1. Introduction
Cancer is a rapid creation of abnormal cells (usually derived from a single abnormal cell) that have lost normal control mechanisms and thus are able to multiply continuously, growing beyond their usual boundaries, and can then invade adjoining tissues, migrate to distant parts of the body and spread to other organs (Mathur et al., 2020; Ekiz et al., 2023). Cancer arises from the transformation of normal cells into tumor cells in a multistage process that generally progresses from a pre-cancerous lesion to a malignant tumor. Symptoms vary widely depending on the location, type, size, and extent of the cancer. Breast, cervical, lung, liver, bone, nerve, melanomas, testicular, prostate, thyroid, pancreatic, oral, colorectal are the most common cancers in human. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, excess body weight, poor nutrition, unhealthy diet, exposure to hazardous chemicals and/or radiations, genetic factors, physical inactivity and air pollution are risk factors for cancer and other noncommunicable diseases (Donalson, 2004; Kumari, 2020; Siegel et al.; 2023). Cancer is considered as a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for nearly 10 million of deaths in 2020. Each year, approximately 400 000 children develop cancer. Cancer mortality can be reduced when detected and treated early. Although some cancers may not necessary required treatment (because they are very slow growing), most cancers do require active treatment. A correct cancer diagnose is indispensable for appropriate and effective treatment because each cancer type requires a specific treatment regimen (type of cancer, stage at diagnosis, and the person’s overall health). Treatment usually includes surgery (if the cancer is confined to only one spot in the body), radiotherapy, and systemic therapy (chemotherapy, hormonal treatments, immune therapy, targeted biological therapies), either individually or in combination (Fuente et al., 2022; Kamal et al., 2022; Ekiz et al., 2023). Treatments are continuously improving to reduce side effects of treatments.
Nanotechnology offers unique opportunities to address limitations, and enhance the therapeutic efficacy of G. Lucidum in cancer treatment. The use of nanoscale materials, such as nanoparticles, allows for the encapsulation, and delivery of G. lucidum bioactive compounds, providing several advantages. Nanoparticles can protect the compounds from degradation, improving their solubility, and enable controlled release, thereby enhancing their bioavailability, and extending their circulation time in the body [4]. Furthermore, nanotechnology enables the development of targeted drug delivery systems using G. lucidum-based nanocarriers [4]. Functionalization of nanoparticles with targeting ligands, such as antibodies or peptides, can facilitate their specific accumulation at the tumor site, minimizing off-target effects, and improving therapeutic outcomes [5]. Additionally, nanotechnology-based strategies can overcome multidrug resistance, a major challenge in cancer therapy, by co-delivering G. Lucidum compounds with chemotherapeutic agents or by modulating drug efflux mechanisms [6]. In summary, the combination of G. lucidum and nanotechnology holds immense promise for advancing cancer therapy. The application of nanotechnology enables improved delivery, enhanced bioavailability, and targeted delivery of bioactive compounds from G. lucidum, overcoming the limitations associated with traditional formulations. The integration of nanomaterials with G. lucidum also offers opportunities for cancer diagnostics, and imaging [7]. Further research, and development in this interdisciplinary field are crucial to harness the full potential of GL in nanotechnology-based cancer therapy, ultimately leading to improved treatment outcomes, and patient well-being.
It is imperative to implement strategies that improve the procedures for quality, and safety control in order to establish clear standards, and consistency for G. lucidum nanotechnology formulations. These measures are essential to gain a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms by which these formulations exert their effects in cancer therapy, and to facilitate the characterization of their active components.
The main objective of this review is to harness the synergistic potential of G. lucidum, and nanotechnology to revolutionize cancer therapy, by providing an updated literature analysis on its the pharmacological properties, toxicity profile, application in cancer therapy, preclinial and clinical trials, as well as regulatory considerations related to the use of new drug delivery nanosystems using G. lucidum. These nanosystems include silver nanoparticles, polymeric micelles, lipid nanoparticles, and polymeric nanoparticles. The review will primarily focus on exploring the anticancer properties of G. lucidum polysaccharides, and triterpenes, along with their underlying mechanisms. Using nanomaterials and innovative strategies, we strive to enhance the delivery, efficacy, and selectivity of G. lucidum bioactive compounds, paving the way for improved treatment outcomes, and the development of personalized therapeutic approaches for cancer patients.
2. Review Methodology
In this review, a complete survey of the chemical composition, the synergistic potential and biological properties of naturals products derived from the mushroom is provided as well as its the uses in traditional medicine. The search terms included the terms Ganoderma lucidum using the electronic databases Scifinder, Pubmed, Science Direct, Dictionnary of Natural Products, Web of Science, Google Scholar, books, theses, and library resources. All data were organized using Microsoft Office 2016 software and the structures were drawn using ChemDraw Professional 16.0.
3. Ganoderma lucidum: Botanical Overview, Characterization, Uses in Traditional Medicine and Chemical Studies
3.1. Botanical Overview and Characterization
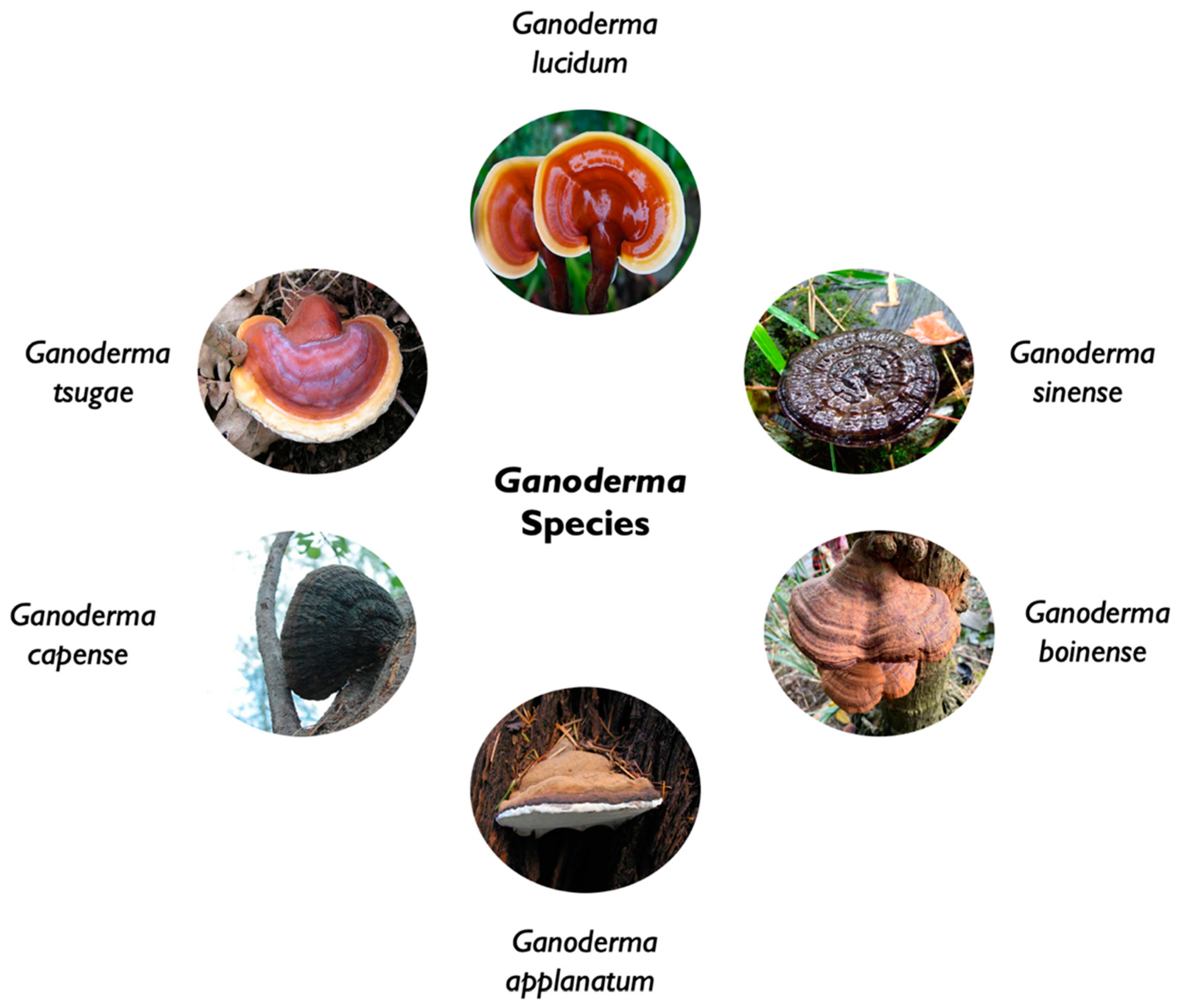
Ganoderma that derive from the greek word «ganos» that refer to shinning and «derma» for skin was establish has a genus in 1881 by the Finnish mycologist Petter Adolf Karsten and included only one species (Karsten, 1881). It was later on revised by Patrouillard in his monograph (1889) who included all species with pigmented spores, adhering tubes, and laccate crusted pilei, which resulted with 48 species (Murrill, 1902; Patouillard, 1889). Due to the lack of reliable morphological characteristics, the overabundance of synonyms, and the widespread misuse of names, members were difficult to classify.
Phylogenic analysis based on DNA sequence information’s have helped the clarification of the understanding the relationships amongst Ganoderma species. The genus ganoderma (Ganodermataceae family) may now be divided into six monophyletic groups with approximately 130 species of polypore wood-decaying fungi than can be annuals or perennials widely distributed in tropical regions (Hong and Jung, 2004; Wang et al., 2020).
Ganoderma lucidum, a large and dark mushroom with a glossy exterior, and a woody texture that grows on plum trees in Asia, also known as “Ling-zhi (meaning «spiritual power grass»” in China and Korea, or “Reishi” or “Mannentake” in Japan, is a well-known medicinal fungus with a rich history of use in traditional Chinese medicine [1]. G lucidum grows worldwide in temperate and subtropical ereas of Africa, America, Canada, China, Europe, India, Japan, Korea, and other Southeast Asian countries (Gariboldi et al., 2023).
During the years, the extract of G. lucidum has been converted to numerous forms, including tea, dietary supplements, and powder, available in the market to treat different illnesses [2]. The physical properties can be characterized by assessing its appearance, texture, color, and moisture content. These properties can vary depending on the growth conditions, cultivation methods, and post-harvest processing [13].
Characterization studies on
G.
lucidum are ongoing and aim to provide a better understanding of its chemical composition, biological activities, and potential therapeutic applications. These studies contribute to the development of standardized extracts, formulations, and quality control measures for the safe, and effective use of
G.
lucidum in various healthcare products. Characterization of
G.
lucidum involves analyzing its chemical composition, identifying, and quantifying the active compounds, and studying its physical, and biological properties (
Table 1).
G.
lucidum has a distinctive appearance that sets it apart from other mushrooms (
Figure 1). It typically has a large, flat, and kidney-shaped cap that can range in size from 5 to 25 centimeters in diameter [14]. The cap is smooth, and shiny, with a reddish-brown, but it can range from a lighter, rusty brown to a dark, almost blackish-brown color. The underside of the cap, and the pores are typically white or light brown. The underside of the cap is usually white or light brown, and may have small, round pores [15]. The texture of
G.
lucidum mushroom can vary depending on its age, and growth conditions. When young, the cap is often soft, and fleshy, but as it matures, it becomes harder, and more woody [15]. The flesh of the mushroom is corky and tough, making it unsuitable for direct consumption. The color of
G.
lucidum can vary depending on its specific variety, and growing conditions.
G.
lucidum mushrooms contain a significant amount of moisture when they are fresh, and just harvested. However, during the drying process, the moisture content is reduced to increase their shelf life, and facilitate storage. The exact moisture content can vary depending on the drying method used, but typically dried
G.
lucidum mushrooms have a moisture content of around 10% or lower [13–15].
As metioned, the colors of
G.
lucidum can vary depending on its specific variety, growing conditions, age, and other environmental factors. While
G.
lucidum is most commonly known for its red, black, and purple varieties (
Table 1), the colors can show variations due to the following factors:
Different varieties or strains of G. lucidum may exhibit distinct colors. Red, black, and purple are some of the most recognized color variations, but there may be other rare colors in specific strains, such as blue, yellow or white [3,15].
- 2.
Growing Substrate
The substrate on which G. lucidum is cultivated or naturally grows can influence its color. Different substrates, such as different types of wood or other materials, may lead to variations in the color of the mushroom [3].
- 3.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors, including temperature, humidity, light exposure, and nutrient availability, can impact the pigmentation, and color expression of G. lucidum [3].
- 4.
Age and Maturity
The age, and maturity of the mushroom can also affect its color. Younger mushrooms may display different colors compared to mature ones [3].
- 5.
Genetic Expression
The expression of genes responsible for pigment production in G. lucidum can contribute to the observed color variations [16].
Some color variations may be more common in certain regions or strains of G. lucidum, and color alone is not always a definitive indicator of the specific variety, or quality of the mushroom [3]. Other factors, such as chemical composition, bioactivity, and morphological characteristics, are also essential for proper identification, and assessment.
3.2. Uses in Traditional Medicine
The G. lucidum mushroom has long been recognized in traditional practices as a “tonic for promoting longevity” and well-being, and has gained recognition as a valuable medicinal resource in the healthcare system [8]. In Oriental culture, it is revered as a “potent elixir” due to its potential health benefits [9]. In China, it is renowned as an “herb with spiritual potency” owing to its association with longevity, spiritual power, and overall well-being [10]. Traditionally, it has been utilized in China to restore vital energy, promote relaxation of the mind, alleviate coughing, and relieve symptoms of asthma. G. lucidum has historically served as a traditional remedy for conditions such as breathlessness, palpitations, dizziness, and insomnia [11]. In addition, it has been recognised and widely used as an adjuvant in the treatment of diffent cancer types incuding breast cancer (Marinez-Montemayor et al., 2019; Barbieri et al., 2017).
3.3. Chemical Studies
G. lucidum mushroom has been extensively studied for its various bioactive compounds and medicinal properties. The huge market attention for G. lucidum mushroom is attributable to it wide range of bioactive compounds that it present. G. lucidum contains a complex mixture of bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, triterpenoids, proteins, peptides, nucleotides, sterols, and phenolic compounds. Characterization involves identification, and quantification of these compounds using techniques such as chromatography (e.g., high-performance liquid chromatography, gas chromatography), and spectroscopy (e.g., mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance) [12].
Approximately 400 bioactive compounds have been reported from different parts that include fruits, mycelia, and spores of G. lucidum [3]. The G. lucidum mushroom’s compounds has been recently recognized to be a traditional optimal source of natural bioactive components including: alkaloids, polyphenols, polysaccharides (α/β-D-glucans), steroids, triterpenoids (ganoderic acids, ganoderenic acids, ganoderol, ganoderiol, lucidenic acids), nucleotides (guanine, adenine), nucleosides (adenosine, iosine, uridine), amino acids, minerals, trace elements, vitamins, and proteins [3].
To obtain, and isolate the specific bioactive compounds from the mushroom extract we have distinct steps:
Extraction is the initial step in which the bioactive compounds are extracted from G. lucidum using a suitable solvent (e.g., water, ethanol, or a mixture of solvents) [17]. During extraction, the mushroom material is mixed with the solvent to dissolve the bioactive compounds and create an extract.
- 2.
Separation
After the extraction, the resulting extract may contain a mixture of various compounds, including the desired bioactive compounds, and other components from the mushroom. Separation techniques, such as chromatography (e.g., column chromatography, HPLC), liquid-liquid extraction, or centrifugation, are used to separate different compounds based on their chemical properties [17]. These methods allow researchers to obtain fractions or individual compounds with specific characteristics.
- 3.
Purification
Purification is the process of further refining the separated compounds to obtain highly pure, and concentrated forms of the desired bioactive compounds. Purification techniques may include additional chromatographic steps, crystallization, or other purification methods to remove impurities, and obtain a more refined product [17].
In summary, extraction is the process of obtaining the bioactive compounds from
G. lucidum using a solvent. Separation involves separating different compounds present in the extract, and purification further refines the compounds to obtain highly pure, and concentrated forms of the bioactive compounds (
Table 2).
Characterization of G. lucidum also involves the study of its biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, and neuroprotective properties [19]. Various in vitro and in vivo assays are used to evaluate these activities, and understand the underlying mechanisms of action. Characterization is essential for quality control purposes to ensure the consistency, and potency of G. lucidum products. This includes establishing standardized methods for identifying, quantifying, and assessing the bioactive compounds, and markers of authenticity, purity, and safety. The bioactive compounds found in G. lucidum have been extensively studied for their pharmacological properties. These compounds contribute to the diverse therapeutic effects associated with G. lucidum mushroom.
Triterpenoids: These compounds, including ganoderic acids, ganoderiol, and lucidenic acids, exhibit various pharmacological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective effects [3,20,21]. They have also shown potential for antitumor activity by inhibiting cancer cell growth, inducing apoptosis, and suppressing angiogenesis [21].
Polysaccharides: G. lucidum polysaccharides (GLPs) are the major class of bioactive compounds found in G. lucidum. GLPs are complex carbohydrates that possess immunomodulatory, antitumor, and antioxidant properties.[3,19,22] They can stimulate immune cells, including macrophages, natural killer cells, and T cells, leading to enhanced immune responses against cancer cells [20,22]. Additionally, polysaccharides have shown potential in modulating inflammatory processes, and promoting the body’s defense mechanisms.[20,21]
Peptides: G. lucidum peptides are small protein fragments with diverse bioactivities. These peptides have demonstrated antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer properties.[3,19] They can scavenge free radicals, inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi, and exhibit cytotoxic effects against cancer cells [20]. Some peptides also possess immunomodulatory effects by regulating cytokine production, and immune cell activation [19].
Sterols and nucleotides: G. lucidum contains various sterols, including ergosterol, which exhibit cholesterol-lowering effects and potential anti-inflammatory properties [3,19]. Nucleotides, such as adenosine and guanosine, found in G. lucidum, contribute to its immunomodulatory effects and have shown potential for neuroprotective activities [19].
Miscellianous bioactive compounds: G. lucidum also contains other bioactive compounds, including ganodermic acids, adenosine, and ganodermanontriol.[3] These compounds have been associated with diverse pharmacological effects, including antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activities [19]. GLPs are complex carbohydrate compounds found in the fruiting body, and mycelium of the GL mushroom, and it represents the major group of active compounds due to their structurally diverse biological macromolecules with wideranging physiochemical properties to overcome multiple diseases [22]. Polysaccharides are found in 10–50% of dry matter of fruitbodies.[23] Over 200 different polysaccharides have been searched from spores, fruiting bodies, and mycelia including β-D-glucans, α-D-glucans, α-D-mannans, and polysaccharide-protein complexes [22,23]. The immunomodulatory effects of GLPs are attributed to their ability to interact with immune receptors, and signaling pathways. They can stimulate the production of cytokines, such as interleukins, and interferons, which regulate immune responses. By modulating the immune system, these polysaccharides may help in the prevention, and treatment of various immune-related disorders [24].
In addition to their immunomodulatory properties, GLPs also possess potent antioxidant activity. They can scavenge free radicals, and reduce oxidative stress, which plays a crucial role in the development of various chronic diseases [25]. By reducing oxidative damage, these polysaccharides may contribute to overall health, and well-being. Furthermore, studies have indicated that GLPs exhibit potential anticancer effects. They have been shown to inhibit the growth, and proliferation of cancer cells, induce apoptosis (programmed cell death), and inhibit angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels that supply tumors) [24]. These properties make them promising candidates for complementary, and alternative cancer therapies. It is important to note that the biological activities of GLPs can vary depending on factors such as extraction methods, molecular weight, and structural composition [22–25]. Therefore, standardized extraction, and purification techniques are crucial to ensure consistency, and reproducibility in their therapeutic applications. GLPs are normally obtained from the mushroom by extraction with hot water followed by precipitation with ethanol or methanol. The most conventional extraction method is Traditional Solvent Extraction (TSE) [17]. Due to GLPs being sensitive to oxidative deactivation, an appropriate encapsulation method must be used to prevent oxidation [23]. The release of therapeutic actives can also be regulated by altering the structure, the morphology, and the surface for personalized delivery. Moreover, sensitive material can be entrapped within the matrix, protecting the bioactive from the external environment, advantageous for GLPs. G. lucidum is clearly rich in triterpenes, and it is this class of compounds that gives the herb its bitter taste, and various health benefits, such as antioxidant and lipid-lowering effects [21]. GLTs have structural similarity to steroid hormones, and exhibit a broad spectrum of anticancer, and anti-inflammatory properties. In general, GLTs have molecular weights ranging from 400 to 600 kDa, and their chemical structure is complex, highly oxidized, and high lipophilicity.[25] Extraction of GLTs is usually done by means of methanol, ethanol, acetone, chloroform, ether, or a mixture of these solvents. The extracts can be further purified by various separation methods, including normal, and reverse-phase HPLC [17].
4. Pharmacological and Toxicological Properties
4.1. Pharmacological Properties
Medicinal mushrooms are affluent sources of pharmacological active compounds.
G. lucidum exhibits a significant role in the treatment, and prevention of various diseases. It has been used in traditional Chinese, and Japanese medicine as an herbal remedy for over 2000 years [3]. As estimated by the World Health Organization (WHO), globally about three-quarters population depends upon traditional remedies for good health. GL is a good source of traditional medicine to provide a healthier life [2].
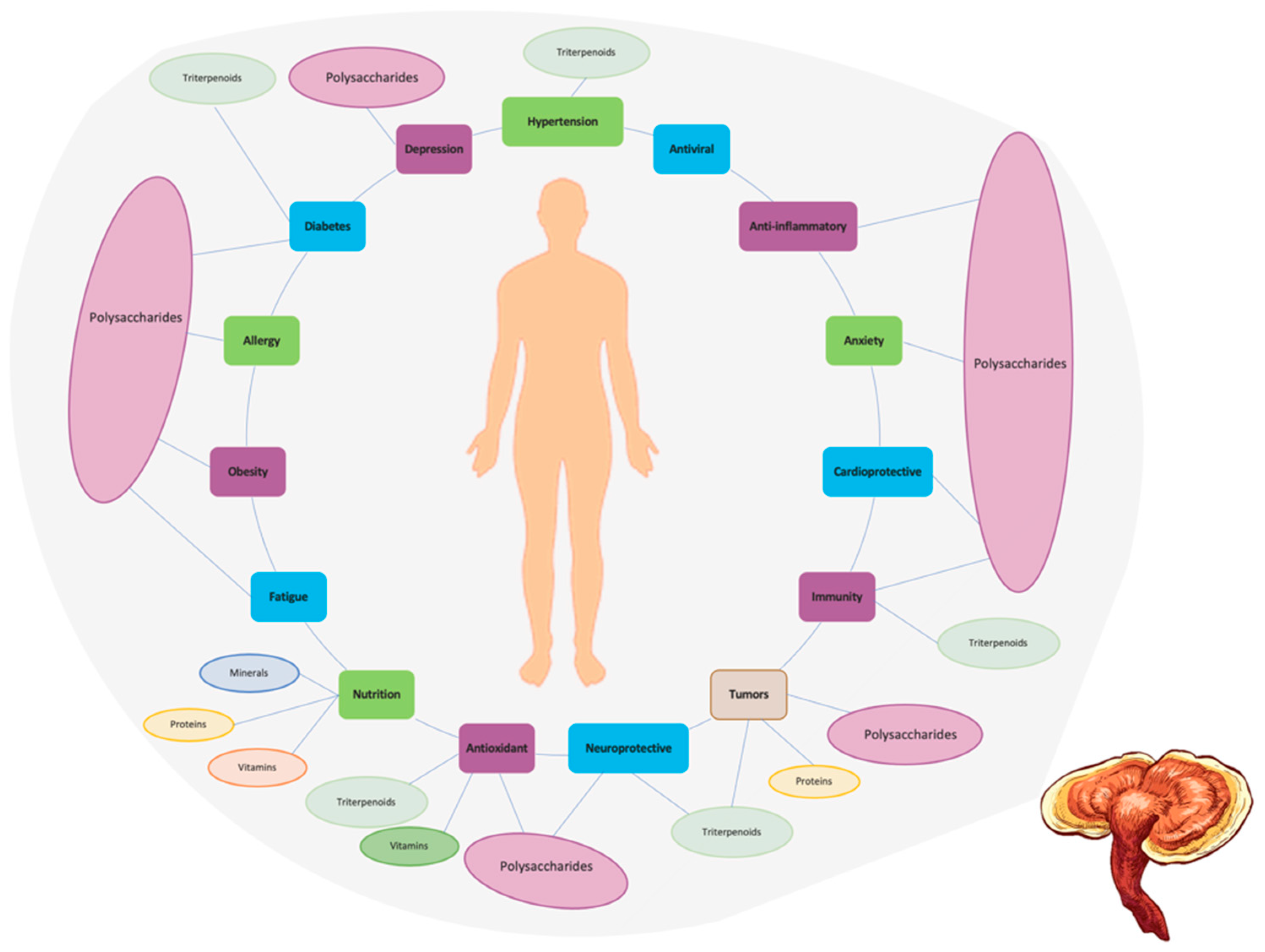
G. lucidum is not only used as a medicinal but also applied as a nutraceutical, health supplement, and cosmetic products. Diverse application as a traditional medicine has drawn the researchers attention towards preclinical, and clinical trials and therapeutical applications such as antioxidant, anticancer, immunomodulator, antiarthritic, hypoglycaemic, cardioprotective, antiinflammatory, carcinostatic, antiangiogenic, antiosteoporotic, antinociceptive, proapoptotic, anti-allergic, antiviral, anti-HIV, antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-androgenic [19].
G. lucidum, is a rich source of bioactive secondary metabolites. To date, approximately 279 of secodary metabolit have been isolated from different parts of the mushroom, including the fruit bodies, mycelium, and spores [3]. The pharmacological activities of these bioactive compounds are attributed to their interactions with various cellular targets, and signaling pathways. They can modulate immune responses, regulate inflammation, scavenge free radicals, inhibit tumor growth, and affect various molecular targets involved in cancer progression [3,19–25]. It is important to note that the bioactive compounds pharmacology of
G. lucidum is complex, and further research is needed to fully elucidate their mechanisms of action, and therapeutic potential. Additionally, the extraction, and purification methods of these compounds can significantly impact their pharmacological activities, making standardized, and quality-controlled preparations essential for consistent, and reliable therapeutic effects. Among these bioactive compounds, polysaccharides, specifically β-glucans, play a significant role in various diseases due to their pharmacological properties [22].
β-Glucans derived from
G. lucidum have demonstrated immunomodulatory, and anticarcinogenic features. The biological activity of
β-glucans is influenced by several factors, including their molecular size, branching, water solubility, and overall form. The presence, and arrangement of lateral branches, as well as the length of the lateral chains, can impact their pharmacological properties. The ratio of the number of bonds within the
β-glucans also affects their activity [21–23] (
Figure 2).
Regarding their immunomodulatory properties,β-glucans have been shown to enhance the immune system’s response by activating immune cells such as macrophages, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells [22–25]. This immune-enhancing effect is beneficial in various diseases, and conditions where immune function plays a crucial role. GLTs have drawn significant attention to their illustrious efficient pharmacological properties. Various highly oxygenated, and pharmacologically active triterpenes have been isolated from GL. Some of them are ganoderiol, lucidenic acid, lucialdehyde, ganolucidinic acids, lanostanoid, and ganodermantriol [21]. Triterpenoids contain carboxyl group is called generally ganoderic acids. These compounds are characterized by a complex structure, high molecular mass, and high lipophilicity. They are highly oxidized derivatives of lanostane. These triterpenoids may contain 30, 27 or 24 carbon atoms in their molecular structure [21,23]. As mentioned earlier, it is believed to possess a wide range of pharmacological properties (
Figure 2). While research on
G. lucidum is ongoing, some of the pharmacological properties that have been reported are:
Immunomodulatory activity: G. lucidum is known for its immunomodulatory effects, which means it can modulate the immune system. It has been shown to enhance the activity of immune cells, such as natural killer cells, macrophages, and T-lymphocytes, thereby strengthening the body’s immune response [3].
Antioxidant activity: G. lucidum contains various bioactive compounds, such as polysaccharides, triterpenoids, and phenolic compounds, which exhibit antioxidant properties. These compounds help neutralize free radicals, and reduce oxidative stress in the body, potentially protecting against cellular damage, and age-related diseases [3].
Anti-inflammatory activity: G. lucidum has been reported to possess anti-inflammatory properties. It can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, and modulate inflammatory pathways, which may contribute to reducing inflammation, and related conditions [3].
Anti-cancer potential: It has been shown to inhibit the growth of cancer cells, inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death), and inhibiting angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels that supply tumors) [3]. G. lucidum extracts or compounds derived from the mushroom have been investigated for their potential as adjuvant therapies in cancer treatment.
Cardiovascular health: It may help to regulate blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, inhibit platelet aggregation, and improve blood flow [3]. These properties contribute to the potential benefits of G. lucidum in supporting cardiovascular health.
Anti-diabetic effects: It has been shown to help regulate blood glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and protect against diabetic complications [3]. G. lucidum extracts or components have been investigated for their potential use in diabetes management.
Neuroprotective effects: It may possess antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects that can help protect nerve cells from damage, and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s diseases [3].
It’s important to note that while G. lucidum shows promising pharmacological properties, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action, optimize dosages, and determine its efficacy, and safety in different therapeutic applications.
4.2. Toxicological Properties
G. lucidum is generally considered safe for consumption and has a long history of use in traditional medicine. However, it’s important to consider the potential toxicological properties, and safety aspects associated with any substance, including G. lucidum. Here are some considerations regarding its toxicological properties:
Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status: G. lucidum is classified as a food supplement or dietary ingredient in many countries and is generally recognized as safe for consumption [3]. It is widely consumed as a food or herbal supplement without significant reports of acute toxicity.
Lack of acute toxicity: G. lucidum has been reported to have a low toxicity profile. Animal studies have shown that even high doses of
G. lucidum extracts did not cause significant acute toxicity or significant adverse effects [3] (
Table 3).
Allergic reactions: While rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to G. lucidum. These reactions can include skin rashes, itching, or respiratory symptoms such as difficulty breathing or wheezing [3]. Individuals with known allergies to mushrooms or fungal species should exercise caution when using G. lucidum products.
Drug interactions: G. lucidum may interact with certain medications. It can inhibit some liver enzymes responsible for metabolizing drugs, potentially affecting their efficacy, and clearance from the body [3].
Quality and contamination concerns: The quality and purity of G. lucidum products can vary, especially with the increasing popularity of supplements. Contamination with heavy metals, pesticides, or other contaminants can pose potential health risks. It is important to source G. lucidum products from reputable manufacturers and ensure proper quality control measures are in place [3].
Specific population considerations: Some specific populations, such as pregnant or lactating women, infants, and individuals with underlying health conditions, may have specific considerations [3].
Overall, while GL shows promise as a therapeutic agent, it is crucial to be aware of the potential toxic effects, allergic reactions, and interactions with certain medications.
4.3. Dosage Forms and Posology
G. lucidum is available in various dosage forms and can be consumed by different routes.
The appropriate dosage, and posology of G. lucidum may depend on factors such as the specific formulation, the individual’s age, overall health, and the intended purpose of use. Some of common dosage forms, and posology options for G. lucidum already presents in the market are:
Capsules or Tablets: G. lucidum is commonly available in the form of capsules or tablets. The recommended dosage may vary depending on the concentration of G. lucidum extract or powder in each capsule/tablet. A common dosage range is 1-3 capsules/tablets per day, taken with water or as directed by a healthcare professional [2,26].
Powder: G. lucidum powder can be mixed with water, juice, smoothies, or other beverages. The dosage may vary depending on the specific product, and the desired effects. Generally, a typical dosage range is 1-3 grams of G. lucidum powder per day [2,26]. It is advisable to start with a lower dosage, and gradually increase if needed, based on individual tolerance, and response.
Extracts: G. lucidum extracts are available in liquid or concentrated forms [2,26]. These extracts are often standardized to contain specific amounts of bioactive compounds. The dosage and posology for G. lucidum extracts can vary depending on the concentration and potency of the extract.
Tea or Decoction: G. lucidum can be brewed as a tea or decoction. Dried G. lucidum slices or powder can be simmered in water for a certain period to extract the bioactive compounds. The dosage of G. lucidum tea or decoction can vary depending on the concentration, brewing time, and individual preferences [1,2]. It is recommended to start with a small amount, and adjust the dosage based on taste, and individual response.
Topical Formulations: G. lucidum extracts or creams are also available for topical use. These formulations are often used for skin health or cosmetic purposes [2,26]. The dosage and posology for topical products may depend on the specific formulation, and intended use.
Table 4.
G. lucidum dosage forms, and posology available [2,26].
It’s important to note that the optimal dosage form, and posology of G. lucidum can vary depending on individual factors, and the specific health goals. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a qualified herbalist is recommended to determine the appropriate dosage, and posology for your specific needs, and to ensure safe, and effective use of G. lucidum.
5. Application of Ganoderma lucidum in Cancer Therapy
Cancer is a complex and devastating disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, and the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Conventional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery, have improved patient outcomes; however, they often come with significant side effects, and limitations. G. lucidum contains bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, triterpenes, and other phytochemicals, which have been studied for their potential anti-cancer properties. These compounds may exert various effects on cancer cells, and the immune system, making them attractive candidates for complementary or alternative approaches in cancer therapy [27].
The potential mechanisms by which GL may impact cancer therapy include [28]:
Inducing Apoptosis: G. lucidum may promote apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, inhibiting their uncontrolled growth, and survival.
Modulating the Immune System: G. lucidum is known for its immunomodulatory effects, enhancing the activity of immune cells that play a crucial role in recognizing, and eliminating cancer cells.
Reducing Inflammation: Chronic inflammation has been linked to cancer development, and progression. G. lucidum’s anti-inflammatory properties may help in controlling tumor growth.
Inhibiting Angiogenesis: G. lucidum’s compounds may help inhibit the formation of new blood vessels that supply tumors, limiting their nutrient supply.
Studies have shown promising results regarding G. lucidum’s effects on various cancer types, including lung cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer, and others [27,42]. However, it’s essential to note that while some findings are encouraging, more rigorous research, including clinical trials in humans, is needed to establish its effectiveness, and safety as a stand-alone cancer treatment.
G. lucidum is not a replacement for conventional cancer therapies, it shows promise as a potential complementary addition to cancer treatment due to its bioactive compounds, and immunomodulatory effects. Ongoing research will further elucidate its role in cancer treatment, and improve our understanding of its full potential in combating this devastating disease.
5.1. Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a specific subtype of breast cancer characterized by the absence of three key receptors: estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) [28]. These receptors are crucial for guiding targeted therapies in breast cancer treatment. However, TNBC lacks these receptors, making it more challenging to treat compared to other breast cancer subtypes.[29] TNBC accounts for about 15% to 20% of all breast cancer cases, and is more commonly diagnosed in younger women, African-American women, and those with a breast cancer 1 (BRCA1) gene mutation [28–30]. It is known to have aggressive behavior, faster growth, and a higher likelihood of metastasis (spreading to other parts of the body) compared to other breast cancer subtypes [30]. Due to the absence of ER, PR, and HER2 receptors, TNBC does not respond to hormone therapy (such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors) or targeted therapies like trastuzumab (Herceptin) [31]. As a result, chemotherapy remains the mainstay of treatment for TNBC. Various chemotherapy regimens are used to target and kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. TNBC research is ongoing to identify new treatment strategies, and targeted therapies. Immunotherapy, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi), and other emerging treatments are being investigated to improve outcomes for TNBC patients [28–31]. Clinical trials play a critical role in testing novel therapies for this aggressive subtype of breast cancer. TNBC patients often experience lower 5-year survival rates compared to other breast cancer subtypes due to the aggressive nature, and resistance of the malignancy [29]. The aggressive behavior of TNBC leads to rapid tumor growth, and a higher likelihood of metastasis, and that’s why the urgent needed for further research to develop new target therapies for TNBC. In the search for new treatment options, natural products have become an area of interest. These products possess diverse chemical structures, and exhibit high specificity in their biochemical actions. As such, they form a valuable compound library for evaluating, and discovering potential new drugs for TNBC, and other malignancies. Studying natural products may lead to the identification of novel compounds with therapeutic potential that could complement existing treatment approaches for TNBC. G. lucidum has attracted interest in the field of cancer research, including its potential effects TNBC. However, it’s important to note that the research in this area is still in its early stages, and more studies are needed to establish the efficacy, and safety of G. lucidum specifically in the treatment of TNBC. Here’s an overview of the current understanding:
Anti-cancer effects: Some studies have shown that G. lucidum extracts or its bioactive compounds may inhibit the growth, and proliferation of breast cancer cells in in vitro studies, and animal models [32–40]. These effects may involve various mechanisms, such as inducing apoptosis, inhibiting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels that support tumor growth), and modulating immune responses.
Immunomodulation: TNBC is characterized by its aggressive nature, and lack of targeted treatment options. Immunomodulatory properties of G. lucidum may be relevant in the context of TNBC, as they can potentially enhance the body’s immune response against cancer cells [32–40]. Some studies suggest that G. lucidum can modulate immune cells, such as natural killer cells (NK cells), and T-lymphocytes, and enhance their activity against cancer cells.
Chemopreventive potential: G. lucidum has been studied for its potential chemopreventive effects, which means it may help prevent the development or progression of cancer. In the case of TNBC, which lacks targeted therapies, chemopreventive strategies may be particularly valuable. Some studies have suggested that GL extracts or its bioactive compounds may help inhibit the initiation or progression of breast cancer, potentially reducing the risk of developing TNBC [32–40].
It’s important to highlight that the research on GL, and TNBC is still limited, and most of the available evidence comes from preclinical studies or studies conducted on cancer cell lines, and animal models. There is a need for well-designed clinical trials to assess the safety, and efficacy of G. lucidum specifically for TNBC in humans.
5.2. Colon Rectal Cancer
Colon and rectal cancer, often referred to as colorectal cancer, is a type of cancer that starts in the colon or rectum, which are parts of the digestive system [41]. These cancers are closely related due to their anatomical proximity, and similar characteristics. Colorectal cancer typically begins as a growth of abnormal cells in the inner lining of the colon or rectum, known as polyps [41,42]. Over time, some of these polyps can develop into cancer if not detected, and removed early. The exact causes of colorectal cancer are not fully understood, but risk factors include age, family history, certain genetic conditions, diet, and lifestyle choices. Symptoms of colorectal cancer may include changes in bowel habits, persistent abdominal discomfort, blood in the stool, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. Early detection is critical, as it allows for a higher chance of successful treatment, and improved outcomes. Screening tests, such as colonoscopy, fecal occult blood test (FOBT), and sigmoidoscopy, can help detect precancerous polyps or early-stage cancers.[43] If colorectal cancer is diagnosed, treatment options depend on the stage of the cancer, and may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. As with any cancer, early detection, and prompt treatment are essential for better prognosis, and improved survival rates. Therefore, regular screenings, and awareness of potential symptoms are crucial for reducing the impact of colorectal cancer on individuals’ health. Leading a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco, and excessive alcohol consumption, can also contribute to reducing the risk of developing colorectal cancer. G. lucidum have been studied for their potential anti-cancer properties in colon rectal cancer. However, it’s important to note that the research in this area is still limited, and more studies are needed to establish the efficacy, and safety of G. lucidum for colon rectal cancer. Here’s an overview of the current understanding:
Anti-cancer effects: Some studies have shown that G. lucidum extracts or its bioactive compounds may inhibit the growth, and proliferation of colon rectal cancer cells in in vitro studies, and animal models [44–46]. These effects may involve various mechanisms, such as inducing apoptosis, inhibiting angiogenesis, and modulating immune responses.
Immunomodulation: G. lucidum is known for its immunomodulatory effects, meaning it can modulate the immune system. Enhancing the immune response may be relevant in the context of colon rectal cancer, as the immune system plays a crucial role in identifying and eliminating cancer cells. Some studies suggest that G. lucidum can modulate immune cells, and enhance their activity against cancer cells, potentially supporting the body’s immune response to colon rectal cancer [44–46].
Chemopreventive potential: In the case of colon rectal cancer, chemopreventive strategies may be valuable, especially in individuals at high risk or with a history of precancerous polyps. Some studies have suggested that G. lucidum extracts or its bioactive compounds may help to inhibit the initiation or progression of colon rectal cancer, potentially reducing the risk of developing this disease [44–46].
It’s important to highlight that the research on G. lucidum and colon rectal cancer is still limited, and most of the available evidence comes from preclinical studies or studies conducted on cancer cell lines, and animal models. There is a need for well-designed clinical trials to assess the safety, and efficacy of G. lucidum specifically for colon rectal cancer in humans.
5.3. Other Types of Cancer
5.3.1. Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs and can spread to other parts of the body. It is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide for both men, and women [47]. There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and small cell lung cancer (SCLC) [48]. NSCLC is the most common type, accounting for about 85% of all lung cancer cases, while SCLC makes up about 15% of cases [49].
The causes and risk factors are:
Smoking: The primary risk factor for lung cancer is tobacco smoking, including cigarette, cigar, and pipe smoking [47,48]. Long-term exposure to secondhand smoke can also increase the risk;
Radon Gas: Exposure to high levels of radon gas, which can be found in some homes, and buildings, is another significant risk factor [48];
Environmental and Occupational Exposures: Exposure to certain carcinogens and toxins, such as asbestos, diesel exhaust, arsenic, and some other chemicals, can also increase the risk of developing lung cancer [47–49].
The major symptoms are:
Persistent cough that doesn’t go away or worsens over time;
Shortness of breath or wheezing;
Chest pain that gets worse with coughing or deep breathing;
Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum;
Hoarseness;
Unintended weight loss and loss of appetite;
Fatigue and weakness.
The treatment for lung cancer depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. It may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these approaches [50]. Early-stage lung cancer may be treated with surgery to remove the tumor, while advanced-stage lung cancer may require a combination of treatments.
Overall, lung cancer is a serious and complex disease, but advancements in research, and treatment options are continually improving outcomes and quality of life for patients. Early detection, smoking cessation, and a healthy lifestyle play crucial roles in reducing the impact of lung cancer on individuals’ health. G. lucidum has been the subject of scientific research for its potential effects on various health conditions, including cancer. In the context of lung cancer, some studies have explored the potential benefits of GL as a complementary or alternative approach to conventional treatments [51]. However, it’s important to note that more research is needed before any definitive conclusions can be made about its efficacy as a stand-alone treatment for lung cancer.
Some potential ways in which G. lucidum may impact lung cancer include:
Anti-Cancer Properties: Bioactive compound from GL may exert anti-tumor effects by inhibiting cancer cell growth, inducing apoptosis, and suppressing tumor angiogenesis [51–53].
Immune System Modulation: G. lucidum can enhance the activity of immune cells, such as natural killer cells, and T-cells. Boosting the immune response may help the body’s natural defense mechanisms in recognizing and eliminating cancer cells [53,54].
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation has been linked to the development, and progression of lung cancer. G. lucidum s anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce inflammation in the lungs, potentially impacting cancer growth and progression [55].
Supporting Quality of Life: Some studies suggest that G. lucidum may help improve the quality of life in cancer patients, including those with lung cancer, by reducing cancer-related symptoms, and side effects of treatments [51–55].
While the research on G. lucidum’s effects on lung cancer is promising, it is essential to approach these findings with caution. Most studies have been conducted in cell cultures or animal models, and more clinical trials involving human subjects are needed to determine its potential benefits and safety in lung cancer patients. Lung cancer requires a comprehensive, and evidence-based approach that may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these treatments, depending on the specific type, and stage of the cancer.
5.3.2. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate gland, a small walnut-sized gland located below the bladder in men. The prostate gland plays a role in producing semen, the fluid that nourishes, and transports sperm [55].
The causes and risk factors are:
Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, and it is most commonly diagnosed in men over the age of 50;
Family History: Men with a family history of prostate cancer, especially in a father or brother, have a higher risk of developing the disease;
Ethnicity: Prostate cancer is more prevalent in African-American men and less common in Asian and Hispanic men;
Genetic Factors: Certain inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer;
Diet: A diet high in red meat and high-fat dairy products and low in fruits and vegetables may be associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer.
Early-stage prostate cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
Frequent urination, especially at night;
Difficulty starting or stopping urination;
Weak or interrupted urine flow;
Blood in the urine or semen;
Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area or lower back.
The treatment for prostate cancer depends on the stage, grade, and overall health of the patient [56,57]. It may include:
Active surveillance: Monitoring the cancer closely without immediate treatment;
Surgery: Removal of the prostate gland (prostatectomy);
Radiation therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells;
Hormone therapy: Lowering the levels of male hormones that can fuel cancer growth;
Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells;
Immunotherapy: Stimulating the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
There is no surefire way to prevent prostate cancer, but some lifestyle choices may reduce the risk, such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, and avoiding tobacco, and excessive alcohol consumption [57]. Regular check-ups, and screenings are essential for early detection, and better outcomes in prostate cancer. In the context of prostate cancer, there is some research exploring the use of G. lucidum as a complementary or alternative approach to traditional treatments [58]. However, it’s important to note that more research is needed before any definitive conclusions can be made about its efficacy. Some potential ways G. lucidum may impact prostate cancer include:
Anti-Cancer Properties: G. lucidum’s bioactive compounds may exhibit anti-tumor effects, including inhibiting cancer cell growth, and promoting apoptosis in prostate cancer cells [58].
Immune System Modulation: G. lucidum can enhance the activity of immune cells, which play a crucial role in recognizing, and eliminating cancer cells. Boosting the immune response may help the body’s natural defense mechanisms to target prostate cancer cells [59,60].
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation has been associated with the development, and progression of prostate cancer. G. lucidum’s anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce inflammation in the prostate, potentially impacting cancer growth, and progression [58,59].
Reducing Side Effects: Some studies suggest that G. lucidum may help reduce the side effects of conventional cancer treatments, such as radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, in prostate cancer patients [58,59].
It’s important to emphasize that while some studies show promising results, the evidence on the efficacy of G. lucidum in treating prostate cancer is still limited, and more rigorous research, including clinical trials in humans, is needed to establish its role as a cancer treatment.
6. Application of Ganoderma lucidum in Nanotechnology
Nanoparticles have been explored as a promising drug delivery method due to their ability to circulate freely in the blood, and escape endocytosis by cells, making them suitable for targeted drug delivery [61]. However, encapsulating GLPs in solid particles is challenging due to their high molecular weight, and hydrophilicity [62]. To overcome this, modifications are made to GLPs, improving their structural composition, molecular weight, bonding, and ionic nature, which in turn can alter their biological functions, and physicochemical properties [61,62].
Most polymer-based nanoparticles used as drug carriers do not have inherent anti-tumor properties. While chitosan, dextran, and cellulose are commonly used in nano-drug delivery systems, they lack anti-tumor effects [63]. In contrast, GLPs themselves exhibit anti-tumor activities, making them an attractive candidate for innovative nanoparticles drug delivery systems [64]. By leveraging the anti-tumor properties of GLPs, these nanoparticles can break biological delivery barriers, reaching tumor cells, and exerting synergistic anti-tumor effects [65].
While G. lucidum has been extensively studied in traditional medicine, and pharmacology, its specific applications in nanotechnology are relatively limited, and recent. In that way, the development of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems using GLPs holds promise in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of G. lucidum, and its anti-tumor effects, offering potential advancements in cancer treatment.
There have been a few studies exploring the potential use of G. lucidum in nanotechnology-related applications. Here are a few examples:
Nanoparticle synthesis
Researchers have investigated the use of G. lucidum extracts in the synthesis of nanoparticles. These extracts can act as reducing, and stabilizing agents to produce metallic nanoparticles, such as gold or silver nanoparticles [63,66]. The resulting nanoparticles may possess unique properties, and find applications in areas like catalysis (where a substance – catalyst - accelerates a chemical reaction without being consumed or permanently altered in the process), sensing (process of detecting or perceiving changes in the environment or within a system through the use of sensors or sensory organs), and drug delivery [63,66].
Nanocarriers for drug delivery:
G. lucidum extracts or its components have been incorporated into nanocarriers for drug delivery purposes. By encapsulating therapeutic agents within nanoscale systems, such as liposomes or nanoparticles, it is possible to enhance drug stability, improve bioavailability, and target specific tissues or cells [67].
Antimicrobial nanomaterials: G. lucidum extracts have shown antimicrobial activity against various microorganisms. Researchers have explored incorporating these extracts into nanomaterials, such as coatings or films, to create antimicrobial surfaces. Such surfaces could find applications in medical devices, food packaging, and other areas where preventing microbial growth is crucial [68].
Biosensors: G. lucidum extracts have demonstrated potential for use in biosensing applications. By immobilizing the mushroom extract or its bioactive compounds into nanomaterials, it is possible to create biosensors capable of detecting specific targets, such as biomarkers or pollutants, with high sensitivity, and selectivity [69]. It’s worth noting that the research, and development of GL in nanotechnology are still in their early stages, and further studies are needed to explore the full potential of this mushroom in various nanotechnological applications. The synthesis of G. lucidum nanoparticles involves the utilization of extracts or components derived from the mushroom to produce nanoparticles with unique properties. The general steps involved in the synthesis process of nanoparticles from G. lucidum are as follow:
Preparation of GL extract: The first step is to prepare an extract from the GL mushroom. This can be done by grinding or pulverizing the mushroom material, and then subjecting it to extraction using solvents like water, ethanol, or a combination of both [70]. The extract contains bioactive compounds that will play a role in the nanoparticle synthesis.
Reduction and stabilization of nanoparticles: The extract obtained from GL contains compounds that act as reducing, and stabilizing agents. These compounds can interact with metal ions to reduce them, and form nanoparticles [71]. Common metals used for nanoparticle synthesis include gold, silver, and copper [63,66,70–72]. The reduction process can be facilitated by heating or by the addition of a reducing agent.
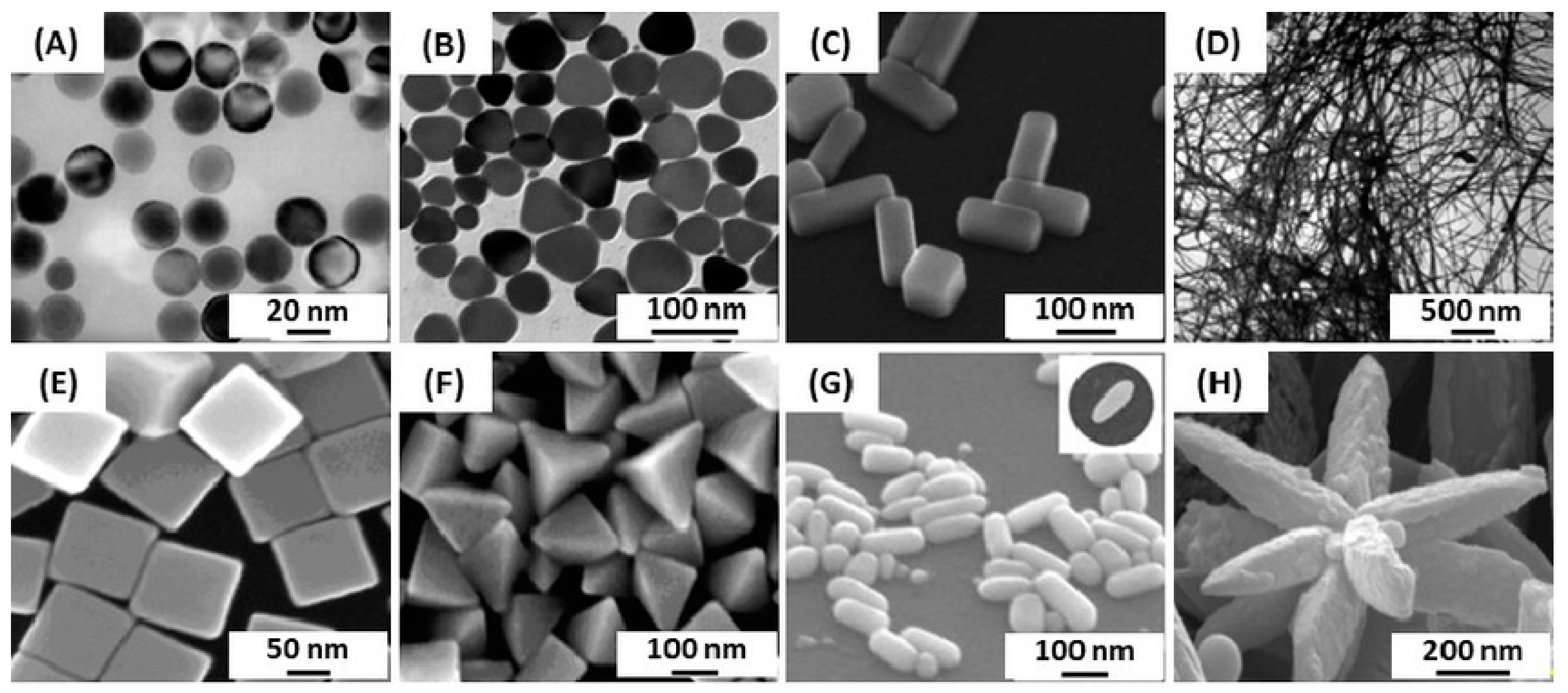
Characterization: Once the nanoparticles are formed, they need to be characterized to determine their size, shape, composition, moprphology, and other properties. Techniques such as transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) are commonly used for nanoparticle characterization [65].
Functionalization: Depending on the intended application, the synthesized G. lucidum nanoparticles can be further functionalized. This involves modifying the surface of the nanoparticles by attaching specific molecules (ligands) or coatings to enhance their stability, biocompatibility, or targeting capabilities [68].
It’s important to note that the specific details of G. lucidum nanoparticle synthesis may vary depending on the research or study. Different extraction methods, metal ions, and reaction conditions can influence the size, shape, and properties of the resulting nanoparticles. Researchers continue to explore, and optimize these synthesis methods to harness the unique properties of G. lucidum in nanoparticle applications.
6.1. Silver Nanoparticles
G. lucidum is often diluted in saline for intravenous administration, but it can also be administered orally [74]. However, oral administration has some disadvantages, such as poor stability, and low bioavailability. To address these issues, novel drug delivery systems like microcapsules, and microspheres have been developed to enhance the bioavailability, and reduce toxicity of GLPs [75]. The anti-tumor properties of GLPs are believed to be linked to their regulation of various biological processes, including immune, and inflammatory responses, inducing toxicity in tumor cells, and promoting apoptosis. Additionally, metal nanomaterials like Au, Ag, and Pt have gained attention due to their unique chemical, and optical properties, offering additional possibilities for advanced drug delivery systems (
Figure 3) [63,66].
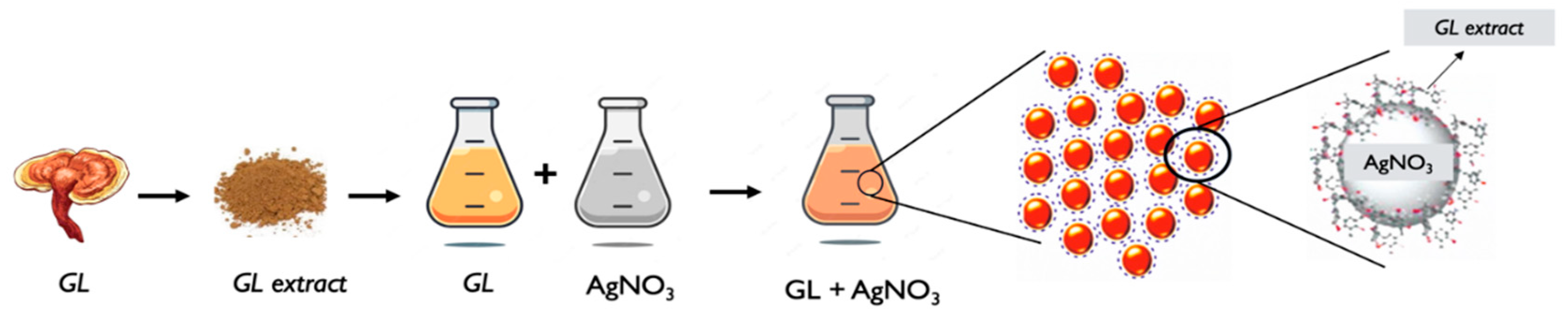
G. lucidum silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) refer to silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) that are synthesized using extracts or components derived from
G. lucidum [76]. Silver nanoparticles have gained significant attention due to their unique properties, including antimicrobial activity, catalytic properties, and potential applications in various fields.
The synthesis of G. lucidum AgNPs typically involves the following steps:
G. lucidum extract preparation: Similar to the general process described earlier, an extract is obtained from G. lucidum. The extraction can be performed using solvents such as water or ethanol. The extract contains bioactive compounds that will serve as reducing, and stabilizing agents during the nanoparticle synthesis process [68,70].
AgNPs synthesis: The G. lucidum extract is mixed with a silver precursor, such as silver nitrate (AgNO3). The bioactive compounds in the extract act as reducing agents, facilitating the reduction of the silver ions into silver nanoparticles. The nanoparticles form, and stabilize in the final solution [68,70–72].
Characterization: The synthesized G. lucidum AgNPs are then characterized to determine their size, shape, distribution, morphology, and other properties. Techniques such as TEM, SEM, XRD, UV-Vis, and FTIR spectroscopy, and DLS can be employed to analyze the nanoparticles, and assess their characteristics [65,70–72].
Functionalization: If desired, the
G. lucidum AgNPs can be further functionalized by modifying their surface. This involve the attachment of specific molecules, called ligands or coatings to enhance their stability, biocompatibility, or targeting cellular capabilities for particular applications [74–76]. The specific synthesis methods and conditions may vary among different studies and researchers. The concentration of
G. lucidum extract, silver precursor, reaction time, and temperature can all influence the size and properties of the resulting silver nanoparticles (
Figure 4). It is worth noting that further research, and optimization are ongoing to explore the potential applications, and benefits of
G. lucidum AgNPs in various fields, including biomedicine, catalysis, and environmental remediation.
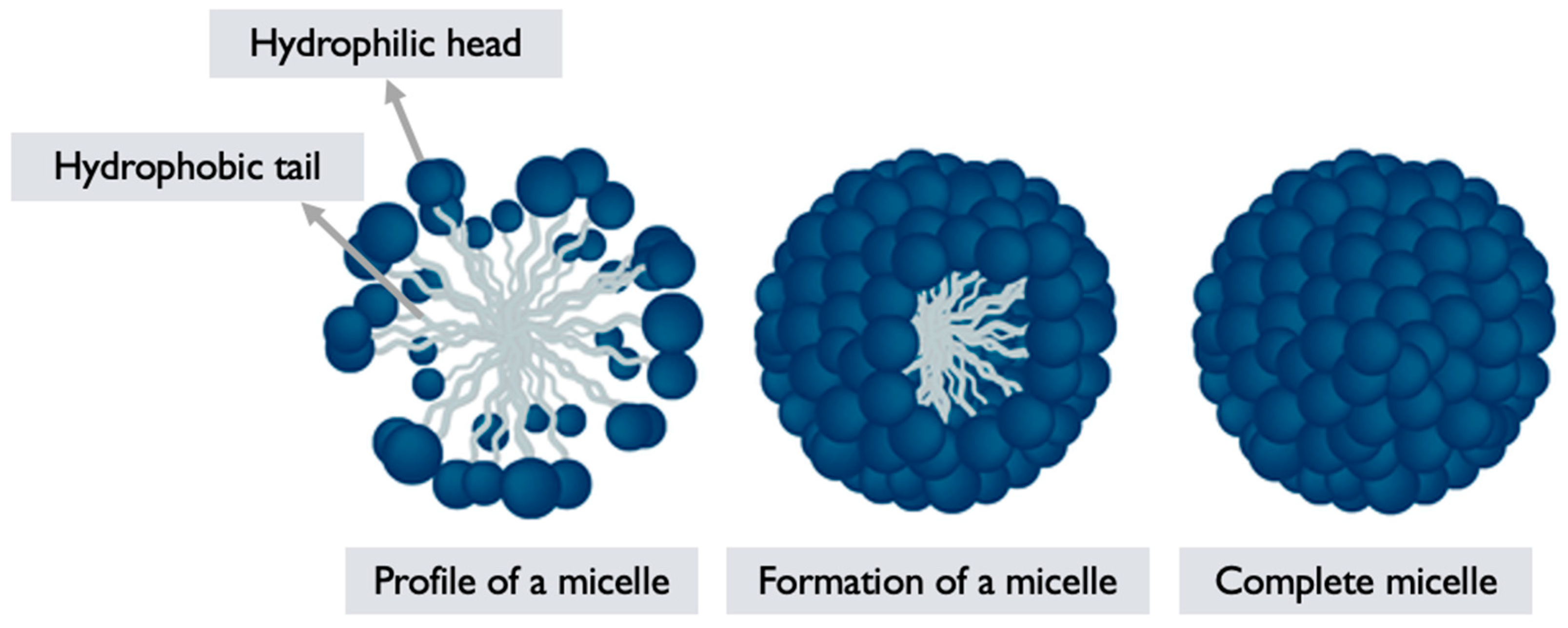
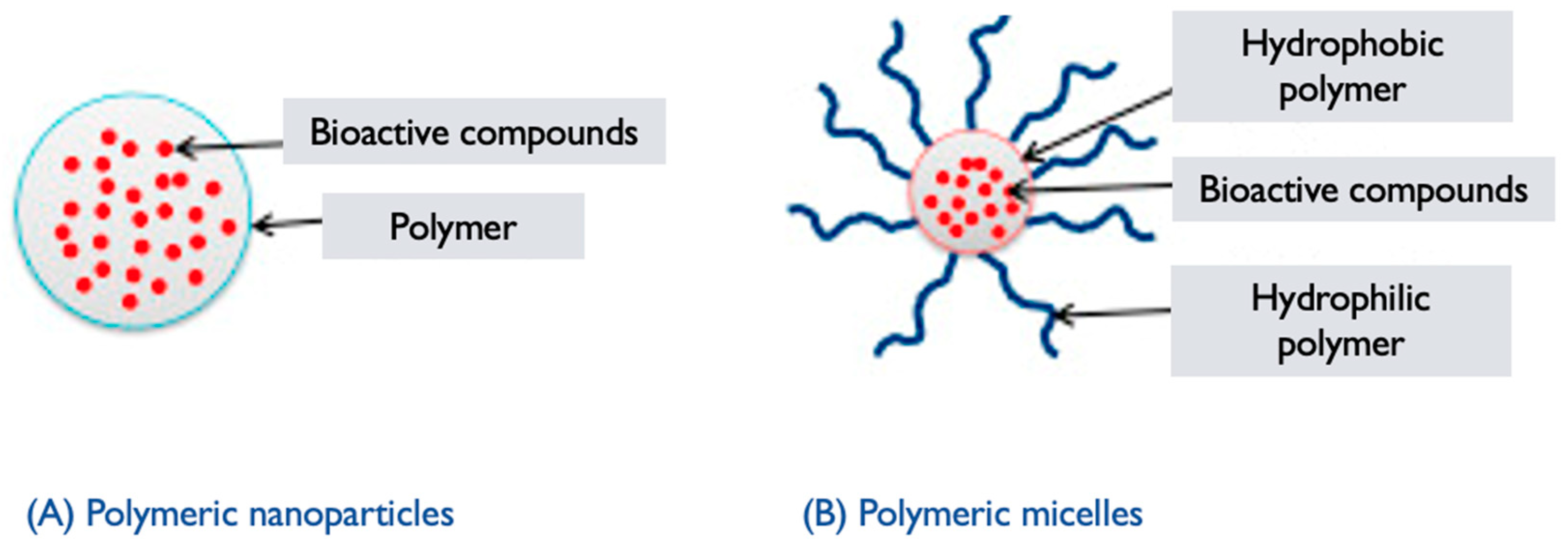
6.2. Polymeric Micelles
G. lucidum polymeric micelles (PMs) refer to micellar structures formed by self-assembly of polymers derived from G. lucidum or incorporating extracts/components from the mushroom [69]. PMs are nanoscale assemblies composed of amphiphilic block copolymers, where one block is hydrophilic, and the other is hydrophobic [79]. These micelles have attracted attention for their potential applications in drug delivery, due to their ability to encapsulate hydrophobic drugs, and enhance their solubility, and stability.
Here are the general steps involved in the synthesis of G. lucidum PMs:
Polymer selection: Suitable polymers derived from G. lucidum or incorporating extracts/components from the mushroom are chosen. These polymers should possess amphiphilic properties, with one segment being hydrophilic, and the other hydrophobic [69,79].
Polymer synthesis: The selected polymers are synthesized using appropriate techniques, such as polymerization or modification reactions [79]. The hydrophilic, and hydrophobic blocks are incorporated into the polymer structure, resulting in an amphiphilic copolymer.
Micelle formation: The synthesized amphiphilic copolymer is then dissolved in a suitable solvent, typically aqueous solution. Due to the amphiphilic nature of the polymer, it self-assembles into micellar structures in the solution. The hydrophilic segments of the polymer form the outer shell of the micelle, while the hydrophobic segments aggregate forming the core, and encapsulating hydrophobic drugs or other cargo [79,81] (
Figure 5).
Characterization and functionalization: The resulting G. lucidum PMs are characterized to assess their size, morphology, stability, critical micelle concentration (CMC), drug-loading capacity, and encapsulation of efficiency. Techniques such as DLS, TEM, and drug release studies are commonly employed [74,76,81]. The micelles can also be further functionalized by modifying the surface with targeting ligands or other functional moieties to enhance their specificity, and therapeutic efficacy. G. lucidum PMs hold promise for targeted drug delivery systems, as the bioactive compounds from the mushroom may contribute to additional therapeutic effects. However, it’s important to note that the research, and development of G. lucidum PMs are still ongoing, and further studies are needed to explore their full potential and optimize their performance in drug delivery applications.
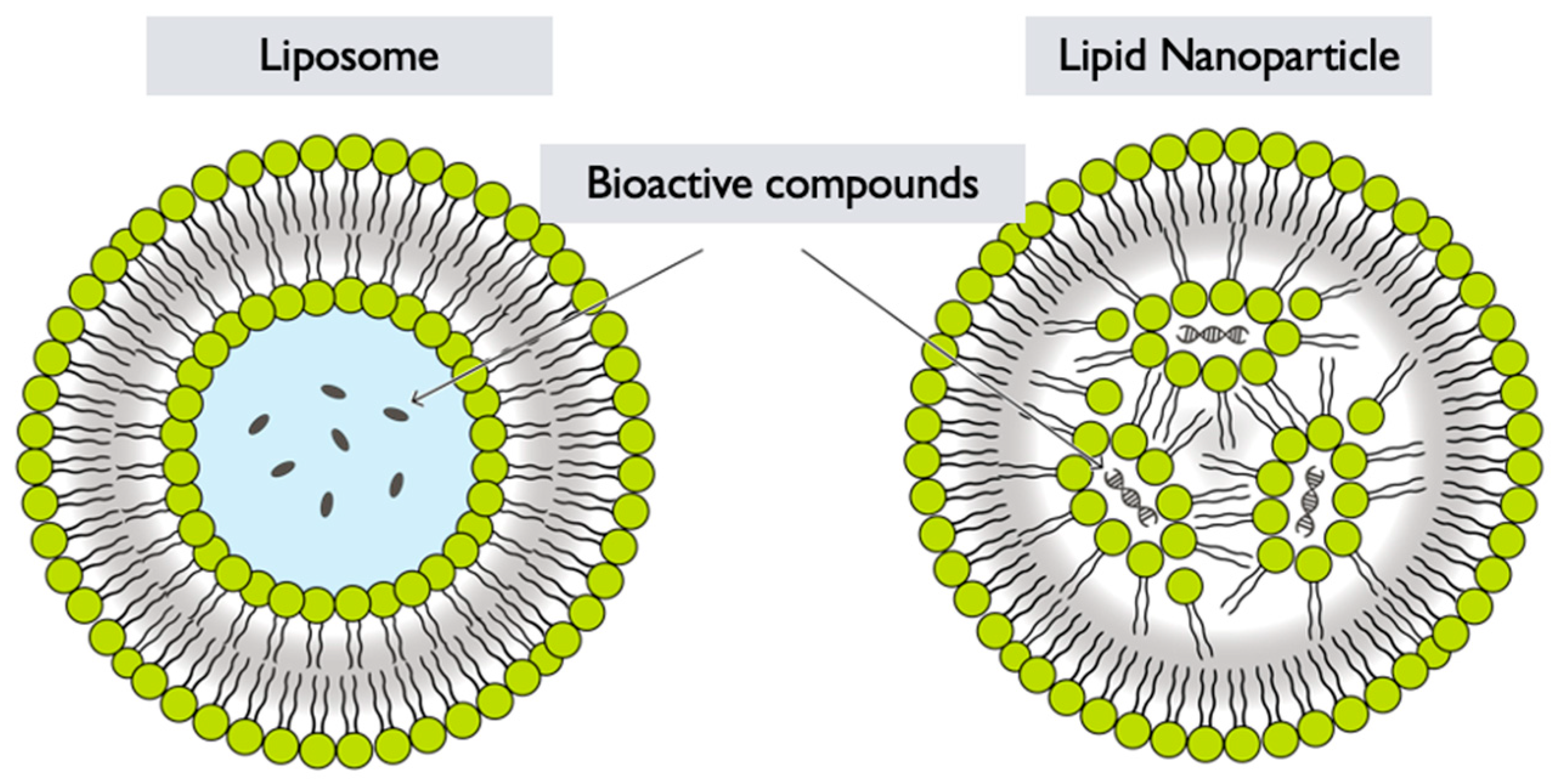
6.3. Lipid Nanoparticles
G. lucidum lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) refer to nanoparticles that are formed by encapsulating G. lucidum extracts or components within a lipid-based delivery system [82]. Lipid nanoparticles are colloidal carriers composed of lipids, and can be used for various applications, including drug delivery, gene delivery, and cosmetic formulations [83]. The synthesis of G. lucidum LNPs generally involves the following steps:
Selection of lipids: Lipids are chosen based on their biocompatibility, stability, and ability to form nanoparticles. Common lipids used in lipid nanoparticle formulations include phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylglycerol, and other lipid-based materials like solid lipids or oils [85] (
Figure 6).
Preparation of lipid solution: The selected lipids are dissolved in an appropriate organic solvent, such as chloroform or ethanol, to form a lipid solution [85,86]. The G. lucidum extracts or components are incorporated into the lipid solution during this step.
Emulsification: The lipid solution containing G. lucidum extracts is then emulsified with an aqueous phase, typically a buffer or water. This can be achieved through techniques like ultrasonication, high-pressure homogenization, or microfluidics, resulting in the formation of small droplets [86].
Nanoparticle formation: After emulsification, the organic solvent is removed by evaporation or other methods, leading to the formation of lipid nanoparticles encapsulating GL extracts [86]. The removal of the organic solvent allows the lipids to solidify and stabilize, forming nanoparticles with the G. lucidum components entrapped within.
Characterization: The G. lucidum LNPs are characterized to determine their size, morphology, encapsulation efficiency, drug loading capacity, and stability. Techniques such as DLS, TEM, SEM, and UV-Vis and FTIR spectroscopic methods, DSC may be employed to assess these properties [69,86].
Functionalization: Depending on the desired application, the surface of the G. lucidum LNPs can be further functionalized with targeting ligands, polymers, or other surface modifications to improve their specificity, stability, or targeting properties. G. lucidum LNPs have the potential to enhance the delivery, and bioavailability of G. lucidum bioactive compounds. However, it is important to note that specific formulation strategies, and optimization processes may vary depending on the desired application and intended use of the LNPs. Further research, and development are necessary to explore the full potential of G. lucidum LNPs in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics.
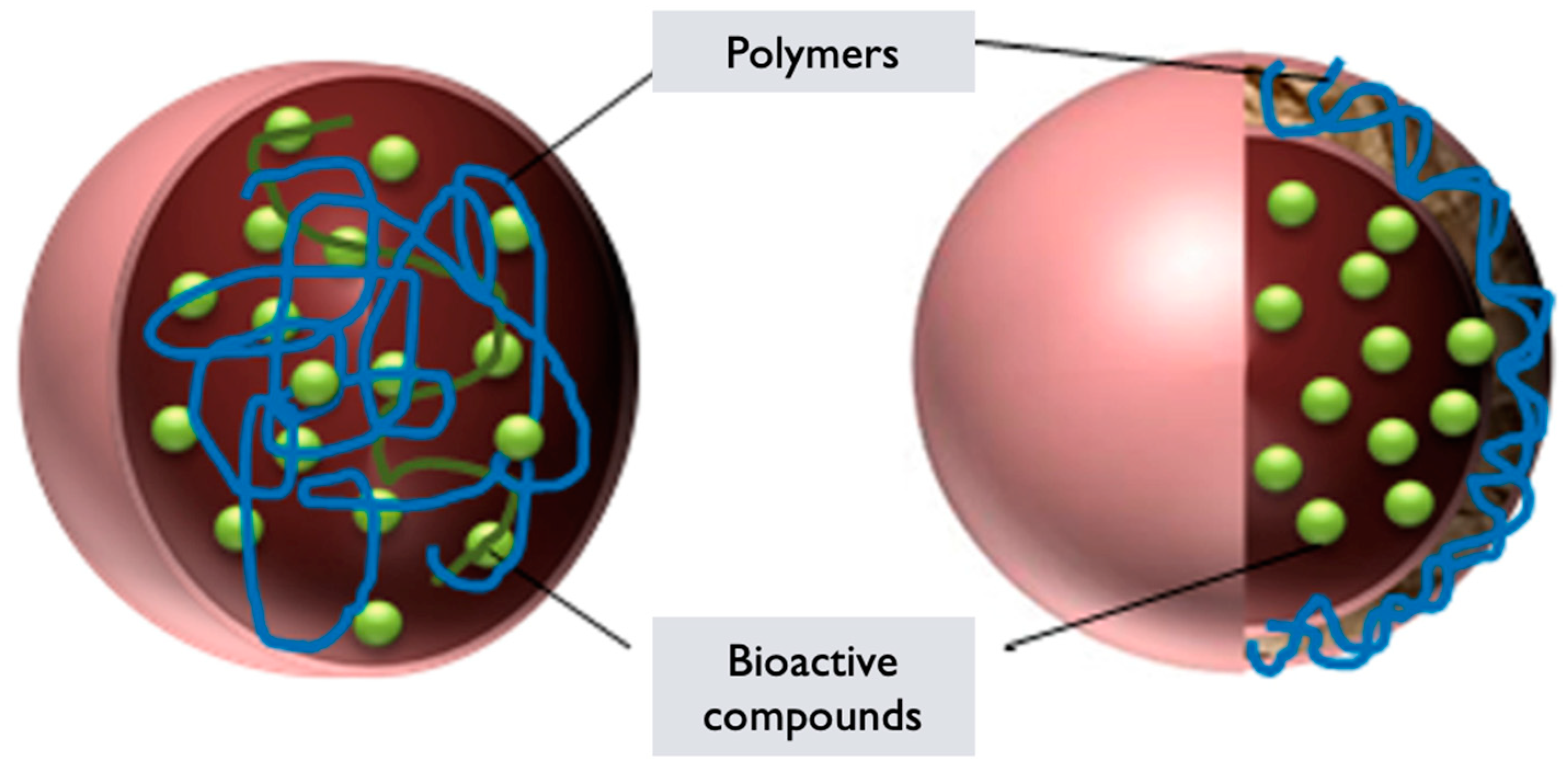
6.4. Polymeric Nanoparticles
G. lucidum PNPs are nanoparticles formed using polymers derived from G. lucidum or incorporating extracts/components from the mushroom. These nanoparticles are created by self-assembling the polymers into nanoscale structures, which can be utilized for various applications, including drug delivery, imaging, and tissue engineering [87]. The synthesis of GL PNPs generally involves the following steps:
Polymer selection: Polymers derived from GL or incorporating extracts/components from the mushroom are chosen based on their biocompatibility, stability, and ability to self-assemble into nanoparticles [87]. These polymers can include G. lucidum derived polysaccharides, proteins, or modified polymers with incorporated mushroom extracts.
Polymer synthesis or modification: The selected polymers are synthesized or modified to incorporate the desired properties for nanoparticle formation. This can involve polymerization techniques or chemical modifications to introduce hydrophilic, and hydrophobic segments within the polymer structure, which are essential for self-assembly into nanoparticles [89].
Nanoparticle formation: The synthesized or modified G. lucidum polymers are dissolved in an appropriate solvent to form a polymer solution. Self-assembly of the polymers occurs spontaneously due to the establishment of hydrophilic, and hydrophobic interactions [89]. This results in the formation of PNPs encapsulating G. lucidum components or with the components integrated within the polymer matrix.
Characterization: The G. lucidum PNPs are characterized to determine their size, morphology, stability, drug-loading capacity, and efficiency of encapsulation. Techniques such as DLS, TEM, SEM, UV-Vis and FTIR spectroscopy can be employed to assess these properties [69,89].
Functionalization: Depending on the desired application, the surface of the G. lucidum PNPs can be further functionalized with targeting ligands, polymers, or other surface modifications to improve their specificity, stability, or targeting properties. Surface modifications can also enable the attachment of imaging agents or other functionalities.
G. lucidum PNPs have the potential to be utilized as carriers for controlled drug release, improving the solubility, and bioavailability of
G. lucidum components, or as vehicles for targeted delivery of therapeutics. However, it’s important to note that further research, and development are required to optimize the formulation strategies, enhance stability, and assess the therapeutic efficacy of
G. lucidum polymeric nanoparticles in various applications (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8).
7. Regulatory Issues and Clinical Trials
Transitioning from the laboratory to practical applications often encounters a complex web of regulatory challenges, and rigorous clinical trials. In the case of G. lucidum in nanotechnology, this transition is no exception. The utilization of G. lucidum in nanotechnology applications within clinical trials presents several regulatory considerations that must be carefully navigated. These considerations are vital for ensuring patient safety, the efficacy of treatments, and adherence to regulatory standards. We may consider:
Safety and Toxicity Assessment: Regulatory bodies require a thorough evaluation of the safety profile of GL-based nanotechnological products. This includes assessing potential adverse effects, toxicity, and interactions with other treatments or medications.
Standardization and Quality Control: Ensuring the consistency, and quality of GL-derived nanoparticles or formulations is crucial. Regulatory agencies often require standardized processes, and rigorous quality control measures to maintain product integrity.
Clinical Trial Authorization: Clinical trials involving G. lucidum in nanotechnology applications typically require authorization from regulatory bodies such as the in the United States or the EMA in Europe. Obtaining these approvals involves providing detailed documentation on the product, its manufacturing process, and preclinical data.
Data Integrity and Reporting: Regulatory agencies expect accurate, and complete reporting of clinical trial data. This includes transparency in reporting both positive, and negative results, adverse events, and patient outcomes.
Good Clinical Practice (GCP): Adherence to GCP guidelines is essential. GCP ensures that clinical trials are conducted ethically, with patient safety in mind, and that the data collected is reliable, and credible.
Post-Market Surveillance: After clinical trials, regulatory agencies may require post-market surveillance to continue monitoring the safety, and efficacy of GL-based nanotechnological products once they are in use by the general population.
7.1. Preclinical Studies
Preclinical studies that explore the application of G. lucidum in nanotechnology have shown promising results for various therapeutic purposes. These studies have been utilized nanotechnology-based approaches to enhance the delivery, efficacy, and selectivity of bioactive compounds derived from G. lucidum.
Enhanced Drug Delivery: Nanoparticles loaded with G. lucidum bioactive compounds have been investigated for improved drug delivery in cancer therapy. In one study, polymeric nanoparticles loaded with GLPs exhibited enhanced cellular uptake, and cytotoxicity against cancer cells, when compared with free polysaccharides [3,19]. The resulted NPs demonstrated sustained release of the bioactive compounds, resulting in prolonged anticancer effects.
Targeted Therapy: Targeted delivery of G. lucidum bioactive compounds to cancer cells has been achieved using functionalized nanoparticles. In a preclinical study, folate-conjugated NPs encapsulating GLTs selectively targeted folate receptor-expressing cancer cells.[3,19] This targeted delivery approach improved the efficacy of the bioactive compounds, and reduced toxicity to healthy cells.
Synergistic Effects: Nanotechnology has been employed to combine G. lucidum bioactive compounds with other therapeutic agents, leading to synergistic effects. For example, in a preclinical study, co-encapsulation of GLTs, and some chemotherapeutic drugs (e.g., Paclitaxel, Doxorubicin, Cisplatin, 5-Fluorouracil, Gemcitabine, Etoposide, and Vinblastine) within nanoparticles resulted in enhanced cytotoxicity against cancer cells compared to the individual treatments alone [3,19]. The combination therapy demonstrated improved antitumor activity, and reduced drug resistance.
Immunomodulation: Nanotechnology-based formulations incorporating G. lucidum bioactive compounds have shown potential for immunomodulatory effects. In a preclinical study, nanocarriers loaded with GLPs effectively stimulated immune responses, and enhanced the activation of immune cells, leading to improved anticancer immune responses [3,19]. The nanotechnology-mediated delivery facilitated the targeted modulation of the immune system.
Theranostics: GL-based nanomaterials have been explored for theranostic applications, combining therapy, and diagnostics. In a preclinical study, multifunctional nanoparticles loaded with G. lucidum bioactive compounds were developed as theranostic agents for simultaneous cancer therapy, and imaging technology [3,19]. The NPs exhibited selective tumor accumulation, efficient tumor regression, and imaging capabilities for real-time monitoring of treatment response.
These preclinical studies highlight the potential of G. lucidum in combination with nanotechnology for enhanced therapeutic outcomes in cancer therapy [3,19]. While these studies show promising results, further research is necessary to evaluate the safety, long-term effects, and clinical translation of these nanotechnology-based approaches. Nevertheless, these preclinical studies lay the foundation for future investigations, and the development of novel therapeutic strategies utilizing G. lucidum in nanotechnology for treatment of chronic diseases like cancer.
A total of 210 articles were reviewed for preclinical studies, investigating the potential activities of G. lucidum in various areas such as anticancer, antiaging, antibacterial, antiobesity, antidepressant, antiosteoporotic, anxiolytic, antidiabetic, anti-dyslipidemia, antiepileptic, antihypertensive, antihypertensive, antihyperlipidaemic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antimutagenic, antioxydant, cardio-protective, hepatoprotective, immune-boosting, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, sedative, nootropic, and radio-protective effects (Venturella et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2016; Ekiz et al., 2023). Among these studies, approximately 33% utilized G. lucidum extract in different forms, 21% focused on isolated polysaccharides, 5% examined triterpenes, and 3% explored the effects of G. lucidum spore powder. The remaining 38% of studies investigated other preparations of G. lucidum. Regarding the study models employed, approximately 40% of the studies utilized mice, 33% used rats, 17% employed various types of cell lines, while a smaller proportion of the studies involved pigs, chickens, bacterial strains, and clinical isolates. The in vitro studies employed a dose range of 1-1,000 μg/mL, while in vivo studies used doses ranging from 10-10,000 mg/kg [3,19].
Table 5.
Preclinical studies and their therapeutic effects realized in G. lucidum.
Table 5.
Preclinical studies and their therapeutic effects realized in G. lucidum.
| Therapeutic effect |
Action mechanisms |
Model |
Reference |
| Anticancer |
|---|
In vitro
In vivo
|
↑ CD47/CD8+ ratio
↑ Immune system activity
↑ Apoptosis
↑ Expression of Bax and caspase-3
↑ mRNA expression
↑ Protein production
↑ Population of Tc-cells
↓ Activation of Akt and its downstream regulator |
Cell lines related to melanoma, lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, osteosarcoma, and human prostate cancer. |
[3,19,27,28,41,47,56,92,93] |
↓ Cellular levels;
Activation of Akt and its downstream regulators;
Inhibition of STAT3 signaling; cell viability, autophagy flux, Rac activity and downstream signaling pathway, osteosarcoma cell activity, and expression of anti-apoptotic proteins;
↑ Autophagy through Akt/TOR signaling, apoptosis with cell cycle arrest via NAG-1 induction, and autophagosome accumulation;
↓ Tumor volume;
↓ Growth;
↓ Metastasis;
Progression and release of matrix metalloproteinases;
↑ Cytotoxicity;
↑ Apoptosis;
↑Immunomodulatory activity. |
Breast cancer, mammary adenocarcinoma, ascitic tumor, cervical carcinoma, hepatoma, lung tumor, and glioma |
| Antibacterial |
|
|
|
In vitro
In vivo
|
↑ Cell permeability and leakage;
↑ Polysaccharides binding to leukocyte surfaces;
Activation of Th/NK/macrophages,;
Upregulation of IgA/RD-5, 6/TLR4 mRNA levels;
Improved attachment and permeability, lncreased oxidative stress and killing of pathogens. |
|
[3,19,94] |
↓ Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes ratio;
↓ Proteobacteria abundance;
↓ Levels of Aerococcus, Ruminococcus, and Corynebacterium.
|
Mice with dysbiosis and rats with type-2 diabetes |
| Anti-obesity |
|
|
|
In vitro
In vivo
|
↓ mRNA expression of SREBP-1c, C/EBPa and PPARy;
Inhibition of MAPK pathway increases energy expenditure with the inhibition of 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes proliferation and differentiation. |
Murine pre-adipocyte cells;
M. miehei lipase.
|
[3,19,95] |
↓ Body and liver weight;
↓ Subcutaneous fat;
↑ Microbiome-gut-liver and gut-brain axes;
Regulate metabolism by modulating gut microbiota composition;
↑ Levels of Clostridiales, Lachnospiraceae, Oscillospira, and Ruminococcaceae;
↓ Levels of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Roseburia. |
High-fat diet-fed;
MK-fat mice. |
| Hepatoprotective |
|
|
|
In vivo
|
↑ Antioxidant activity;
↓ Oxidative stress;
Regulating key molecular pathways: FOXO4/mTOR/SIRT1;
↓ Expression of hepatic glucose regulatory enzymes, p-AMPK/AMPK, lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, MDA, and heat shock proteins;
↓ Expression of inflammatory markers: iNOS, COX2, TNF-α, NF-KB, and IL-6;
↑ Superoxide dismutase activity, lipid peroxidation, and apoptosis;
Inhibits fatty acid synthesis;
↓ Serum ALT levels indicating its potential in protecting liver health. |
|
[3,19,96] |
| Anti-dyslipidaemia |
|
|
|
In vitro
In-vivo
|
↓ 3T-L1 pre-adipocytes proliferation/differentiation;
↓ Key lipid-metabolizing enzymes. |
|
[3,19,97] |
↓ Haemorrhage/thrombosis;
↓ Stroke, cardiac necrosis;
↓ Atherosclerotic plaque;
↑ HDL-c;
↑ Total BAs. |
|
| Cardioprotective |
|
|
|
In vitro
In vivo:
|
↓ Cardiomyocyte necrosis;
Reperfusion contracture;
Antioxidant effects;
Activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway;
Modulation of specific molecular targets. |
|
[3,19,97] |
↓ Haemorrhage/thrombosis;
↓ Stroke;
↓ Cardiac necrosis;
↓ Atherosclerotic plaque;
↑ Anti-angiogenic;
↑ Antioxidant properties. |
|
| Antidiabetic |
|
|
|
In vitro
In vivo
|
↓ Hepatic PECK gene expression;
↓ Glucose level;
↓ SREBP1;
↓ FAS-mRNA expression;
↓ mRNA level for gluconeogenesis enzymes and H2O; |
Human breast adenocarcinoma cell line (MCF-7/ADR) and HepG2 cells
|
[3,19,97] |
↑ Glucose uptake
↑ Insulin level
↑ Hepatic glycogen level
↑ Insulin sensitivity
↑ Glycogen synthesis
↑ Glucose transport via the PI3K/Akt pathway. |
Mice and rat models |
| Immunomodulatory |
|
|
|
In vitro
In vivo
|
Upregulation of immunomodulators IL-12, IF-4, IL-2, IL-6, IL-4, IL-17, TNF-a, IFN-%, granulysin, perforin, and NKG2D/NCR cell surface receptors;
↑ Production of nitric oxide (NO);
Activates ERK, JNK, and p38 signaling pathways. |
Mice, rats, and pigs |
[3,19,27,28,41,47,56,92–97] |
Activates humoral and cellular immune responses;
Promotes antigen-specific IgG production;
Enhances haematopoiesis, macrophage phagocytosis, and proliferation of spleen lymphocytes and undifferentiated spleen cells;
Stimulates the activity of T/B-cells, LAK cells, CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T-cells;
Activation of NF-KB/MAPK, NK cells, NF cells, TNF activity, and cytokine secretion. |
| Anti-inflammatory |
|
|
|
In vitro
In vivo
|
↓ Expression of NF-κB, MAPK, and AP-1;
↓ Activity of G-CSF, IL-1α, MCP-5, and MIP3α;
↓ mRNA expression of CHUK and NFκB1/p150;
↓ NO, MDA, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels;
↓ iNOS and COX-2 expression;
↑level of SOD. |
|
[3,19] |
Suppression of inflammatory mediators TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP1, and hydroxyproline;
↑ Expression of keratinocyte differentiation markers;
↓ Serum Ig-E level;
↑ SOD/TOAC level. |
|
| Neuroprotective |
|
|
|
| In vivo |
Downregulating caspases-3, -8, and -9;
Modulation of Bcl-2/Bax ratio;
Protects DNA and cell membranes from the harmful effects of radiation;
↑ Cerebral blood flow;
↓ Neuronal damage and apoptosis;
Promotes mitochondrial movement;
Enhances the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines;
Improves spatial learning and memory-related behavior;
↓ Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by Aβ and oxidative stress induced by spinal cord injury;
Inhibits apoptosis caused by hydrogen peroxide, lipid peroxidation, and GSH. |
|
[3,19] |
| Anti-epileptic |
|
|
|
| In vivo |
↓ Hippocampal neurons;
↓ Number of excitatory neurons and delays the onset of epilepsy;
Prevents CA3 degeneration;
↓ Astrocytic reactivity;
↓ Levels of pro-inflammatory;
↑ Cytokines IL-1B and TNF-α;
threshold for psychomotor seizures;
↑ Content of GABA;
↓ Seizures and convulsions. |
|
[3,19] |
| Sedative |
|
|
|
| In vivo |
Inducing a hypnotic effect in rat and mice models;
Promote relaxation and sleep;
Modulation of cytokines, specifically TNF-a;
Sedative effects;
Regulate sleep-related processe;
↓ Sleep latency;
↑ Sleep duration. |
|
[3,19] |
| Nootropic |
|
|
|
In vivo
|
Improving cerebral blood flow, brain energy supply, memory-related neurotransmitters, and cognition;
↓ Brain cell apoptosis and ameliorates spatial memory deficits;
Inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity;
Antioxidant properties;
Improves anterograde amnesia. |
|
[3,19] |
| Antidepressant |
|
|
|
| In vivo |
Blocking 5-HT2A receptors;
Inhibiting MAO;
Antagonizing preganglionic 5-HT receptors;
↓Depression-related activities. |
|
[3,19] |
| Anti-osteoporotic |
|
|
|
| In vivo |
Promoting bone healing;
Regeneration;
↑ Trabecular bone volume;
Inhibits osteoclastogenesis and reverses bone loss;
↑ OPG/RANKL ratio;
↓ Bone differentiation;
Formation of RANKL-induced osteoclast;
Facilitates cross-talk between the Wnt/B-catenin and BMP/SMAD signaling pathways;
Protective effects on bone. |
|
[3,19] |
| Anxiolytic |
|
|
|
| In vivo |
↓ Anxiety levels at ranging doses between 20 to 400 mg/kg. |
Swiss Albino mice |
[3,19] |
| Radioprotective |
|
|
|
| In vivo |
Antioxidant and free radical scavenging properties;
↑ Levels of GSH;
Protection against radiation-induced damage;
↓ Reactive oxygen species ROS;
Restoration of TNF-d production;
Repair of damaged T-cells;
Protection against gamma rays;
Reducing DNA strand breaks and micronuclei formation;
↓ MDA levels;
Promoting the recovery of SOD activity. |
|
[3,19] |
7.2. Clinical Studies
The information available on clinical studies specifically investigating the use of G. lucidum in nanotechnology-based approaches for human subjects is limited. However, the information founded on clinical studies involving G. lucidum, and its bioactive compounds in general may include some studies that do not specifically focus on nanotechnology. Clinical studies on G. lucidum have explored its potential therapeutic effects in various health conditions, including cancer. Some of these studies have investigated the administration of G. lucidum extracts or preparations, which may or may not involve nanotechnology-based formulations. A few examples of clinical studies involving G. lucidum are:
Cancer Therapy: Clinical trials have evaluated the efficacy, and safety of G. lucidum in cancer patients. These studies have explored its potential as an adjuvant therapy to conventional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy [3,19,24]. While some studies have reported positive outcomes, including improved quality of life, immune system modulation, and enhanced treatment response, the overall evidence is limited, and more rigorous studies are needed.
Immunomodulation: Clinical studies have investigated the immunomodulatory effects of G. lucidum in various populations, including healthy individuals, and patients with chronic diseases. These studies have explored the impact of G. lucidum on immune parameters, such as cytokine levels, immune cell activity, and antioxidant status [3,19,92–97]. Results have indicated potential immunomodulatory effects, but further research is needed to establish clear clinical recommendations.
Liver Health: G. lucidum has been studied in clinical trials focusing on liver health, particularly in patients with hepatitis B or hepatitis C. These studies have assessed its potential hepatoprotective effects, antiviral activity, and impact on liver function. While some studies have reported positive outcomes, the evidence is still limited and larger, well-controlled trials are needed to confirm these findings [3,19,96].
Cardiovascular Health: Clinical studies have investigated the effects of G. lucidum on cardiovascular health markers, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and oxidative stress. Some trials have reported potential benefits, including improved lipid profiles, and antioxidant status [3,19,97]. However, more robust clinical trials are required to establish the efficacy, and safety of G. lucidum in cardiovascular health management.
It is important to note that while these clinical studies provide insights into the potential therapeutic effects of G. lucidum, the specific use of nanotechnology-based approaches in these studies may be limited. Further research is needed to explore the application of G. lucidum in nanotechnology-based formulations in clinical settings, assessing their safety, efficacy, and potential advantages over conventional formulations.
In the 22 clinical studies conducted on G. lucidum, various preparations were used, including G. lucidum tablets, capsules, supplements, extracts, purified polysaccharides, and polysaccharide peptides. Among these studies, 32% utilized G. lucidum tablets/capsules/supplements, 27% used extracts, 23% used purified polysaccharides, 9% used polysaccharide peptides, and the remaining 2 studies utilized supplements. The sample sizes (n) in these studies varied from 2 patients (hay fever) to 170 asymptomatic children. The administered doses ranged from 150 mg/day to 6,000 mg/day [3,19].
7.3. Critical Assessments of the Pharmacological Activities
7.3.1. Preclinical Studies
Preclinical studies play a vital role in advancing our understanding of human diseases. These studies involve investigating the biochemical events, physiological processes, and behavioral implications associated with diseases. They also allow for the testing of novel pharmacotherapeutic interventions. In this context, in vitro studies are commonly conducted as they are relatively easy to perform, requiring lower costs, and do not necessitate high technical skills. However, it’s important to note that the controlled laboratory environment in in vitro studies may not accurately replicate the complexities of the natural environment, resulting in limited chances of identifying lead compounds with therapeutic potential. On the other hand, in vivo models provide valuable tools for studying the mechanisms, and etiology of human diseases. By using living organisms, such as animal models, researchers can better understand the interactions between various physiological systems, and assess the effects of potential interventions. In vivo studies allow for a more holistic evaluation of the disease process and its response to treatments. However, despite their advantages, it is worth noting that the number of new leads identified through in vivo studies that ultimately reach clinical trials is relatively limited. While in vitro studies offer advantages like cost-effective, and accessible methods for preliminary screening, they may have limitations in terms of replicating the complex natural human environment. In vivo models provide a more comprehensive understanding of diseases but may face challenges in translating findings to successful clinical trials. Both approaches are important and complement each other in preclinical research to enhance our understanding, and development of potential therapies for human diseases. The translation of preclinical studies to clinical studies faces limitations, and hindrances, which can contribute to the lack of reproducibility in many preclinical trials. The findings and data from preclinical studies often do not withstand the test of time. To address these issues, it is recommended that preclinical investigators be blinded to the treatment, and control arms, and use rigorously validated reagents.[19] Experiments should include appropriate positive, and negative controls. Critical investigations should be repeated, preferably by different investigators within the same laboratory, and only after obtaining consistent results should the final data set be published.
Several reasons can be inferred for the limited number of preclinical studies transitioning to clinical studies. These include the lack of proper preclinical models, inadequate blinding of investigators to treatment protocols, and the use of reagents, chemicals, and tools without rigorous validation [3]. Additionally, many studies focused on known species, and diseases without delving into the underlying mechanisms or understanding them in-depth.
Improper standards, and strains used in preclinical studies also contribute to limitations. The standards (positive and negative controls), and their doses used in these reports may not be comparable to the test doses, hampering the development of novel conclusions, and drug advancements [3,19]. Moreover, the microbial strains utilized often represent common, and easily manageable species, lacking resistance traits. However, in recent years, there has been a significant increase in antibiotic resistance, highlighting the need for studies focusing on life-threatening species such as methicillin/vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA/VRSA) [101]. The literature on G. lucidum has been observed to suffer from these deficiencies, and limitations in preclinical studies. Addressing these issues, and conducting studies with more robust methodologies, and relevant strains is crucial to obtain significant outcomes and develop novel interventions. One of the challenges in herbal extracts research, particularly with herbs like G. lucidum, is the unreliability of extracts, and geographical variation in the herb. The quality and quantity of mycochemicals can vary significantly when herbs are collected from different geographic origins. Different authors have reported the same pharmacological activity using G. lucidum collected from different locations. However, the statistical significance of the results can vary widely due to the non-uniform distribution of active compounds in the samples used for similar pharmacological activity [3,19]. Another factor that contributes to the complexity, and reproducibility of the data is the application of different statistical models in each study, even when G. lucidum is collected, and extracted from similar origins. This variation in statistical models can make it challenging to compare, and reproduce experimental data across studies. The dose range used in many studies may not be applicable in clinical settings, and needs to be reconsidered.[19] Additionally, while some studies mention proposed mechanisms of action, these mechanisms are often cited from previous literature, and may not be unanimously investigated or informative for further studies. The presence of multiple mycochemicals in a plant can contribute to its pharmacological effects, making it difficult to hypothesize a single mechanism of action [3,19].
Overall, the unreliability of extracts, and the geographical variation of herbs, along with the use of different statistical models, and the complexities of dose range, and underlying mechanisms, pose challenges in herbal extract research, including studies on G. lucidum. Addressing these issues, and ensuring standardized protocols, and methodologies can improve the reliability, and comparability of research findings. In addition to efficacy and potency, it is crucial to monitor the toxicity, adverse effects, and chronic use of test drugs or products. Adverse effects, toxicities, allergies, and other potential risks should be assessed, particularly in chronic use or at high doses [102–104]. It is important to consider the potential of drugs or extracts to mask drawbacks or suppress certain physiological processes, as seen with some cancer drugs. Dependency and withdrawal effects should also be addressed. The impact of drugs or extracts on liver enzymes is significant, and a comprehensive understanding of enzyme saturation, interactions, agonistic/antagonistic effects, and the overall effect on liver function is necessary [3]. In the case of G. lucidum, which has been tested for diseases requiring long-term drug use such as epilepsy, and Alzheimer’s disease, establishing relevant preclinical models that accurately reflect the possible toxicities associated with its chronic use is very relevant. These suggested loopholes highlight the need to thoroughly investigate, and address the potential adverse effects, toxicities, and long-term usage implications of test drugs or extracts. Understanding and mitigating these factors are essential for improving the transition rate of preclinical studies into clinical studies, and trials.
7.3.2. Clinical Studies
Clinical studies are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness, and safety of medicinal products like G. lucidum. However, there is a limited number of clinical studies on G. lucidum mushroom compared to preclinical studies, which might be due to the challenges in translating preclinical findings into clinical settings. Most of the clinical studies on G. lucidum have small sample sizes, which can limit the interpretation of results, and increase the risk of false positive or negative outcomes. These preliminary studies provide valuable data that can be used to design larger confirmatory studies. To establish the efficacy and safety of G. lucidum for marketing purposes, advanced clinical studies covering different phases (Phase I to Phase V) are necessary. It is important to have a consistent dose range, and standardized preparation methods for G. lucidum in clinical studies. However, there is variation in the dose range used, and the reporting of mechanisms in some studies. A more systematic, and reproducible approach, including sequential Phase I to Phase III studies, is needed to generate reliable data [3,19]. The source of G. lucidum used in clinical studies also varies in terms of geographical origin, extraction methods, and final product concentration. This variability can lead to differences in the concentration of bioactive compounds, and subsequently affect the therapeutic, and toxic outcomes observed. Challenges such as heterogeneity, small sample sizes, inappropriate research methodologies, lack of multicenter involvement, and inadequate statistical models have hindered the progress of G. lucidum as a potential conventional drug for treatment [3,19].
In summary, there is a need for well-designed clinical studies with larger sample sizes, standardized dosing, reproducible data, appropriate research methodologies, and multicenter collaboration to fully explore the potential of G. lucidum as a conventional drug.
G. lucidum has attracted significant interest in cancer therapy, and other chronic diseases due to its bioactive compounds, and potential health benefits. As mentioned throughout this review, in recent years nanotechnology has emerged as a promising approach to enhance the delivery, and effectiveness of therapeutic agents, including G. lucidum bioactive compounds in cancer treatment [64]. The combination of G. lucidum with nanotechnology offers exciting prospects for improving cancer therapy, and patient outcomes. G. lucidum bioactive compounds, such as GLPs and GLTs, and other secondary metabolites, have shown promising anti-tumor properties in preclinical studies.[21–25] Their ability to modulate immune responses, induce apoptosis, and inhibit tumor growth makes them attractive candidates for cancer therapy. Nanotechnology-based formulations can overcome the limitations for the delivery of G. lucidum bioactive compounds to specific target sites, including improved delivery, increased bioavailability and stability, targeted drug delivery, and synergistic effects with other therapeutic agents [24]. Nano-sized carriers, such as nanoparticles and liposomes, offer controlled, and sustained drug release, enhancing therapeutic efficacy [61–67,74–76,81–85]. Functionalized nanoparticles, and liposomes offer controlled and sustained drug release, can enhance targeted delivery to cancer cells, minimizing off-target effects, and maximizing therapeutic efficacy. Furthermore, the immunomodulatory effects of G. lucidum can be amplified through nanotechnology, leading to enhanced activation of the immune system against cancer cells [3,19]. Nanotechnology-based approaches also offer opportunities for cancer diagnostics, and imaging, facilitating early detection, and personalized treatment strategies. However, further research and clinical studies are needed to fully explore the potential of G. lucidum in nanotechnology-based cancer therapy. The safety, long-term effects, and clinical translation of these approaches require thorough investigation. Additionally, the scalability, standardization, and optimization of nanotechnology-based formulations incorporating G. lucidum need to be addressed to ensure their practical application in clinical settings. The combination of G. lucidum bioactive compounds with chemotherapeutic drugs within nanoparticles has demonstrated synergistic effects in preclinical studies [27–60]. This approach has the potential to enhance cytotoxicity against cancer cells, reduce drug resistance, and minimize systemic toxicity. Furthermore, nanoparticles can be engineered with specific surface modifications or ligands to enable targeted drug delivery to tumor cells, enhancing precision medicine approaches, and minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Although clinical studies specifically focusing on G. lucidum in nanotechnology-based approaches are currently limited.
Despite the promising preclinical findings, more research is needed to further elucidate the mechanisms of action, and optimize the formulations of GL-based nanomedicines. Rigorous preclinical studies, and clinical trials are essential to evaluate the safety and efficacy of these novel therapies. Future perspectives in this field involve the development of robust clinical trials specifically focused on G. lucidum in nanotechnology-based approaches for cancer therapy. These trials should evaluate the safety, efficacy, and long-term outcomes of these formulations. Furthermore, efforts should be made to establish standardized manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and regulatory frameworks for these nanotechnology-based formulations.
In this way, the future perspectives in this field could involve:
Continued research on the bioactive compounds of G. lucidum, and their interactions with nanocarriers will provide valuable insights for designing optimized nano-formulations.
Large-scale preclinical studies, and well-designed clinical trials are necessary to validate the effectiveness, and safety of G. lucidum-based nanomedicines in humans.
The development of personalized nanotherapies using G. lucidum bioactive compounds tailored to individual patient profiles could pave the way for personalized cancer treatment strategies.
Further exploration of the combination of G. lucidum with other advanced therapies, such as immunotherapy, and targeted therapies, may open new avenues for synergistic cancer treatment approaches.
Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical industries is crucial to accelerate the translation of G. lucidum-based nanotherapies from the laboratory to clinical applications.
G. lucidum, in nanotechnology for cancer therapy holds great promise as a complementary approach to conventional treatments. Harnessing the potential of G. lucidum, bioactive compounds in nanoparticles, and other nanocarriers presents an exciting opportunity to advance cancer treatment strategies, and improve patient outcomes.
Table 6.
Clinical studies and their therapeutic effects realized in G. lucidum.
Table 6.
Clinical studies and their therapeutic effects realized in G. lucidum.
| Activity |
Effect |
| Anticancer |
↑Mitogenic reactivity to concanavalin-A and phytohemagglutinin;
Lymphocyte;
CD3/CD4 and natural killer cells activity;
CD3/CD4/CD8/CD56, IL-2 IL-6, IFN-Y, and NK activity. |
| Antioxidant and hepatoprotective |
↑Antioxidant activity
↓Thiobarbituric acid, 8-OH-dG. GOT and GPT levels;
↓Triglycerides;
↑HDL-c. |
| Cardioprotective |
↓Blood pressure and atherosclerosis;
Improve chest pain/ palpitation/angina pectoris;
↓Diastolic/systolic pressure, TAG, MDA, CEC, EPC levels;
↑ capillary loop diameter, density, RBC velocity, and HDL-cholesterol. |
| Antidiabetic |
↓Cell resistance to insulin and HbA1c, FPG, and PPG values;
The antiplatelet effect GL though contains a high level of adenosine;
Lack of effect on platelets aggregation. |
| Anti-histaminic |
Most symptoms were relleved in hay fever patients due to restored normal balance between Th1 and Th2. |
| Anti-viral |
Inhibition of virus replication in hepatitis-B and HIV patients;
↓HBeAg. HBV, DNA, and liver enzymes. |
| Immunomodulatory |
↑CD3+, CD4+, CD8+ T cells. |
| Anti-fibromyalgia |
Aerobic endurance was improved along with lower body flexibility and velocity via the antioxidant effect of GL. |
| Anti-Alzheimer |
↓Ab, 3, 4-methylenedioxyamphetamine, Fasl, caspase-3, and tau hyperphosphorylation. |
| Anti-macular degeneration |
Improvement of pre-ganglionic retinal elements in age-related macular degeneration patients with an increase in mfERG R1 and R2, and RADs. |
8. Conclusions
The exploration of Ganoderma lucidum in the realm of nanotechnology reveals a compelling convergence of natural healing wisdom, and cutting-edge science. This mushroom, known for its rich bioactive compounds, is finding new life in the world of nanotechnology. One of the most exciting aspects is the enhancement of drug delivery systems. By encapsulating GL’s bioactive components within nanoparticles, nanofibers, and nanocomposites, researchers are increasing their bioavailability, stability, and controlled release. This has the potential to revolutionize how medicines are delivered, making treatments more effective, and reducing side effects. The integration of G. lucidum into nanofabrication techniques has yielded novel materials with remarkable properties. Incorporating its nanoparticles into polymeric matrices, for instance, has resulted in composite materials with improved mechanical strength, antimicrobial activity, and wound healing properties. These materials hold immense promise for applications in tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and antimicrobial coatings. Furthermore, nanoparticles loaded with bioactive compounds derived from this mushroom have exhibited potent anticancer activity by targeting cancer cells, inducing apoptosis, and inhibiting tumor growth. This represents a promising avenue for developing more effective, and targeted cancer treatments. Additionally, immunomodulatory effects have been observed through nanotechnology-based formulations, which promote the activation of immune cells, and enhance the body’s defense mechanisms. This has significant implications for bolstering the immune system, and improving overall health. In conclusion, G. lucidum integration with nanotechnology opens up a world of possibilities for innovative solutions in healthcare, and beyond. While the initial strides are promising, further research, and development are warranted to fully exploit the synergistic benefits offered by this remarkable mushroom, and nanotechnology. Together, they have the potential to reshape the landscape of medicine, and wellness, offering new hope for improved human health, and well-being.
9. Patents
This section is not mandatory but may be added if there are patents resulting from the work reported in this manuscript.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, A.E. and A.F.; methodology, A.E. and A.F.; investigation, A.E. and A.F resources, A.E. and A.F.; data curation, A.E., C.D. and I.J.; writing—original draft preparation, A.E.; writing—review and editing, A.E., A.F. and Y.F.; visualization, A.F. and Y.F.; supervision, A.F.; project administration, A.F. and F.M.; funding acquisition, A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.” Please turn to the CRediT taxonomy for the term explanation. Authorship must be limited to those who have contributed substantially to the work reported.
Funding
Please add: “This research was funded by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia, with the reference PTDC/NAN-MAT/1431/2021, and DOI 10.54499/PTDC/NAN-MAT/1431/2021 and C.D. acknowledges financial support from the “Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia” (FCT—Portugal) through the Ph.D. grant 2021.08095.BD.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
List of abbreviation and acronyms
Aβ: Amyloid beta; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; Ag – Silver; Au: Gold; AgNPs: Ganoderma lucidum silver nanoparticles; BRCA1: Breast cancer 1; CMC: Critical micellar concentration; CPC: Centrifugal partition chromatography; DLS: Dynamic light scattering; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; EMA: European Medicines Agency; ER: Estrogen receptor; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; FOBT: Fecal occult blood test; FTIR: Infrared spectroscopy; GABA: Gamma-aminobutyric acid; GC: Gas chromatography; GCP: Good Clinical Practice; GL: Ganoderma lucidum; GLPs: Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides; GLTs: Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids; GRAS: Generally recognized as safe; GSH: Glutathione; HER2: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HPLC: High-performance liquid chromatography; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-8: Interleukin-8; LNPs: Lipid nanoparticles; MDA: Malondialdehyde; NK cells: Natural killer cells; MMP2: Matrix metallopeptidase 2; MMP9: Matrix metallopeptidase 9; MRSA/VRSA: Methicillin/vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; NPs: Nanoparticles; NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer; PARP: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; PARPi: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors; PMs – Polymeric micelles; PNPs – Polymeric nanoparticles; PR: Progesterone receptor; Pt: Platinum; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SCLC: Small cell lung cancer; SEC: Size-exclusion chromatography; SEM: Scanning electron microscopy; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; SPE: Solid-phase extraction; Tc-cells: Cytotoxic T cells; TEM: Transmission electron microscopy; TNBC: Triple negative breast cancer; TSE: Tradicional solvent extraction; UV-Vis: Ultraviolet-visible; WHO: World health organization; XRD: X-ray diffraction.
References
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Wachtel-Galor, S. Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects. (2nd ed.). CRC Press/Taylor Francis, 2011. [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Ahmad, N.; AlHudaithi, N.; AlHebshi, A.; Bukhari, A. Extraction and UHPLC-DAD detection of undeclared substances in market-available dietary supplements and slimming products in Eastern region, Saudi Arabia: An application of principal component analysis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2020, 34(1), e4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Riaz, M.; Khan, A.; Aljamea, A.; Algheryafi, M.; Sewaket, D.; Alqathama, A. Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi) an edible mushroom; a comprehensive and critical review of its nutritional, cosmeceutical, mycochemical, pharmacological, clinical, and toxicological properties. Phytother. Res., 2021, 35(11), 6030–6062. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, S.; Fu, J.; Zhang, W.; Shu, G.; Lin, J.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Tang, H.; Peng, G.; Zhao, L.; Chen, S.; Fu, H. Nanocarriers for combating biofilms: Advantages and challenges. J. Applied Microbiol., 2022, 133(3), 1273–1287. [CrossRef]
- Batra, P.; Sharma, A.K.; Khajuria, R. Probing Lingzhi or Reishi medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum (higher Basidiomycetes): a bitter mushroom with amazing health benefits. Inter. J. Med. Mushrooms, 2013, 15(2), 127–143. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, M.; Venerando, A.; Macone, A.; Canettieri, G.; Agostinelli, E.; Vianello, F. Nanotechnology-based strategies to develop new anticancer therapies. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(5), 735. [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhou, X.; Chen, G.; Su, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, P.; Weng, J.; Min, Y. Advances of functional nanomaterials for magnetic resonance imaging and biomedical engineering applications. Nanomed. Nanobiotech., 2022, 14(4), e1800. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Cao, B., Zhao, H., Feng, J. (2017). Emerging roles of Ganoderma lucidum in anti-aging. Aging and disease, 8(6), 691–707. [CrossRef]
- Sanodiya, B.S.; Thakur, G.S.; Baghel, R.K.; Prasad, G.B.; Bisen, P.S. Ganoderma lucidum: a potent pharmacological macrofungus. Curr. Pharm. Biotech., 2009, 10(8), 717–742. [CrossRef]
- Wachtel-Galor, S.; Yuen, J.; Buswell, J.A.; Benzie, I.F.F. Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi or Reishi): A medicinal mushroom. In Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and clinical aspects. (2nd ed.). CRC Press/Taylor Francis, 2011. [PubMed]
- Amiri-Sadeghan, A.; Aftabi, Y.; Arvanaghi, H.R.; Shokri, E.; Khalili, M.; Seyedrezazadeh, E.; Kuhar, F. A review of substrates for solid-state fermentation of Lingzhi or Reishi medicinal mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum (Agaricomycetes), for basidiome production and effect on bioactive compounds. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms, 2022, 24(4), 15–29. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X.; Lan, J.; Wei, F.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sun, X. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute pneumonia via inhibiting NRP1-mediated inflammation. Pharm. Biol., 2022, 60(1), 2201–2209. [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Chinthanom, P.; Choeyklin, R.; Thummarukcharoen, T.; Rachtawee, P.; Sappan, M.; Srichomthong, K.; Fujii, R.; Kawashima, K.; Mori, S. Highly modified lanostane triterpenes from the wood-rot basidiomycete Ganoderma colossus: Comparative chemical investigations of natural and artificially cultivated fruiting bodies and mycelial cultures. J. Nat. Prod., 2020, 83(7), 2066–2075. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; He, R.; Sun, P.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zhang, A. Molecular mechanisms of bioactive polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi), a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 150, 765–774. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Ye, L.; Jia, D.; Gan, B.; Tan, W. Temperature affects substrate-associated bacterial composition during Ganoderma lucidum hyphal growth. Can. J. Microbiol., 2021, 67(4), 281–289. [CrossRef]
- Gurovic, M.S.V.; Viceconte, F.R.; Pereyra, M.T.; Bidegain, M.A.; Cubitto, M.A. DNA damaging potential of Ganoderma lucidum extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol., 2018, 217, 83–88. [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.F.; Zhu, L.F.; Wu, Z.; Wang, G.; Ahmad, Z.; Chang, M.W. Extraction of triterpenoid compounds from Ganoderma lucidum spore powder through a dual-mode sonication process. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 2020, 46(6), 963–974. [CrossRef]
- Boh, B. Ganoderma lucidum: a potential for biotechnological production of anti-cancer and immunomodulatory drugs. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov., 2013, 8(3), 255–287. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.F. Ganoderma lucidum: Persuasive biologically active constituents and their health endorsement. Biomed. Pharmacother., 2018, 107, 507–519. [CrossRef]
- Soccol, C.R.; Bissoqui, L.Y.; Rodrigues, C.; Rubel, R.; Sella, S.R.; Leifa, F.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Soccol, V.T. Pharmacological properties of biocompounds from spores of the Lingzhi or Reishi medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum (Agaricomycetes): A Review. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms, 2016, 18(9), 757–767. [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, S.; Lee, K.E.; Dwivedi, V.D.; Yadava, U.; Panwar, A.; Lucas, S.J.; Pandey, A.; Kang, S.G. Discovery of Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids as potential inhibitors against Dengue virus NS2B-NS3 protease. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), 19059. [CrossRef]
- Seweryn, E.; Ziała, A.; Gamian, A. Health-promoting of polysaccharides extracted from Ganoderma lucidum. Nutrients, 2021, 13(8), 2725. [CrossRef]
- Cör, D.; Knez, Ž.; Knez-Hrnčič, M. Antitumour, antimicrobial, antioxidant and antiacetylcholinesterase effect of Ganoderma lucidum terpenoids and polysaccharides: a review. Molecules, 2018, 23(3), 649. [CrossRef]
- Sliva, D.; Loganathan, J.; Jiang, J.; Jedinak, A.; Lamb, J.G.; Terry, C.; Baldridge, L.A.; Adamec, J.; Sandusky, G.E.; Dudhgaonkar, S. Mushroom Ganoderma lucidum prevents colitis-associated carcinogenesis in mice. PloS ONE, 2012, 7(10), e47873. [CrossRef]
- Cör, D., Knez, Ž., Knez Hrnčič, M. (2018). Antitumour, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antiacetylcholinesterase Effect of Ganoderma Lucidum Terpenoids and Polysaccharides: A Review. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 23(3), 649. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazzi, F.; Adsuar, J.C.; Domínguez-Muñoz, F.J.; García-Gordillo, M.Á.; Gusi, N.; Collado-Mateo, D. Effects of Ganoderma lucidum and Ceratonia siliqua on blood glucose, lipid profile, and body composition in women with fibromyalgia. Efectos de Ganoderma lucidum y Ceratonia siliqua sobre la glucosa en sangre, el perfil lipídico y la composición corporal en mujeres con fibromialgia. Nutr. Hosp., 2021, 38(1), 139–145. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.S.; Guo, J.J.; Bao, J.L.; Li, X.W.; Chen, X.P.; Lu, J.J.; Wang, Y.T. Anti-cancer properties of triterpenoids isolated from Ganoderma lucidum - a review. Exp. Opin. Investig. Drugs, 2013, 22(8), 981–992. [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, A.; Quagliariello, V.; Del Vecchio, V.; Falco, M.; Luciano, A.; Amruthraj, N.J.; Nasti, G.; Ottaiano, A.; Berretta, M.; Iaffaioli, R.V.; Arra, C. Anticancer and anti-Inflammatory properties of Ganoderma lucidum extract effects on melanoma and triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Nutrients, 2017, 9(3), 210. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, J.; Cao, Y.; Gao, X. The signaling pathways and targets of traditional Chinese medicine and natural medicine in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Ethnopharmacol., 2021, 264, 113249. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Jiang, X.T.; Qin, F.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Cheng, Y.X. Gancochlearols E-I, meroterpenoids from Ganoderma cochlear against COX-2 and triple negative breast cancer cells and the absolute configuration assignment of ganomycin K. Bioorg. Chem., 2021, 109, 104706. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Lian, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, G.; Wang, W.; Xu, H.; Huang, M.; Katanaev, V.; Jia, L.; Lu, Y. Ganoderma lucidum extract promotes tumor cell pyroptosis and inhibits metastasis in breast cancer. Food Chem. Toxicol., 2023, 174, 113654. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Lu, X. The natural products and extracts: anti-triple-negative breast cancer in vitro. Chem. Biodivers., 2021, 18(7), e2001047. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bimonte, S.; Barbieri, A.; Palma, G.; Rea, D.; Luciano, A.; D’Aiuto, M.; Arra, C.; Izzo, F. Dissecting the role of curcumin in tumour growth and angiogenesis in mouse model of human breast cancer. BioMed Res. Int., 2015, 878134. [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.J.; Yen, G.C. The in vitro and in vivo experimental evidences disclose the chemopreventive effects of Ganoderma lucidum on cancer invasion and metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis, 2010, 27(5), 361–369. [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Wei, Y.; Popovich, D.G. Distinct responses of cytotoxic Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids in human carcinoma cells. Phytothe. Res., 2015, 29(11), 1744–1752. [CrossRef]
- Dethlefsen, C.; Højfeldt, G.; Hojman, P. The role of intratumoral and systemic IL-6 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 2013, 138(3), 657–664. [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.; Junius, S.; Benoy, I.; Van Dam, P.; Vermeulen, P.; Van Marck, E.; Huget, P.; Dirix, L.Y. Circulating interleukin-6 predicts survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer, 2003, 103(5), 642–646. [CrossRef]
- Benoy, I.H.; Salgado, R.; Van Dam, P.; Geboers, K.; Van Marck, E.; Scharpé, S.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Dirix, L.Y. Increased serum interleukin-8 in patients with early and metastatic breast cancer correlates with early dissemination and survival. Clin. Cancer Research, 2004, 10(21), 7157–7162. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Wang, J.H.; Redmond, H.P. Silencing of TLR4 increases tumor progression and lung metastasis in a murine model of breast cancer. Annals of Surg. Oncol., 2013, 20(3), S389–S396. [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Díaz, A.; Ortiz-Soto, G.; Suárez-Arroyo, I.J.; Zayas-Santiago, A.; Martínez-Montemayor, M.M. Ganoderma lucidum Extract reduces the motility of breast cancer cells mediated by the RAC⁻Lamellipodin axis. Nutrients, 2019, 11(5), 1116. [CrossRef]
- Brenner, H.; Kloor, M.; Pox, C.P. Colorectal cancer. Lancet, 2014, 383(9927), 1490–1502. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.N. Colorectal Cancer: Preoperative evaluation and staging. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am., 2022, 31(2), 127–141. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, B.A.; Noujaim, M.; Roper, J. Cause, epidemiology, and histology of polyps and pathways to colorectal cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clini. N. Am., 2022, 32(2), 177–194. [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Guo, D.; Fang, L.; Sang, T.; Wu, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, X. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide modulates gut microbiota and immune cell function to inhibit inflammation and tumorigenesis in colon. Carbohydr. Polym., 2021, 267, 118231. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.E.; Yi, Y.J.; Guo, Y.T.; Wang, R.C.; Hu, Q.L.; Xiong, X.Y. Inhibition of migration and induction of apoptosis in LoVo human colon cancer cells by polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum. Mol. Med. Rep., 2015, 12(5), 7629–7636. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.T.; Wang, C.Z.; Wicks, S.; Yin, J.J.; Kong, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.C.; Yuan, C.S. Ganoderma lucidum extract inhibits proliferation of SW 480 human colorectal cancer cells. Exp. Oncol., 2006, 28(1), 25–29. [PubMed]
- Bade, B.C.; Dela-Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin. Chest Med., 2020, 41(1), 1–24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasim, F.; Sabath, B.F.; Eapen, G.A. Lung cancer. Med. Clin. N. Am, 2019, 103(3), 463–473. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrella, F.; Rizzo, S.; Attili, I.; Passaro, A.; Zilli, T.; Martucci, F.; Bonomo, L.; del Grande, F.; Casiraghi, M.; de Marinis, F.; Spaggiari, L. Stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: an overview of treatment options. Curr. Oncol., 2023, 30(3), 3160–3175. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, L.G.; Haines, C.; Perkel, R.; Enck, R.E. Lung cancer: diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician, 2007, 75(1), 56–63. [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Hsu, H.Y. Ling Zhi-8 reduces lung cancer mobility and metastasis through disruption of focal adhesion and induction of MDM2-mediated Slug degradation. Cancer Lett., 2016, 375(2), 340–348. [CrossRef]
- Gill, B.S.; Navgeet, Kumar, S. Ganoderma lucidum targeting lung cancer signaling: A review. Tumour Biol., 2017, 39(6), 1010428317707437. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mao, J.J.; Li, S.Q.; Lin, H. Preliminary efficacy and safety of Reishi privet formula on quality of life among non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Integr. Cancer Ther., 2020, 19, 1534735420944491. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.X.; Li, W.D.; Lin, Z.B.; Duan, X.S.; Li, X.F.; Yang, N.; Lan, T.F.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Yu, M.; Lu, J. Protection against lung cancer patient plasma-induced lymphocyte suppression by Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides. Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2014, 33(2), 289–299. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yuan, R.; Hou, A.; Tan, S.; Liu, X.; Tan, P.; Huang, X.; Wang, J. Ganoderma triterpenoids attenuate tumour angiogenesis in lung cancer tumour-bearing nude mice. Pharm. Biol., 2020, 58(1), 1061–1068. [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, D.; Spring, D.J.; DePinho, R.A. Genetics and biology of prostate cancer. Genes Dev., 2018, 32(17-18), 1105–1140. [CrossRef]
- Schatten H. Brief overview of prostate cancer statistics, grading, diagnosis and treatment strategies. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 2018, 1095, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Zaidman, B.Z.; Wasser, S.P.; Nevo, E.; Mahajna, J. Coprinus comatus and Ganoderma lucidum interfere with androgen receptor function in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Rep., 2008, 35(2), 107–117. [CrossRef]
- Stanley, G.; Harvey, K.; Slivova, V.; Jiang, J.; Sliva, D. Ganoderma lucidum suppresses angiogenesis through the inhibition of secretion of VEGF and TGF-beta1 from prostate cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2005, 330(1), 46–52. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Slivova, V.; Valachovicova, T.; Harvey, K.; Sliva, D. Ganoderma lucidum inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells PC-3. Int. J. Oncol., 2004, 24(5), 1093–1099. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najahi-Missaoui, W.; Arnold, R.D.; Cummings, B.S. Safe nanoparticles: Are we there yet? Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 22(1), 385. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewinski, N.; Colvin, V.; Drezek, R. Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Small, 2008, 4(1), 26–49. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Feng, L. The basic properties of gold nanoparticles and their applications in tumor diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21(7), 2480. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Jin, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Lei, J.; Li, Z. Self-assembled pH-sensitive nanoparticles based on Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide-methotrexate conjugates for the co-delivery of anti-tumor drugs. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2021, 7(8), 3764–3773. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Hu, Y.L.; He, C.X.; Hu, C.J.; Zhou, J.; Tang, G.P.; Gao, J.Q.. Preparation, characterisation and anti-tumour activity of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 2010, 62(1), 139–144. [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansari, M.M.; Dhasarathan, P.; Ranjitsingh, A.J.A.; Al-Humaid, L.A. Ganoderma lucidum inspired silver nanoparticles and its biomedical applications with special reference to drug resistant Escherichia coli isolates from CAUTI. Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 2020, 27(11), 2993–3002. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, T.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, P.; Qiu, T.; Bo, R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, D. Adjuvanticity of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide liposomes on porcine circovirus type-II in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2019, 141, 1158–1164. [CrossRef]
- Constantin, M., Răut, I., Suica-Bunghez, R., Firinca, C., Radu, N., Gurban, A.M., Preda, S., Alexandrescu, E., Doni, M., Jecu, L. Ganoderma lucidum-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity. Materials, 2023, 16(12), 4261. [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Raofie, F.; Karimi, M. Production Ganoderma lucidum extract nanoparticles by expansion of supercritical fluid solution and evaluation of the antioxidant ability. Sci. Rep., 2022, 12(1), 9904. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygün, A.; Özdemir, S.; Gülcan, M.; Cellat, K.; Şen, F. Synthesis and characterization of Reishi mushroom-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for the biochemical applications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2020, 178, 112970. [CrossRef]
- Kou, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, W.; Mei, Y.; Cao, L.; Wei, X.; Xiao, H.; Wu, X. A review of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides: Health benefit, structure-activity relationship, modification, and nanoparticle encapsulation. Int.l J. Bio. Macromol., 2023, 243, 125199. [CrossRef]
- Karwa, A.; Gaikwad, S.; Rai, M.K. Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lingzhi or Reishi medicinal mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum (W. Curt.:Fr.) P. Karst. and their role as antimicrobials and antibiotic activity enhancers. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms, 2011, 13(5), 483–491. [CrossRef]
- Socala, K.; Nieoczym, D.; Grzywnowicz, K.; Stefaniuk, D.; Wlaz, P. Evaluation of anticonvulsant, antidepressant, and anxiolytic-like effects of an aqueous extract from cultured Mycelia of the Lingzhi or Reishi medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum (Higher Basidiomycetes) in mice. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms, 2015, 17(3), 209–218. [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Xuan, S.; Wu, W.; Qu, L. Encapsulation efficiency and controlled release of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide microcapsules by spray drying using different combinations of wall materials. Int. J. Biol Macromol, 2019, 125, 962–969. [CrossRef]
- Vinh, P.N.; Hieu, L.T.; Thu, H.N.; Dong, Q.H.; Thai, H.T. Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles with eco-friendly processes using Ganoderma lucidum extract and evaluation of their theranostic applications. J. Nanomater., 2021, 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, A.; Asila, V.; Boitel-Aullen, G.; Lam, M.; Salmain, M.; Boujday, S. Silver-based plasmonic nanoparticles for and their use in biosensing. Biosensors, 2019, 9(2), 78. [CrossRef]
- Accessed on July 28, 2023 at 12:32pm via: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272509889/figure/fig1/AS:294666592374790@1447265398382/Schematic-illustration-of-the-mycosynthesis-of-silver-nanoparticles-Ag-NPs-using.png.
- Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Polymeric micelles in cancer therapy: State of the art. J. Control. Release, 2021, 332, 127–147. [CrossRef]
- Accessed on August 1, 2023 at 10:02pm via: https://api.naradaclinic.com/images/1592972825480.png.
- Hwang, D.; Ramsey, J.D.; Kabanov, A.V. Polymeric micelles for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: From nanoformulation to clinical approval. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2020, 156, 80–118. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.R.; Yang, M.; Guan, S.H.; Wu, X.H.; Pang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J.; Guo, D.A. Pharmacokinetics of ganoderic acid D and its main metabolite by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fourniols, T.; Labrak, Y.; Préat, V.; Beloqui, A.; des Rieux, A. Surface modification of lipid-based nanoparticles. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(5), 7168–7196. [CrossRef]
- Accessed on August 1, 2023 at 16:50pm via: https://www.exeleadbiopharma.com.
- Hald, A.C.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Lind, M.; Petersson, K.; Simonsen, J.B. The role of lipid components in lipid nanoparticles for vaccines and gene therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2022, 188, 114416. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Marioli, M.; Zhang, K. Analytical characterization of liposomes and other lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2021, 192, 113642. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, I L.; Tsai, C.Y.; Kuo, L.L.; Woung, L.C.; Ku, R.Y.; Cheng, Y.H. PLGA nanoparticles containing Lingzhi extracts rescue corneal epithelial cells from oxidative damage. Exp. Eye Res., 2021, 206, 108539. [CrossRef]
- Accessed on August 3, 2023 at 9:00pm via: https://media.springernature.com/lw685/springer-static/image/chp%3A10.1007%2F978-3-319-99602-8_17/MediaObjects/460157_1_En_17_Fig1_HTML.png.
- Zielińska, A.; Carreiró, F.; Oliveira, A.M.; Neves, A.; Pires, B.; Venkatesh, D.N.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Eder, P.; Silva, A.M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Polymeric nanoparticles: production, characterization, toxicology and ecotoxicology. Molecules, 2020, 25(16), 3731. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accessed on August 3, 2023 at 11:21pm via: https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1021949815000356-gr1.jpg.
- Chang, S.T.; Wasser, S.P. The role of culinary-medicinal mushrooms on human welfare with a pyramid model for human health. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms, 2012, 14(2), 95–134. [CrossRef]
- Sohretoglu, D.; Huang, S. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides as an anti-cancer agent. Anticancer Agents in Med. Chem., 2018, 18(5), 667–674. [CrossRef]
- Unlu, A.; Nayir, E.; Kirca, O.; Ozdogan, M. Ganoderma Lucidum (Reishi mushroom) and cancer. J.B.U.ON, 2016, 21(4), 792–798. [PubMed]
- Cör, A.D.; Knez, Ž.; Knez, M.M. Antioxidant, antibacterial, antitumor, antifungal, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and nevro-protective activity of Ganoderma lucidum: An overview. Front. Pharmacol., 2022, 13, 934982. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Lin, C.S.; Lu, C.C.; Martel, J., Ko; Y.F., Ojcius, D.M.; Tseng, S.F.; Wu, T.R.; Chen, Y.Y.; Young, J.D.; Lai, H.C. Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat. Commun, 2015, 6, 7489. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.F., Ahmad, F.A., Zeyaullah, M., Alsayegh, A.A., Mahmood, S.E., AlShahrani, A.M., Khan, M.S., Shama, E., Hamouda, A., Elbendary, E.Y., Attia, K.A.H.A. (2023). Ganoderma lucidum: Novel Insight into Hepatoprotective Potential with Mechanisms of Action. Nutrients, 15(8), 1874. [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.W.; Tomlinson, B.; Chan, P.; Lam, C.W.K. The beneficial effects of Ganoderma lucidum on cardiovascular and metabolic disease risk. Pharm. Biol., 2021, 59(1), 1161–1171. [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.H.; Ng, T.B.; Chan, H.H.L.; Liu, Q.; Man, G.C.W.; Zhang, C.Z.; Guan, S.; Ng, C.C.W.; Fang, E.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Ye, X.; Rolka, K.; Naude, R.; Zhao, S.; Sha, O.; Li, C.; Xia, L. Mushroom extracts and compounds with suppressive action on breast cancer: evidence from studies using cultured cancer cells, tumor-bearing animals, and clinical trials. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2020, 104(11), 4675–4703. [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zhong, D.; Su, L.; Lin, Z.; Yang, B. Preventive and therapeutic effect of Ganoderma lucidum on kidney injuries and diseases. Adv.Pharmacol., 2020, 87, 257–276. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.F. (2020). Ganoderma lucidum: a rational pharmacological approach to surmount cancer. J. Ethnopharmacol., 260, 113047. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnthima, R.; Khammaung, S.; Sa-Ard, P. (2017). Culture broth of Ganoderma lucidum exhibited antioxidant, antibacterial and α-amylase inhibitory activities. J. Food Sci. Technol., 2017, 54(11), 3724–3730. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).