Submitted:
03 January 2024
Posted:
04 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. INTRODUCTION
2. RESULTS
2.1. Properties of extracts and spray-drying solutions
2.2. Yield of drying (YD)
2.3. Morphology and particle size
2.4. Thermal behavior of the microparticles
2.5. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC), Total Phenolic Content (TPC), Yield of encapsulation (YE) and encapsulation efficiency (EE)
2.6. Antioxidant activity
2.7. Characterization and quantification of phenolics in the microparticles by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC-DAD)
3. DISCUSSION
4. MATERIALS AND METHODS
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of the encapsulated samples
4.3. Yield of drying (YD)
4.4. Characterization of the microparticles
4.5. Sample preparation for quantitative spectroscopic analyses
4.6. Thermogravimetric analysis/derivative thermogravimetry
4.7. Differential scanning calorimetry
4.8. Quali-quantitative analyses of microparticles using high performance liquid chromatography
4.9. Statistical analysis
CONCLUSIONS
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- AGUIAR, J. , COSTA, R., ROCHA, F., ESTEVINHO, B. N., SANTOS, L. Design of microparticles containing natural antioxidants: Preparation, characterization and controlled release studies. Powder Technol. 2017, 313, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AHMADIAN, Z. , NIAZMAND, R., POURFARZAD, A. Microencapsulation of saffron petal phenolic extract: Their characterization, in vitro gastrointestinal digestion, and storage stability. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AHMAD, M. , ASHRAF, B., GANI, A., GANI, A. Microencapsulation of saffron anthocyanins using β glucan and β cyclodextrin: Microcapsule characterization, release behaviour & antioxidant potential during in-vitro digestion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ALOTHMAN, M. , BHAT, R., KARIM, A. A. Antioxidant capacity and phenolic content of selected tropical fruits from Malaysia, extracted with different solvents. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANISH, C. , UPADHYAY, A. K., SEHGAL, D., PANDA, A. K. Influences of process and formulation parameters on powder flow properties and immunogenicity of spray dried polymer particles entrapping recombinant pneumococcal surface protein A. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 466, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AUGUSTO, T. R. , SALINAS, E. S. S., ALENCAR, S. M., D'ARCE, M. A. B. R., CAMARGO, A. C. D., VIEIRA, T. M. F. D. S. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of hydroalcoholic extracts of wild and cultivated murtilla (Ugni molinae Turcz.). Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AZEVEDO, M. S. , MANSO, C. Oxygen free radicals and complications of diabetes mellitus. Acta Medica Port. 1992, 5, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- BALDUCCI, A. G. , CAGNANI, S., SONVICO, F., ROSSI, A., BARATA, P., COLOMBO, G., COLOMBO, P., BUTTINI, F. Pure insulin highly respirable powders for inhalation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 51, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BELŠČAK-CVITANOVIĆ, A. , LEVIĆ, S., KALUŠEVIĆ, A., ŠPOLJARIĆ, I., ĐORĐEVIĆ, V., KOMES, D., MRŠIĆ, G., NEDOVIĆ, V. Efficiency assessment of natural biopolymers as encapsulants of green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) bioactive compounds by spray drying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 2444–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BHANDARI, B. , HOWES, T. Relating the stickiness property of foods undergoing drying and dried products to their surface energetics. Dry. Technol. 2005, 23, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BHANDARI, B. R. , DATTA, N., HOWES, T. Problems associated with spray drying of sugar-rich foods. Dry. Technol. 1997, 15, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BOEING, J. S. , BARIZÃO, É. O., MONTANHER, P. F., DE CINQUE ALMEIDA, V., VISENTAINER, J. V. Evaluation of solvent effect on the extraction of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacities from the berries: application of principal component analysis. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL. Farmacopeia Brasileira. 1ª edição, 1926.
- BRASIL. Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). Farmacopeia Brasileira, 6ª edição, Brasília: Editora do Ministério da Saúde, 2019.
- BRATU, M. M. , BIRGHILA, S., POPESCU, A., NEGREANU-PIRJOL, B. S., NEGREANU-PIRJOL, T. Correlation of antioxidant activity of dried berry infusions with the polyphenols and selected microelements contents. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2018, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CALISKAN, G. , DIRIM, S. N. The effects of the different drying conditions and the amounts of maltodextrin addition during spray drying of sumac extract. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CARVALHO, A. A. , SANTOS, L. R. D., FARIAS, R. R. S. D., CHAVES, M. H., FEITOSA, C. M., VIEIRA JÚNIOR, G. M., ARAÚJO, M. R. S., FERREIRA, P. M. P., PESSOA, C. D. Ó. Phenolic derivatives and antioxidant activity of polar extracts from Bauhinia pulchella. Química Nova 2018, 41, 405–411. [Google Scholar]
- CHAUMUN, M. , GOËLO, V., RIBEIRO, A. M., ROCHA, F., ESTEVINHO, B. N. In vitro evaluation of microparticles with Laurus nobilis L. extract prepared by spray-drying for application in food and pharmaceutical products. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 122, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHORDIYA, M. A. , SENTHILKUMARAN, K. Cyclodextrin in drug delivery: A review. Res. Rev. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 1, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- CID-ORTEGA, S. , GUERRERO-BELTRÁN, J. Á. Microencapsulation of Hibiscus sabdariffa (Roselle) extracts by spray drying using maltodextrin and gum arabic as carriers. J. Food Res. 2020, 9, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COSTA, R. S. , TEIXEIRA, C. B., GABBAY ALVES, T. V., RIBEIRO-COSTA, R. M., CASAZZA, A. A., ALIAKBARIAN, B., CONVERTI, A., SILVA JÚNIOR, J. O. C., PEREGO, P. Optimization of spray drying conditions to microencapsulate cupuassu (Theobroma grandiflorum) seed by-product extract. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2600–2608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- COSTA, R. S., PINHEIRO, W. B. D. S., ARRUDA, M. S. P., COSTA, C. E. F., CONVERTI, A., RIBEIRO COSTA, R. M., SILVA JÚNIOR, J. O. C. Thermoanalytical and phytochemical study of the cupuassu (Theobroma grandiflorum Schum.) seed by-product in different processing stages. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 1–10.
- CUNHA, A. M. , MENON, S., MENON, R., COUTO, A. G., BÜRGER, C., BIAVATTI, M. W. Hypoglycemic activity of dried extracts of Bauhinia forficata Link. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEWANTO, V. , WU, X., ADOM, K. K., LIU, R. H. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3010–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DÍAZ-BANDERA, D. , VILLANUEVA-CARVAJAL, A., DUBLÁN-GARCÍA, O., QUINTERO-SALAZAR, B., DOMINGUEZ-LOPEZ, A. Assessing release kinetics and dissolution of spray-dried Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) extract encapsulated with different carrier agents. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DING, Z. , TAO, T., WANG, X., PRAKASH, S., ZHAO, Y., HAN, J., WANG, Z. Influences of different carbohydrates as wall material on powder characteristics, encapsulation efficiency, stability and degradation kinetics of microencapsulated lutein by spray drying. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2872–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DÜRIG, T., KARAN, K. Binders in wet granulation. In: Handbook of Pharmaceutical Wet Granulation. Academic Press, 2019. p. 317-349.
- EINHORN-STOLL, U. , HATAKEYAMA, H., HATAKEYAMA, T. Influence of pectin modification on water binding properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EINHORN-STOLL, U., VASILEVA, E., HECHT, T., DRUSCH, S. Investigation of pectin-water interactions: A practical approach. In: Gums and Stabilisers for the Food Industry 18: Hydrocolloid Functionality for Affordable and Sustainable Global Food Solutions, 2016. p. 3-12.
- ESCOBAR-AVELLO, D. , AVENDAÑO-GODOY, J., SANTOS, J., LOZANO-CASTELLÓN, J., MARDONES, C., VON BAER, D., LUENGO, J., LAMUELA-RAVENTÓS, R. M., VALLVERDÚ-QUERALT, A., GÓMEZ-GAETE, C. Encapsulation of phenolic compounds from a grape cane pilot-plant extract in hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin and maltodextrin by spray drying. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ESPEJEL-NAVA, J. A. , VEGA-AVILA, E., ALARCON-AGUILAR, F., CONTRERAS-RAMOS, A., DIAZ-ROSAS, G., TREJO-AGUILAR, G., ORTEGA-CAMARILLO, C. A phenolic fraction from Catharanthus roseus L. stems decreases glycemia and stimulates insulin secretion. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ETZBACH, L. , MEINERT, M., FABER, T., KLEIN, C., SCHIEBER, A., WEBER, F. Effects of carrier agents on powder properties, stability of carotenoids, and encapsulation efficiency of goldenberry (Physalis peruviana L.) powder produced by co-current spray drying. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAN, L. , PENG, M., ZHOU, X., WU, H., HU, J., XIE, W., LIU, S. Modification of carboxymethyl cellulose grafted with collagen peptide and its antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FANG, Z. , BHANDARI, B. Effect of spray drying and storage on the stability of bayberry polyphenols. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FARÍAS-CERVANTES, V. S. , SALINAS-MORENO, Y., CHÁVEZ-RODRÍGUEZ, A., LUNA-SOLANO, G., MEDRANO-ROLDAN, H., ANDRADE-GONZÁLEZ, I. Stickiness and agglomeration of blackberry and raspberry spray dried juices using agave fructans and maltodextrin as carrier agents. Czech J. Food Sci. 2020, 38, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FLOEGEL, A. , KIM, D. O., CHUNG, S. J., KOO, S. I., CHUN, O. K. Comparison of ABTS·+/DPPH∙ assays to measure antioxidant capacity in popular antioxidant-rich US foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FLORA DO BRASIL EM CONSTRUÇÃO, 2019 - Algas, fungos e plantas. Disponível em:http://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/reflora/listaBrasil/PrincipalUC/PrincipalUC.do;jsessionid=5923F194BDA7DA1448013CFF9EB8DC9A#CondicaoTaxonCP. Acesso em: 14 de fevereiro de 2019.
- FORTIS-BARRERA, M. D. L. Á. , ALARCÓN-AGUILAR, F. J., BECERRIL-GARCÍA, A., FLORES-SÁENZ, J. L. E., ALMANZA-PÉREZ, J. C., GARCÍA-LORENZANA, M., ROBERTO CARLOS LAZZARINI-LECHUGA, R. C., ROMÁN-RAMOS, R., BLANCAS-FLORES, G. Mechanism of the hypoglycemic activity and hepatoprotective effect of the aqueous extract of Cecropia obtusifolia Bertol. J. Med. Food 2019, 23, 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- FREITAS, C. M. P. , COIMBRA, J. S. R., SOUZA, V. G. L., SOUSA, R. C. S. Structure and applications of pectin in food, biomedical, and pharmaceutical industry: A review. Coatings 2021, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GABBAY ALVES, T. V. , SILVA DA COSTA, R., ALIAKBARIAN, B., CASAZZA, A. A., PEREGO, P., CARRERA SILVA JUNIOR, J. O., RIBEIRO-COSTA, R. M., CONVERTI, A. Microencapsulation of Theobroma cacao L. waste extract: optimization using response surface methodology. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GALLEGOS-INFANTE, J. A. , ROCHA-GUZMÁN, N. E., GONZÁLEZ-LAREDO, R. F., MEDINA-TORRES, L., GOMEZ-ALDAPA, C. A., OCHOA-MARTÍNEZ, L. A., MARTÍNEZ-SÁNCHEZ, A. E., HERNÁNDEZ-SANTOS, B., RODRÍGUEZ-RAMÍREZ, J. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant capacity of oak (Quercus resinosa) leaf infusions encapsulated by spray-drying. Food Biosci. 2013, 2, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- GALLO, L. , RAMÍREZ-RIGO, M. V., PIÑA, J., BUCALÁ, V. A comparative study of spray-dried medicinal plant aqueous extracts. Drying performance and product quality. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 104, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GALLO, L. , RAMÍREZ-RIGO, M. V., PIÑA, J., PALMA, S., ALLEMANDI, D., BUCALÁ, V. Valeriana officinalis dry plant extract for direct compression: preparation and characterization. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- GANDHI, G. R. , IGNACIMUTHU, S., PAULRAJ, M. G. Solanum torvum Swartz. fruit containing phenolic compounds shows antidiabetic and antioxidant effects in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2725–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GARCIA, J. G. , GARCIA, M. L., ZAMILPA, A., PEREZ, C. J. A., VILLAGOMEZ, I. E. J., ROMAN, R. R., ALARCON-AGUILAR, J. F. Chemical characterization of a hypoglycemic extract from Cucurbita ficifolia Bouche that induces liver glycogen accumulation in diabetic mice. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 14, 218–230. [Google Scholar]
- GAVARIĆ, A. , VIDOVIĆ, S., ZEKOVIĆ, Z., VLADIĆ, J. Influence of storage time on quality of spray-dried extracts of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Hrana U Zdr. I Boles.: Znan. -Stručni Časopis Za Nutr. I Dijetetiku 2019, 8, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- GOULA, A. M. , KARAPANTSIOS, T. D., ACHILIAS, D. S., ADAMOPOULOS, K. G. Water Sorpt. Isotherms Glass Transit. Temp. Spray Dried Tomato Pulp. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- HAGO, S. , MAHROUS, E. A., MOAWAD, M., ABDEL-WAHAB, S., ABDEL-SATTAR, E. Evaluation of antidiabetic activity of Morus nigra L. and Bauhinia variegata L. leaves as Egyptian remedies used for the treatment of diabetes. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 35, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HOSSAIN, M. A., PERVIN, R. Current antidiabetic drugs: review of their efficacy and safety. Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome, p. 455-473, 2018.
- JAIN, M. S. , LOHARE, G. B., BARI, M. M., CHAVAN, R. B., BARHATE, S. D., SHAH, C. B. Spray drying in pharmaceutical industry: A review. Res. J. Pharm. Dos. Forms Technol. 2012, 4, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- JAKOBEK, L. , MATIĆ, P. Non-covalent dietary fiber-polyphenol interactions and their influence on polyphenol bioaccessibility. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JINAPONG, N. , SUPHANTHARIKA, M., JAMNONG, P. Production of instant soymilk powders by ultrafiltration, spray drying and fluidized bed agglomeration. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JOVANOVIĆ, M. , ĆUJIĆ-NIKOLIĆ, N., DRINIĆ, Z., JANKOVIĆ, T., MARKOVIĆ, S., PETROVIĆ, P., ŠAVIKIN, K. Spray drying of Gentiana asclepiadea L. root extract: Successful encapsulation into powders with preserved stability of bioactive compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 114044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KEOGH, M. K. , MURRAY, C. A., T O’KENNEDY, B. Effects of ultrafiltration of whole milk on some properties of spray-dried milk powders. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KIM, D. O. , LEE, K. W., LEE, H. J., LEE, C. Y. Vitamin C equivalent antioxidant capacity (VCEAC) of phenolic phytochemicals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KOMOROWSKA, P. , ROZANSKA, S., ROZANSKI, J. Effect of the degree of substitution on the rheology of sodium carboxymethylcellulose solutions in propylene glycol/water mixtures. Cellulose 2017, 24, 4151–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KONO, H. , OSHIMA, K., HASHIMOTO, H., SHIMIZU, Y., TAJIMA, K. NMR characterization of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose: Substituent distribution and mole fraction of monomers in the polymer chains. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KRISHNAIAH, D. , NITHYANANDAM, R., SARBATLY, R. A critical review on the spray drying of fruit extract: Effect of additives on physicochemical properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 449–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KUCK, L. S. , NOREÑA, C. P. Z. Microencapsulation of grape (Vitis labrusca var. Bordo) skin phenolic extract using gum Arabic, polydextrose, and partially hydrolyzed guar gum as encapsulating agents. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KWON, O. , ECK, P., CHEN, S., CORPE, C. P., LEE, J. H., KRUHLAK, M., LEVINE, M. Inhibition of the intestinal glucose transporter GLUT2 by flavonoids. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LABUSCHAGNE, P. Impact of wall material physicochemical characteristics on the stability of encapsulated phytochemicals: A review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LI, Y. , GAO, F., SHAN, F., BIAN, J., ZHAO, C. Study on the interaction between 3 flavonoid compounds and a-amylase by fluorescence spectroscopy and enzymatic kinetics. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LI, Y. Q., ZHOU, F. C., GAO, F., BIAN, J. S., SHAN, F. Comparative evaluation of quercetin, Isoquercetin and Rutin as inhibitors of a-glucosidase. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2009, 57, 11463–11468. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LI, A. N. , LI, S., ZHANG, Y. J., XU, X. R., CHEN, Y. M., LI, H. B. Resources and biological activities of natural polyphenols. Nutrients 2014, 6, 6020–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LOARCA-PIÑA, G. , MENDOZA, S., RAMOS-GÓMEZ, M., REYNOSO, R. Antioxidant, antimutagenic, and antidiabetic activities of edible leaves from Cnidoscolus chayamansa Mc. Vaugh. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- LÓPEZ-NICOLÁS, J. M. , RODRÍGUEZ-BONILLA, P., GARCÍA-CARMONA, F. Cyclodextrins and antioxidants. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LU, W. , YANG, X., SHEN, J., LI, Z., TAN, S., LIU, W., CHENG, Z. Choosing the appropriate wall materials for spray-drying microencapsulation of natural bioactive ingredients: Taking phenolic compounds as examples. Powder Technol. 2021, 394, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MA, Y. , HOU, C. J., FA, H. B., HUO, D. Q., YANG, M. Synthesis and antioxidant property of hydroxycinnamoyl maltodextrin derivatives. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2450–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAHDAVI, S. A. , JAFARI, S. M., ASSADPOOR, E., DEHNAD, D. Microencapsulation optimization of natural anthocyanins with maltodextrin, gum Arabic and gelatin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEDINA-TORRES, L. , SANTIAGO-ADAME, R., CALDERAS, F., GALLEGOS-INFANTE, J. A., GONZÁLEZ-LAREDO, R. F., ROCHA-GUZMÁN, N. E., NÚÑEZ-RAMIREZ, D. M., BERNAD-BERNAD, M. J, MANERO, O. Microencapsulation by spray drying of laurel infusions (Litsea glaucescens) with maltodextrin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 90, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MELO, P. S. , BERGAMASCHI, K. B., TIVERON, A. P., MASSARIOLI, A. P., OLDONI, T. L. C., ZANUS, M. C., PEREIRA, G. E., ALENCAR, S. M. D. Composição fenólica e atividade antioxidante de resíduos agroindustriais. Ciência Rural 2011, 41, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOSELEY, R. , LEAVER, M., WALKER, M., WADDINGTON, R. J., PARSONS, D., CHEN, W. Y. J., EMBERY, G. Comparison of the antioxidant properties of HYAFF®-11p75, AQUACEL® and hyaluronan towards reactive oxygen species in vitro. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOSELEY, R. , WALKER, M., WADDINGTON, R. J., CHEN, W. Y. J. Comparison of the antioxidant properties of wound dressing materials - carboxymethylcellulose, hyaluronan benzyl ester and hyaluronan, towards polymorphonuclear leukocyte-derived reactive oxygen species. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NADEEM, H. Ş. , TORUN, M., ÖZDEMIR, F. Spray drying of the mountain tea (Sideritis stricta) water extract by using different hydrocolloid carriers. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NAVARRO-FLORES, M. J. , VENTURA-CANSECO, L. M. C., MEZA-GORDILLO, R., AYORA-TALAVERA, T. D. R., ABUD-ARCHILA, M. Spray drying encapsulation of a native plant extract rich in phenolic compounds with combinations of maltodextrin and non-conventional wall materials. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 4111–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEGRÃO-MURAKAMI, A. N. , NUNES, G. L., PINTO, S. S., MURAKAMI, F. S., AMANTE, E. R., PETRUS, J. C. C., PRUDÊNCIO, E. S., AMBONI, R. D. Influence of DE-value of maltodextrin on the physicochemical properties, antioxidant activity, and storage stability of spray dried concentrated mate (Ilex paraguaiensis A. St. Hil.). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- NIAMNUY, C. , POOMKOKRAK, J., DITTANET, P., DEVAHASTIN, S. Impacts of spray drying conditions on stability of isoflavones in microencapsulated soybean extract. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 1844–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NUNES, G. L. , BOAVENTURA, B. C. B., PINTO, S. S., VERRUCK, S., MURAKAMI, F. S., PRUDÊNCIO, E. S., AMBONI, R. D. D. M. C. Microencapsulation of freeze concentrated Ilex paraguaiensis extract by spray drying. J. Food Eng. 2015, 151, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OLIVEIRA, O. W. , PETROVICK, P. R. Spray drying of plant extracts: basic remarks and application. Rev. Bras. De Farmacogn. 2010, 20, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PALSIKOWSKI, P. A. , BESEN, L. M., SANTOS, K. A., SILVA, C., SILVA, E. A. Supercritical CO2 oil extraction from Bauhinia forficata link subsp. pruinosa leaves: Composition, antioxidant activity and mathematical modeling. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 153, 104588. [Google Scholar]
- Pashazadeh, H. , Zannou, O., Ghellam, M., Koca, I., Galanakis, C. M., Aldawoud, T. M. Optimization and encapsulation of phenolic compounds extracted from maize waste by freeze-drying, spray-drying, and microwave-drying using maltodextrin. Foods 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PASRIJA, D. , EZHILARASI, P. N., INDRANI, D., ANANDHARAMAKRISHNAN, C. Microencapsulation of green tea polyphenols and its effect on incorporated bread quality. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PATEL, R. P.; PATEL, M. P.; SUTHAR, A. M. Spray drying technology: an overview. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 2, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PEI, K. , OU, J., HUANG, J., OU, S. p-Coumaric acid and its conjugates: dietary sources, pharmacokinetic properties and biological activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2952–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PEREZ-PEREZ, L. M. , HUERTA-OCAMPO, J. Á., RUIZ-CRUZ, S., CINCO-MOROYOQUI, F. J., WONG-CORRAL, F. J., RASCÓN-VALENZUELA, L. A., ROBLES-GARCÍA, M. A., GONZÁLEZ-VEGA, R. I., ROSAS-BURGOS, E. C., CORELLA-MADUEÑO, M. A. G., DEL-TORO-SÁNCHEZ, C. L. Evaluation of quality, antioxidant capacity, and digestibility of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L. cv Blanoro) stored under N2 and CO2 atmospheres. Molecules 2021, 26, 2773. [Google Scholar]
- PICOT-ALLAIN, M. C. N. , RAMASAWMY, B., EMMAMBUX, M. N. Extraction, characterisation, and application of pectin from tropical and sub-tropical fruits: a review. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 38, 282–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- POOMKOKRAK, J. , NIAMNUY, C., CHOICHAROEN, K., DEVAHASTIN, S. Encapsulation of soybean extract using spray drying. J. Food Sci. Agric. Technol. 2015, 1, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- PORT’S, P. S. , CHISTÉ, R. C., GODOY, H. T., PRADO, M. A. The phenolic compounds and the antioxidant potential of infusion of herbs from the Brazilian Amazonian region. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 875–881. [Google Scholar]
- POURASHOURI, P. , SHABANPOUR, B., RAZAVI, S. H., JAFARI, S. M., SHABANI, A., AUBOURG, S. P. Oxidative stability of spray-dried microencapsulated fish oils with different wall materials. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2014, 23, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PUDZIUVELYTE, L. , MARKSA, M., JAKSTAS, V., IVANAUSKAS, L., KOPUSTINSKIENE, D. M., BERNATONIENE, J. Microencapsulation of Elsholtzia ciliata Herb Ethanolic Extract by Spray-Drying: Impact of resistant-maltodextrin complemented with sodium caseinate, skim milk, and beta-cyclodextrin on the quality of spray-dried powders. Molecules 2019, 24, 1461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- RAJABI, H. , GHORBANI, M., JAFARI, S. M., MAHOONAK, A. S., RAJABZADEH, G. Retention of saffron bioactive components by spray drying encapsulation using maltodextrin, gum Arabic and gelatin as wall materials. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RE, R. , PELLEGRINI, N., PROTEGGENTE, A., PANNALA, A., YANG, M., RICE-EVANS, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS·+ radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- REZENDE, Y. R. R. S. , NOGUEIRA, J. P., NARAIN, N. Microencapsulation of extracts of bioactive compounds obtained from acerola (Malpighia emarginata DC) pulp and residue by spray and freeze drying: Chemical, morphological and chemometric characterization. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RICE-EVANS, C. A. , MILLER, N. J., PAGANGA, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RIVERO-PÉREZ, M. D. , MUNIZ, P. I. L. A. R., GONZÁLEZ-SANJOSÉ, M. L. Antioxidant profile of red wines evaluated by total antioxidant capacity, scavenger activity, and biomarkers of oxidative stress methodologies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5476–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROBERT, P. , GORENA, T., ROMERO, N., SEPULVEDA, E., CHAVEZ, J., SAENZ, C. Encapsulation of polyphenols and anthocyanins from pomegranate (Punica granatum) by spray drying. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROCHA, F. D. , TEIXEIRA, V. L., PEREIRA, R. C., KAPLAN, M. A. C. Diabetes mellitus e estresse oxidativo: produtos naturais como alvo de novos modelos terapêuticos. Rev. Bras. De Farmacogn. 2006, 87, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- ROOS, Y. , KAREL, M. Phase transitions of mixtures of amorphous polysaccharides and sugars. Biotechnol. Prog. 1991, 7, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RUDRAPAL, M. , KHAIRNAR, S. J., KHAN, J., DUKHYIL, A. B., ANSARI, M. A., ALOMARY, M. N., ALSHABRMI, F. M., PALAI, S., DEB, P. K., DEVI, R. Dietary polyphenols and their role in oxidative stress-induced human diseases: insights into protective effects, antioxidant potentials and mechanism (s) of action. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar]
- RUFINO, M. D. S. M. , ALVES, R. E., DE BRITO, E. S., DE MORAIS, S. M., SAMPAIO, C. D. G., PÉREZ-JIMENEZ, J., SAURA-CALIXTO, F. D. Metodologia científica: determinação da atividade antioxidante total em frutas pela captura do radical livre DPPH∙. Embrapa Agroindústria Trop. - Comun. Técnico 2007, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- SANSONE, F. F. , MENCHERINI, T., PICERNO, P., ESPOSITO, T., DEL GAUDIO, P., RUSSO, P., PEPE, G., LAURO, M. R., AQUINO, R. P. Microencapsulation by spray drying of Lannea microcarpa extract: Technological characteristics and antioxidant activity. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2014, 2, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SARRATE, R. , TICÓ, J. R., MIÑARRO, M., CARRILLO, C., FÀBREGAS, A., GARCÍA-MONTOYA, E., PÉREZ-LOZANO, P., SUÑÉ-NEGRE, J. M. Modification of the morphology and particle size of pharmaceutical excipients by spray drying technique. Powder Technol. 2015, 270, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCOLES, R. Sabiduría popular y plantas medicinales: el ejemplo de la comunidad negra de Itacoã, Acará, Pará. Bol. Do Mus. Para. Emílio Goeldi Ciências Nat. 2006, 1, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHEKUNOV, B. Y. , CHATTOPADHYAY, P., TONG, H. H., CHOW, A. H. Particle size analysis in pharmaceutics: principles, methods and applications. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHIBANO, M. , KAKUTANI, K., TANIGUCHI, M., YASUDA, M., BABA, K. Antioxidant constituents in the dayflower (Commelina communis L.) and their α-glucosidase-inhibitory activity. J. Nat. Med. 2008, 62, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHRESTHA, A. K. , UA-ARAK, T., ADHIKARI, B. P., HOWES, T., BHANDARI, B. R. Glass transition behavior of spray dried orange juice powder measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermal mechanical compression test (TMCT). Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 10, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIEMONS, I. , POLITIEK, R. G. A., BOOM, R. M., VAN DER SMAN, R. G. M., SCHUTYSER, M. A. I. Dextrose equivalence of maltodextrins determines particle morphology development during single sessile droplet drying. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SOSNIK, A. , SEREMETA, K. P. Advantages and challenges of the spray-drying technology for the production of pure drug particles and drug-loaded polymeric carriers. Advances in colloid and interface science 2015, 223, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SRIVASTAVA, P. , MALVIYA, R. Sources of pectin, extraction and its applications in pharmaceutical industry− An overview. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2011, 2, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- SOWNDHARARAJAN, K. , KANG, S. C. Free radical scavenging activity from different extracts of leaves of Bauhinia vahlii Wight & Arn. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 319–325. [Google Scholar]
- SUN, D. , CHEN, X., ZHU, C. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of pectin from hawthorn wine pomace: A comparison of different extraction methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TAKEITI, C. Y. , KIECKBUSCH, T. G., COLLARES-QUEIROZ, F. P. Morphological and physicochemical characterization of commercial maltodextrins with different degrees of dextrose-equivalent. Int. J. Food Prop. 2010, 13, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TCHABO, W. , MA, Y., KAPTSO, G. K., KWAW, E., CHENO, R. W., XIAO, L., OSAE, R., WU, M., FAROOQ, M. Process analysis of mulberry (Morus alba) leaf extract encapsulation: Effects of spray drying conditions on bioactive encapsulated powder quality. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 12, 122–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TOBAR-GRANDE, B. , GODOY, R., BUSTOS, P., VON PLESSING, C., FATTAL, E., TSAPIS, N., OLAVE, C., GOMEZ-GAETE., C. Development of biodegradable methylprednisolone microparticles for treatment of articular pathology using a spray-drying technique. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar]
- TONON, R. V. , BRABET, C., HUBINGER, M. D. Influence of process conditions on the physicochemical properties of açai (Euterpe oleraceae Mart.) powder produced by spray drying. J. Food Eng. 2008, 88, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TONON, R. V. , BRABET, C., PALLET, D., BRAT, P., HUBINGER, M. D. Physicochemical and morphological characterisation of açai (Euterpe oleraceae Mart.) powder produced with different carrier agents. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TROPICOS. Disponível em: https://www.tropicos.org/Name/100297284. Acesso em 15 de maio de 2019.
- TRUONG, V. , BHANDARI, B. R., HOWES, T. Optimization of co-current spray drying process of sugar-rich foods. Part I - Moisture and glass transition temperature profile during drying. J. Food Eng. 2005, 71, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- URIAS-ORONA, V. , RASCÓN-CHU, A., LIZARDI-MENDOZA, J., CARVAJAL-MILLÁN, E., GARDEA, A. A., RAMÍREZ-WONG, B. A novel pectin material: extraction, characterization and gelling properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3686–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VALENTOVÁ, K. , VRBA, J., BANCÍŘOVÁ, M., ULRICHOVÁ, J., KŘEN, V. Isoquercitrin: pharmacology, toxicology, and metabolism. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VAN DEN BERG, M. E. , SILVA, M. H. L. D. Contribuição ao conhecimento da flora medicinal de Roraima. Acta Amaz. 1988, 18, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VAZ, A. M. S. F. , TOZZI, A. M. G. A. Bauhinia Ser. Cansenia (Leguminosae: Caesalpinioideae) in Brazil. Rodriguesia 2003, 54, 55–143. [Google Scholar]
- VEHRING, R. Pharmaceutical particle engineering via spray drying. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 999–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VIDOVIĆ, S. S. , VLADIĆ, J. Z., VAŠTAG, Ž. G., ZEKOVIĆ, Z. P., POPOVIĆ, L. M. Maltodextrin as a carrier of health benefit compounds in Satureja montana dry powder extract obtained by spray drying technique. Powder Technol. 2014, 258, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VLADIĆ, J. , AMBRUS, R., SZABÓ-RÉVÉSZ, P., VASIĆ, A., CVEJIN, A., PAVLIĆ, B., VIDOVIĆ, S. Recycling of filter tea industry by-products: Production of A. millefolium powder using spray drying technique. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 80, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VYAS, P. , BRAGANZA, V. J. Effect of solvents and extraction methods on the phenolic content, flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of and Bauhinia variegata Leptadenia reticulata. Asian J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 5, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG, J. , LI, H., CHEN, Z., LIU, W., CHEN, H. Characterization and storage properties of a new microencapsulation of tea polyphenols. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 89, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WATHONI, N. , SHAN, C. Y., SHAN, W. Y., ROSTINAWATI, T., INDRADI, R. B., PRATIWI, R., MUCHTARIDI, M. Characterization and antioxidant activity of pectin from Indonesian mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) rind. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ZAIDEL, N. D. A. , MAKHTAR, N. A., JUSOH, Y. M. M., MUHAMAD, I. I. Efficiency and thermal stability of encapsulated anthocyanins from red dragon fruit (Hylocereus polyrhizus (Weber) Britton & Rose) using microwave-assisted technique. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- ZHANG, L. , ZHANG, S. T., YIN, Y. C., XING, S., LI, W. N., FU, X. Q. Hypoglycemic effect and mechanism of Isoquercitrin as an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 in type 2 diabetic mice. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14967–14974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ZHAO, Y. , LU, H., WANG, Q., LIU, H., SHEN, H., XU, W., GE, J., HE, D. Rapid qualitative profiling and quantitative analysis of phenolics in Ribes meyeri leaves and their antioxidant and antidiabetic activities by HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS and UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 1404–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHU, J. , LI, X., LIU, L., LI, Y., QI, B., JIANG, L. Preparation of spray-dried soybean oil body microcapsules using maltodextrin: Effects of dextrose equivalence. LWT 2022, 154, 112874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

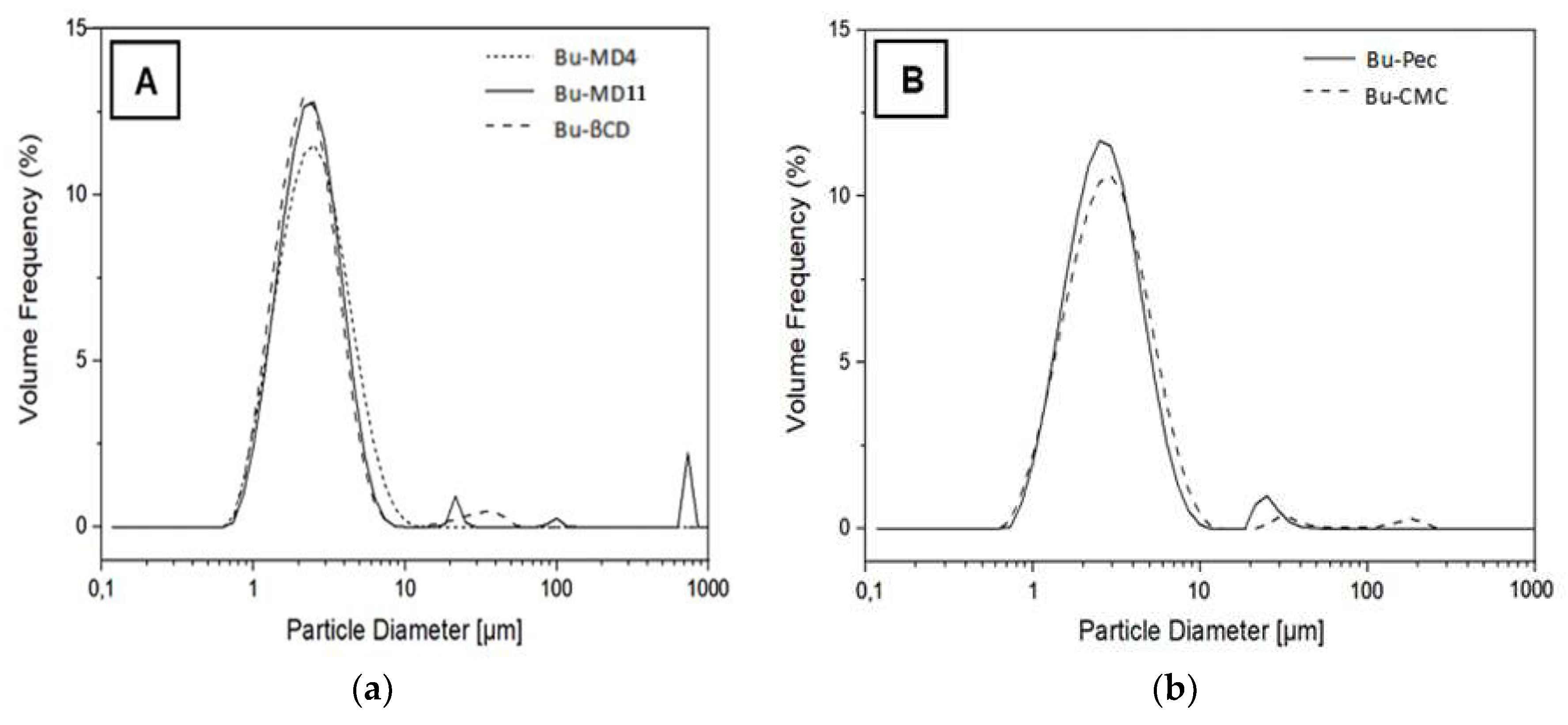
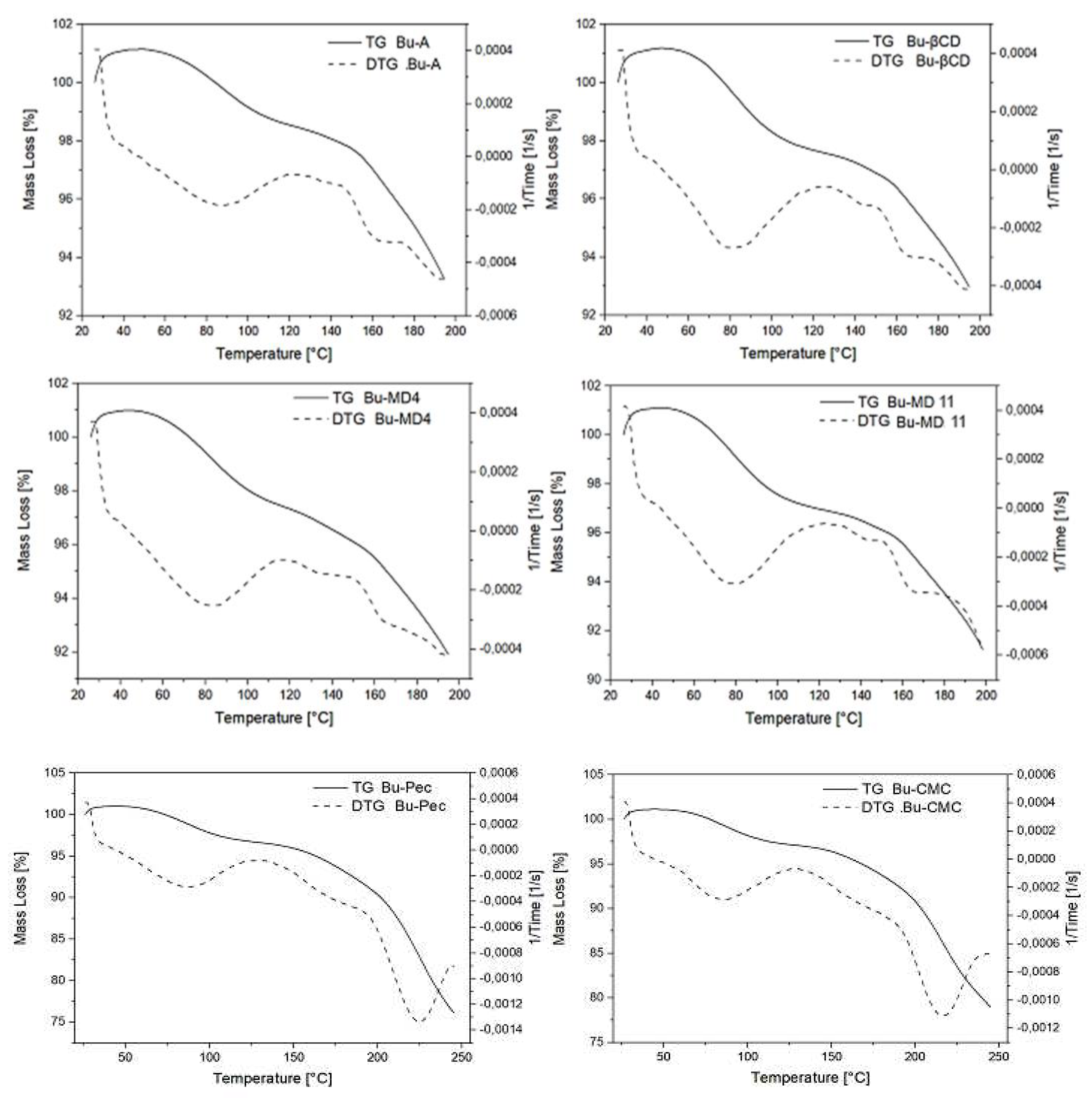
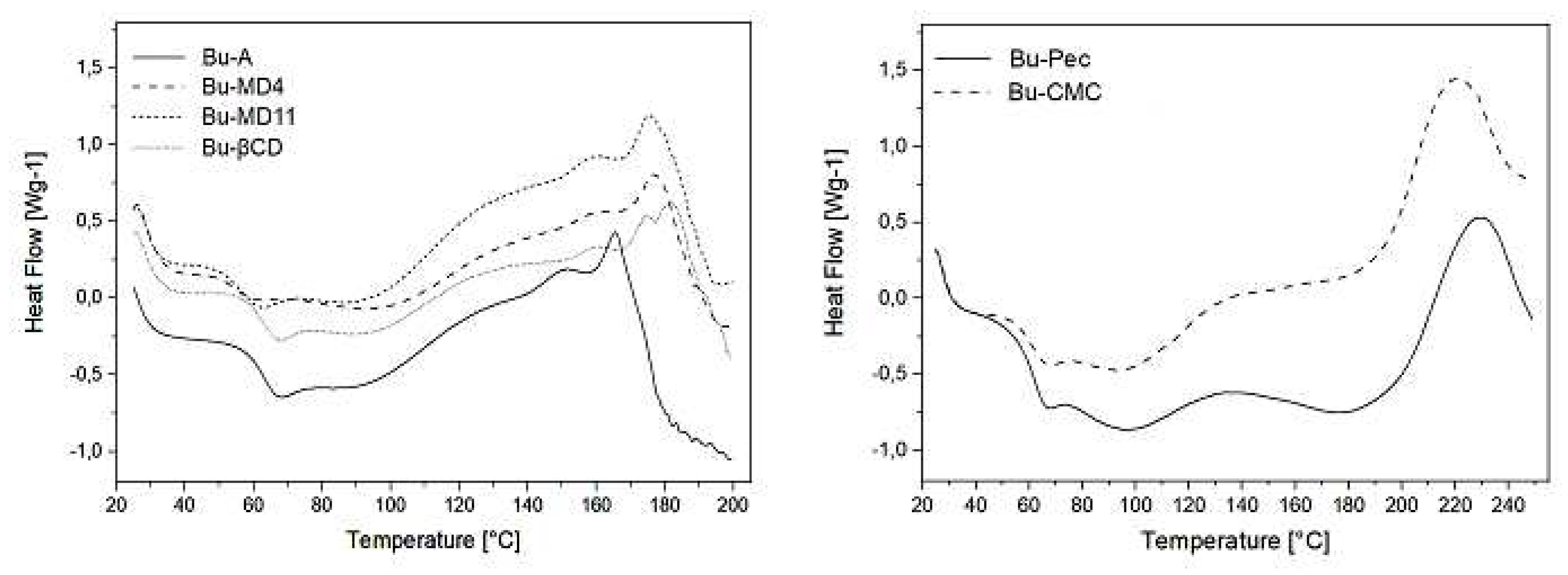
| Solution | Wall material | Solids content (g/L) | Viscosity (mPa.s) | YD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bu-A | None | 8.234 ± 0.001 | 1.45 ± 0.03a | 64.20 ± 0.72a |
| Bu-MD4 | Maltodextrin DE 4-7 | 9.146 ± 0.003 | 1.44 ± 0.04a | 88.52 ± 0.72b |
| Bu-MD11 | Maltodextrin DE 11-14 | 9.142 ± 0.003 | 1.43 ± 0.03a | 77.41 ± 4.63ab |
| Bu-βCD | β-Cyclodextrin | 9.139 ± 0.002 | 1.43 ± 0.02a | 78.93 ± 7.11ab |
| Bu-Pec | Pectin LM-22-CG | 9.162 ± 0.005 | 1.41 ± 0.01a | 73.19 ± 1.01a |
| Bu-CMC | Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose | 9.145 ± 0.004 | 3.46 ± 0.03b | 76.31 ± 1.54ab |
| Sample | Dv10 (µm) | Dv50 (µm) | Dv90 (µm) | Span (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bu-MD4 | 1.22 ± 0.02a | 2.23 ± 0.17abc | 4.66 ± 0.71abc | 1.53 ± 0.21a |
| Bu-MD11 | 1.19 ± 0.08a | 2.41 ± 0.39abc | 4.54 ± 0.79abc | 1.40 ± 0.30a |
| Bu-βCD | 1.15 ± 0.07a | 2.01 ± 0.13b | 3.76 ± 0.40b | 1.29 ± 0.10a |
| Bu-Pec | 1.29 ± 0.02a | 2.50 ± 0.02abc | 4.82 ± 0.11abc | 1.41 ± 0.04a |
| Bu-CMC | 1.29 ± 0.07a | 2.87 ± 0.25c | 5.54 ± 0.34c | 1.50 ± 0.23a |
| Sample | Moisture content (%) | Tg (°C) | Tinitial decomposition (ºC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bu-A | 2.90 ± 0.10a | 60.4 ± 3.5a | 160.2 ± 1.6a |
| Bu-MD4 | 3.43 ± 0.16ab | 56.8 ± 2.9a | 165.8 ± 3.6a |
| Bu-MD11 | 3.89 ± 0.27b | 57.6 ± 2.4a | 163.6 ± 3.9a |
| Bu-βCD | 3.63 ± 0.27ab | 61.5 ± 0.4a | 162.6 ± 6.4a |
| Bu-Pec | 4.05 ± 0.40b | 58.4 ± 4.8a | 191.4 ± 0.9b |
| Bu-CMC | 4.25 ± 0.48b | 57.8 ± 5.6a | 188.2 ± 1.1b |
|
Sample |
TFC (mgRUTE/g Extract) |
PME (mgGAEq/g Extract) |
PS (mgGAEq/g Extract) |
EE (%) | YE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bu-L | 21.93 ± 0.30a | 101.43 ± 1.68a | ⎯ | ⎯ | ⎯ |
| Bu-A | 22.69 ± 0.45ac | 101.28 ± 1.65a | ⎯ | ⎯ | ⎯ |
| Bu-MD4 | 12.75 ± 0.57b | 84.28 ± 5.47b | 38.69 ± 0.64a | 44.95 ± 5.17a | 83.09 ± 5.40a |
| Bu-MD11 | 12.69 ± 0.21b | 90.99 ± 2.31b | 32.82 ± 2.51ab | 57.35 ± 2.24b | 89.71 ± 2.28a |
| Bu-βCD | 12.69 ± 0.31b | 84.78 ± 1.70b | 33.57 ± 1.28ab | 50.49 ± 2.92ab | 83.59 ± 1.68a |
| Bu-Pec | 21.73 ± 0.34a | 69.98 ± 3.44c | 33.59 ± 3.87ab | 35.87 ± 3.49c | 68.99 ± 3.39b |
| Bu-CMC | 23.07 ± 0.50c | 75.15 ± 3.13c | 27.96 ± 1.99b | 46.53 ± 1.13a | 74.09 ± 3.09b |
|
Sample |
DPPH∙ | ABTS·+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage scavenging (%) | TAA (µMTEq/gExtract) |
Percentage scavenging (%) | TAA (µMTEq/gExtract) |
|
| Bu-L | 22.09 ± 0.66a | 308.67 ± 2.64a | 23.97 ± 0.22a | 956.40 ± 2.81a |
| Bu-A | 25.65 ± 0.25b | 323.45 ± 1.07a | 29.49 ± 0.55b | 1031.33 ± 8.04b |
| Bu-MD4 | 30.41 ± 0.60c | 345.58 ± 2.98b | 23.84 ± 1.89a | 955.17 ± 23.65a |
| Bu-MD11 | 38.34 ± 1.04d | 390.06 ± 6.66c | 25.24 ± 1.34a | 972.82 ± 17.26a |
| Bu-βCD | 38.22 ± 0.43d | 389.26 ± 2.72c | 24.58 ± 1.26a | 964.31 ± 16.12a |
| Bu-Pec | 34.61 ± 1.17e | 367.86 ± 6.65d | 31.54 ± 0.77bc | 1062.32 ± 11.94bc |
| Bu-CMC | 36.10 ± 1.74de | 376.55 ± 10.16cd | 33.02 ± 0.92c | 1085.72 ± 14.84c |
|
Sample |
Content |
Compound | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorogenic acid | p-coumaric acid | Rutin | Isoquercitrin | ||
| Bu-L |
µg/mL |
15.38 ± 0.22a | 0.60 ± 0.05a | 102.02 ± 2.52a | 4.30 ± 0.21a |
| Bu-A | 19.17 ± 0.51b | 0.76 ± 0.08a | 125.13 ± 1.12b | 5.17 ± 0.67a | |
| Bu-MD4 | 17.08 ± 0.06cd | 0.58 ± 0.11a | 108. 30 ± 0.60c | 4.82 ± 0.27a | |
| Bu-MD11 | 16.72 ± 0.46d | 0.69 ± 0.01a | 110.19 ± 1.58cd | 4.66 ± 0.40a | |
| Bu-βCD | 17.43 ± 0.15cde | 0.60 ± 0.04a | 113.07 ± 0.94de | 4.90 ± 0.42a | |
| Bu-Pec | 17.90 ± 0.12e | 0.70 ± 0.04a | 115.10 ± 0.76e | 5.01 ± 0.12a | |
| Bu-CMC | 17.80 ± 0.15ce | 0.68 ± 0.10a | 112.59 ± 1.47de | 4.84 ± 0.30a | |
| Bu-L |
mg/g Extract |
1.669 ± 0.024a | 0.066 ± 0.005a | 11.077 ± 0.274a | 0.466 ± 0.022a |
| Bu-A | 1.975 ± 0.052b | 0.078 ± 0.008a | 12.886 ± 0.115b | 0.533 ± 0.069a | |
| Bu-MD4 | 1.769 ± 0.007c | 0.060 ± 0.012a | 11.216 ± 0.062a | 0.500 ± 0.029a | |
| Bu-MD11 | 1.740 ± 0.048ac | 0.072 ± 0.001a | 11.465 ± 0.164ac | 0.485 ± 0.041a | |
| Bu-βCD | 1.808 ± 0.016cd | 0.062 ± 0.004a | 11.724 ± 0.098cd | 0.508 ± 0.044a | |
| Bu-Pec | 1.867 ± 0.013d | 0.073 ± 0.004a | 12.003 ± 0.080d | 0.522 ± 0.013a | |
| Bu-CMC | 1.858 ± 0.016d | 0.070 ± 0.011a | 11.755 ± 0.153cd | 0.505 ± 0.032a | |
| Solution | Concentration (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorogenic acid | p-Coumaric acid | Rutin | Isoquercitrin | |
| 1 | 50 | 5.00 | 200 | 15.00 |
| 2 | 25 | 2.50 | 100 | 7.50 |
| 3 | 10 | 1.00 | 40 | 3.00 |
| 4 | 5 | 0.50 | 20 | 1.50 |
| 5 | 2.5 | 0.25 | 10 | 0.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





