Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Anti-fatigue herbals
3.1. Rhodiola rosea L. (Crassulaceae)
3.2. Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze (Theaceae)
3.3. Panax ginseng C.A. MEYER (Araliaceae)
4. Secondary metabolites with anti-fatigue properties
4.1. Phenolics compounds
4.2. Terpenoids
4.3. Alkaloid
5. Primary metabolites with sports endurance property
5.1. Protein
5.2. Polysaccharides
| Class | Molecule | Subjects | Exercises Tests | Doses et duration of administration | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| steroidal glycoside |
Ginsenoside | sedentary Individuals | Aerobic exercises and muscle strengthening. | 100mg/j and 500mg/j 12 weeks |
ꜛVO2max ꜛmuscle strength |
[42] |
| Ginsenoside-Rg1 | Rats | Exhaustive swimming | 0.1 mg/kg bodyweight per day for 10-week. | ꜛantioxidant defense system in skeletal muscle ꜜmembrane lipid peroxidation | [108] | |
| 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol | Mice | Weight-loaded wimming and rota-rod tests | 5 and 10 mg/kg | ꜛriding time in the rota-rod test, inhibiting corticosterone, lactate, and creatinine levels. | [49] | |
| 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 |
Mice | Forced swimming tests | 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg once a day lasting for 28 days | ꜛexhaustive exercise time, ꜜdecreased blood lactic acid, serum urea nitrogen levels, ꜛGLU, SOD, glutathione peroxidase and catalase in liver and muscle, ꜜMDA levels | [95] | |
| Alkaloid |
Capsaicin | Male ICR mice | Forelimb grip strength, exhaustive swimming | 4 weeks at 0, 205, 410, and 1025 mg/kg/day | ꜜserum lactate, ammonia, BUN and CK levels ꜛglucose concentration |
[109] |
| Caffeine C + ephedrine E | Athletes | Cycling exercise | C (5 mg / kg), E (1 mg / kg), C+E |
ꜛexercise time to exhaustion and central nervous system stimulation. | [110] | |
| Flavonoid |
Eleutheroside | Mice | load-weighted swimming test, sleep deprivation test | 500 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg | Relief of physical and mental fatigue | [51] |
| Resvératrol | Mice | forelimb grip strength, exhaustive swimming | 25 mg/kg mice/day for 28 consecutive days | Improved muscle strength and endurance |
[111] | |
| Resveratrol | Male ICR mice | forelimb grip strength, exhaustive swimming time |
0, 25, 50, and 125 mg/kg/day 21 days | ꜛexhaustive swimming time and grip strength, CK activity and glucose levels ꜜserum lactate, ammonia levels |
[92] | |
| (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate | mice | forced swimming exercise | 50, 100, and 200 mg/ kg by oral gavage for 28 days. | ꜛexhaustive swimming time, glycogen contents, antioxydant activities. ꜜlevels of blood lactic acid, serum urea nitrogen, serum CK and MDA |
[9] | |
| Glabridin | Male mice | swimming exhaustive exercise | 5, 10, 20 mg/kg) for 28 consecutive days | inhibited fatigue, delayed the elevation of blood lactic acid and increase storage of liver and muscle glycogen | [57] | |
| Vitamin | vitamin C supplementation | healthy endurance trained males | single bout of endurance exercise (2.5 h cycling exercise in man) | 2 weeks of supplementation with vitamin C, 1,000 mg /day | ꜛantioxidant defence, modulating the leukocytosis and neutrophilia responses | [56] |
| Amino acid | Aspartate and Asparagine | Wistar rats | exercised to exhaustion by swimming | 350 mM ASP + 400 mM ASG day–1 for 7 days | ꜛexercise time ꜜblood lactate concentration |
[102] |
| Amino acid | γ-aminobutyric acid | Mice | loaded-swimming test | 0.15, 0.3, 0.9 g/kg GABA/animal weight, | ꜛ swimming time |
[112] |
| Amino acid | L-Citrulline | Athletes | maximum effort test in a cycloergometer | reduce the recovery heart rate and muscle soreness after 24 h. | [83] |
| Substance | Subjects | Exercises Tests | Doses | Results | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panax quinquefolium proteins | mice | Forced swimming test | 125, 250 and 500 mg/kg of body weight for 28 days | ꜛswimming ability, ꜛGLU levels ꜜaccumulation of BLA and SUN, |
[66] |
| Ginseng polysaccharides | mice | Forced swim test | 15 days | ꜛanti-fatigue activity | [45] |
| Polysaccharides from Portulaca oleracea L. | mice, | Rotarod test, Forced swimming test | 75 /150and 300 mg/kg bw duringg 30 days |
ꜛGLU contents, ꜜblood lactic acid and serum urea nitrogen level | [17] |
| Taraxacum officinale extract | male | Forced swimming test | 10, 30 and 100mg/kg b.w for a period of 42 days. | ꜛswimming capacity, ꜜlactate and triglyceride concentrations | [11] |
| Extract of Rubus coreanus fruit | Mice | Forced swimming test | (500 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks | ꜛforced swimming capacity of mice ,ꜜplasma ammonia accumulation | [76] |
| Extract of Toona sinensis Roemor | Mice | Swimming test | 40, 80 and 160 mg/kg) for 21 days | ꜛswimming time of the mice, ꜜlactic acid,ꜛliver and muscle GLU, ꜜoxidative stress. | [79] |
| Extract of saponins of Radix notoginseng | Mice | Swimming test | 20, 40 and 80 mg/kg body weight/day for 28 days | ꜛexhaustive swimming time , ꜜlactate in the blood, ꜛtissue glycogen contents | [72] |
| Extract of Siraitia grosvenorii Fruits | Mice | Swimming test | 100, 200 and 400 mg/Kg bw/day for 28 days. | ꜛswimming time,liver muscle glycogen , ꜜBLA, SUN | [78] |
| Extract of Acanthopanax senticosus. | Mice | forced swimming test | 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg | ꜛtissue glycogen contents ꜜ BLA, SUN contents |
[52] |
| Triterpenoid-Rich Extract from Antrodia camphorata | Mice | Swimming test. | 0, 50, and 200 mg/kg/day | ꜛexhaustive swimming time, tissue GLU contents and activity of enzymes, ꜜBLA, BUN | [54] |
| Pentacyclic triterpenoid from Bambusa tuldoides Munro | Mice | weight-loaded swimming test and climbing test | 0.04; 0.08 and 0.25 g/kg body weight | ꜛswim time, blood glucose, muscular and hepatic GLU levels, ꜜplasma lactate and ammonia levels and CK activity | [56] |
| Antrodia camphorata and Panax ginseng extract | Mice | swimming test forelimb grip | orally administered for 4 weeks at 0.984, 2.952 and 5.904 g/kg/day. | ꜜlactate, ammonia, BUN and CK activity, ꜛexhaustive swimming time and forelimb grip strength | [48] |
| Beetroot Juice | young men | Wingate and jump tests | 70 mL of BJ (containing 6.4 mmol of NO3−) | Ergogenic effect in a 30-s all-out Wingate test increasing Wpeak, | [15] |
| watermelon juice | seven athletes | maximum effort test in a cycloergometer | 500 mL of natural watermelon juice (1.17 g of L-citrulline) | helped to reduce the recovery heart rate and muscle soreness after 24 h. | [83] |
| Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) | Mice | Exhaustive Swimming Time of Mice | 60, 120 and 240 mg/kg body weight every day for 28 days | ꜛexhaustive swimming time, tissue GLU contents and the activities of antioxidant enzymes, ꜜBLA, BUN | [62] |
| Astragali Radix and Angelicae Sinensis Radix | Mice | weight-loaded and forced swimming | 21.64 ;10.82 and 5.41 g/kg bw daily for 15 days | ꜜlevels of BLA and BUN ꜛ SOD. |
[113] |
| Tea seed oil (Camellia oleifera Abel) | Mice | weight-Loaded Forced Swimming | 0.5 ,1.0, 2.0 g/kg/day At 0 week, 2 weeks and 4 weeks | anti-fatigue effects; improve the effects much better on BUN and hepatic GLU | [10] |
| Eriobotrya japonica extract | Mice | Exhaustive Swimming | 1 g kg-1 per day for 14 days | Enhancing utilization of fatty acid, facilitating lipid catabolism, and ꜛ antioxidant capability. |
[61] |
|
Irpex lacteus extract |
Mice. | swim test, rotating rod and running test. | 0.04, 0.2 and 1.0g/kg Seven-day | increased the level of super oxide dismutase reduced the level of malondialdehyde in the liver | [114] |
| Extract of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. | rat | weight loaded forced swim test |
10 mg/kg of bw/per day) for a period of two weeks. | Ameliorating various impairments associated with physical fatigue. | [80] |
| Extract of Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze | mice | swimming test | 125, 250; 500 mg/kg/day for 28 days |
ꜛswimming time, hepatic GLU muscle glycogen levels, ꜜtriglyceride, ammonia levels | [53] |
| Extract of Cistanche deserticola | Mice | forced swimming test | 0.25, 0.50, 1.00 g/kg administered orally to mice for 3 weeks. | ꜛswimming capacity of mice, ꜜmuscle damage, ꜜlactic acid, ꜛenergy storage | [59] |
| Extract of Allium sativum L. | rats | Endurance exercise | 2.86 g/kg 30 min before every exercise for 4 weeks | ꜜ levels of NO metabolites, ꜛSDH and SOD activities, | [8] |
| γ-aminobutyric acid from Morus alba L. leaves | Mice | -swimming test | 0.15, 0.3, 0.9 g/kg GABA/animal weight, | Increase swimming time |
[112] |
| vitamin and mineral supplement + guarana | young adults ( | Cognitive Demand Battery | 200 mg/day, and 400 mg/day | Improved cognitive performance and mental fatigue | [115] |
| creatine + guarana | athletes | test of six maximal sprints | creatine (1000 mg) + guarana (1500 mg) | Beneficial effect on muscle power and decisional cognitive performance | [116] |
6. Methodology used for anti-fatigue phyto molecules identification
7. Antioxidant, immune system and sports activities
7.1. Exercise and the antioxidant system
7.2. Exercise and immune system
8. Method and technique for evaluating sport performance
8.1. Measurement of variables related to physical capacities
8.1.1. Non-human Animal model
- -
- Forced swim
- -
- Rotarod test
- -
- Treadmill test
- -
- Tail suspension test
- -
- Forelimb Grip Strength Test
- -
- Open field test
- -
- Hole-board test
8.1.2. Human Animal model test
8.2. Evaluation of biochemical parameters
9. Toxicity of doping molecules and herbal
10. Conclusions
References
- Yesalis CE, Bahrke MS. Histoire du dopage dans le sport. 2002;24.
- Bouaziz W, Vogel T, Schmitt E, Kaltenbach G, Geny B, Lang PO. Bénéfices de l’activité physique en endurance chez les seniors âgés de 70 ans ou plus : une revue systématique. La Presse Médicale. 2017 Sep;46(9):794–807.
- Law J, Pennington CG. Physical Activity for Individuals with Cerebral Palsy. Int J Phys Educ Fit Sports. 2021 Jun 21;73–9. [CrossRef]
- Cazassus N, Cugy E. Impact de l’activité physique sur la fatigue. 2019 [cited 2023 Jul 27]; Available from: https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.33549.28642.
- Bagchi D, Nair S, Sen CK, editors. Nutrition and enhanced sports performance: muscle building, endurance, and strength. Amsterdam ; Boston: Elsevier/AP, Academic Press is an imprint of Elsevier; 2013. 540 p.
- Barnard N, Goldman D, Loomis J, Kahleova H, Levin S, Neabore S, Batts T. Plant-Based Diets for Cardiovascular Safety and Performance in Endurance Sports. Nutrients. 2019 Jan 10;11(1):130. [CrossRef]
- Światowy WJ, Drzewiecka H, Kliber M, Sąsiadek M, Karpiński P, Pławski A, Jagodziński PP. Physical Activity and DNA Methylation in Humans. IJMS. 2021 Nov 30;22(23):12989. [CrossRef]
- Morihara N, Ushijima M, Kashimoto N, Sumioka I, Nishihama T, Hayama M, Takeda H. Aged Garlic Extract Ameliorates Physical Fatigue. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 2006;29(5):962–6. [CrossRef]
- Teng Y song, Wu D. Anti-fatigue effect of green tea polyphenols (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG). Phcog Mag. 2017;13(50):326.
- Hu L, Fang X, Du M, Zhang J. Anti-Fatigue Effect of Blended <i>Camellia oleifera Abel</i> Tea Oil and Ge-132 in Mice. FNS. 2015;06(15):1479–87.
- Jinchun Z, Jie C. The effects of taraxacum officinale extracts (toe) supplementation on physical fatigue in mice. Afr J Trad Compl Alt Med [Internet]. 2011 Jan 17 [cited 2023 Jun 29];8(2). Available from: http://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajtcam/article/view/63198.
- Luo X, Liu W, Zhong H, Yan Y, Feng F, Zhao M. Synergistic effect of combined oyster peptide and ginseng extracts on anti-exercise-fatigue and promotion of sexual interest activity in male ICR mice. Journal of Functional Foods. 2021 Nov;86:104700. [CrossRef]
- Morana C, Perrey S. ÉVALUATION DE LA FATIGUE MUSCULAIRE. 2009.
- Chabib L, Trianloka AMB, Hidayat AUMJ, Awaluddin R, Firmansyah F. Potential Tropical Fruits to Aid Sports Performance and its Prospect to be Developed into Nano supplement. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci. 2020 Mar 1;448(1):012019. [CrossRef]
- Cuenca E, Jodra P, Pérez-López A, González-Rodríguez L, Fernandes Da Silva S, Veiga-Herreros P, Domínguez R. Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Performance and Fatigue in a 30-s All-Out Sprint Exercise: A Randomized, Double-Blind Cross-Over Study. Nutrients. 2018 Sep 4;10(9):1222. [CrossRef]
- Megna M, Pamico A, Cristella G, Saggini R, Jirillo E, Ranieri M. Effects of Herbal Supplements on the Immune System in Relation to Exercise. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;25(1_suppl):43–9. [CrossRef]
- Xu Z, Shan Y. Anti-fatigue effects of polysaccharides extracted from Portulaca oleracea L. in mice. INDIAN J BIOCHEM BIOPHYS. 2014;51.
- Sellami M, Slimeni O, Pokrywka A, Kuvačić G, D Hayes L, Milic M, Padulo J. Herbal medicine for sports: a review. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2018 Jan 5;15(1):14.
- Zhang YD, Liu LY, Wang D, Yuan XL, Zheng Y, Wang Y. Isolation and identification of bioactive compounds from Antrodia camphorata against ESKAPE pathogens. Al-Judaibi AA, editor. PLoS ONE. 2023 Oct 27;18(10):e0293361. [CrossRef]
- Luo C, Xu X, Wei X, Feng W, Huang H, Liu H, Xu R, Lin J, Han L, Zhang D. Natural medicines for the treatment of fatigue: Bioactive components, pharmacology, and mechanisms. Pharmacological Research. 2019 Oct;148:104409. [CrossRef]
- Lu X, Chen J, Huang L, Ou Y, Wu J, Guo Z, Zheng B. The Anti-Fatigue Effect of Glycoprotein from Hairtail Fish (Trichiurus lepturus) on BALB/c Mice. Foods. 2023 Mar 14;12(6):1245. [CrossRef]
- Ma S, Ono M, Mizugaki A, Kato H, Miyashita M, Suzuki K. Cystine/Glutamine Mixture Supplementation Attenuated Fatigue during Endurance Exercise in Healthy Young Men by Enhancing Fatty Acid Utilization. Sports. 2022 Sep 27;10(10):147. [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan S, Chen Y, Saravanan D, Sundram KM, Yoga Latha L. Extraction, Isolation and Characterization of Bioactive Compounds from Plants’ Extracts. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2010 Oct 2;8(1):1–10.
- Williams M. Dietary Supplements and Sports Performance: Herbals. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2006 Jun 1;3(1):1.
- Chen CK, Muhamad AS, Ooi FK. Herbs in exercise and sports. J Physiol Anthropol. 2012 Dec;31(1):4. [CrossRef]
- Bucci LR. Selected herbals and human exercise performance. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2000 Aug;72(2):624S-636S. [CrossRef]
- Kpatcha T, Dosseh K, Idoh K, Agbonon A, Gbéassor M. EFFECT OF ADANSONIA DIGITATA L. ON PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE AND HAEMATOLOGICAL PARAMETERS IN RATS. 2016.
- Sama H, Traoré M, Guenné S, Séré I, Hilou A, Dicko MH. Ethnobotanical and Phytochemical Profiling of Medicinal Plants from Burkina Faso Used to Increase Physical Performance. Medicines. 2022 Jan 28;9(2):10. [CrossRef]
- Ouédraogo C, Guenné S, Bienvenu Somda M, Blanche M’Po SM, Sidibé I, Séré I, Roland Méda NT. Perceptions sur les Conduites Dopantes dans le Sport dans la Ville de Bobo-Dioulasso (Burkina Faso). ESJ. 2022 Jan 31;18(3):262.
- Ivanova Stojcheva E, Quintela JC. The Effectiveness of Rhodiola rosea L. Preparations in Alleviating Various Aspects of Life-Stress Symptoms and Stress-Induced Conditions—Encouraging Clinical Evidence. Molecules. 2022 Jun 17;27(12):3902.
- Cerulli C, Borrione P, Sabatini S. Effects of chronic rhodiola rosea supplementation on sport performance and antioxidant capacpitryeilnimItrinaCainreydrAemsuallets: A. PARISI 1, E. TRANCHITA 1, G. DURANTI 2, E. CIMINELLI 1, F. QUARANTA 1, R. CECI 2,. THE JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE AND PHYSICAL FITNESS. 2010;50(1).
- Kang DZ, Hong HD, Kim KI, Choi SY. Anti-Fatigue Effects of Fermented Rhodiola rosea Extract in Mice. JFN. 2015 Mar 31;20(1):38–42. [CrossRef]
- Lee FT, Kuo TY, Liou SY, Chien CT. Chronic Rhodiola rosea Extract Supplementation Enforces Exhaustive Swimming Tolerance. Am J Chin Med. 2009 Jan;37(03):557–72. [CrossRef]
- Jówko E, Sadowski J, Długołęcka B, Gierczuk D, Opaszowski B, Cieśliński I. Effects of Rhodiola rosea supplementation on mental performance, physical capacity, and oxidative stress biomarkers in healthy men. Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2018 Oct;7(4):473–80. [CrossRef]
- Williams TD, Langley HN, Roberson CC, Rogers RR, Ballmann CG. Effects of Short-Term Golden Root Extract (Rhodiola rosea) Supplementation on Resistance Exercise Performance. IJERPH. 2021 Jun 29;18(13):6953. [CrossRef]
- Noreen EE, Buckley JG, Lewis SL, Brandauer J, Stuempfle KJ. The Effects of an Acute Dose of Rhodiola rosea on Endurance Exercise Performance. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. 2013 Mar;27(3):839–47. [CrossRef]
- De Bock K, Eijnde BO, Ramaekers M, Hespel P. Acute Rhodiola Rosea Intake Can Improve Endurance Exercise Performance. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. 2004 Jun;14(3):298–307. [CrossRef]
- Shevtsov VA, Zholus BI, Shervarly VI, Vol’skij VB, Korovin YP, Khristich MP, Roslyakova NA, Wikman G. A randomized trial of two different doses of a SHR-5 Rhodiola rosea extract versus placebo and control of capacity for mental work. Phytomedicine. 2003 Jan;10(2–3):95–105.
- Liu C, Zhao H, Yan Y, Yang W, Chen S, Song G, Li X, Gu Y, Yun H, Li Y. Synergistic Effect of Rhodiola rosea and Caffeine Supplementation on the Improvement of Muscle Strength and Muscular Endurance: A Pilot Study for Rats, Resistance Exercise-Untrained and -Trained Volunteers. Nutrients. 2023 Jan 22;15(3):582.
- Liudong F, Feng Z, Daoxing S, Xiufang Q, Xiaolong F, Haipeng L. Evaluation of antioxidant properties and anti- fatigue effect of green tea polyphenols. Scientific Research and Essays. 2011;6(13):2624–9.
- Machado ÁS, Da Silva W, Souza MA, Carpes FP. Green Tea Extract Preserves Neuromuscular Activation and Muscle Damage Markers in Athletes Under Cumulative Fatigue. Front Physiol. 2018 Aug 17;9:1137. [CrossRef]
- Lee ES, Yang YJ, Lee JH, Yoon YS. Effect of high-dose ginsenoside complex (UG0712) supplementation on physical performance of healthy adults during a 12-week supervised exercise program: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Journal of Ginseng Research. 2018 Apr;42(2):192–8. [CrossRef]
- Mishra JN, Verma NK. An Overview on Panax ginseng. 2017;3(3).
- Valdés-González JA, Sánchez M, Moratilla-Rivera I, Iglesias I, Gómez-Serranillos MP. Immunomodulatory, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Ginseng: A Pharmacological Update. Molecules. 2023 May 3;28(9):3863. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Li S, Fan Y, Chen Y, Liu D, Cheng H, Gao X, Zhou Y. Anti-fatigue activity of the water-soluble polysaccharides isolated from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2010 Jul;130(2):421–3. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee I, Bandyopadhyay A. Effects of Acute Supplementation of Panax ginseng on Endurance Performance in Healthy Adult Males of Kolkata, India. IJCEP. 2020 Jul 7;7(2):63–8. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira ACCD, Perez AC, Prieto JG, Duarte IDG, Alvarez AI. Protection of Panax ginseng in injured muscles after eccentric exercise. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2005 Feb;97(2):211–4. [CrossRef]
- Hsiao CY, Hsu YJ, Tung YT, Lee MC, Huang CC, Hsieh CC. Effects of Antrodia camphorata and Panax ginseng supplementation on anti-fatigue properties in mice. The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science. 2018;80(2):284–91. [CrossRef]
- Oh HA, Kim DE, Choi HJ, Kim NJ, Kim DH. Anti-fatigue Effects of 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol and 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol in Mice. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 2015;38(9):1415–9. [CrossRef]
- Kulaputana O, Thanakomsirichot S, Anomasiri W. Ginseng Supplementation Does Not Change Lactate Threshold and Physical Performances in Physically Active Thai Men. 2007;90(6).
- Huang LZ, Huang BK, Ye Q, Qin LP. Bioactivity-guided fractionation for anti-fatigue property of Acanthopanax senticosus. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2011 Jan;133(1):213–9. [CrossRef]
- Zhang XL, Ren F, Huang W, Ding RT, Zhou QS, Liu XW. Anti-Fatigue Activity of Extracts of Stem Bark from Acanthopanax senticosus. Molecules. 2010 Dec 24;16(1):28–37. [CrossRef]
- Chen CS, Wang ML, Liu RH, Chen SP, Lu TM, Tsai WY, Huang CF, Yang CC, Tzeng YM. Anti-Fatigue Effect of Aqueous Extract of Anisomeles indica (L) Kuntze in Mice. Trop J Pharm Res. 2016 Apr 8;15(3):489. [CrossRef]
- Huang CC, Hsu MC, Huang WC, Yang HR, Hou CC. Triterpenoid-Rich Extract from Antrodia camphorata Improves Physical Fatigue and Exercise Performance in Mice. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2012;2012:1–8. [CrossRef]
- Miao X, Xiao B, Shui S, Yang J, Huang R, Dong J. Metabolomics analysis of serum reveals the effect of Danggui Buxue Tang on fatigued mice induced by exhausting physical exercise. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2018 Mar;151:301–9. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Yao X, Bao B, Zhang Y. Anti-fatigue activity of a triterpenoid-rich extract from Chinese bamboo shavings ( Caulis bamfusae in taeniam): Anti-fatigue activity of bamboo shavings. Phytother Res. 2006 Oct;20(10):872–6.
- Zhu J, Yi J, Kang Q, Huang J, Cui Y, Zhang G, Wang Z, Zhang L, Zheng Z, Lu J, Hao L. Anti-fatigue activity of hemp leaves water extract and the related biochemical changes in mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2021 Apr; 150:112054. [CrossRef]
- Peng F, Yin H, Du B, Niu K, Ren X, Yang Y. Anti-fatigue activity of purified flavonoids prepared from chestnut (Castanea mollissima) flower. Journal of Functional Foods. 2021 Apr; 79:104365. [CrossRef]
- Cai RL, Yang MH, Shi Y, Chen J, Li YC, Qi Y. Antifatigue activity of phenylethanoid-rich extract from Cistanche deserticola: Antifatigue activity of phenylethanoid-rich extract from c. deserticola. Phytother Res. 2010 Feb;24(2):313–5.
- Zhong L, Zhao L, Yang F, Yang W, Sun Y, Hu Q. Evaluation of anti-fatigue property of the extruded product of cereal grains mixed with Cordyceps militaris on mice. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017 Jan 3;14(1):15. [CrossRef]
- Jeong H, Kim OK, Park J, Kim K, Chung JW, Shim S, You Y, Jun W. Ethanol Extract of Eriobotrya japonica Leaves Enhanced Swimming Capacity in Mice. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research. 2017;5(6):413–7.
- Jin HM, Wei P. Anti-Fatigue Properties of Tartary Buckwheat Extracts in Mice. IJMS. 2011 Jul 25;12(8):4770–80. [CrossRef]
- Chen YJ, Baskaran R, Shibu MA, Lin WT. Anti-Fatigue and Exercise Performance Improvement Effect of Glossogyne tenuifolia Extract in Mice. Nutrients. 2022 Feb 27;14(5):1011. [CrossRef]
- Lamou B, Taiwe GS, Hamadou A, Abene, Houlray J, Atour MM, Tan PV. Antioxidant and Antifatigue Properties of the Aqueous Extract of Moringa oleifera in Rats Subjected to Forced Swimming Endurance Test. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2016; 2016:1–9.
- Chen H, He X, Liu Y, Li J, He Q, Zhang C, Wei B, Zhang Y, Wang J. Extraction, purification and anti-fatigue activity of γ-aminobutyric acid from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves. Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 8;6(1):18933.
- Qi B, Liu L, Zhang H, Zhou G xin, Wang S, Duan X zheng, Bai X yuan, Wang S ming, Zhao D qing. Anti-fatigue effects of proteins isolated from Panax quinquefolium. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2014 Apr;153(2):430–4.
- Hu M, Du J, Du L, Luo Q, Xiong J. Anti-fatigue activity of purified anthocyanins prepared from purple passion fruit (P. edulis Sim) epicarp in mice. Journal of Functional Foods. 2020 Feb; 65:103725. [CrossRef]
- Dorneles IMP, Fucks MB, Fontela PC, Frizzo MN, Winkelmann ER. Guarana (Paullinia cupana) presents a safe and effective anti-fatigue profile in patients with chronic kidney disease: A randomized, double-blind, three-arm, controlled clinical trial. Journal of Functional Foods. 2018 Dec; 51:1–7. [CrossRef]
- Chu H, Sun H, Yan GL, Zhang&Chang Liu AH, Dong H, Meng XC, Wang XJ, National TCM Key Lab of Serum Pharmacochemistry, Key Laboratory of Metabolomics and Chinmedomics, Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Heping Road 24, Harbin 150040, China. Metabolomics Analysis of Health Functions of Physalis Pubescens L. using by Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization Quadruple Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. World Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2015;1(3):9–20. [CrossRef]
- Ding X, Tang K, Lu P, Putheti R. Antifatigue effects of polydatin from Chinese herb Polygonum Cuspidatum in swimming mice. African Journal of Microbiology Research. 2009;3(7):358–61.
- D’Angelo S, Roberta R. L’impact de la supplémentation en grenade (punica granatum l.) sur la performance sportive. Sciences du sport. 2020;13.
- Yong-xin X, Jian-jun Z. Evaluation of anti-fatigue activity of total saponins of Radix notoginseng. INDIAN J MED RES. 2013.
- Shanely RA, Nieman DC, Zwetsloot KA, Knab AM, Imagita H, Luo B, Davis B, Zubeldia JM. Evaluation of Rhodiola rosea supplementation on skeletal muscle damage and inflammation in runners following a competitive marathon. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2014 Jul;39:204–10. [CrossRef]
- Spasov AA, Wikman GK, Mandrikov VB, Mironova IA, Neumoin VV. A double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of the stimulating and adaptogenic effect of Rhodiola rosea SHR-5 extract on the fatigue of students caused by stress during an examination period with a repeated low-dose regimen. Phytomedicine. 2000 Apr;7(2):85–9. [CrossRef]
- Olennikov DN, Nikolaev VM, Chirikova NK. Sagan Dalya Tea, a New “Old” Probable Adaptogenic Drug: Metabolic Characterization and Bioactivity Potentials of Rhododendron adamsii Leaves. Antioxidants. 2021 May 27;10(6):863. [CrossRef]
- Jung KA, Han D, Kwon EK, Lee CH, Kim YE. Antifatigue Effect of Rubus coreanus Miquel Extract in Mice. Journal of Medicinal Food. 2007 Dec;10(4):689–93. [CrossRef]
- Agbodjogbe WKDD, Tito ASI, Adjakpahoun G, Messan F, Dansou PH. Antioxidant properties of Senna siamea and effects on sports performance in Wistar rats. Int J Bio Chem Sci. 2022 Aug 28;16(3):1193–203. [CrossRef]
- Liu DD, Ji XW, Li RW. Effects of Siraitia grosvenorii Fruits Extracts on Physical Fatigue in Mice. 2013.
- Feng H, Ma H, Lin H, Putheti R. Antifatigue activity of water extracts of Toona sinensis Roemor leaf and exercise-related changes in lipid peroxidation in endurance exercise. 2009;3(11):949–54.
- Kumar GP, Anand T, Singsit D, Khanum F, Anilakumar KR. Evaluation of antioxidant and anti-fatigue properties of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. in rats subjected to weight loaded forced swim test. Pharmacognosy Journal. 2013 Mar;5(2):66–71. [CrossRef]
- Didio FP, Duarte AR, Stefani GP. Effects of the Withania somnifera supplementation on sports performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nor Afr J Food Nutr Res. 2022 Jan 2;6(13):1–8. [CrossRef]
- Zhao H peng, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Chen J yue, Zhang S yan, Yang X dong, Zhou H li. Acute toxicity and anti-fatigue activity of polysaccharide-rich extract from corn silk. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2017 Jun;90:686–93.
- Tarazona-Díaz MP, Alacid F, Carrasco M, Martínez I, Aguayo E. Watermelon Juice: Potential Functional Drink for Sore Muscle Relief in Athletes. J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Aug 7;61(31):7522–8.
- Dave Mehta S, Rathore P, Rai G. Ginseng: Pharmacological Action and Phytochemistry Prospective. In: Hano C, Chen JT, editors. Ginseng - Modern Aspects of the Famed Traditional Medicine [Internet]. IntechOpen; 2022 [cited 2023 Jul 27]. Available from: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/78426.
- Bowtell J, Kelly V. Fruit-Derived Polyphenol Supplementation for Athlete Recovery and Performance. Sports Med. 2019 Feb;49(S1):3–23. [CrossRef]
- Kennedy DO. Phytochemicals for Improving Aspects of Cognitive Function and Psychological State Potentially Relevant to Sports Performance. Sports Med. 2019 Feb;49(S1):39–58. [CrossRef]
- Jo E, Bartosh R, Auslander AT, Directo D, Osmond A, Wong MW. Post-Exercise Recovery Following 30-Day Supplementation of Trans-Resveratrol and Polyphenol-Enriched Extracts. Sports. 2019 Oct 20;7(10):226. [CrossRef]
- Miao F, Wu D, Ni G. Evaluation of Anti-Fatigue Activity of Flavonoids from Tartary Buckwheat in Mice. Afr J Trad Compl Alt Med. 2016 Feb 19;13(2):52.
- Xiaoming W, Ling L, Jinghang Z. Antioxidant and Anti-Fatigue Activities of Flavonoids from Puerariae radix. Afr J Trad Compl Alt Med. 2012 Jan 18;9(2):221–7. [CrossRef]
- Murase T, Haramizu S, Ota N, Hase T. Suppression of the aging-associated decline in physical performance by a combination of resveratrol intake and habitual exercise in senescence-accelerated mice. Biogerontology. 2009 Aug;10(4):423–34. [CrossRef]
- Qin L, Lu T, Qin Y, He Y, Cui N, Du A, Sun J. In Vivo Effect of Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles to Relieve Physical Fatigue for Sports Nutrition Supplements. Molecules. 2020 Nov 13;25(22):5302. [CrossRef]
- Wu RE, Huang WC, Liao CC, Chang YK, Kan NW, Huang CC. Resveratrol Protects against Physical Fatigue and Improves Exercise Performance in Mice. Molecules. 2013 Apr 19;18(4):4689–702. [CrossRef]
- Yang W, Chen X, Li Y, Guo S, Wang Z, Yu X. Advances in Pharmacological Activities of Terpenoids. Natural Product Communications. 2020 Mar;15(3):1934578X2090355. [CrossRef]
- Geng P, Siu KC, Wang Z, Wu JY. Antifatigue Functions and Mechanisms of Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms. BioMed Research International. 2017;2017:1–16. [CrossRef]
- Li S, Chan Z. Evaluation of Antifatigue Effects of 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 in Forced Swimming Mice. pharmaceutical-sciences [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 Jun 30];80(3). Available from: http://www.ijpsonline.com/articles/evaluation-of-antifatigue-effects-of-20s-ginsenosiderg3-in-forced-swimming-mice-3493.html.
- Rajput A, Sharma R, Bharti R. Pharmacological activities and toxicities of alkaloids on human health. Materials Today: Proceedings. 2022;48:1407–15. [CrossRef]
- Hsu YJ, Huang WC, Chiu CC, Liu YL, Chiu WC, Chiu CH, Chiu YS, Huang CC. Capsaicin Supplementation Reduces Physical Fatigue and Improves Exercise Performance in Mice. Nutrients. 2016 Oct 20;8(10):648. [CrossRef]
- Pesta DH, Angadi SS, Burtscher M, Roberts CK. The effects of caffeine, nicotine, ethanol, and tetrahydrocannabinol on exercise performance. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2013 Dec;10(1):71. [CrossRef]
- Spriet LL. Exercise and Sport Performance with Low Doses of Caffeine. Sports Med. 2014 Nov;44(S2):175–84. [CrossRef]
- Trexler ET, Smith-Ryan AE, Roelofs EJ, Hirsch KR, Mock MG. Effects of coffee and caffeine anhydrous on strength and sprint performance. European Journal of Sport Science. 2016 Aug 17;16(6):702–10.
- Wang P, Wang D, Hu J, Tan BK, Zhang Y, Lin S. Natural bioactive peptides to beat exercise-induced fatigue: A review. Food Bioscience. 2021 Oct;43:101298. [CrossRef]
- Marquezi ML, Roschel HA, Costa ADS, Sawada LA, Lancha Jr. AH. Effect of Aspartate and Asparagine Supplementation on Fatigue Determinants in Intense Exercise. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. 2003 Mar;13(1):65–75.
- Thirupathi A, Freitas S, Sorato HR, Pedroso GS, Effting PS, Damiani AP, Andrade VM, Nesi RT, Gupta RC, Muller AP, Pinho RA. Modulatory effects of taurine on metabolic and oxidative stress parameters in a mice model of muscle overuse. Nutrition. 2018 Oct;54:158–64. [CrossRef]
- Xu M, Liang R, Li Y, Wang J. Anti-fatigue effects of dietary nucleotides in mice. Food & Nutrition Research. 2017 Jan;61(1):1334485. [CrossRef]
- Yen CH, Tsao TH, Huang CU, Yang CB, Kuo CS. Effects of sweet cassava polysaccharide extracts on endurance exercise in rats. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2013 Jan 3;10(1):18. [CrossRef]
- Liu J, Du C, Wang Y, Yu Z. Anti-fatigue activities of polysaccharides extracted from Hericium erinaceus. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2015 Feb;9(2):483–7. [CrossRef]
- Moon JM, Ratliff KM, Blumkaitis JC, Harty PS, Zabriskie HA, Stecker RA, Currier BS, Jagim AR, Jäger R, Purpura M, Kerksick CM. Effects of daily 24-gram doses of rice or whey protein on resistance training adaptations in trained males. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2020 Jan 3;17(1):60. [CrossRef]
- Yu SH, Huang HY, Korivi M, Hsu MF, Huang CY, Hou CW, Chen CY, Kao CL, Lee RP, Lee SD, Kuo CH. Oral Rg1 supplementation strengthens antioxidant defense system against exercise-induced oxidative stress in rat skeletal muscles. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2012 Feb 6;9(1):23. [CrossRef]
- Hsu YJ, Huang WC, Chiu CC, Liu YL, Chiu WC, Chiu CH, Chiu YS, Huang CC. Capsaicin Supplementation Reduces Physical Fatigue and Improves Exercise Performance in Mice. Nutrients. 2016 Oct 20;8(10):648. [CrossRef]
- Bell DG, Ira J, Jiri Z. Effects of caffeine, ephedrine and their combination on time to exhaustion during high-intensity exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 1998;(77):427–33.
- Kan NW, Ho CS, Chiu YS, Huang WC, Chen PY, Tung YT, Huang CC. Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation and Exercise Training on Exercise Performance in Middle-Aged Mice. Molecules. 2016 May 18;21(5):661. [CrossRef]
- Chen H, He X, Liu Y, Li J, He Q, Zhang C, Wei B, Zhang Y, Wang J. Extraction, purification and anti-fatigue activity of γ-aminobutyric acid from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves. Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 8;6(1):18933.
- Miao X, Xiao B, Shui S, Yang J, Huang R, Dong J. Metabolomics analysis of serum reveals the effect of Danggui Buxue Tang on fatigued mice induced by exhausting physical exercise. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2018 Mar;151:301–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Li C, Hu W, Li L, Cai G, Liu Y, Wang D. Studies on the anti-fatigue activities of Irpex lacteus polysaccharide- enriched extract in mouse model. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019.
- Kennedy DO, Haskell CF, Robertson B, Reay J, Brewster-Maund C, Luedemann J, Maggini S, Ruf M, Zangara A, Scholey AB. Improved cognitive performance and mental fatigue following a multi-vitamin and mineral supplement with added guaraná (Paullinia cupana). Appetite. 2008 Mar;50(2–3):506–13. [CrossRef]
- Pomportes L, Davranche K, Hays A, Brisswalter J. Effet d’un complexe créatine–guarana sur la puissance musculaire et la performance cognitive chez des sportifs de haut niveau de performance. Science & Sports. 2015 Sep;30(4):188–95. [CrossRef]
- Hu M, Du J, Du L, Luo Q, Xiong J. Anti-fatigue activity of purified anthocyanins prepared from purple passion fruit (P. edulis Sim) epicarp in mice. Journal of Functional Foods. 2020 Feb 1;65:103725. [CrossRef]
- Kwon DA, Kim YS, Kim SK, Baek SH, Kim HK, Lee HS. Antioxidant and antifatigue effect of a standardized fraction (HemoHIM) from Angelica gigas, Cnidium officinale, and Paeonia lactiflora. Pharmaceutical Biology. 2021 Jan 1;59(1):389–98.
- Heaney LM, Deighton K, Suzuki T. Non-targeted metabolomics in sport and exercise science. Journal of Sports Sciences. 2019 May 3;37(9):959–67. [CrossRef]
- Duft RG, Castro A, Chacon-Mikahil MPT, Cavaglieri CR. Metabolomics and Exercise: possibilities and perspectives. Motriz: rev educ fis [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 Jul 27];23(2). Available from: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1980-65742017000200201&lng=en&tlng=en.
- Bongiovanni T, Pintus R, Dessì A, Noto A, Sardo S, Finco G, Corsello G, Fanos V. Sportomics: metabolomics applied to sports. The new revolution? European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2019;23:11011–9.
- Krambeck K, Oliveira A, Santos D, Pintado MM, Baptista Silva J, Sousa Lobo JM, Amaral MH. Identification and Quantification of Stilbenes (Piceatannol and Resveratrol) in Passiflora edulis By-Products. Pharmaceuticals. 2020 Apr 20;13(4):73. [CrossRef]
- Zakharenko AM, Razgonova MP, Pikula KS, Golokhvast KS. Simultaneous Determination of 78 Compounds of Rhodiola rosea Extract by Supercritical CO2-Extraction and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Spectrometry. Tayyab S, editor. Biochemistry Research International. 2021 Jul 6;2021:1–16. [CrossRef]
- Wu F, Yao X, Xu J, Wu Y, Yang Y, Jin Y, Xie H, Liu Y, Yang Y, Zheng X. One New Phenolic Compound from Castanea mollissima Shells and its Suppression of HepatomaCell Proliferation and Inflammation by Inhibiting NF-κB Pathway. IJMS. 2019 Jan 22;20(3):466.
- Malathy R, Prabakaran M, Kalaiselvi K, Chung IM, Kim SH. Comparative Polyphenol Composition, Antioxidant and Anticorrosion Properties in Various Parts of Panax ginseng Extracted in Different Solvents. Applied Sciences. 2020 Dec 24;11(1):93.
- Zhang L, Gao H yuan, Baba M, Okada Y, Okuyama T, Wu L jun, Zhan L bin. Extracts and compounds with anti-diabetic complications and anti-cancer activity from Castanea mollissina Blume (Chinese chestnut). BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec;14(1):422.
- Zhang YN, Zhu SJ, Li N, Jing YN, Yue XF. Screening and identification of the active components from Puerariae Radix by HUVEC/CMC-LC-MS2. Journal of Chromatography B. 2019 Nov;1132:121825. [CrossRef]
- Rana A, Singh HP, Gulati A. Investigation of major phenolic antioxidants from Camellia sinensis fruits. Weaver G, editor. Cogent Chemistry. 2015 Dec 31;1(1):1080652. [CrossRef]
- Hu Y, Ding J, Sun Z, Zong Z, Song H, Sun X, Xu B, Qi Z, Liu B, Li W. Identification and analysis of chemical constituents of total glycosides of Cistanche deserticola YC Ma in rat hepatic metabolism by ultra performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS). mat express. 2022 Aug 1;12(8):1059–71. [CrossRef]
- Fuzzati N, Gabetta B, Jayakar K, Pace R, Peterlongo F. Liquid chromatography–electrospray mass spectrometric identification of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng roots. Journal of Chromatography A. 1999 Aug;854(1–2):69–79. [CrossRef]
- Gao HY, Wang XB, Xi RG, Sun BH, Huang J, Wu LJ. Structure and Absolute Configuration of a Diterpenoid from Castanea mollissima. Natural Product Communications. 2010 Jan;5(1):1934578X1000500. [CrossRef]
- Lee DG, Lee JS, Kim KT, Jacinto SD, Lee S. Analysis of terpenoids and steroids in the seeds of Panax ginseng. Hortic Environ Biotechnol. 2020 Jun;61(3):609–13. [CrossRef]
- Basappa G, Kumar V, Sarojini BK, Poornima DV, Gajula H, Sannabommaji TK, Rajashekar J. Chemical composition, biological properties of Anisomeles indica Kuntze essential oil. Industrial Crops and Products. 2015;77:89–96. [CrossRef]
- Belliardo F, Martelli A, Valle MG. HPLC determination of caffeine and theophylline inPaullinia cupana Kunth (Guarana) and Cola spp. samples. Z Lebensm Unters Forch. 1985 May;180(5):398–401. [CrossRef]
- Ciulu-Costinescu F, Calina D, Chirigiu L, Averis LME, Rosulescu E, Bubulica MV. Identification and Quantification of Capsaicin from Capsicum Annuum L. by RP-HPLC. 2015.
- Benjamin MAZ, Ng SY, Saikim FH, Rusdi NA. The Effects of Drying Techniques on Phytochemical Contents and Biological Activities on Selected Bamboo Leaves. Molecules. 2022 Sep 30;27(19):6458. [CrossRef]
- Barreira S, Moutinho C, Silva AMN, Neves J, Seo EJ, Hegazy MEF, Efferth T, Gomes LR. Phytochemical characterization and biological activities of green tea (Camellia sinensis) produced in the Azores, Portugal. Phytomedicine Plus. 2021 Feb;1(1):100001. [CrossRef]
- Tessier F, Marconnet P. Radicaux libres, systèmes antioxydants et exercice. Science & Sports. 1995 Jan;10(1):1–13.
- Powers SK, Goldstein E, Schrager M, Ji LL. Exercise Training and Skeletal Muscle Antioxidant Enzymes: An Update. Antioxidants. 2022 Dec 25;12(1):39. [CrossRef]
- El Assar M, Álvarez-Bustos A, Sosa P, Angulo J, Rodríguez-Mañas L. Effect of Physical Activity/Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Muscle and Vascular Aging. IJMS. 2022 Aug 5;23(15):8713. [CrossRef]
- Atalay M, Seene T, Hänninen O, Sen CK. Skeletal muscle and heart antioxidant defences in response to sprint training. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 1996 Oct;158(2):129–34. [CrossRef]
- Leeuwenburgh C, Hollander J, Leichtweis S, Griffiths M, Gore M, Ji LL. Adaptations of glutathione antioxidant system to endurance training are tissue and muscle fiber specific. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 1997 Jan 1;272(1):R363–9. [CrossRef]
- Viña J, Salvador-Pascual A, Tarazona-Santabalbina FJ, Rodriguez-Mañas L, Gomez-Cabrera MC. Exercise training as a drug to treat age associated frailty. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2016 Sep;98:159–64. [CrossRef]
- Meo SD, Napolitano G, Venditti P. Mediators of Physical Activity Protection against ROS-Linked Skeletal Muscle Damage. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Simioni C, Zauli G, Martelli AM, Vitale M, Sacchetti G, Gonelli A, Neri LM. Oxidative stress: role of physical exercise and antioxidant nutraceuticals in adulthood and aging. Oncotarget. 2018 Mar 30;9(24):17181–98. [CrossRef]
- Hollander J, Fiebig R, Gore M, Bejma J, Ookawara T, Ohno H, Ji LL. Superoxide dismutase gene expression in skeletal muscle: fiber-specific adaptation to endurance training. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 1999 Sep 1;277(3):R856–62. [CrossRef]
- Steinbacher P, Eckl P. Impact of Oxidative Stress on Exercising Skeletal Muscle. Biomolecules. 2015 Apr 10;5(2):356–77. [CrossRef]
- Improta-Caria AC, Soci ÚPR, Pinho CS, Aras Júnior R, De Sousa RAL, Bessa TCB. Physical Exercise and Immune System: Perspectives on the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2021;67(suppl 1):102–7. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira LF, Laitano O. Regulation of NADPH oxidases in skeletal muscle. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2016 Sep; 98:18–28. [CrossRef]
- Jackson MJ, Vasilaki A, McArdle A. Cellular mechanisms underlying oxidative stress in human exercise. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2016 Sep; 98:13–7. [CrossRef]
- Powers SK, Deminice R, Ozdemir M, Yoshihara T, Bomkamp MP, Hyatt H. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Friend or foe? Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2020 Sep;9(5):415–25.
- Suzuki K, Hayashida H. Effect of Exercise Intensity on Cell-Mediated Immunity. Sports. 2021 Jan 11;9(1):8. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen BK, Hoffman-Goetz L. Exercise and the Immune System: Regulation, Integration, and Adaptation. Physiological Reviews. 2000 Jul 1;80(3):1055–81. [CrossRef]
- Senchina DS, Kohut ML. Immunological outcomes of exercise in older adults. Clinical Interventions in Aging. 2007 Mar;2(1):3–16. [CrossRef]
- Scheffer DDL, Latini A. Exercise-induced immune system response: Anti-inflammatory status on peripheral and central organs. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 2020 Oct;1866(10):165823. [CrossRef]
- Simpson RJ, Campbell JP, Gleeson M, Krüger K, Nieman DC, Pyne DB, Turner E, Walsh NP. Can exercise affect immune function to increase susceptibility to infection? 2020.
- Valle L, Hernandez R. Physical activity as antioxidant and palliative beneficial option in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Oxid Antioxid Med Sci. 2013;2(4):231. [CrossRef]
- Leung A, Gregory NS, Allen LAH, Sluka KA. Regular physical activity prevents chronic pain by altering resident muscle macrophage phenotype and increasing IL-10 in mice. 2017.
- Ellingsgaard H, Hojman P, Pedersen BK. Exercise and health — emerging roles of IL-6. Current Opinion in Physiology. 2019 Aug;10:49–54.
- Chen H, Shen L, Liu Y, Ma X, Long L, Ma X, Ma L, Chen Z, Lin X, Si L, Chen X. Strength Exercise Confers Protection in Central Nervous System Autoimmunity by Altering the Gut Microbiota. Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 16;12:628629. [CrossRef]
- Moon PD, Kim KY, Rew KH, Kim HM, Jeong HJ. Anti-fatigue effects of porcine placenta and its amino acids in a behavioral test on mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014 Nov;92(11):937–44. [CrossRef]
- Garige BSR, Keshetti S, Vattikuti UMR. CNS Depressant effects and muscle relaxant activity of Galphimia glauca leaf methanol extract. International Journal of PharmTech Research. 2016;9(6):230–40.
- Chen J, Lu X, Chen P, Shen Y, Zheng B, Guo Z. Anti-fatigue effect of glycoprotein from hairtail (Trichiurus lepturus) by-products in a behavioral mouse model. Food Chemistry: X. 2023 Jun;18:100645. [CrossRef]
- Squillacioti G, Guglieri F, Colombi N, Ghelli F, Berchialla P, Gardois P, Bono R. Non-Invasive Measurement of Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress in Response to Physical Activity. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants. 2021 Dec 17;10(12):2008. [CrossRef]
- Clarkson PM, Thompson HS. Antioxidants: what role do they play in physical activity and health? The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2000 Aug;72(2):637S-646S.
- Enioutina EY, Job KM, Sherwin CMT. Spotlight Commentary: Why we need to pay attention to toxicity associated with herbal medicines. Brit J Clinical Pharma. 2020 Sep;86(9):1793–4. [CrossRef]
- Zhao H peng, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Chen J yue, Zhang S yan, Yang X dong, Zhou H li. Acute toxicity and anti-fatigue activity of polysaccharide-rich extract from corn silk. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2017 Jun;90:686–93.
- Lynch H, Johnston C, Wharton C. Plant-Based Diets: Considerations for Environmental Impact, Protein Quality, and Exercise Performance. Nutrients. 2018 Dec 1;10(12):1841. [CrossRef]
- Om AS, Song YN, Noh G, Kim H, Choe J. Nutrition Composition and Single, 14-Day and 13-Week Repeated Oral Dose Toxicity Studies of the Leaves and Stems of Rubus coreanus Miquel. Molecules. 2016 Jan 8;21(1):65.
- Ajibade TO, Arowolo R, Olayemi FO. Phytochemical screening and toxicity studies on the methanol extract of the seeds of moringa oleifera. Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine [Internet]. 2013 Jan 12 [cited 2023 Aug 7];10(1). Available from: https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/jcim-2012-0015/html.
- Osman H, Me S, Em B, Ao F, Ahmed MM, Osman B, Elhassan M, Kk T. Assessment of acute toxicity and LD50 of Moringa oleifera ethanolic leave extract in albino rats and rabbits. 2015.
- Pareek A, Pant M, Gupta MM, Kashania P, Ratan Y, Jain V, Pareek A, Chuturgoon AA. Moringa oleifera: An Updated Comprehensive Review of Its Pharmacological Activities, Ethnomedicinal, Phytopharmaceutical Formulation, Clinical, Phytochemical, and Toxicological Aspects. IJMS. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2098.
- Shafi S, Tabassum N. Toxicity evaluation of hydro-alcoholic extract of portulaca oleracea (whole plant) in swiss albino mice. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2014;7(2).
- Basappa G, Kumar V. Toxicity Evaluation of Anisomeles indica Kuntze Leaf Flavonoid Fraction. J Pharmacogn Nat Prod [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2023 Jul 21];2(3). Available from: https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/toxicity-evaluation-of-anisomeles-indica-kuntze-leaf-flavonoid-fraction-2472-0992-1000122.php?aid=78821.
- Sergi CM. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Toxicity in Children: A Potential and Current Toxicological Event in the Differential Diagnosis With Virus-Triggered Fulminant Hepatic Failure. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 29;10:1563. [CrossRef]
- Lambert JD, Kennett MJ, Sang S, Reuhl KR, Ju J, Yang CS. Hepatotoxicity of high oral dose (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2010 Jan;48(1):409–16. [CrossRef]
- Parn KW, Ling WC, Chin JH, Lee SK. Safety and Efficacy of Dietary Epigallocatechin Gallate Supplementation in Attenuating Hypertension via Its Modulatory Activities on the Intrarenal Renin–Angiotensin System in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Nutrients. 2022 Nov 1;14(21):4605. [CrossRef]
- Isbrucker RA, Bausch J, Edwards JA, Wolz E. Safety studies on epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) preparations. Part 1: Genotoxicity. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2006 May;44(5):626–35.
- Mbaveng AT, Hamm R, Kuete V. Harmful and Protective Effects of Terpenoids from African Medicinal Plants. In: Toxicological Survey of African Medicinal Plants [Internet]. Elsevier; 2014 [cited 2023 Dec 24]. p. 557–76. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780128000182000194.
- Perestrelo R, Silva C, Fernandes MX, Câmara JS. Prediction of Terpenoid Toxicity Based on a Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship Model. Foods. 2019 Dec 1;8(12):628. [CrossRef]
- Hudson A, Lopez E, Almalki AJ, Roe AL, Calderón AI. A Review of the Toxicity of Compounds Found in Herbal Dietary Supplements. Planta Med. 2018 Jul;84(09/10):613–26. [CrossRef]
- Meredith SE, Juliano LM, Hughes JR, Griffiths RR. Caffeine Use Disorder: A Comprehensive Review and Research Agenda. Journal of Caffeine Research. 2013 Sep;3(3):114–30. [CrossRef]
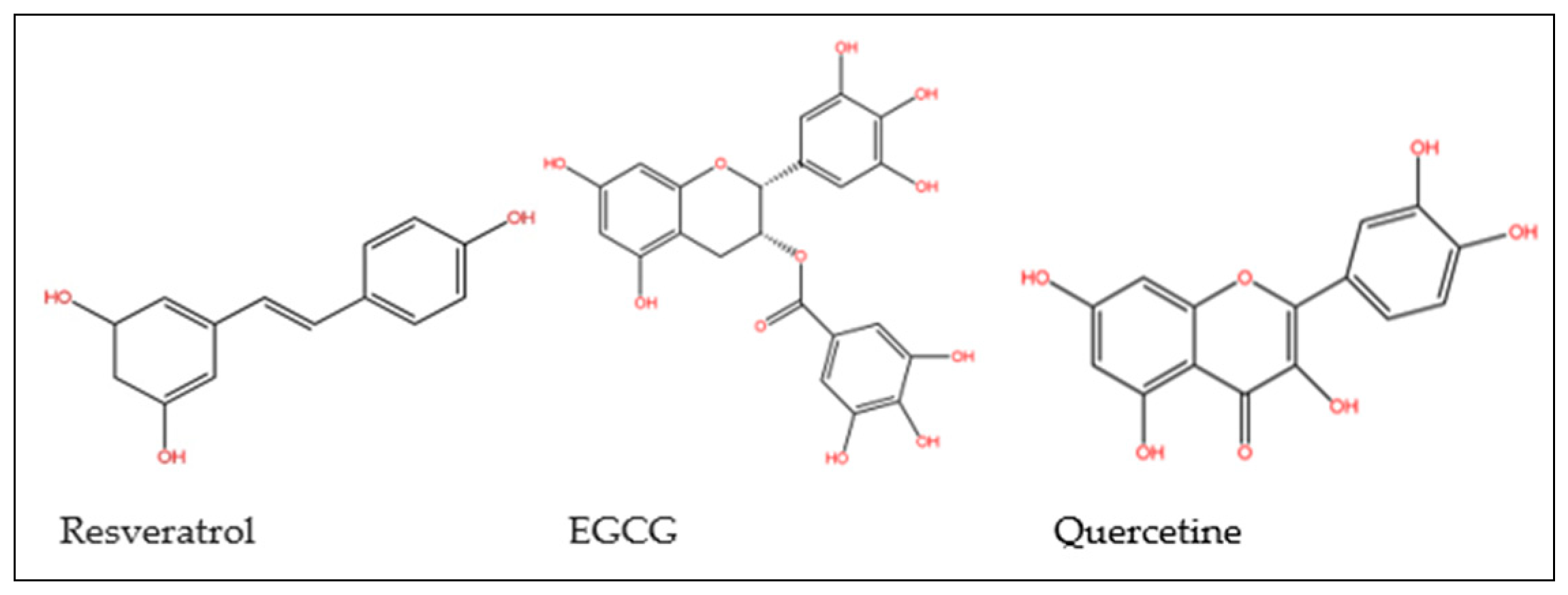
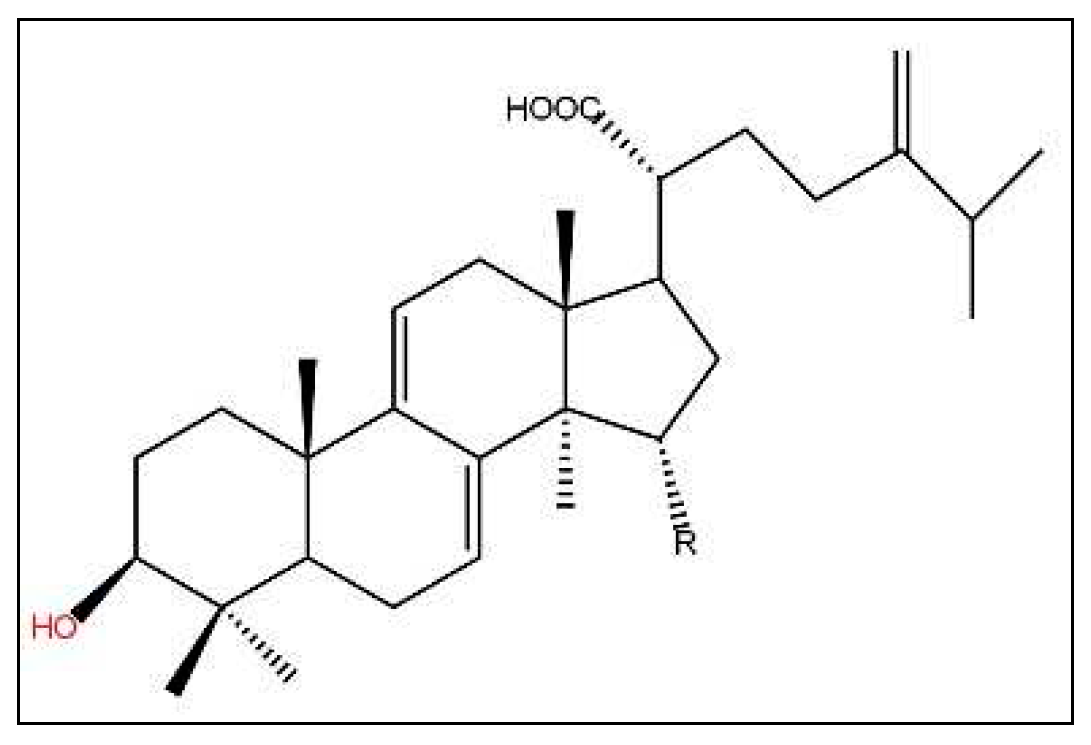
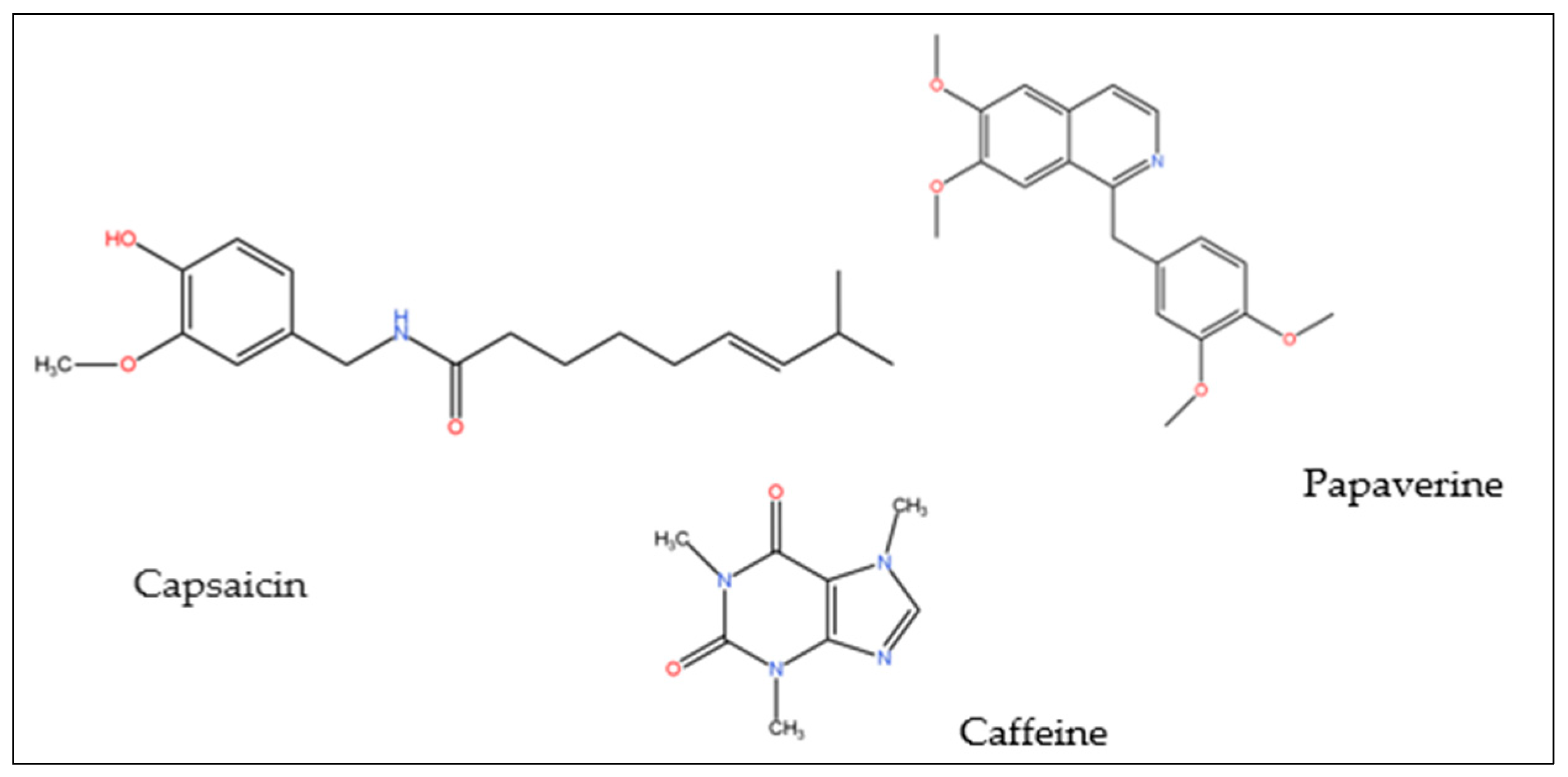
| Species names | Famillies | Properties | Parts used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acanthopanax senticosus | Araliaceae | anti-fatigue | Root | [51] |
| Acanthopanax senticosus | Araliaceae | anti-fatigue | stem bark | [52] |
| Anisomeles indica | Lamiaceae | Anti-fatigue | Whole plants | [53] |
| Antrodia camphorata | Fomitopsidaceae | Physical fatigue | Fruiting body | [48,54] |
| Astragali Radix and Angelicae Sinensis Radix | Antifatigue | root | [55] | |
| Bambusa tuldoides Munro | Gramineae | Anti-fatigue | [56] | |
| Cannabis sativa L | Cannabaceae | Anti-fatigue | leaves | [57] |
| Castanea mollissima Blume | Fagaceae | anti-fatigue | flowers | [58] |
| Cistanche deserticola Y.C. Ma | Orobanchaceae | Antifatigue | stems | [59] |
| Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze var. | Theacaea | Antifatigue | [34,40,41] | |
| Cordyceps militaris | Cordycipitaceae | anti-fatigue | [60] | |
| Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. | Rosaceae | Physical capacity | leave | [61] |
| Fagopyrum tataricum | Polygonaceae | Antifatigue | grain | [62] |
| Fagopyrum esculentum Moench | Polygonaceae | Antifatigue | grain | [55] |
| Glossogyne tenuifolia | Anti-Fatigue | [63] | ||
| Moringa oleifera Lam. | Moringaceae | antifatigue | leave | [64] |
| Morus alba L. (Mulberry ) | Moraceae | anti-fatigue | leave | [65] |
| Panax ginseng CA Meyer | Araliaceae | anti-fatigue | [42,45,46,48] | |
| Panax quinquefolium | Araliaceae | anti-fatigue | [66] | |
| Passiflora edulis Sim | Passifloraceae | Anti-fatigue | fruit epicarp | [67] |
| Paullinia cupana linn | Sapindaceae | Anti-fatigue | [68] | |
| Physalis pubescens L | Solanaceae | anti-fatigue | Fruit | [69] |
| Polygonum cuspidatum | Polygonaceae | Physical capacity | root , rhizome | [70] |
| Portulaca oleracea L. | Portulacaceae | Anti-fatigue | leave | [17] |
| Punica granatum L. | Punicaceae | physical performance | fruit | [71] |
| Radix notoginseng | Araliaceae | anti-fatigue | Root | [72] |
| Rhodiola rosea | Crassulaceae | Antifatigue | root | [30,32,34,35,39,73,74] |
| Rhododendron adamsii Rehder | Ericaceae | physical performance | Leave | [75] |
| Rubus coreanus Miquel | Rosaceae | Antifatigue | Fruit | [76] |
| Senna siamea | Polygonaceae | Antifatigue | leaves | [77] |
| Siraitia grosvenorii | Cucurbitaceae | anti-fatigue. | Fruits | [78] |
| Taraxacum officinale | Asteraceae | physical fatigue | [11] | |
| Toona sinensis Roemor | Meliaceae | antifatigue | leavef | [79] |
| Trigonella foenum-graecum L. | Fabaceae | anti-fatigue | Dry seeds | [80] |
| Withania somnifera | Solanaceae | physical performance | root | [81] |
| Zea mays L. | Poaceae | anti-fatigue | Corn silk | [82] |
| Citrullus lanatus cv | Cucurbitaceae | Sore Muscle Relief in Athletes | watermelon juice | [83] |
| flavonoid | Identification technical | Compounds identified | Plant species | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic | HPLC -RP | Resveratrol | Passiflora edulis | [122] |
| Phenolic | HPLC - MS/MS | salidroside, rhodiolosides, luteolin, catechin, quercetin,quercitrin, sacranoside | Rhodiola rosea | [123] |
| Phenolic | HPLC - MS | castanolB | Castanea mollissima | [124] |
| Phenols | UHPLC | Chlorogenic acid, gentisic acid, rutin, p-coumaric acid; m-coumaric acid, protocatechuic acid; p-hydroxybenzoic | P. ginseng | [125] |
| Flavonoid | H-NMR, 13C-NMR, HMBC, HMQC and ESI-Q-TOF MS | Kaempferol | Castanea mollissina Blume | [126] |
| Flavonoids | HUVEC/CMC-LC-MS | puerarin, daidzin, pueroside D and 3'-hydroxypuerarin | Puerariae Radix | [127] |
| Flavonoids | HPLC, ESI-MS and NMR | epigallocatechin, epicatechin, EGCG and epicatechin gallate | C. sinensis fruits | [128] |
| Flavonoids | PLC-MS/MS analysis | myricetin-3-O-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside, kaempferol | Castanea mollissima flower | |
| anthocyanins | HPLC/UPLC-MS/MS analysis | cyanidin-3-O-glucoside ; cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside, peonidin 3-O-glucoside | Passiflora edulis Sims fruits | [67] |
| Terpenoids | UPLC-Q-TOF-MS | Kankanoside E , Daucosterol, Diosgenin | Cistanche deserticola YC Ma | [129] |
| Terpenoids | LC electrospray mass spectrometric | Ginsenosides | Panax ginseng | [130] |
| TERPENOID | HR-FAB-MS, 1D, 2D-NMR and CD MS | kauranoid diterpene glycoside mollioside | nuts of Castanea mollissima Blume | [131] |
| terpenoids | HPLC analysis. | lupeol, stigmasterol, β-sitosterol, and squalene | seeds of Panax ginseng | [132] |
| terpenoids | NMR and MS analyses | antcins B, C, H, I, K (ergostane-type triterpenoids) and dehydrosulphurenic acid, 15α-acetyldehydrosulphurenic acid (lanostane-type triterpenoids). | fruiting of Antrodia camphorata | [54] |
| terpenoids | GC–MS analysis. | Farnesyl acetone, nootkatone and jasmatone leaf | Anisomeles indica Kuntze essential oil | [133] |
| allkaloid | RP-HPLC | caffeine and theophylline | seeds of Paulinia cupana Kunth | [134] |
| allkaloid | DART -TOF-MS | capsaicin | Capsicum annuum | |
| allkaloid | RP-HPLC | capsaicin | Capsicum annuum | [135] |
| Alkaloid | LC-MS analysis | Sparteine, papaverine, Caffeine, naloxone | Bambusa. tuldoides | [136] |
| alkaloid | HPLC-ESI-MS- NMR | caffeine | Camellia sinensis fruits | [128] |
| alkaloid | HPLC-DAD | Theophiline; Caffeine | Camellia sinensis leaves |
[137] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





