Submitted:
04 January 2024
Posted:
05 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Platelet activation in Antiphospholipid Syndrome
2.1. Platelet Activation
2.2. The Relationship between Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Platelet Activation
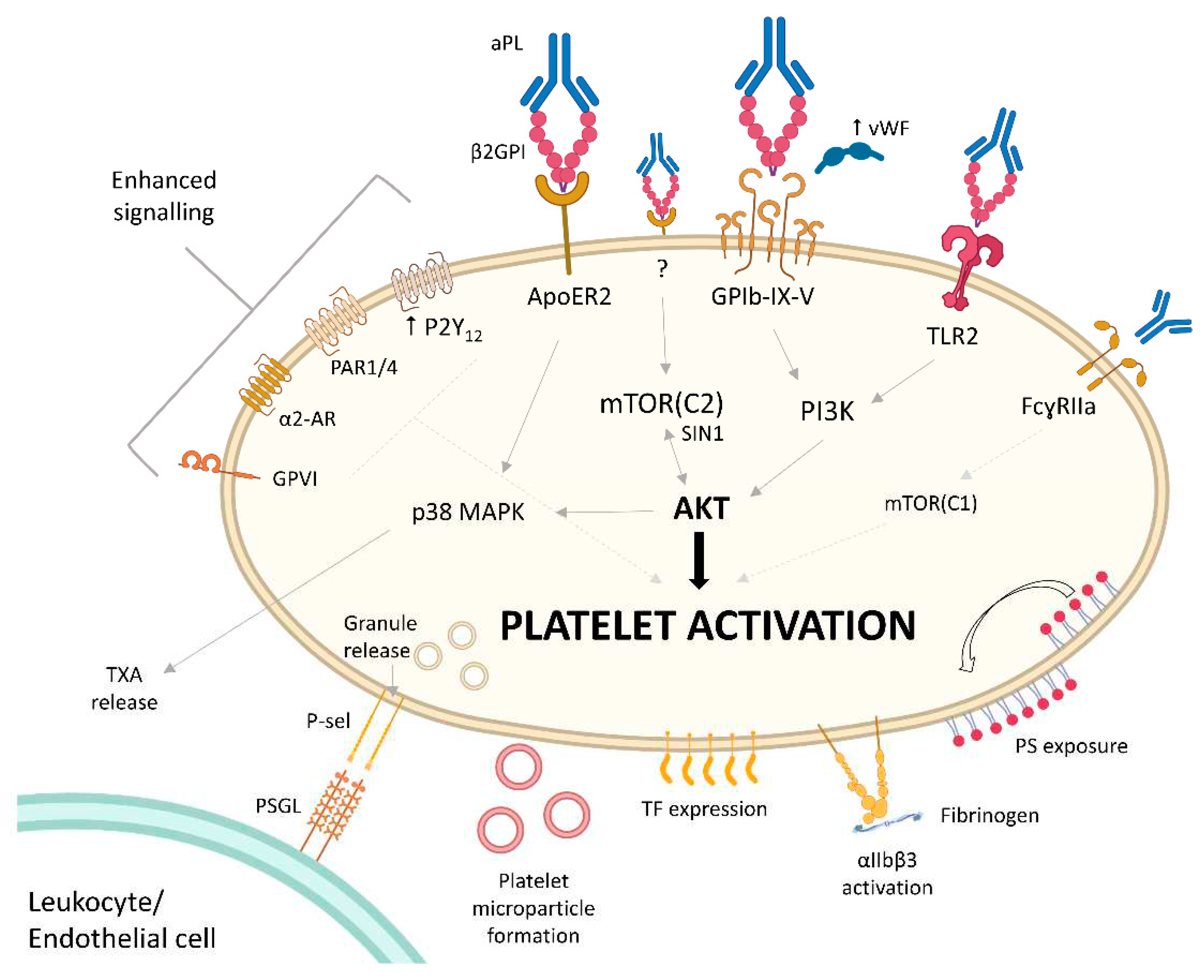
2.3. Mechanisms of aPL-Induced Platelet Activation
2.4. Thrombocytopenia in APS
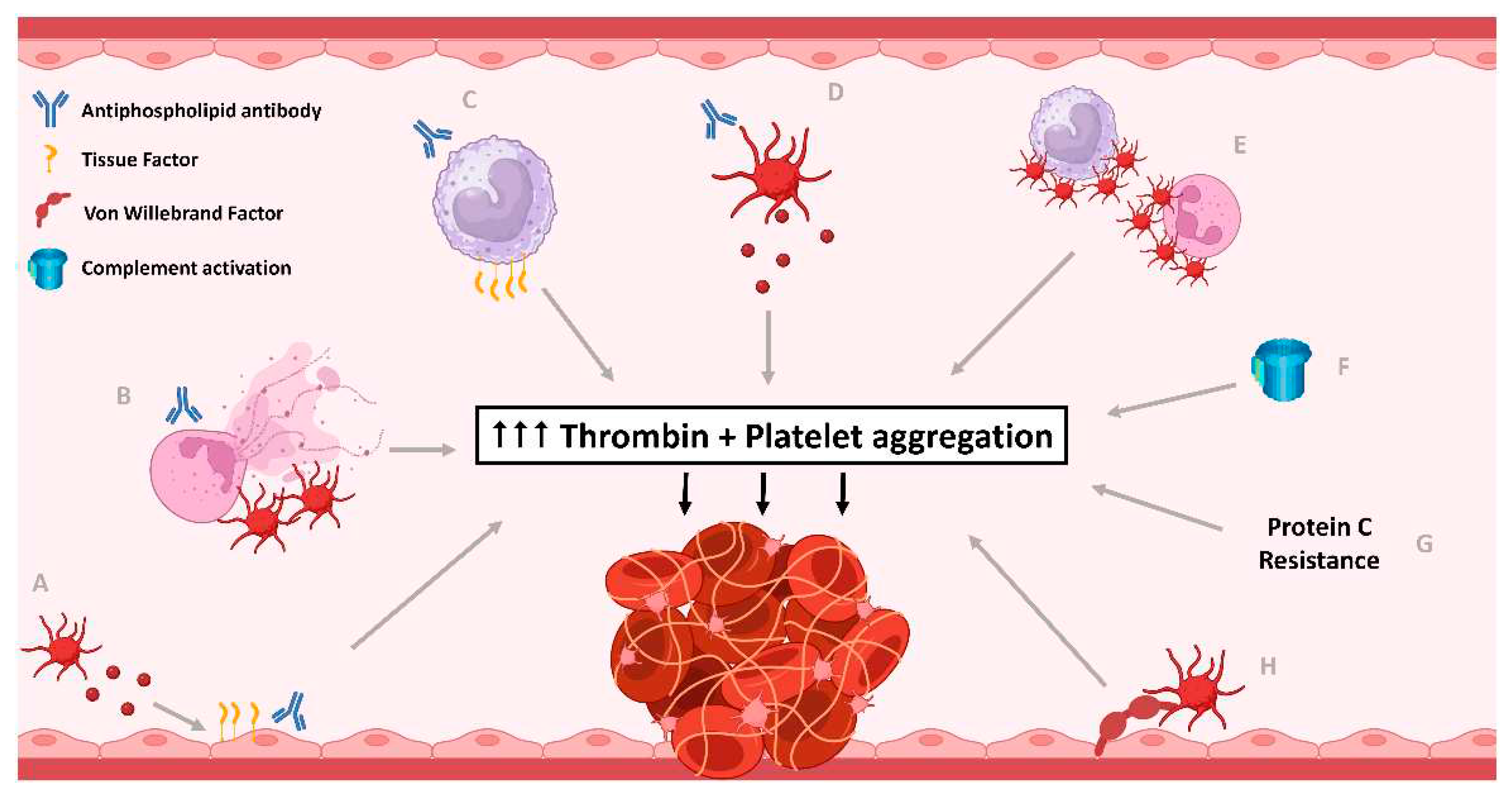
3. The Prothrombotic Interaction of Platelets with Other Cells in APS
4. Platelets and Complement in APS
5. The Role of Antiplatelets in Management of Thrombosis in APS
5.1. Antiplatelets as Primary Prophylaxis for Thrombosis in APS
5.2. Antiplatelets as Secondary Prophylaxis for Thrombosis in APS
5.3. How Can Platelets Be Targeted Better to Improve Outcomes in APS?
6. Conclusion
References
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.W.M.; De Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2006, 4, 295-306, . [CrossRef]
- Sevim, E.; Zisa, D.; Andrade, D.; Sciascia, S.; Pengo, V.; Tektonidou, M.G.; Ugarte, A.; Gerosa, M.; Belmont, H.M.; Zamorano, M.A.A.; et al. Characteristics of Patients With Antiphospholipid Antibody Positivity in the APS ACTION International Clinical Database and Repository. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2022, 74, 324-335, . [CrossRef]
- Duarte-García, A.; Pham, M.M.; Crowson, C.S.; Amin, S.; Moder, K.G.; Pruthi, R.K.; Warrington, K.J.; Matteson, E.L. The Epidemiology of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Population-Based Study. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019, 71, 1545-1552, . [CrossRef]
- Miranda, S.; Park, J.; Le Gal, G.; Piran, S.; Kherani, S.; Rodger, M.A.; Delluc, A. Prevalence of confirmed antiphospholipid syndrome in 18-50 years unselected patients with first unprovoked venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Haemost 2020, 18, 926-930, . [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Sanna, G.; Khamashta, M.A.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Erkan, D.; Andreoli, L.; Bertolaccini, M.L. The estimated frequency of antiphospholipid antibodies in young adults with cerebrovascular events: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis 2015, 74, 2028-2033, . [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pintó, I.; Espinosa, G.; Erkan, D.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Cervera, R. The effect of triple therapy on the mortality of catastrophic anti-phospholipid syndrome patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2018, 57, 1264-1270, . [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Erkan, D.; Duarte-Garcia, A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Knight, J.S.; Ortel, T.L.; Rahman, A.; Salmon, J.E.; Tektonidou, M.G.; et al. 16th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies Task Force Report on Antiphospholipid Syndrome Treatment Trends. Lupus 2020, 29, 1571-1593, . [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Amoura, Z.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Dörner, T.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Hambly, K.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome in adults. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019, 78, 1296, . [CrossRef]
- Ortel, T.L.; Meleth, S.; Catellier, D.; Crowther, M.; Erkan, D.; Fortin, P.R.; Garcia, D.; Haywood, N.; Kosinski, A.S.; Levine, S.R.; et al. Recurrent thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies and an initial venous or arterial thromboembolic event: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost 2020, 18, 2274-2286, . [CrossRef]
- Aibar, J.; Schulman, S. Arterial Thrombosis in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Semin Thromb Hemost 2021, 47, 709-723, . [CrossRef]
- Proulle, V.; Furie, R.A.; Merrill-Skoloff, G.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. Platelets are required for enhanced activation of the endothelium and fibrinogen in a mouse thrombosis model of APS. Blood 2014, 124, 611-622, . [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Shi, H.; Chen, C.; Teng, J.; Dai, J.; Ouyang, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; Cheng, X.; Ye, J.; et al. Activation of Platelet mTORC2/Akt Pathway by Anti-β2GP1 Antibody Promotes Thrombosis in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2023, 43, 1818-1832, . [CrossRef]
- Koupenova, M.; Kehrel, B.E.; Corkrey, H.A.; Freedman, J.E. Thrombosis and platelets: an update. European Heart Journal 2017, 38, 785-791, . [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.; Schoeman, R.M.; Krohl, P.J.; Wallbank, A.M.; Samaniuk, J.R.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Neeves, K.B. Platelets Drive Thrombus Propagation in a Hematocrit and Glycoprotein VI–Dependent Manner in an In Vitro Venous Thrombosis Model. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2018, 38, 1052-1062, . [CrossRef]
- Tohidi-Esfahani, I.; Lee, C.S.M.; Liang, H.P.H.; Chen, V.M.Y. Procoagulant platelets: Laboratory detection and clinical significance. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology 2020, 42, 59-67, . [CrossRef]
- Pfeiler, S.; Massberg, S.; Engelmann, B. Biological basis and pathological relevance of microvascular thrombosis. Thromb Res 2014, 133 Suppl 1, S35-37, . [CrossRef]
- Fernández, D.I.; Kuijpers, M.J.E.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. Platelet calcium signaling by G-protein coupled and ITAM-linked receptors regulating anoctamin-6 and procoagulant activity. Platelets 2021, 32, 863-871, . [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, L.; Roden, R.C.; Bergmeier, W. CalDAG-GEFI is at the nexus of calcium-dependent platelet activation. Blood 2009, 114, 2506-2514, . [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, A.; Tadokoro, S.; Eto, K.; Pampori, N.; Parise, L.V.; White, G.C.; Shattil, S.J. Relationships between Rap1b, affinity modulation of integrin alpha IIbbeta 3, and the actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 25715-25721, . [CrossRef]
- Wurm, H. beta 2-Glycoprotein-I (apolipoprotein H) interactions with phospholipid vesicles. Int J Biochem 1984, 16, 511-515, . [CrossRef]
- Khamashta, M.A.; Harris, E.N.; Gharavi, A.E.; Derue, G.; Gil, A.; Vázquez, J.J.; Hughes, G.R. Immune mediated mechanism for thrombosis: antiphospholipid antibody binding to platelet membranes. Ann Rheum Dis 1988, 47, 849-854, . [CrossRef]
- Agar, C.; van Os, G.M.; Mörgelin, M.; Sprenger, R.R.; Marquart, J.A.; Urbanus, R.T.; Derksen, R.H.; Meijers, J.C.; de Groot, P.G. Beta2-glycoprotein I can exist in 2 conformations: implications for our understanding of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2010, 116, 1336-1343, . [CrossRef]
- de Laat, B.; Derksen, R.H.; van Lummel, M.; Pennings, M.T.; de Groot, P.G. Pathogenic anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies recognize domain I of beta2-glycoprotein I only after a conformational change. Blood 2006, 107, 1916-1924, . [CrossRef]
- de Laat, B.; van Berkel, M.; Urbanus, R.T.; Siregar, B.; de Groot, P.G.; Gebbink, M.F.; Maas, C. Immune responses against domain I of β(2)-glycoprotein I are driven by conformational changes: domain I of β(2)-glycoprotein I harbors a cryptic immunogenic epitope. Arthritis Rheum 2011, 63, 3960-3968, . [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Seta, N.; Kaburaki, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsuura, E.; Kuwana, M. Excessive exposure to anionic surfaces maintains autoantibody response to beta(2)-glycoprotein I in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2007, 110, 4312-4318, . [CrossRef]
- Sikara, M.P.; Routsias, J.G.; Samiotaki, M.; Panayotou, G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G. {beta}2 Glycoprotein I ({beta}2GPI) binds platelet factor 4 (PF4): implications for the pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2010, 115, 713-723, . [CrossRef]
- Lutters, B.C.; Derksen, R.H.; Tekelenburg, W.L.; Lenting, P.J.; Arnout, J.; de Groot, P.G. Dimers of beta 2-glycoprotein I increase platelet deposition to collagen via interaction with phospholipids and the apolipoprotein E receptor 2'. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 33831-33838, . [CrossRef]
- Forastiero, R.; Martinuzzo, M.; Carreras, L.O.; Maclouf, J. Anti-beta2 glycoprotein I antibodies and platelet activation in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: association with increased excretion of platelet-derived thromboxane urinary metabolites. Thromb Haemost 1998, 79, 42-45.
- Robbins, D.L.; Leung, S.; Miller-Blair, D.J.; Ziboh, V. Effect of anticardiolipin/beta2-glycoprotein I complexes on production of thromboxane A2 by platelets from patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol 1998, 25, 51-56.
- Breen, K.A.; Sanchez, K.; Kirkman, N.; Seed, P.T.; Parmar, K.; Moore, G.W.; Hunt, B.J. Endothelial and platelet microparticles in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Thromb Res 2015, 135, 368-374, . [CrossRef]
- Štok, U.; Blokar, E.; Lenassi, M.; Holcar, M.; Frank-Bertoncelj, M.; Erman, A.; Resnik, N.; Sodin-Šemrl, S.; Čučnik, S.; Pirkmajer, K.P.; et al. Characterization of Plasma-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Indicates Ongoing Endothelial and Platelet Activation in Patients with Thrombotic Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Cells 2020, 9, . [CrossRef]
- Bontadi, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Falcinelli, E.; Giannini, S.; Marturano, A.; Tonello, M.; Hoxha, A.; Pengo, V.; Punzi, L.; Momi, S.; et al. Platelet and endothelial activation in catastrophic and quiescent antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost 2013, 109, 901-908, . [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.E.; Harrison, P.; Mackie, I.J.; Isenberg, D.A.; Machin, S.J. Increased circulating platelet-leucocyte complexes and platelet activation in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Haematol 2001, 115, 451-459, . [CrossRef]
- Warner, M.N.; Pavord, S.; Moore, J.C.; Warkentin, T.E.; Hayward, C.P.; Kelton, J.G. Serum-induced platelet procoagulant activity: an assay for the characterization of prothrombotic disorders. J Lab Clin Med 1999, 133, 129-133, . [CrossRef]
- Membre, A.; Wahl, D.; Latger-Cannard, V.; Max, J.P.; Lacolley, P.; Lecompte, T.; Regnault, V. The effect of platelet activation on the hypercoagulability induced by murine monoclonal antiphospholipid antibodies. Haematologica 2008, 93, 566-573, . [CrossRef]
- Reverter, J.C.; Tàssies, D.; Font, J.; Khamashta, M.A.; Ichikawa, K.; Cervera, R.; Escolar, G.; Hughes, G.R.; Ingelmo, M.; Ordinas, A. Effects of human monoclonal anticardiolipin antibodies on platelet function and on tissue factor expression on monocytes. Arthritis Rheum 1998, 41, 1420-1427, . [CrossRef]
- Reverter, J.C.; Tàssies, D.; Escolar, G.; Font, J.; López Soto, A.; Ingelmo, M.; Ordinas, A. Effect of plasma from patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome on platelet function in a collagen rich perfusion system. Thromb Haemost 1995, 73, 132-137.
- Romay-Penabad, Z.; Aguilar-Valenzuela, R.; Urbanus, R.T.; Derksen, R.H.; Pennings, M.T.; Papalardo, E.; Shilagard, T.; Vargas, G.; Hwang, Y.; de Groot, P.G.; et al. Apolipoprotein E receptor 2 is involved in the thrombotic complications in a murine model of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2011, 117, 1408-1414, . [CrossRef]
- Willems, G.M.; Janssen, M.P.; Pelsers, M.M.; Comfurius, P.; Galli, M.; Zwaal, R.F.; Bevers, E.M. Role of divalency in the high-affinity binding of anticardiolipin antibody-beta 2-glycoprotein I complexes to lipid membranes. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13833-13842, . [CrossRef]
- Arnout, J.; Wittevrongel, C.; Vanrusselt, M.; Hoylaerts, M.; Vermylen, J. Beta-2-glycoprotein I dependent lupus anticoagulants form stable bivalent antibody beta-2-glycoprotein I complexes on phospholipid surfaces. Thromb Haemost 1998, 79, 79-86.
- Lutters, B.C.; Meijers, J.C.; Derksen, R.H.; Arnout, J.; de Groot, P.G. Dimers of beta 2-glycoprotein I mimic the in vitro effects of beta 2-glycoprotein I-anti-beta 2-glycoprotein I antibody complexes. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 3060-3067, . [CrossRef]
- Urbanus, R.T.; Pennings, M.T.; Derksen, R.H.; de Groot, P.G. Platelet activation by dimeric beta2-glycoprotein I requires signaling via both glycoprotein Ibalpha and apolipoprotein E receptor 2'. J Thromb Haemost 2008, 6, 1405-1412, . [CrossRef]
- Pennings, M.T.; Derksen, R.H.; van Lummel, M.; Adelmeijer, J.; VanHoorelbeke, K.; Urbanus, R.T.; Lisman, T.; de Groot, P.G. Platelet adhesion to dimeric beta-glycoprotein I under conditions of flow is mediated by at least two receptors: glycoprotein Ibalpha and apolipoprotein E receptor 2'. J Thromb Haemost 2007, 5, 369-377, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, F.; Lu, D.; Sun, N.; Yin, X.; Jin, M.; Liu, Y. Anti-β2 glycoprotein I antibodies in complex with β2 glycoprotein I induce platelet activation via two receptors: apolipoprotein E receptor 2' and glycoprotein I bα. Front Med 2016, 10, 76-84, . [CrossRef]
- Vega-Ostertag, M.; Harris, E.N.; Pierangeli, S.S. Intracellular events in platelet activation induced by antiphospholipid antibodies in the presence of low doses of thrombin. Arthritis Rheum 2004, 50, 2911-2919, . [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Giannakopoulos, B.; Yan, X.; Yu, P.; Berndt, M.C.; Andrews, R.K.; Rivera, J.; Iverson, G.M.; Cockerill, K.A.; Linnik, M.D.; et al. Anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies in complex with beta2-glycoprotein I can activate platelets in a dysregulated manner via glycoprotein Ib-IX-V. Arthritis Rheum 2006, 54, 2558-2567, . [CrossRef]
- Terrisse, A.D.; Laurent, P.A.; Garcia, C.; Gratacap, M.P.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Sié, P.; Payrastre, B. The class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases α and β control antiphospholipid antibodies-induced platelet activation. Thromb Haemost 2016, 115, 1138-1146, . [CrossRef]
- Bryckaert, M.; Rosa, J.P.; Denis, C.V.; Lenting, P.J. Of von Willebrand factor and platelets. Cell Mol Life Sci 2015, 72, 307-326, . [CrossRef]
- Falati, S.; Edmead, C.E.; Poole, A.W. Glycoprotein Ib-V-IX, a receptor for von Willebrand factor, couples physically and functionally to the Fc receptor gamma-chain, Fyn, and Lyn to activate human platelets. Blood 1999, 94, 1648-1656.
- Lindsey, N.J.; Dawson, R.A.; Henderson, F.I.; Greaves, M.; Hughes, P. Stimulation of von Willebrand factor antigen release by immunoglobulin from thrombosis prone patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and the anti-phospholipid syndrome. Br J Rheumatol 1993, 32, 123-126, . [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.J.; McCrae, K.R.; Ashworth, K.; Sosa, L.J.; Betapudi, V.; Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Liu, A.; Dong, J.F.; Chung, D.; White-Adams, T.C.; et al. Effects of anti-β2GPI antibodies on VWF release from human umbilical vein endothelial cells and ADAMTS13 activity. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 2018, 2, 380-389, . [CrossRef]
- Der, H.; Kerekes, G.; Veres, K.; Szodoray, P.; Toth, J.; Lakos, G.; Szegedi, G.; Soltesz, P. Impaired endothelial function and increased carotid intima-media thickness in association with elevated von Willebrand antigen level in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2007, 16, 497-503, . [CrossRef]
- Hulstein, J.J.; Lenting, P.J.; de Laat, B.; Derksen, R.H.; Fijnheer, R.; de Groot, P.G. beta2-Glycoprotein I inhibits von Willebrand factor dependent platelet adhesion and aggregation. Blood 2007, 110, 1483-1491, . [CrossRef]
- Krilis, M.; Qi, M.; Ioannou, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ahmadi, Z.; Wong, J.W.H.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Koike, T.; Sturgess, A.D.; et al. Clinical relevance of nitrated beta 2-glycoprotein I in antiphospholipid syndrome: Implications for thrombosis risk. J Autoimmun 2021, 122, 102675, . [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, G.R.; Lescano, C.H.; Costa, J.L.; Mazetto, B.; Orsi, F.A.; Monica, F.Z. Adenosine diphosphate-induced aggregation is enhanced in platelets obtained from patients with thrombotic primary antiphospholipid syndrome (t-PAPS): Role of P2Y(12) -cAMP signaling pathway. J Thromb Haemost 2022, 20, 1699-1711, . [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Wang, C.T. Activation of human platelets by the rabbit anticardiolipin antibodies. Blood 1992, 80, 3135-3143.
- Martinuzzo, M.E.; Maclouf, J.; Carreras, L.O.; Lévy-Toledano, S. Antiphospholipid antibodies enhance thrombin-induced platelet activation and thromboxane formation. Thromb Haemost 1993, 70, 667-671.
- Campbell, A.L.; Pierangeli, S.S.; Wellhausen, S.; Harris, E.N. Comparison of the effects of anticardiolipin antibodies from patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome and with syphilis on platelet activation and aggregation. Thromb Haemost 1995, 73, 529-534.
- Arvieux, J.; Roussel, B.; Pouzol, P.; Colomb, M.G. Platelet activating properties of murine monoclonal antibodies to beta 2-glycoprotein I. Thromb Haemost 1993, 70, 336-341.
- Amirkhosravi, A.; Boulaftali, Y.; Robles-Carrillo, L.; Meyer, T.; McKenzie, S.E.; Francis, J.L.; Bergmeier, W. CalDAG-GEFI deficiency protects mice from FcγRIIa-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenia induced by CD40L and β2GPI immune complexes. J Thromb Haemost 2014, 12, 2113-2119, . [CrossRef]
- Hollerbach, A.; Müller-Calleja, N.; Ritter, S.; Häuser, F.; Canisius, A.; Orning, C.; Jurk, K.; Lackner, K.J. Platelet Activation by Antiphospholipid Antibodies Depends on Epitope Specificity and is Prevented by mTOR Inhibitors. Thromb Haemost 2019, 119, 1147-1153, . [CrossRef]
- Chayoua, W.; Nicolson, P.L.R.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Kardeby, C.; Garcia-Quintanilla, L.; Devreese, K.M.J.; de Laat, B.; Watson, S.P.; de Groot, P.G. Antiprothrombin antibodies induce platelet activation: A possible explanation for anti-FXa therapy failure in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome? J Thromb Haemost 2021, 19, 1776-1782, . [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M.; Vreys, I.; Wittevrongel, C.; Boon, D.; Vermylen, J.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Arnout, J. Thrombogenicity of beta 2-glycoprotein I-dependent antiphospholipid antibodies in a photochemically induced thrombosis model in the hamster. Blood 2003, 101, 157-162, . [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, A.; Manganelli, V.; Riitano, G.; Recalchi, S.; Truglia, S.; Alessandri, C.; Longo, A.; Garofalo, T.; Misasi, R.; Valesini, G.; et al. Tissue factor over-expression in platelets of patients with anti-phospholipid syndrome: induction role of anti-β2-GPI antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol 2019, 196, 59-66, . [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, A.; Riitano, G.; Recalchi, S.; Manganelli, V.; Costi, R.; Saccoliti, F.; Pulcinelli, F.; Garofalo, T.; Misasi, R.; Longo, A.; et al. Effect of heparanase inhibitor on tissue factor overexpression in platelets and endothelial cells induced by anti-β2-GPI antibodies. J Thromb Haemost 2021, 19, 2302-2313, . [CrossRef]
- Eustes, A.S.; Campbell, R.A.; Middleton, E.A.; Tolley, N.D.; Manne, B.K.; Montenont, E.; Rowley, J.W.; Krauel, K.; Blair, A.; Guo, L.; et al. Heparanase expression and activity are increased in platelets during clinical sepsis. J Thromb Haemost 2021, 19, 1319-1330, . [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, H.; Huang, C.; Qi, W.; Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Tian, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Thrombocytopenia in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: association with prognosis and clinical implications. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022, 62, 256-263, . [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, M.J.; Mujic, F.; Muñoz, E.; Khamashta, M.A.; Hughes, G.R. Thrombocytopenia in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 1997, 56, 194-196, . [CrossRef]
- Unlu, O.; Erkan, D.; Barbhaiya, M.; Andrade, D.; Nascimento, I.; Rosa, R.; Banzato, A.; Pengo, V.; Ugarte, A.; Gerosa, M.; et al. The Impact of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus on the Clinical Phenotype of Antiphospholipid Antibody-Positive Patients: Results From the AntiPhospholipid Syndrome Alliance for Clinical Trials and InternatiOnal Clinical Database and Repository. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2019, 71, 134-141, . [CrossRef]
- Thrombosis and thrombocytopenia in antiphospholipid syndrome (idiopathic and secondary to SLE): first report from the Italian Registry. Italian Registry of Antiphospholipid Antibodies (IR-APA). Haematologica 1993, 78, 313-318.
- Hisada, R.; Kato, M.; Sugawara, E.; Fujieda, Y.; Oku, K.; Bohgaki, T.; Amengual, O.; Yasuda, S.; Atsumi, T. Thrombotic risk stratification by platelet count in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: a longitudinal study. J Thromb Haemost 2017, 15, 1782-1787, . [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Fan, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. A novel aGAPSS-based nomogram for the prediction of ischemic stroke in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 930087, . [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, L.; Stojanovich, L.; Djokovic, A.; Andreoli, L.; Tincani, A.; Maślińska, M.; Sciascia, S.; Infantino, M.; Garcinuño, S.; Kostyra-Grabczak, K.; et al. Circulating immune-complexes of IgG/IgM bound to B2-glycoprotein-I associated with complement consumption and thrombocytopenia in antiphospholipid syndrome. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 957201, . [CrossRef]
- Pardos-Gea, J.; Marques-Soares, J.R.; Buján, S.; Ordi-Ros, J.; Alijotas-Reig, J. Persistent thrombocytopenia predicts poor long-term survival in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: a 38-year follow-up study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022, 61, 1053-1061, . [CrossRef]
- Pontara, E.; Banzato, A.; Bison, E.; Cattini, M.G.; Baroni, G.; Denas, G.; Calligaro, A.; Marson, P.; Tison, T.; Ruffatti, A.; et al. Thrombocytopenia in high-risk patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. J Thromb Haemost 2018, 16, 529-532, . [CrossRef]
- López-Benjume, B.; Rodríguez-Pintó, I.; Amigo, M.C.; Erkan, D.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Cervera, R.; Espinosa, G. Eculizumab use in catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS): Descriptive analysis from the "CAPS Registry". Autoimmun Rev 2022, 21, 103055, . [CrossRef]
- Galli, M.; Daldossi, M.; Barbui, T. Anti-glycoprotein Ib/IX and IIb/IIIa antibodies in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Thromb Haemost 1994, 71, 571-575.
- Panzer, S.; Gschwandtner, M.E.; Hütter, D.; Spitzauer, S.; Pabinger, I. Specificities of platelet autoantibodies in patients with lupus anticoagulants in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Hematol 1997, 74, 239-242, . [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jiang, H.; Huang, C.; Hu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Zeng, X. Platelet distribution width is highly associated with thrombotic events in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 2021, 40, 4581-4588, . [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, M.; Rojas, M.; Abrahams, V.M.; Escudero, C.; Cadavid Á, P. Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Association With Clinical Manifestations. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 1840, . [CrossRef]
- Gresele, P.; Migliacci, R.; Vedovati, M.C.; Ruffatti, A.; Becattini, C.; Facco, M.; Guglielmini, G.; Boscaro, E.; Mezzasoma, A.M.; Momi, S.; et al. Patients with primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome and without associated vascular risk factors present a normal endothelial function. Thromb Res 2009, 123, 444-451, . [CrossRef]
- Cugno, M.; Borghi, M.O.; Lonati, L.M.; Ghiadoni, L.; Gerosa, M.; Grossi, C.; De Angelis, V.; Magnaghi, G.; Tincani, A.; Mari, D.; et al. Patients with antiphospholipid syndrome display endothelial perturbation. J Autoimmun 2010, 34, 105-110, . [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.M.; Parmar, K.; Hughes, G.R.; Hunt, B.J. Systemic endothelial cell markers in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost 2000, 84, 742-746.
- Di, L.; Zha, C.; Liu, Y. Platelet-derived microparticles stimulated by anti-β(2)GPI/β(2)GPI complexes induce pyroptosis of endothelial cells in antiphospholipid syndrome. Platelets 2023, 34, 2156492, . [CrossRef]
- Sorice, M.; Longo, A.; Capozzi, A.; Garofalo, T.; Misasi, R.; Alessandri, C.; Conti, F.; Buttari, B.; Riganò, R.; Ortona, E.; et al. Anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies induce monocyte release of tumor necrosis factor alpha and tissue factor by signal transduction pathways involving lipid rafts. Arthritis Rheum 2007, 56, 2687-2697, . [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wolberg, A.S.; Roubey, R.A. Characterization of monocyte tissue factor activity induced by IgG antiphospholipid antibodies and inhibition by dilazep. Blood 2004, 104, 2353-2358, . [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, M.J.; López-Pedrera, C.; Khamashta, M.A.; Camps, M.T.; Tinahones, F.; Torres, A.; Hughes, G.R.; Velasco, F. Thrombosis in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: a pivotal role for monocyte tissue factor expression. Arthritis Rheum 1997, 40, 834-841, . [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, II; Apta, B.H.R.; Bonna, A.M.; Harper, M.T. Platelet P-selectin triggers rapid surface exposure of tissue factor in monocytes. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 13397, . [CrossRef]
- López-Pedrera, C.; Aguirre, M.A.; Buendía, P.; Barbarroja, N.; Ruiz-Limón, P.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Velasco, F.; Khamashta, M.; Cuadrado, M.J. Differential expression of protease-activated receptors in monocytes from patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 2010, 62, 869-877, . [CrossRef]
- Martinod, K.; Wagner, D.D. Thrombosis: tangled up in NETs. Blood 2014, 123, 2768-2776, . [CrossRef]
- Yalavarthi, S.; Gould, T.J.; Rao, A.N.; Mazza, L.F.; Morris, A.E.; Núñez-Álvarez, C.; Hernández-Ramírez, D.; Bockenstedt, P.L.; Liaw, P.C.; Cabral, A.R.; et al. Release of neutrophil extracellular traps by neutrophils stimulated with antiphospholipid antibodies: a newly identified mechanism of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015, 67, 2990-3003, . [CrossRef]
- Zha, C.; Zhang, W.; Gao, F.; Xu, J.; Jia, R.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y. Anti-β(2)GPI/β(2)GPI induces neutrophil extracellular traps formation to promote thrombogenesis via the TLR4/MyD88/MAPKs axis activation. Neuropharmacology 2018, 138, 140-150, . [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Yalavarthi, S.; Gockman, K.; Madison, J.A.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Joseph McCune, W.; Bockenstedt, P.L.; Karp, D.R.; Knight, J.S. Anti-Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Antibodies and Impaired Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Degradation in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020, 72, 2130-2135, . [CrossRef]
- Wienkamp, A.K.; Erpenbeck, L.; Rossaint, J. Platelets in the NETworks interweaving inflammation and thrombosis. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 953129, . [CrossRef]
- Vulliamy, P.; Gillespie, S.; Armstrong, P.C.; Allan, H.E.; Warner, T.D.; Brohi, K. Histone H4 induces platelet ballooning and microparticle release during trauma hemorrhage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 17444-17449, . [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.; Urrutia, R.; Yipp, B.G.; Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. Intravascular neutrophil extracellular traps capture bacteria from the bloodstream during sepsis. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 324-333, . [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Sweet, D.R.; Thomas, A.; Lapping, S.D.; Kalikasingh, K.; Madera, A.; Vinayachandran, V.; Padmanabhan, R.; Vasudevan, N.T.; Myers, J.T.; et al. A targetable pathway in neutrophils mitigates both arterial and venous thrombosis. Sci Transl Med 2022, 14, eabj7465, . [CrossRef]
- Agbani, E.O.; Mahe, E.; Chaturvedi, S.; Yamaura, L.; Schneider, P.; Barber, M.R.W.; Choi, M.; Lee, A.; Skeith, L. Platelets and neutrophils co-drive procoagulant potential in secondary antiphospholipid syndrome during pregnancy. Thromb Res 2022, 220, 141-144, . [CrossRef]
- Breen, K.A.; Seed, P.; Parmar, K.; Moore, G.W.; Stuart-Smith, S.E.; Hunt, B.J. Complement activation in patients with isolated antiphospholipid antibodies or primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost 2012, 107, 423-429, . [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.D.; Brey, R.L. Antiphospholipid antibodies and complement activation in patients with cerebral ischemia. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1992, 10, 455-460.
- Oku, K.; Atsumi, T.; Bohgaki, M.; Amengual, O.; Kataoka, H.; Horita, T.; Yasuda, S.; Koike, T. Complement activation in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 2009, 68, 1030-1035, . [CrossRef]
- Arachchillage, D.R.; Mackie, I.J.; Efthymiou, M.; Chitolie, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Isenberg, D.A.; Khamashta, M.; Machin, S.J.; Cohen, H. Rivaroxaban limits complement activation compared with warfarin in antiphospholipid syndrome patients with venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Haemost 2016, 14, 2177-2186, . [CrossRef]
- Pierangeli, S.S.; Vega-Ostertag, M.; Liu, X.; Girardi, G. Complement activation: a novel pathogenic mechanism in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2005, 1051, 413-420, . [CrossRef]
- Fischetti, F.; Durigutto, P.; Pellis, V.; Debeus, A.; Macor, P.; Bulla, R.; Bossi, F.; Ziller, F.; Sblattero, D.; Meroni, P.; et al. Thrombus formation induced by antibodies to beta2-glycoprotein I is complement dependent and requires a priming factor. Blood 2005, 106, 2340-2346, . [CrossRef]
- Carrera-Marín, A.; Romay-Penabad, Z.; Papalardo, E.; Reyes-Maldonado, E.; García-Latorre, E.; Vargas, G.; Shilagard, T.; Pierangeli, S. C6 knock-out mice are protected from thrombophilia mediated by antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus 2012, 21, 1497-1505, . [CrossRef]
- Dzik, S. Complement and Coagulation: Cross Talk Through Time. Transfus Med Rev 2019, 33, 199-206, . [CrossRef]
- Del Conde, I.; Crúz, M.A.; Zhang, H.; López, J.A.; Afshar-Kharghan, V. Platelet activation leads to activation and propagation of the complement system. J Exp Med 2005, 201, 871-879, . [CrossRef]
- Peerschke, E.I.; Yin, W.; Alpert, D.R.; Roubey, R.A.; Salmon, J.E.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Serum complement activation on heterologous platelets is associated with arterial thrombosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus 2009, 18, 530-538, . [CrossRef]
- Lood, C.; Tydén, H.; Gullstrand, B.; Sturfelt, G.; Jönsen, A.; Truedsson, L.; Bengtsson, A.A. Platelet activation and anti-phospholipid antibodies collaborate in the activation of the complement system on platelets in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One 2014, 9, e99386, . [CrossRef]
- Gartshteyn, Y.; Mor, A.; Shimbo, D.; Khalili, L.; Kapoor, T.; Geraldino-Pardilla, L.; Alexander, R.V.; Conklin, J.; Dervieux, T.; Askanase, A.D. Platelet bound complement split product (PC4d) is a marker of platelet activation and arterial vascular events in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin Immunol 2021, 228, 108755, . [CrossRef]
- Svenungsson, E.; Gustafsson, J.T.; Grosso, G.; Rossides, M.; Gunnarsson, I.; Jensen-Urstad, K.; Larsson, A.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Nilsson, B.; Bengtsson, A.A.; et al. Complement deposition, C4d, on platelets is associated with vascular events in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2020, 59, 3264-3274, . [CrossRef]
- Polley, M.J.; Nachman, R.L. Human platelet activation by C3a and C3a des-arg. J Exp Med 1983, 158, 603-615, . [CrossRef]
- Gushiken, F.C.; Han, H.; Li, J.; Rumbaut, R.E.; Afshar-Kharghan, V. Abnormal platelet function in C3-deficient mice. J Thromb Haemost 2009, 7, 865-870, . [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.; Jurk, K.; Hobohm, L.; Jäckel, S.; Saffarzadeh, M.; Schwierczek, K.; Wenzel, P.; Langer, F.; Reinhardt, C.; Ruf, W. Distinct contributions of complement factors to platelet activation and fibrin formation in venous thrombus development. Blood 2017, 129, 2291-2302, . [CrossRef]
- Sauter, R.J.; Sauter, M.; Reis, E.S.; Emschermann, F.N.; Nording, H.; Ebenhöch, S.; Kraft, P.; Münzer, P.; Mauler, M.; Rheinlaender, J.; et al. Functional Relevance of the Anaphylatoxin Receptor C3aR for Platelet Function and Arterial Thrombus Formation Marks an Intersection Point Between Innate Immunity and Thrombosis. Circulation 2018, 138, 1720-1735, . [CrossRef]
- Wiedmer, T.; Esmon, C.T.; Sims, P.J. Complement proteins C5b-9 stimulate procoagulant activity through platelet prothrombinase. Blood 1986, 68, 875-880.
- Wiedmer, T.; Esmon, C.T.; Sims, P.J. On the mechanism by which complement proteins C5b-9 increase platelet prothrombinase activity. J Biol Chem 1986, 261, 14587-14592.
- Sims, P.J.; Faioni, E.M.; Wiedmer, T.; Shattil, S.J. Complement proteins C5b-9 cause release of membrane vesicles from the platelet surface that are enriched in the membrane receptor for coagulation factor Va and express prothrombinase activity. J Biol Chem 1988, 263, 18205-18212.
- Cohen, H.; Isenberg, D.A. How I treat anticoagulant-refractory thrombotic antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2021, 137, 299-309, . [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, L.; Mathian, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Erkan, D.; Tektonidou, M.; Cervera, R.; Forastiero, R.; Pengo, V.; Lambert, M.; Martinez-Zamora, M.A.; et al. Efficacy of aspirin for the primary prevention of thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: an international and collaborative meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev 2014, 13, 281-291, . [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, L.; Mathian, A.; Devilliers, H.; Ruffatti, A.; Tektonidou, M.; Forastiero, R.; Pengo, V.; Lambert, M.; Lefevre, G.; Martinez-Zamora, M.A.; et al. Patient-level analysis of five international cohorts further confirms the efficacy of aspirin for the primary prevention of thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Autoimmun Rev 2015, 14, 192-200, . [CrossRef]
- Crowther, M.A.; Ginsberg, J.S.; Julian, J.; Denburg, J.; Hirsh, J.; Douketis, J.; Laskin, C.; Fortin, P.; Anderson, D.; Kearon, C.; et al. A comparison of two intensities of warfarin for the prevention of recurrent thrombosis in patients with the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003, 349, 1133-1138, . [CrossRef]
- Finazzi, G.; Marchioli, R.; Brancaccio, V.; Schinco, P.; Wisloff, F.; Musial, J.; Baudo, F.; Berrettini, M.; Testa, S.; D'Angelo, A.; et al. A randomized clinical trial of high-intensity warfarin vs. conventional antithrombotic therapy for the prevention of recurrent thrombosis in patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome (WAPS). J Thromb Haemost 2005, 3, 848-853, . [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Hunt, B.J.; Khamashta, M.A. A systematic review of secondary thromboprophylaxis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 2007, 57, 1487-1495, . [CrossRef]
- Jackson, W.G.; Oromendia, C.; Unlu, O.; Erkan, D.; DeSancho, M.T. Recurrent thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies and arterial thrombosis on antithrombotic therapy. Blood Adv 2017, 1, 2320-2324, . [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.R.; Brey, R.L.; Tilley, B.C.; Thompson, J.L.; Sacco, R.L.; Sciacca, R.R.; Murphy, A.; Lu, Y.; Costigan, T.M.; Rhine, C.; et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies and subsequent thrombo-occlusive events in patients with ischemic stroke. Jama 2004, 291, 576-584, . [CrossRef]
- Okuma, H.; Kitagawa, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Tokuoka, K.; Takagi, S. Comparison between single antiplatelet therapy and combination of antiplatelet and anticoagulation therapy for secondary prevention in ischemic stroke patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Int J Med Sci 2009, 7, 15-18, . [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, N.; Fujieda, Y.; Hisada, R.; Nakamura, H.; Kato, M.; Oku, K.; Bohgaki, T.; Amengual, O.; Yasuda, S.; Atsumi, T. Efficacy of dual antiplatelet therapy for preventing recurrence of arterial thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2019, 58, 969-974, . [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.D.; Nylander, S.; Whatling, C. Anti-platelet therapy: cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and the use of aspirin with particular regard to dual anti-platelet therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2011, 72, 619-633, . [CrossRef]
- Pasalic, L.; Wing-Lun, E.; Lau, J.K.; Campbell, H.; Pennings, G.J.; Lau, E.; Connor, D.; Liang, H.P.; Muller, D.; Kritharides, L.; et al. Novel assay demonstrates that coronary artery disease patients have heightened procoagulant platelet response. J Thromb Haemost 2018, 16, 1198-1210, . [CrossRef]
- Verro, P.; Gorelick, P.B.; Nguyen, D. Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus aspirin for prevention of vascular events after stroke or TIA: a meta-analysis. Stroke 2008, 39, 1358-1363, . [CrossRef]
- Harker, L.A.; Kadatz, R.A. Mechanism of action of dipyridamole. Thromb Res Suppl 1983, 4, 39-46, . [CrossRef]
- Toti, F.; Satta, N.; Fressinaud, E.; Meyer, D.; Freyssinet, J.M. Scott syndrome, characterized by impaired transmembrane migration of procoagulant phosphatidylserine and hemorrhagic complications, is an inherited disorder. Blood 1996, 87, 1409-1415.
- Hua, V.M.; Abeynaike, L.; Glaros, E.; Campbell, H.; Pasalic, L.; Hogg, P.J.; Chen, V.M. Necrotic platelets provide a procoagulant surface during thrombosis. Blood 2015, 126, 2852-2862, . [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.H.; Pierangeli, S.; Liu, X.; Barker, J.H.; Anderson, G.; Harris, E.N. Hydroxychloroquine reverses thrombogenic properties of antiphospholipid antibodies in mice. Circulation 1997, 96, 4380-4384, . [CrossRef]
- Espinola, R.G.; Pierangeli, S.S.; Gharavi, A.E.; Harris, E.N. Hydroxychloroquine reverses platelet activation induced by human IgG antiphospholipid antibodies. Thromb Haemost 2002, 87, 518-522.
- Lopez-Pedrera, C.; Ruiz-Limon, P.; Aguirre, M.A.; Rodriguez-Ariza, A.; Cuadrado, M.J. Potential use of statins in the treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2012, 14, 87-94, . [CrossRef]
- Nenna, A.; Nappi, F.; Lusini, M.; Satriano, U.M.; Schilirò, D.; Spadaccio, C.; Chello, M. Effect of Statins on Platelet Activation and Function: From Molecular Pathways to Clinical Effects. Biomed Res Int 2021, 2021, 6661847, . [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Braunstein, E.M.; Yuan, X.; Yu, J.; Alexander, A.; Chen, H.; Gavriilaki, E.; Alluri, R.; Streiff, M.B.; Petri, M.; et al. Complement activity and complement regulatory gene mutations are associated with thrombosis in APS and CAPS. Blood 2020, 135, 239-251, . [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic strategy | Available agents | Potential benefits/limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Inhibiting P2Y12 receptor | Clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor, etc | Benefits: • Overexpression of P2Y12 in APS and associated platelet hyperreactivity • Pre-clinical studies demonstrate ticagrelor can reverse platelet hyperreactivity to ADP in APS • Known safety profile and clinical use together with anticoagulation Limitations: • Increased bleeding risk, especially in combination with current standard therapy |
| Increasing cyclic AMP | Cilastazol, dipyridamole | Benefits: • Can reverse downregulation of cyclic AMP seen in APS platelets • Known safety profile Limitations: • Increased bleeding risk, especially in combination with current standard therapy |
| Reducing procoagulant platelet formation | Ciclosporin, acetazolamide | Benefits: • Procoagulant platelets predominantly involved in thrombosis, less impact on haemostasis • Procoagulant platelets are downstream of many of the pathological processes in APS • Will block the platelet-derived thrombin generation induced by aPL Limitations: • Current agents have many off-target adverse effects that limit use |
| mTOR inhibition | Everolimus, sirolimus | Benefits: • Preclinical studies have demonstrated reduction in platelet hyperreactivity downstream of FcɣRIIa signalling induced by aPL • Will inhibit mTOR-mediated endothelial activation in APS also • No impact on haemostasis Limitations: • Current agents have many off-target adverse effects that limit use |
| Inhibition of mTORC2 (SIN1)-AKT axis | ? | Benefits: • Mouse models have demonstrated reversal of platelet hyperreactivity and thrombosis in any vascular bed induced by aPL, • No prolongation of tail bleeding time in mouse model with SIN1 deficiency, so appears thrombosis-specific • Could potentially target AKT upstream with available PI3K inhibitors Limitations: • No specific available agents with known safety profiles in humans. • AKT inhibitors and any developed agents have many off-target adverse effects that limit use |
| Reducing Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) | Dipyridamole, ? | Benefits: • Excess NETs formation and impaired clearance in APS with prothrombotic effect • Dipyridamole has known safety profile • Potential for repurposing agents that could reduce NETs, e.g. crizanlizumab (blocks P-selectin-PSGL interaction required for platelet-neutrophil interaction, used in sickle cell disease) Limitations: • Increased bleeding risk with dipyridamole • Direct NETs inhibition will likely compromise normal response to pathogens |
| Inhibiting excessive complement activation | Eculizumab (C5), ravalizumab (C5), sutimlimab (C1s), pegcetacoplan (C3), etc | Benefits: • Complement activation plays a key role in APS thrombosis and can induce procoagulant platelets • Known safety profiles and clinical experience • Would not impact haemostasis Limitations: • Current agents have many off-target adverse effects that limit use |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





