journal of molecular sciences 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annual review of biochemistry 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, C.M.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer's Disease Risk Genes and Mechanisms of Disease Pathogenesis. Biological psychiatry 2015, 77, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Howard, V.; Loosbrock, N.; Dickson, D.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E. Amyloid-Beta Immunization Effectively Reduces Amyloid Deposition in Fcrgamma-/- Knock-out Mice. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2003, 23, 8532–8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Golenbock, D.T.; Latz, E. Innate Immunity in Alzheimer's Disease. Nature immunology 2015, 16, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zott, B.; Busche, M.A.; Sperling, R.A.; Konnerth, A. What Happens with the Circuit in Alzheimer's Disease in Mice and Humans? Annual review of neuroscience 2018, 41, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.J.; Brand, M.D. Reactive Oxygen Species Production by Mitochondria. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ) 2009, 554, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, A.; Hauptmann, S.; Scherping, I.; Rhein, V.; Müller-Spahn, F.; Götz, J.; et al. Soluble Beta-Amyloid Leads to Mitochondrial Defects in Amyloid Precursor Protein and Tau Transgenic Mice. Neuro-degenerative diseases 2008, 5, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, M.; Di Mauro, M.; Di Mauro, M.; Luca, A. Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer's Disease, Depression, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Role of Oxidative Stress. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2019, 2019, 4730539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative Stress and the Amyloid Beta Peptide in Alzheimer's Disease. Redox biology 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Peng, F. Radiopharmaceuticals for Assessment Of altered Metabolism and Biometal Fluxes In brain Aging and Alzheimer's Disease With positron Emission Tomography. Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 2017, 59, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Jie, C.; Zheng, W.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z. Investigation of Underlying Association between Whole Brain Regions and Alzheimer's Disease: A Research Based on an Artificial Intelligence Model. Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2022, 14, 872530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.S.; Park, J.S.; Yang, Y.; Na, S.H.; Chung, Y.A.; Song, I.U. Cerebral Perfusion Changes after Acetyl-L-Carnitine Treatment in Early Alzheimer's Disease Using Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography. Dementia and neurocognitive disorders 2017, 16, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochocki, B.; Boon, B.D.C.; Verheul, S.R.; Zada, L.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Ariese, F.; et al. Multimodal, Label-Free Fluorescence and Raman Imaging of Amyloid Deposits in Snap-Frozen Alzheimer's Disease Human Brain Tissue. Communications biology 2021, 4, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V.; McCook, B.M.; Torok, F.S. An Introduction to Pet-Ct Imaging. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc 2004, 24, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omami, G.; Tamimi, D.; Branstetter, B.F. Basic Principles and Applications of (18)F-Fdg-Pet/Ct in Oral and Maxillofacial Imaging: A Pictorial Essay. Imaging science in dentistry 2014, 44, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chalich, Y.; Deen, M.J. Sensors for Positron Emission Tomography Applications. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 19, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanoudaki, V.; Levin, C.S. Photo-Detectors for Time of Flight Positron Emission Tomography (Tof-Pet). Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2010, 10, 10484–10505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr; Shiung, M.M.; Weigand, S.D.; O'Brien, P.C.; Gunter, J.L.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Brain Atrophy Rates Predict Subsequent Clinical Conversion in Normal Elderly and Amnestic Mci. Neurology 2005, 65, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.A.; Jones, K.; Holman, B.L.; Becker, J.A.; Spiers, P.A.; Satlin, A.; et al. Preclinical Prediction of Alzheimer's Disease Using Spect. Neurology 1998, 50, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagust, W.; Thisted, R.; Devous, M.D., Sr.; Van Heertum, R.; Mayberg, H.; Jobst, K.; et al. Spect Perfusion Imaging in the Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease: A Clinical-Pathologic Study. Neurology 2001, 56, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Kim, H.K. Multispectral Image-Guided Surgery in Patients. Nature biomedical engineering 2020, 4, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.L.; Schuck, T.; Sheridan, S.; Kung, M.P.; Kung, H.; Zhuang, Z.P.; et al. The Fluorescent Congo Red Derivative, (Trans, Trans)-1-Bromo-2,5-Bis-(3-Hydroxycarbonyl-4-Hydroxy)Styrylbenzene (Bsb), Labels Diverse Beta-Pleated Sheet Structures in Postmortem Human Neurodegenerative Disease Brains. The American journal of pathology 2001, 159, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laforce, R., Jr.; Tosun, D.; Ghosh, P.; Lehmann, M.; Madison, C.M.; Weiner, M.W.; et al. Parallel Ica of Fdg-Pet and Pib-Pet in Three Conditions with Underlying Alzheimer's Pathology. NeuroImage Clinical 2014, 4, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, C.; Gamez, J.E.; Singh, U.; Sadowsky, C.H.; Villena, T.; Sabbagh, M.N.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of Flutemetamol Labeled with Radioactive Fluorine 18 Imaging and Neuritic Plaque Density. JAMA neurology 2015, 72, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, O.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Seibyl, J.; Barthel, H.; Akatsu, H.; Ouchi, Y.; et al. Florbetaben Pet Imaging to Detect Amyloid Beta Plaques in Alzheimer's Disease: Phase 3 Study. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2015, 11, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, K.L.; Sbarboro, J.; Sureka, R.; De, M.; Bicca, M.A.; Wang, J.; et al. Towards Non-Invasive Diagnostic Imaging of Early-Stage Alzheimer's Disease. Nature nanotechnology 2015, 10, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H. [Development of Spect Probes for in Vivo Imaging of Β-Amyloid and Tau Aggregates in the Alzheimer's Disease Brain]. Yakugaku zasshi : Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 2017, 137, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiotis, K.; Stenkrona, P.; Almkvist, O.; Stepanov, V.; Ferreira, D.; Arakawa, R.; et al. Dual Tracer Tau Pet Imaging Reveals Different Molecular Targets for (11)C-Thk5351 and (11)C-Pbb3 in the Alzheimer Brain. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2018, 45, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooten, D.W.; Guehl, N.J.; Verwer, E.E.; Shoup, T.M.; Yokell, D.L.; Zubcevik, N.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of the Tau Pet Radiotracer (18)F-T807 ((18)F-Av-1451) in Human Subjects. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine 2017, 58, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, D.R.; Jones, D.; Reba, R.C.; Mann, U.; Coppola, R.; Gibson, R.; et al. A Comparison of Fdg Pet and Iqnb Spect in Normal Subjects and in Patients with Dementia. The Journal of neuropsychiatry and clinical neurosciences 1992, 4, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazère, J.; Mayo, W.; Pariscoat, G.; Schulz, J.; Allard, M.; Fernandez, P.; et al. Simplified Quantification Method for in Vivo Spect Imaging of the Vesicular Acetylcholine Transporter with 123i-Iodobenzovesamicol. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine 2015, 56, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, N.; Lange, C.; Timäus, C.; Wiltfang, J.; Bouter, C. Assessing Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Pathways Via 123i-Fp-Cit Spect in Dementia with Lewy Bodies in a Psychiatric Patient Cohort. Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2021, 13, 672956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Yanai, K.; Okamura, N.; Meguro, K.; Arai, H.; Itoh, M.; et al. Histamine H(1) Receptors in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease Assessed by Positron Emission Tomography. Neuroscience 2000, 99, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayne, D.J.; Lim, S.; Donnelly, P.S. Metal Complexes Designed to Bind to Amyloid-Β for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. Chemical Society reviews 2014, 43, 6701–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Nelson, J.C.; Bend, E.G.; Rodríguez-Laureano, L.; Tueros, F.G.; Cartagenova, L.; et al. Glycolytic Enzymes Localize to Synapses under Energy Stress to Support Synaptic Function. Neuron 2016, 90, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traver, S.; Salthun-Lassalle, B.; Marien, M.; Hirsch, E.C.; Colpaert, F.; Michel, P.P. The Neurotransmitter Noradrenaline Rescues Septal Cholinergic Neurons in Culture from Degeneration Caused by Low-Level Oxidative Stress. Molecular pharmacology 2005, 67, 1882–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).