Submitted:
24 December 2023
Posted:
26 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. miRNAs
3. miRNAs role in cancer
4. RNA therapeutics
5. miRNA therapeutics
5.1. Examples of miRNA therapeutics in clinical trials
5.2. Small molecule modulators of miRNA expression
6. Advances in delivery of miRNA therapeutics
7. Progress in chemical modifications of miRNAs for improved stability and cellular uptake
8. Progress in predicting and validating miRNA targets
9. Progress in preclinical validation of miRNA therapeutics
10. Off-target effects of miRNA therapeutics
11. Challenges and future perspectives
12. Conclusions
Abbreviations and acronyms
| AGO | Argonaute |
| AGO2 | Argonaute RISC Catalytic Component 2 |
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| ASO | Antisense oligonucleotides |
| CLL | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia |
| CTCL | Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma |
| ATLL | Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| DICER1 | Dicer 1, Ribonuclease III |
| DLBCL | Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| DGCR8 | DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region 8 |
| DROSHA | Drosha Ribonuclease III |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| GalNAc | N-acetylgalactosamine |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LNA | Locked nucleic acid (LNA) |
| MF | Mycosis fungoides |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| ncRNAs | non-coding RNAs |
| P-bodies | Processing bodies |
| pre-miRNA | precursor microRNA |
| pri-miRNA | primary microRNA |
| RNA Pol II | RNA polymerase II |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| sgRNA | Single guide RNA |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| TDMD | Target-directed miRNA degradation mechanism |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TRBP | The TAR RNA-binding protein |
| TTR | Transthyretin |
| UTR | Untranslated region |
| XenomiRs | Exogenous miRNAs |
| XPO5 | Exportin 5 |
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Review criteria
References
- Rands, C. M.; Meader, S.; Ponting, C. P.; Lunter, G. 8.2% of the Human genome is constrained: variation in rates of turnover across functional element classes in the human lineage. PLoS Genet 2014, 10, e1004525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, I.; Kundaje, A.; Aldred, S. F.; Collins, P. J.; Davis, C. A.; Doyle, F.; Epstein, C. B.; Frietze, S.; Harrow, J.; Kaul, R.; Khatun, J.; Lajoie, B. R.; Landt, S. G.; Lee, B.-K.; Pauli, F.; Rosenbloom, K. R.; Sabo, P.; Safi, A.; Sanyal, A.; Shoresh, N.; Simon, J. M.; Song, L.; Trinklein, N. D.; Altshuler, R. C.; Birney, E.; Brown, J. B.; Cheng, C.; Djebali, S.; Dong, X.; Dunham, I.; Ernst, J.; Furey, T. S.; Gerstein, M.; Giardine, B.; Greven, M.; Hardison, R. C.; Harris, R. S.; Herrero, J.; Hoffman, M. M.; Iyer, S.; Kellis, M.; Khatun, J.; Kheradpour, P.; Kundaje, A.; Lassmann, T.; Li, Q.; Lin, X.; Marinov, G. K.; Merkel, A.; Mortazavi, A.; Parker, S. C. J.; Reddy, T. E.; Rozowsky, J.; Schlesinger, F.; Thurman, R. E.; Wang, J.; Ward, L. D.; Whitfield, T. W.; Wilder, S. P.; Wu, W.; Xi, H. S.; Yip, K. Y.; Zhuang, J.; Bernstein, B. E.; Birney, E.; Dunham, I.; Green, E. D.; Gunter, C.; Snyder, M.; Pazin, M. J.; Lowdon, R. F.; Dillon, L. A. L.; Adams, L. B.; Kelly, C. J.; Zhang, J.; Wexler, J. R.; Green, E. D.; Good, P. J.; Feingold, E. A.; Bernstein, B. E.; Birney, E.; Crawford, G. E.; Dekker, J.; Elnitski, L.; Farnham, P. J.; Gerstein, M.; Giddings, M. C.; Gingeras, T. R.; Green, E. D.; Guigó, R.; Hardison, R. C.; Hubbard, T. J.; Kellis, M.; Kent, W. J.; Lieb, J. D.; Margulies, E. H.; Myers, R. M.; Snyder, M.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J. A.; Tenenbaum, S. A.; Weng, Z.; White, K. P.; Wold, B.; Khatun, J.; Yu, Y.; Wrobel, J.; Risk, B. A.; Gunawardena, H. P.; Kuiper, H. C.; Maier, C. W.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Giddings, M. C.; Bernstein, B. E.; Epstein, C. B.; Shoresh, N.; Ernst, J.; Kheradpour, P.; Mikkelsen, T. S.; Gillespie, S.; Goren, A.; Ram, O.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Issner, R.; Coyne, M. J.; Durham, T.; Ku, M.; Truong, T.; Ward, L. D.; Altshuler, R. C.; Eaton, M. L.; Kellis, M.; Djebali, S.; Davis, C. A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; Xue, C.; Marinov, G. K.; Khatun, J.; Williams, B. A.; Zaleski, C.; Rozowsky, J.; Röder, M.; Kokocinski, F.; Abdelhamid, R. F.; Alioto, T.; Antoshechkin, I.; Baer, M. T.; Batut, P.; Bell, I.; Bell, K.; Chakrabortty, S.; Chen, X.; Chrast, J.; Curado, J.; Derrien, T.; Drenkow, J.; Dumais, E.; Dumais, J.; Duttagupta, R.; Fastuca, M.; Fejes-Toth, K.; Ferreira, P.; Foissac, S.; Fullwood, M. J.; Gao, H.; Gonzalez, D.; Gordon, A.; Gunawardena, H. P.; Howald, C.; Jha, S.; Johnson, R.; Kapranov, P.; King, B.; Kingswood, C.; Li, G.; Luo, O. J.; Park, E.; Preall, J. B.; Presaud, K.; Ribeca, P.; Risk, B. A.; Robyr, D.; Ruan, X.; Sammeth, M.; Sandhu, K. S.; Schaeffer, L.; See, L.-H.; Shahab, A.; Skancke, J.; Suzuki, A. M.; Takahashi, H.; Tilgner, H.; Trout, D.; Walters, N.; Wang, H.; Wrobel, J.; Yu, Y.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Harrow, J.; Gerstein, M.; Hubbard, T. J.; Reymond, A.; Antonarakis, S. E.; Hannon, G. J.; Giddings, M. C.; Ruan, Y.; Wold, B.; Carninci, P.; Guigó, R.; Gingeras, T. R.; Rosenbloom, K. R.; Sloan, C. A.; Learned, K.; Malladi, V. S.; Wong, M. C.; Barber, G. P.; Cline, M. S.; Dreszer, T. R.; Heitner, S. G.; Karolchik, D.; Kent, W. J.; Kirkup, V. M.; Meyer, L. R.; Long, J. C.; Maddren, M.; Raney, B. J.; Furey, T. S.; Song, L.; Grasfeder, L. L.; Giresi, P. G.; Lee, B.-K.; Battenhouse, A.; Sheffield, N. C.; Simon, J. M.; Showers, K. A.; Safi, A.; London, D.; Bhinge, A. A.; Shestak, C.; Schaner, M. R.; Ki Kim, S.; Zhang, Z. Z.; Mieczkowski, P. A.; Mieczkowska, J. O.; Liu, Z.; McDaniell, R. M.; Ni, Y.; Rashid, N. U.; Kim, M. J.; Adar, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Winter, D.; Keefe, D.; Birney, E.; Iyer, V. R.; Lieb, J. D.; Crawford, G. E.; Li, G.; Sandhu, K. S.; Zheng, M.; Wang, P.; Luo, O. J.; Shahab, A.; Fullwood, M. J.; Ruan, X.; Ruan, Y.; Myers, R. M.; Pauli, F.; Williams, B. A.; Gertz, J.; Marinov, G. K.; Reddy, T. E.; Vielmetter, J.; Partridge, E.; Trout, D.; Varley, K. E.; Gasper, C.; The, E. P. C.; Overall, c.; Data production, l.; Lead, a.; Writing, g.; management, N. p.; Principal, i.; Boise State, U. ; University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Proteomics, g.; Broad Institute, G.; Cold Spring Harbor, U. o. G. C. f. G. R. B. R. S. I. U. o. L. G. I. o. S. g.; Data coordination center at, U. C. S. C.; Duke University, E. B. I. U. o. T. A. U. o. N. C.-C. H. g.; Genome Institute of Singapore, g.; HudsonAlpha Institute, C. U. C. I. S. g. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Halldorsson, B. V.; Eggertsson, H. P.; Moore, K. H. S.; Hauswedell, H.; Eiriksson, O.; Ulfarsson, M. O.; Palsson, G.; Hardarson, M. T.; Oddsson, A.; Jensson, B. O.; Kristmundsdottir, S.; Sigurpalsdottir, B. D.; Stefansson, O. A.; Beyter, D.; Holley, G.; Tragante, V.; Gylfason, A.; Olason, P. I.; Zink, F.; Asgeirsdottir, M.; Sverrisson, S. T.; Sigurdsson, B.; Gudjonsson, S. A.; Sigurdsson, G. T.; Halldorsson, G. H.; Sveinbjornsson, G.; Norland, K.; Styrkarsdottir, U.; Magnusdottir, D. N.; Snorradottir, S.; Kristinsson, K.; Sobech, E.; Jonsson, H.; Geirsson, A. J.; Olafsson, I.; Jonsson, P.; Pedersen, O. B.; Erikstrup, C.; Brunak, S.; Ostrowski, S. R.; Andersen, S.; Banasik, K.; Burgdorf, K.; Didriksen, M.; Dinh, K. M.; Erikstrup, C.; Gudbjartsson, D.; Hansen, T. F.; Hjalgrim, H.; Jemec, G.; Jennum, P.; Johansson, P. I.; Larsen, M. A. H.; Mikkelsen, S.; Nielsen, K. R.; Nyegaard, M.; Ostrowski, S. R.; Sækmose, S.; Sørensen, E.; Thorsteinsdottir, U.; Brun, M. T.; Ullum, H.; Werge, T.; Thorleifsson, G.; Jonsson, F.; Melsted, P.; Jonsdottir, I.; Rafnar, T.; Holm, H.; Stefansson, H.; Saemundsdottir, J.; Gudbjartsson, D. F.; Magnusson, O. T.; Masson, G.; Thorsteinsdottir, U.; Helgason, A.; Jonsson, H.; Sulem, P.; Stefansson, K.; Consortium, D. G. The sequences of 150,119 genomes in the UK Biobank. Nature 2022, 607, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraiwesh, B.; Arif, M. A.; Seumel, G. I.; Ossowski, S.; Weigel, D.; Reski, R.; Frank, W. Transcriptional control of gene expression by microRNAs. Cell 2010, 140, 111–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samad, A. F. A.; Sajad, M.; Nazaruddin, N.; Fauzi, I. A.; Murad, A. M. A.; Zainal, Z.; Ismail, I. MicroRNA and Transcription Factor: Key Players in Plant Regulatory Network. Front Plant Sci 2017, 8, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Cui, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. TransmiR v2.0: an updated transcription factor-microRNA regulation database. Nucleic Acids Research 2018, 47, D253–D258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyhan, A. A. microRNAs with different functions and roles in disease development and as potential biomarkers of diabetes: progress and challenges. Mol Biosyst 2015, 11, 1217–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P. Y.; Meister, G. microRNA-guided posttranscriptional gene regulation. 2005, 386, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in Control of Gene Expression: An Overview of Nuclear Functions. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Meng, Q.; Qian, J.; Li, M.; Gu, C.; Yang, Y. Review: RNA-based diagnostic markers discovery and therapeutic targets development in cancer. Pharmacol Ther 2022, 234, 108123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Maki, M.; Ding, R.; Yang, Y.; zhang, B.; Xiong, L. Genome-wide survey of tissue-specific microRNA and transcription factor regulatory networks in 12 tissues. Scientific Reports 2014, 4, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienholds, E.; Kloosterman, W. P.; Miska, E.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Berezikov, E.; de Bruijn, E.; Horvitz, H. R.; Kauppinen, S.; Plasterk, R. H. MicroRNA expression in zebrafish embryonic development. Science 2005, 309, 310–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboobaker, A. A.; Tomancak, P.; Patel, N.; Rubin, G. M.; Lai, E. C. Drosophila microRNAs exhibit diverse spatial expression patterns during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 18017–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J. C.; Harland, R. M. Expression of microRNAs during embryonic development of Xenopus tropicalis. Gene Expr Patterns 2008, 8, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kowdley, K. V. MicroRNAs in Common Human Diseases. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics 2012, 10, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- De Guire, V.; Robitaille, R.; Tetreault, N.; Guerin, R.; Menard, C.; Bambace, N.; Sapieha, P. Circulating miRNAs as sensitive and specific biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of human diseases: promises and challenges. Clin Biochem 2013, 46, 846–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C. E.; Thompson, D. C.; Barbu, M. G.; Bugnar, O. L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S. M.; Voinea, S. C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareev, I.; de Jesus Encarnacion Ramirez, M.; Goncharov, E.; Ivliev, D.; Shumadalova, A.; Ilyasova, T.; Wang, C. MiRNAs and lncRNAs in the regulation of innate immune signaling. Noncoding RNA Res 2023, 8, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauley, K. M.; Cha, S.; Chan, E. K. MicroRNA in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 2009, 32, 189–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, C. S.; Ganem, D. MicroRNAs and viral infection. Mol Cell 2005, 20, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalsky, R. L.; Cullen, B. R. Viruses, microRNAs, and host interactions. Annu Rev Microbiol 2010, 64, 123–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbu, M. G.; Condrat, C. E.; Thompson, D. C.; Bugnar, O. L.; Cretoiu, D.; Toader, O. D.; Suciu, N.; Voinea, S. C. MicroRNA Involvement in Signaling Pathways During Viral Infection. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Izneid, T.; AlHajri, N.; Ibrahim, A. M.; Javed, M. N.; Salem, K. M.; Pottoo, F. H.; Kamal, M. A. Micro-RNAs in the regulation of immune response against SARS CoV-2 and other viral infections. Journal of Advanced Research 2021, 30, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfimova, N.; Schlattjan, M.; Sowa, J. P.; Dienes, H. P.; Canbay, A.; Odenthal, M. Circulating microRNAs: promising candidates serving as novel biomarkers of acute hepatitis. Front Physiol 2012, 3, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. J.; Xu, M.; Gao, Z. H.; Wang, Y. Q.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, Y. X.; Li, X. X.; Zhang, C.; Xie, S. Y.; Wang, P. Y. Alterations of serum levels of BDNF-related miRNAs in patients with depression. PLoS One 2013, 8, e63648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K. A.; Hoban, A. E.; Clarke, G.; Moloney, G. M.; Dinan, T. G.; Cryan, J. F. Thinking small: towards microRNA-based therapeutics for anxiety disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2015, 24, 529–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Shu, P.; Yin, B.; Gong, Y.; Qiang, B.; Yuan, J.; Peng, X. MicroRNA-16 targets amyloid precursor protein to potentially modulate Alzheimer’s-associated pathogenesis in SAMP8 mice. Neurobiol Aging 2012, 33, 522–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, D. W.; Sturrock, A.; Leavitt, B. R. Development of biomarkers for Huntington’s disease. Lancet Neurol 2011, 10, 573–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, Y.; Pu, J. Circulating microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction. Intern Med 2011, 50, 1789–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchioni, R.; Marcheselli, F.; Olivieri, F.; Ricci, S.; Procopio, A. D.; Antonicelli, R. Conventional and novel diagnostic biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction: a promising role for circulating microRNAs. Biomarkers 2013, 18, 547–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez Lopez, Y. O.; Coen, P. M.; Goodpaster, B. H.; Seyhan, A. A. Gastric bypass surgery with exercise alters plasma microRNAs that predict improvements in cardiometabolic risk. Int J Obes (Lond) 2017, 41, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez Lopez, Y. O.; Garufi, G.; Pasarica, M.; Seyhan, A. A. Elevated and Correlated Expressions of miR-24, miR-30d, miR-146a, and SFRP-4 in Human Abdominal Adipose Tissue Play a Role in Adiposity and Insulin Resistance. Int J Endocrinol 2018, 2018, 7351902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Minto, A. W.; Wang, J.; Shi, Q.; Li, X.; Quigg, R. J. MicroRNA-377 is up-regulated and can lead to increased fibronectin production in diabetic nephropathy. Faseb j 2008, 22, 4126–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyhan, A. A.; Nunez Lopez, Y. O.; Xie, H.; Yi, F.; Mathews, C.; Pasarica, M.; Pratley, R. E. Pancreas-enriched miRNAs are altered in the circulation of subjects with diabetes: a pilot cross-sectional study. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 31479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez Lopez, Y. O.; Garufi, G.; Seyhan, A. A. Altered levels of circulating cytokines and microRNAs in lean and obese individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Mol Biosyst 2016, 13, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez Lopez, Y. O.; Pittas, A. G.; Pratley, R. E.; Seyhan, A. A. Circulating levels of miR-7, miR-152 and miR-192 respond to vitamin D supplementation in adults with prediabetes and correlate with improvements in glycemic control. J Nutr Biochem 2017, 49, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluiver, J.; Poppema, S.; de Jong, D.; Blokzijl, T.; Harms, G.; Jacobs, S.; Kroesen, B. J.; van den Berg, A. BIC and miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and diffuse large B cell lymphomas. J Pathol 2005, 207, 243–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E. A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B. L.; Mak, R. H.; Ferrando, A. A.; Downing, J. R.; Jacks, T.; Horvitz, H. R.; Golub, T. R. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F. J. Oncomirs — microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, S.; Chiocca, E. A. Emerging functions of microRNAs in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 2009, 92, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A.; Jacks, T. MicroRNAs and cancer: short RNAs go a long way. Cell 2009, 136, 586–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Maruyama, R.; Yamamoto, E.; Kai, M. Epigenetic alteration and microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Front Genet 2013, 4, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C. M. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.; Peruzzi, P. P.; Lawler, S. MicroRNAs in cancer: biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol Med 2014, 20, 460–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graveel, C. R.; Calderone, H. M.; Westerhuis, J. J.; Winn, M. E.; Sempere, L. F. Critical analysis of the potential for microRNA biomarkers in breast cancer management. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press) 2015, 7, 59–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, A.; Lieberman, J. Dysregulation of microRNA biogenesis and gene silencing in cancer. Sci Signal 2015, 8, re3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R. I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2015, 15, 321–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Kashima, R. Dysregulation of microRNA biogenesis machinery in cancer. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2016, 51, 121–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C. M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulla, A. R.; Slifker, M. J.; Zhou, Y.; Lev, A.; Einarson, M. B.; Dicker, D. T.; El-Deiry, W. S. miR-6883 Family miRNAs Target CDK4/6 to Induce G(1) Phase Cell-Cycle Arrest in Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 6902–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S. MicroRNAs as Therapeutic Agents: The Future of the Battle Against Cancer. Curr Top Med Chem 2018, 18, 2544–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Tan, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Tang, J. Functional miRNAs in breast cancer drug resistance. Onco Targets Ther 2018, 11, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikova, O.; Baranova, A.; Skoblov, M. Comprehensive Analysis of Human microRNA-mRNA Interactome. Front Genet 2019, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Syeda, Z.; Langden, S. S. S.; Munkhzul, C.; Lee, M.; Song, S. J. Regulatory Mechanism of MicroRNA Expression in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annese, T.; Tamma, R.; De Giorgis, M.; Ribatti, D. microRNAs Biogenesis, Functions and Role in Tumor Angiogenesis. Front Oncol 2020, 10, 581007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Di, M.; Liang, J.; Shi, S.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-183 in Cancer Progression. J Cancer 2020, 11, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Taheri, M. Emerging roles of miRNAs in the development of pancreatic cancer. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 141, 111914. [Google Scholar]
- Galka-Marciniak, P.; Urbanek-Trzeciak, M. O.; Nawrocka, P. M.; Kozlowski, P. A pan-cancer atlas of somatic mutations in miRNA biogenesis genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Inazawa, J. Cancer-associated miRNAs and their therapeutic potential. Journal of Human Genetics 2021, 66, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, M. J.; Alemany-Cosme, E.; Goni, S.; Bandres, E.; Palanca-Ballester, C.; Sandoval, J. Epigenetic Regulation of microRNAs in Cancer: Shortening the Distance from Bench to Bedside. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczyński, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Hogendorf, P. The Role of microRNA in Pancreatic Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczyński, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Szyłło, K.; Hogendorf, P. miRNAs in Cancer (Review of Literature). Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.; Abd-Aziz, N.; Khalid, K.; Poh, C. L.; Naidu, R. miRNA: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raufi, A. G.; May, M. S.; Hadfield, M. J.; Seyhan, A. A.; El-Deiry, W. S. Advances in Liquid Biopsy Technology and Implications for Pancreatic Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricarte-Filho, J. C.; Casado-Medrano, V.; Reichenberger, E.; Spangler, Z.; Scheerer, M.; Isaza, A.; Baran, J.; Patel, T.; MacFarland, S. P.; Brodeur, G. M.; Stewart, D. R.; Baloch, Z.; Bauer, A. J.; Wasserman, J. D.; Franco, A. T. DICER1 RNase IIIb domain mutations trigger widespread miRNA dysregulation and MAPK activation in pediatric thyroid cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1083382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyhan, A. A. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer-Advances and Challenges. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaal, A. M.; Sohal, I. S.; Iyer, S.; Sudarshan, K.; Kothandaraman, H.; Lanman, N. A.; Low, P. S.; Kasinski, A. L. A first-in-class fully modified version of miR-34a with outstanding stability, activity, and anti-tumor efficacy. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2985–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, D.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Bian, Z.; Liang, X.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Chen, Q.; Ba, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C. Y. Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA. Cell Res 2012, 22, 107–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K. W. XenomiRs and miRNA homeostasis in health and disease: evidence that diet and dietary miRNAs directly and indirectly influence circulating miRNA profiles. RNA Biol 2012, 9, 1147–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A. E.; Piegholdt, S.; Ferraro, M.; Pallauf, K.; Rimbach, G. Food derived microRNAs. Food Funct 2015, 6, 714–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, T.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, C. Y.; Zhang, Y. L. Dietary microRNA-A Novel Functional Component of Food. Adv Nutr 2019, 10, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Sainz, E.; Lorente-Cebrián, S.; Aranaz, P.; Riezu-Boj, J. I.; Martínez, J. A.; Milagro, F. I. Potential Mechanisms Linking Food-Derived MicroRNAs, Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier Functions in the Context of Nutrition and Human Health. Front Nutr 2021, 8, 586564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieślik, M.; Bryniarski, K.; Nazimek, K. Dietary and orally-delivered miRNAs: are they functional and ready to modulate immunity? AIMS Allergy and Immunology 2023, 7, 104–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Petrick, J. S.; Heck, G.; Ivashuta, S.; Marshall, W. S. Lack of detectable oral bioavailability of plant microRNAs after feeding in mice. Nat Biotechnol 2013, 31, 965–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, C.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet 2022, 38, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, K. M. T.; Elliott, E. K.; Haupt, L. M.; Griffiths, L. R. Regulatory Mechanisms of Epigenetic miRNA Relationships in Human Cancer and Potential as Therapeutic Targets. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machowska, M.; Galka-Marciniak, P.; Kozlowski, P. Consequences of genetic variants in miRNA genes. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2022, 20, 6443–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoletto, A. S.; Parchem, R. J. KRAS Hijacks the miRNA Regulatory Pathway in Cancer. Cancer Research 2023, 83, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. J.; Leng, R. X.; Fan, Y. G.; Pan, H. F.; Ye, D. Q. Translation of noncoding RNAs: Focus on lncRNAs, pri-miRNAs, and circRNAs. Exp Cell Res 2017, 361, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M. S.; Brenner, A. J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y. K.; Stoudemire, J.; Smith, S.; Bader, A. G.; Kim, S.; Hong, D. S. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D. S.; Kang, Y. K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H. Y.; Brenner, A. J.; Park, K.; Lee, J. L.; Kim, T. Y.; Shin, S.; Becerra, C. R.; Falchook, G.; Stoudemire, J.; Martin, D.; Kelnar, K.; Peltier, H.; Bonato, V.; Bader, A. G.; Smith, S.; Kim, S.; O’Neill, V.; Beg, M. S. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desantis, V.; Saltarella, I.; Lamanuzzi, A.; Melaccio, A.; Solimando, A. G.; Mariggiò, M. A.; Racanelli, V.; Paradiso, A.; Vacca, A.; Frassanito, M. A. MicroRNAs-Based Nano-Strategies as New Therapeutic Approach in Multiple Myeloma to Overcome Disease Progression and Drug Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.; Hossain, G. S.; Kocerha, J. The Potential for microRNA Therapeutics and Clinical Research. Front Genet 2019, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R. C.; Feinbaum, R. L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, B.; Ha, I.; Ruvkun, G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993, 75, 855–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquinelli, A. E.; Reinhart, B. J.; Slack, F.; Martindale, M. Q.; Kuroda, M. I.; Maller, B.; Hayward, D. C.; Ball, E. E.; Degnan, B.; Müller, P.; Spring, J.; Srinivasan, A.; Fishman, M.; Finnerty, J.; Corbo, J.; Levine, M.; Leahy, P.; Davidson, E.; Ruvkun, G. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 2000, 408, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. C.; Chan, W. C.; Hu, L. Y.; Lai, C. H.; Hsu, C. N.; Lin, W. C. Identification of homologous microRNAs in 56 animal genomes. Genomics 2010, 96, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedländer, M. R.; Lizano, E.; Houben, A. J. S.; Bezdan, D.; Báñez-Coronel, M.; Kudla, G.; Mateu-Huertas, E.; Kagerbauer, B.; González, J.; Chen, K. C.; LeProust, E. M.; Martí, E.; Estivill, X. Evidence for the biogenesis of more than 1,000 novel human microRNAs. Genome Biology 2014, 15, R57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R. J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A. J. miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, D140–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Chen, J.; Tao, Z.; Miao, L.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J. Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: coordination between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2019, 76, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooij, E. The art of microRNA research. Circ Res 2011, 108, 219–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R. C.; Farh, K. K.; Burge, C. B.; Bartel, D. P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rie, D.; Abugessaisa, I.; Alam, T.; Arner, E.; Arner, P.; Ashoor, H.; Åström, G.; Babina, M.; Bertin, N.; Burroughs, A. M.; Carlisle, A. J.; Daub, C. O.; Detmar, M.; Deviatiiarov, R.; Fort, A.; Gebhard, C.; Goldowitz, D.; Guhl, S.; Ha, T. J.; Harshbarger, J.; Hasegawa, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Herlyn, M.; Heutink, P.; Hitchens, K. J.; Hon, C. C.; Huang, E.; Ishizu, Y.; Kai, C.; Kasukawa, T.; Klinken, P.; Lassmann, T.; Lecellier, C. H.; Lee, W.; Lizio, M.; Makeev, V.; Mathelier, A.; Medvedeva, Y. A.; Mejhert, N.; Mungall, C. J.; Noma, S.; Ohshima, M.; Okada-Hatakeyama, M.; Persson, H.; Rizzu, P.; Roudnicky, F.; Sætrom, P.; Sato, H.; Severin, J.; Shin, J. W.; Swoboda, R. K.; Tarui, H.; Toyoda, H.; Vitting-Seerup, K.; Winteringham, L.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yasuzawa, K.; Yoneda, M.; Yumoto, N.; Zabierowski, S.; Zhang, P. G.; Wells, C. A.; Summers, K. M.; Kawaji, H.; Sandelin, A.; Rehli, M.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Carninci, P.; Forrest, A. R. R.; de Hoon, M. J. L. An integrated expression atlas of miRNAs and their promoters in human and mouse. Nat Biotechnol 2017, 35, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, S.; Rinaldi, F.; Lepore, S. M.; Viola, A.; Loro, E.; Angelini, C.; Vergani, L.; Novelli, G.; Botta, A. Overexpression of microRNA-206 in the skeletal muscle from myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients. J Transl Med 2010, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, C.; Claus, R.; Frenzel, L. P.; Zucknick, M.; Park, Y. J.; Gu, L.; Weichenhan, D.; Fischer, M.; Pallasch, C. P.; Herpel, E.; Rehli, M.; Byrd, J. C.; Wendtner, C. M.; Plass, C. Extensive promoter DNA hypermethylation and hypomethylation is associated with aberrant microRNA expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 2012, 72, 3775–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achey, R. L.; Khanna, V.; Ostrom, Q. T.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J. S. Incidence and survival trends in oligodendrogliomas and anaplastic oligodendrogliomas in the United States from 2000 to 2013: a CBTRUS Report. J Neurooncol 2017, 133, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, M.; Scherr, M. MicroRNA and lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2005, 352, 2446–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C. W.; Verhaak, R. G.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S. R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J. Z.; Berman, S. H.; Beroukhim, R.; Bernard, B.; Wu, C. J.; Genovese, G.; Shmulevich, I.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.; Zou, L.; Vegesna, R.; Shukla, S. A.; Ciriello, G.; Yung, W. K.; Zhang, W.; Sougnez, C.; Mikkelsen, T.; Aldape, K.; Bigner, D. D.; Van Meir, E. G.; Prados, M.; Sloan, A.; Black, K. L.; Eschbacher, J.; Finocchiaro, G.; Friedman, W.; Andrews, D. W.; Guha, A.; Iacocca, M.; O’Neill, B. P.; Foltz, G.; Myers, J.; Weisenberger, D. J.; Penny, R.; Kucherlapati, R.; Perou, C. M.; Hayes, D. N.; Gibbs, R.; Marra, M.; Mills, G. B.; Lander, E.; Spellman, P.; Wilson, R.; Sander, C.; Weinstein, J.; Meyerson, M.; Gabriel, S.; Laird, P. W.; Haussler, D.; Getz, G.; Chin, L.; Network, T. R. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. E.; Crowder, R. N.; El-Deiry, W. S. First-In-Class Small Molecule ONC201 Induces DR5 and Cell Death in Tumor but Not Normal Cells to Provide a Wide Therapeutic Index as an Anti-Cancer Agent. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0143082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedewy, A. M. L.; Elmaghraby, S. M.; Shehata, A. A.; Kandil, N. S. Prognostic Value of miRNA-155 Expression in B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Turk J Haematol 2017, 34, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kline, C. L. B.; Ralff, M. D.; Lulla, A. R.; Wagner, J. M.; Abbosh, P. H.; Dicker, D. T.; Allen, J. E.; El-Deiry, W. S. Role of Dopamine Receptors in the Anticancer Activity of ONC201. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, B.; Zhu, J. The diagnostic and prognostic value of the miR-17-92 cluster in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Front Genet 2022, 13, 927079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidigal, J. A.; Ventura, A. The biological functions of miRNAs: lessons from in vivo studies. Trends Cell Biol 2015, 25, 137–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujambio, A.; Ropero, S.; Ballestar, E.; Fraga, M. F.; Cerrato, C.; Setien, F.; Casado, S.; Suarez-Gauthier, A.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M.; Git, A.; Spiteri, I.; Das, P. P.; Caldas, C.; Miska, E.; Esteller, M. Genetic unmasking of an epigenetically silenced microRNA in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 1424–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, D.; Schaefer, A. General principals of miRNA biogenesis and regulation in the brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Ashurst, J. L.; Bradley, A. Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and transcription units. Genome Res 2004, 14, 1902–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D. P. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoda, M.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Katsuma, S.; Suzuki, T.; Tomari, Y. Hsc70/Hsp90 chaperone machinery mediates ATP-dependent RISC loading of small RNA duplexes. Mol Cell 2010, 39, 292–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, G. C.; Singh, J.; Barik, S. MicroRNAs: Processing, Maturation, Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol 2011, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akgul, B.; Erdogan, I. Intracytoplasmic Re-localization of miRISC Complexes. Front Genet 2018, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghini, F.; Rubolino, C.; Climent, M.; Simeone, I.; Marzi, M. J.; Nicassio, F. Endogenous transcripts control miRNA levels and activity in mammalian cells by target-directed miRNA degradation. Nature Communications 2018, 9, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu-Gruttadauria, J.; Pawlica, P.; Klum, S. M.; Wang, S.; Yario, T. A.; Schirle Oakdale, N. T.; Steitz, J. A.; MacRae, I. J. Structural Basis for Target-Directed MicroRNA Degradation. Mol Cell 2019, 75, 1243–1255.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Croce, C. M. microRNAs: Master regulators as potential therapeutics in cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2011, 51, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selbach, M.; Schwanhäusser, B.; Thierfelder, N.; Fang, Z.; Khanin, R.; Rajewsky, N. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 2008, 455, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlmann, S.; Mannsperger, H.; Zhang, J. D.; Horvat, E.; Schmidt, C.; Küblbeck, M.; Henjes, F.; Ward, A.; Tschulena, U.; Zweig, K.; Korf, U.; Wiemann, S.; Sahin, O. Global microRNA level regulation of EGFR-driven cell-cycle protein network in breast cancer. Mol Syst Biol 2012, 8, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimson, A.; Farh, K. K.; Johnston, W. K.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Lim, L. P.; Bartel, D. P. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell 2007, 27, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetrom, P.; Heale, B. S.; Snøve, O. Jr.; Aagaard, L.; Alluin, J.; Rossi, J. J. Distance constraints between microRNA target sites dictate efficacy and cooperativity. Nucleic Acids Res 2007, 35, 2333–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desterro, J.; Bak-Gordon, P.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Targeting mRNA processing as an anticancer strategy. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2020, 19, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Velculescu, V. E.; Zhou, S.; Diaz, L. A., Jr.; Kinzler, K. W. Cancer genome landscapes. Science 2013, 339, 1546–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Chen, F.; Au-Yeung, K. K.; Shi, C. MicroRNA as an Important Target for Anticancer Drug Development. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 736323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Cao, Y.; Qi, C.; Zong, Z. Dysregulated microRNAs participate in the crosstalk between colorectal cancer and atrial fibrillation. Hum Cell 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Peng, R.; Wang, J.; Qin, Z.; Xue, L. Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: the advantage and disadvantage. Clinical Epigenetics 2018, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, H.; Xue, S.; Li, P. Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for early diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2018, 28, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A. O.; Landthaler, M.; Lin, C.; Socci, N. D.; Hermida, L.; Fulci, V.; Chiaretti, S.; Foa, R.; Schliwka, J.; Fuchs, U.; Novosel, A.; Muller, R. U.; Schermer, B.; Bissels, U.; Inman, J.; Phan, Q.; Chien, M.; Weir, D. B.; Choksi, R.; De Vita, G.; Frezzetti, D.; Trompeter, H. I.; Hornung, V.; Teng, G.; Hartmann, G.; Palkovits, M.; Di Lauro, R.; Wernet, P.; Macino, G.; Rogler, C. E.; Nagle, J. W.; Ju, J.; Papavasiliou, F. N.; Benzing, T.; Lichter, P.; Tam, W.; Brownstein, M. J.; Bosio, A.; Borkhardt, A.; Russo, J. J.; Sander, C.; Zavolan, M.; Tuschl, T. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stahler, C.; Meese, E.; Keller, A. Distribution of miRNA expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, 3865–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda El Sayed, S.; Cristante, J.; Guyon, L.; Denis, J.; Chabre, O.; Cherradi, N. MicroRNA Therapeutics in Cancer: Current Advances and Challenges. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, T. The Risks of miRNA Therapeutics: In a Drug Target Perspective. Drug Des Devel Ther 2021, 15, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. 2018 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullard, A. 2019 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020, 19, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urits, I.; Swanson, D.; Swett, M. C.; Patel, A.; Berardino, K.; Amgalan, A.; Berger, A. A.; Kassem, H.; Kaye, A. D.; Viswanath, O. A Review of Patisiran (ONPATTRO®) for the Treatment of Polyneuropathy in People with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Neurol Ther 2020, 9, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição, I.; González-Duarte, A.; Obici, L.; Schmidt, H. H.; Simoneau, D.; Ong, M. L.; Amass, L. “Red-flag” symptom clusters in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2016, 21, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vormehr, M.; Türeci, Ö.; Sahin, U. Harnessing Tumor Mutations for Truly Individualized Cancer Vaccines. Annu Rev Med 2019, 70, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L. A.; Sethna, Z.; Soares, K. C.; Olcese, C.; Pang, N.; Patterson, E.; Lihm, J.; Ceglia, N.; Guasp, P.; Chu, A.; Yu, R.; Chandra, A. K.; Waters, T.; Ruan, J.; Amisaki, M.; Zebboudj, A.; Odgerel, Z.; Payne, G.; Derhovanessian, E.; Müller, F.; Rhee, I.; Yadav, M.; Dobrin, A.; Sadelain, M.; Łuksza, M.; Cohen, N.; Tang, L.; Basturk, O.; Gönen, M.; Katz, S.; Do, R. K.; Epstein, A. S.; Momtaz, P.; Park, W.; Sugarman, R.; Varghese, A. M.; Won, E.; Desai, A.; Wei, A. C.; D’Angelica, M. I.; Kingham, T. P.; Mellman, I.; Merghoub, T.; Wolchok, J. D.; Sahin, U.; Türeci, Ö.; Greenbaum, B. D.; Jarnagin, W. R.; Drebin, J.; O’Reilly, E. M.; Balachandran, V. P. Personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines stimulate T cells in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2023, 618, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Derhovanessian, E.; Miller, M.; Kloke, B. P.; Simon, P.; Löwer, M.; Bukur, V.; Tadmor, A. D.; Luxemburger, U.; Schrörs, B.; Omokoko, T.; Vormehr, M.; Albrecht, C.; Paruzynski, A.; Kuhn, A. N.; Buck, J.; Heesch, S.; Schreeb, K. H.; Müller, F.; Ortseifer, I.; Vogler, I.; Godehardt, E.; Attig, S.; Rae, R.; Breitkreuz, A.; Tolliver, C.; Suchan, M.; Martic, G.; Hohberger, A.; Sorn, P.; Diekmann, J.; Ciesla, J.; Waksmann, O.; Brück, A. K.; Witt, M.; Zillgen, M.; Rothermel, A.; Kasemann, B.; Langer, D.; Bolte, S.; Diken, M.; Kreiter, S.; Nemecek, R.; Gebhardt, C.; Grabbe, S.; Höller, C.; Utikal, J.; Huber, C.; Loquai, C.; Türeci, Ö. Personalized RNA mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer. Nature 2017, 547, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, F.; Hemmi, H.; Hochrein, H.; Ampenberger, F.; Kirschning, C.; Akira, S.; Lipford, G.; Wagner, H.; Bauer, S. Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like receptor 7 and 8. Science 2004, 303, 1526–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, S. S.; Kaisho, T.; Hemmi, H.; Akira, S.; Reis e Sousa, C. Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science 2004, 303, 1529–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, O.; Nielsen, M.; Kesmir, C.; Petersen, A. G.; Lundegaard, C.; Worning, P.; Sylvester-Hvid, C.; Lamberth, K.; Røder, G.; Justesen, S.; Buus, S.; Brunak, S. Definition of supertypes for HLA molecules using clustering of specificity matrices. Immunogenetics 2004, 55, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, L. M.; Diken, M.; Haas, H.; Kreiter, S.; Loquai, C.; Reuter, K. C.; Meng, M.; Fritz, D.; Vascotto, F.; Hefesha, H.; Grunwitz, C.; Vormehr, M.; Hüsemann, Y.; Selmi, A.; Kuhn, A. N.; Buck, J.; Derhovanessian, E.; Rae, R.; Attig, S.; Diekmann, J.; Jabulowsky, R. A.; Heesch, S.; Hassel, J.; Langguth, P.; Grabbe, S.; Huber, C.; Türeci, Ö.; Sahin, U. Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2016, 534, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F. P.; Thomas, S. J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J. L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E. D.; Zerbini, C.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K. A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Koury, K.; Li, P.; Kalina, W. V.; Cooper, D.; Frenck, R. W.; Hammitt, L. L.; Türeci, Ö.; Nell, H.; Schaefer, A.; Ünal, S.; Tresnan, D. B.; Mather, S.; Dormitzer, P. R.; Şahin, U.; Jansen, K. U.; Gruber, W. C. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A. R.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.-S. Therapeutic advances of miRNAs: A preclinical and clinical update. Journal of Advanced Research 2021, 28, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuri, K.; Bechtold, C.; Quijano, E.; Pham, H.; Gupta, A.; Vikram, A.; Bahal, R. Antisense Oligonucleotides: An Emerging Area in Drug Discovery and Development. J Clin Med 2020, 9, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L. R.; Frampton, A. E.; Jacob, J.; Pellegrino, L.; Krell, J.; Giamas, G.; Tsim, N.; Vlavianos, P.; Cohen, P.; Ahmad, R.; Keller, A.; Habib, N. A.; Stebbing, J.; Castellano, L. MicroRNAs targeting oncogenes are down-regulated in pancreatic malignant transformation from benign tumors. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacomino, G. miRNAs: The Road from Bench to Bedside. Genes (Basel) 2023, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raue, R.; Frank, A. C.; Syed, S. N.; Brune, B. Therapeutic Targeting of MicroRNAs in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Pan, M. H.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Jiang, C.; He, J.; Abouzid, K.; Liu, L. Z.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, B. H. Hypoxia-mediated mitochondria apoptosis inhibition induces temozolomide treatment resistance through miR-26a/Bad/Bax axis. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, H. E.; Ivan, C.; Calin, G. A.; Ivan, M. HypoxamiRs and cancer: from biology to targeted therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal 2014, 21, 1220–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Xia, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Qiu, Z. miR-301a plays a pivotal role in hypoxia-induced gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Exp Cell Res 2018, 369, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, H.; Liu, H.; Lv, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, R.; Liu, H.; Ding, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Fu, S.; Xie, D.; Wu, M.; Zhou, W.; Qian, Q. MiRNA-99a directly regulates AGO2 through translational repression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2014, 3, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Kumar, V.; Lin, F.; Kumar, V.; Bhattarai, R.; Bhatt, V. R.; Tan, C.; Mahato, R. I. Redox-responsive nanoplatform for codelivery of miR-519c and gemcitabine for pancreatic cancer therapy. Sci Adv 2020, 6, (46). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, L. F.; Rebhan, M. A.; Crivelli, S. E.; Denzler, R.; Stoffel, M.; Hall, J. Miravirsen (SPC3649) can inhibit the biogenesis of miR-122. Nucleic Acids Res 2014, 42, 609–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P. S.; Liao, C. J.; Huang, Y. H.; Yeh, C. T.; Chen, C. Y.; Tang, H. C.; Chang, C. C.; Lin, K. H. Functional and Clinical Significance of Dysregulated microRNAs in Liver Cancer. Cancers (Basel), 2021; 13, (21). [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, J.; Stessl, M.; Amartey, J.; Noe, C. R. Off-target effects related to the phosphorothioate modification of nucleic acids. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 1344–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacomino, G.; Siani, A. Role of microRNAs in obesity and obesity-related diseases. Genes Nutr 2017, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Ree, M. H.; de Vree, J. M.; Stelma, F.; Willemse, S.; van der Valk, M.; Rietdijk, S.; Molenkamp, R.; Schinkel, J.; van Nuenen, A. C.; Beuers, U.; Hadi, S.; Harbers, M.; van der Veer, E.; Liu, K.; Grundy, J.; Patick, A. K.; Pavlicek, A.; Blem, J.; Huang, M.; Grint, P.; Neben, S.; Gibson, N. W.; Kootstra, N. A.; Reesink, H. W. Safety, tolerability, and antiviral effect of RG-101 in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a phase 1B, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, A. G.; Beatty, X.; Lynch, J. M.; Hermreck, M.; Tetzlaff, M.; Duvic, M.; Jackson, A. L. Cobomarsen, an oligonucleotide inhibitor of miR-155, co-ordinately regulates multiple survival pathways to reduce cellular proliferation and survival in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2018, 183, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Seto, A. G.; Beatty, X.; Hermreck, M.; Gilles, M. E.; Stroopinsky, D.; Pinter-Brown, L. C.; Pestano, L.; Marchese, C.; Avigan, D.; Trivedi, P.; Escolar, D. M.; Jackson, A. L.; Slack, F. J. Cobomarsen, an Oligonucleotide Inhibitor of miR-155, Slows DLBCL Tumor Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo. Clin Cancer Res 2021, 27, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallant-Behm, C. L.; Piper, J.; Dickinson, B. A.; Dalby, C. M.; Pestano, L. A.; Jackson, A. L. A synthetic microRNA-92a inhibitor (MRG-110) accelerates angiogenesis and wound healing in diabetic and nondiabetic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 2018, 26, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant-Behm, C. L.; Piper, J.; Lynch, J. M.; Seto, A. G.; Hong, S. J.; Mustoe, T. A.; Maari, C.; Pestano, L. A.; Dalby, C. M.; Jackson, A. L.; Rubin, P.; Marshall, W. S. A MicroRNA-29 Mimic (Remlarsen) Represses Extracellular Matrix Expression and Fibroplasia in the Skin. J Invest Dermatol 2019, 139, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegel, A. J.; Liu, Y.; Cohen, B.; Usa, K.; Liu, Y.; Liang, M. MiR-382 targeting of kallikrein 5 contributes to renal inner medullary interstitial fibrosis. Physiol Genomics 2012, 44, 259–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zandwijk, N.; Pavlakis, N.; Kao, S. C.; Linton, A.; Boyer, M. J.; Clarke, S.; Huynh, Y.; Chrzanowska, A.; Fulham, M. J.; Bailey, D. L.; Cooper, W. A.; Kritharides, L.; Ridley, L.; Pattison, S. T.; MacDiarmid, J.; Brahmbhatt, H.; Reid, G. Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: a first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol 2017, 18, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, T.; Gansevoort, R. T.; Meijer, E. Drugs in Clinical Development to Treat Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Drugs 2022, 82, 1095–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A. R.; Sharma, G.; Sarkar, B. K.; Lee, S. S. The novel strategies for next-generation cancer treatment: miRNA combined with chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 10164–10174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H. W.; Cho, W. C. The emerging role of miRNAs in combined cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2015, 15, 923–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, M.; Lambert, B.; Meryet-Figuière, M.; Brotin, E.; Weiswald, L. B.; Paysant, H.; Vigneron, N.; Wambecke, A.; Abeilard, E.; Giffard, F.; Louis, M. H.; Blanc-Fournier, C.; Gauduchon, P.; Poulain, L.; Denoyelle, C. Functional miRNA Screening Identifies Wide-ranging Antitumor Properties of miR-3622b-5p and Reveals a New Therapeutic Combination Strategy in Ovarian Tumor Organoids. Mol Cancer Ther 2020, 19, 1506–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, S.; Xie, H.; Peng, X.; Yin, W.; Tao, Y.; Wang, X. miRNA-based biomarkers, therapies, and resistance in Cancer. Int J Biol Sci 2020, 16, 2628–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P. Inhibition of RNA-binding proteins with small molecules. Nat Rev Chem 2020, 4, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galm, O.; Herman, J. G.; Baylin, S. B. The fundamental role of epigenetics in hematopoietic malignancies. Blood Rev 2006, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.; Villanueva, A.; Moutinho, C.; Davalos, V.; Spizzo, R.; Ivan, C.; Rossi, S.; Setien, F.; Casanovas, O.; Simo-Riudalbas, L.; Carmona, J.; Carrere, J.; Vidal, A.; Aytes, A.; Puertas, S.; Ropero, S.; Kalluri, R.; Croce, C. M.; Calin, G. A.; Esteller, M. Small molecule enoxacin is a cancer-specific growth inhibitor that acts by enhancing TAR RNA-binding protein 2-mediated microRNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 4394–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldo, C.; Missiaglia, E.; Hagan, J. P.; Falconi, M.; Capelli, P.; Bersani, S.; Calin, G. A.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C. G.; Scarpa, A.; Croce, C. M. MicroRNA expression abnormalities in pancreatic endocrine and acinar tumors are associated with distinctive pathologic features and clinical behavior. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24, 4677–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, M. T.; Liu, A.; Xu, X.; Master, S. R.; Baldwin, D. A.; Tobias, J. W.; Livolsi, V. A.; Baloch, Z. W. Differential expression of miRNAs in papillary thyroid carcinoma compared to multinodular goiter using formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissues. Endocr Pathol 2007, 18, 163–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asangani, I. A.; Rasheed, S. A.; Nikolova, D. A.; Leupold, J. H.; Colburn, N. H.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Wang, Z. X.; Wang, R. MicroRNA-21: a novel therapeutic target in human cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2010, 10, 1224–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watashi, K.; Yeung, M. L.; Starost, M. F.; Hosmane, R. S.; Jeang, K. T. Identification of small molecules that suppress microRNA function and reverse tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 24707–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B. P.; Arenz, C. A homogenous assay for micro RNA maturation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2006, 45, 5550–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, D. D.; Connelly, C. M.; Grohmann, C.; Deiters, A. Small molecule modifiers of microRNA miR-122 function for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Chem Soc 2010, 132, 7976–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, M.; Jacquemin, E.; Munnich, A.; Lyonnet, S.; Henrion-Caude, A. miR-122, a paradigm for the role of microRNAs in the liver. J Hepatol 2008, 48, 648–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esau, C.; Davis, S.; Murray, S. F.; Yu, X. X.; Pandey, S. K.; Pear, M.; Watts, L.; Booten, S. L.; Graham, M.; McKay, R.; Subramaniam, A.; Propp, S.; Lollo, B. A.; Freier, S.; Bennett, C. F.; Bhanot, S.; Monia, B. P. miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab 2006, 3, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jopling, C. L.; Yi, M.; Lancaster, A. M.; Lemon, S. M.; Sarnow, P. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific MicroRNA. Science 2005, 309, 1577–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thum, T.; Catalucci, D.; Bauersachs, J. MicroRNAs: novel regulators in cardiac development and disease. Cardiovasc Res 2008, 79, 562–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wystub, K.; Besser, J.; Bachmann, A.; Boettger, T.; Braun, T. miR-1/133a clusters cooperatively specify the cardiomyogenic lineage by adjustment of myocardin levels during embryonic heart development. PLoS Genet 2013, 9, e1003793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S. B.; Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Small molecular inhibitors of miR-1 identified from photocycloadducts of acetylenes with 2-methoxy-1,4-naphthalenequinone. Bioorg Med Chem 2013, 21, 6124–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, D. Y.; Huang, L. In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: challenges and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2015, 81, 128–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonarakis, E. S.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Nakazawa, M.; Roeser, J. C.; Chen, Y.; Mohammad, T. A.; Chen, Y.; Fedor, H. L.; Lotan, T. L.; Zheng, Q.; De Marzo, A. M.; Isaacs, J. T.; Isaacs, W. B.; Nadal, R.; Paller, C. J.; Denmeade, S. R.; Carducci, M. A.; Eisenberger, M. A.; Luo, J. AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2014, 371, 1028–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z. Recent progress in microRNA-based delivery systems for the treatment of human disease. ExRNA 2019, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J. D.; Reidenbach, D.; Salomon, N.; Sahin, U.; Türeci, Ö.; Vormehr, M.; Kranz, L. M. mRNA therapeutics in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer 2021, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jivrajani, M.; Nivsarkar, M. Ligand-targeted bacterial minicells: Futuristic nano-sized drug delivery system for the efficient and cost effective delivery of shRNA to cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, I.; Chatterjee, A. Recent Advances in miRNA Delivery Systems. Methods Protoc 2021, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T. C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M. J. A. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020, 19, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosta, P.; Cryer, A. M.; Dion, M. Z.; Shiraishi, T.; Langston, S. P.; Lok, D.; Wang, J.; Harrison, S.; Hatten, T.; Ganno, M. L.; Appleman, V. A.; Taboada, G. M.; Puigmal, N.; Ferber, S.; Kalash, S.; Prado, M.; Rodríguez, A. L.; Kamoun, W. S.; Abu-Yousif, A. O.; Artzi, N. Investigation of the enhanced antitumour potency of STING agonist after conjugation to polymer nanoparticles. Nature Nanotechnology 2023, 18, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, B. R.; Chamberlain, J. S. Recombinant adeno-associated virus transduction and integration. Mol Ther 2008, 16, 1189–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Carrillo, E.; Liu, Y. P.; Berkhout, B. Improving miRNA Delivery by Optimizing miRNA Expression Cassettes in Diverse Virus Vectors. Hum Gene Ther Methods 2017, 28, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascellino, M. T.; Di Timoteo, F.; De Angelis, M.; Oliva, A. Overview of the Main Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Mechanism of Action, Efficacy and Safety. Infect Drug Resist 2021, 14, 3459–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, S.; Brouwers, C. C.; Sogorb-Gonzalez, M.; Martier, R.; Depla, J. A.; Vallès, A.; van Deventer, S. J.; Konstantinova, P.; Evers, M. M. AAV5-miHTT Lowers Huntingtin mRNA and Protein without Off-Target Effects in Patient-Derived Neuronal Cultures and Astrocytes. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 2019, 15, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miniarikova, J.; Zanella, I.; Huseinovic, A.; van der Zon, T.; Hanemaaijer, E.; Martier, R.; Koornneef, A.; Southwell, A. L.; Hayden, M. R.; van Deventer, S. J.; Petry, H.; Konstantinova, P. Design, Characterization, and Lead Selection of Therapeutic miRNAs Targeting Huntingtin for Development of Gene Therapy for Huntington’s Disease. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaranch, L.; Blits, B.; San Sebastian, W.; Hadaczek, P.; Bringas, J.; Sudhakar, V.; Macayan, M.; Pivirotto, P. J.; Petry, H.; Bankiewicz, K. S. MR-guided parenchymal delivery of adeno-associated viral vector serotype 5 in non-human primate brain. Gene Ther 2017, 24, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monahan, P. E.; Négrier, C.; Tarantino, M.; Valentino, L. A.; Mingozzi, F. Emerging Immunogenicity and Genotoxicity Considerations of Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Gene Therapy for Hemophilia. J Clin Med 2021, 10, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol 2015, 33, 941–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Kao, S. C.; Pavlakis, N.; Brahmbhatt, H.; MacDiarmid, J.; Clarke, S.; Boyer, M.; van Zandwijk, N. Clinical development of TargomiRs, a miRNA mimic-based treatment for patients with recurrent thoracic cancer. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 1079–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkasy, O. M.; Nordin, J. Z.; Hagey, D. W.; de Jong, O. G.; Schiffelers, R. M.; Andaloussi, S. E.; Vader, P. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Why and how? Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2020, 159, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldari, S.; Di Rocco, G.; Magenta, A.; Picozza, M.; Toietta, G. Extracellular Vesicles-Encapsulated MicroRNA-125b Produced in Genetically Modified Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation. Cells 2019, 8, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: current potential and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2017, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Paciocco, A.; Affinito, A.; Roscigno, G.; Fiore, D.; Palma, F.; Galasso, M.; Volinia, S.; Fiorelli, A.; Esposito, C. L.; Nuzzo, S.; Inghirami, G.; de Franciscis, V.; Condorelli, G. Aptamer-miR-34c Conjugate Affects Cell Proliferation of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, T. P.; Graham, M. J.; Yu, J.; Carty, R.; Low, A.; Chappell, A.; Schmidt, K.; Zhao, C.; Aghajan, M.; Murray, H. F.; Riney, S.; Booten, S. L.; Murray, S. F.; Gaus, H.; Crosby, J.; Lima, W. F.; Guo, S.; Monia, B. P.; Swayze, E. E.; Seth, P. P. Targeted delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to hepatocytes using triantennary N-acetyl galactosamine improves potency 10-fold in mice. Nucleic Acids Res 2014, 42, 8796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessen, E. A.; Vietsch, H.; Rump, E. T.; Fluiter, K.; Kuiper, J.; Bijsterbosch, M. K.; van Berkel, T. J. Targeted delivery of oligodeoxynucleotides to parenchymal liver cells in vivo. Biochem J 1999, 340 (Pt 3) Pt 3, 783–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenth, J. P. H.; Schattenberg, J. M. The nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) drug development graveyard: established hurdles and planning for future success. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2020, 29, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Preclinical and Clinical Advances of GalNAc-Decorated Nucleic Acid Therapeutics. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2017, 6, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelnar, K.; Peltier, H. J.; Leatherbury, N.; Stoudemire, J.; Bader, A. G. Quantification of therapeutic miRNA mimics in whole blood from nonhuman primates. Anal Chem 2014, 86, 1534–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelma, F.; van der Ree, M. H.; Sinnige, M. J.; Brown, A.; Swadling, L.; de Vree, J. M. L.; Willemse, S. B.; van der Valk, M.; Grint, P.; Neben, S.; Klenerman, P.; Barnes, E.; Kootstra, N. A.; Reesink, H. W. Immune phenotype and function of natural killer and T cells in chronic hepatitis C patients who received a single dose of anti-MicroRNA-122, RG-101. Hepatology 2017, 66, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Mukai, Y.; Wada, F.; Terada, C.; Kayaba, Y.; Oh, K.; Yamayoshi, A.; Obika, S.; Harada-Shiba, M. Highly Potent GalNAc-Conjugated Tiny LNA Anti-miRNA-122 Antisense Oligonucleotides. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardani, A.; Yaghoobi, H.; Alibakhshi, A.; Khatami, M. Inhibition of miR-155 in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line by gold nanoparticles functionalized with antagomir and AS1411 aptamer. J Cell Physiol 2020, 235, 6887–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, M. P.; Chavali, M. S. Recent advances in biomaterials for 3D scaffolds: A review. Bioact Mater 2019, 4, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-de-Leyva, Á.; Linares, V.; Casas, M.; Caraballo, I. 3D Printed Drug Delivery Systems Based on Natural Products. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.; Trivedi, R. 3D Printed Bioconstructs: Regenerative Modulation for Genetic Expression. Stem Cell Rev Rep 2021, 17, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, K. A.; Behlke, M. A. Chemical modification and design of anti-miRNA oligonucleotides. Gene Ther 2011, 18, 1111–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünweller, A.; Hartmann, R. K. Locked nucleic acid oligonucleotides: the next generation of antisense agents? BioDrugs 2007, 21, 235–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshkin, A. A.; Singh, S. K.; Nielsen, P.; Rajwanshi, V. K.; Kumar, R.; Meldgaard, M.; Olsen, C. E.; Wengel, J. LNA (Locked Nucleic Acids): Synthesis of the adenine, cytosine, guanine, 5-methylcytosine, thymine and uracil bicyclonucleoside monomers, oligomerisation, and unprecedented nucleic acid recognition. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 3607–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprey, K.; Batistatou, N.; Kritzer, J. A. A critical analysis of methods used to investigate the cellular uptake and subcellular localization of RNA therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 7623–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C. M.; Tanowitz, M.; Donner, A. J.; Prakash, T. P.; Swayze, E. E.; Harris, E. N.; Seth, P. P. Receptor-Mediated Uptake of Phosphorothioate Antisense Oligonucleotides in Different Cell Types of the Liver. Nucleic Acid Ther 2018, 28, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, J.; Hanss, B.; Kopp, J. B.; Copeland, T. D.; Bruggeman, L. A.; Coffman, T. M.; Klotman, P. E. Transport of phosphorothioate oligonucleotides in kidney: implications for molecular therapy. Kidney Int 1995, 47, 1462–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, I. G.; MacKenna, D. A.; Johnson, B. G.; Kaimal, V.; Roach, A. M.; Ren, S.; Nakagawa, N.; Xin, C.; Newitt, R.; Pandya, S.; Xia, T. H.; Liu, X.; Borza, D. B.; Grafals, M.; Shankland, S. J.; Himmelfarb, J.; Portilla, D.; Liu, S.; Chau, B. N.; Duffield, J. S. Anti-microRNA-21 oligonucleotides prevent Alport nephropathy progression by stimulating metabolic pathways. J Clin Invest 2015, 125, 141–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washietl, S.; Will, S.; Hendrix, D. A.; Goff, L. A.; Rinn, J. L.; Berger, B.; Kellis, M. Computational analysis of noncoding RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2012, 3, 759–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekprasert, P.; Mayhew, M.; Ohler, U. Assessing the utility of thermodynamic features for microRNA target prediction under relaxed seed and no conservation requirements. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, P.; Takahashi, K.; Saito, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Okita, K.; Watanabe, A.; Inoue, H.; Yamashita, J. K.; Todani, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Osawa, M.; Yashiro, Y.; Yamanaka, S.; Osafune, K. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Use in Human Models of Disease and Development. Physiol Rev 2019, 99, 79–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, O.; Sugai, K.; Yamaguchi, R.; Tashiro, S.; Nagoshi, N.; Kohyama, J.; Iida, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Itakura, G.; Isoda, M.; Shinozaki, M.; Fujiyoshi, K.; Kanemura, Y.; Yamanaka, S.; Nakamura, M.; Okano, H. Concise Review: Laying the Groundwork for a First-In-Human Study of an Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Intervention for Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells 2019, 37, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebert, L. F. R.; MacRae, I. J. Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2019, 20, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestdagh, P.; Boström, A. K.; Impens, F.; Fredlund, E.; Van Peer, G.; De Antonellis, P.; von Stedingk, K.; Ghesquière, B.; Schulte, S.; Dews, M.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Schulte, J. H.; Zollo, M.; Schramm, A.; Gevaert, K.; Axelson, H.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. The miR-17-92 microRNA cluster regulates multiple components of the TGF-β pathway in neuroblastoma. Mol Cell 2010, 40, 762–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuk, R.; Zhou, L.; Chang, W. I.; Zhang, Y.; Sharma, A.; Prabhu, V. V.; Tapinos, N.; Lulla, R. R.; El-Deiry, W. S. Potent preclinical sensitivity to imipridone-based combination therapies in oncohistone H3K27M-mutant diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma is associated with induction of the integrated stress response, TRAIL death receptor DR5, reduced ClpX and apoptosis. Am J Cancer Res 2021, 11, 4607–4623. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Nakaoka, T.; Saito, H. microRNA-34a as a Therapeutic Agent against Human Cancer. J Clin Med 2015, 4, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchie, A. First microRNA mimic enters clinic. Nat Biotechnol 2013, 31, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daige, C. L.; Wiggins, J. F.; Priddy, L.; Nelligan-Davis, T.; Zhao, J.; Brown, D. Systemic delivery of a miR34a mimic as a potential therapeutic for liver cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2014, 13, 2352–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelnar, K.; Bader, A. G. A qRT-PCR Method for Determining the Biodistribution Profile of a miR-34a Mimic. Methods Mol Biol 2015, 1317, 125–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diener, C.; Hart, M.; Alansary, D.; Poth, V.; Walch-Rückheim, B.; Menegatti, J.; Grässer, F.; Fehlmann, T.; Rheinheimer, S.; Niemeyer, B. A.; Lenhof, H. P.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Modulation of intracellular calcium signaling by microRNA-34a-5p. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, M.; Nickl, L.; Walch-Rueckheim, B.; Krammes, L.; Rheinheimer, S.; Diener, C.; Taenzer, T.; Kehl, T.; Sester, M.; Lenhof, H. P.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Wrinkle in the plan: miR-34a-5p impacts chemokine signaling by modulating CXCL10/CXCL11/CXCR3-axis in CD4(+), CD8(+) T cells, and M1 macrophages. J Immunother Cancer 2020, 8, (2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, T. M.; Reed, K.; Shi, D.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. Delivering the next generation of cancer immunotherapies with RNA. Cell 2023, 186, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, E. E.; Frenck, R. W.; Falsey, A. R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M. J.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K. A.; Li, P.; Koury, K.; Kalina, W.; Cooper, D.; Fontes-Garfias, C.; Shi, P.-Y.; Türeci, Ö.; Tompkins, K. R.; Lyke, K. E.; Raabe, V.; Dormitzer, P. R.; Jansen, K. U.; Şahin, U.; Gruber, W. C. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidates. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E. J.; Rouphael, N. G.; Widge, A. T.; Jackson, L. A.; Roberts, P. C.; Makhene, M.; Chappell, J. D.; Denison, M. R.; Stevens, L. J.; Pruijssers, A. J.; McDermott, A. B.; Flach, B.; Lin, B. C.; Doria-Rose, N. A.; O’Dell, S.; Schmidt, S. D.; Corbett, K. S.; Swanson, P. A.; Padilla, M.; Neuzil, K. M.; Bennett, H.; Leav, B.; Makowski, M.; Albert, J.; Cross, K.; Edara, V. V.; Floyd, K.; Suthar, M. S.; Martinez, D. R.; Baric, R.; Buchanan, W.; Luke, C. J.; Phadke, V. K.; Rostad, C. A.; Ledgerwood, J. E.; Graham, B. S.; Beigel, J. H. Safety and Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccine in Older Adults. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383, 2427–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales-Aloy, E.; Connerty, P.; Salik, B.; Liu, B.; Woo, A. J.; Haber, M.; Norris, M. D.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Y. miR-101 suppresses the development of MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2019, 104, e296–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, R.; Yang, F.; Yu, M.; Wang, C.; Cui, S.; Hong, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, M.; Zhao, C.; Ding, M.; Sun, W.; Liu, Z.; Sun, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X. The Jun/miR-22/HuR regulatory axis contributes to tumourigenesis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer 2018, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Cheng, X.; Wang, R.; Tan, Y.; Ge, M.; Li, D.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, H. Restoration of microRNA function impairs MYC-dependent maintenance of MLL leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2484–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, D.; Jayaraj, G.; Suryawanshi, H.; Agarwala, P.; Pore, S. K.; Banerjee, R.; Maiti, S. The tuberculosis drug streptomycin as a potential cancer therapeutic: inhibition of miR-21 function by directly targeting its precursor. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2012, 51, 1019–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qian, X.; Han, L.; Zhang, K.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, A.; Pu, P.; Kang, C. AC1MMYR2, an inhibitor of dicer-mediated biogenesis of Oncomir miR-21, reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses tumor growth and progression. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 5519–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumireddy, K.; Young, D. D.; Xiong, X.; Hogenesch, J. B.; Huang, Q.; Deiters, A. Small-molecule inhibitors of microrna miR-21 function. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2008, 47, 7482–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasinghe, N. S.; Manavalan, T. T.; Dougherty, S. M.; Riggs, K. A.; Li, Y.; Klinge, C. M. Estradiol downregulates miR-21 expression and increases miR-21 target gene expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 2584–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C. S.; Wang, X. M.; Zhang, S. Q.; Meng, L. S.; Zhu, W. H.; Xu, J.; Lu, S. M. Discovery of 4-benzoylamino-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)benzamides as novel microRNA-21 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 2015, 23, 6510–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naro, Y.; Thomas, M.; Stephens, M. D.; Connelly, C. M.; Deiters, A. Aryl amide small-molecule inhibitors of microRNA miR-21 function. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015, 25, 4793–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velagapudi, S. P.; Gallo, S. M.; Disney, M. D. Sequence-based design of bioactive small molecules that target precursor microRNAs. Nat Chem Biol 2014, 10, 291–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, C.; Pang, H.; Zeng, F.; Cheng, L.; Fang, B.; Ma, J.; Shi, Y.; Hong, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J. Arsenic trioxide suppresses cell growth and migration via inhibition of miR-27a in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 469, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, D.; Jayaraj, G. G.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, S. A molecular-beacon-based screen for small molecule inhibitors of miRNA maturation. ACS Chem Biol 2013, 8, 930–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs-Disney, J. L.; Disney, M. D. Small Molecule Targeting of a MicroRNA Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Chem Biol 2016, 11, 375–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J. P.; Chirayil, R.; Chirayil, S.; Tom, M.; Head, K. J.; Luebke, K. J. Association of a peptoid ligand with the apical loop of pri-miR-21 inhibits cleavage by Drosha. Rna 2014, 20, 528–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashtan, C. E.; Gross, O. Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Alport syndrome in children, adolescents, and young adults-an update for 2020. Pediatr Nephrol 2021, 36, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashtan, C. E.; Gross, O. Correction to: Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Alport syndrome in children, adolescents, and young adults-an update for 2020. Pediatr Nephrol 2021, 36, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abplanalp, W. T.; Fischer, A.; John, D.; Zeiher, A. M.; Gosgnach, W.; Darville, H.; Montgomery, R.; Pestano, L.; Allée, G.; Paty, I.; Fougerousse, F.; Dimmeler, S. Efficiency and Target Derepression of Anti-miR-92a: Results of a First in Human Study. Nucleic Acid Ther 2020, 30, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Pel, M. E.; Kirschner, M. B.; Cheng, Y. Y.; Mugridge, N.; Weiss, J.; Williams, M.; Wright, C.; Edelman, J. J.; Vallely, M. P.; McCaughan, B. C.; Klebe, S.; Brahmbhatt, H.; MacDiarmid, J. A.; van Zandwijk, N. Restoring expression of miR-16: a novel approach to therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann Oncol 2013, 24, 3128–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Täubel, J.; Hauke, W.; Rump, S.; Viereck, J.; Batkai, S.; Poetzsch, J.; Rode, L.; Weigt, H.; Genschel, C.; Lorch, U.; Theek, C.; Levin, A. A.; Bauersachs, J.; Solomon, S. D.; Thum, T. Novel antisense therapy targeting microRNA-132 in patients with heart failure: results of a first-in-human Phase 1b randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Heart J 2021, 42, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batkai, S.; Genschel, C.; Viereck, J.; Rump, S.; Bär, C.; Borchert, T.; Traxler, D.; Riesenhuber, M.; Spannbauer, A.; Lukovic, D.; Zlabinger, K.; Hašimbegović, E.; Winkler, J.; Garamvölgyi, R.; Neitzel, S.; Gyöngyösi, M.; Thum, T. CDR132L improves systolic and diastolic function in a large animal model of chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 2021, 42, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olena, A. F.; Patton, J. G. Genomic organization of microRNAs. J Cell Physiol 2010, 222, 540–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V. N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2014, 15, 509–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottosen, S.; Parsley, T. B.; Yang, L.; Zeh, K.; van Doorn, L. J.; van der Veer, E.; Raney, A. K.; Hodges, M. R.; Patick, A. K. In vitro antiviral activity and preclinical and clinical resistance profile of miravirsen, a novel anti-hepatitis C virus therapeutic targeting the human factor miR-122. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015, 59, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmén, J.; Lindow, M.; Schütz, S.; Lawrence, M.; Petri, A.; Obad, S.; Lindholm, M.; Hedtjärn, M.; Hansen, H. F.; Berger, U.; Gullans, S.; Kearney, P.; Sarnow, P.; Straarup, E. M.; Kauppinen, S. LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2008, 452, 896–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanford, R. E.; Hildebrandt-Eriksen, E. S.; Petri, A.; Persson, R.; Lindow, M.; Munk, M. E.; Kauppinen, S.; Ørum, H. Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Science 2010, 327, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H. L.; Reesink, H. W.; Lawitz, E. J.; Zeuzem, S.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Patel, K.; van der Meer, A. J.; Patick, A. K.; Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; Persson, R.; King, B. D.; Kauppinen, S.; Levin, A. A.; Hodges, M. R. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N Engl J Med 2013, 368, 1685–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A. M.; Ruckman, J.; Pestano, L. A.; Hopkins, R. D.; Rodgers, R. C.; Marshall, W. S.; Rubin, P.; Escolar, D. SOLAR: A PHASE 2, GLOBAL, RANDOMIZED, ACTIVE COMPARATOR STUDY TO INVESTIGATE THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF COBOMARSEN IN SUBJECTS WITH MYCOSIS FUNGOIDES (MF). Hematological Oncology 2019, 37, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfeld, C.; Pacheco, T.; Foss, F. M.; Halwani, A. S.; Porcu, P.; Seto, A. G.; Ruckman, J.; Landry, M. L.; Jackson, A. L.; Pestano, L. A.; Dickinson, B. A.; Sanseverino, M.; Rodman, D. M.; Gordon, G.; Marshall, W. Preliminary Results of a Phase 1 Trial Evaluating MRG-106, a Synthetic microRNA Antagonist (LNA antimiR) of microRNA-155, in Patients with CTCL. Blood 2016, 128, 1829–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Suhr, O. B.; Dyck, P. J.; Litchy, W. J.; Leahy, R. G.; Chen, J.; Gollob, J.; Coelho, T. Trial design and rationale for APOLLO, a Phase 3, placebo-controlled study of patisiran in patients with hereditary ATTR amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. BMC Neurol 2017, 17, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D. P.; Conde, J. Gold Nanoconjugates for miRNA Modulation in Cancer Therapy: From miRNA Silencing to miRNA Mimics. ACS Materials Au 2022, 2, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durso, M.; Gaglione, M.; Piras, L.; Mercurio, M. E.; Terreri, S.; Olivieri, M.; Marinelli, L.; Novellino, E.; Incoronato, M.; Grieco, P.; Orsini, G.; Tonon, G.; Messere, A.; Cimmino, A. Chemical modifications in the seed region of miRNAs 221/222 increase the silencing performances in gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 111, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
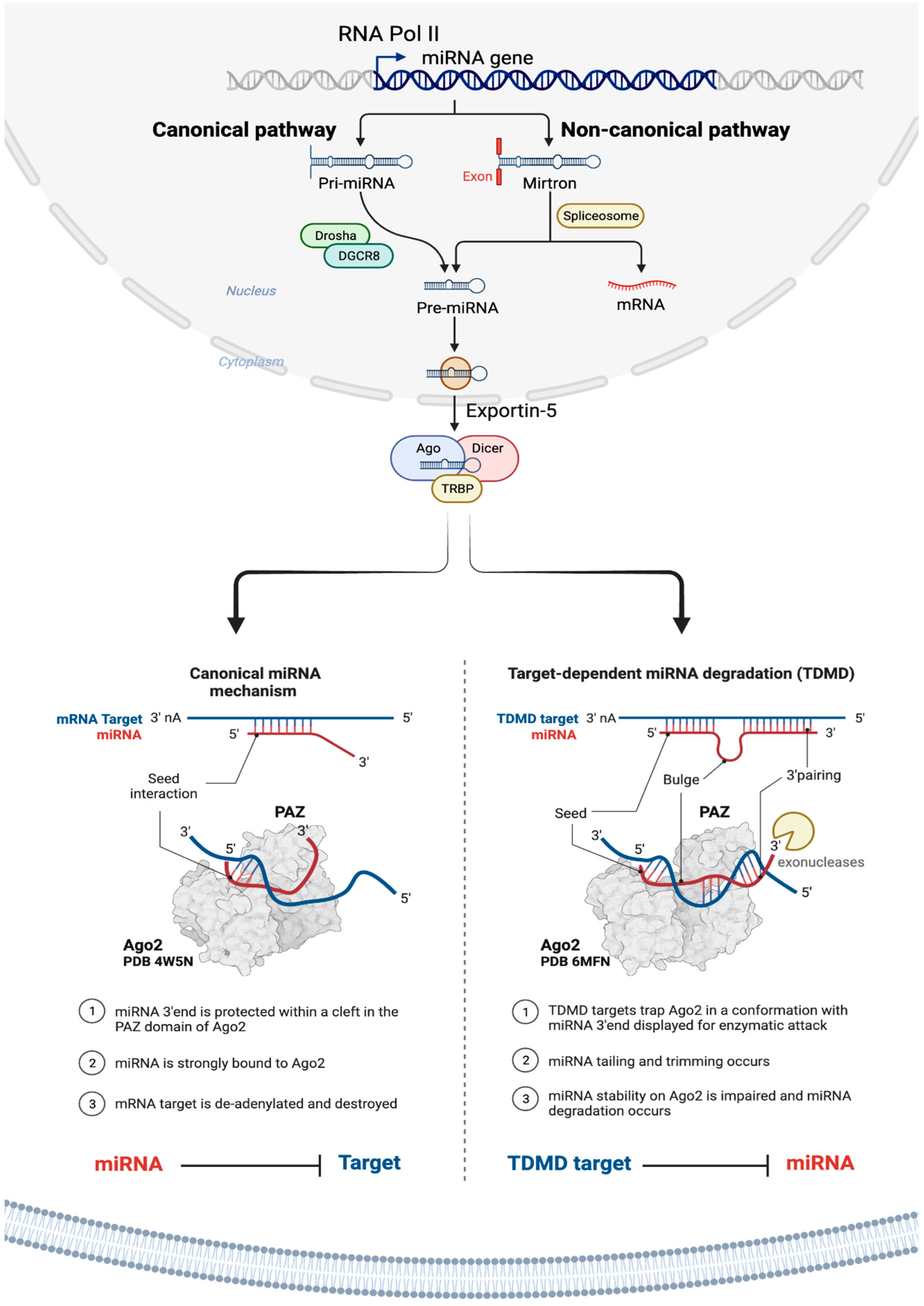
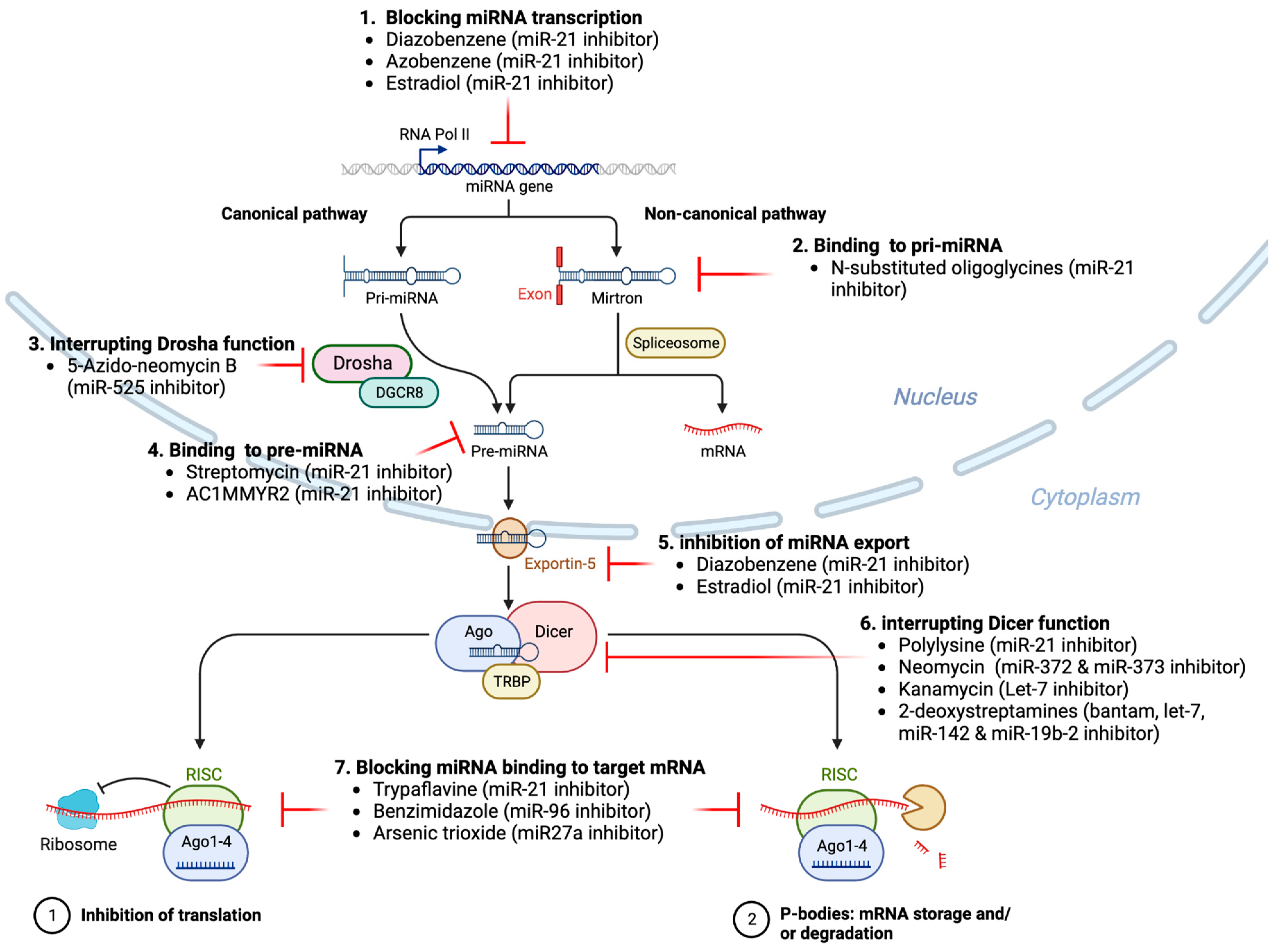

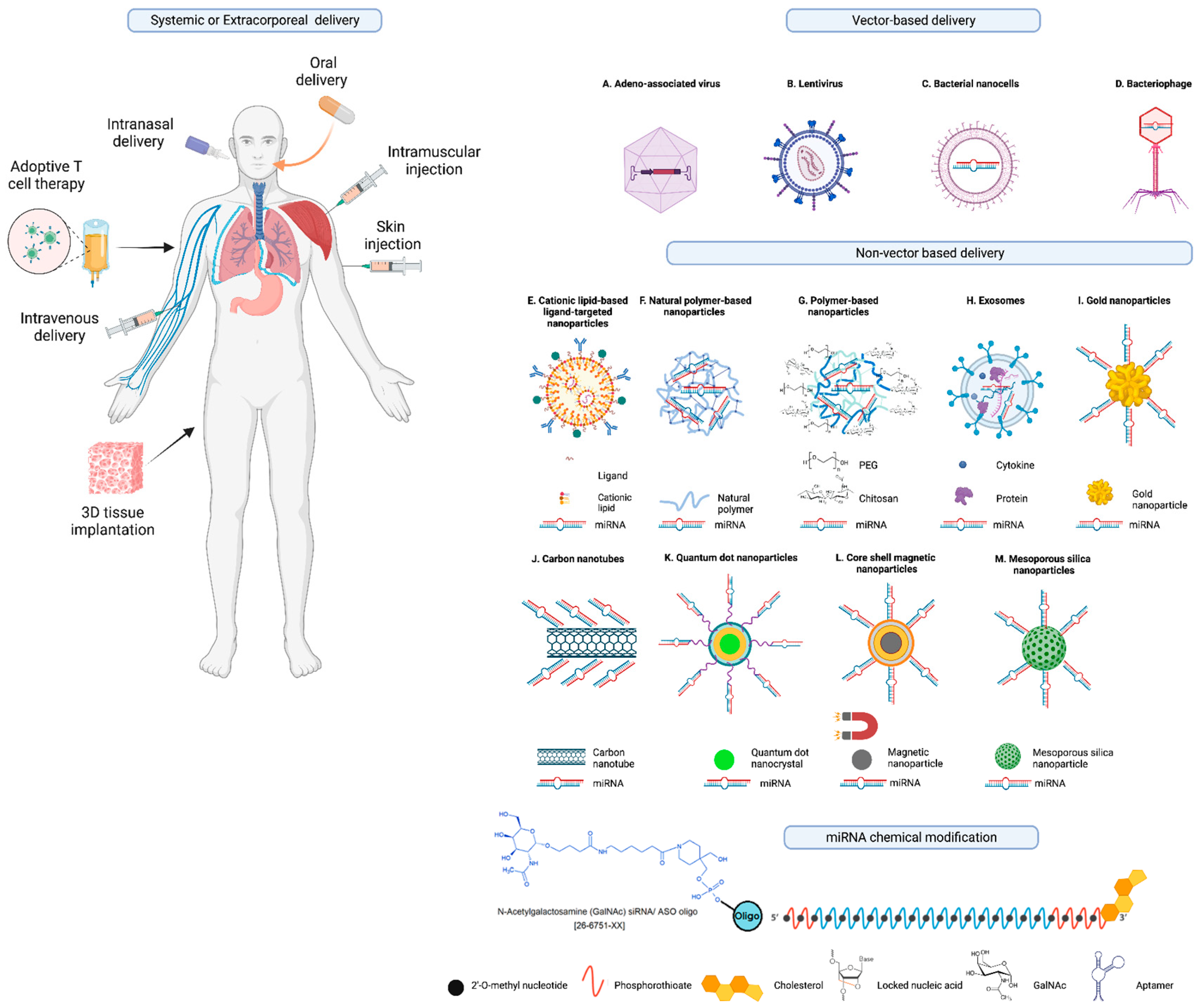
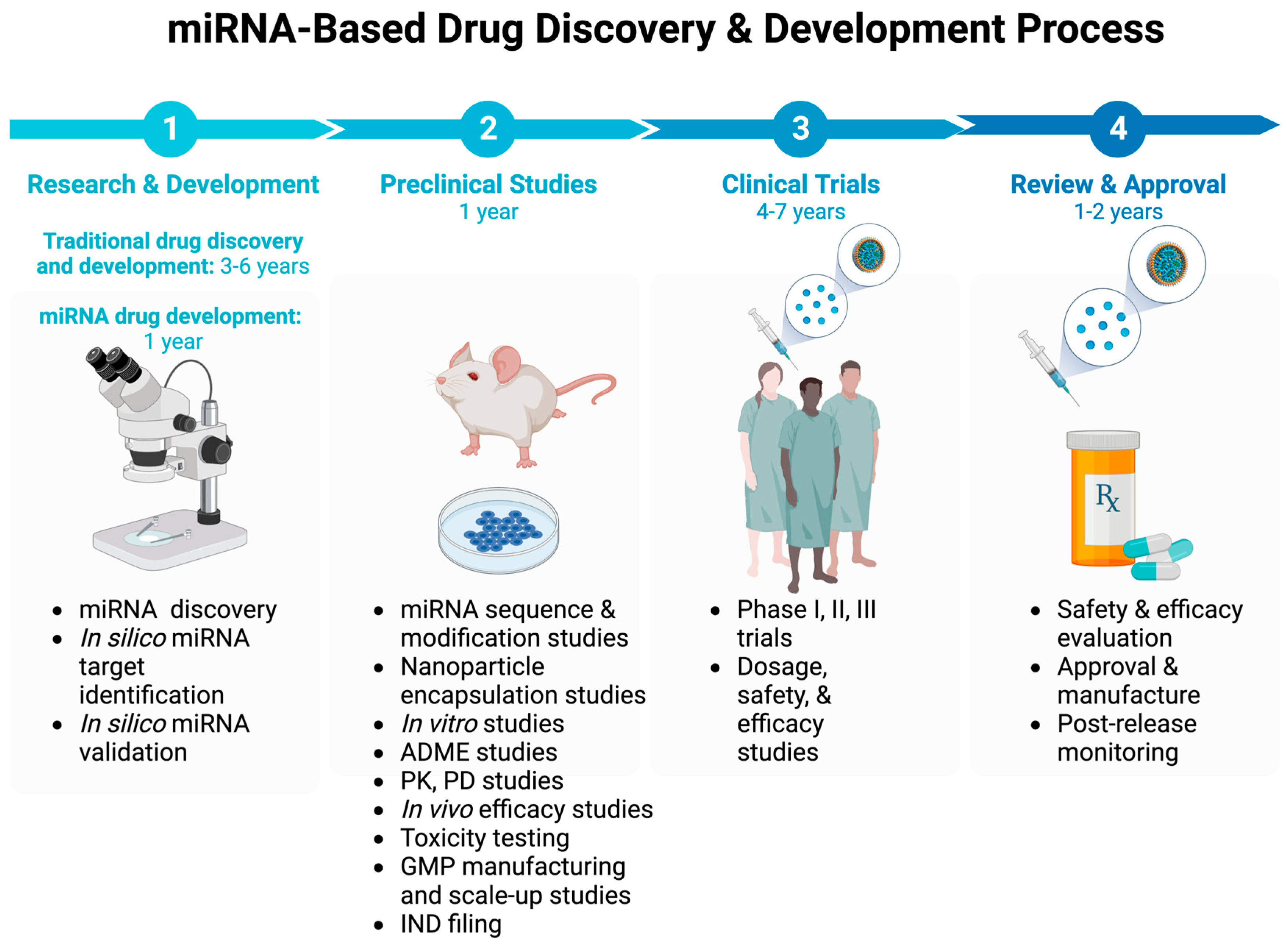
| Therapeutic molecule | Target miRNA | Disease | Biopharmaceutical company | Stage of development |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG-012 | miRNA-21 | Alport nephropathy | Regulus therapeutics (with the strategic alliance with Genzyme) | Preclinical stage |
| MGN-1374 | miRNA-15 and miR-195 | Post-myocardial infarction | miRagen therapeutics | Preclinical stage |
| MGN-2677 | miR-143/145 | Vascular disease | miRagen therapeutics | Preclinical stage |
| MGN-4220 | miR-29 | Cardiac fibrosis | miRagen therapeutics | Preclinical stage |
| MGN-4893 | miR-451 | For the treatment of disorders like abnormal red blood cell production | miRagen therapeutics. | Preclinical stage |
| MGN-5804 | miR-378 | Cardiometabolic disease | miRagen therapeutics | Preclinical stage |
| MGN-6114 | miR-92 | Peripheral arterial disease | miRagen therapeutics | Preclinical stage |
| MGN-9103 | miR-208 | Chronic heart failure | miRagen therapeutics | Preclinical stage |
| MRG-107 | miR-155 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | miRagen therapeutics | Completed preclinical stage |
| miRNA drug name | Targeted miRNA | Study Title | Mode of action | Disease/condition | Mode of delivery | Phase | Status | Clinical trial number(s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-10b | miR-10b | Evaluating the Expression Levels of MicroRNA-10b in Patients With Gliomas | miR-10b as diagnostic and in vitro testing of anti-mir-10b as therapeutic | AstrocytomaOligodendrogliomaOligoastrocytomaAnaplastic AstrocytomaAnaplastic OligodendrogliomaAnaplastic OligoastrocytomaGlioblastomaBrain TumorsBrain Cancer | Observational | Recruiting | NCT01849952 | ||
| INT-1B3 | miR-193a-3p mimic | First-in-Human Study of INT-1B3 in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors | miRNA mimic | Advanced solid tumors | Phase I | Recruiting | NCT04675996 | NA | |
| AMT-130 | Artificial miRNA | Safety and Proof-of-Concept (POC) Study With AMT-130 in Adults With Early Manifest Huntington’s Disease | A miRNA expression | Huntington disease | Stereotaxic infusion/viral transfer (adeno-associated vector) | Phase I | Ongoing | NCT04120493 | [23,24,25,195,196,197] |
| RG-012/lademirsen/SAR339375 | miR-21 | A Study of RG-012 in Subjects With Alport Syndrome | Anti-miR-21 Lademirsen—also known as RG-012, RG456070 or (SAR339375) | Alport syndrome | Subcutaneous injection/chemical modification (phosphorothioate) | Phase II | Completed | NCT03373786 | [209,222,253,254] |
| RG-012/lademirsen/SAR339375 | miR-21 | Study of Lademirsen (SAR339375) in Patients With Alport Syndrome | Anti-miR-21 Lademirsen—also known as RG-012, RG456070 or (SAR339375) | Alport syndrome | Subcutaneous injection/chemical modification (phosphorothioate) | Phase II | Terminated | NCT02855268 | [209,222,253,254] |
| RGLS4326 | miR-17 | A Study of RGLS4326 in Patients With Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease | Anti-miR-17 | Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease | Administered via subcutaneous injection | Phase I | Completed | NCT04536688 | |
| RG-125/AZD4076 | miR-103/107 | A Study to Assess the Safety and Tolerability of Single Doses of AZD4076 in Healthy Male Subjects | Anti-miR | Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) | Subcutaneous injection/biomolecule conjugation (GalNAc) | Phase I | Active, not recruiting | NCT02612662, NCT02826525 | [207,208,209] |
| RG-125/AZD4076 | miR-103/107 | AZD4076 in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease | Anti-miR | T2DM With NAFLD | Subcutaneous injection/biomolecule conjugation (GalNAc) | Phase I | Completed | NCT02826525 | [207,208,209] |
| MRG-110 | miR-92a | Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of MRG-110 Following Intradermal Injection in Healthy Volunteers | Anti-miR | Healthy Volunteer | Skin injection/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase I | Completed | NCT03603431 | [159,255] |
| MesomiR 1 | miR-16 | MesomiR 1: A Phase I Study of TargomiRs as 2nd or 3rd Line Treatment for Patients With Recurrent MPM and NSCLC | miRNA mimic | Malignant pleural mesothelioma, non–small cell lung cancer | Intravenously/vehicle transfer (nonliving bacterial nanocells (EDVs or TargomiRs) | Phase I | Completed | NCT02369198 | [162,200,256] |
| CDR132L | miR-132 | Clinical Study to Assess Safety, PK and PD Parameters of CDR132L | Anti-miR | Heart failure | Intravenously/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase I | Completed | NCT04045405 | [257,258] |
| Remlarsen/MRG-201 | miR-29 | Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Remlarsen (MRG-201) Following Intradermal Injection in Subjects With a History of Keloids | miRNA mimic | Keloid disorder | Skin injection/biomolecule conjugation (cholesterol) | Phase II | Completed | NCT03601052 | [160,259,260] |
| Miravirsen/SPC3649 | miR-122 | Long-Term Extension Study of Miravirsen Among Participants With Genotype 1 Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC) Who Have Not Responded to Pegylated-Interferon Alpha Plus Ribavirin | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase IIPhase IIPhase IIPhase IIPhase IIPhase I | CompletedCompletedCompletedUnknownUnknownCompleted | NCT02508090NCT02508090, NCT02452814, NCT01200420, NCT01872936, NCT01727934, NCT01646489 | [152,261,262,263,264] |
| Miravirsen/SPC3649 | miR-122 | Long Term Extension Study is Designed to Monitor Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Miravirsen Sodium in Combination With Telaprevir and Ribavirin in Subjects With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1 Infection | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase II | Completed | NCT02452814 | [152,261,262,263,264] |
| Miravirsen/SPC3649 | miR-122 | Multiple Ascending Dose Study of Miravirsen in Treatment-Naïve Chronic Hepatitis C Subjects | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase IIPhase IIPhase IIPhase I | CompletedUnknownUnknownCompleted | NCT01200420 | [152,261,262,263,264] |
| Miravirsen/SPC3649 | miR-122 | Miravirsen in Combination With Telaprevir and Ribavirin in Null Responder to Pegylated-Interferon Alpha Plus Ribavirin Subjects With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase IIPhase IIPhase I | Unknown | NCT01872936 | [152,261,262,263,264] |
| Miravirsen/SPC3649 | miR-122 | Miravirsen Study in Null Responder to Pegylated Interferon Alpha Plus Ribavirin Subjects With Chronic Hepatitis C | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase IIPhase IIPhase I | Unknown | NCT01727934 | [152,261,262,263,264] |
| Miravirsen/SPC3649 | miR-122 | Drug Interaction Study to Assess the Effect of Co-Administered Miravirsen and Telaprevir in Healthy Subjects | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase IIPhase IIPhase I | Completed | NCT01646489 | [152,261,262,263,264] |
| RG-101 | miR-122 | A Randomized, Multi-Center, Phase 2 Study to Evaluate Safety and Efficacy of Subcutaneous Injections of RG-101 in Combination with Oral Agents in Treatment Naïve, Genotype 1 and 4, Chronic Hepatitis. | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/biomolecule conjugation (GalNAc) | Phase II | EudraCT numbers 2015-001535-21, 2015-004702-42, 2016-002069-77 | [156,209,210] | |
| RG-101 | miR-122 | A Multi-Center, Parallel Group, Open-Label, Phase 2 Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of a Single Subcutaneous Injection of RG-101 Combined with Oral GSK2878175 | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/biomolecule conjugation (GalNAc) | Phase II | EudraCT numbers 2015-004702-42 | [156,209,210] | |
| RG-101 | miR-122 | An Observational Long-Term Safety and Efficacy Follow-Up Study of Subjects Who Have Previously Received RG-101 | Anti-miR | Chronic hepatitis C virus | Subcutaneous injection/biomolecule conjugation (GalNAc) | Observational | Unknown | EudraCT numbers 2016-002069-77 | [156,209,210] |
| MRX34 | miR-34a | A Multicenter Phase I Study of MRX34, MicroRNA miR-RX34 Liposomal Injection | miRNA mimic | Primary Liver CancerSCLCLymphomaMelanomaMultiple MyelomaRenal Cell CarcinomaNSCLC | Intravenously/vehicle transfer (liposomal) | Phase I | Terminated (5 immune related serious adverse events) | NCT01829971 | [29,32,133][65,82,83] |
| MRX34 | miR-34a | Pharmacodynamics Study of MRX34, MicroRNA Liposomal Injection in Melanoma Patients With Biopsy Accessible Lesions | miRNA mimic | Solid tumors (e.g., hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, SCLC, NSCLC, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, renal cell carcinoma | Intravenously/vehicle transfer (liposomal) | Phase IPhase II | Withdrawn (5 immune related serious adverse events in Phase I) | NCT02862145 | [29,32,133][65,82,83] |
| Cobomarsen/MRG-106 | miR-155 | Anti-miR | Mycosis fungoides (MF)Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma (CTCL)Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL), ABC SubtypeAdult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (ATLL) | Intravenously/chemical modification (LNA) | Phase IPhase IIPhase II | CompletedTerminatedTerminated | NCT02580552, NCT03713320, NCT03837457 | [157,265,266] | |
| Serum MicroRNA-25 | miR-25 | Serum miR-25 as diagnostic | Pancreatic cancer | Serum miR-25 | Observational | Not yet recruiting | NCT03432624 | ||
| Patisiran (ALN-TTR02), | RNAi therapeutic | Transthyretin (TTR)-Mediated Amyloidosis | ALN-TTR02 administered by intravenous infusion | Phase III | Completed | NCT01960348 | [267] | ||
| miR-10 | miR-10 | Evaluating the Expression Levels of MicroRNA-10b in Patients With Gliomas | anti-miR-10 | Glioma | Evaluating the expression levels of microRNA-10b in patients with gliomas | Observational | Recruiting | NCT01849952 |
| Small molecule inhibitors of miRNAs | Target miRNAs | Mechanism of action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trypaflavine | miR-21 | Blocking the assembly of miR-21 with Ago2 | [175] |
| Streptomycin | miR-21/ miR-27a | Blocking the cleavage of pre-miR-21 by Dicer | [242] |
| AC1MMYR2 | miR-21 | Blocking the cleavage of pre-miR-21 to produce mature miR-21 | [243] |
| Diazobenzene | miR-21 | Inhibition the transcription of miR-21 gene | [244] |
| Azobenzene | miR-21 | Inhibition the transcription of miR-21 gene | [244] |
| Estradiol | miR-21 | Inhibition the transcription of miR-21 gene | [245] |
| Polylysine | miR-21 | Blocking the formation of mature of pre-miR-21 by the inhibition of Dicer | [175] |
| 4-benzoylamino-N-(prop-2-yn- 1-yl)benzamides | miR-21 | Up-regulation of PDCD4, the function target of miR-21 | [246] |
| Arylamide derivatives | miR-21 | Blocking the mature of pre-miR-21 | [247] |
| Kanamycin A | Let-7/ miR-27a | Binding to pre-let-7 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 1 | Let-7 | Binding to pre-let-7 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 2 | Let-7 | Binding to pre-let-7 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 3 | Let-7 | Binding to pre-let-7 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 4 | Let-7 | Binding to pre-let-7 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 5 | Let-7 | Binding to pre-let-7 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 6 | Let-7 | Binding to pre-let-7 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 7 | Bantam | Binding to pre-bantam and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 8 | miR-142 | Binding to pre-miR-142 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| 2-DOS Compound 9 | miR-19b-2 | Binding to pre-miR-19b-2 and blocking the function of Dicer | [176] |
| NSC 158959 | miR-122 | Inhibition of the transcription of miR-122 | [177] |
| NSC 5476 | miR-122 | Inhibition of the transcription of miR-122 | [177]) |
| Benzimidazole | miR-96 | Up-regulation of FOXO1, the function target of miR-21 | [248] |
| 2-methoxy-1,4-naphthalenequin | miR-1 | Down-regulation the expression level of miR-1 | [183] |
| Arsenic trioxide | miR-27a | Down-regulation the expression level of miR-27a | [249] |
| Neomycin | miR-27a | Blocking the mature of miR-27a by the inhibition of Dicer | [250] |
| Amikacin | miR-27a | Blocking the mature of miR-27a by the inhibition of Dicer | [250] |
| Tobramycin | miR-27a | Blocking the mature of miR-27a by the inhibition of Dicer | [250] |
| 5″-azido-neomycin B | miR-525 | Binding to the processing site of Drosha to block the generation of pre- miR-525 | [251] |
| N-substituted oligoglycines | miR-21 | A specific ligand binding with pri-miR-21. | [252] |
| 1 | What methods can be used to effectively guide therapeutic miRNAs/miRNA inhibitors to their intended target tissue and cells in vivo? |
| 2 | How can the design of miRNA/miRNA-based drugs and delivery vehicles be optimized to reduce or, ideally, eliminate unintended impacts on non-targeted cells? |
| 3 | What other strategies can be used to improve more accurate targeting for miRNA/miRNA inhibitor therapeutics? |
| 4 | Is there a risk of incompatibilities when using diverse carrier materials for advanced miRNA/miRNA inhibitor-based drug delivery, which may lead to undesired interactions between the materials and miRNA therapeutics? |
| 5 | Is there a risk of incompatibilities when using miRNA/miRNA inhibitor therapeutics in combination with traditional drugs pose the risk of incompatibilities? |
| 6 | Do modifications of miRNA/miRNA inhibitors such as LNA miRNA/miRNA inhibitors and other synthetic miRNAs, as well as agents such cell-permeable molecules, delivery methods such as biodegradable 3D matrices, carriers like functionalized metals, viral transfer systems, or biomolecule combinations such as aptamers invoke immunogenic responses? If so, can the activation of immunogenic responses be ameliorated through the masking of reactive components or moieties? |
| 7 | What is the level of risk associated with genomic integrations of viral transduction constructs that carry miRNA or miRNA inhibitors? |
| 8 | What is the impact of the expression of endogenous miRNAs and mRNAs on exogenously delivered therapeutic miRNAs and miRNA inhibitors which may be also affected by factors like cell type, cell cycle, and the cellular environment? |
| 9 | What is the necessary dosage for particular administration techniques for miRNA/miRNA inhibitors, such as skin injection, infusion, or inhalation, and for carrier-based methods like biodegradable 3D matrices? |
| 10 | How can the administration of miRNA/miRNA inhibitor therapeutic doses be regulated along intricate in vivo delivery pathways? |
| 11 | Is it possible to achieve consistent and sustainable rates of cellular uptake of miRNA/miRNA inhibitor therapeutics under varying in vivo conditions? |
| 12 | In what ways can dosing of miRNA mimics and inhibitors support the desired gene targeting outcome? |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





