Submitted:
29 December 2023
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Theory
Vibrotactile feedback / tactile internet.
Form this point of view the following questions arise.
2. Materials and Methods
Sample
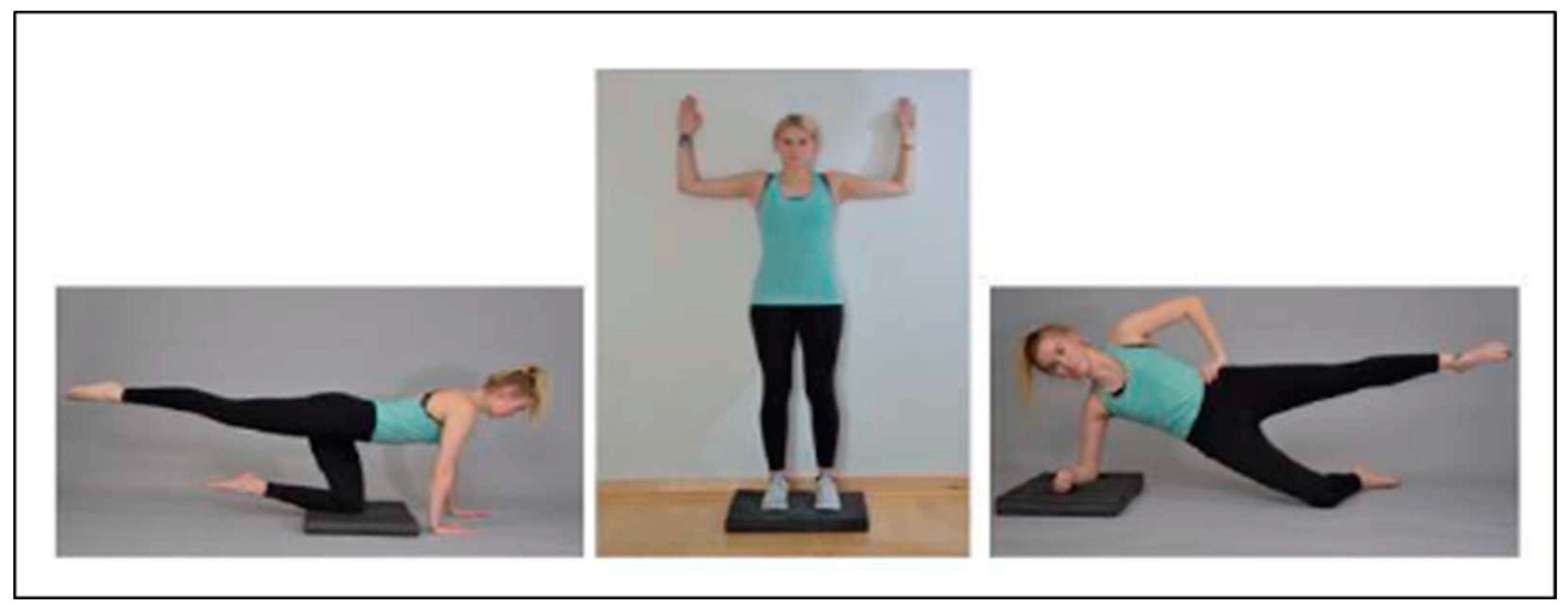
Materials
Study procedure.
3. Results
Research question 1.
Quality of movement and feasibility
Workload
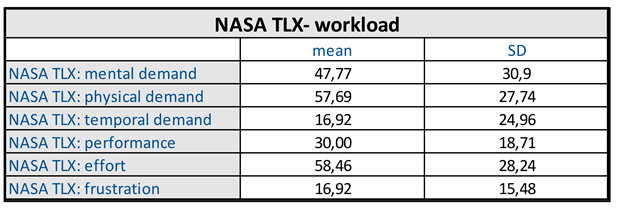 |
Research question 2.
Perceived purpose of the feedback
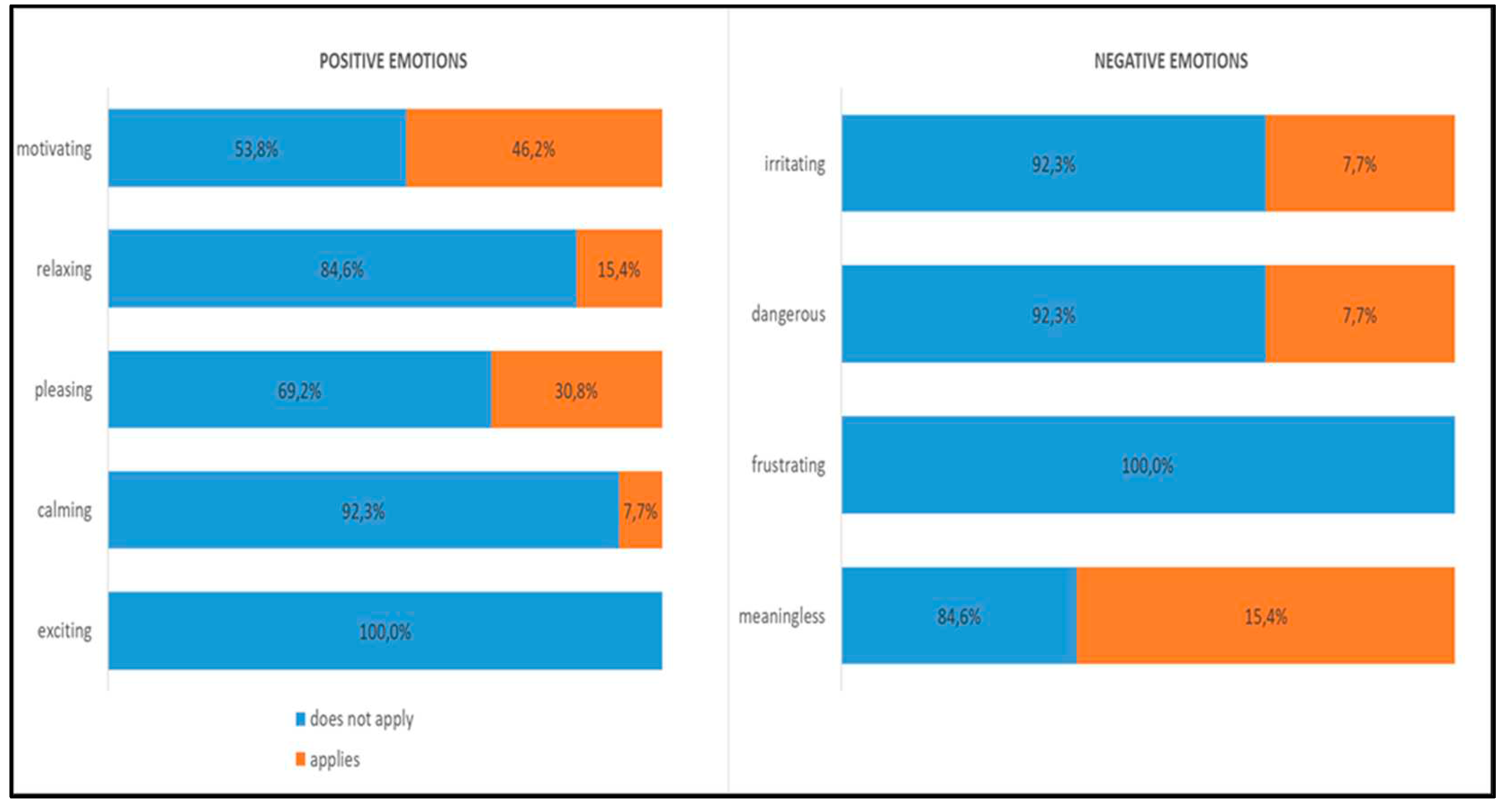
Feedback-associated emotions
4. Discussion
Quality of movement and feasibility
Workload
Intensity of the vibration
Perceived purpose of the feedback
Feedback-associated affective emotions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboagye E, Lilje S, Bengtsson C, Peterson A, Persson U, Skillgate E. Manual therapy versus advice to stay active for nonspecific back and/or neck pain: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Chiropr \& Man Ther. 2022;30(1):1–10. [CrossRef]
- Balagué F, Mannion AF, Pellisé F, Cedraschi C. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet. 2012;379(9814):482–91.
- Apeldoorn AT, Ostelo RW, van Helvoirt H, Fritz JM, de Vet HCW, van Tulder MW. The cost-effectiveness of a treatment-based classification system for low back pain: design of a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010 Mar;11:58. [CrossRef]
- Hartvigsen J, Hancock MJ, Kongsted A, Louw Q, Ferreira ML, Genevay S, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2356–67. [CrossRef]
- Harris SA, Rampersaud YR. The importance of identifying and modifying unemployment predictor variables in the evolution of a novel model of care for low back pain in the general population. Spine J. 2016;16(1):16–22. [CrossRef]
- Abdelraouf OR, Abdel-aziem AA. The relationship between core endurance and back dysfunction in collegiate male athletes with and without nonspecific low back pain. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016;11(3):337.
- Ferreira PH, Ferreira ML, Maher CG, Refshauge K, Herbert RD, Hodges PW. Changes in recruitment of transversus abdominis correlate with disability in people with chronic low back pain. Br J Sports Med. 2010 Dec;44(16):1166–72. [CrossRef]
- Lemos LFC, Teixeira CS, Mota CB. Low back pain and corporal balance of female brazilian selection canoeing flatwater athletes. Brazilian J Kinanthropometry Hum Perform. 2010;12(6):457–63.
- Mueller J, Mueller S, Stoll J, Baur H, Mayer F. Trunk extensor and flexor strength capacity in healthy young elite athletes aged 11--15 years. J Strength Cond Res. 2014;28(5):1328–34. [CrossRef]
- Engel T, Arampatzis A, Català MM, Kopinski S, Mayer F. Perturbations in Prevention and Therapy of Low Back Pain: a New Approach. Ger J Sport Med Zeitschrift fur Sport. 2018;69. [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein J, Floessel P, Engel T, Klewinghaus L, Stoll J, Behrens Ma, et al. Individualised exercise in chronic non-specific low back pain: a systematic review with meta-analysis on the effects of exercise alone or in combination with psychological interventions on pain and disability. medRxiv. 2021;
- Ogbeivor C, Elsabbagh L. Management approach combining prognostic screening and targeted treatment for patients with low back pain compared with standard physiotherapy: A systematic review & meta-analysis. Musculoskeletal Care. 2021 Mar; [CrossRef]
- Sowden G, Hill JC, Morso L, Louw Q, Foster NE. Advancing practice for back pain through stratified care (STarT Back). Brazilian J Phys Ther. 2018;22(4):255–64.
- Salkeld G, Cumming RG, Thomas M, Szonyi G, Westbury C, O’Neill E. The cost effectiveness of a home hazard reduction program to reduce falls among older persons. Aust N Z J Public Health. 2000;24(3):265–71. [CrossRef]
- Hohmann E, Tetsworth K, Bryant A. Physiotherapy-guided versus home-based, unsupervised rehabilitation in isolated anterior cruciate injuries following surgical reconstruction. Knee surgery, Sport Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:1158–67. [CrossRef]
- Szabo D, Gulyas A, Fitzek FHP, Lucani DE. Towards the tactile internet: Decreasing communication latency with network coding and software defined networking. In: Proceedings of European Wireless 2015; 21th European Wireless Conference. 2015. p. 1–6.
- Sigrist R, Rauter G, Riener R, Wolf P. Augmented visual, auditory, haptic, and multimodal feedback in motor learning: a review. Psychon Bull \& Rev. 2013;20(1):21–53. [CrossRef]
- Asseman F, Bronstein AM, Gresty MA. Using vibrotactile feedback of instability to trigger a forward compensatory stepping response. J Neurol. 2007;254(11):1555–61. [CrossRef]
- Kinnaird C, Lee J, Carender WJ, Kabeto M, Martin B, Sienko KH. The effects of attractive vs. repulsive instructional cuing on balance performance. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016;13(1):1–5.
- Ma CZ-H, Lee WC-C. A wearable vibrotactile biofeedback system improves balance control of healthy young adults following perturbations from quiet stance. Hum Mov Sci. 2017;55:54–60. [CrossRef]
- Nanhoe-Mahabier W, Allum JH, Pasman EP, Overeem S, Bloem BR. The effects of vibrotactile biofeedback training on trunk sway in Parkinson’s disease patients. Park \& Relat Disord. 2012;18(9):1017–21.
- Ballardini G, Florio V, Canessa A, Carlini G, Morasso P, Casadio M. Vibrotactile feedback for improving standing balance. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:94. [CrossRef]
- Islam MS, Lim S. Vibrotactile feedback in virtual motor learning: A systematic review. Appl Ergon. 2022;101:103694.
- Galy E, Paxion J, Berthelon C. Measuring mental workload with the NASA-TLX needs to examine each dimension rather than relying on the global score: an example with driving. Ergonomics [Internet]. 2018;61(4):517–27. Available from: http://doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2017.1369583.
- Kim E, Schneider O. Defining haptic experience: Foundations for understanding, communicating, and evaluating HX. In: Proceedings of the 2020 CHI conference on human factors in computing systems. 2020. p. 1–13.
- Bao T, Su L, Kinnaird C, Kabeto M, Shull PB, Sienko KH. Vibrotactile display design: Quantifying the importance of age and various factors on reaction times. PLoS One. 2019;14(8):e0219737. [CrossRef]
- Stuart M, Turman AB, Shaw J, Walsh N, Nguyen V. Effects of aging on vibration detection thresholds at various body regions. BMC Geriatr. 2003;3:1–10. [CrossRef]
- Morioka M, Griffin MJ. Thresholds for the perception of hand-transmitted vibration: Dependence on contact area and contact location. Somatosens \& Mot Res. 2005;22(4):281–97. [CrossRef]
- Tannert I, Schulleri KH, Michel Y, Villa S, Johannsen L, Hermsdörfer J, et al. Immediate effects of vibrotactile biofeedback instructions on human postural control. In: 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine \& Biology Society (EMBC). 2021. p. 7426–32.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





