1. Introduction
Owing to its inherent strength, durability, and attractive fiber structure, teak wood is widely used for various applications. Commercial teak wood usually comes from mature trees, which can be expensive to produce as a finished product as well as a raw resource. The challenge of supply and demand imbalance cannot be overlooked. Therefore, the development of fast-growing teak varieties has emerged as a potential solution to address this issue [
1,
2,
3].
Several studies have shown that the fast-growing teak can produce satisfactory quality in shorter rotations. However, it is still lower than conventional teak wood, especially in density and hardness [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Fast-growing teak is more susceptible to external disturbances such as weather and attacks from wood-decaying organisms. In many field cases, cavity portions inside the wood are often found during harvesting, which impacts its market value. To avoid losses due to poor quality, it is necessary to make efforts to evaluate the tree's condition to ensure that it is in a suitable state for felling. Tree health monitoring is the process of regularly monitoring and evaluating trees' condition. Monitoring aims to identify tree problems quickly so that appropriate treatment can be taken to prevent further damage. Several studies evaluating tree conditions have led to nondestructive methods due to their practicality, eliminating the need to fall the trees [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. The principle of nondestructive methods is to build a model to predict a parameter's value based on the observed variables' characteristics.
Some studies revealed the existence of electrical properties potentials in trees that could be related to physiological processes in trees [
15,
16]. The tree electrical properties approach is also used to determine the quality of trees for sawlogs and breeding programs [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Quality prediction through the electrical potential approach in wood has been done in several studies on small wood samples [
21,
22,
23]. Wood has dielectric properties, especially capacitance, which correlate highly with its hardness and specific gravity [
21]. Understanding the electrical properties of wood and the electrical potential in trees is still an evolving research area and requires further research for a better understanding. A study about predicting wood quality through dielectric properties at low frequency has been conducted and has shown promising results for predicting MC at wood chips [
22]. Yet, the prediction model for trees can be challenging due to the fresh conditions with moisture content above 100%. Some studies have shown that fresh wood affects the signal inaccurately in model prediction [
24,
25,
26].
Dielectric spectroscopy (DS), also known as impedance spectroscopy, is a widely employed technique for examining the response of a sample when subjected to an electric field of varying frequency. It enables the characterization of a material's dielectric properties concerning frequency. DS is commonly used to investigate the molecular dynamics and relaxation processes of materials, such as polymers, liquids, glasses, and biological systems. By analyzing the dielectric response over a range of frequencies, valuable information about the molecular structure, dynamics, and interactions within the material can be obtained. The measurement setup typically involves applying an alternating electric field to the material under study and measuring the resulting current or charge response. Using appropriate mathematical models, the complex permittivity is then calculated from the measured impedance or admittance. DS can be applied across an extensive frequency range, from very low frequencies in the millihertz (mHz) range to extremely high frequencies in the terahertz range (THz) [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31]. Overall, dielectric spectroscopy is a powerful tool for understanding the electrical behavior of materials and has broad applications in both fundamental research and practical applications.
In NDT evaluation, the data analysis and modeling method to predict wood quality are important in determining the model's accuracy. Preprocessing data is necessary to avoid electrical system noises and normalize the data that carry important information [
32]. The modeling approach that is commonly used is a regression [
21,
22,
23]. The development of machine learning (ML)-based regression models is increasingly being explored [
33,
34,
35]. ML models can deal with complex datasets encompassing nonlinearity or missing data.
The main of this study was to analyze the dielectric characteristics of a fast-growing teak standing tree using DS method at multiple frequencies (ranges 250 kHz – 60 MHz) and to determine the relationships between dielectric characteristics and the physical and anatomical properties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site, Tree Selection, and Sampling
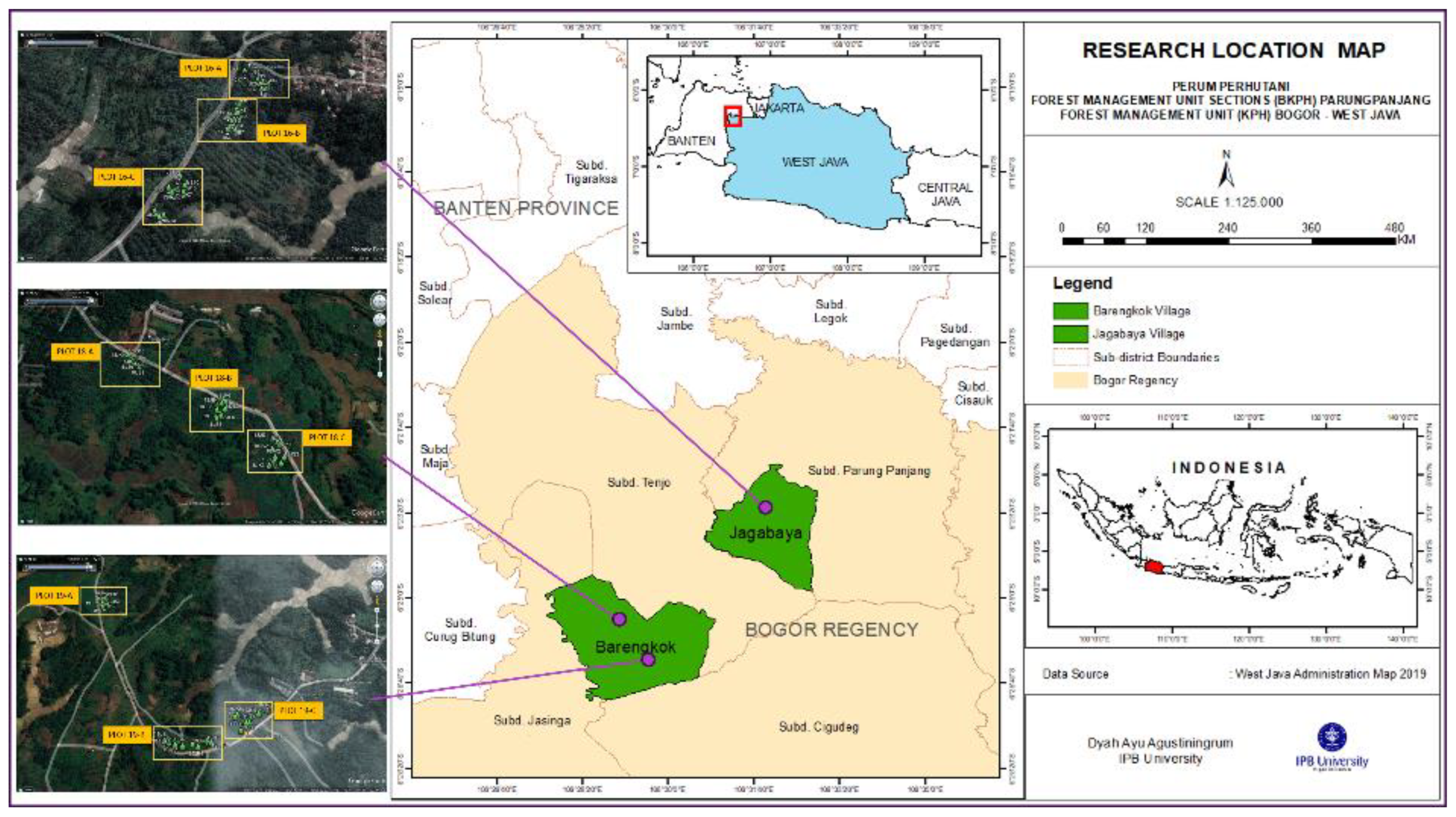
This study observed fast-growing standing teak trees cultivated at the state-owned company of plantation forest, namely Perhutani KPH Bogor, BKPH Parungpanjang, in West Java, Indonesia. Trees were selected from three different ages, i.e., 4-, 5- and 7-year-old, from three different plots for each age. Information related to location, planting year, and planting plots are shown in
Table 1 and
Figure 1. A Total of 90 trees were chosen, which were taken out from 30 trees from each age.
2.2. Field measurement
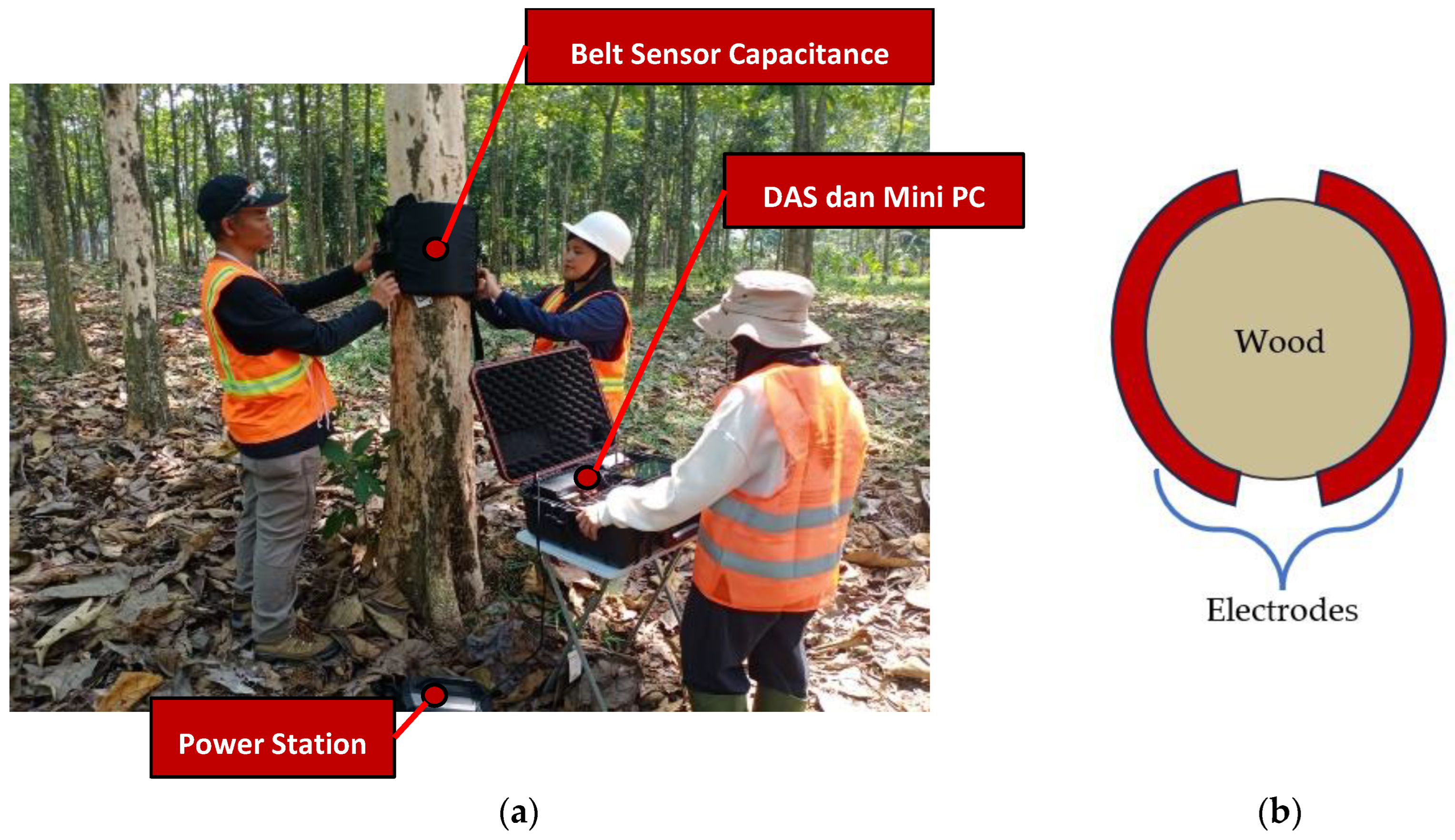
The main data on electrical capacitance value was collected using a capacitance measurement system for small wood samples with various moisture content [
22]. The working principle of this device involves using the DS method by emitting multi-frequency static electricity. This study's frequency range is 250 kHz – 60 MHz. The tool built-in includes a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) and other accessories for the display monitor, including a portable battery. The sensor used is designed like a belt tied tightly to a tree trunk and equipped with a buckle to lock the position of the sensor so that it does not shift easily. (
Figure 3a). The sensor consists of transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx) electrodes made of copper foil, covered with a ground electrode to minimize noise. The two electrodes on the sensor are installed facing each other and cover the perimeter of the tree trunk (
Figure 3b). The maximum diameter of the tree measured is 30 cm.
Figure 2.
Set-up testing of wood capacitance measurement system: (a) placement of the sensor and testing processing, (b) sensor covering the tree trunk.
Figure 2.
Set-up testing of wood capacitance measurement system: (a) placement of the sensor and testing processing, (b) sensor covering the tree trunk.
The tree was measured by switching on the device and setting the system. The measurement software sets the frequency ranges at 250 kHz – 60 MHz. Frequency selection in this range is based on tool capacity and preliminary research. Testing begins with the calibration process carried out on the measurement port. After that, the connection cable of the computer was connected to the capacitive sensor, and the sensor was installed on the tree trunk at the diameter breast height (DBH). It should be noted that the sensor installation must ensure that the two electrodes face with precision and are attached to the tree securely so as not to shift because it will affect the signal read. After the sensor has been installed properly, the electrical waves are generated through the control system, which will be forwarded by the Tx electrode, through the bark and log media, and then received by the Rx electrode. The spectrum of the captured signal is displayed on the monitor display as raw data.
2.4. Physical and Anatomical Properties Observation
To evaluate physical and anatomical properties, the core sample was collected using increment borer Ø 0.5 cm along bark until the tree pith. The core sample then stored into straw to prevent any damage during storage and prevent the moisture loss and to maintain the actual moisture. The physical properties observed were moisture content (MC), green wood density (GD), and specific gravity (SG).
Moisture content testing was carried out using the gravimetric method based on the initial weight and oven dry weight of the sample at a temperature of 103 ± 2 °C until a consistent mass was achieved after referring to [
36] with calculations based on equation (1).
Meanwhile, GD and SG are determined using the displacement method. The displacement method that uses water as a fluid is effective when applied to green materials because of minimal water absorption by wood [
37]. GD and SG are calculated using equations (2) and (3).
The anatomical structure observation was conducted on sectioned specimens prepared from the core sample. Wood samples were softened in a mixture of water and glycerol (1:1) and then heated in the microwave gradually. The samples were then sliced in 18 μm thickness using a sliding microtome for cross, radial, and tangential sections. The sections were stained with 2.5% safranin solution, dehydrated with graded alcohol, soaked with xylene and toluene to remove the dehydrating agent, then mounted on the glass slide with Entellan. The sample of maceration was prepared by making a small stick from each sample code and then put into a test tube that contains hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and acetic acid glacial (CH3COOH) in the ratio of 1:1 (v/v), heated on the water bath.
Anatomical features were evaluated according to the International Association of Wood Anatomists (IAWA) list for hardwood species [
38] using a Digital Microscope Olympus DP22. The microscopic features include the dimensions of fiber length (FL), fiber diameter (FD), lumen diameter (LD), and fiber wall thickness (FWT). Measurements were also made for vessel length (VL) and vessel diameter (VD). At each sample, 30 measurements were conducted randomly for each microscopic feature.
2.5. Data Analysis
The raw imaginary data collected from the capacitance measurement system were analyzed to obtain the real data value. Analysis was performed using the Python programming language and the sci-kit-learn package. The imaginary data from the prototype capacitance monitoring system is still raw data, so it needs to be processed to obtain electrical values such as impedance, resistance, and capacitance. This process is mentioned as preprocessing data. There are many methods to preprocess raw data to obtain the right data that brings important information without erasing another. This preprocessing data involved several steps data extracting, outlier detection, outlier removement, filtering clean data, data scaler, and data transformation.
Statistical analysis was carried out to develop correlations between variables were analyzed using Spearman’s correlation, while the predictive relationship model was processed using multivariate regression. This process involved filtering and regression analysis to develop the prediction models [
32,
34].
3. Results
3.1. Dielectric Characteristics of Fast-Growing Teak
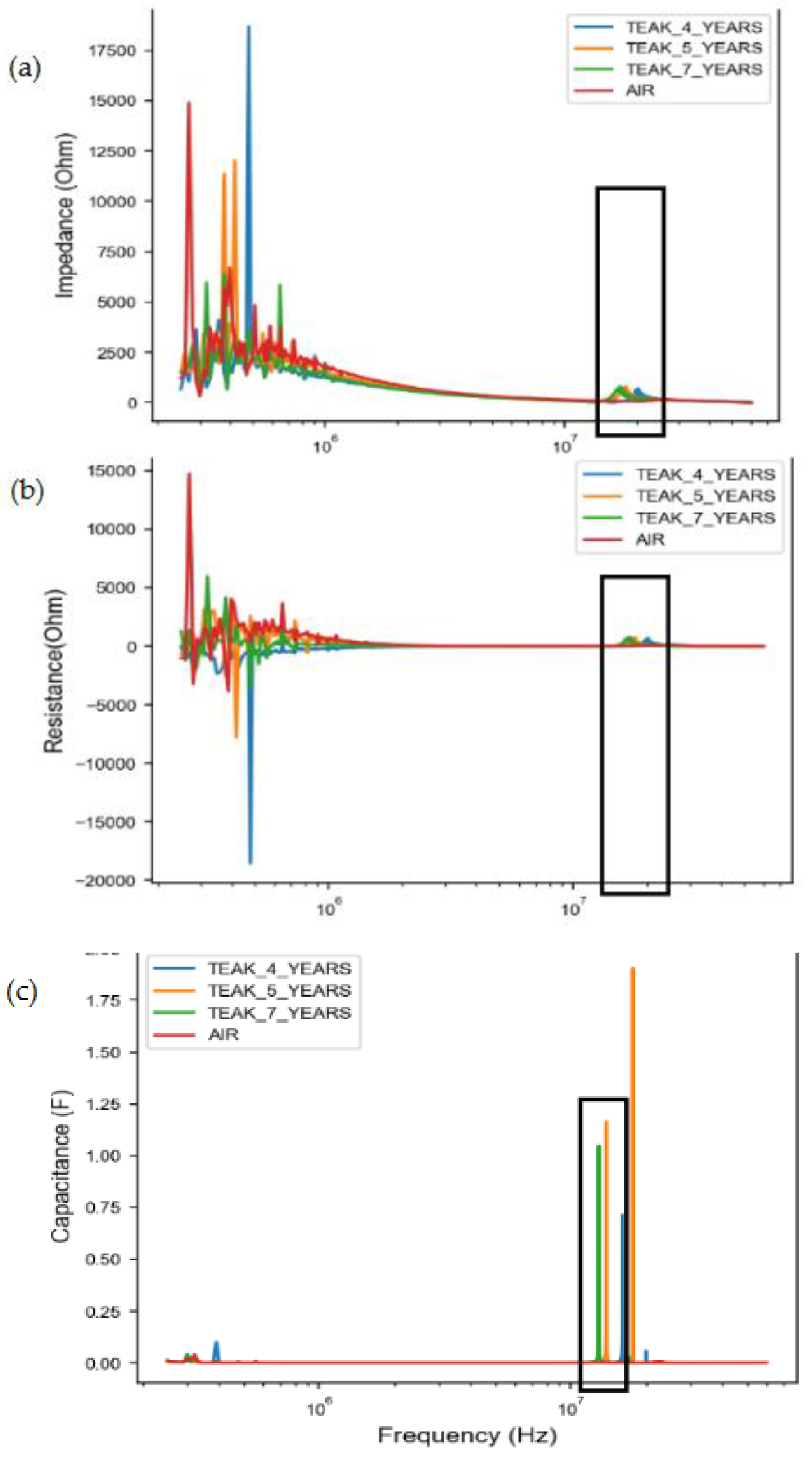
The measurement results obtained using the capacitance measurement system on fast-growing standing teak tree were still in raw data form. Subsequently, data extraction was required to determine the real values of impedance, resistance, and capacitance within the frequency range of 250 kHz - 60 MHz. The results of extraction process were visualized into graphics that showing the distribution of each dielectric value along frequencies. The graphics can be seen in
Figure 3.
In
Figure 6a and 6b, the distribution of dielectric values for impedance and resistance exhibits a decreasing trend as the frequency of emitted static electricity increases within the observed frequency range. According to previous research [
30], at nearly all temperature levels, it is observed that the dielectric loss diminishes with increasing frequency. Nevertheless, in the high-frequency range (>1 MHz), the dielectric loss curves reach a saturation point. The low-frequency region exhibits significant energy loss, which can be attributed to dipolar polarization, space charge, and polarization associated with rotation-direction that emerges in this particular frequency range.
The capacitance value exhibited a notable increase within the frequency range of 15 to 17 MHz, whereas at other frequencies, the capacitance value approached zero. However, it should be noted that the data at this stage is in its raw form, including outliers and missing values resulting from measurement errors that may be influenced by environmental factors, sensors, or the measurement system itself [
29,
31]. The subsequent step involves identifying and addressing outliers and missing data, thereby retaining the intact data that holds crucial information regarding the material's polarization response to the electric field.
Figure 3.
Distribution of dielectric value at frequency ranges 250 kHz – 60 MHz: (a) Impedance, (b) Resistance, (c) Capacitance.
Figure 3.
Distribution of dielectric value at frequency ranges 250 kHz – 60 MHz: (a) Impedance, (b) Resistance, (c) Capacitance.
The study conducted a wide range of frequencies to explore the optimal dielectric frequency that can differentiate wood mass from air based on impedance, resistance, and capacitance properties. The dielectric value spectra of a standing tree and air are expected to exhibit different shapes due to their distinct permittivity. Permittivity refers to the material's influence on the electric field in response to an electric charge. Air has lower permittivity compared to solid materials like wood, especially fresh tree wood with high water content, as water has a very high permittivity [
40]. Therefore, a spectrum analysis is necessary to identify distinct peaks that represent the characteristics of teak wood.
The graphical representation of raw data extraction revealed significant differences between the dielectric values of wood and air at specific frequencies. Furthermore, variations in frequency peaks were observed among different tree ages. Specifically, the dielectric values of 4-year-old teak trees exhibited the highest frequency peaks, followed by 5-year-old teak trees, and the lowest frequency peaks were observed in 7-year-old teak trees.
In
Figure 3, the optimal frequency range is identified by a black-outlined box. The peaks in the graph revealed distinctive characteristics for different tree ages. Specifically, a 4-year-old teak tree exhibits peak values of Z and R at a frequency of 23 MHz, and a peak value of C at 20 MHz. For a 5-year-old teak tree, the characteristic peaks for Z and R were observed at a frequency of 21 MHz, while the peak value of C is at 19 MHz. In comparison, a 7-year-old teak tree shows peak values of Z, R and C at a frequency of 18 MHz. These results indicate that the electrical properties of trees can be differentiated based on their age, with older trees displaying lower peak frequencies. However, further research is required to validate these findings.
Table 2 provides information on the optimal peak frequency characteristics for each tree age.
Table 2.
The characteristics of the dielectric value at each tree age identified based on the frequency that contains the peak.
Table 2.
The characteristics of the dielectric value at each tree age identified based on the frequency that contains the peak.
| Tree Age |
Frequency containing peak |
| Z |
R |
C |
| 4 years |
23 MHz |
23 MHz |
20 MHz |
| 5 years |
21 MHz |
21 MHz |
19 MHz |
| 7 years |
18 MHz |
18 MHz |
18 MHz |
The dielectric frequencies mentioned in the
Table 2 were considered to indicate the properties of wood in fast-growing standing teak trees. Accordingly, these variables will be utilized as predictors in developing a model for estimating the physical and anatomical properties.
3.2. Physical and Anatomical Properties
In the construction of a predictive model to determine wood quality, the inclusion of data derived from destructive testing of the observed wood is deemed essential. Destructive testing data is necessary to build a more reliable and dependable predictive model. Destructive testing data provides a set of data that has not been seen by the model during the training process. By using this data, we can obtain a more objective estimate of how well our model will perform on new data that has not been seen be-fore. Evaluation on the destructive testing data provides a more accurate insight into the actual predictive capabilities of the model. The results of destructive testing are shown at
Table 3 and
Table 4.
Table 2.
Information of tree age and mean data of DBH and physical properties analysis from the core sample.
Table 2.
Information of tree age and mean data of DBH and physical properties analysis from the core sample.
| Tree Age |
DBH (cm) |
MC (%) |
GD (gr/cm3) |
SG |
| 4 years |
12.463 |
132.908a
|
1.078a
|
0.465a
|
| 5 years |
13.953 |
133.881a
|
1.084a
|
0.465 a
|
| 7 years |
21.317 |
138.360a
|
1.134a
|
0.479a
|
The results of statistical analysis on the core samples physical properties revealed no significant differences in MC, GD, and SG among different tree ages. This indicates that MC, GD, and SG remain relatively consistent regardless of the tree's age. However, there was an overall increase in MC, GD, and SG values as the tree age advanced. Notably, 7-year-old teak trees exhibited the highest GD value. This occurrence can be attributed to the close relationship between density and hardwood growth rate. Density tends to increase with a higher growth rate, as a larger portion of mature wood is formed over time, leading to increased density [
37,
39]. Both MC and GD values increase with increasing tree age, while SG only demonstrated an increase in 7-year-old trees. It is possible that the minimal differences in growth rates between 4 and 5-year-old teak trees contribute to the limited disparity observed in their properties.
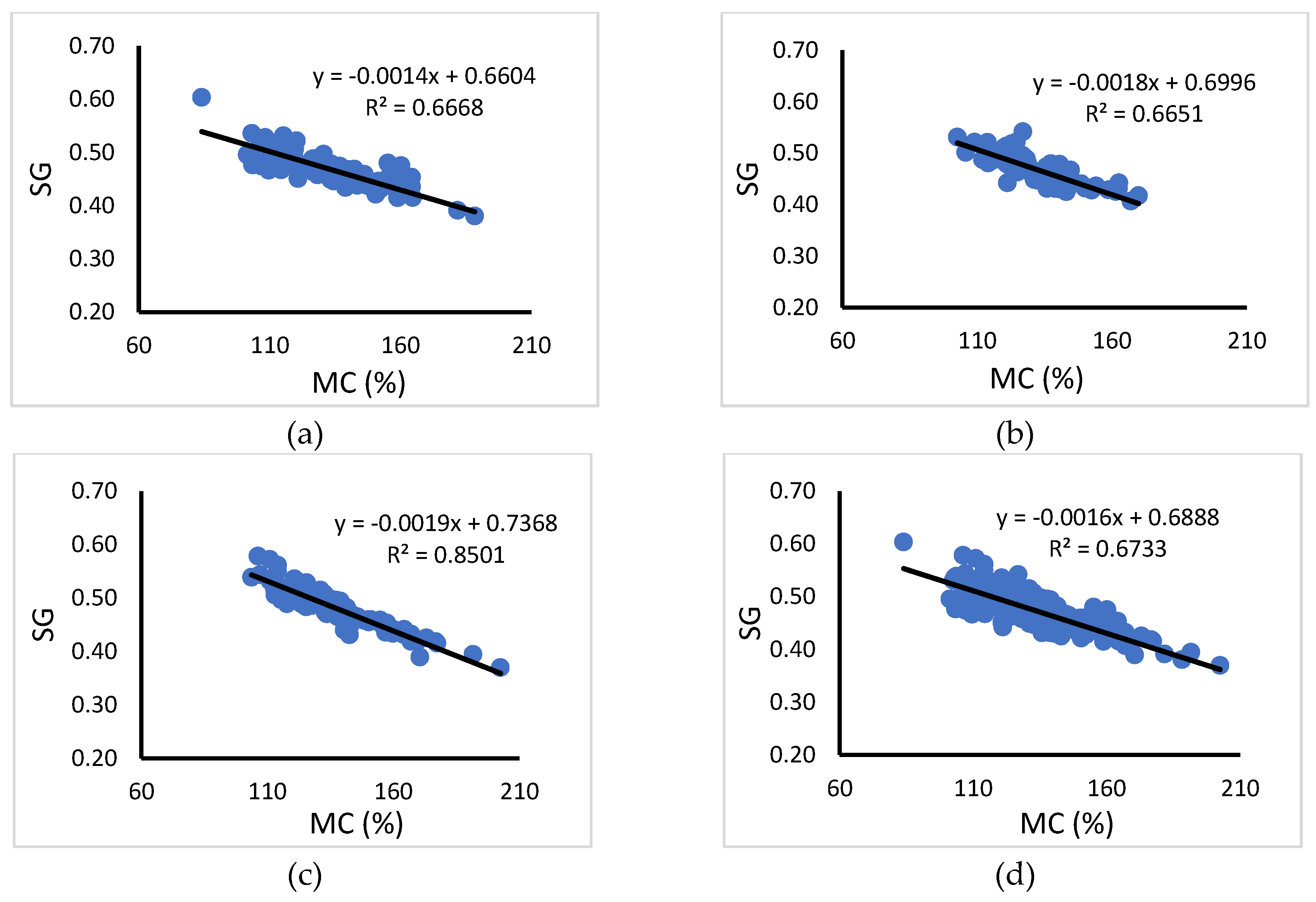
Figure 4.
Relationship between SG and MC: (a) Teak 4-years, (b) Teak 5-years, (c) Teak 7-years, (d) Total teak at all ages.
Figure 4.
Relationship between SG and MC: (a) Teak 4-years, (b) Teak 5-years, (c) Teak 7-years, (d) Total teak at all ages.
Figure 4 shows the results of correlation analysis between MC and SG, where the correlation that occurs was negative (-) with R
2 = 0.67 which mean the higher the MC, the lower the GD. The negative correlation between MC and SG in wood is primarily due to the fact that as moisture content increases, the overall density of the wood decreases. Moisture content represents the amount of water present in the wood, while specific gravity measures the density of the wood relative to the density of water. When wood has a higher moisture content, it means that a larger proportion of its weight is made up of water. Since water has a lower density than the solid wood material, the overall density of the wood decreases as moisture content increases. As a result, the specific gravity of the wood decreases. Conversely, when moisture content decreases, the water within it evaporates, causing the volume of the wood to shrink while the mass remains relatively constant. As a result, the density of the wood increases. This is because water has a lower density compared to the wood fibers themselves. Therefore, as the moisture content of the wood decreases, its density increases [
16,
41].
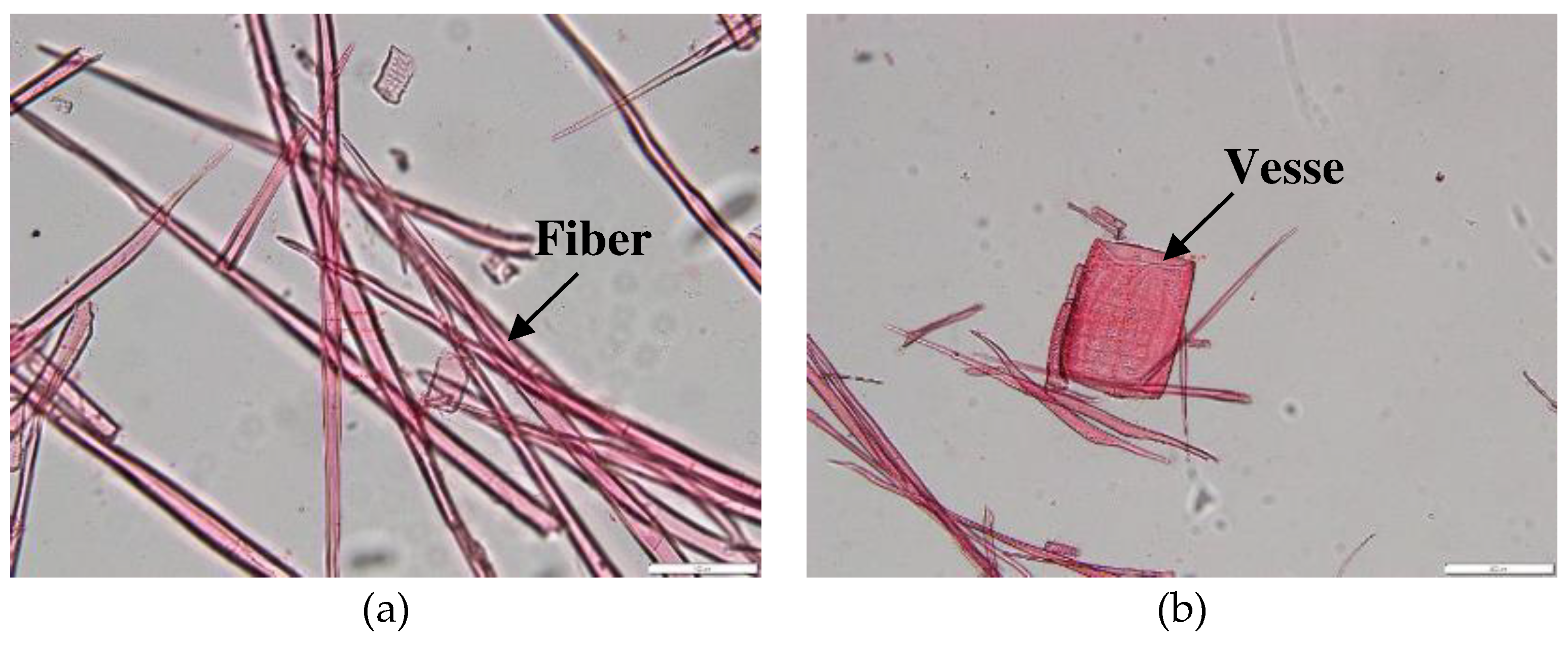
Anatomical properties analysis was conducted to obtain microscopic dimensional characteristics of the wood at each tree age. Dimensional measurements were performed on sectioned and macerated samples as shown in
Figure 5. These measurements were carried out to determine the characteristics of the tree's anatomical structure and to assess whether there was a correlation with the tree's dielectric values. The average measurement results are presented in
Table 3.
Figure 5.
Microscopic features measurement method at maceration sample: (a) fiber; (b) vessel.
Figure 5.
Microscopic features measurement method at maceration sample: (a) fiber; (b) vessel.
According to the anatomical data analysis, there were found that FL, LD, and FWT, were significantly different among each tree ages. As presented in
Table 3, the FL value tends to increase with the tree's age, along with the FWT. Conversely, LD tends to become narrower or smaller. This reduction in lumen diameter can be attributed to the thickening of wood fiber walls during tree growth [
39]. This observation is supported by the increased FWT with tree age. Other anatomical structures did not exhibit significant differences based on tree age. However, it was noted that FD tends to decrease, while VL and VD increase. Microscopic images of the cross, radial, and tangential sections of fast-growing teak wood can be found in
Figure 6.
Table 3.
Mean data of anatomical properties dimension measurements.
Table 3.
Mean data of anatomical properties dimension measurements.
| Tree Age |
FL |
FD |
LD |
FWT |
VL |
VD |
| 4 years |
1,329.38a |
24.69a |
11.49a |
5.41a |
287.12a |
161.22a |
| 5 years |
1,270.24ab |
24.00a |
12.52a |
5.93b |
289.27a |
178.54a |
| 7 years |
1,483.18b |
23.16a |
11.14b |
6.04b |
291.05a |
168.89a |
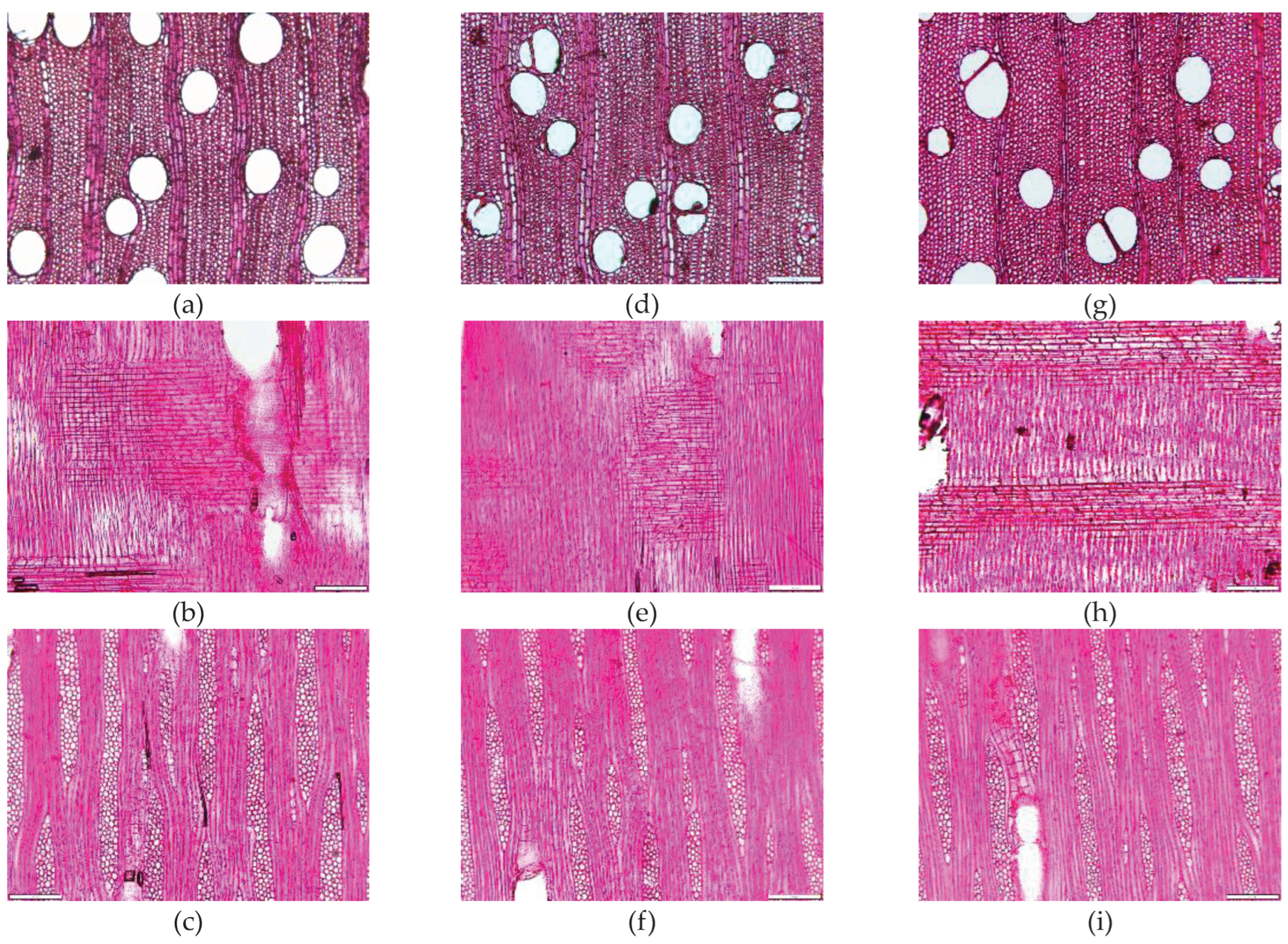
Figure 6.
Microscopic sections (magnify 20x) of fast-growing teak core samples, each consisting of cross-section, radial, and tangential sections in teak 4-years for (a), (b), (c), teak 5-years for (d), (e), (f), and teak 7-years for (g), (h), (c).
Figure 6.
Microscopic sections (magnify 20x) of fast-growing teak core samples, each consisting of cross-section, radial, and tangential sections in teak 4-years for (a), (b), (c), teak 5-years for (d), (e), (f), and teak 7-years for (g), (h), (c).
Figure 6 illustrates a magnified microscopic image of sectioned fast-growing teak wood, taken from a core sample. The images were captured at a 20x magnification level, with a scale of 200µm. Analyzing the microscopic images in the cross-section revealed that the lumen diameter of the 7-year-old teak appears smaller, while the fiber walls appear thicker compared to teak of 4 and 5 years of age. Additionally, examining the radial plane demonstrates that the ray parenchyma of the 7-year-old wood is longer in comparison to the other samples.
The observed smaller lumen diameter of the 7-year-old teak compared to the younger samples can be attributed to the natural process of wood maturation and growth. As trees age, their wood undergoes structural changes and becomes denser. In the case of teak, which is known for its high-density characteristics, the growth rings become more distinct with age [
2,
3,
39].
3.3. Regression Model Development
Modeling was conducted on Z, R, and C at frequencies mentioned on the
Table 2 as independent variables to estimate dependent variables namely MC, GD, SG, FL, FD, LD, FWT, VD, and VL. Since MC is very sensitive acts as the main physical characteristic of standing trees, it was also included as an independent variable. The modeling was performed using the multivariate regression method. The resulting model is presented in
Table 4.
Table 4.
Model prediction for each dependent variable.
Table 4.
Model prediction for each dependent variable.
| Variable |
Model |
R |
R2
|
Adj. R2
|
| GD |
GD= 0.997 + 0.001 MC + 0.021 Z23M – 0.044 C20M
|
0.403 |
0.124 |
0.115 |
| SG |
SG= 0.696 – 0.002 MC – 0.06 Z21M + 0.010 Z23M – 0.006 R23M – 0.019 C20M
|
0.826 |
0.680 |
0.676 |
| FL |
FL= 1220.419 + 0.419 MC – 56.750 Z21M + 128.039 R18M – 80.542 C18M – 0.019 C19M |
0.157 |
0.025 |
0.006 |
| FD |
FD= 27.021 – 0.027 MC + 1.752 Z23M – 1.197 R21M – 1.064 C18M – 1.095 C19M
|
0.163 |
0.023 |
0.005 |
| LD |
LD= 12.214 – 0.013 MC + 1.154 Z18M – 1.493 R21M + 2.663 R23M + 1.156 C19M
|
0.178 |
0.032 |
0.015 |
| FWT |
FWT= 7.019 – 0.007 MC – 0.564 Z18M + 0.744 Z21M + 1.071 R18M – 1.408 C18M – 0.957 C19M
|
0,209 |
0.044 |
0.022 |
| VD |
VD= 139.843 + 37.449 MC + 37.768 Z21M – 55.786 Z23M + 55.505 R21M + 44.834 R23M
|
0.217 |
0.047 |
0.029 |
| VL |
VL= 337.448 – 0.290 MC – 53.424 Z18M + 54.630 C18M + 22.411 C19M – 34.574 C20M
|
0.175 |
0.031 |
0.012 |
Based on the regression model developed using the frequency variables Z, R, C, and MC, it was known that the variables exhibit a strong relationship with SG with coefficient regression R = 0.826. Additionally, it is observed that the variable moderately related with GD with R = 0.403. On the other hand, the variables did not exhibit a satisfactory relationship with the anatomical properties.
In creating a multivariate linear regression model, there are several alternative models with different complexities. However, the model chosen is the model with the highest Adjusted R-squared. In interpreting regression results, R-squared is often used to assess how well a regression model fits the observed data as a whole, while adjusted R-squared is more useful when comparing different regression models with different numbers of independent variables. Adjusted R-squared provides a fairer assessment of model performance by taking into account the complexity of the model and the number of samples used. In addition, a better adjusted R-squared value indicates a lower standard error of the estimation.
4. Discussion
Dialectical spectroscopy (DS) analyzes the frequency-dependent behavior of materials in the frequency domain [
9]. Polarization is the relation between molecular properties and its charges when subjected to the influence of an electric field [
27]. The main polarization processes from the higher frequency process up to the lowest frequency process are: atomic or electronic polarization, ionic polarization, dipole or orientation polarization, and space charge polarization [
28]. At low frequencies, the direction of the electric field is allowed by the free rotation of the electric dipole of the water molecules. A form of energy storage is presented by this type of polarization. Simultaneously, positive and negative ions of dissolved salts move in accordance with the electric field. Thus, the energy loss will be the result of such an electric current. The water molecules will not be able to keep up with the variations in the electric field direction when the frequency rises. This is considered the main reason behind the decrease in the electric field energy storage and the increase in the energy losses. Water molecules do not respond to the electric field at higher frequencies [
26].
This literature explains why in the frequency range that emitted to standing teak trees, there was no significant response from the material is seen at high frequencies (
Figure 3), unlike at low frequencies where the distribution that interprets the response of the material is clearly recognized. Most hygroscopic materials, including wood, contain water, which is the dominant factor in influencing the dielectric properties of a material. Apart from that, dielectric properties are also influenced by several factors such as the physical properties of the material (density, material structure), the frequency used, temperature, and chemical composition [
42]. If the water content of a material is very high, the dielectric will be predominantly influenced by water because its permittivity is higher than other chemical components (in the case of wood material it is the extractive substance). Especially, standing tree wood where the water content is very high, up to more than 100% (saturated) [
43].
The theories may also explain why at difference age of trees, the dielectric properties have different characteristics, especially the frequency that contain the peak value. As shown at
Table 3, MC of the fast-growing standing teak trees was increasing as the tree age advanced. Consequently, the dielectric peak also affected to lower frequencies. Further study is required under various conditions and sample variations to examine the impact of water content on the dielectric frequency of standing trees.
However, the dielectric values as in the
Table 2 were used as variables to estimate the physical and anatomical properties of fast-growing standing teak trees, instead of using dielectric at low frequency. The absence of a distinct peak difference between wood and air materials at low frequencies, as illustrated in
Figure 3, explains this decision. Frequencies >18 MHz were considered optimal as they can effectively distinguish between wood and air dielectric materials.
5. Conclusions
Based on the conducted research, it is known that there are differences in the characteristics of dielectric, physical, and anatomical properties in fast-growing teak trees at various ages. The physical and anatomical properties are influenced by the tree's growth rate. Meanwhile, the varying dielectric properties can be attributed to internal factors such as MC (moisture content), density, and extractive substances, as well as external factors like environmental temperature.
The regression model constructed using the frequency variables Z, R, C, and MC revealed a strong correlation with SG, achieving an accuracy of R = 0.826. Furthermore, a moderate correlation was observed between the variables and GD, with an accuracy of R = 0.403. However, it was known that the variables did not demonstrate a satisfactory relationship with the anatomical properties.
Overall, further research is needed to explore the relationship between dielectric properties and the physical and anatomical characteristics of standing trees. In order to better understand the correlation between dielectric properties and the physical and anatomical properties of wood, additional research will be required. This will help uncover the factors that influence these properties and their potential applications in various fields related to wood and forestry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.A.A., L.K., I.Z.S., R.D., W.P.T.; methodology, D.A.A, L.K., W.P.T.; software, D.A.A and H.N.; validation, D.A.A and H.N.; formal analysis, D.A.A. and H.N.; investigation, D.A.A.; data curation, D.A.A. and H.N.; writing—original draft preparation, D.A.A.; writing—review and editing, L.K., I.Z.S., R.D., W.P.T..; visualization, D.A.A. and H.N.; supervision, L.K., I.Z.S., R.D., W.P.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research was funded by The Indonesia Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology (KEMENDIKBUDRISTEK) and IPB University supported this research through the Doctoral Dissertation Research Grant, FY 2023 (grant number: 1881/IT3.D10/PT.01.03/P/B/2023, and 102/E5/PG.02.00.PL/2023).
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data underlying the research are included in the article. The raw data that support the results are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology (KEMENDIKBUDRISTEK) and IPB University for the assistance and funding provided through the Doctoral Dissertation Research Grant for the Fiscal Year 2023. The authors are also grateful to Perum Perhutani for their assistance and providing samples for this project, and to Ms. Ulfa Adzkia for the valuable contribution in project administration. Furthermore, the authors are grateful to BRIN Team for the assistance rendered with the field and laboratory work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Corryanti; Muharyani, N. The opportunities and challenges of Jati Plus Perhutani. Wood Research Journal, 2018, 9, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizanti, D.E.; Darmawan, W.; George, B.; Merlin, A.; Dumarcay, S.; Chapuis, H.; Gérardin, C.; Gelhaye, E.; Raharivelomanana, P.; Sari, R.K.; Syafii, W.; Mohamed, R.; Gerardin, P. Comparison of Teak Wood Properties According to Forest Management Short Versus Long Rotation. Annals of Forest Secience, 2018, 75, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riantin, N.V.; Wahyudi, I.; Priadi, T. Anatomical Structure and Physical Properties of the 13 Years Old Solomon-Clone Teakwood Planted in Bogor, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 935, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adi, D.S.; Himmi, S.K.; Sudarmanto, Amin, Y. ; Darmawan, T.; Dwianto, W. Radial Variation of Wood Properties of Eight Years-old Fast-Growing Teak (Tectona grandis – Platinum Teak Wood). IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2020, 591, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, E.; and Wahyudi, I. Wood Basic Properties of Jati Plus Perhutani from Different Ages and Their Relationships to Drying Properties and Qualities. J. Penelitian Hasil Hutan, 2013, 31, 2, pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayati, F.; Sulistyo, J.; Lukmandaru, G.; Listyanto, T.; Praptoyo, H.; Pujiarti, R. Physical and Mechanical Properties of 10-Year Old Superior and Conventional Teak Planted in Randublatung Central Java Indonesia. J Ilmu Teknol Kayu Tropis, 2015, 13, 1, pp. 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listyanto, T.; Yudhana, F.; Putera, H.P.; Purwanta, S.; Lukmandaru, G.; Sulistyo, J.; Marsoem, S.N. Physical Properties and Natural Durability of Fast-Growing Teak at 12 Years-old Against Subterranean and Drywood Termites. J Ilmu Teknol Kayu Tropis, 2017; 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Damayanti, R.; Ozarska, B.; Pandit, I.K.N.; Febrianto, F.; Pari, G. Wood Properties of 5-year-old Fast Grown Teak. Wood Research Journal, 2018, 9, 2, pp. 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolotti, G.; Socco, L.V.; Martinis, R.; Godio, A.; Sambuelli, L. Application and comparison of three tomographic techiques for detection decay in trees. Journal Of Arboriculture, 2003, 29, 2, 66–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wu, C.K.; Zhu, H.; Tsang, K.F. NB-IoT based tree health monitoring system. IEEE, 2019, 1796–1799. [CrossRef]
- Nandika, D.; Kusuma, H.; Kusumawardhani, D.T.; Rumiyati, E.T.; Karlinasari, L.; et al. Health asessment of large and old trees in Ragunan Zoo, Jakarta. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 935, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlinasari, L.; Adzkia, U.; Puspitasari, T.; Nandika, D.; Nugroho, N.; Syafitri, U.D.; et al. Tree morphometric relationships and dynamic elasticity properties in tropical rain tree (Samanea saman Jacq. Merr). Forests, 2021, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiansyah, I.; Zulkarnaen, R.N.; Hariri, M.R.; Hutabarat, P.W.K.; Wardani, F.F. Tree health monitoring of risky trees in the hotel open space: a case study in Rancamaya, Bogor. Jurnal Sylva Lestari, 2022, 10, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarmu, T.; Kiviste, A.; Näkk, A.; Sims, A.; Laarmann, D. The Appalication of Sonic Tomography (PICUS 3 Sonic Tomograph) to Detect and Quantify Hidden Wood Decay in Managed Norway Spruce Stands. Forests 2022, 13, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zheng, Yili. ; Liu, W.; Development of Non-Destructive Testing Device for Plant Leaf Expansion Monitoring. Electronics, 2023, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. A Non-Destructive Measurement of Trunk Moisture Content in Living Trees Based on Multi-Sensory Data Fusion. Appl. Sci., 2023, 13, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Liziniewicz, M.; Lindeberg, J.; Adamopoulos, S. Non-Destructive Evaluation of Downy and Silver Birch Wood Quality and Stem Features from a Progeny Trial in Southern Sweden. Forests 2023, 14, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, F.; Coops, N.C.; Ratcliffe, B.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Lucieer, A. Modelling Internal Tree Attributes for Breeding in Applications in Douglas-Fir Progeny Trials Using RPAS-ALS. Science of Remote Sensing, 2023, 7, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlinasari, L.; Danu, M.I.; Nandika, D.; Turjaman, M. Drilling resistance method to evacuate density and hardness properties of resinous wood of agarwood (Aquilaria malaccensis). Wood Research. 2017, 62, 5, 683–690. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Siregar, I.Z.; Abad, J.I.M.; Karlinasari, L. Non-destructive modeling using a drilling resistane tool to predict wood basic density of standing trees in a Eucalyptus plantation in North Sumatra, Indonesia. Biodiversitas. 2022, 23, 12, 6218–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esofita, M.; Djamal, M.; Taruno, W.P.; Al Huda, M.; Baidillah, M.; Pari, G.; et al. Analysis of Wood’s Capacitance Characteristic to Its Hardness. Applied Mechanics and Materials 2015, 771, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridh, L.; Eliasson, L.; Bergström, D. Precision and accuracy in moisture content determination of wood fuel chips using a handheld electric capacitance moisture meter. Silva. Fenn. 2018, 52, 6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, J.; Kˇrepˇcík, V.; Šarauskis, E.; Kumhála, F. Electrical Capacitance Characteristics of Wood Chips at Low Frequency Ranges: A Cheap Tool for Quality Assessment. Sensors 2021, 21, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oktapiani, C.; Damayanti, R.; Karlinasari, L.; Agustiningrum, D.A.; Pari, R.; Djarwanto; et al. The effect of anatomical structure on hygroscopicity of four wood species. Accepted paper proceeding of the 14th International Symposium of IWoRS, Jatinangor, August 4th, 2022.
- Mačiulaitis, R.; Jefimovas, A.; Lipinskas, D. 2014. Research on the Electrical Capacitance and Electrical Conductivity of Char Resulting from Natural and Treated Wood. Journal of Civil engineering and Management, 2015, 21, 1, pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietsch, P.; Franke, S.; Franke, B.; Gamper, A.; Winter, S. Methods to Determine Wood Moisture Content and Their Applicability in Monitoring Concepts. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2014, 5, 2, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hadad, A.; Brodie, G.; Ahmed, B. The Effect of Wood Condition on Sound Wave Propagation. Open Journal of Acoustics, 2018, 8, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, M.S.; Raghavan, G.S.V. An overview of microwave processing and dielectric properties of agri-food materials. Biosys. Eng, 2004, 88, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skierucha,W. ;Wilczek, A.; Szypłowska, A. Dielectric spectroscopy in agrophysics. Int. Agrophys. 2012, 26, 187–197. [CrossRef]
- Khaled, D.E.; Castellano, N.N.; Gázquez, J.A. ; Perea-Moreno, A-J. ; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Dielectric Spectroscopy in Biomaterials: Agrophysics. Materials, 2016, 3, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, K.; Sankaran, S.; Ahamed, B.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Pasha, K.S.K.; Ponnama, D.; Sreekanth, P.S.R.; Chidambaram, K. Dielectric Spectroscopy. Spectroscopic Methods for Nanomaterials Characterization, 2017; 237–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitzke, J.P.; and Zangl, H. A Review on Electrical Impedance Tomography Spectroscopy. Sensors, 2020, 20, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogales, R.E.; and Benalcázar. Analysis and Evaluation of Feature Selection and Feature Extraction Methods. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 2023, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellan-Nebot, J.V.; Subir´on, F.R. A review of machining monitoring systems based on artificial intelligence process models. Int J Adv Manuf Technol, 2010, 47, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokland, J.; Nasir, V.; Cool, J.; Avramidis, S.; Adamopoulos, S. Machine Learning-based Prediction of Surface Checks and Bending Properties in Weathered Thermally Modified Timber. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 307, 124996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P. Wood Quality Defect Detection Based on Deep Learning and Multicriteria Framework. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2022; 4878090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 14774-1:2009. Solid Biofuels—Determination of Moisture Content—Oven Dry Method—Part 1: Total Moisture—Reference Method. Available online: https://www.sis.se/api/document/preview/71672/ (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Wheleer, E.A.; Baas, P.; Gasson, P.C. IAWA List of Microscopic Features for Hardwood Identification; IAWA Bull: US, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Shmulsky, R.; Jones, P.D. Forest Products and Wood Science: An Introduction, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ellingson, S.W. Electromagnetics I; Virginia Tech: LibreTexts. Available online: https://phys.libretexts.org/@go/page.24330 (acessed on 15 December 2023).
- Simpson, W.T. Specific Gravity, Moisture Content, and Density Relationship for Wood. Gen. Tech. Rep. FPL-GTR-76. Madison, WI: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory, 1993, pp. 1–13.
- Simanjuntak, T. Measurement of Dielectric Properties Values of Pepper (Piper nigrum L.) and Andaliman (Zanthoxylum acanthopodium DC.) in the Radio Frequency. Range. Thesis, : IPB University, INA, 2002; p. 7p. [Google Scholar]
- Tiitta, M.; Kainulainen, P.; Harju, A.M.; Venäläinen, M.; Manninen, A-M. ; Vuorinen, M.; Viitanen, H. Comparing the Effect of Chemical and Physical Properties on Complex Electrical Impedance of Scots Pine Wood. Holzforschung, 2003, 57, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).