1. Introduction
During the last decades, a growing number of studies have shown that infections acquired during pregnancy have an important impact on both pregnant women and their fetuses, with increased risk of complications on neonatal outcomes [
1]. The first case of human coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in humans, which was caused by SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus), was reported in December 2019 [
2]. Since then, SARS-CoV-2 has affected over 765 million people worldwide, causing more than 6.9 million deaths. Among pregnant population, its prevalence has been reported to be approximately 14% to 15%, with over 220,000 cases, most of them being asymptomatic [
3].
In utero SARS-CoV-2 transmission has been the topic of discussion since the start of the global health crisis. Third trimester fetal infection has been reported to occur in 3.2% of cases [
4]. The primary action mechanism that leads to vertical transmission involves angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and S protein protease receptors, which facilitate virus entry into the cell. These receptors can be found in developing human embryos, during the early stages of development. As a result, SARS-CoV-2 has the ability to penetrate fetal cells in the preliminary phases of evolution and affect cell transformation and growth, leading to early intrauterine infection [
5].
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy has been carefully managed, due to the fact that pregnant women were initially excluded from the vaccine trials. To this date, vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 infection plays a crucial role in preventing maternal illness. While several observational studies examined neonatal benefits via antibodies transfer across the placenta, large-scale assessments of neonatal safety are scarce [
6].
Viruses such as varicella and rubella can cross the placenta and harm the fetus. Miscarriage, growth restriction, hydrops, and even death are all possible outcomes of fetal viral infection. During the first 6 gestational weeks, SARS-CoV-2 has a higher chance of developing congenital birth defects [
5]. Compared to the evidence that influenza infection during the first trimester of pregnancy is teratogenic (more precisely hyperthermia and fever), it is presumed that fever associated with COVID-19 in the first trimester could induce congenital anomalies. Limited data about the effects of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection during the first trimester of pregnancy on the risk of major congenital malformations (MCMs) is available [
7,
8].
Therefore, our goal for this study was to identify newborns from pregnancies with SARS-CoV-2 infection and to investigate the extension of neonatal complications using cardiac, abdominal and cerebral ultrasonography, hearing testing and indirect ophthalmoscopy. By contrast, neonates whose mothers were vaccinated against COVID-19 during pregnancy and those from pathology-free pregnancies have been examined.
2. Materials and Methods
Our study was conducted over a period of 10 months (November 2021 – August 2022) in the Clinic of Neonatology of the Première Hospital, Regina Maria Health Network, where both birth and neonatal follow-up took place. This study was approved by the Première Hospital’s Ethics Commission Board (No. 330/18.11.2021), as well as by the Ethics Committee of Scientific Research of “Victor Babeș” University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timișoara (No. 76/2020). The patients agreed and signed an informed consent form that followed the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. This study was approved by our institutional review board.
A total of 458 newborns were included, divided into 3 groups. The COVID-19 group included 167 newborns from mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy, followed by the vaccination group which consisted of 91 neonates born from mothers immunized against SARS-CoV-2 during the gestational period and the control group, with 200 newborns.
Inclusion criteria were represented by maternal COVID-19 infection during pregnancy, confirmed using RT-PCR testing, for the first group, immunization against SARS-CoV-2 with BioNTech-Pfizer or Moderna vaccine during the gestational period, for the second group, and no acquired infections or vaccination during pregnancy, for the third group, respectively. Exclusion criteria were represented by vaccination during pregnancy along with SARS-CoV-2 infection, or any other infection acquired during the gestational period.
The study aimed to evaluate the changes occurred after maternal infection and vaccination during pregnancy, mainly regarding neonatal heart, brain, kidney using ultrasonography, hearing impairment using evoked otoacoustic emissions along with auditory brainstem response (EOAE-ABR) screening and ocular anomalies using indirect ophthalmoscopy compared to the control group.
For the cerebral and ultrasonographic examinations, Voluson E8 equipment with microconvex transducer at a bandwidth of 3-9 MHz was used. Cerebral ultrasonography evaluated brain structures, hemodynamic parameters of cerebral arteries, dimensions of ventricles and pericerebral fluid spaces. In relation to the cases of hydronephrosis found, the severity was assessed according to the Society of Fetal Urology’s numerical grading system.
Transthoracic cardiac ultrasound was performed using a Samsung HS 60 ultrasound scanner and a PA3-8B phased array probe, with a frequency between 3 and 8 MHz. The results of morphological measurements were indexed using Z-scores as a reference, according to sex, age and body surface area.
2.1. Statistical Analysis
Categorical data are summarized as counts and percentages. The regression coefficient (R), R2 (coefficient of determination), and p-values for individual predictors were calculated assess the strength of association between variables. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Differences between groups for continuously normal data were tested using Welch’s t-test for two groups or ANOVA if there were more than two groups. Differences between categorical data were tested using the test or Fisher’s exact test when the expected cell count was less than five. We performed a binomial logistic regression to determine independent risk factors. The selection of cases was guided by the lowest Akaike Information Criterion (AIC), which helps in identifying models that best explain the data with minimal information loss. A backward regression model was used, which involves starting with all potential predictors and systematically removing those that contribute the least to the model’s predictive power. This approach ensures a more efficient and accurate model by retaining only the most significant variables. All statistical analysis was performed with R (version 3.6.3) using the „gtsummary” and „V8” packages.
3. Results
Our research compared the effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy with COVID-19 vaccination and normal pregnancies on the neonatal brain, heart and kidney using ultrasonographic examinations during the first 4 days after birth, together with auditory screening and ophthalmologic evaluation.
The cardiac ultrasonography was performed by a Pediatric Cardiologist in all cases, between the first and the 4
th day after birth, respectively. A great number of newborns, 152 (91%) from the COVID-19 group had normal echocardiographic exams, compared to the vaccine group with 86 (95%) normal evaluations and 190 from the control group (95%). The pathological findings were separated into 2 categories: patent foramen ovale (PFO) and congenital heart disease (CHD). For the persistent foramen ovale class, 8 cases were found in the COVID-19 group (4,8%), 3 cases in the vaccine group (3,3%) and 9 in the control group (4,5%). No association was achieved for this category (p>0.9
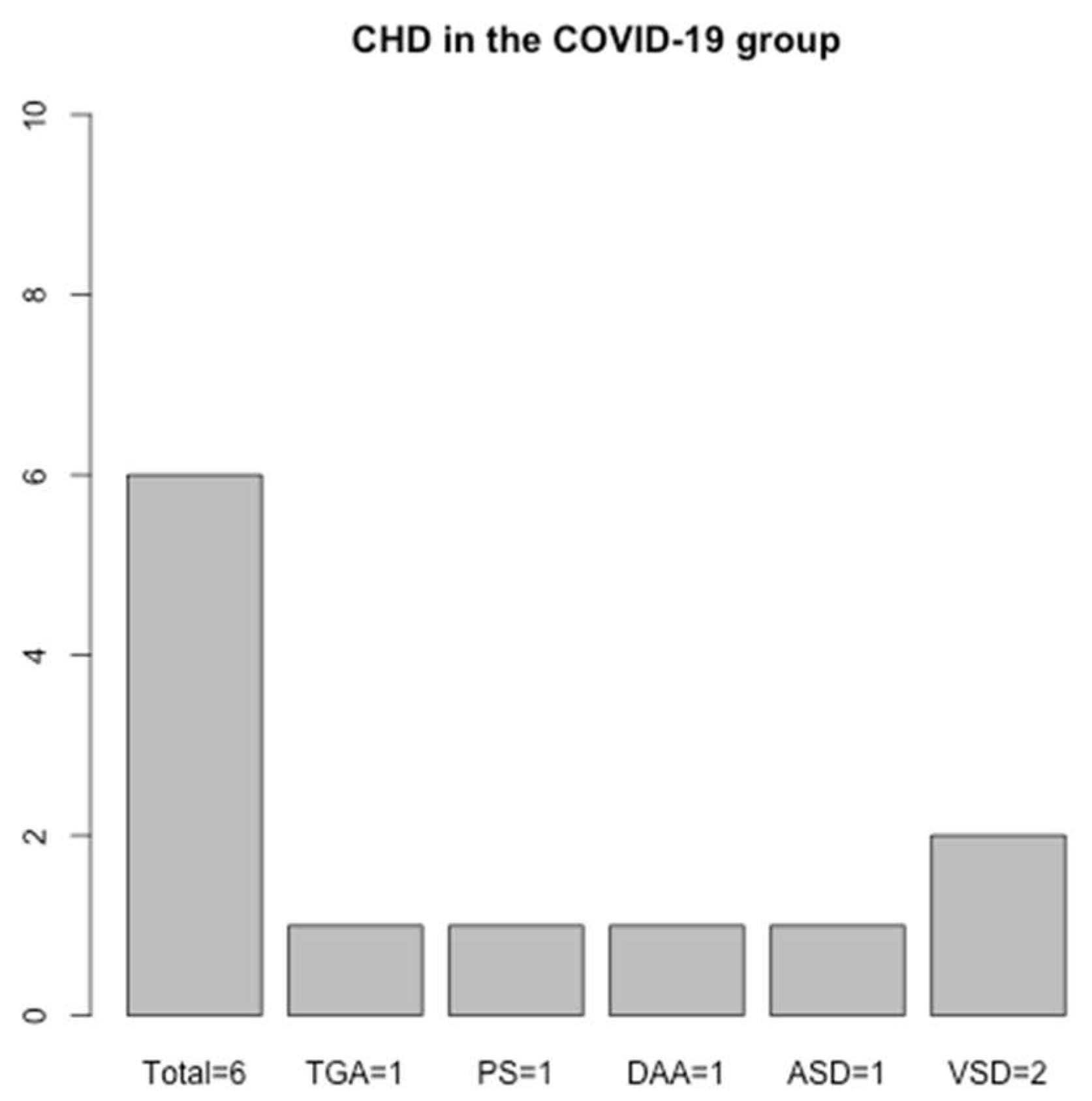
). As for congenital heart malformations, only 1 occurred in the control group (0,5%), 2 in the vaccine group (2,2%) and 6 in the COVID-19 group (3,6%). Although the number of CHD is greater than other groups, no statistical difference was found (p=0.07
), as seen in
Table 1. A detailed graphic of the CHDs found in the COVID-19 group can be observed in
Figure 1. It is necessary here to specify that for transposition of the great arteries, pulmonary stenosis and double aortic arch, the SARS-CoV-2 infection occurred during the first trimester of pregnancy, while for atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect cases, the infection was acquired during the second trimester. Three patients from the CHD group came from in vitro fertilization pregnancies.
Cerebral ultrasonography detected several anomalies, from intraventricular hemorrhage (grade 1, 2 and 3), to hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (grade 1, 2 and 3), choroid plexus cysts, severe ventriculomegaly and cerebral infarction. The most prevalent abnormality was represented by grade 1 intraventricular hemorrhage and grade 1 hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy for all groups.
Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) grade 1 appeared as the most frequent type of lesion, with 24 cases (14%) in the COVID-19 group, 12 cases in the control group (6%) and only 3 in the vaccine group (3,3%), making a difference among ultrasonographic changes for those born from SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy (p<0.002). Grade 2 and grade 3 IVH were not that common, with 3 findings among the COVID-19 lot (1,8%) for grade 2 and 1 (0,6%) for grade 3 and almost none for the other groups.
For the hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) injury, the differences were with greater disparities. We determined statistically significant data for grade 1 HIE patients: 35 within the COVID-19 lot (21%) versus 12 in the control group (6%) and 2 in the vaccine group (2,2%), resulting in a p-value of <0.001, demonstrating how the infection during the gestational period can induce bleeding disorders (
Table 2).
HIE grade 2 and 3 between groups did not have such a great difference, with fewer cases and no statistical relevance.
Other cerebral abnormalities found consisted of choroid plexus cyst, with 6 cases in the COVID-19 group (3,6%), more than the vaccine group (1,1%), or the control group (0,5%). Severe ventriculomegaly was observed in 2 situations only, 1 of the COVID-19 group patients (0,6%) and 1 of the vaccine group (1,1%). Cerebral infarction was solely seen in a COVID-19 group patient (0,6%).
In
Table 2, COVID-19 group comprised the most cerebral ultrasonographic anomalies, with only 98 normal examinations (59%), compared to the vaccine group (88%) or the control group (85%), suggestive for a greater risk of unfavorable neonatal outcome in cases with SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy (p<0.001).
Abdominal ultrasonography observed a number of anomalies, such as unilateral and bilateral hydronephrosis, kidney duplication, megaureter, pyeloureteral duplication, horseshoe kidney and septate gallbladder.
The most common finding among the COVID-19 group of patients was grade 1 unilateral hydronephrosis, with 27 cases (16%), compared to the vaccine group with only 3 cases (3,3%) and the control group with almost a third, 11 cases (5,5%), suggesting a possible connection between SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy and the fetal and neonatal kidney (p<0.001), as shown in
Table 3.
Grade 2 and 3 unilateral hydronephrosis were seen in much smaller numbers in all groups, accounting for 1 case in the COVID-19 group (0,6%) for grade 2 and 4 cases (2,4%) for grade 3 versus 2 cases for the vaccine group (2,2%) and 2 for the control group (1%) for grade 2 and no cases for unilateral grade 3 hydronephrosis.
Bilateral hydronephrosis, other kidney anomalies and septate gallbladder were seen in small numbers for each group, but altogether the COVID-19 group had the higher incidence for all of the above. As a consequence, only 124 patients (74%) of the COVID-19 group had normal abdominal ultrasonographic exams, compared to the vaccine group with 82 (90%) and the control group with 183 normal investigations (92%), suggesting a possible correlation between maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection during the gestational period and the neonatal abnormalities identified (p<0.001).
Backward binomial logistic regression model was performed to assess whether gestational age, APGAR score, birthweight and maternal age could have an impact on ultrasonographic findings. No statistical significance was found (F-statistic: 2.366, p-value: 0.2118).
For our study population, all patients were tested for hearing impairment using otoacoustic emissions along with auditory brainstem response (EOAE-ABR) screening. None of the COVID-19 group and vaccine group presented a negative test result. Only 4 patients from the control group had a REFER after the first examination and a positive test during the repeated examination after several weeks of life, indicating no effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy or vaccination on the ability to hear.
All patients underwent eye examination, and were investigated by our ophthalmologist specialized in neonatal indirect ophthalmoscopy. The study found no anomalies in neonates from SARS-CoV-2 infected mothers during pregnancy compared to the other assessed groups, suggesting infection during the gestational period has no effect on eye abnormalities.
4. Discussion
One of the first hypotheses tested during this study was how COVID-19 disease during pregnancy can impact the fetal heart. Due to the fact that SARS-CoV-2 is considered to have a teratogenic effect if acquired during the first trimester of pregnancy, presumably as a consequence of fever, congenital anomalies were investigated [
7]. Goncu et al. showed that the fetal heart does not seem to be negatively affected by moderate COVID-19 after recovery [
9]. Our research shows that even though 6 congenital heart diseases (CHDs) occurred in the COVID-19 group, 2 in the vaccine group and 1 in the control group, the normal ultrasonographic examination revealed no significant difference between lots (p=0.3). Goldshtein et al. investigated whether the vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 could be associated with congenital heart disease, compared to the control group. Therefore, the risk of any congenital malformations was nonsignificantly different with RR = 0.69 (95% CI, 0.44-1.04), as well as for heart malformations with RR = 0.75 (95% CI, 0.43-1.26). The risk for major heart malformations was lower among the exposed group with RR = 0.46 (95% CI, 0.24-0.82) [
6]. The study conducted by Murat et al. did not observe any neurologic and cardiologic teratogenic effects associated with COVID-19 infection during pregnancy [
10].
Goldshtrom et al. describes the cases of seven neonates with complex congenital heart and lung malformations born to women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. Notably, of the seven, three women were asymptomatic during their hospital course and denied prior history of COVID-19 symptoms [
11].
Three of the 9 congenital heart disease patients came from in vitro fertilization pregnancies, indicating a strong possibility for the assisted reproductive technologies to be the main reason for this outcome, as suggested by literature [
12].
Patent foramen ovale was seen in all three groups, but from our perspective, the reason for its apparition can mainly be attributed to the examination being done within the first 24 to 96 hours of life, although Douarte et al. similarly observed that the findings in the transthoracic echocardiogram, performed in 36 newborns, were: patent foramen ovale (69.4%), atrial septal defect (27.7%), and ventricular septal defect (2.7%) [
13]. In a study that investigated fetal tissues and their ACE-2 receptors, it was reported that fetal heart tissue does not express ACE-2 receptors which is a gate for SARS-CoV-2 to the cell entrance. Therefore, fetal heart seems not to be an exact target for SARS-CoV-2 [
14]. Another study showed that none of the newborns from SARS-CoV-2 infected mothers developed cardiac dysfunction, (myocarditis, cardiomyopathy) and that structural abnormalities (ventricular septal defect, arch hypoplasia) were not considered to be related to COVID-19 [
15].
According to the literature, SARS-CoV-2 disease during pregnancy is not characterized by differential prenatal brain growth patterns and cortical development at least in women with mild symptoms [
16]. Likewise, one study revealed, that even though perinatal hypoxic-ischemic event was more common in the group with severe COVID-19 course (p<0.01), there were no differences between the group with mild COVID-19 course and the control group in terms of perinatal outcomes [
17]. In our lot, hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy grade 1 was the most frequent apparition in the COVID-19 group versus vaccine or control group (p<0.001). On the contrary, another paper stated that hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, transient tachypnea, meconium aspiration, pneumonia, sepsis, and hypoglycemia also did not differ significantly between the 2 groups (infants of SARS-CoV-2–positive women versus infants of comparator women) [
18].
We identified one case of severe ventriculomegaly in the COVID-19 group and one in the vaccine group. Archuleta et al. described two cases of severe ventriculomegaly, neurological dysfunction, and seizures which were found in neonates with prenatal exposure to COVID-19 infection during the first and third trimesters of pregnancy [
19]. Blakeway et al. described 3 fetal abnormalities in women who received COVID-19 vaccination: spina bifida, ventriculomegaly, and hydronephrosis. The spina bifida case was diagnosed before the pregnant woman received the first dose of the vaccine. The ventriculomegaly case was diagnosed at 37 weeks’ gestation and was isolated, with no associated brain abnormalities, as confirmed by fetal brain magnetic resonance imaging. The hydronephrosis was mild, with no associated abnormality at birth [
20].
In a study by Kurokawa et al., a total of 90 neonates, including two pairs of twins, and their 88 mothers with confirmed COVID-19, were included in the analysis. The neonates were divided into Sym-M-N (n ¼ 34; M:F ¼ 20:14) and Asym-M-N groups (n ¼ 56; M:F ¼ 30:26). The most common imaging feature was intracranial hemorrhage (germinal matrix hemorrhage, n ¼ 2 [22.2%]; parenchymal hemorrhage, n ¼ 2 [22.2%]; intraventricular hemorrhage, n ¼ 1 [11.1%]), followed by hypoxic brain injury (diffuse white matter and magnetic resonance spectroscopy abnormalities) [
21]. Duarte et al. described that among the 35 newborns who underwent cranial ultrasound, the following results were observed: no abnormal findings (71.0%), grade I or II periventricular hemorrhage (22.0%), ventricular dilatation (2.8%), and linear calcifications (2.8%) [
13]. Our findings revealed a high prevalence of grade 1 intraventricular hemorrhage in the COVID-19 group compared to the vaccine and control group (p=0.002).
A small case report described 2 neonates born to SARS-CoV-2 positive mothers, who displayed early-onset (day 1) seizures, acquired microcephaly, and significant developmental delay over time. Sequential MRI showed severe parenchymal atrophy and cystic encephalomalacia [
22].
A possible consequence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is the development of an exacerbated thrombophilic status, and cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is a rare but possible complication of SARS-CoV-2 infection reported both in adults and in children. Campi et al. presented a case report that described the clinical course of a term neonate showing extended CVT of unclear origin, whose mother had developed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the third trimester of pregnancy [
23]. Our study found 1 (0,6%) case of cerebral infarction and 6 (3,6%) cases of choroid plexus cysts, probably suggesting intrauterine coagulation disorders.
Another paper, including 201 born to mothers exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection and 18 from unexposed controls, performed a neuroimaging evaluation at 6 months of adjusted chronological age and revealed 18 grayscale and 21 Doppler abnormalities. Predominant findings were hyperechogenicity of deep brain white matter and basal ganglia (caudate nuclei/thalamus) and a reduction in the resistance and pulsatility indices of intracranial arterial flow [
24].
COVID-19 has been known as a respiratory disease, mainly pneumonia. In addition to affecting the respiratory tract and lungs, the disease can cause thrombogenic ischemia in various parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal tract [
25].
In our study, the most important renal anomaly found in the COVID-19 group was unilateral grade 1 hydronephrosis, with 27 (16%) cases, compared to the vaccine or control group (p<0.001). To our knowledge, no studies correlating SARS-CoV-2 intrauterine infection and neonatal hydronephrosis were published so far. In a paper published by He et al., both cystatin C and β2-microglobulin were increased in all included newborns, which was not reported in previous studies. Their study indicates that confirmed COVID-19 in pregnant women may lead to fetal kidney damage. [
26]
Out of 33 female and 32 male infants born to 64 pregnant women, one being a twin birth, included in the study, eleven infants failed the standard "Auditory Brainstem Response" (ABR) hearing screening test, so a second test was performed. Only two infants required further investigation after the second test [
10]. Similarly, our paper shows no effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy on hearing impairment.
Morhart et al. described 27 newborns of women who had acquired a SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy. One of these women delivered a boy with a severe eye malformation. Her newborn son was later diagnosed with unilateral microphthalmia, microcornea, and hypoplasia of both the optic nerve and the neurosensory retina. Similar eye abnormalities, uni- or bilaterally, are seen in neonates with rubella embryopathy [
27]. In our study, no eye anomalies were detected from the COVID-19 group, nor the other comparative groups.
Our study’s limitations refer to time constraints, due to the fact that not all patients came back for a second ultrasonographic evaluation so no conclusion could be drawn regarding the long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 or vaccination, respectively.
5. Conclusions
Our study aimed to compare the effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy with COVID-19 vaccination and normal pregnancies on the neonatal brain, heart and kidney using ultrasonographic examinations during the first 4 days after birth, together with auditory screening and ophthalmologic evaluation. The main findings were that the fetal heart does not seem to be negatively affected, although 6 cardiac malformations were found in the COVID-19 group, no correlation was made compared to the vaccine and control group. Grade 1 intraventricular hemorrhage and hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy were the most prevalent among neonates from mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection (p=0.002 and p<0.001, respectively). The kidney anomaly found to be most frequent in this group was grade 1 unilateral hydronephrosis (p<0.001). COVID-19 disease during the gestational period had no effect on the auditory or visual function. Time constraints are one of our study’s limitations mainly because not all patients returned for a second ultrasonographic evaluation, making it impossible to draw conclusions about the long-term effects of either the vaccination or SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy. Despite the fact that our observations are relevant, further studies investigating the effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy and the neonatal outcome are necessary.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.E.P. and A.M.C.J.; methodology, D.E.P. and D.Ș.; software, A.M.C.J.; validation, D.E.P., F.G. and C.C.; formal analysis, D.E.P. and A.M.C.J.; investigation, D.Ș., A.C. and F.S.; resources, D.E.P.; data curation, A.M.C.J.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.C.J.; writing—review and editing, D.E.P.; visualization, S.Ș.; supervision, M.B.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Première Hospital’s Ethics Commission Board (No. 330/18.11.2021), as well as by the Ethics Committee of Scientific Research of “Victor Babeș” University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timișoara (No. 76/2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rasmussen, S.A.; Smulian, J.C.; Lednicky, J.A.; Wen, T.S.; Jamieson, D.J. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Pregnancy: What Obstetricians Need to Know. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2020, 222, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntley, B.J.F.; Mulder, I.A.; Di Mascio, D.; Vintzileos, W.S.; Vintzileos, A.M.; Berghella, V.; Chauhan, S.P. Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes Among Individuals With and Without Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Obstet Gynecol 2021, 137, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.Y.; Mok, T.; Cambou, M.C.; Fuller, T.; Fajardo, V.M.; Kerin, T.; Han, C.S.; Nielsen-Saines, K.; Rao, R. Can Prenatal Ultrasound Predict Adverse Neonatal Outcomes in SARS-CoV-2–Affected Pregnancies? American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology MFM 2023, 5, 101028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Case Report: Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy & Pneumonia in a Neonate after SARS-CoV-2 Intrauterine Transmission - IOS Press. Available online: https://content.iospress.com/articles/journal-of-neonatal-perinatal-medicine/npm221026 (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Abdelkader, M.A.; Abbas, H.M.; Aboelkhair, I.M.; Alafify, A.S.A.; Elgazzar, B.A.; Koura, M.S.E.-D. Congenital Heart Disease in a Patient with COVID-19 Infection during Early Pregnancy: A Case Report. Egypt Heart J 2022, 74, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshtein, I.; Steinberg, D.M.; Kuint, J.; Chodick, G.; Segal, Y.; Shapiro Ben David, S.; Ben-Tov, A. Association of BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccination During Pregnancy With Neonatal and Early Infant Outcomes. JAMA Pediatrics 2022, 176, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Díaz, S.; Smith, L.H.; Wyszynski, D.F.; Rasmussen, S.A. First Trimester COVID-19 and the Risk of Major Congenital Malformations–International Registry of Coronavirus Exposure in Pregnancy. Birth Defects Research 2022, 114, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolk, H.; Damase-Michel, C.; Morris, J.K.; Loane, M. COVID-19 in Pregnancy—What Study Designs Can We Use to Assess the Risk of Congenital Anomalies in Relation to COVID-19 Disease, Treatment and Vaccination? Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology 2022, 36, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncu Ayhan, S.; Turgut, E.; Ozden Tokalioglu, E.; Oluklu, D.; Sakcak, B.; Uyan Hendem, D.; Tanacan, A.; Moraloglu Tekin, O.; Sahin, D. Post-COVID-19 Fetal Cardiac Evaluation in Moderate Infection Group of Pregnant Women. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound 2022, 50, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBSCOhost | 158903137 | Evaluation of Neurological and Cardiac Development of Newborn Infants Born to Mothers Infected with COVID-19. Available online: https://web.s.ebscohost.com/abstract?direct=true&profile=ehost&scope=site&authtype=crawler&jrnl=26022079&AN=158903137&h=MkgOw9y5xTlWIX%2b%2b0n4LfiK%2bW99CBPNj8L86QC3snuL%2bXRhv3%2fDCqj3sMbxKgne7Jgn%2bQo2IG1XRVG%2faHaIoXA%3d%3d&crl=c&resultNs=AdminWebAuth&resultLocal=ErrCrlNotAuth&crlhashurl=login.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26profile%3dehost%26scope%3dsite%26authtype%3dcrawler%26jrnl%3d26022079%26AN%3d158903137 (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Neonates With Complex Cardiac Malformation and Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Born to SARS-CoV-2 Positive Women—A Single Center Experience - Nimrod Goldshtrom, Diana Vargas, Angelica Vasquez, Faith Kim, Kinjal Desai, Mariel E. Turner, Oliver Barry, Alejandro Torres, Stéphanie Levasseur, Svetlana Strletsova, Palka R. Gupta, Jennifer R. Defazio, Vincent Duron, William Middlesworth, Lisa Saiman, Russell Miller, Dena Goffman, Emile A. Bacha, David Kalfa, Damien J. LaPar, Ganga Krishnamurthy, 2020. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2150135120950256 (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Roșca, I.; Turenschi, A.; Raris-Denisa, A.; Popescu, D.-E.; Stoica, C.; Carp, A.; Jura, A.-M.-C.; Constantin, A.T. Association of Assisted Reproductive Technology with the Risk of Congenital Heart Defects: A 5-Year Retrospective Study – Experience from a Tertiary Maternity Hospital in Bucharest. 2023.
- Duarte, B. de P.; Krebs, V.L.J.; Calil, V.M.L.T.; Carvalho, W.B. de; Gibelli, M.A.B.C.; Francisco, R.P.V. Clinical Characteristics and Evolution of 71 Neonates Born to Mothers with COVID-19 at a Tertiary Center in Brazil. Clinics 2023, 77, 100136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, E.; Sakcak, B.; Uyan Hendem, D.; Oluklu, D.; Goncu Ayhan, S.; Sahin, D. Decreased Fetal Cardiac Output in Pregnant Women with Severe SARS-Cov-2 Infection. Echocardiography 2022, 39, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, L.G.; Riskin, A.; Sharkansky, L. EP32.12: The Impact of Maternal COVID-19 during Pregnancy on the Fetal Heart: Does It Cause Subclinical Postnatal Echocardiographic Myocardial Dysfunction? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2022, 60, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mappa, I.; Pietrolucci, M.E.; Pavjola, M.; Maruotti, G.; D’Antonio, F.; Rizzo, G. Fetal Brain Biometry and Cortical Development after Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnancy: A Prospective Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound 2023, 51, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turdybekova, Y.G.; Kopobayeva, I.L.; Kamyshanskiy, Y.K.; Turmukhambetova, A.A. Comparative Clinical and Placental Pathologic Characteristics in Pregnancies with and without SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 2023, 51, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, M.; Navér, L.; Söderling, J.; Ahlberg, M.; Hervius Askling, H.; Aronsson, B.; Byström, E.; Jonsson, J.; Sengpiel, V.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; et al. Association of Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnancy With Neonatal Outcomes. JAMA 2021, 325, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archuleta, C.; Wade, C.; Micetic, B.; Tian, A.; Mody, K. Maternal COVID-19 Infection and Possible Associated Adverse Neurological Fetal Outcomes, Two Case Reports. Am J Perinatol 2022, 39, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeway, H.; Prasad, S.; Kalafat, E.; Heath, P.T.; Ladhani, S.N.; Le Doare, K.; Magee, L.A.; O’Brien, P.; Rezvani, A.; von Dadelszen, P.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccination during Pregnancy: Coverage and Safety. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2022, 226, 236–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, M.; Kurokawa, R.; Lin, A.Y.; Capizzano, A.A.; Baba, A.; Kim, J.; Johnson, T.D.; Srinivasan, A.; Moritani, T. Neurological and Neuroradiological Manifestations in Neonates Born to Mothers With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Pediatric Neurology 2023, 141, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benny, M.; Bandstra, E.S.; Saad, A.G.; Lopez-Alberola, R.; Saigal, G.; Paidas, M.J.; Jayakumar, A.R.; Duara, S. Maternal SARS-CoV-2, Placental Changes and Brain Injury in 2 Neonates. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022058271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neonatal Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Following Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnancy | Neonatology | Karger Publishers Available online:. Available online: https://karger.com/neo/article/119/2/268/828749 (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Alves de Araujo Junior, D.; Motta, F.; Fernandes, G.M.; Castro, M.E.C.D.; Sasaki, L.M.P.; Luna, L.P.; Rodrigues, T.S.; Kurizky, P.S.; Soares, A.A.D.S.M.; Nobrega, O.deT.; et al. Neuroimaging Assessment of Pediatric Cerebral Changes Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection during Pregnancy. Frontiers in Pediatrics 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerçel, G.; Anadolulu, A.İ. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia in a Newborn with COVID-19: A Case Report. International Journal of Surgery Case Reports 2022, 98, 107548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Huang, X.; Lei, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, D. Vertical Transmission and Kidney Damage in Newborns Whose Mothers Had Coronavirus Disease 2019 during Pregnancy. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2021, 57, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morhart, P.; Mardin, C.; Rauh, M.; Jüngert, J.; Hammersen, J.; Kehl, S.; Schuh, W.; Maier-Wohlfart, S.; Hermes, K.; Neubert, A.; et al. Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection during Pregnancy: Possible Impact on the Infant. Eur J Pediatr 2022, 181, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).