Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
04 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Materials
Milk Collection
Isolation of SM-EV
Flow Cytometry
Determination of Protein Concentration of EV
RNA Isolation and miRNA Analysis
Cell Culture
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assays
Measurement of CCL2 Secretion
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of Sheep Milk Derived LEV and sEV
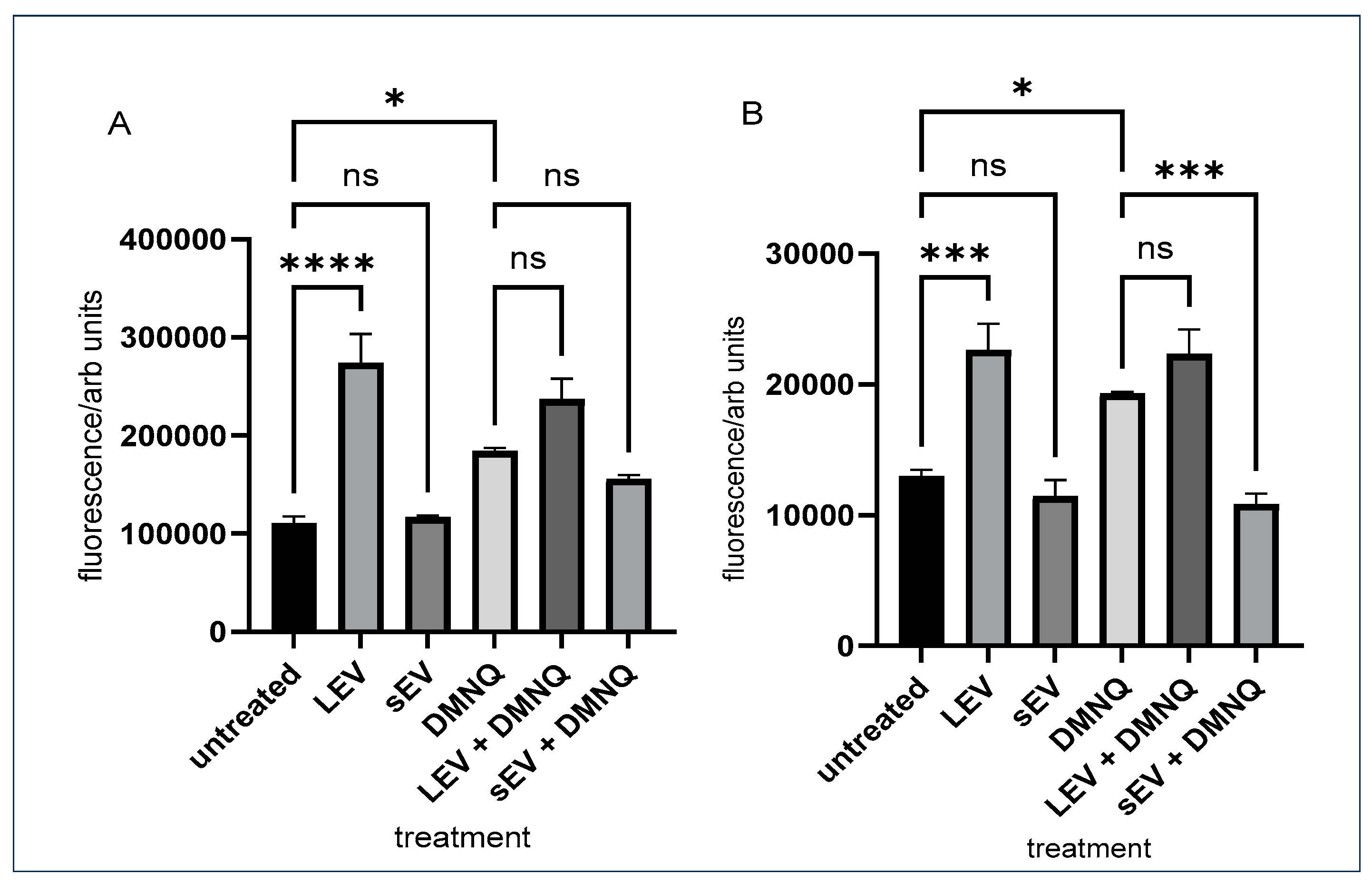
3.2. Monocyte and Macrophage ROS Production Induced by Sheep Milk Derived LEV and sEV
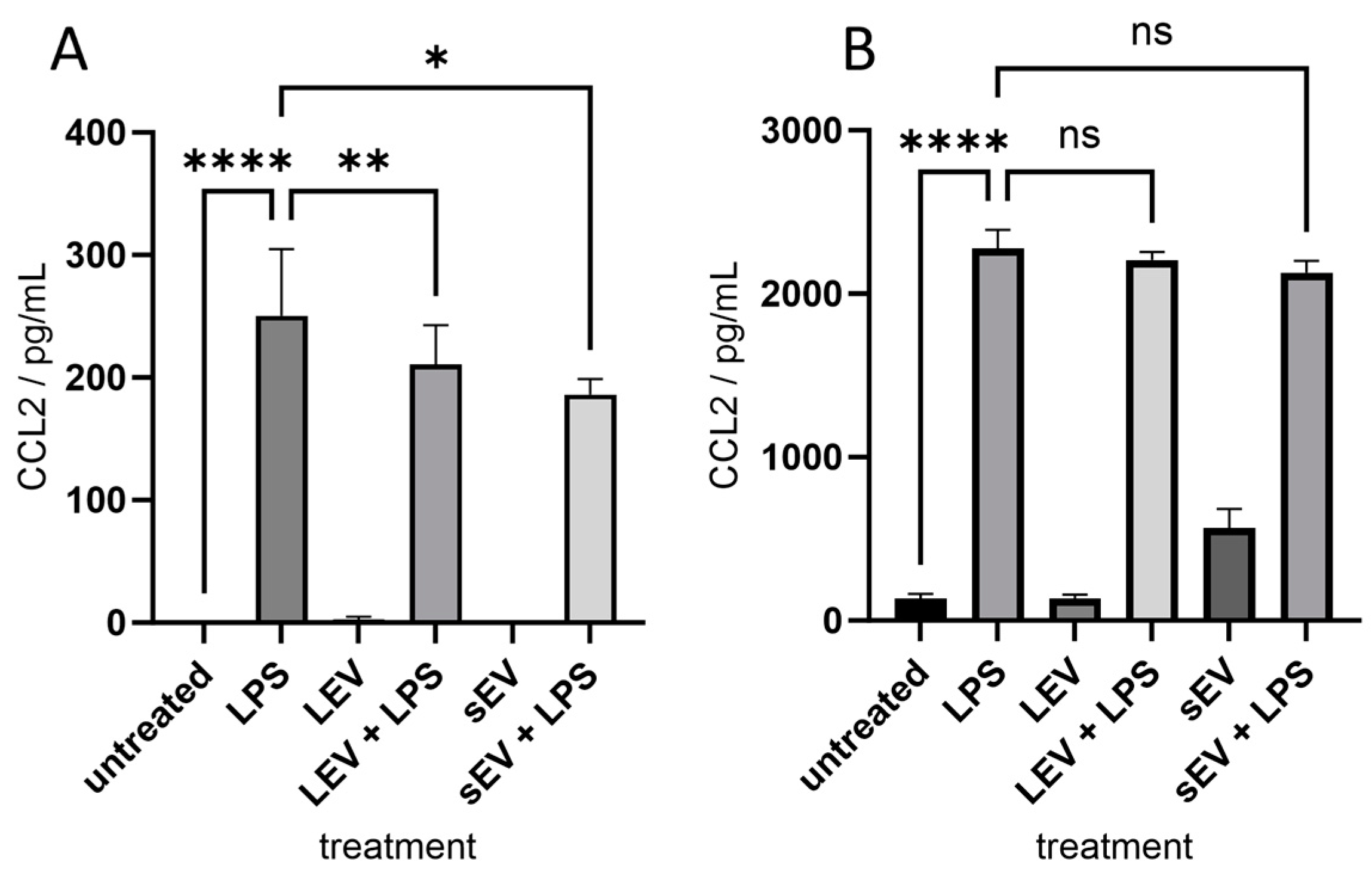
3.3. Secretion of CCL2 Chemokine Induced by Sheep Milk Derived LEV and sEV
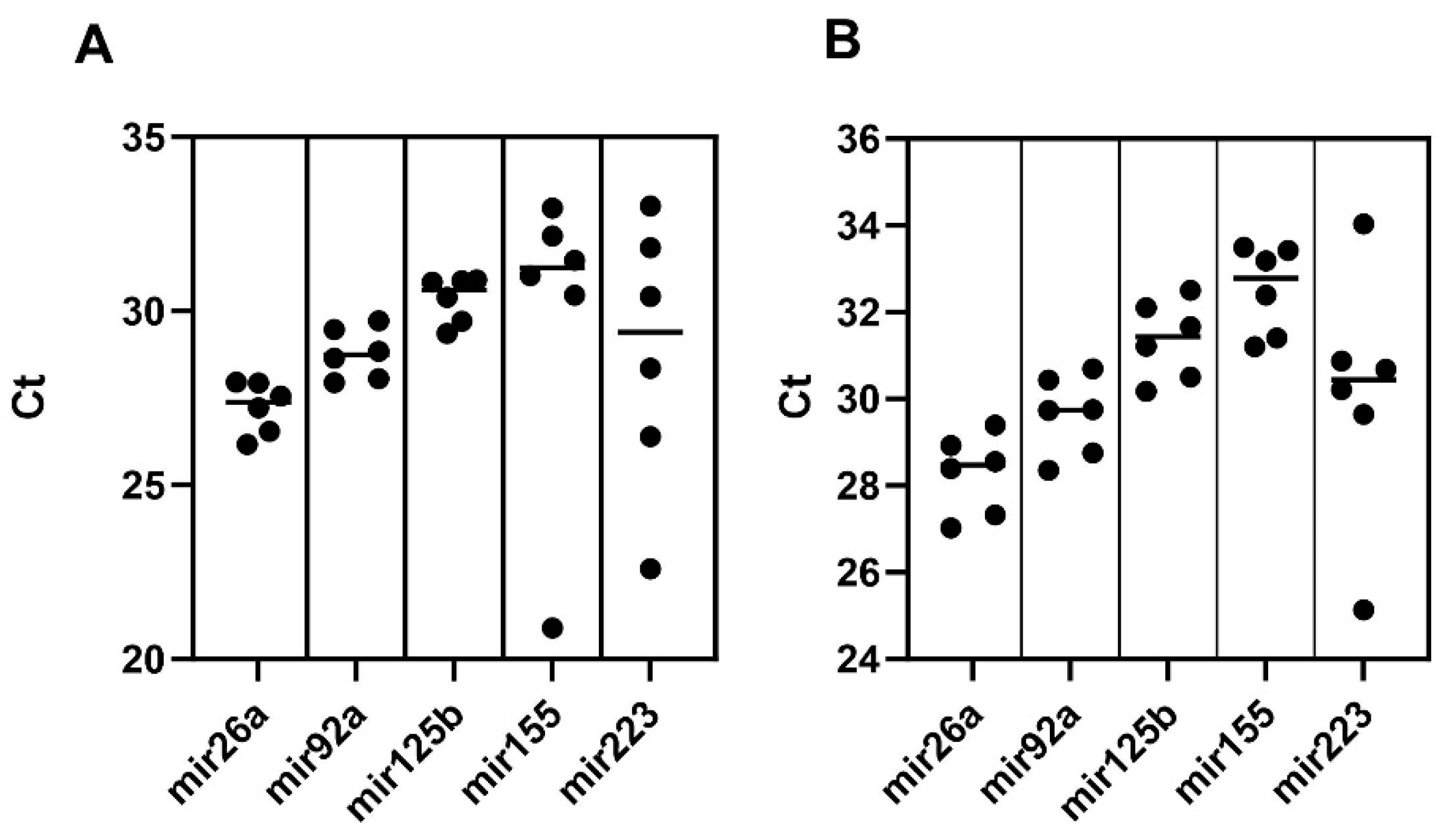
3.4. miRNA Contents of Sheep Milk Derived LEV and sEV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AHDB. Dairy Market Dashboard https://ahdb.org.uk/dairy-market-dashboard. (accessed on 29th December 2023).
- Costa, A.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Sneddon, N.W.; Shalloo, L.; Franzoi, M.; De Marchi, M.; Penasa, M. Invited review: Milk lactose-Current status and future challenges in dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 2019, 102, 5883–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mee, J.F.; Boyle, L.A. Assessing whether dairy cow welfare is "better" in pasture-based than in confinement-based management systems. N Z Vet J 2020, 68, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Ye, A.; Moughan, P.J.; Singh, H. Composition, Structure, and Digestive Dynamics of Milk From Different Species-A Review. Front Nutr 2020, 7, 577759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Gaudio, E.; Santhanam, R.; Lovat, F.; Fadda, P.; Mao, C.; Nuovo, G.J.; et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, E2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borràs, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: a compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Chen, M.; Li, N.; Han, R.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y. Bioactive Functions of Lipids in the Milk Fat Globule Membrane: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, K.; Lago-Novais, D.; Bevilacqua, C.; Mobuchon, L.; Crapart, N.; Faulconnier, Y.; Boby, C.; Carvalho, G.; Martin, P.; Leroux, C. Different miRNA contents between mammary epithelial cells and milk fat globules: a random or a targeted process? Mol Biol Rep 2020, 47, 8259–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.C.; Rushton, J.; Wathes, C.M. Past trends and future challenges for a sustainable UK dairy industry. 2011, 172, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shortall, O. Cows eat grass, don't they? Contrasting sociotechnical imaginaries of the role of grazing in the UK and Irish diary sectors. Journal of Rural Studies 2019, 72, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trewern, J.; Chenoweth, J.; Christie, I.; Keller, E.; Halevy, S. Are UK retailers well placed to deliver ‘less and better’meat and dairy to consumers? Sustainable Production and Consumption 2021, 28, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zempleni, J.; Aguilar-Lozano, A.; Sadri, M.; Sukreet, S.; Manca, S.; Wu, D.; Zhou, F.; Mutai, E. Biological Activities of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Cargos from Bovine and Human Milk in Humans and Implications for Infants. J Nutr 2017, 147, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; You, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, X.; Zhong, H.; Sun, X.; Ji, C.; Chi, X. Biological Properties of Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions in Infant. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 693534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmoussa, A.; Lee, C.H.; Laffont, B.; Savard, P.; Laugier, J.; Boilard, E.; Gilbert, C.; Fliss, I.; Provost, P. Commercial Dairy Cow Milk microRNAs Resist Digestion under Simulated Gastrointestinal Tract Conditions. J Nutr 2016, 146, 2206–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, S.R.; Nguyen, C.; Xie, F.; Wood, J.R.; Zempleni, J. MicroRNAs are absorbed in biologically meaningful amounts from nutritionally relevant doses of cow milk and affect gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, HEK-293 kidney cell cultures, and mouse livers. J Nutr 2014, 144, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallier, S.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Prosser, C. Comparison of the Bifidogenic Effects of Goat and Cow Milk-Based Infant Formulas to Human Breast Milk in an. Front Nutr 2020, 7, 608495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arntz, O.J.; Pieters, B.C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Broeren, M.G.; Bennink, M.B.; de Vries, M.; van Lent, P.L.; Koenders, M.I.; van den Berg, W.B.; van der Kraan, P.M.; et al. Oral administration of bovine milk derived extracellular vesicles attenuates arthritis in two mouse models. Mol Nutr Food Res 2015, 59, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhya, A.; Santoro, J.; O'Driscoll, L. Extracellular vesicle separation from milk and infant milk formula using acid precipitation and ultracentrifugation. STAR Protoc 2021, 2, 100821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, L.F.; Andersen, D.K.; Cleasby, M.E.; Lawson, C. Long-term high fat feeding of rats results in increased numbers of circulating microvesicles with pro-inflammatory effects on endothelial cells. Br J Nutr 2015, 113, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgaladze, D.; Preiss, S.; Dröse, S.; Brandt, U.; Brüne, B. Phospholipase A2-modified low density lipoprotein induces mitochondrial uncoupling and lowers reactive oxygen species in phagocytes. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.K.; Heilmann, R.M.; Paital, B.; Patel, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Wong, D.; Jergens, A.E. Oxidative stress, hormones, and effects of natural antioxidants on intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1217165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.P.; Singh, N.P.; Murphy, E.A.; Price, R.L.; Fayad, R.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Chemokine and cytokine levels in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Cytokine 2016, 77, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moadab, F.; Khorramdelazad, H.; Abbasifard, M. Role of CCL2/CCR2 axis in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: Latest evidence and therapeutic approaches. Life Sci 2021, 269, 119034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Kaminga, A.C.; Wen, S.W.; Liu, A. Chemokines in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 622438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthumana, J.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Xu, L.; Coca, S.G.; Garg, A.X.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bhatraju, P.K.; Ikizler, T.A.; Siew, E.D.; Ware, L.B.; et al. Biomarkers of inflammation and repair in kidney disease progression. J Clin Invest 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Bernhagen, J.; Heitman, L.H.; Weber, C.; Dichgans, M. Targeting the CCL2-CCR2 axis for atheroprotection. Eur Heart J 2022, 43, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martynowicz, H.; Janus, A.; Nowacki, D.; Mazur, G. The role of chemokines in hypertension. Adv Clin Exp Med 2014, 23, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, C.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Sun, Q.; Dong, Y.; Tian, C.; Gao, S.; Dong, H.; Guan, D.; et al. Identification and characterization of microRNAs in raw milk during different periods of lactation, commercial fluid, and powdered milk products. Cell Res 2010, 20, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, T. Comparison of miRNA profiles in milk-derived extracellular vesicles and bovine mammary glands. International Dairy Journal 2022, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.; Nan, X.; Wang, K.; Jiang, L.; Yao, J.; Xiong, B. Characterization of Sheep Milk Extracellular Vesicle-miRNA by Sequencing and Comparison with Cow Milk. Animals (Basel) 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, B.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Dumpler, J.; von Mutius, E.; Ege, M.J. microRNA in native and processed cow's milk and its implication for the farm milk effect on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016, 137, 1893–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.C.; Fujikawa, T.; Maemura, T.; Ando, T.; Kitahara, G.; Endo, Y.; Yamato, O.; Koiwa, M.; Kubota, C.; Miura, N. Inflammation-related microRNA expression level in the bovine milk is affected by mastitis. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0177182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Ou-Yang, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, T.; Tang, L.; Tan, Y.F.; Luo, H.Y.; Xiao, Z.H.; Li, S.J. MiR-125b enhances autophagic flux to improve septic cardiomyopathy via targeting STAT3/HMGB1. Exp Cell Res 2021, 409, 112842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luoreng, Z.M.; Wei, D.W.; Wang, X.P. MiR-125b regulates inflammation in bovine mammary epithelial cells by targeting the NKIRAS2 gene. Vet Res 2021, 52, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AHDB. https://ruminanthw.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Cattle-and-sheep-HW-priorities-survey-May-2021-FINAL.pdf. (accessed on 29th December 2023).
- Whatford, L.; van Winden, S.; Häsler, B. A systematic literature review on the economic impact of endemic disease in UK sheep and cattle using a One Health conceptualisation. Prev Vet Med 2022, 209, 105756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.M.; Willis, Z.N.; Blakeley, M.; Lovatt, F.; Purdy, K.J.; Green, L.E. Bacterial species and their associations with acute and chronic mastitis in suckler ewes. J Dairy Sci 2015, 98, 7025–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, C.; Smith, E.M.; Green, L.E. A longitudinal study of factors associated with acute and chronic mastitis and their impact on lamb growth rate in 10 suckler sheep flocks in Great Britain. Prev Vet Med 2016, 127, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, H.; Kosaka, N.; Shimizu, T.; Sekine, K.; Ochiya, T.; Takase, M. Bovine milk contains microRNA and messenger RNA that are stable under degradative conditions. J Dairy Sci 2012, 95, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, M.A. microRNAs and the immune response. Trends Immunol 2008, 29, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, Q.; Li, Z.; Qi, X.; Chen, F.; Xu, L.; Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; et al. MiR-155 promotes acute organ injury in LPS-induced endotoxemic mice by enhancing CCL-2 expression in macrophages. Shock 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Barkema, H.W.; Gao, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Kastelic, J.P.; Khan, S.; Liu, G.; Han, B. MicroRNA miR-223 modulates NLRP3 and Keap1, mitigating lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells and murine mammary glands. Vet Res 2023, 54, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Jiao, P.; Wang, X.P.; Wang, J.P.; Feng, F.; Bao, B.W.; Dong, Y.W.; Luoreng, Z.M.; Wei, D.W. RNA-seq reveals the role of miR-223 in alleviating inflammation of bovine mammary epithelial cells. Res Vet Sci 2023, 159, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Phospholipids of Animal and Marine Origin: Structure, Function, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, L.; Behrens, P.; Tukker, A. Opportunity for a dietary win-win-win in nutrition, environment, and animal welfare. One Earth 2019, 1, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
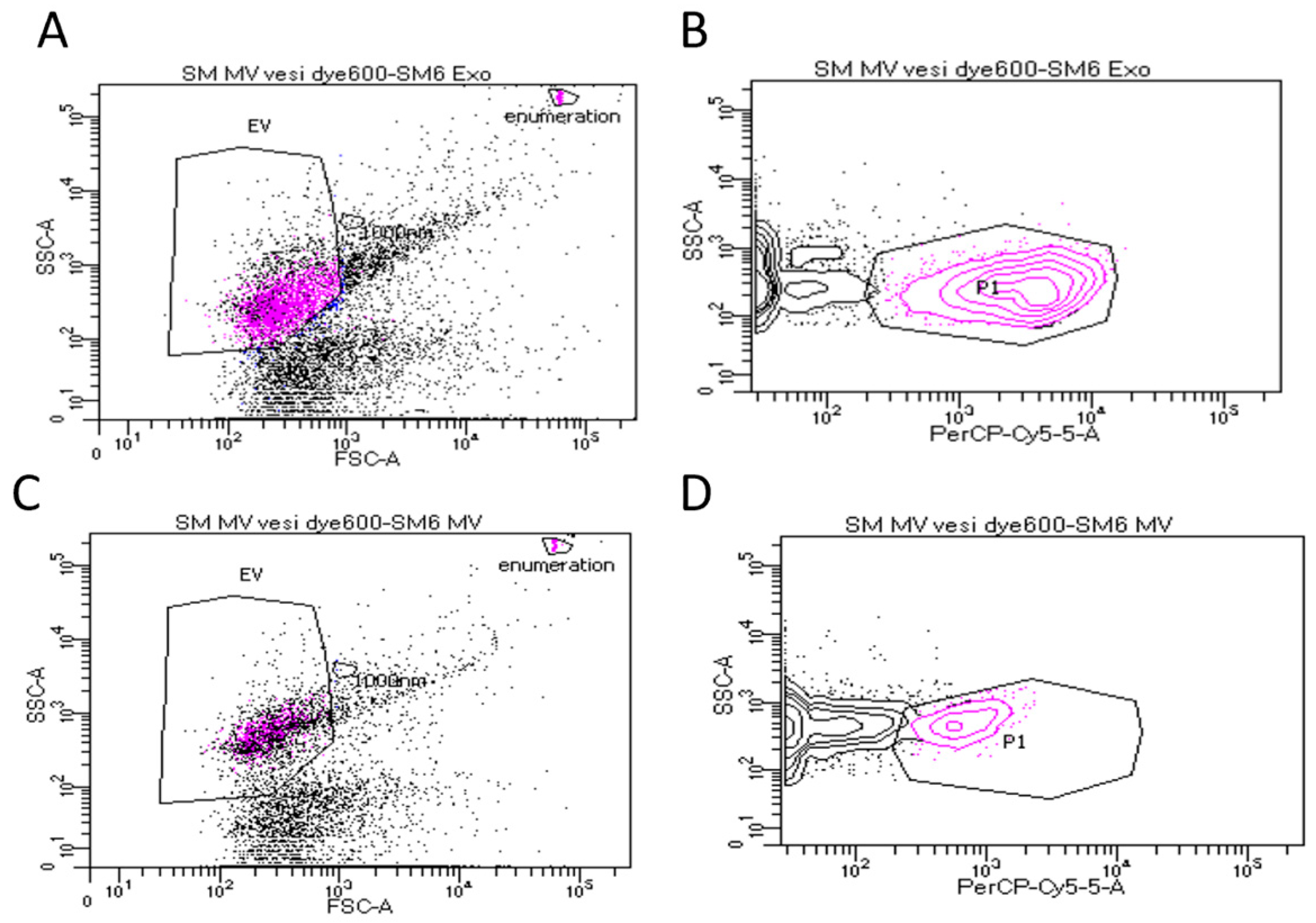
| small EV | large EV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| total RNA (ng/µl) | total protein (µg/µl) | VesiDye positive EV/µl | total RNA (ng/µl) | total protein (µg/µl) | VesiDye positive EV/µl | |
| SMEV1 | 22.1 | 145.58 | 18411.52 | 59.053 | 1675.15 | 90541.44 |
| SMEV2 | 52.0 | 140.23 | 26384.11 | 159.075 | 1915.58 | 39303.23 |
| SMEV3 | 23.0 | 153.25 | 36564.71 | 79.977 | 1915.85 | 17200.00 |
| SMEV4 | 100.3 | 127.4 | 32495.47 | 92.803 | 1414.13 | 134833.3 |
| SMEV5 | 49.4 | 197.95 | 23083.8 | 54.648 | 1810.05 | 56615.38 |
| SMEV6 | 39.0 | 136.35 | 30837.61 | 54.485 | 1618.4 | 18077.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





