Submitted:
23 December 2023
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
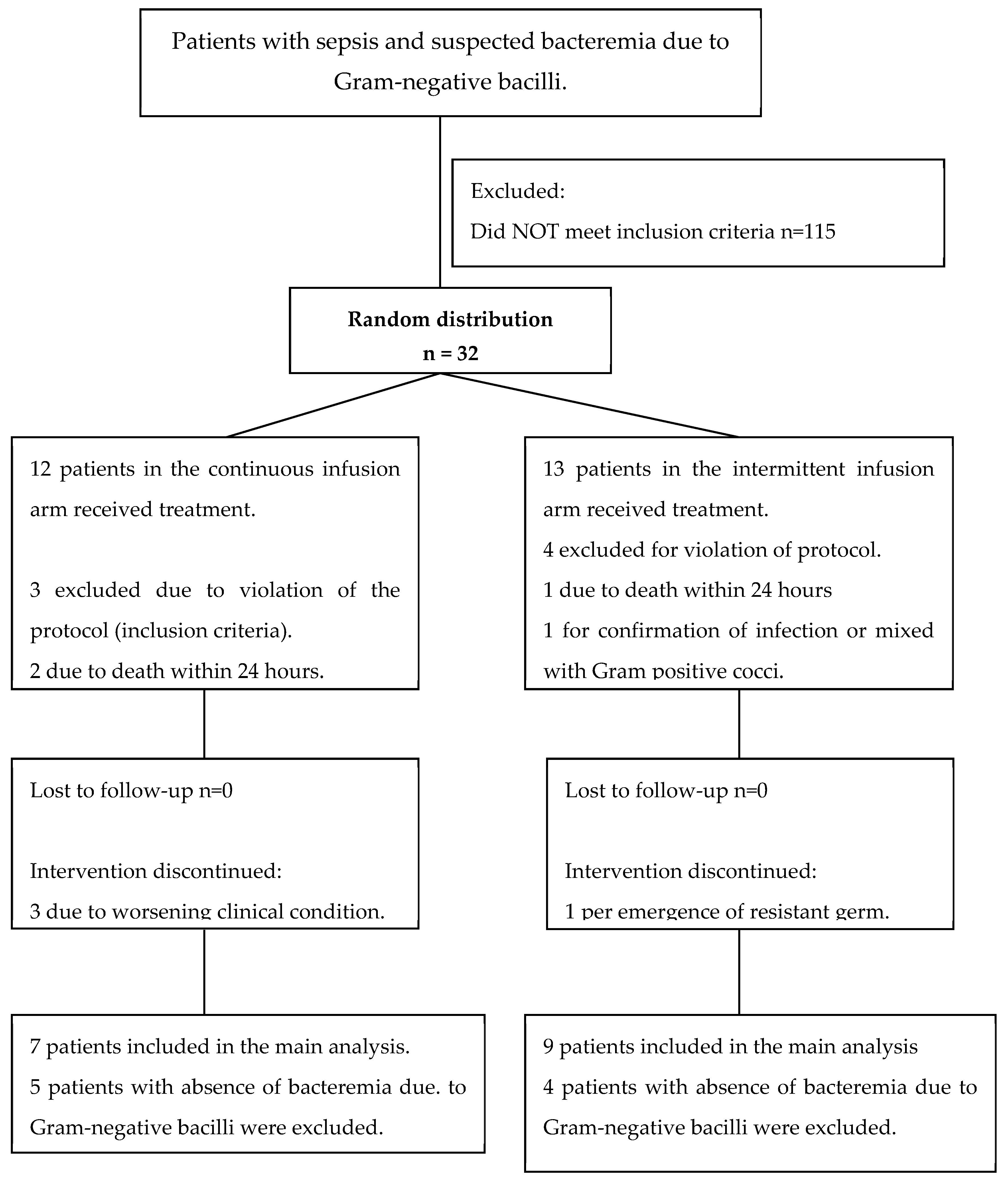
| Characteristics | Intermittent infusion n=12 |
Continuous infusion n=12 |
p+ Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality at discharge (n, %) | 2 (15.3) | 2 (16.6) | 0.47* |
|
Day 3 Presence of SIRS (n/total number evaluated, %) Clinical response* (n, %)
|
5/12 (41.6) 1 (7.69) 11 (84.62) 1 (7.69) |
6/12 (50.0) 0 (0) 10 (83.3) 2 (16.7) |
0.99 0.99 |
|
Day 7 Presence of SIRS (n/total number evaluated, %) Clinical response* (n, %)
|
5/12 (41.6) 5 (38.4) 5 (38.4) 3 (23.0) |
5/10 (50.0) 5 (41.6) 4 (33.3) 3 25.0) |
0.99 0.99 |
|
Day 14 Presence of SIRS (n/total number evaluated, %) Clinical response* (n, %) - Complete favorable - Favorable improvement - Unfavorable |
5/9 (55.5) 8 (61.5) 1 (7.7) 4 (30.7) |
5/9 (55.5) 9 (75.0) 0 3 (25.0) |
0.99 0.99 |
|
Day 28 Relapse (n/total number tested, %) |
1/10 (10) |
0/8 (0) |
0.99 |
| Length of stay in ICU (mean days, SD) |
18.7+/- 10.5 | 23+/-14.7 | 0.4+ |
| ICU length of stay after diagnosis of infection (mean days, SD) | 10.76+/- 9.5 | 17.9+/- 13.1 | 0.6+ |
| Time of hospitalization (mean days, SD) |
31.6+/- 15.9 | 35.8 +/- 24.8 | 0.9+ |
| Duration of cefepime administration (mean days +/-DS) | 10.6+/- 4.21 | 9.3+/-3.4 | 0.8+ |
| Cefepime discontinuation ratio (n, %) Improvement Worsening of clinical picture Appearance of multi-resistant germ |
10 (77) 2 (15.4) 1 (7.6) |
9 (75) 3 (25) 0 |
0.99* |
| Characteristics | Intermittent infusion n = 9 |
Continuous infusion n = 7 |
p+ Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality at discharge (n, %) | 2 (22) | 0 | 0.30* |
|
Day 3 Presence of SIRS (n/total number evaluated, %) Clinical response* (n, %)
|
3/9 (33.3) 4 (44.4) 4 (44.4) 1 (11.1) |
4/7 (57.1) 4 (57.1) 2 (28.6) 1 (14.3) |
0.40 0.99 |
|
Day 7 Presence of SIRS (n/total number evaluated, %) Clinical response* (n, %)
Total favorable response (n, %) |
2/8 (25) 4 (44.4) 4 (44.4) 1 (11.1) 6/8 (75.0) 6/8 (75.0) |
4/7 (57.1) 4 (57.1) 2 (28.6) 1 (14.3) 4/4 (100) 3/4 (75.0) |
0.23 0.99 0.41 0.28 |
|
Day 14 Presence of SIRS (n/total number evaluated, %) Clinical response* (n, %)
|
2/5 (40) 6 (66.7) 1 (11.1) 2 (22.2) |
4/6 (66.7) 6 (85.7) 0 1 (14.3) |
0.39 0.99 |
|
Day 28 Relapse (n, %) |
1/7 (14.3) |
0/6 (0) |
0.99 |
| ICU length of stay (days, SD) | 16.8+/- 8.8 | 22+/-13.31 | 0.9+ |
| Length of ICU stay after diagnosis of infection (days, SD) | 8.22+/- 6.5 | 17+/- 7.8 | 0.6+ |
| Duration of cefepime administration (mean days +/-SD) | 10.6+/- 4.7 | 10.3+/-0.75 | 0.8+ |
| Cefepime discontinuation ratio (n, %) Improvement Worsening of clinical picture Appearance of multi-resistant germ |
8 (88.8) 0 1 (11.2) |
6 (85.7) 1 (14.3) 0 |
0.7* |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
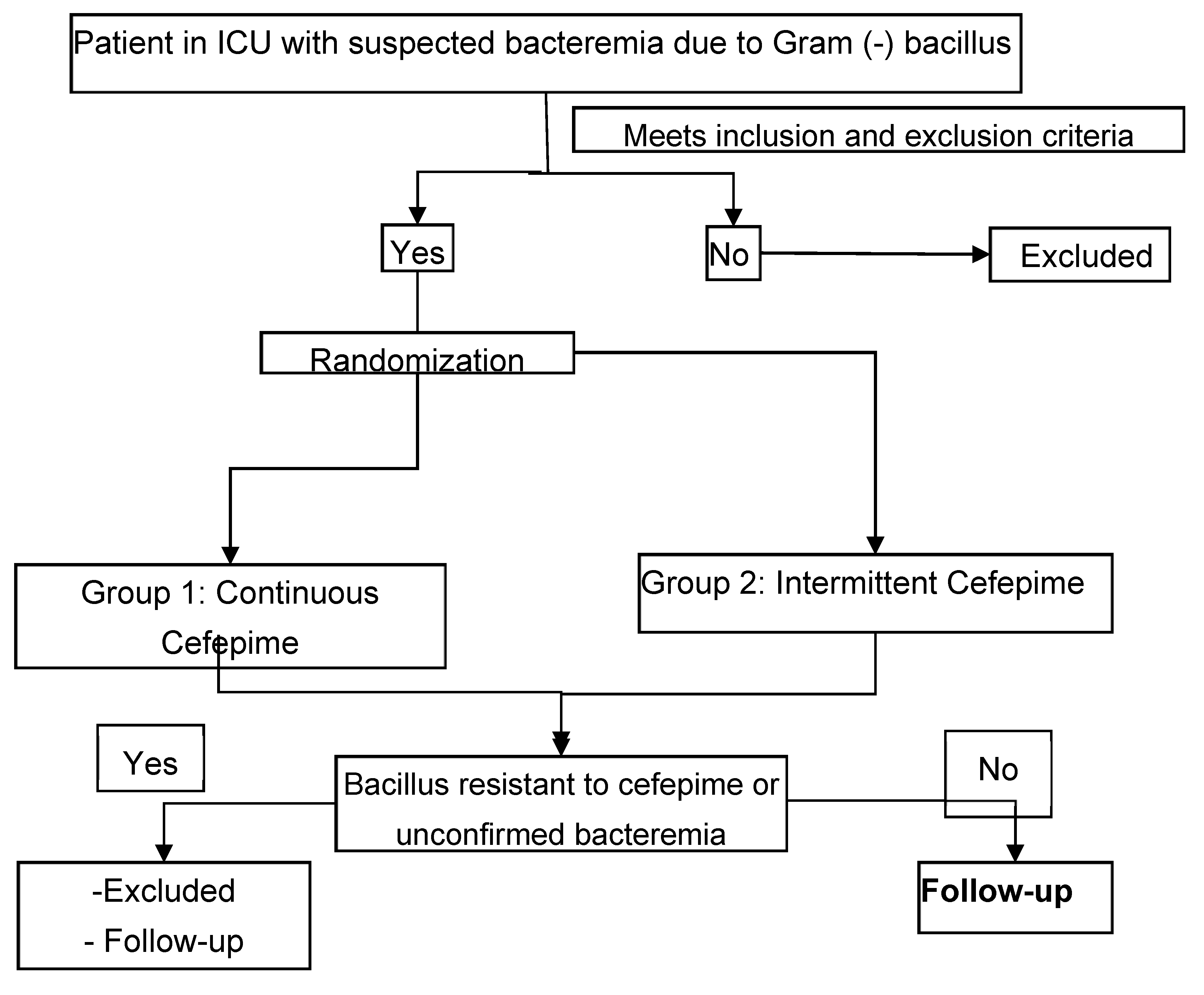
ICU: Intensive care unit
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guilhaumou R, Benaboud S, Bennis Y, Dahyot-Fizelier C, Dailly E, Gandia P, et al. Optimization of the treatment with beta-lactam antibiotics in critically ill patients-guidelines from the French Society of Pharmacology and Therapeutics (Société Française de Pharmacologie et Thérapeutique-SFPT) and the French Society of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine (Société Française d'Anesthésie et Réanimation-SFAR). Crit Care. 2019;23(1):104. Epub 20190329. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Han Y, Zhang J, Zhang HZ, Zhang XY, Wang YM. Multidrug-resistant organisms in intensive care units and logistic analysis of risk factors. World J Clin Cases. 2022;10(6):1795-805. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barradell LB, Bryson HM. Cefepime. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1994;47(3):471-505. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais GM, Chang J, Barreto EF, Stitt G, Downes KJ, Alshaer MH, et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Cefepime. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022;61(7):929-53. Epub 20220629. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Burgess DS, Hastings RW, Hardin TC. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cefepime administered by intermittent and continuous infusion. Clin Ther. 2000;22(1):66-75. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeRyke CA, Lee SY, Kuti JL, Nicolau DP. Optimising dosing strategies of antibacterials utilising pharmacodynamic principles: impact on the development of resistance. Drugs. 2006;66(1):1-14. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasiakou SK, Lawrence KR, Choulis N, Falagas ME. Continuous versus intermittent intravenous administration of antibacterials with time-dependent action: a systematic review of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters. Drugs. 2005;65(17):2499-511. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georges B, Conil JM, Cougot P, Decun JF, Archambaud M, Seguin T, et al. Cefepime in critically ill patients: continuous infusion vs. an intermittent dosing regimen. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;43(8):360-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Early Communication About an Ongoing Safety Review Cefepime (marketed as Maxipime). http://www.fda.gov/Cder/Drug/early_comm/cefepime.htm. Acceso 25 de febrero del 2008.
- Yahav D, Paul M, Fraser A, Sarid N, Leibovici L. Efficacy and safety of cefepime: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7(5):338-48. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim PW, Wu YT, Cooper C, Rochester G, Valappil T, Wang Y, et al. Meta-analysis of a possible signal of increased mortality associated with cefepime use. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51(4):381-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georges, B. Georges, B., Saivin, S., Cougot, P. et al. Cefepime in critically ill patients: continuous infusion versus intermittent regimen. Crit Care 5 (Suppl 1), P093 (2001). [CrossRef]
- Roberts JA, Boots R, Rickard CM, Thomas P, Quinn J, Roberts DM, et al. Is continuous infusion ceftriaxone better than once-a-day dosing in intensive care? A randomized controlled pilot study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;59(2):285-91. Epub 20061128. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zanten AR, Oudijk M, Nohlmans-Paulssen MK, van der Meer YG, Girbes AR, Polderman KH. Continuous vs. intermittent cefotaxime administration in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and respiratory tract infections: pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics, bacterial susceptibility and clinical efficacy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63(1):100-9. Epub 20060721. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lau WK, Mercer D, Itani KM, Nicolau DP, Kuti JL, Mansfield D, et al. Randomized, open-label, comparative study of piperacillin-tazobactam administered by continuous infusion versus intermittent infusion for treatment of hospitalized patients with complicated intra-abdominal infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(11):3556-61. Epub 20060828. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chapuis TM, Giannoni E, Majcherczyk PA, Chioléro R, Schaller MD, Berger MM, et al. Prospective monitoring of cefepime in intensive care unit adult patients. Crit Care. 2010;14(2):R51. Epub 20100401. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Philpott CD, Droege CA, Droege ME, Healy DP, Courter JD, Ernst NE, et al. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Extended-Infusion Cefepime in Critically Ill Patients Receiving Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: A Prospective, Open-Label Study. Pharmacotherapy. 2019;39(11):1066-76. Epub 20191022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean-Michel V, Homey C, Devos P, Delannoy PY, Boussekey N, Caulier T, et al. Continuous Infusion of High Doses of Cefepime in Intensive Care Unit: Assessment of Steady-State Plasma Level and Incidence on Neurotoxicity. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022;12(1). Epub 20221230. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chow SC, Shao J, Wang H. Sample Size calculation in clinical research. Marcel Dekker Inc.New York 2004: 1-15; 27-32; 204-211.
- Marshall JC, Cook DJ, Christou NV, Bernard GR, Sprung CL, Sibbald WJ. Multiple organ dysfunction score: a reliable descriptor of a complex clinical outcome. Crit Care Med. 1995;23(10):1638-52. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med. 2003;31(4):1250-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra T, Cohen J. The international sepsis forum consensus conference on definitions of infection in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(7):1538-48. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Intermittent infusion n = 13 |
Continuous infusion n = 12 |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (n, %) Female |
9 (69.2) |
4 (33.3) |
| Age (mean years, SD) | 54.2 +/- 21.4 | 60.2 +/- 16.9 |
| Average ICU stay prior to infection (days, SD) | 8.+/-4.5 | 5.6+/-5.1 |
| APACHE II score at study entry (mean, SD) | 15.2 +/- 8.01 | 12.7 +/- 6.3 |
| SOFA score at study entry, (mean, SD) | 6+/- 3.3 | 8 +/- 3.5 |
| Classification (n, %) Sepsis Severe sepsis Septic shock Multiple organ failure |
9 (69.2) 3 (23.0) 1 (7.7) 0 |
6 (50.0) 2 (16.7) 2 (16.7) 2 (16.7) |
| Bacteremia (n, %) | 9 (69.2) | 7 (58.3) |
| Origin of infection (n, %) Pneumonia Urosepsis Catheter sepsis Peritonitis Skin and soft tissue Tracheobronchitis Surgical site infection Bloodstream infection |
1 (7.7) 5 (38.5) 2 (14.4) 1 (7.7) 1 (7.7) 1 (7.7) 1 (7.7) 1 (7.7) |
3 (25.0) 2 (16.6) 3 (25.0) 1 (8.3) 1 (8.3) 1 (8.3) 1 (8.3) 0 |
| Characteristics | Intermittent infusion n = 9 |
Continuous infusion n = 7 |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (n, %) Female |
6 (67) |
3 (43) |
| Age (years, SD) | 55.3 +/- 20.5 | 63.4 +/- 15.4 |
| Mean ICU stay before infection (days, SD) | 8.6+/-5.6 | 5+/-5.9 |
| APACHE II score at study entry (mean, SD) | 16.55 +/- 9.3 | 13.28 +/- 5.40 |
| SOFA score at study entry, (mean, SD) | 5.33+/- 1.42 | 7.6 +/- 1.72 |
| Classification (n, %) Sepsis Severe sepsis Septic shock Multiple organ failure |
6 (66.7) 2 (22.2) 1 (11.1) 0 (0.0) |
3 (42.8) 2 (28.6) 1 (14.3) 1 (14.3) |
| Isolated germ (n, %) E. coli P. aeruginosa E. cloacae S. marcencens P. mirabilis K. oxytoca |
6 (66.7) 1 (11.1) 2 (22.2) |
2 (28.6) 2 (28.6) 0 1 (14.3) 1 (14.3) 1(14.3) |
| Origin of infection (n, %) Pneumonia Bloodstream Catheter sepsis Surgical site infection Urosepsis Skin and soft tissue |
1 (11.1) 2 (22.2) 1 (11.1) 4 (44.4) 1 (11.1) |
1 (12.5) 0 3 (37.5) 1 (12.5) 2 (25) 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





