Submitted:
28 December 2023
Posted:
28 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
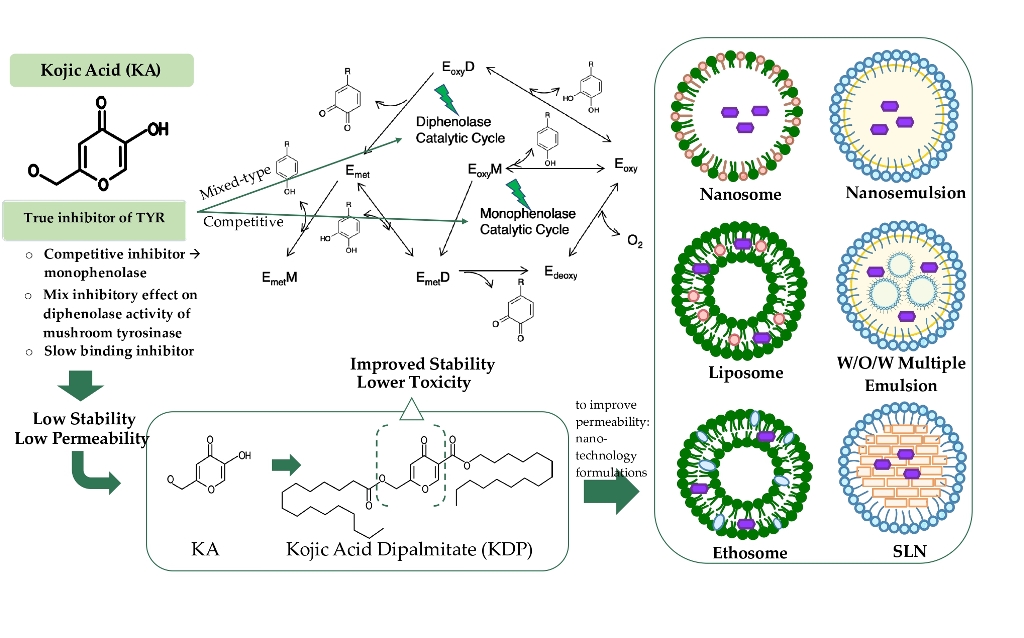
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Sythesis of Kojic Acid Dipalmitate
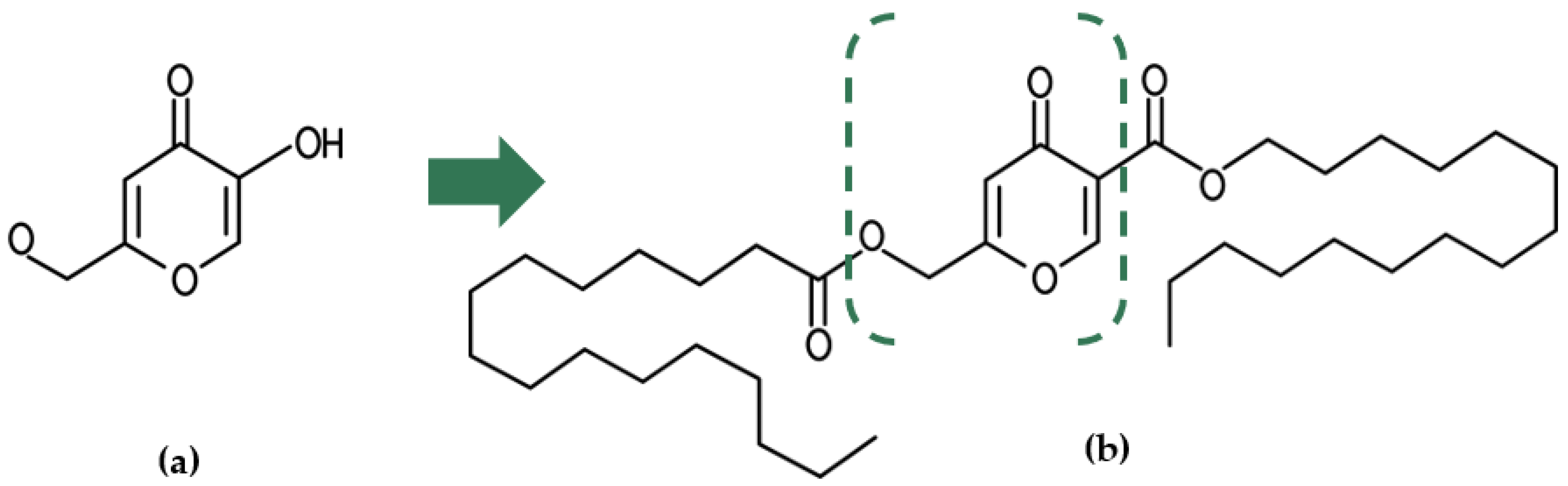
3. Physical and Chemical Propreties of Kojic Acid Dipalmitate
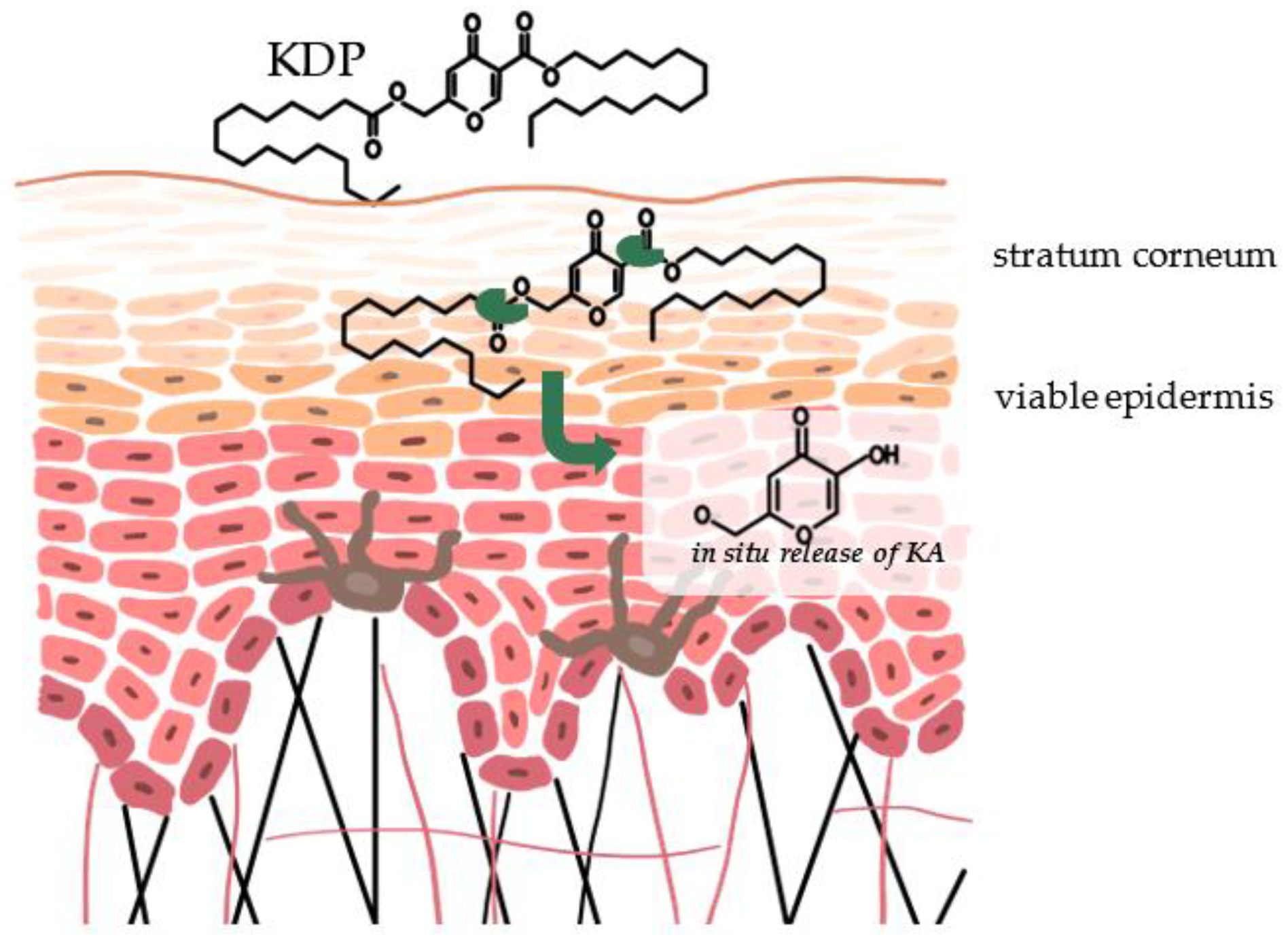
4. Mechanism of Action of Kojic Acid Dipalmitate
5. Cosmetic Application of Kojic Acid Dipalmitate
5.1. Cosmetic Products Containing KDP
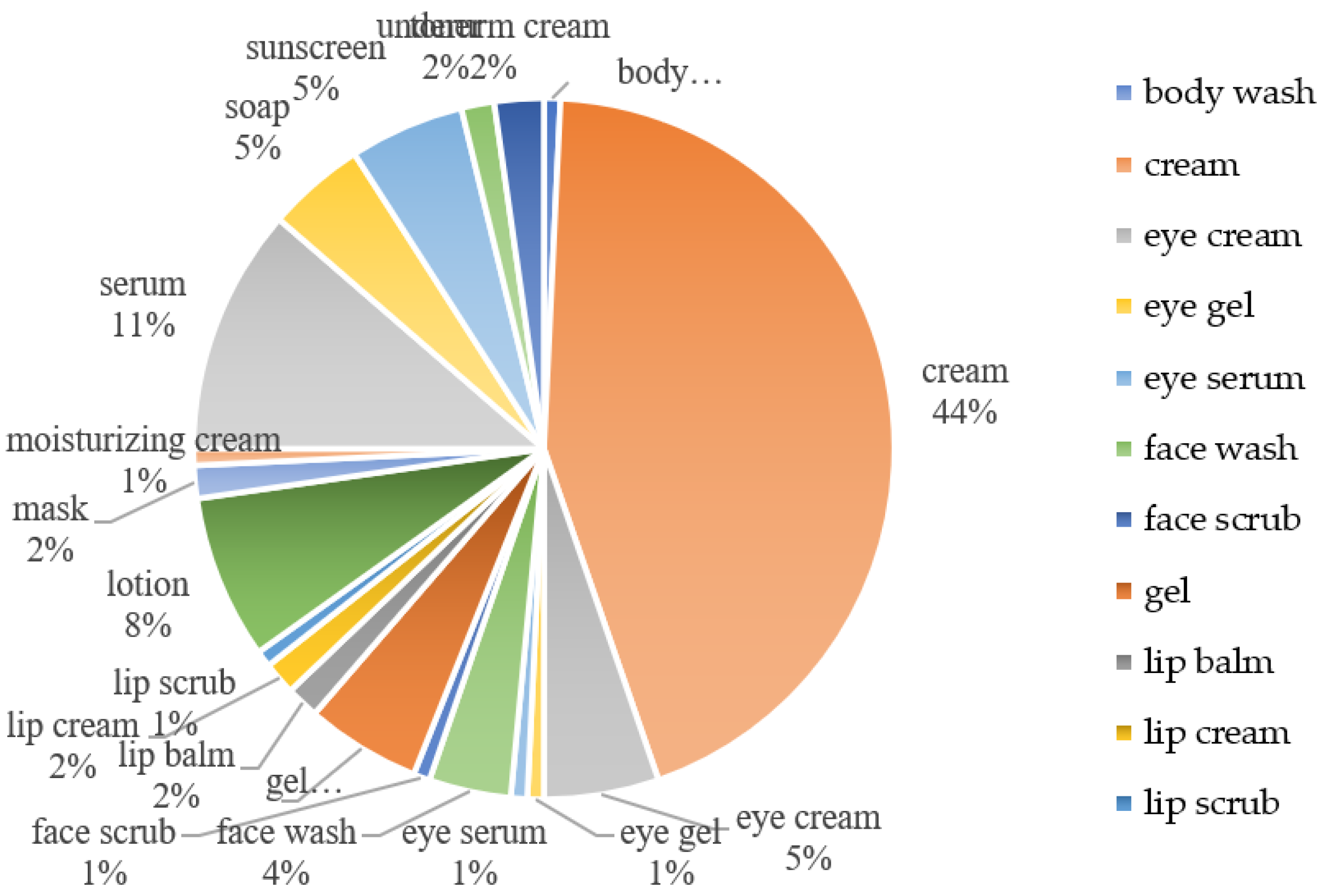
3.3. Patent Products of KDP
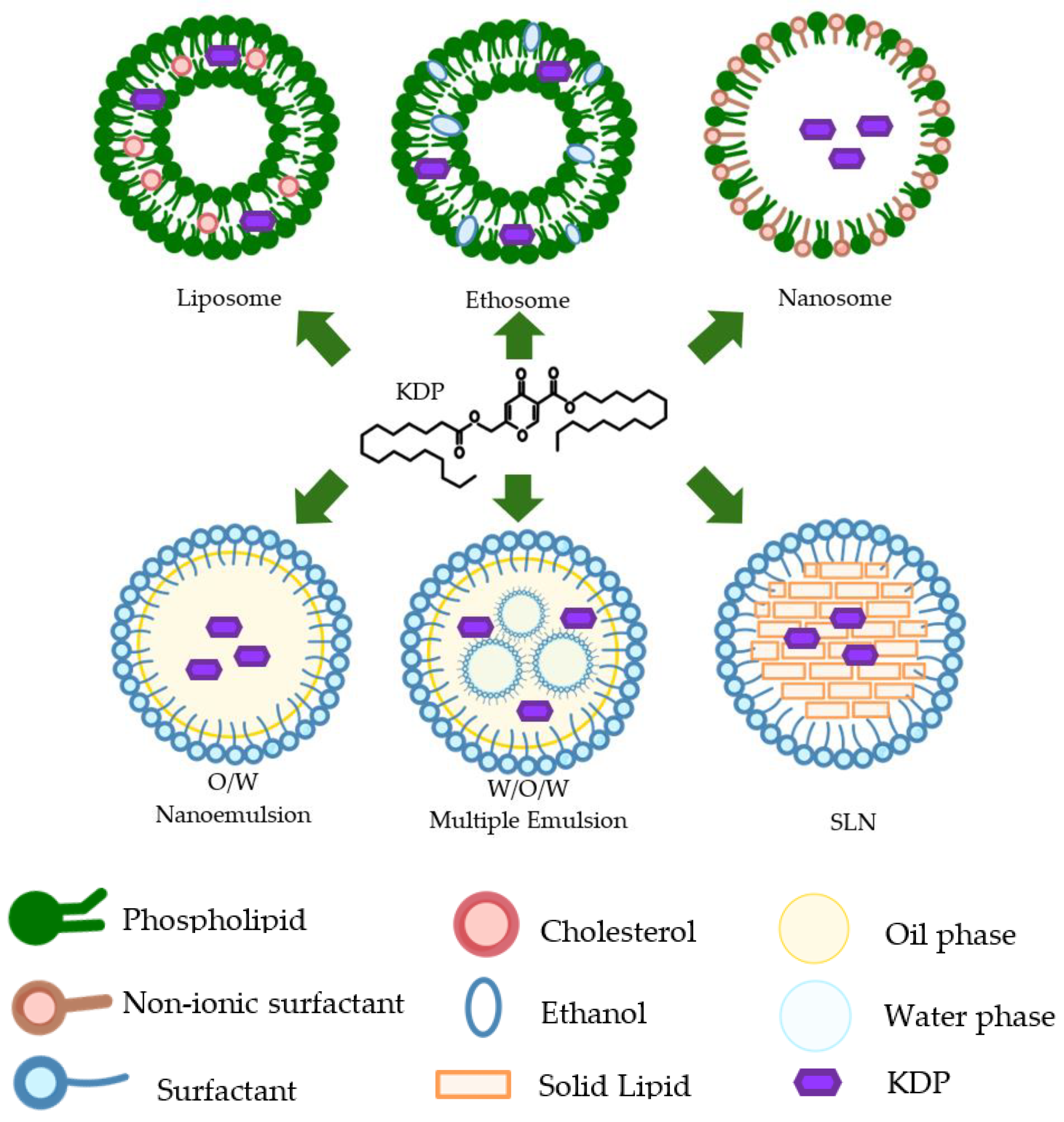
6. Nanotechnology Formulations of Kojic Acid Dipalmitate
| Published in | Preparation of KDP | The research objective | Diameter of particle/droplet | Zeta Potentials | Loading capacity | Results | Refference |
| 2000 | Nanosome | Development of KDP nanosome in mono-vesicle and increase stability | 57-75,7 nm | -24mV | NA | Turbidity was very good transparency compared nanosome with liposome. It formed the monovesicle in the opposite direction to form the multi-lamelar vesicle of the liposome. The stability of nanosomes was very good for 6 months | [108] |
| 2010 | Nanocream | Increased release and permeability through skin in vitro | < 350 nm | NA | NA | nano-creams had shown to produce a higher drug release and permeability through Franz diffusion cells, although there was no significant variation than that in normal cream at P value < 0.05. Nano-creams penetrate faster and the cumulative amount of KDP is higher than in normal creams | [58] |
| 2015 | W/O/W Multiple Emulsions | Increase safety and activity of KDP in vitro$$$$ | 0,056μm-12.487μm$$$$ | NA | N/A | Incorporation of KDP into MEs improved the safety and antioxidant activity of KDP in vitro | [71] |
| 2020 | Liposome | Increasing stability and loading capacity | 80-100 nm;$$$$PDI ≤ 0.2 | -0.5 to -0.6 mV | 0.61% to 28.12 % | Ethosomal gel had a good stability at lower temperature (8, 25°C).$$$$KDP loading capacity increased from 0.61 to 28.12% | [109] |
| 2020 | Solid Lipid Nanoparticle (SLN) | Increase release profile and permeability through skin ex vivo | 70 nm | NA | 47% | The KDP loaded in the SLN presented a slower release profile of KDP in comparison with the formulations loaded with KDP. The KDP loaded into SLN had the highest concentration in the stratum corneum. | [53] |
| 2022 | Ethosomal suspension | Increases stability and skin benefits | 148 nm | −23.4 mV | 90.0008% | Ethosomal gel gave a significant decrease in skin melanin, erythema, and sebum levels while improving in skin hydration level and elasticity during non-invasive in vivo studies. The formulation had good stability at a lower temperature (8, 25°C). | [106] |
| 2023 | Nanoemulsion | Increase permeation, antioxidant and depigmentation efficiency, and lower cytotoxicity | < 130 nm | -10mV | > 95% | The nanoemulsion containing 1 mg/mL KDP exhibited antioxidant and depigmenting activities and allowed the active compound to reach the epidermis without permeating to deeper layers of the skin, showing potential for use in cosmetic formulations for melasma treatment. Such nanoemulsion was safe for fibroblast-like cells (3T3-L1) at concentrations up to 1%. | [110] |
6.1. Nanoemulsion
6.2. Nanocream
6.3. Liposome
6.4. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
6.5. Ethosome
6.6. Nanosome
6.7. Multiple Emulsion
5. Conclusions
References
- G. Casanola-Martin et al., “Tyrosinase Enzyme: 1. An Overview on a Pharmacological Target,” Curr. Top. Med. Chem., vol. 14, no. 12, pp. 1494–1501, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Y. Qu et al., “Catalysis-based specific detection and inhibition of tyrosinase and their application,” J. Pharm. Anal., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 414–425, 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. Matos, A. Paranhos, M. T. Batista, and A. Figueirinha, “Synergistic Effect of DIBOA and Verbascoside from Acanthus mollis Leaf on Tyrosinase Inhibition,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 23, no. 21, 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Pillaiyar, M. Manickam, and V. Namasivayam, “Skin whitening agents: Medicinal chemistry perspective of tyrosinase inhibitors,” J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 403–425, 2017. [CrossRef]
- X. Lai, H. J. Wichers, M. Soler-Lopez, and B. W. Dijkstra, “Structure and Function of Human Tyrosinase and Tyrosinase-Related Proteins,” Chem. - A Eur. J., vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 47–55, 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. V. Ortiz-Ruiz, J. Berna, J. Tudela, R. Varon, and F. Garcia-Canovas, “Action of ellagic acid on the melanin biosynthesis pathway,” J. Dermatol. Sci., vol. 82, no. 2, pp. 115–122, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Dettori et al., “Synthesis and studies of the inhibitory effect of hydroxylated phenylpropanoids and biphenols derivatives on tyrosinase and laccase enzymes,” Molecules, vol. 25, no. 11, pp. 1–21, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Kumari, S. T. G. Thng, N. K. Verma, and H. K. Gautam, “Melanogenesis inhibitors,” Acta Derm. Venereol., vol. 98, no. 10, pp. 924–931, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Gillbro and M. J. Olsson, “The melanogenesis and mechanisms of skin-lightening agents - Existing and new approaches,” Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 210–221, 2011. [CrossRef]
- S. Zolghadri et al., “A comprehensive review on tyrosinase inhibitors,” J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 279–309, 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. Wang and D. N. Hebert, “Tyrosinase maturation through the mammalian secretory pathway: Bringing color to life,” Pigment Cell Res., vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 3–18, 2006. [CrossRef]
- B. Deri et al., “The unravelling of the complex pattern of tyrosinase inhibition,” Sci. Rep., vol. 6, no. June, pp. 1–10, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Mine, H. Mizuguchi, and T. Takayanagi, “Kinetic analyses of two-steps oxidation from L-tyrosine to L-dopaquinone with tyrosinase by capillary electrophoresis/dynamic frontal analysis,” Anal. Biochem., vol. 655, no. April, p. 114856, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. C. Boo, “Human skin lightening efficacy of resveratrol and its analogs: From in vitro studies to cosmetic applications,” Antioxidants, vol. 8, no. 9, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. A. N. D’Mello, G. J. Finlay, B. C. Baguley, and M. E. Askarian-Amiri, “Signaling pathways in melanogenesis,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 1–18, 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Slominski, D. J. Tobin, S. Shibahara, and J. Wortsman, “Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation,” Physiol. Rev., vol. 84, no. 4, pp. 1155–1228, 2004. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Ebanks, R. R. Wickett, and R. E. Boissy, “Mechanisms regulating skin pigmentation: The rise and fall of complexion coloration,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 10, no. 9, pp. 4066–4087, 2009. [CrossRef]
- K. Peltzer, S. Pengpid, and C. James, “The globalization of whitening: Prevalence of skin lighteners (or bleachers) use and its social correlates among university students in 26 countries,” Int. J. Dermatol., vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 165–172, 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. Qamar et al., “Novel 1,3-oxazine-tetrazole hybrids as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors and free radical scavengers: Synthesis, kinetic mechanism, and molecular docking studies,” Chem. Biol. Drug Des., vol. 93, no. 2, pp. 123–131, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Eimpunth, R. Wanitphadeedecha, and W. Manuskiatti, “A focused review on acne-induced and aesthetic procedure-related postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in Asians,” J. Eur. Acad. Dermatology Venereol., vol. 27, no. SUPPL. 1, pp. 7–18, 2013. [CrossRef]
- T. J. Lieu and A. G. Pandya, “Melasma Quality of Life Measures,” Dermatol. Clin., vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 269–280, 2012. [CrossRef]
- T. Z. da S. Marques et al., “Development And Characterization Of A Nanoemulsion Containing Propranolol For Topical Delivery,” Int. J. Nanomedicine, vol. 13, pp. 2827–2837, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Z. D. Draelos, G. Deliencourt-Godefroy, and L. Lopes, “An effective hydroquinone alternative for topical skin lightening,” J. Cosmet. Dermatol., vol. 19, no. 12, pp. 3258–3261, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. O. Owolabi, O. S. Fabiyi, L. A. Adelakin, and M. C. Ekwerike, “Effects of skin lightening cream agents - hydroquinone and kojic acid, on the skin of adult female experimental rats,” Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol., vol. 13, pp. 283–289, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Chandra, J. Levitt, and C. A. Pensabene, “Hydroquinone therapy for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation secondary to acne: Not just prescribable by dermatologists,” Acta Derm. Venereol., vol. 92, no. 3, pp. 232–235, 2012. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Rossi and M. I. Perez, “Treatment of Hyperpigmentation,” Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. North Am., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 313–324, 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Picardo and M. Carrera, “New and Experimental Treatments of Cloasma and Other Hypermelanoses,” Dermatol. Clin., vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 353–362, 2007. [CrossRef]
- N. Smit, J. Vicanova, and S. Pavel, “The hunt for natural skin whitening agents,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 10, no. 12, pp. 5326–5349, 2009. [CrossRef]
- A. Singhal, D. Kumar, and M. Bansal, “SKIN WHITENING- A BRIEF REVIEW,” vol. Pharmatuto, no. February 2013, 2013.
- P. Arora, V. Garg, S. Sonthalia, N. Gokhale, and R. Sarkar, “Melasma update,” Indian Dermatol. Online J., vol. 5, no. 4, p. 426, 2014. [CrossRef]
- P. Hariyono, J. R. Karamoy, and M. Hariono, “Exploration of Indonesian Plants as Skin Lightening against Tyrosinase: A Virtual Screening,” Indones. J. Pharm. Sci. Technol., vol. 1, no. Suppl. 1, No. 2 (2019), pp. 25–32, 2019.
- K. Jurica, I. B. Karačonji, V. Benković, and N. Kopjar, “In vitro assessment of the cytotoxic, DNA damaging, and cytogenetic effects of hydroquinone in human peripheral blood lymphocytes,” Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol., vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 322–335, 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. F. Chang et al., “Study of hydroquinone mediated cytotoxicity and hypopigmentation effects from UVB-irradiated arbutin and deoxyarbutin,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 18, no. 5, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Balaguer, A. Salvador, and A. Chisvert, “A rapid and reliable size-exclusion chromatographic method for determination of kojic dipalmitate in skin-whitening cosmetic products,” Talanta, vol. 75, no. 2, pp. 407–411, 2008. [CrossRef]
- M. Saeedi, M. Eslamifar, and K. Khezri, “Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations,” Biomed. Pharmacother., vol. 110, no. December 2018, pp. 582–593, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. L. Burnett et al., “Final Report of The Safety Assessment of Kojic Acid As Used in Cosmetics,” Int. J. Toxicol., vol. 29, no. 6, 2010. [CrossRef]
- F. Bashir, K. Sultana, M. Khalid, H. Rabia, and H. Khan, “Kojic Acid : A Comprehensive Review Abstract : Keywords : The Applications of Kojic Acid Kojic acid,” Ajahas, vol. 06, no. 01, pp. 13–17, 2021.
- A. D. Sharma, I. Kaur, and M. Farmaha, “Preparation and Characterization of O / W Nanoemulsion with Eucalyptus Essential Oil and Study of In vitro Antibacterial Activity,” Nanomed Res J, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 347–354, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Asadzadeh, H. Sirous, M. Pourfarzam, P. Yaghmaei, and A. Fassihi, “In vitro and in silico studies of the inhibitory effects of some novel kojic acid derivatives on tyrosinase enzyme,” Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 132–144, 2016.
- A. F. B. Lajis, M. Hamid, and A. B. Ariff, “Depigmenting effect of kojic acid esters in hyperpigmented B16F1 melanoma cells,” J. Biomed. Biotechnol., vol. 2012, 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. Schurink, W. J. H. van Berkel, H. J. Wichers, and C. G. Boeriu, “Novel peptides with tyrosinase inhibitory activity,” Peptides, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 485–495, 2007. [CrossRef]
- Y. Kobayashi, H. Kayahara, K. Tadasa, T. Nakamura, and H. Tanaka, “Synthesis of Amino Acid Derivatives of Kojic Acid and their Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity,” Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., vol. 59, no. 9, pp. 1745–1746, 1995. [CrossRef]
- J. Kadokawa, T. Nishikura, R. Muraoka, H. Tagaya, and N. Fukuoka, “Synthesis of kojic acid derivatives containing phenolic hydroxy groups,” Synth. Commun., vol. 33, no. 7, pp. 1081–1086, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Y. S. Lee, J. H. Park, M. H. Kim, S. H. Seo, and H. J. Kim, “Synthesis of tyrosinase inhibitory kojic acid derivative,” Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim)., vol. 339, no. 3, pp. 111–114, 2006. [CrossRef]
- K. M. Lewis, N. Robkin, K. Gaska, and L. C. Njoki, “Investigating Motivations for Women’s Skin Bleaching in Tanzania,” Psychol. Women Q., vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 29–37, 2010. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Noh, S. Y. Kwak, H. S. Seo, J. H. Seo, B. G. Kim, and Y. S. Lee, “Kojic acid-amino acid conjugates as tyrosinase inhibitors,” Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett., vol. 19, no. 19, pp. 5586–5589, 2009. [CrossRef]
- H. S. Rho, S. M. Ahn, D. S. Yoo, M. K. Kim, D. H. Cho, and J. Y. Cho, “Kojyl thioether derivatives having both tyrosinase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory properties,” Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett., vol. 20, no. 22, pp. 6569–6571, 2010. [CrossRef]
- I. Michael and F. Wempe, “( 12 ) United States Patent ( 10 ) Patent No .:,” vol. 2, no. 12, 2012.
- H. A. M. Ammar, S. M. Ezzat, and A. M. Houseny, “Improved production of kojic acid by mutagenesis of Aspergillus flavus HAk1 and Aspergillus oryzae HAk2 and their potential antioxidant activity,” 3 Biotech, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 1–13, 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Ahn et al., “Inhibitory activity of novel kojic acid derivative containing trolox moiety on melanogenesis,” Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett., vol. 21, no. 24, pp. 7466–7469, 2011. [CrossRef]
- R. Sarkar, P. Arora, and Kv. Garg, “Cosmeceuticals for hyperpigmentation: What is available?,” J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg., vol. 6, no. 1, p. 4, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Tazesh, E. Tamizi, M. S. Shadbad, N. Mostaghimi, and F. Monajjemzadeh, “Comparative Stability of Two Anti-hyperpigmentation Agents: Kojic Acid as a Natural Metabolite and Its Di-Palmitate Ester, Under Oxidative Stress; Application to Pharmaceutical Formulation Design,” Adv. Pharm. Bull., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 329–335, 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. Mohammadi, R. Giti, M. N. Meibodi, A. M. Ranjbar, A. R. Bazooband, and V. Ramezani, “Preparation and evaluation of kojic acid dipalmitate solid lipid nanoparticles,” J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol., vol. 61, p. 102183, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Zilles, F. L. dos Santos, I. C. Kulkamp-Guerreiro, and R. V. Contri, “Biological activities and safety data of kojic acid and its derivatives: A review,” Exp. Dermatol., vol. 31, no. 10, pp. 1500–1521, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Nakagawa, K. Kawai, and K. Kawai, “Contact allergy to kojic acid in skin care products,” Contact Dermatitis, vol. 32, no. 1. pp. 9–13, 1995. [CrossRef]
- E. Serra-Baldrich, M. J. Tribó, and J. G. Camarasa, “Allergic contact dermatitis from kojic acid,” Contact Dermatitis, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 86–87, 1998. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Ashari, R. Mohamad, A. Ariff, M. Basri, and A. B. Salleh, “Optimization of enzymatic synthesis of palm-based kojic acid ester using response surface methodology,” J. Oleo Sci., vol. 58, no. 10, pp. 503–510, 2009. [CrossRef]
- S. Al-Edresi and S. Baie, “In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation of a photo-protective kojic dipalmitate loaded into nano-creams,” Asian J. Pharm. Sci., vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 251–265, 2010.
- M. DellaGreca et al., “The issue of misidentification of kojic acid with flufuran in aspergillus flavus,” Molecules, vol. 24, no. 9, pp. 1–11, 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. Karkeszov, “Regioselective Enzymatic Synthesis of Kojic Acid Monoesters of acid without acid possibly present incorrect product structures . ample , for lipase from Chromobacterium viscosum [ 2,” pp. 1–12, 2021.
- K. J. Liu and J. F. Shaw, “Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of kojic acid esters in organic solvents,” JAOCS, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., vol. 75, no. 11, pp. 1507–1511, 1998. [CrossRef]
- A. F. B. Lajis et al., “Enzymatic synthesis of kojic acid esters and their potential industrial applications,” Chem. Pap., vol. 67, no. 6, pp. 573–585, 2013. [CrossRef]
- T. Kobayashi, S. Adachi, K. Nakanishi, and R. Matsuno, “Semi-continuous production of lauroyl kojic acid through lipase-catalyzed condensation in acetonitrile,” Biochem. Eng. J., vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 85–89, 2001. [CrossRef]
- N. H. Khamaruddin et al., “Enzymatic synthesis and characterization of palm-based kojic acid ester,” J. Oil Palm Res., vol. 20, no. JUNE, pp. 461–469, 2008.
- S. Kumar, R. P. Qla, S. Pahujani, R. Kaushal, S. S. Kanwar, and R. Gupta, “Thermostability and esterification of a polyethylene-immobilized lipase from Bacillus coagulons BTS-3,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., vol. 102, no. 4, pp. 3986–3993, 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Zong, H. Wu, and Z. yang Tan, “Substantially enhancing enzymatic regioselective acylation of 1-β-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine with vinyl caprylate by using a co-solvent mixture of hexane and pyridine,” Chem. Eng. J., vol. 144, no. 1, pp. 75–78, 2008. [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information, “Kojic dipalmitate,” “PubChem Compound Summary for CID 71587292, Kojic dipalmitate,” 2021. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Kojic-dipalmitate (accessed Nov. 28, 2023).
- C. S. Chen, K. J. Liu, Y. H. Lou, and C. J. Shieh, “Optimisation of kojic acid monolaurate synthesis with lipase PS from Pseudomonas cepacia,” J. Sci. Food Agric., vol. 82, no. 6, pp. 601–605, 2002. [CrossRef]
- S. Madhogaria and I. Ahmed, “Leucoderma After Use Of A Skin-Lightening Cream Containing kojic dipalmitate, Liquorice root extract and Mitracarpus scaber Extract,” Clin. Exp. Dermatol., vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 103–105, 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. Bährle-Rapp, “Kojic Dipalmitate,” in Springer Lexikon Kosmetik und Körperpflege, 2007, pp. 300–300.
- M. L. Gonçalez, D. G. Marcussi, G. M. F. Calixto, M. A. Corrêa, and M. Chorilli, “Structural characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity of kojic dipalmitate loaded W/O/W multiple emulsions intended for skin disorders,” Biomed Res. Int., vol. 2015, 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. Rosfarizan, M. S. Mohamed, N. Suhaili, M. M. Salleh, and A. B. Ariff, “Kojic acid: Applications and development of fermentation process for production,” Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 24–37, 2010.
- “Chang, 2009.pdf.” .
- G. Battaini, E. Monzani, L. Casella, L. Santagostini, and R. Pagliarin, “Inhibition of the catecholase activity of biomimetic dinuclear copper complexes by kojic acid,” J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 262–268, 2000. [CrossRef]
- K. D. Karlin, Y. Gultneh, T. Nicholson, and J. Zubieta, “Catecholate Coordination to Copper: Structural Characterization of a Tetrachloro-o-catecholate-Bridged Dicopper(II) Complex as a Model for Intermediates in Copper-Catalyzed Oxidation of Catechols,” Inorg. Chem., vol. 24, no. 23, pp. 3725–3727, 1985. [CrossRef]
- T. Plenge, R. Dillinger, L. Santagostini, L. Casella, and F. Tuczek, “Catecholate Adducts of Binuclear Copper Complexes Modelling the Type 3 Copper Active Site - Spectroscopic Characterization and Relevance to the Tyrosinase Reaction,” Zeitschrift fur Anorg. und Allg. Chemie, vol. 629, no. 12–13, pp. 2258–2265, 2003. [CrossRef]
- J. Ackermann, F. Meyer, E. Kaifer, and H. Pritzkow, “Tuning the activity of catechol oxidase model complexes by geometric changes of the dicopper core,” Chem. - A Eur. J., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 247–258, 2002. [CrossRef]
- L. Bubacco, E. Vijgenboom, C. Gobin, A. W. J. W. Tepper, J. Salgado, and G. W. Canters, “Kinetic and paramagnetic NMR investigations of the inhibition of Streptomyces antibioticus tyrosinase,” J. Mol. Catal. - B Enzym., vol. 8, no. 1–3, pp. 27–35, 2000. [CrossRef]
- L. Bubacco, R. Spinazze, S. della Longa, and M. Benfatto, “X-ray absorption analysis of the active site of Streptomyces antibioticus Tyrosinase upon binding of transition state analogue inhibitors,” Arch. Biochem. Biophys., vol. 465, no. 2, pp. 320–327, 2007. [CrossRef]
- C. Bochot et al., “Probing kojic acid binding to tyrosinase enzyme: Insights from a model complex and QM/MM calculations,” Chem. Commun., vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 308–310, 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. Whittemore and R. Neis, “Kojic Dipalmitate Skin Whitening Cosmetic Composition,” United States Pat., no. 19, pp. 1–6, 1998.
- Y. Chusiri et al., “Non-Genotoxic Mode Of Action And Possible Threshold For Hepatocarcinogenicity Of Kojic Acid In F344 Rats,” Food Chem. Toxicol., vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 471–476, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Incidecoder, “Decode ingredients lists like a pro,” 2023. https://incidecoder.com/ (accessed Nov. 28, 2023).
- K. Amouzegar, G. St. Amant, and S. Harrison, “United States Patent ( 19 ) 11 Patent Number : BATTERY-49,” 2000.
- 张婉萍朱海洋刘晓慧, “Nanometer solid lipid carrier covering kojic acid dipalmitate and preparing method.”.
- 蔡惠民周莉, “Method for quantitatively analyzing kojic dipalmitate.”.
- Y. Khan et al., “Nanoparticles , and Their Applications in Various Fields of Nanotechnology : A Review,” Catalysts, vol. 12, no. 11, p. 1386, 2022.
- Z. A. A. Aziz et al., “Role of Nanotechnology for Design and Development of Cosmeceutical: Application in Makeup and Skin Care,” Front. Chem., vol. 7, no. November, pp. 1–15, 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. B. Sutradhar and M. L. Amin, “Nanotechnology in Cancer Drug Delivery and Selective Targeting,” ISRN Nanotechnol., vol. 2014, pp. 1–12, 2014. [CrossRef]
- E. B. Souto et al., “Nanomaterials for skin delivery of cosmeceuticals and pharmaceuticals,” Appl. Sci., vol. 10, no. 5, 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Oberdörster, E. Oberdörster, and J. Oberdörster, “Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles,” Environ. Health Perspect., vol. 113, no. 7, pp. 823–839, 2005. [CrossRef]
- S. R. Yearla and K. Padmasree, “Preparation and characterisation of lignin nanoparticles: evaluation of their potential as antioxidants and UV protectants,” J. Exp. Nanosci., vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 289–302, 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. L. Slomberg, R. Catalano, V. Bartolomei, and J. Labille, “Release and fate of nanoparticulate TiO2 UV filters from sunscreen: Effects of particle coating and formulation type,” Environ. Pollut., vol. 271, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Liu and W. X. Wang, “The protective roles of TiO2 nanoparticles against UV-B toxicity in Daphnia magna,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 593–594, pp. 47–53, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Bartoszewska, E. Adamska, A. Kowalska, and B. Grobelna, “Novelty Cosmetic Filters Based on Nanomaterials Composed of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles,” Molecules, vol. 28, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. Dragicevic and H. I. Maibach, “Percutaneous penetration enhancers chemical methods in penetration enhancement: Nanocarriers,” Percutaneous Penetration Enhanc. Chem. Methods Penetration Enhanc. Nanocarriers, pp. 1–384, 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Radmard, M. Saeedi, K. Morteza-Semnani, S. M. H. Hashemi, and A. Nokhodchi, “An eco-friendly and green formulation in lipid nanotechnology for delivery of a hydrophilic agent to the skin in the treatment and management of hyperpigmentation complaints: Arbutin niosome (Arbusome),” Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces, vol. 201, no. January, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. L. Gonçalez, M. A. Corrêa, and M. Chorilli, “Skin delivery of kojic acid-loaded nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of skin aging,” Biomed Res. Int., vol. 2013, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Hoeller, A. Sperger, and C. Valenta, “Lecithin based nanoemulsions: A comparative study of the influence of non-ionic surfactants and the cationic phytosphingosine on physicochemical behaviour and skin permeation,” Int. J. Pharm., vol. 370, no. 1–2, pp. 181–186, 2009. [CrossRef]
- S. N. A. Syed Azhar, S. E. Ashari, S. Ahmad, and N. Salim, “In vitro kinetic release study, antimicrobial activity and in vivo toxicity profile of a kojic acid ester-based nanoemulsion for topical application,” RSC Adv., vol. 10, no. 71, pp. 43894–43903, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Kaul, N. Gulati, D. Verma, S. Mukherjee, and U. Nagaich, “Role of Nanotechnology in Cosmeceuticals: A Review of Recent Advances,” J. Pharm., vol. 2018, pp. 1–19, 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. E. Effiong et al., “Nanotechnology in Cosmetics: Basics, Current Trends and Safety Concerns—A Review,” Adv. Nanoparticles, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 1–22, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Lohani, A. Verma, H. Joshi, N. Yadav, and N. Karki, “Nanotechnology-Based Cosmeceuticals,” vol. 2014, 2018.
- S. K. Dubey, A. Dey, G. Singhvi, M. M. Pandey, V. Singh, and P. Kesharwani, “Emerging trends of nanotechnology in advanced cosmetics,” Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces, vol. 214, no. March, p. 112440, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. C. Santos et al., “Nanotechnology for the development of new cosmetic formulations,” Expert Opin. Drug Deliv., vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 313–330, 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. Tanveer, H. M. S. Khan, and N. Akhtar, “Whitening effect of kojic acid dipalmitate loaded nanosized ethosomal gel for the treatment of hyperpigmentation: In vitro and in vivo characterization,” J. Cosmet. Dermatol., vol. 21, no. 12, pp. 6850–6862, 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Aulton, M., & Taylor, Aulton’s Pharmaceutics: The Design and Manufacture of Medicines (6th ed). 2022.
- I.-Y. Kim, G.-H. Je, and J.-D. Lee, “The Manufacturing Mechanism of Nano-some of Capsulation of Kojic Acid and Kojic Dipalmitate with Hydrogenated Lecithin and Co-emulsifiers,” J. Korean Oil Chem. Soc, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 248–256, 2000.
- S. S. Aledresi, A. J. Alshaibani, and A. N. Abood, “Enhancing the loading capacity of kojic acid dipalmitate in liposomes,” Lat. Am. J. Pharm., vol. 39, no. 7, pp. 1333–1339, 2020.
- J. C. Zilles, L. P. Duarte, T. C. Ruaro, A. R. Zimmer, I. C. Kulkamp-Guerreiro, and R. V. Contri, “Nanoemulsion Containing Kojic Dipalmitate and Rosehip Oil: A Promising Formulation to Treat Melasma,” Pharmaceutics, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 1–16, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Al-Edresi and S. Baie, “Formulation and stability of whitening VCO-in-water nano-cream,” Int. J. Pharm., vol. 373, no. 1–2, pp. 174–178, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Y. Singh et al., “Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery,” J. Control. Release, vol. 252, pp. 28–49, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Sarkar, V. Garg, S. Bansal, S. Sethi, and C. Gupta, “Comparative evaluation of efficacy and tolerability of glycolic acid, salicylic Mandelic acid, and Phytic acid combination peels in Melasma,” Dermatologic Surg., vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 384–391, 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Zainol, T. S. Ming, and Y. Darwis, “Development and characterization of cinnamon leaf oil nanocream for topical application,” Indian J. Pharm. Sci., vol. 77, no. 4, pp. 422–433, 2015. [CrossRef]
- K. Charoenkul and D. Phromyothin, “Development and characterization of nano-cream preparation containing natural extract using nanoemulsion techniques,” Mater. Today Proc., vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 6105–6110, 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. H. Arbain, N. Salim, H. R. F. Masoumi, T. W. Wong, M. Basri, and M. B. Abdul Rahman, “In vitro evaluation of the inhalable quercetin loaded nanoemulsion for pulmonary delivery,” Drug Deliv. Transl. Res., vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 497–507, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Suyal, “Nanoemulsion: A Novel Approach in Various Pharmaceutical Applications,” J. Pharm. Sci. Biosci., vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 153–157, 2017.
- A. Qadir, M. D. Faiyazuddin, M. D. Talib Hussain, T. M. Alshammari, and F. Shakeel, “Critical steps and energetics involved in a successful development of a stable nanoemulsion,” J. Mol. Liq., vol. 214, pp. 7–18, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Abdulkarim et al., “Stability studies of nano-cream containing piroxicam.,” Int. J. Drug Deliv., vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 333–339, 2010. [CrossRef]
- G. Urbina-villalba and E. Cruz-Barrios, “Influence of Creaming and Ripening on the Aggregation Rate of Non-Ionic Dodecane-in-Water Nanoemulsions,” Rev. del CEIF, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 22–29, 2014.
- S. Bajpai et al., “Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based Cancer Treatment: A Review,” ACS Appl. Nano Mater., vol. 4, no. 7, pp. 6441–6470, 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. T. Hsieh, J. S. Chang, and T. H. Chou, “The impact of the surfactant type on physicochemical properties, encapsulation, and in vitro biocompatibility of coconut oil nanoemulsions,” J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., vol. 137, p. 104217, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. O. Eloy, M. Claro de Souza, R. Petrilli, J. P. A. Barcellos, R. J. Lee, and J. M. Marchetti, “Liposomes as carriers of hydrophilic small molecule drugs: Strategies to enhance encapsulation and delivery,” Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces, vol. 123, pp. 345–363, 2014, . [CrossRef]
- A. U. Andar, R. R. Hood, W. N. Vreeland, D. L. Devoe, and P. W. Swaan, “Microfluidic preparation of liposomes to determine particle size influence on cellular uptake mechanisms,” Pharm. Res., vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 401–413, 2014, . [CrossRef]
- S. G. Antimisiaris et al., “Overcoming barriers by local drug delivery with liposomes,” Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., vol. 174, pp. 53–86, 2021, . [CrossRef]
- T. Garg and A. K. Goyal, “Liposomes: Targeted and Controlled Delivery System,” Drug Deliv. Lett., 4, 62-71, vol. 4, pp. 62–71, 2014.
- E. Nogueira, A. C. Gomes, A. Preto, and A. Cavaco-Paulo, “Design of liposomal formulations for cell targeting,” Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces, vol. 136, pp. 514–526, 2015, . [CrossRef]
- N. Mignet, J. Seguin, and G. G. Chabot, “Bioavailability of polyphenol liposomes: A challenge ahead,” Pharmaceutics, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 457–471, 2013, . [CrossRef]
- M. C. Teixeira, C. Carbone, and E. B. Souto, “Beyond liposomes: Recent advances on lipid based nanostructures for poorly soluble/poorly permeable drug delivery,” Prog. Lipid Res., vol. 68, pp. 1–11, 2017, . [CrossRef]
- C. Has and P. Sunthar, “A comprehensive review on recent preparation techniques of liposomes,” J. Liposome Res., vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 336–365, 2020, . [CrossRef]
- 131. S. Pande, “Liposomes for drug delivery: review of vesicular composition, factors affecting drug release and drug loading in liposomes,” Artif. Cells, Nanomedicine Biotechnol., vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 428–440, 2023, . [CrossRef]
- N. Mendoza-Muñoz, Z. Urbán-Morlán, G. Leyva-Gómez, M. De La Luz Zambrano-Zaragoza, E. Piñón-Segundo, and D. Quintanar-Guerrero, “Solid lipid nanoparticles: An approach to improve oral drug delivery,” J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., vol. 24, pp. 509–532, 2021, . [CrossRef]
- V. Mishra et al., “Solid lipid nanoparticles: Emerging colloidal nano drug delivery systems,” Pharmaceutics, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 1–21, 2018, . [CrossRef]
- M. Qushawy and A. Nasr, “Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) as nano drug delivery carriers: Preparation, characterization and application,” Int. J. Appl. Pharm., vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1–9, 2020, . [CrossRef]
- R. Paliwal, S. R. Paliwal, R. Kenwat, B. Das Kurmi, and M. K. Sahu, “Solid lipid nanoparticles: a review on recent perspectives and patents,” Expert Opin. Ther. Pat., vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 179–194, 2020, . [CrossRef]
- S. Kotta, H. M. Aldawsari, S. M. Badr-Eldin, A. B. Nair, and K. YT, “Progress in Polymeric Micelles for Drug Delivery Applications,” Pharmaceutics, vol. 14, no. 8, pp. 1–32, 2022, . [CrossRef]
- S. Shaker, A. Gardouh, and M. Ghorab, “Factors affecting liposomes particle size prepared by ethanol injection method,” Res. Pharm. Sci., vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 346–352, 2017, . [CrossRef]
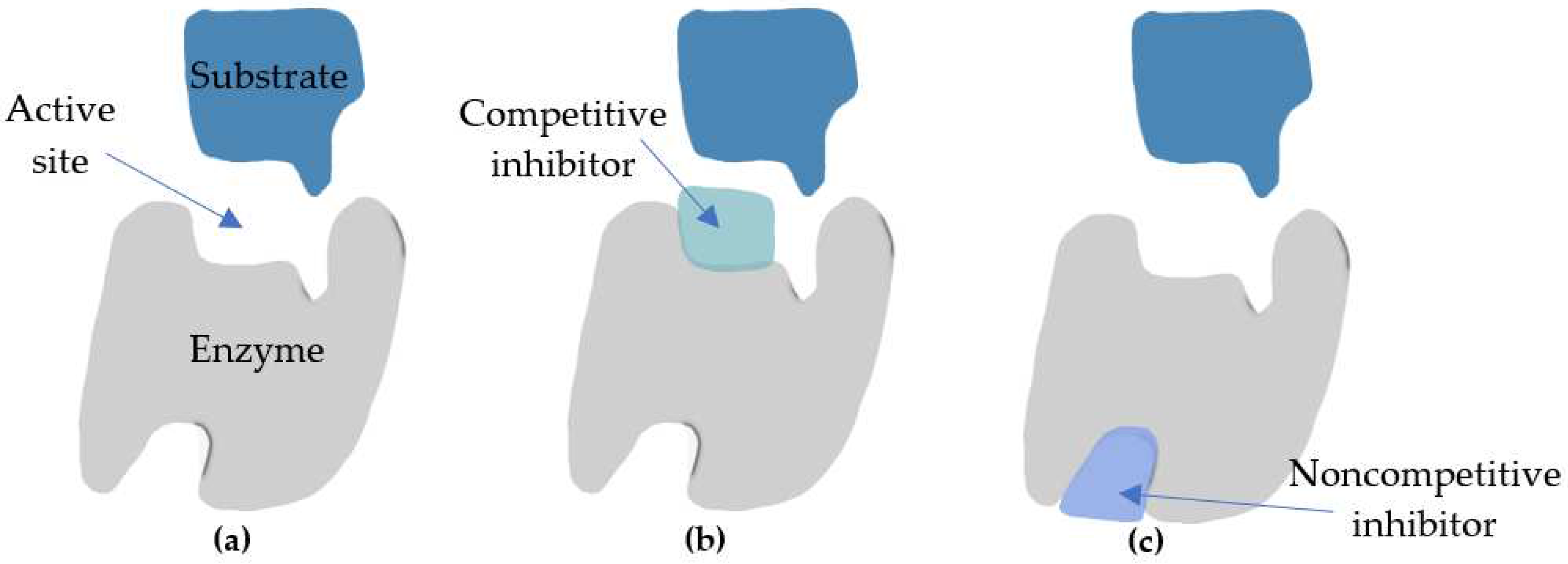
| Pantent’s holder | Field of Invention | Year | No. of patent | Refference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jerry Whittemore Robert Neis | The present invention relates to a skin-whitening cosmetic compositions and in particular to such a composition that is anhydrous and incorporates kojic dipalmitate. | 1998-2018 | US5824327A | [84] |
| Shanghai Institute of Technology | A kind of nano-solid lipid carrier and preparation method of coated kojic acid acid dipalmitate | 2014-2034 | CN104116643A | [85] |
| Shanghai Jahwa United Co Ltd | The present invention relates to a kind of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analytical approach, be specifically related to method with the HPLC quantitatively analyzing kojic dipalmitate. | 2002-2022 | CN1188700C | [86] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





