Submitted:
29 December 2023
Posted:
29 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Hypothermia improved functional outcome and cognitive function
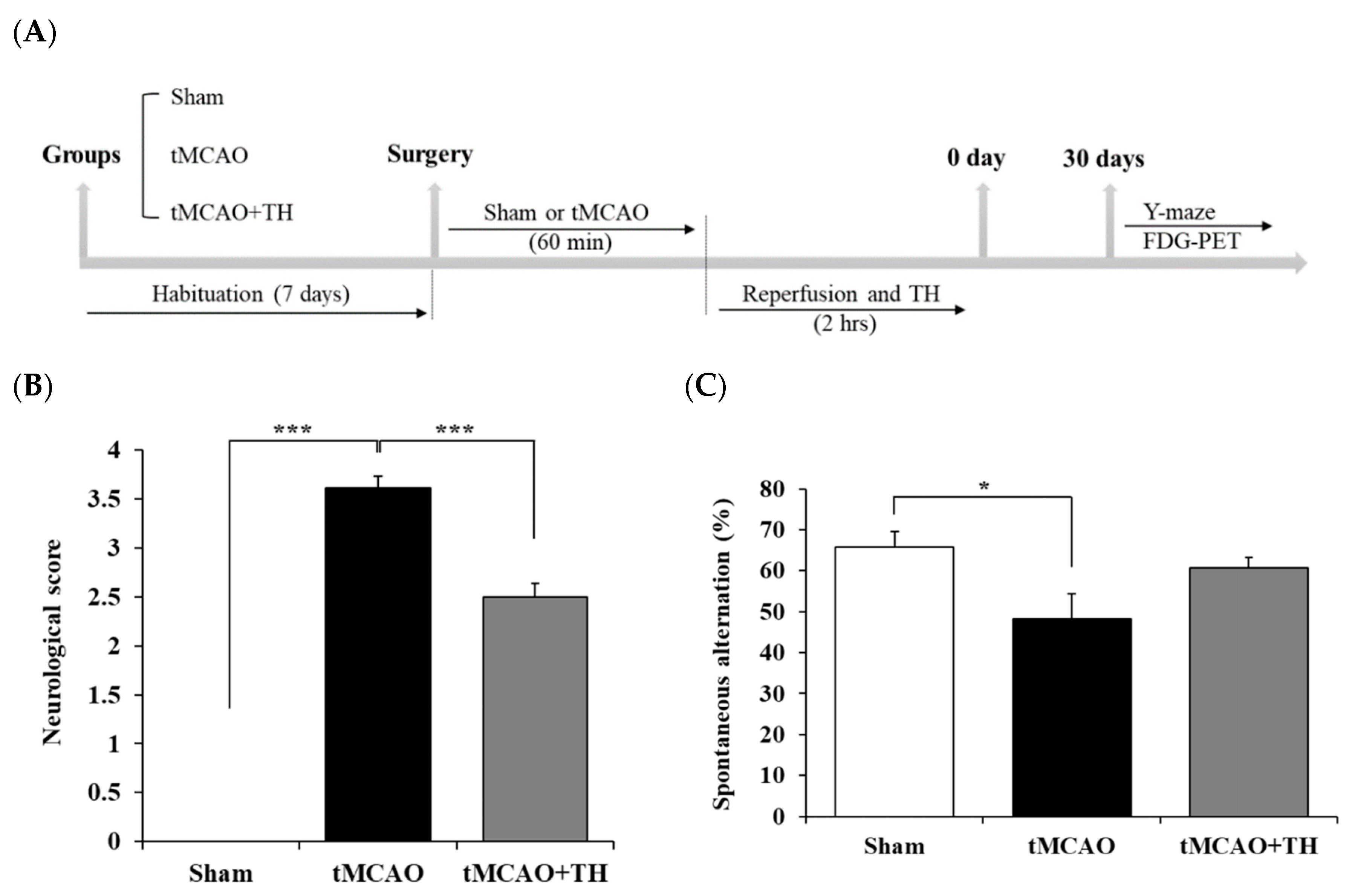
3.2. Cerebral glucose metabolism
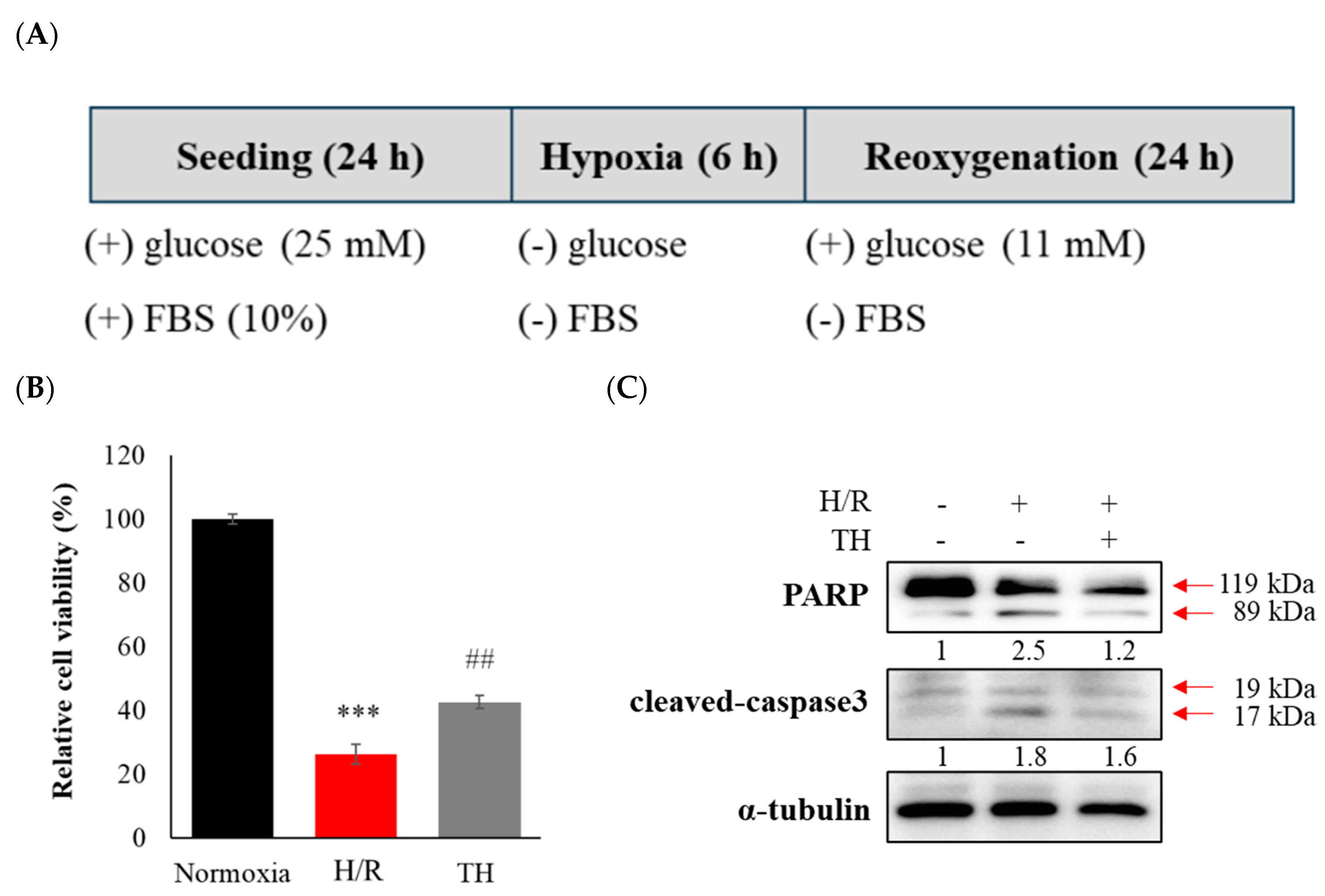
3.3. Therapeutic hypothermia attenuated H/R-induced neuronal apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanc R, Escalard S, Baharvadhat H, Desilles JP, Boisseau W, Fahed R; et al. Recent advances in devices for mechanical thrombectomy. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2020, 17, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuma A, You JS, Yenari MA. Targeting Reperfusion Injury in the Age of Mechanical Thrombectomy. Stroke. 2018, 49, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettelt P, Maier IL, Schnieder M, Bahr M, Behme D, Psychogios MN; et al. Bridging therapy is associated with improved cognitive function after large vessel occlusion stroke - an analysis of the German Stroke Registry. Neurol Res Pract. 2020, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun JH, Tan L, Yu JT. Post-stroke cognitive impairment: Epidemiology, mechanisms and management. Ann Transl Med. 2014, 2, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Boysen G, Christensen H. Stroke severity determines body temperature in acute stroke. Stroke. 2001, 32, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter EJ, Carraretto M. The neurological and cognitive consequences of hyperthermia. Crit Care. 2016, 20, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diprose WK, Liem B, Wang MTM, Sutcliffe JA, Brew S, Caldwell JR; et al. Impact of Body Temperature Before and After Endovascular Thrombectomy for Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke. Stroke. 2020, 51, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada M, Alkayed NJ, Goto S, Crain BJ, Traystman RJ, Shaivitz A; et al. Estrogen receptor antagonist ICI182, 780 exacerbates ischemic injury in female mouse. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 2000, 20, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Lee H, Park M-N, Lim JS, Baek HS, Kim S, Kim HW; et al. The Effect of Hypothermia on Cognitive Impairment and Anxiety-like Behavior in a Cardiac Arrest Mouse Model. Quant BioSci. 2023:9-16.
- Maier CM, Ahern Kv, Cheng ML, Lee JE, Yenari MA, Steinberg GK. Optimal depth and duration of mild hypothermia in a focal model of transient cerebral ischemia: Effects on neurologic outcome, infarct size, apoptosis, and inflammation. Stroke. 1998, 29, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang Y, Liu X, Zhao J, Tan X, Liu B, Zhang G; et al. Hypothermia-induced ischemic tolerance is associated with Drp1 inhibition in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury of mice. Brain Research. 2016, 1646, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori K, Lee H, Hurn PD, Crain BJ, Traystman RJ, DeVries AC. Cognitive deficits after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke. 2000, 31, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi M, Lee Y, Cho S-H. Angelica tenuissima Nakai ameliorates cognitive impairment and promotes neurogenesis in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Chinese journal of integrative medicine. 2018, 24, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park J-H, Hong J-H, Lee S-W, Ji HD, Jung J-A, Yoon K-W; et al. The effect of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion on the pathology of Alzheimer's disease: A positron emission tomography study in rats. Scientific reports. 2019, 9, 14102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casteels C, Vunckx K, Aelvoet S-A, Baekelandt V, Bormans G, Van Laere K; et al. Construction and evaluation of quantitative small-animal PET probabilistic atlases for [18F] FDG and [18F] FECT functional mapping of the mouse brain. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e65286.
- Thiel A, Cechetto DF, Heiss W-D, Hachinski V, Whitehead SN. Amyloid burden, neuroinflammation, and links to cognitive decline after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2014, 45, 2825–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost NS, Brodtmann A, Pase MP, van Veluw SJ, Biffi A, Duering M; et al. Post-stroke cognitive impairment and dementia. Circulation Research. 2022, 130, 1252–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dichgans M, Leys D. Vascular cognitive impairment. Circulation research. 2017, 120, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher M, Feuerstein G, Howells DW, Hurn PD, Kent TA, Savitz SI; et al. Update of the stroke therapy academic industry roundtable preclinical recommendations. Stroke. 2009, 40, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallmünzer B, Kollmar R. Temperature management in stroke–an unsolved, but important topic. Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2011, 31, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridar A, Bershad EM, Emiru T, Iaizzo PA, Suarez JI, Divani AA. Therapeutic hypothermia in stroke and traumatic brain injury. Frontiers in neurology. 2011, 2, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Tveita T, Sieck GC. Physiological impact of hypothermia: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Physiology. 2022, 37, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir RA, Pabaney AH. Therapeutic hypothermia and ischemic stroke: A literature review. Surgical Neurology International. 2016;7:S381.
- Xue D, Huang Z-G, Smith KE, Buchan AM. Immediate or delayed mild hypothermia prevents focal cerebral infarction. Brain research. 1992, 587, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber PA, Hoyte L, Colbourne F, Buchan AM. Temperature-regulated model of focal ischemia in the mouse: A study with histopathological and behavioral outcomes. Stroke. 2004, 35, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenari MA, Hemmen TM. Therapeutic hypothermia for brain ischemia: Where have we come and where do we go? Stroke. 2010;41:S72-S4.
- Wu D, Chen J, Zhang X, Ilagan R, Ding Y, Ji X. Selective therapeutic cooling: To maximize benefits and minimize side effects related to hypothermia. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 2022, 42, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S, Zhang X, Zhong H, Li X, Wu Y, Ju J; et al. Hypothermia evoked by stimulation of medial preoptic nucleus protects the brain in a mouse model of ischaemia. Nature Communications. 2022, 13, 6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield DA, Halliwell B. Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019, 20, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato T, Inui Y, Nakamura A, Ito K. Brain fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET in dementia. Ageing research reviews. 2016, 30, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellar D, Craft S. Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders: Mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. The Lancet Neurology. 2020, 19, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An Y, Varma VR, Varma S, Casanova R, Dammer E, Pletnikova O; et al. Evidence for brain glucose dysregulation in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & dementia. 2018, 14, 318–329. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver NA, Kuijf HJ, Aben HP, Abrigo J, Bae H-J, Barbay M; et al. Strategic infarct locations for post-stroke cognitive impairment: A pooled analysis of individual patient data from 12 acute ischaemic stroke cohorts. The Lancet Neurology. 2021, 20, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao L, Biesbroek JM, Shi L, Liu W, Kuijf HJ, Chu WW; et al. Strategic infarct location for post-stroke cognitive impairment: A multivariate lesion-symptom mapping study. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 2018, 38, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Karussis D, Leker R, Abramsky O. Cognitive dysfunction following thalamic stroke: A study of 16 cases and review of the literature. Journal of the neurological sciences. 2000, 172, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obayashi, S. Cognitive and linguistic dysfunction after thalamic stroke and recovery process: Possible mechanism. AIMS neuroscience. 2022, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgstedt L, Bratke S, Blobner M, Pötzl C, Ulm B, Jungwirth B; et al. Isoflurane has no effect on cognitive or behavioral performance in a mouse model of early-stage Alzheimer's disease. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2022;16.
- Lin D, Zuo Z. Isoflurane induces hippocampal cell injury and cognitive impairments in adult rats. Neuropharmacology. 2011, 61, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
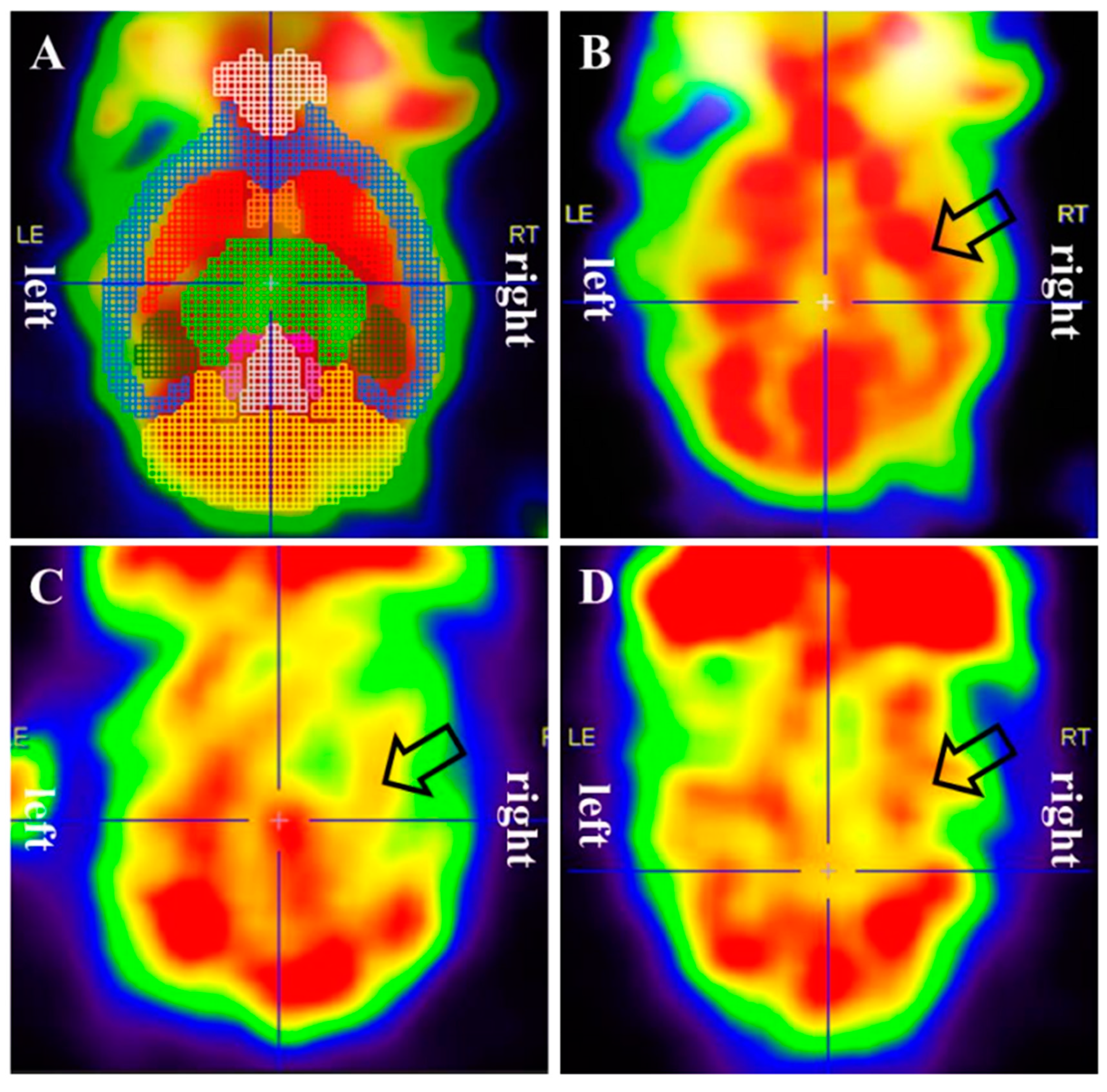
| Regions | Side | Mean (standard deviation) | p-value | |||||
| Sham | tMCAO | tMCAO+TH | Sham vstMCAO | Sham vstMCAO+TH | tMCAO vstMCAO+TH | |||
| Amygdala | left | 0.828 (0.081) | 0.904 (0.064) | 0.890 (0.066) | 0.115 | 0.213 | 1.000 | |
| right | 0.883 (0.107) | 0.856 (0.087) | 0.904 (0.088) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.883 | ||
| Cortex | left | 0.960 (0.036) | 0.970 (0.043) | 0.943 (0.035) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.438 | |
| right | 0.998 (0.085) | 0.948 (0.107) | 0.942 (0.094) | 0.867 | 0.624 | 1.000 | ||
| Hippocampus | left | 1.141 (0.070) | 1.062 (0.079) | 1.151 (0.079) | 0.134 | 1.000 | 0.065 | |
| right | 1.187 (0.109) | 1.062 (0.078) | 1.162 (0.102) | 0.044* | 1.000 | 0.127 | ||
| Midbrain | left | 1.280 (0.131) | 1.175 (0.086) | 1.260 (0.108) | 0.193 | 1.000 | 0.362 | |
| right | 1.282 (0.152) | 1.143 (0.081) | 1.243 (0.135) | 0.106 | 1.000 | 0.345 | ||
| Striatum | left | 1.165 (0.078) | 1.082 (0.031) | 1.133 (0.069) | 0.040* | 0.887 | 0.307 | |
| right | 1.191 (0.116) | 1.074 (0.052) | 1.145 (0.091) | 0.043* | 0.845 | 0.345 | ||
| Thalamus | left | 1.224 (0.086) | 1.102 (0.049) | 1.213 (0.079) | 0.007** | 1.000 | 0.012* | |
| right | 1.280 (0.136) | 1.135 (0.067) | 1.248 (0.113) | 0.038* | 1.000 | 0.127 | ||
| Inferior colliculi | left | 1.336 (0.165) | 1.205 (0.074) | 0.265 (0.084) | 0.083 | 0.570 | 0.850 | |
| right | 1.390 (0.209) | 1.222 (0.083) | 1.331 (0.124) | 0.089 | 1.000 | 0.412 | ||
| Superior colliculi | 1.318 (0.152) | 1.182 (0.053) | 1.261 (0.099) | 0.056 | 0.827 | 0.438 | ||
| Basal forebrain | 1.046 (0.041) | 1.031 (0.037) | 1.006 (0.042) | 1.000 | 0.126 | 0.602 | ||
| Central gray | 1.434 (0.177) | 1.237 (0.079) | 0.328 (0.138) | 0.023* | 0.325 | 0.551 | ||
| Hypothalamus | 1.078 (0.086) | 1.043 (0.058) | 1.083 (0.053) | 0.899 | 1.000 | 0.675 | ||
| Olfactory bulb | 1.377 (0.135) | 1.321 (0.173) | 1.248 (0.142) | 1.000 | 0.220 | 0.944 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





