Submitted:
31 December 2023
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Role of Artificial Intelligence in MCED
2. Trajectory of Early Cancer Detection Methods
2.1. Evolutionary Overview of Multiple Cancer Early Detection
2.2. Advancements in Imaging and Endoscopic Tools
2.3. Emergence of Liquid Biopsy-Based Approaches
3. Serum Biomarkers as Critical Indicators
3.1. Protein Biomarkers: Unveiling Diagnostic Potential
3.2. cfDNA Biomarkers: Unleashing Genomic Clues
4. Synergizing AI Algorithms for Biomarker Analysis
4.1. Classical Machine Learning Techniques in Biomarker Interpretation
4.2. Unveiling Deep Learning's Potential in Biomarker Analysis
5. Training and Validation of AI Models for MCED
5.1. Impacts of training dataset: case-control, retrospective cohort, or prospective cohort?
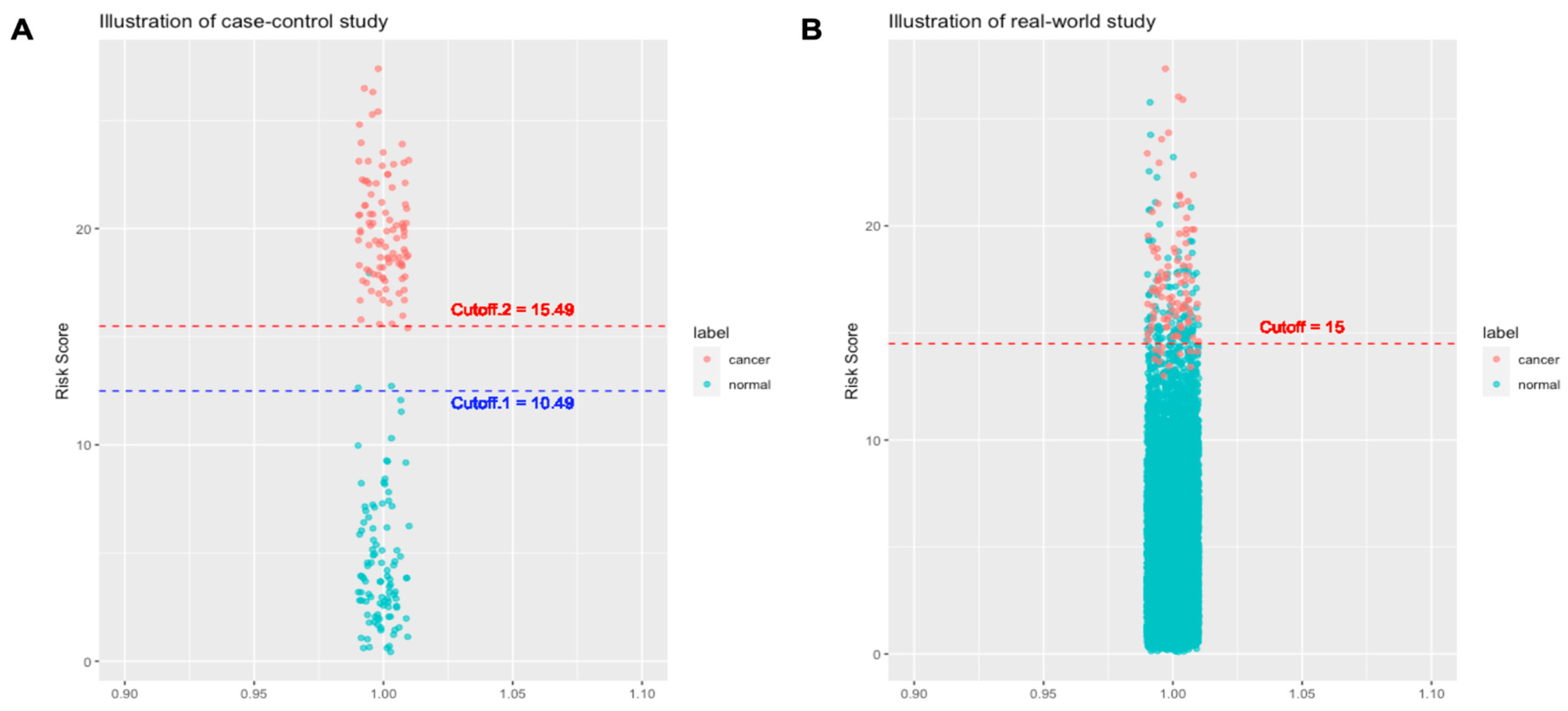
- On cancer cases: Specimens of the cancer cases in a case-control study are typically collected in more advanced stages than the specimens of a real-world cohort study. The reason for that is that the specimens of the cancer cases in a case-control study are collected when the diagnosis of cancer has been made, which is often associated with symptoms/signs that are caused by cancers. In this case, the cancers show their malignant behaviors like space occupying or mass effect. By contrast, specimens of the cancer cases in a real-world cohort are collected long before cancer diagnosis or any symptom/sign. Such conditions are usually closer to the health check-ups population in the real-world. Theoretically, biomarkers in presymptomatic or asymptomatic cancer cases would be closer to those of healthy controls than in the symptomatic cancer cases.
- On healthy cases: The number of healthy control cases in a case-control study is usually up to several hundred given the fact that the ratio of cancer versus control ratio is set around 1:1-1:4 (15,17,34,49). The relatively small number cannot represent the large diversity in the healthy control cases. As a result, there are fewer outlier cases. Fewer healthy outliers would simplify the classification problem (i.e. classify cancers versus healthy). AI models trained with fewer healthy outliers may therefore not have a classification threshold that can be used in the real world.
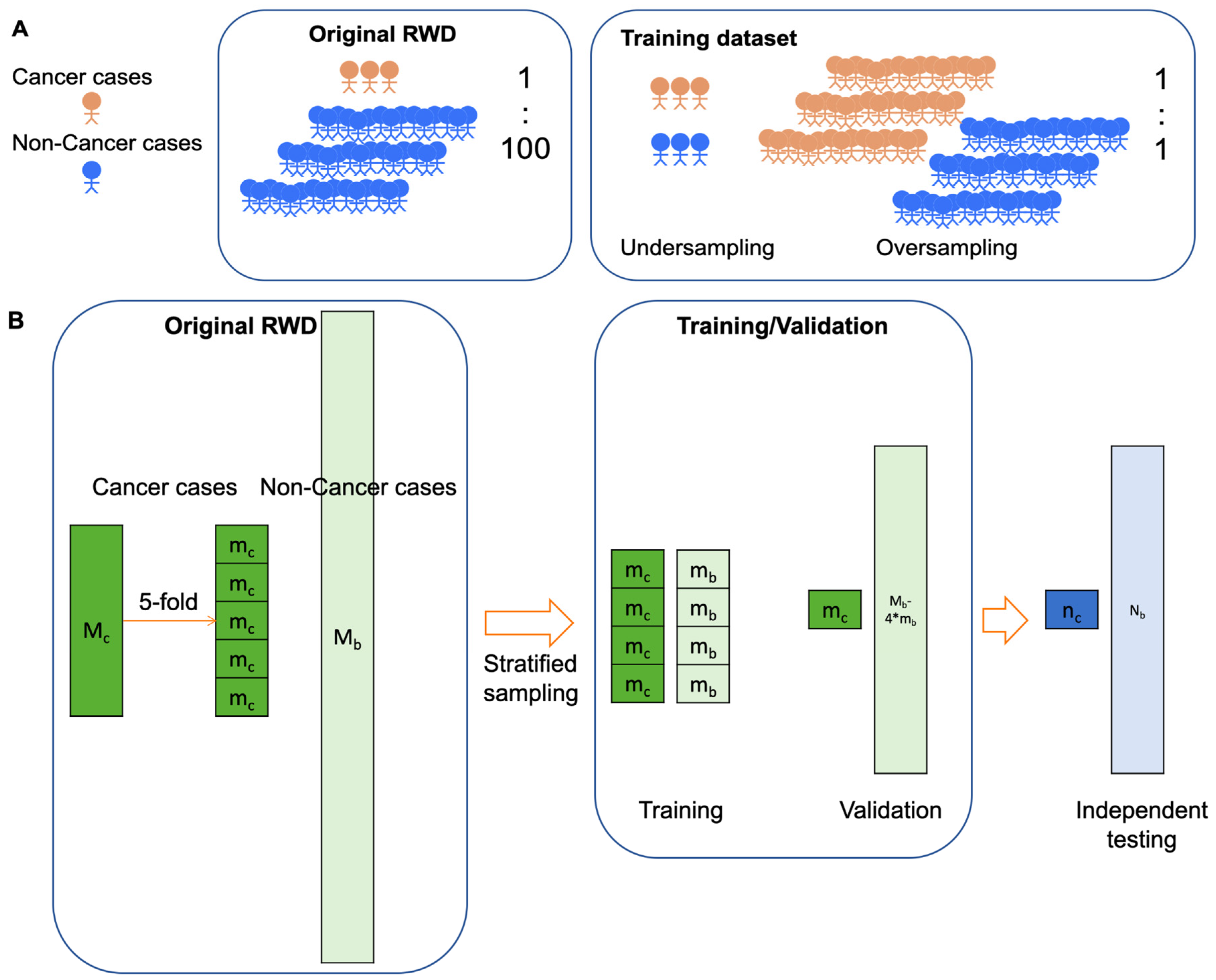
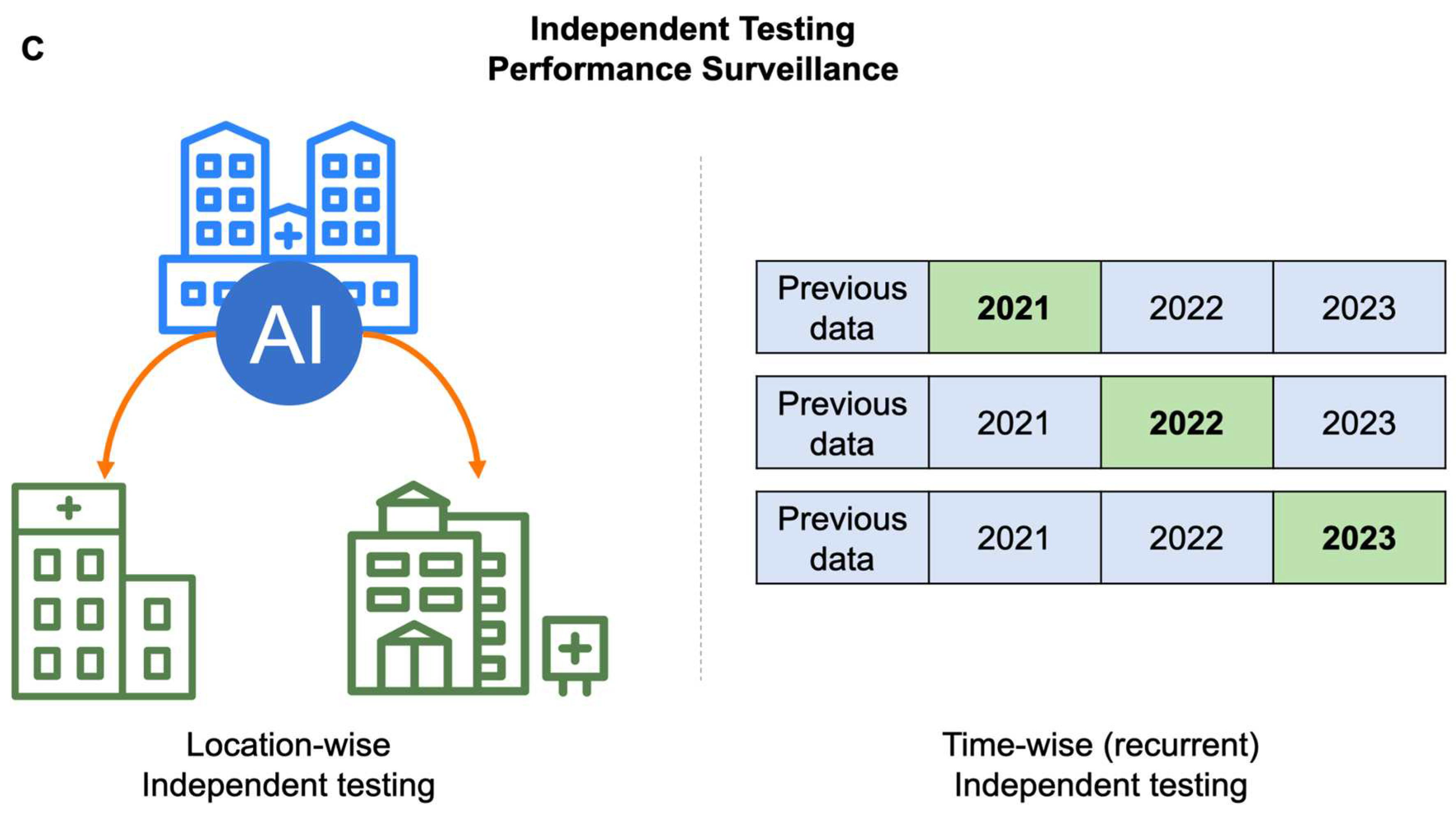
5.2. Cross-Validation vs. Independent Testing: generalizability or continual monitoring matters?
6. Challenges and Opportunities
6.1. Data Quality and Quantity: Navigating the Complex Landscape
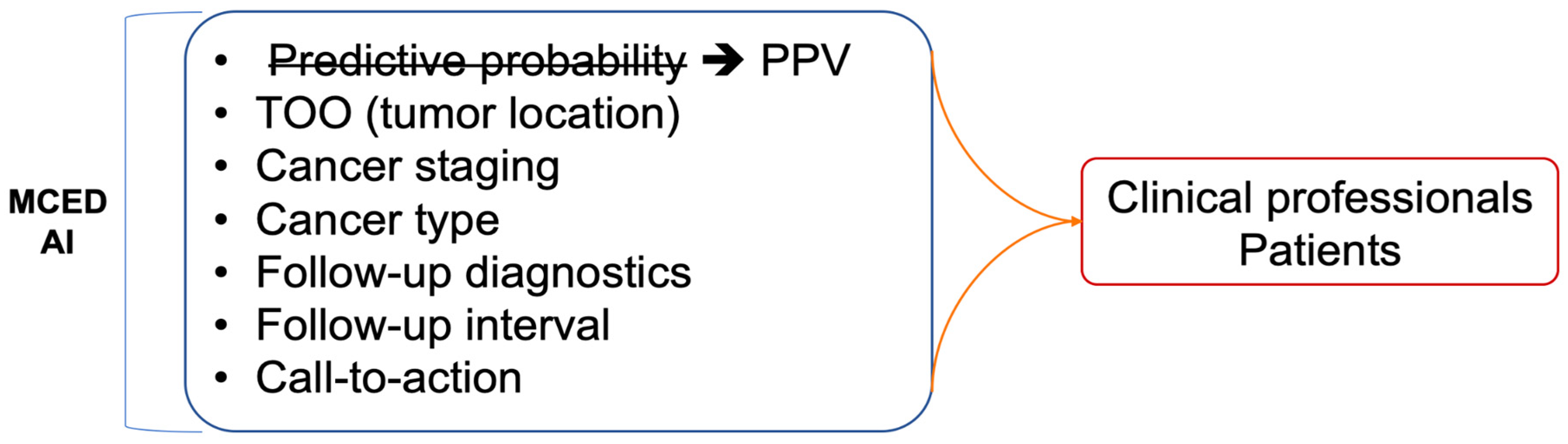
6.2. Interpretability, Explainability, and integration: Bridging the Gap in AI-Driven Insights
7. Conclusion
References
- Zutshi V, Kaur G. Remembering George Papanicolaou: A Revolutionary Who Invented the Pap Smear Test. J Colposc Low Genit Tract Pathol. 2023 Aug;1(2):47. [CrossRef]
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33.
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. The Path to Cancer — Three Strikes and You’re Out. N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 12;373(20):1895–8.
- Fedeli U, Barbiellini Amidei C, Han X, Jemal A. Changes in cancer-related mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst. 2023 Sep 9;djad191. [CrossRef]
- Guerra CE, Sharma PV, Castillo BS. Multi-Cancer Early Detection: The New Frontier in Cancer Early Detection. Annu Rev Med. 2024;75(1):null. [CrossRef]
- Wang HY, Chen CH, Shi S, Chung CR, Wen YH, Wu MH, et al. Improving Multi-Tumor Biomarker Health Check-Up Tests with Machine Learning Algorithms. Cancers. 2020 Jun;12(6):1442. [CrossRef]
- Loud JT, Murphy J. Cancer Screening and Early Detection in the 21st Century. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2017 May;33(2):121–8. [CrossRef]
- Uncertainty Around Tests That Screen for Many Cancers - NCI [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 Oct 25]. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2022/finding-cancer-early-mced-tests.
- Huguet N, Angier H, Rdesinski R, Hoopes M, Marino M, Holderness H, et al. Cervical and colorectal cancer screening prevalence before and after Affordable Care Act Medicaid expansion. Prev Med. 2019 Jul;124:91–7. [CrossRef]
- Hackshaw A, Cohen SS, Reichert H, Kansal AR, Chung KC, Ofman JJ. Estimating the population health impact of a multi-cancer early detection genomic blood test to complement existing screening in the US and UK. Br J Cancer. 2021 Nov;125(10):1432–42. [CrossRef]
- Wang HY, Chang SC, Lin WY, Chen CH, Chiang SH, Huang KY, et al. Machine Learning-Based Method for Obesity Risk Evaluation Using Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Derived from Next-Generation Sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2018 Dec;25(12):1347–60. [CrossRef]
- Tseng YJ, Huang CE, Wen CN, Lai PY, Wu MH, Sun YC, et al. Predicting breast cancer metastasis by using serum biomarkers and clinicopathological data with machine learning technologies. Int J Med Inf [Internet]. 2019; Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1386505618311213?via%3Dihub. [CrossRef]
- Tseng YJ, Wang HY, Lin TW, Lu JJ, Hsieh CH, Liao CT. Development of a Machine Learning Model for Survival Risk Stratification of Patients With Advanced Oral Cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Aug 21;3(8):e2011768. [CrossRef]
- Voitechovič E, Pauliukaite R. Electrochemical multisensor systems and arrays in the era of artificial intelligence. Curr Opin Electrochem. 2023 Oct 13;101411. [CrossRef]
- Cohen JD, Li L, Wang Y, Thoburn C, Afsari B, Danilova L, et al. Detection and localization of surgically resectable cancers with a multi-analyte blood test. Science. 2018 Feb 23;359(6378):926–30. [CrossRef]
- Wang HY, Hsieh CH, Wen CN, Wen YH, Chen CH, Lu JJ. Cancers Screening in an Asymptomatic Population by Using Multiple Tumour Markers. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0158285. [CrossRef]
- Luan Y, Zhong G, Li S, Wu W, Liu X, Zhu D, et al. A panel of seven protein tumour markers for effective and affordable multi-cancer early detection by artificial intelligence: a large-scale and multicentre case–control study. eClinicalMedicine [Internet]. 2023 Jul 1 [cited 2023 Nov 6];61. Available from: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370(23)00218-3/fulltext. [CrossRef]
- Schrag D, Beer TM, McDonnell CH, Nadauld L, Dilaveri CA, Reid R, et al. Blood-based tests for multicancer early detection (PATHFINDER): a prospective cohort study. The Lancet. 2023 Oct;402(10409):1251–60. [CrossRef]
- Ahlquist, DA. Ahlquist DA. Universal cancer screening: revolutionary, rational, and realizable. Npj Precis Oncol. 2018 Oct 29;2(1):1–5. [CrossRef]
- Neal RD, Johnson P, Clarke CA, Hamilton SA, Zhang N, Kumar H, et al. Cell-Free DNA–Based Multi-Cancer Early Detection Test in an Asymptomatic Screening Population (NHS-Galleri): Design of a Pragmatic, Prospective Randomised Controlled Trial. Cancers. 2022 Jan;14(19):4818.
- Hall, IJ. Hall IJ. Patterns and Trends in Cancer Screening in the United States. Prev Chronic Dis [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 Oct 25];15. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2018/17_0465.htm. [CrossRef]
- Zugni F, Padhani AR, Koh DM, Summers PE, Bellomi M, Petralia G. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) for cancer screening in asymptomatic subjects of the general population: review and recommendations. Cancer Imaging. 2020 May 11;20(1):34. [CrossRef]
- Brenner DJ, Elliston CD. Estimated Radiation Risks Potentially Associated with Full-Body CT Screening. Radiology. 2004 Sep;232(3):735–8. [CrossRef]
- Brito-Rocha T, Constâncio V, Henrique R, Jerónimo C. Shifting the Cancer Screening Paradigm: The Rising Potential of Blood-Based Multi-Cancer Early Detection Tests. Cells. 2023 Jan;12(6):935. [CrossRef]
- Furtado CD, Aguirre DA, Sirlin CB, Dang D, Stamato SK, Lee P, et al. Whole-Body CT Screening: Spectrum of Findings and Recommendations in 1192 Patients. Radiology. 2005 Nov;237(2):385–94. [CrossRef]
- Schöder H, Gönen M. Screening for cancer with PET and PET/CT: potential and limitations. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med. 2007 Jan;48 Suppl 1:4S-18S.
- Han W, Kong R, Wang N, Bao W, Mao X, Lu J. Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Detection of Early Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer. Cancers. 2023 Jan;15(3):776. [CrossRef]
- Kim SY, Kim HS, Park HJ. Adverse events related to colonoscopy: Global trends and future challenges. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan 14;25(2):190–204. [CrossRef]
- Barbany G, Arthur C, Liedén A, Nordenskjöld M, Rosenquist R, Tesi B, et al. Cell-free tumour DNA testing for early detection of cancer – a potential future tool. J Intern Med. 2019;286(2):118–36. [CrossRef]
- Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, Kinde I, Wang Y, Agrawal N, et al. Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA in Early- and Late-Stage Human Malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 2014 Feb 19;6(224):224ra24-224ra24.
- Cree IA, Uttley L, Buckley Woods H, Kikuchi H, Reiman A, Harnan S, et al. The evidence base for circulating tumour DNA blood-based biomarkers for the early detection of cancer: a systematic mapping review. BMC Cancer. 2017 Oct 23;17(1):697. [CrossRef]
- Aravanis AM, Lee M, Klausner RD. Next-Generation Sequencing of Circulating Tumor DNA for Early Cancer Detection. Cell. 2017 Feb 9;168(4):571–4. [CrossRef]
- Wen YH, Chang PY, Hsu CM, Wang HY, Chiu CT, Lu JJ. Cancer screening through a multi-analyte serum biomarker panel during health check-up examinations: Results from a 12-year experience. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem. 2015 Oct 23;450:273–6. [CrossRef]
- Molina R, Marrades RM, Augé JM, Escudero JM, Viñolas N, Reguart N, et al. Assessment of a Combined Panel of Six Serum Tumor Markers for Lung Cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016 Feb 15;193(4):427–37. [CrossRef]
- Wu X, Wang HY, Shi P, Sun R, Wang X, Luo Z, et al. Long short-term memory model - A deep learning approach for medical data with irregularity in cancer predication with tumor markers. Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105362. [CrossRef]
- Bodaghi A, Fattahi N, Ramazani A. Biomarkers: Promising and valuable tools towards diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of Covid-19 and other diseases. Heliyon. 2023 Feb;9(2):e13323. [CrossRef]
- Hartl J, Kurth F, Kappert K, Horst D, Mülleder M, Hartmann G, et al. Quantitative protein biomarker panels: a path to improved clinical practice through proteomics. EMBO Mol Med. 2023 Apr 11;15(4):e16061. [CrossRef]
- Messner CB, Demichev V, Wendisch D, Michalick L, White M, Freiwald A, et al. Ultra-High-Throughput Clinical Proteomics Reveals Classifiers of COVID-19 Infection. Cell Syst. 2020 Jul 22;11(1):11-24.e4. [CrossRef]
- Landegren U, Hammond M. Cancer diagnostics based on plasma protein biomarkers: hard times but great expectations. Mol Oncol. 2021 Jun;15(6):1715–26. [CrossRef]
- Vignoli A, Tenori L, Morsiani C, Turano P, Capri M, Luchinat C. Serum or Plasma (and Which Plasma), That Is the Question. J Proteome Res. 2022 Apr 1;21(4):1061–72.
- Rai AJ, Gelfand CA, Haywood BC, Warunek DJ, Yi J, Schuchard MD, et al. HUPO Plasma Proteome Project specimen collection and handling: towards the standardization of parameters for plasma proteome samples. Proteomics. 2005 Aug;5(13):3262–77.
- Wong YL, Ramanathan A, Yuen KM, Mustafa WMW, Abraham MT, Tay KK, et al. Comparative sera proteomics analysis of differentially expressed proteins in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PeerJ. 2021;9:e11548. [CrossRef]
- Bader JM, Albrecht V, Mann M. MS-Based Proteomics of Body Fluids: The End of the Beginning. Mol Cell Proteomics MCP. 2023 Jul;22(7):100577. [CrossRef]
- Fu Q, Kowalski MP, Mastali M, Parker SJ, Sobhani K, van den Broek I, et al. Highly Reproducible Automated Proteomics Sample Preparation Workflow for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2018 Jan 5;17(1):420–8. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Tober-Lau P, Farztdinov V, Lemke O, Schwecke T, Steinbrecher S, et al. The human host response to monkeypox infection: a proteomic case series study. EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Nov 8;14(11):e16643. [CrossRef]
- Percy AJ, Yang J, Chambers AG, Mohammed Y, Miliotis T, Borchers CH. Protocol for Standardizing High-to-Moderate Abundance Protein Biomarker Assessments Through an MRM-with-Standard-Peptides Quantitative Approach. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;919:515–30.
- Füzéry AK, Levin J, Chan MM, Chan DW. Translation of proteomic biomarkers into FDA approved cancer diagnostics: issues and challenges. Clin Proteomics. 2013 Oct 2;10(1):13. [CrossRef]
- Van Gorp T, Cadron I, Despierre E, Daemen A, Leunen K, Amant F, et al. HE4 and CA125 as a diagnostic test in ovarian cancer: prospective validation of the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm. Br J Cancer. 2011 Mar 1;104(5):863–70. [CrossRef]
- Kim YS, Kang KN, Shin YS, Lee JE, Jang JY, Kim CW. Diagnostic value of combining tumor and inflammatory biomarkers in detecting common cancers in Korea. Clin Chim Acta. 2021 May 1;516:169–78. [CrossRef]
- Salvi S, Gurioli G, De Giorgi U, Conteduca V, Tedaldi G, Calistri D, et al. Cell-free DNA as a diagnostic marker for cancer: current insights. OncoTargets Ther. 2016;9:6549–59. [CrossRef]
- De Mattos-Arruda L, Caldas C. Cell-free circulating tumour DNA as a liquid biopsy in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2016 Mar;10(3):464–74. [CrossRef]
- Gao Q, Zeng Q, Wang Z, Li C, Xu Y, Cui P, et al. Circulating cell-free DNA for cancer early detection. The Innovation. 2022 May 6;3(4):100259. [CrossRef]
- Bronkhorst AJ, Ungerer V, Holdenrieder S. The emerging role of cell-free DNA as a molecular marker for cancer management. Biomol Detect Quantif. 2019 Mar;17:100087. [CrossRef]
- Kalendar R, Shustov AV, Akhmetollayev I, Kairov U. Designing Allele-Specific Competitive-Extension PCR-Based Assays for High-Throughput Genotyping and Gene Characterization. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:773956. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad E, Ali A, Nimisha null, Kumar Sharma A, Ahmed F, Mehdi Dar G, et al. Molecular approaches in cancer. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem. 2022 Dec 1;537:60–73. [CrossRef]
- Ito K, Suzuki Y, Saiki H, Sakaguchi T, Hayashi K, Nishii Y, et al. Utility of Liquid Biopsy by Improved PNA-LNA PCR Clamp Method for Detecting EGFR Mutation at Initial Diagnosis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Observational Study of 190 Consecutive Cases in Clinical Practice. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018 Mar;19(2):181–90. [CrossRef]
- Heitzer E, Haque IS, Roberts CES, Speicher MR. Current and future perspectives of liquid biopsies in genomics-driven oncology. Nat Rev Genet. 2019 Feb;20(2):71–88. [CrossRef]
- Zhai J, Arikit S, Simon SA, Kingham BF, Meyers BC. Rapid construction of parallel analysis of RNA end (PARE) libraries for Illumina sequencing. Methods San Diego Calif. 2014 May 1;67(1):84–90. [CrossRef]
- Belic J, Koch M, Ulz P, Auer M, Gerhalter T, Mohan S, et al. Rapid Identification of Plasma DNA Samples with Increased ctDNA Levels by a Modified FAST-SeqS Approach. Clin Chem. 2015 Jun;61(6):838–49. [CrossRef]
- Murtaza M, Dawson SJ, Tsui DWY, Gale D, Forshew T, Piskorz AM, et al. Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature. 2013 May 2;497(7447):108–12. [CrossRef]
- Newman AM, Lovejoy AF, Klass DM, Kurtz DM, Chabon JJ, Scherer F, et al. Integrated digital error suppression for improved detection of circulating tumor DNA. Nat Biotechnol. 2016 May;34(5):547–55. [CrossRef]
- Lanman RB, Mortimer SA, Zill OA, Sebisanovic D, Lopez R, Blau S, et al. Analytical and Clinical Validation of a Digital Sequencing Panel for Quantitative, Highly Accurate Evaluation of Cell-Free Circulating Tumor DNA. PloS One. 2015;10(10):e0140712. [CrossRef]
- García-Foncillas J, Alba E, Aranda E, Díaz-Rubio E, López-López R, Tabernero J, et al. Incorporating BEAMing technology as a liquid biopsy into clinical practice for the management of colorectal cancer patients: an expert taskforce review. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2017 Dec 1;28(12):2943–9. [CrossRef]
- Fiala C, Diamandis EP. Utility of circulating tumor DNA in cancer diagnostics with emphasis on early detection. BMC Med. 2018 Oct 2;16(1):166. [CrossRef]
- Manokhina I, Singh TK, Peñaherrera MS, Robinson WP. Quantification of cell-free DNA in normal and complicated pregnancies: overcoming biological and technical issues. PloS One. 2014;9(7):e101500. [CrossRef]
- Davies MPA, Sato T, Ashoor H, Hou L, Liloglou T, Yang R, et al. Plasma protein biomarkers for early prediction of lung cancer. eBioMedicine. 2023 Jul 1;93:104686. [CrossRef]
- Trinidad CV, Pathak HB, Cheng S, Tzeng SC, Madan R, Sardiu ME, et al. Lineage specific extracellular vesicle-associated protein biomarkers for the early detection of high grade serous ovarian cancer. Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 26;13(1):18341. [CrossRef]
- Tivey A, Church M, Rothwell D, Dive C, Cook N. Circulating tumour DNA — looking beyond the blood. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022 Sep;19(9):600–12. [CrossRef]
- Han SJ, Yoo S, Choi SH, Hwang EH. Actual half-life of alpha-fetoprotein as a prognostic tool in pediatric malignant tumors. Pediatr Surg Int. 1997;12(8):599–602.
- Riedinger JM, Wafflart J, Ricolleau G, Eche N, Larbre H, Basuyau JP, et al. CA 125 half-life and CA 125 nadir during induction chemotherapy are independent predictors of epithelial ovarian cancer outcome: results of a French multicentric study. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2006 Aug;17(8):1234–8. [CrossRef]
- Halner A, Hankey L, Liang Z, Pozzetti F, Szulc DA, Mi E, et al. DEcancer: Machine learning framework tailored to liquid biopsy based cancer detection and biomarker signature selection. iScience. 2023 May 19;26(5):106610. [CrossRef]
- Lin WY, Chen CH, Tseng YJ, Tsai YT, Chang CY, Wang HY, et al. Predicting post-stroke activities of daily living through a machine learning-based approach on initiating rehabilitation. Int J Med Inf. 2018/02/10 ed. 2018 Mar;111:159–64. [CrossRef]
- Uddin S, Khan A, Hossain ME, Moni MA. Comparing different supervised machine learning algorithms for disease prediction. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019 Dec 21;19(1):281. [CrossRef]
- Cruz JA, Wishart DS. Applications of machine learning in cancer prediction and prognosis. Cancer Inform. 2007 Feb 11;2:59–77. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Huang G. Application of support vector machine in cancer diagnosis. Med Oncol Northwood Lond Engl. 2011 Dec;28 Suppl 1:S613-618. [CrossRef]
- Wang HY, Chung CR, Chen CJ, Lu KP, Tseng YJ, Chang TH, et al. Clinically Applicable System for Rapidly Predicting Enterococcus faecium Susceptibility to Vancomycin. Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0091321. [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou E, Ma J, Collins GS, Steyerberg EW, Verbakel JY, Van Calster B. A systematic review shows no performance benefit of machine learning over logistic regression for clinical prediction models. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019/02/15 ed. 2019 Jun;110:12–22. [CrossRef]
- Liu MC, Oxnard GR, Klein EA, Swanton C, Seiden MV, CCGA Consortium. Sensitive and specific multi-cancer detection and localization using methylation signatures in cell-free DNA. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2020 Jun;31(6):745–59. [CrossRef]
- Cebekhulu E, Onumanyi AJ, Isaac SJ. Performance Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms for Energy Demand–Supply Prediction in Smart Grids. Sustainability. 2022 Jan;14(5):2546. [CrossRef]
- Yu JR, Chen CH, Huang TW, Lu JJ, Chung CR, Lin TW, et al. Energy Efficiency of Inference Algorithms for Clinical Laboratory Data Sets: Green Artificial Intelligence Study. J Med Internet Res. 2022 Jan 25;24(1):e28036.
- Kelly CJ, Karthikesalingam A, Suleyman M, Corrado G, King D. Key challenges for delivering clinical impact with artificial intelligence. BMC Med. 2019 Oct 29;17(1):195. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Faes L, Kale AU, Wagner SK, Fu DJ, Bruynseels A, et al. A comparison of deep learning performance against health-care professionals in detecting diseases from medical imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Digit Health. 2019 Oct;1(6):e271–97. [CrossRef]
- Yang S, Zhu F, Ling X, Liu Q, Zhao P. Intelligent Health Care: Applications of Deep Learning in Computational Medicine. Front Genet. 2021;12:607471. [CrossRef]
- Wan KW, Wong CH, Ip HF, Fan D, Yuen PL, Fong HY, et al. Evaluation of the performance of traditional machine learning algorithms, convolutional neural network and AutoML Vision in ultrasound breast lesions classification: a comparative study. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021 Apr;11(4):1381–93. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues AJ, Schonfeld E, Varshneya K, Stienen MN, Staartjes VE, Jin MC, et al. Comparison of Deep Learning and Classical Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Postoperative Outcomes for Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Procedures With State-of-the-art Performance. Spine. 2022 Dec 1;47(23):1637–44. [CrossRef]
- Chung CR, Wang HY, Lien F, Tseng YJ, Chen CH, Lee TY, et al. Incorporating Statistical Test and Machine Intelligence Into Strain Typing of Staphylococcus haemolyticus Based on Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. Front Microbiol. 2019/10/02 ed. 2019;10:2120. [CrossRef]
- Feng J, Phillips RV, Malenica I, Bishara A, Hubbard AE, Celi LA, et al. Clinical artificial intelligence quality improvement: towards continual monitoring and updating of AI algorithms in healthcare. NPJ Digit Med. 2022 May 31;5:66. [CrossRef]
- Editor, MB. Editor MB. What are T Values and P Values in Statistics? [Internet]. [cited 2023 Dec 13]. Available from: https://blog.minitab.com/en/statistics-and-quality-data-analysis/what-are-t-values-and-p-values-in-statistics.
- Parsons, VL. Parsons VL. Stratified Sampling. In: Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online [Internet]. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2017 [cited 2023 Dec 29]. p. 1–11. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781118445112.stat05999.pub2.
- Eche T, Schwartz LH, Mokrane FZ, Dercle L. Toward Generalizability in the Deployment of Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: Role of Computation Stress Testing to Overcome Underspecification. Radiol Artif Intell. 2021 Oct 27;3(6):e210097. [CrossRef]
- Lapić I, Šegulja D, Dukić K, Bogić A, Lončar Vrančić A, Komljenović S, et al. Analytical validation of 39 clinical chemistry tests and 17 immunoassays on the Alinity analytical system. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2022 May;82(3):199–209. [CrossRef]
- Sun Y, Li J, Xu Y, Zhang T, Wang X. Deep learning versus conventional methods for missing data imputation: A review and comparative study. Expert Syst Appl. 2023 Oct 1;227:120201. [CrossRef]
- Ndugga N, Published SA. Disparities in Health and Health Care: 5 Key Questions and Answers [Internet]. KFF. 2023 [cited 2023 Dec 24]. Available from: https://www.kff.org/racial-equity-and-health-policy/issue-brief/disparities-in-health-and-health-care-5-key-question-and-answers/.
- Kruk ME, Gage AD, Arsenault C, Jordan K, Leslie HH, Roder-DeWan S, et al. High-quality health systems in the Sustainable Development Goals era: time for a revolution. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6:e1196–252. [CrossRef]
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023 Jan;73(1):17–48.
- Youssef A, Ng MY, Long J, Hernandez-Boussard T, Shah N, Miner A, et al. Organizational Factors in Clinical Data Sharing for Artificial Intelligence in Health Care. JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Dec 19;6(12):e2348422. [CrossRef]
- Johnson AEW, Bulgarelli L, Shen L, Gayles A, Shammout A, Horng S, et al. MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset. Sci Data. 2023 Jan 3;10(1):1.
- Wang, H. Wang H. DARTA - A Permissionless Biomarker Data Marketplace [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Dec 24]. Available from: https://github.com/HsinYaoWang/DARTA.
- Shah NH, Halamka JD, Saria S, Pencina M, Tazbaz T, Tripathi M, et al. A Nationwide Network of Health AI Assurance Laboratories. JAMA [Internet]. 2023 Dec 20 [cited 2023 Dec 27]; Available from: . [CrossRef]
- Gregg AR, Skotko BG, Benkendorf JL, Monaghan KG, Bajaj K, Best RG, et al. Noninvasive prenatal screening for fetal aneuploidy, 2016 update: a position statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med. 2016 Oct 1;18(10):1056–65.
| MCED Products | Biomarkers | Algorithms | Model development | Report |
| Gallery (18,78) | cfDNA methylation | Logistic regression |
Train: CCD Validation:
|
|
| OneTest (6,35) | Protein biomarkers | Classical ML algorithmsLong short term memory algorithm |
Train: RWD Validation:
|
|
| OncoSeek (17) | Protein biomarkers | Classical ML algorithms |
Train: CCD Validation:
|
|
| CancerSeek (15) | cfDNA + protein biomarkers | Logistic regression |
Train: CCD Validation:
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





