1. Introduction
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium [
1], that produces catalase, oxidase, and urease [
2]. It is estimated that approximately 4.4 billion people have bacteria colonizing their stomach mucosa.
H. pylori can cause a series of gastric diseases, including peptic ulcer disease, gastric adenocarcinoma, atrophic gastritis, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma [
3]. Three morphological forms of
H. pylori have been described. Spiral forms are viable, culturable, and have a strong colonizing ability; coccoid forms are viable but not culturable (VBNC) and represent persistent forms of this bacterium; and degenerate forms are characterized by the breakdown of the cytoplasmic membrane and are most likely a manifestation of bacterial death [
4]. The transition from the spiral to the coccoid form is caused by extreme conditions, e.g. changes in temperature, pH, or the presence of antibiotics [
5]. There have been reports for a long time about the possibility of converting
H. pylori from the coccoid to the spiral form, stimulated by an enriched environment [
6,
7].
It is commonly believed that
H. pylori infections in humans are related to gastritis [
8]. Bacteria in the stomach survive thanks to many virulence factors, including urease, vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA), and spiral shape, and it is suspected that they also form a bacterial biofilm in the stomach [
9]. But there are different routes of infection possible. There have been reports that bacteria have been isolated from dental plaque and drinking water sources [
8]. Young et al. [
10] reported that the spiral and viable coccoid forms of
H. pylori are present in the oral cavity in the form of biofilm [
2,
8]. It has been proven also that bacteria can form biofilms in water systems and can survive from > 10 days (spiral form) to one year (VBNC coccoidal form) in fresh water [
8]. Both places where bacteria are present outside the gastric mucosa are important from the point of view of both the spread of infections from one person to another and recurrent infections in people undergoing antibiotic therapy [
8].
Biofilm is a population of bacteria attached to abiotic and biotic surfaces, surrounded on the outside by a polymeric substance. In the case of
Helicobacter pylori, biofilm formation begins with a spiral form that attaches to the surface, and then morphological changes of the cells occur, creating various forms: spiral, rod-shaped, curved, coccoid, and filamentous. Finally, all cells transform into a coccoid form that is resistant to environmental factors [
11]. Biofilm has tolerance of, or resistance to, antibiotics by expression of efflux pumps (transport proteins with roles in the export of toxic substances, including antibiotics) [
1].
First-line antibiotics for the treatment of
H. pylori infections are proton pump inhibitor, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin (may be replaced by levofloxacin) or metronidazole. It is recommended that the combination of drugs is used for 10–14 days. After failure, second-line therapy is introduced: proton pump inhibitor, bismuth, metronidazole, and tetracycline [
12]; other introduced compounds include vonoprazan and rifabutin [
3].
H. pylori resistance to antibiotics in Europe currently remains at a primary resistance level of 21.8% for clarithromycin, 15.8% for levofloxacin, and 38.9% for metronidazole. In the current situation, special attention should be paid to the appropriate level of
H. pylori eradication, and alternative, effective methods of eliminating the pathogen should be proposed [
13].
In accordance with WHO recommendations, new compounds that act on resistant bacteria are being sought. Extracts from plant raw materials containing secondary metabolites such as flavonoids, terpenes, and saponins offer hope for obtaining compounds with antibacterial properties. Research on plant raw materials to obtain anti-
Helicobacter pylori compounds is being carried out by many research teams [
11,
12,
14,
15,
16,
17]. There are several reports regarding the effects of extracts from plants of the
Rubus spp. genus on
Helicobacter bacteria. Martini et al. [
18] studied the effect of extract from
Rubus ulmifolius growing in Italian forests on
Helicobacter pylori, which showed anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antimicrobial properties. Park et al. [
19] studied the effect of
Rubus crataegifolius extract in the treatment of impotence, inflammation, hepatotoxicity, enuresis, allergic diseases, and antibacterial properties. In turn, Krazue Baranowska et al. [
20] and Krauze Baranowska et al. [
21] studied the influence of raw fruit extracts from 3 cultivar varieties of
Rubus idaeus 'Ljulin', 'Veten', and 'Poranna Rosa', one variety of black raspberry –
Rubus occidentalis 'Litacz', and
R. idaeus 'Willamette' shoot extract on many bacteria, including
H. pylori. Raspberries are rich in phenolic compounds, mainly anthocyanins, ellagitannins, and other phenols, such as flavonoids and phenolic acids, including free ellagic acid conjugates named ellagitannins. The characteristic and predominant ellagitannin in
Rubus berries is sanguiin H-6. However, the effects of the extracts of the plants mentioned above against
Helicobacter pylori biofilm have not yet been investigated.
Some compounds of natural origin and their interactions with antibiotics used in chemotherapy against
H. pylori have also been tested [
13], but there are no studies on synergism with
R. ideaus and
R. occidentalis extracts.
In our publication, we present the results of research on the effects of selected fruit and shoot extracts against the biofilm produced by H. pylori. Additionally, we have developed a new model for testing H. pylori biofilm using intravenous infusions, in which we have shown the possibility of creating and examining such a biofilm.
4. Discussion
In combating H. pylori in the population, it is more important to detect the bacteria and kill them quickly, rather than inhibiting their growth. Therefore, research on the activity of compounds against H. pylori should include the detection of live bacteria.
Various teams studying H. pylori use media to test the activity of different compounds. Tests using the microdilution method (MIC determination) allowed us to demonstrate that Brucella broth with 5% horse serum and resazurin gives the weakest signal in the remaining samples. While the use of brain heart infusion (BHI), Brucella broth, and MTT dye gives clear test results. Further studies allowed us to demonstrate that the Brucella broth medium produces a higher percentage of live bacteria in the biofilm formed on the microtiter plate, which was detected using the MTT marker.
For the colorimetric tests for the estimation of metabolic activity of cells, resazurin and MTT markers were used. NAD(P)H-dependent cellular oxidoreductase enzymes can, under certain conditions, reflect the number of viable cells present. These enzymes are capable of reducing the tetrazolium dye 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) to its insoluble purple-colored formazan. Resazurin (7-hydroxy-3H-phenoxazin-3-one 10-oxide) is a blue dye, itself weakly fluorescent until it is irreversibly reduced to the pink colored and highly red fluorescent resorufin. It is used as an oxidation-reduction indicator in cell viability assays for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Chatterjee et al. [
30] tested extracts of raspberry, cranberry, elderberry, strawberry, bilberry, blueberry, and OptiBerry ® (a blend of the 6 berries) on
H. pylori strain ATCC 49503. They used tryptic soy broth (TSA) supplemented with 5% defibrinated sheep blood. All extracts at the 0.5 and 1% concentration inhibited growth of bacteria by > 70%.
Goodman et al. [
31] analyzed commercially available black raspberry (
Rubus occidentalis; BRB), blackberry (
Rubus fruticosus; BB), and red raspberry (
Rubus idaeus; RRB).
H. pylori PMSS1 was cultured on Brucella broth supplemented with 10% FBS, and it was visualized with a proprietary redox-sensitive tetrazolium dye (2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride [TTC]). Assays were performed in 96-well plates using an OmniLog (Biolog, Hayward, CA, USA) plate reader-incubator. All berry preparations tested had antibacterial activity with complete inhibition of
H. pylori growth at a concentration of about 4%.
Martini et al. [
18] determined the activity of plant leaves from R
ubus ulmifolius. The studies were performed in microtiter plates using Brucella broth–bovine fetal serum, and
H. pylori G21 and 10K strains were tested. They showed that all the isolated polyphenols (ellagic acid, gallic acid, quercetin) and extracts had antibacterial activity against both of the
H. pylori strains. The MBC values of the extract, after 24 h of exposure, against
H. pylori G21 and 10K strains were 1200 µg/mL and 1500 µg/mL, respectively. In turn, after 48 h of exposure, the MBC values were 134 µg/mL and 270 µg/mL, respectively.
Park et al. [
19] determined minimum inhibitory concentrations using Brucella media containing 10% FBS in the Petri plates. Agar plates contained 0, 10, 50, 75, 100, 150, and 200 μg/mL of plant extract:
Rubus crataegifolius (RF, Family: Rosaceae) or
Ulmus macrocarpa (UL, Family: Ulmaceae). Tests were performed on 2 reference strains of
Helicobacter pylori (ATCC: 43504, SS1) and 11 clinical isolates. RF extract inhibited growth of
H. pylori at 150 μg/mL, whereas UL showed MIC
50 at 200 μg/mL.
Nakase et al. [
32]
tested modified Gingyo-san, several Chinese herbal medicines, and Kampo medicines using Mueller-Hinton broth (CAMHB) supplemented with 10% inactivated FBS, and 25 µg/mL and 10 µg/mL of Ca
2+ and Mg
2+, respectively. Incubation was performed in microaerobic conditions at 37°C for 5 days. The MIC values of the tested extracts against the
H. pylori strains were in the range of 512 to > 8192 µg/mL.
Trung et al. [
33] tested the effects of naringenin (NRG), luteolin (LUT), myricetin (MCT), and protocatechuic acid (PCA) identified in the
Hibiscus rosa sinensis flower against 2 reference strains and 5 clinical isolates of
Helicobacter pylori. MIC was determined by serial dilutions of concentrations of the test compounds in 10% NBS (newborn bovine serum)-supplemented Brucella broth in sterile 96-well plates using resazurin. The MIC values for NRG, LUT, MCT, and PCA were as follows: 100, 125, 150, and 250 mg/L, respectively.
Krzyżak et al. [
9], testing the MICs of myricetin (MYR), used flat-bottomed, ventilated 12-well microtiter plates. MYR comprised a series of dilutions, which were made in brain heart infusion broth supplemented with 7% fetal calf serum. The MIC was taken to be the lowest concentration in which no microbial growth was observed visually after a 3-day microaerophilic incubation at 37°C. The MIC for both tested strains (
H. pylori J99 and Tx30a) were determined in a concentration of 160 µg/mL. The compound was dissolved in DMSO, hence its good penetration through bacterial membranes. The viability of
H. pylori was examined by staining bacterial cells with the LIVE/DEAD kit and analyzing by fluorescence microscopy.
Chen et al. [
23] determined the MIC values of clarithromycin (CLR), amoxicillin (AMX), and rhamnolipid (RHL) by broth dilution assay using BHI broth containing 2% FBS in 96-well microtiter plates. Samples were incubated at 37°C for 48 h in microaerophilic conditions with 200 rpm shaking, and then the OD
600nm was measured by microplate reader. The obtained MIC values were as follows: MICs
90 was 0.96 μg/mL for CLR, 0.06 μg/mL for AMX, while the MIC
90 of RHL was 307.2 μg/mL.
For minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination according to Sposito et al. [
34] MHB supplemented with 50% BFS was added to each well of a 96-well microplate;
H. pylori ATCC 43504 was used for the tests. The essential oil, ethanolic extract, fractions, sub-fractions, casearin J, and hydrolyzed casearin J from
C. sylvestris leaves were tested. For visual reading of the bacterial strains, 0.01% of resazurin aqueous solution was added to each microplate well. The MIC of the ethanol extract and fractions showed MICs ranging from 62.5 to 1000 µg/mL. The ethanol extract was fractionated into 63 subfractions, casearins were detected in fractions marked SF20, SF13, SF46, and SF17, and the range of MIC values was from 250 to > 1000 µg/mL. When tested as a standard, Cas J (casearin J) showed weak antibacterial activity, and the essential oil itself showed an effect of 125 µg/mL.
Research on the
H. pylori biofilm mainly includes tests performed on titration plates or coverslips using Brucella broth fetal calf serum (FCS). First, we wanted to investigate which substrate and dyes would more effectively determine live cells in biofilm grown on titration plates. BHI and Brucella broth with 5% horse serum were used, and the dyes were MTT and TTC. The use of TTC as a dye was due to scientific findings [
35].
Triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (2,3,5-triphenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride) (TTC) is a redox indicator commonly used in biochemical experiments, especially to indicate cellular respiration (for example, to check for the viability of seeds). The white compound is enzymatically reduced to red TPF (1,3,5-triphenylformazan) in living cells due to the activity of various dehydrogenases (enzymes important in the oxidation of organic compounds and thus cellular metabolism).
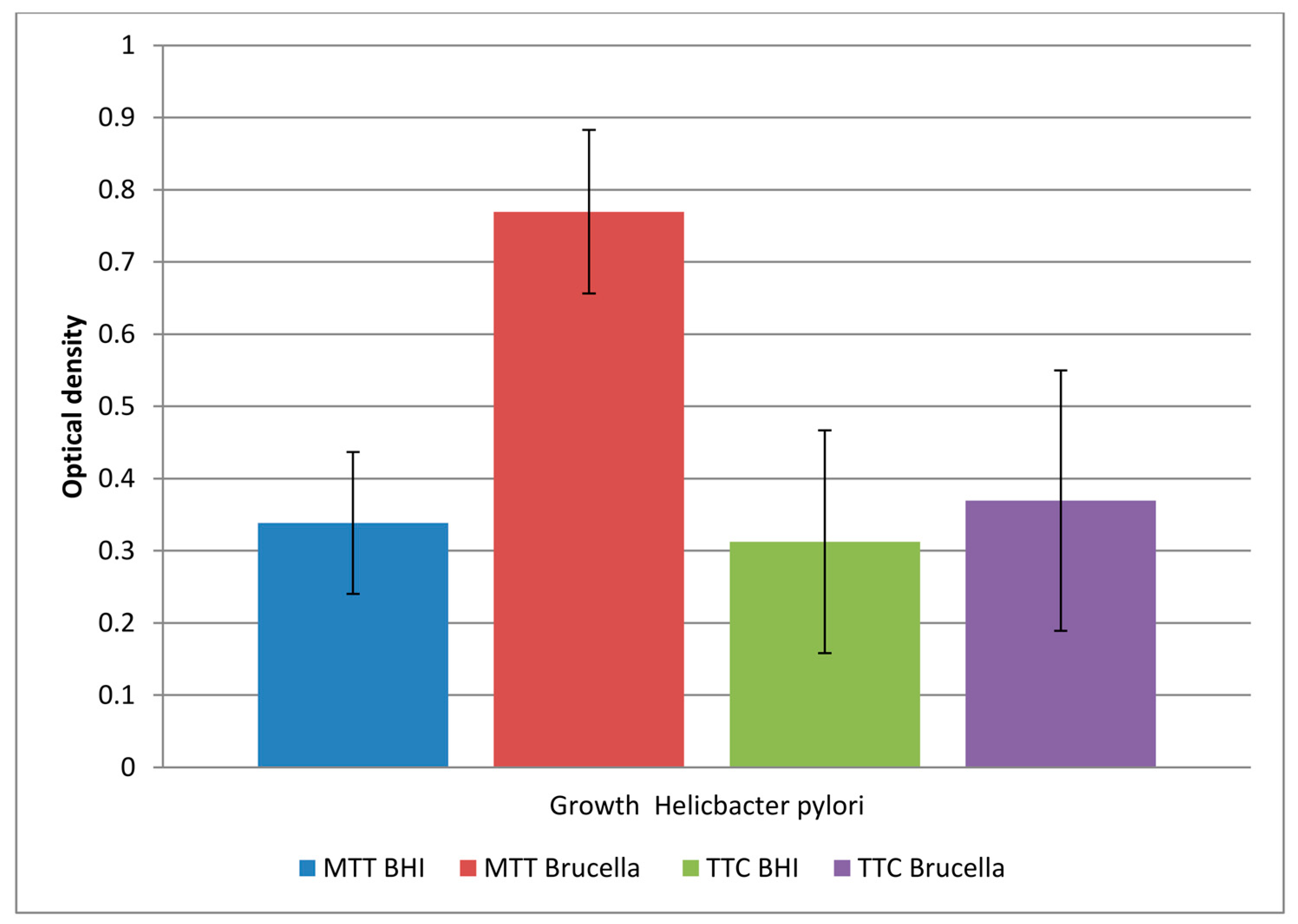
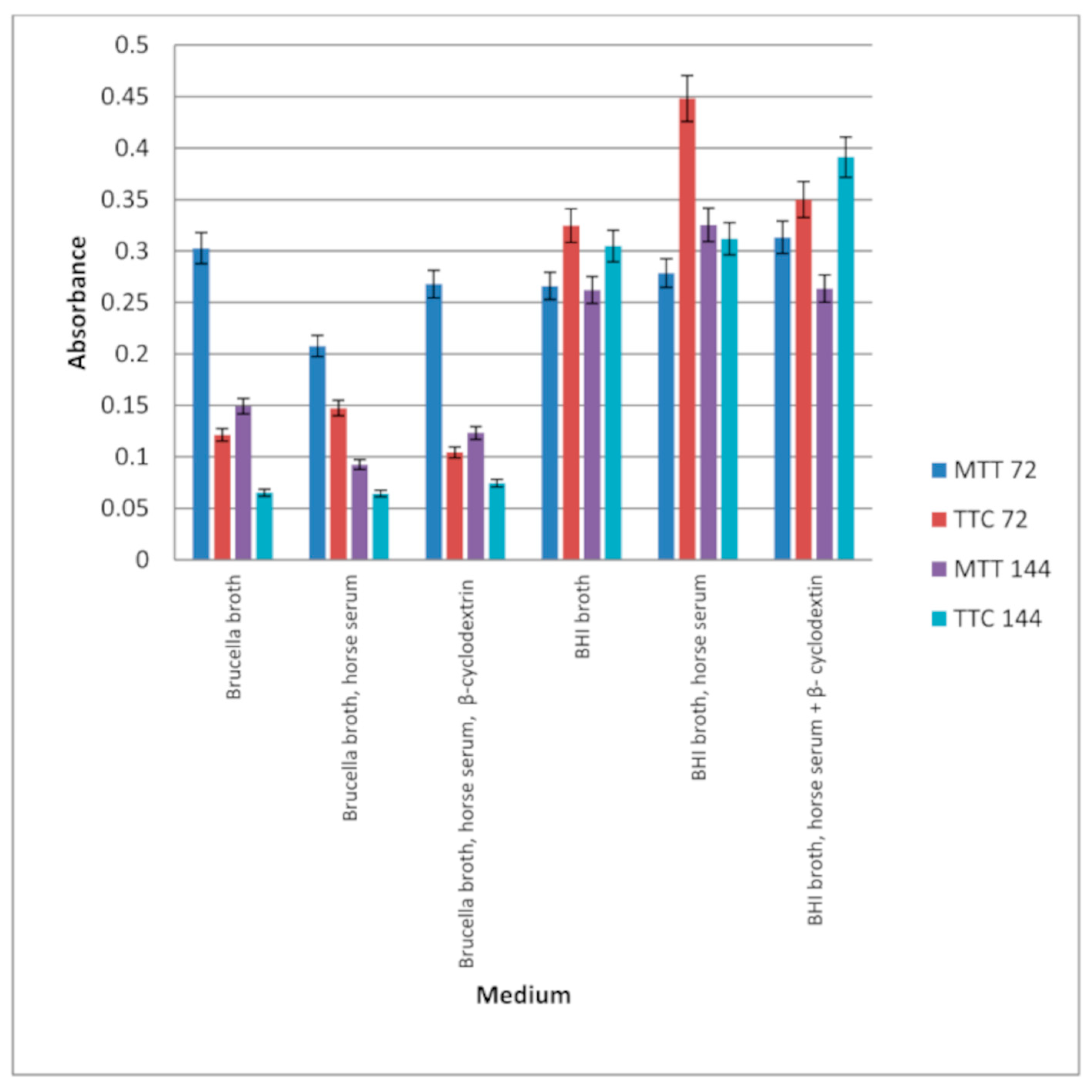
Our research, including testing in a 96-well titration plate in the presence of Brucella and BHI broth, and using TTC and MTT as dyes, showed that
H. pylori can form a biofilm with more viable cells in Brucella than in BHI broth with the addition of 5% horse serum (
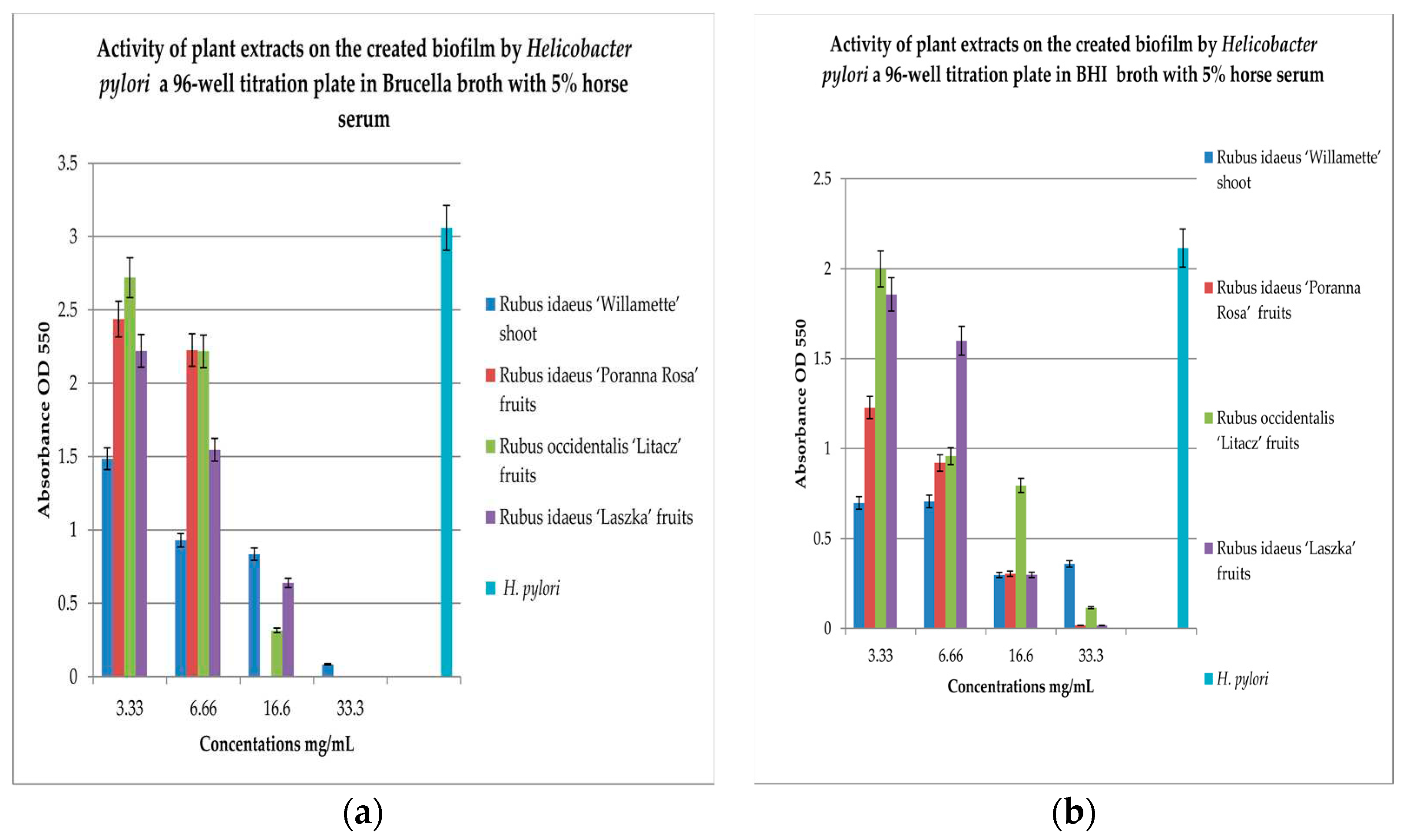
Figure 1). Studies on the effect of extracts on the formation of biofilm by
H. pylori in a 96-well titration plate demonstrated that the extract form
R. idaeus ‘Willamette’ shoot at concentrations of 3.33 mg/mL and 16.6 mg/mL were the most active. While the remaining extracts showed lower activities, depending on the medium used (BHI and Brucella broth with 5% horse serum was used with MTT) relative to the control (
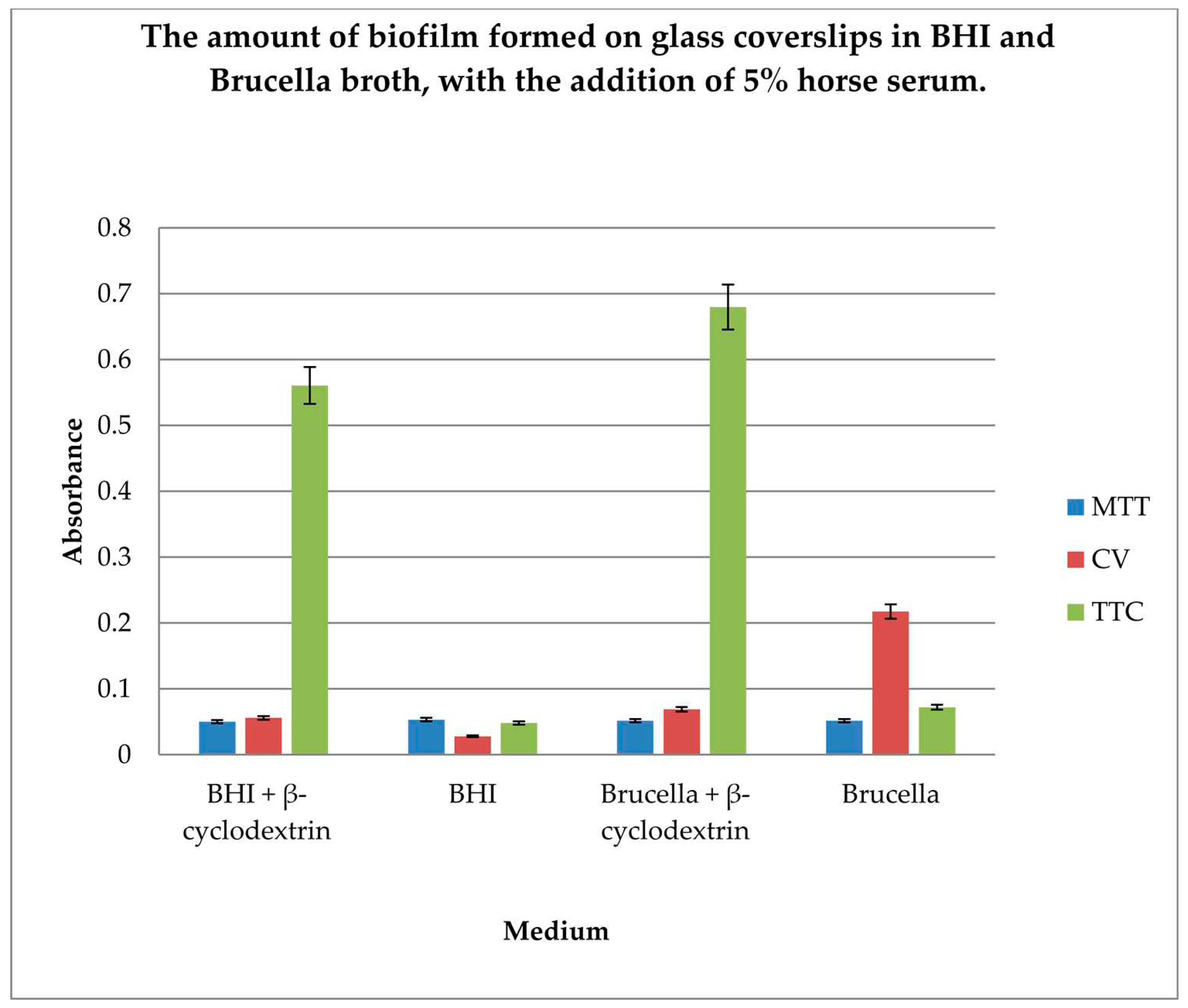
Figure 2a,b). Our studies using coverslips for biofilm formation by
H. pylori demonstrated that the highest level of live cells in biofilm is obtained when cultured in BHI and Brucella broth with the addition of 5% horse serum and 0.1% TTC-labelled β-cyclodextrin. Moreover, the obtained results showed that both media with β-cyclodextrin allow the formation of a biofilm, but only TTC shows how many live bacteria can be found there. The TTC level significantly exceeds that achieved by crystal violet.
Studies showing that H. pylori can form a biofilm on plastics (titration plates, pipes with treated water, on tissues) allow us to assume that bacterial cells may behave similarly if they encounter plastics in higher organisms, such as stents, prostheses, or central insertions. An additional element that helps create these formations is the presence of tissue fluids, including serum and the nutrients it contains. This led us to propose a different research model for H. pylori biofilms.
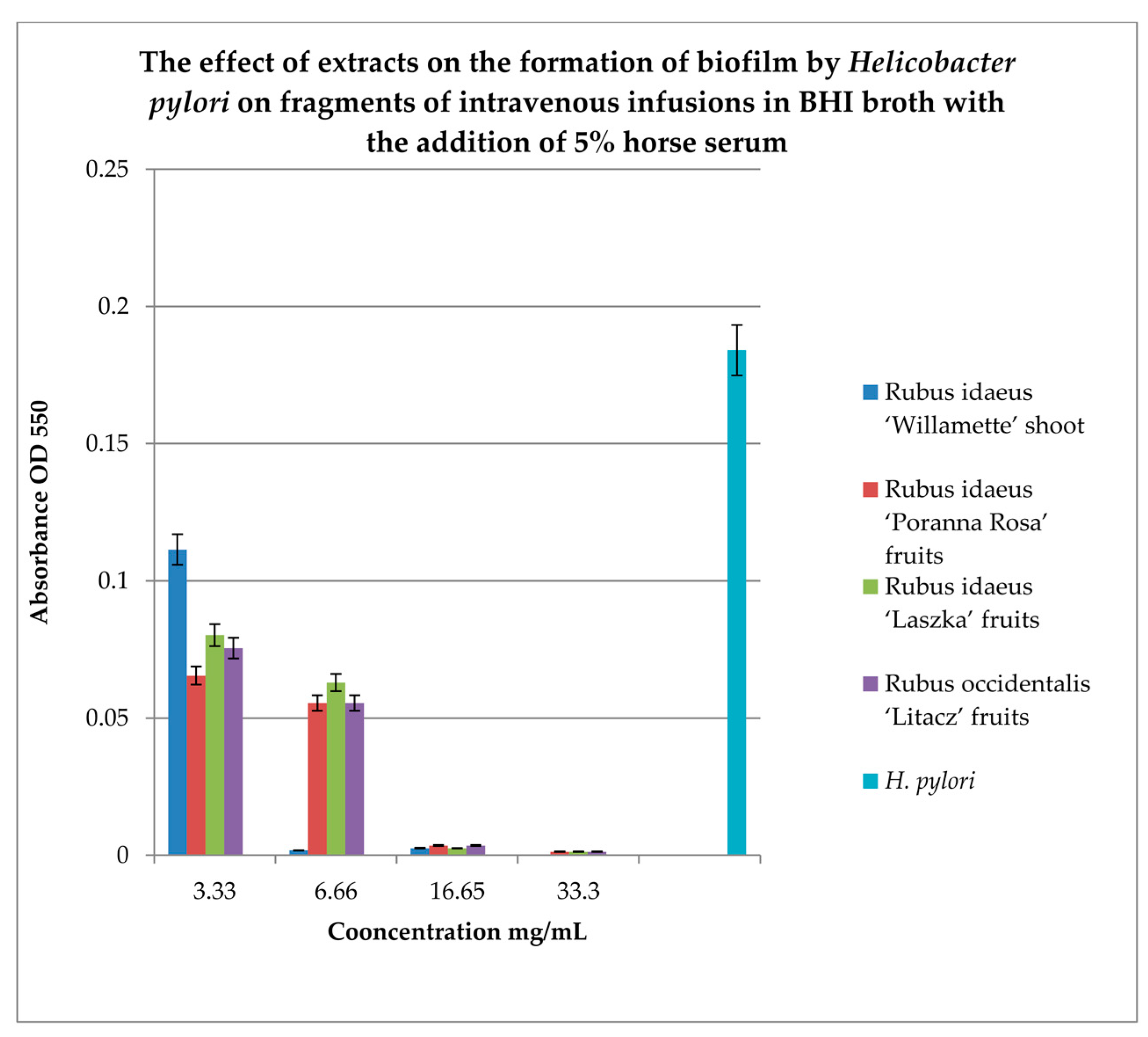
Studies on biofilm formation on the intravenous infusion fragments showed that the highest number of living bacteria in the biofilm, incubated for 3 days (6 days) in BHI broth with horse serum and β-cyclodextrin, were detected using TTC indicator. A large number of live bacteria were also detected in BHI medium containing horse serum, in which TTC was used after 3 days of incubation. Biofilm in BHI broth was detected using MTT and TTC at a similar level. However, more live cells were detected in the biofilm after 72 hours by TTC.
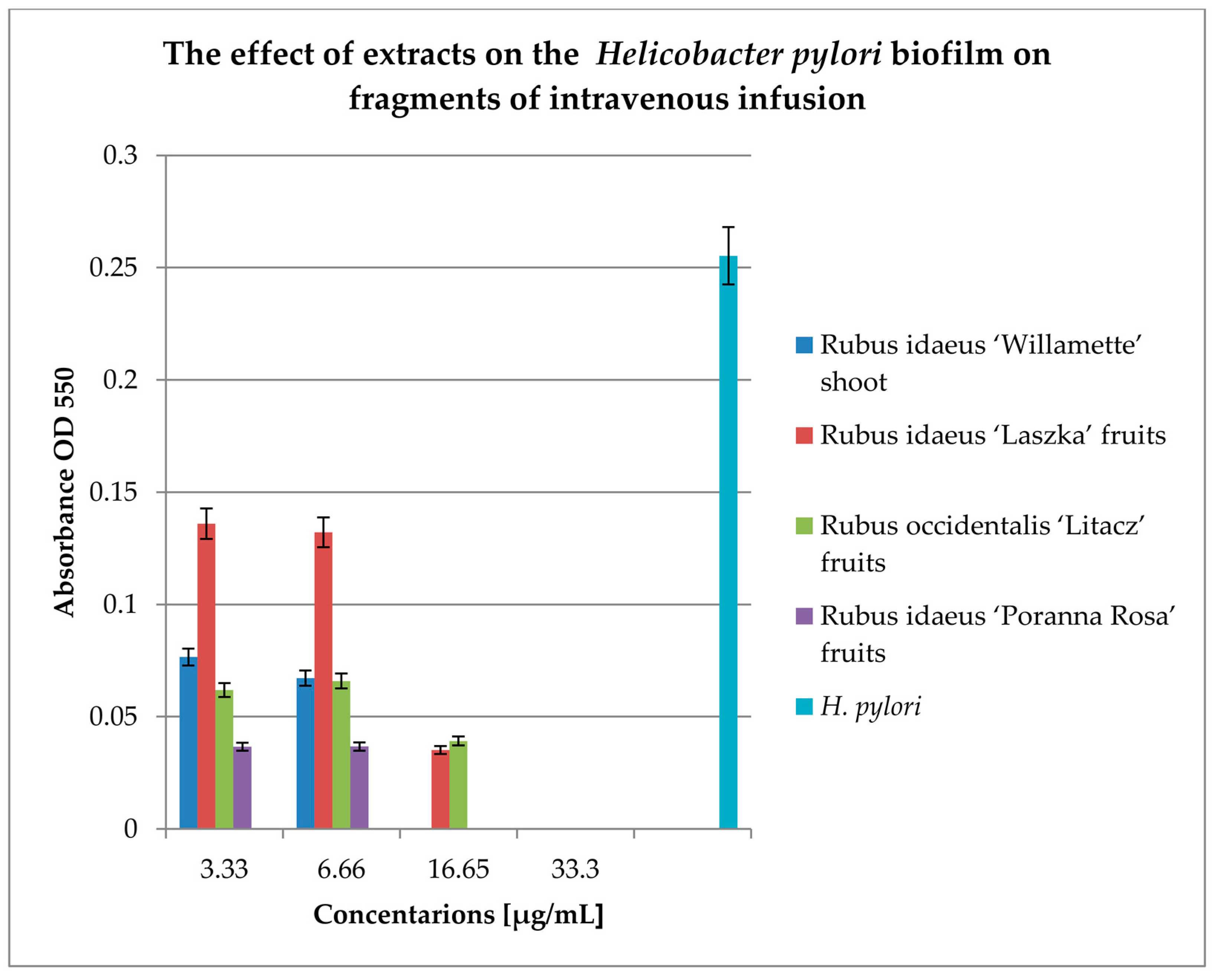
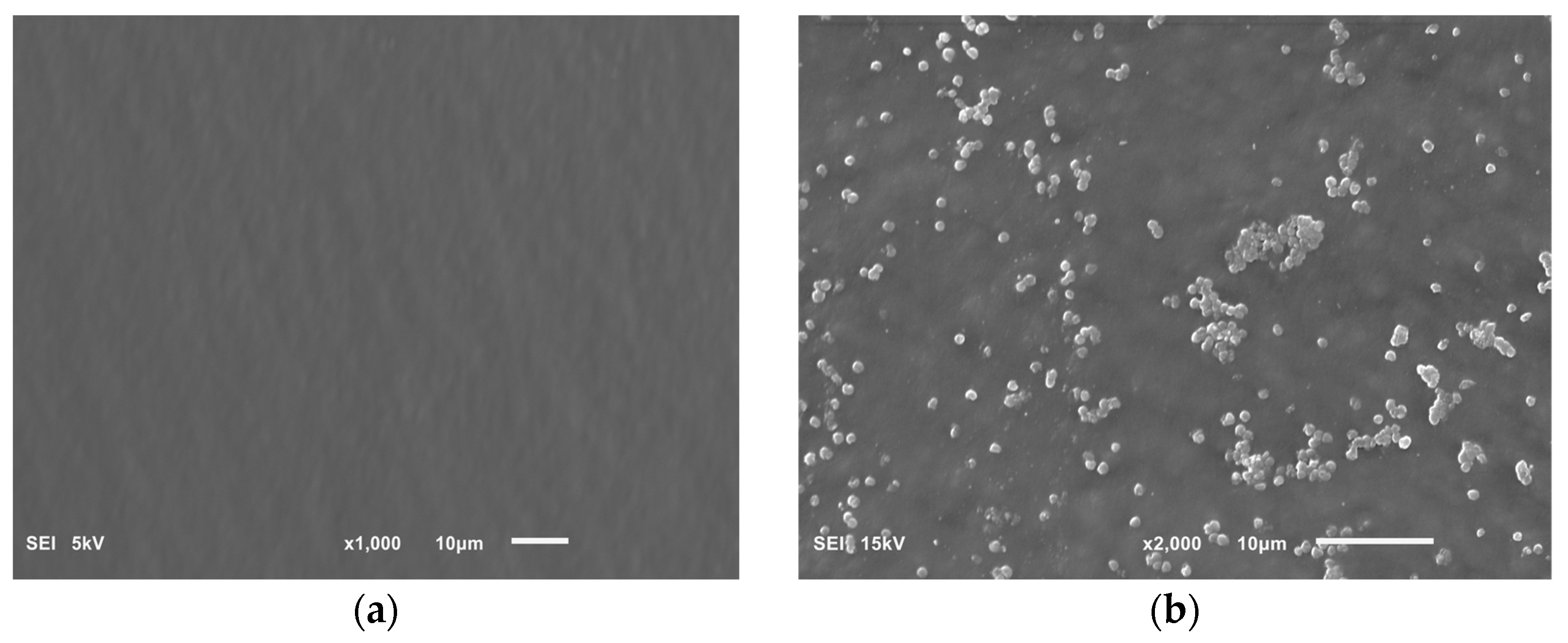
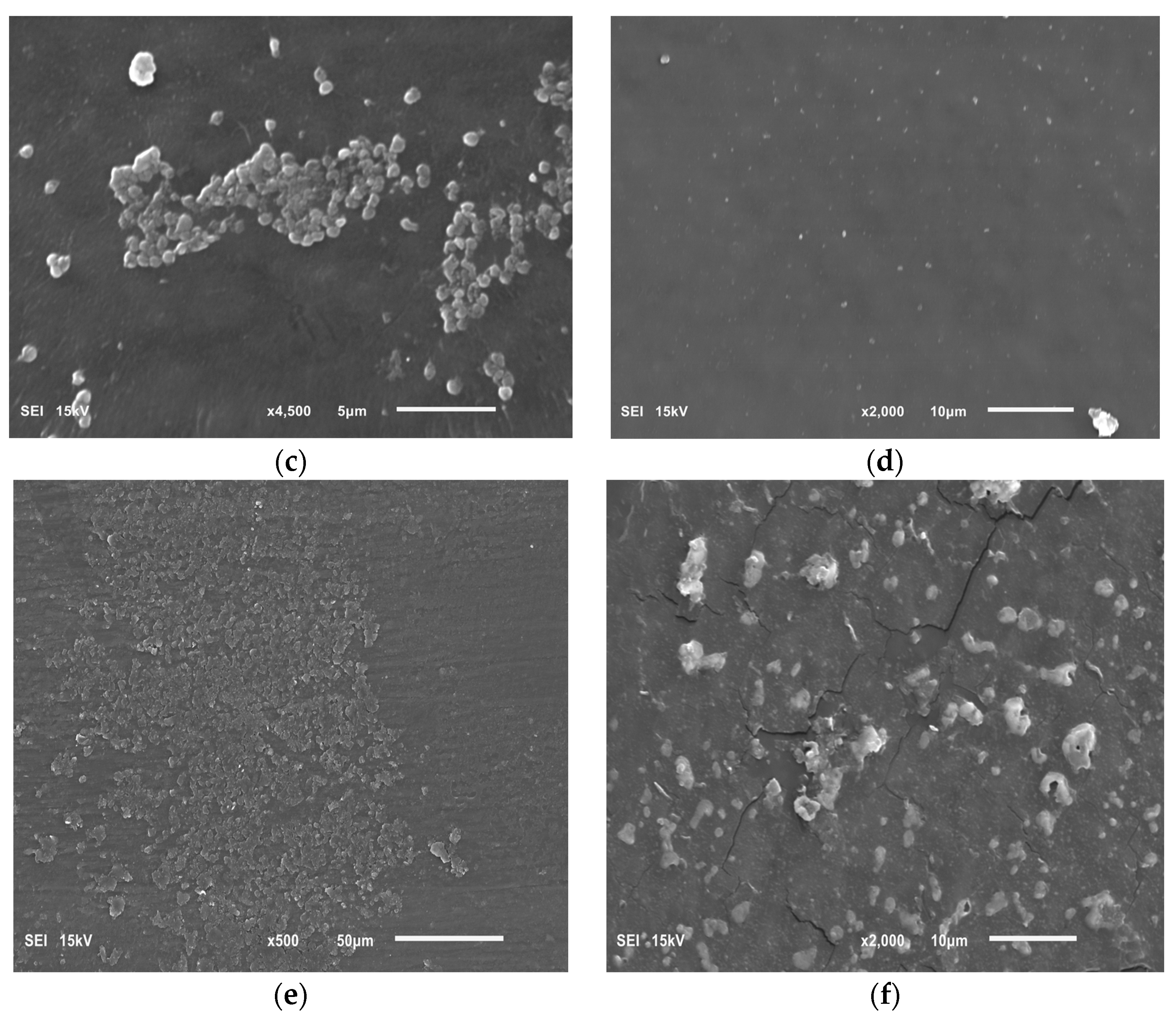
Our research on the influence of extracts on the formation of biofilm showed that concentrations of 6.66 and 16.65 mg/mL of the extracts from the shoots and fruit of R. idaeus 'Willamette', respectively, inhibit the formation of biofilm on fragments of the intravenous infusion. However, all extracts at concentrations of 33.3 and 16.65 mg/mL reduce the number of viable bacteria in the 144-hour biofilm formed by H. pylori. Based on these results, we tested the effect of Rubus sp. fruit and shoot extracts on biofilm formation and on the biofilm already formed by H. pylori. The research results were confirmed by SEM photos, in which the destructive effect of the R. idaeus 'Willamette' shoot extract on the biofilm was clearly visible. Our results from studies of interactions of extracts from Rubus sp. and only the 2 most active antibiotics on planktonic bacteria H. pylori showed synergism of all extracts with doxycycline, and only the extract of R. occidentalis 'Litacz' with levofloxacin. The remaining extracts tested showed indifference with levofloxacin. However, studies on the interaction of antibiotics and extracts of R. idaeus 'Willamette' shoot were carried out on intravenous infusion fragments and showed synergism with doxycycline and levofloxacin, additivity with amoxicillin, and indifference with clarithromycin and metronidazole.
Windham et al. [
36] studied biofilm formation by
H. pylori DSM-1 using various substrates: BB (Brucella broth) supplemented with 10% FBS (fetal bovine serum) and 10 µg/mL vancomycin, brain heart infusion medium supplemented with 0.1% β-cyclodextrin and 10 µg/mL vancomycin, and BB supplemented with 2% FBS, 10 µg/mL vancomycin, and 0.2% glucose. They tested different surfaces, and standard 24-well tissue culture-treated plates were replaced by either untreated or poly-D-lysine-treated 24-well plates. The studies were performed for the time points T
24, T
48, and T
72. The researchers used crystal violet to test the number of bacteria in biofilm. They did not notice any differences in the formation of biofilm according to the tested strain after using different media with different additives. They indicated also that their observation of biofilm formation is not an artifact of medium choice.
Cole et al. [
24] compared the number of bacteria in biofilm of 16
H. pylori mutants on coverslips using 3 methods. The first method included staining with carbolic fuchsin and observation under a light microscope, the second method was staining with the Live/Dead BacLight kit (Molecular Probes), and the third method was scanning electron microscopy (SEM). They checked the efficiency of biofilm formation of mutants (mutations in several genes, including the quorum-sensing ones) on a 12-unit microtiter using BHI broth containing 0.1% β-cyclodextrin (5 days of incubation) or 5% heat-inactivated (56°C, 20 min) fetal calf serum (at 3 to 4 days of incubation) with or without gentle shaking. They detected bacteria in the biofilm using MTT. The researchers found, in preliminary experiments, that incubation of
H. pylori with MTT gave higher values and less background absorbance than other tetrazolium reagents in BHI broth.
Trung et al. [
33] employed biofilm inhibition assay in 96-well plates on 10% NBS (newborn bovine serum)-supplemented Brucella broth by the crystal violet assay. Naringenin showed a reduction of
H. pylori biofilm formation by 85.9 and 52.7% at concentrations of 50 mg/L and 25 mg/L, respectively. The use of myricetin resulted in a reduction in biofilm formation by 39.5% at a concentration of 75 mg/L, while luteolin and protocatechuic acid showed no effect.
Krzyżak et al. [
9] used the following conditions to create biofilm: a BHI broth with 2% fetal calf serum, sterile 96-well polystyrene microtiter plates, a microaerophilic atmosphere, and 3 days incubation at 37°C with shaking (50 rpm). The crystal violet method was used to assess biofilm formation. The authors showed that exposure to 1/8 × MIC and 1/4 × MIC of myricetin resulted in a 50% and 70% reduction in the biofilm formation of
H. pylori Tx30a and 60% and 70% decrease for
H. pylori J99, respectively. The viability of
H. pylori was examined by staining bacterial cells with the LIVE/DEAD kit and analysis by fluorescence microscopy.
Results obtained by Spósito et al. [
34] showed that the incorporated and non-incorporated ethanolic extract of
C. sylvestris leaf, in the nanostructured lipid system, inhibited
H. pylori biofilm formation at the assayed concentrations, except for the extract incorporated at 78.12 μg/mL. At lower concentrations, the incorporated ethanol extract had better activity than the unincorporated extract (625, 312.5, and 156.2 µg/mL) and inhibited a higher percentage of biofilm at the same concentration. Although
C. sylvestris extracts inhibited
H. pylori biofilm formation, none was superior to amoxicillin, which inhibited a greater percentage of biofilm at a lower concentration.
Krzyżek et al. [
11] assumed that the formation of a biofilm by
H. pylori depends on the flow speed of the medium (which is inversely proportional to adhesion), surface charge, and pH of the solution in which the biofilm is formed. The authors stated that the minimum serum concentration necessary for biofilm formation is 2%, and the maximum amount of biofilm to be tested in culture is one cultured for 72 hours; extending the incubation time may even result in its reduction.
Hathroubi et al. [
37] investigated the activity of amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and tetracycline on
H. pylori wild type, clinical strains, and several mutants using Brucella broth (Difco) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (BB10; Gibco/BRL). Bacteria were grown under microaerobic conditions (10% CO
2, 5% O
2, 85% N
2) at 37°C. Biofilms were incubated for 2 days on a sterile 96-well polystyrene microtiter plate and then marked by crystal violet. To determine the number of viable cells in planktonic cultures,
H. pylori samples incubated overnight or for 2 or 3 days were plated for enumeration by counting CFU.
Chen et al. [
23] showed that clarithromycin could inhibit approximately 90% of
H. pylori biofilm formation at MIC concentrations of 0.03 µg/mL and 0.48 µg/mL (1/2 MIC). Amoxicillin can inhibit less than 50% of biofilm formation at 0.03 µg/mL (1/2 MIC), and RHL can inhibit more than 90% of biofilm formation at 1/2MIC – 76.8 µg/mL. The inhibitory effect of clarithromycin and amoxicillin on biofilm formation increases with increasing rhamnolipid concentration up to 76.8 μg/mlL. Chen et al. [
23] studied the synergy of 2 antibacterial agents using 96-well microtiter plates as a checkerboard. After incubation, OD
600nm measurement was performed, and a synergy effect between CLR, AMX, and RHL in inhibiting the growth of
H. pylori planktonic cells was found, i.e., an inhibitory fraction concentration (FIC). The determined FIC values for CLR and AMX, RHL and CLR were 0.75, indicating an additive effect. However, the combination of RHL and AMX did not show a stronger effect than the individual compounds alone, with an FIC value of 1.0. Chen et al. [
23], testing
H. pylori biofilm formation, performed incubation in 48-well microtiter plates at 37°C for 24 h, in static microaerophilic conditions. Biofilm biomass was evaluated by crystal violet test and LIVE/DEAD BacLight Bacterial Viability kits (Invitrogen, USA) were used to evaluate the viability and architecture of the biofilm. Active concentrations towards the formed biofilm were 61.44 μg/mL for clarithromycin (CLR) and 122.88 μg/mL for amoxicillin (AMX); CLR and AMX could eradicate about 50–60% of
H. pylori biofilm. CLR + AMX eradicated mature biofilm. The rhamnolipid (RHL) alone eradicated mature
H. pylori biofilm at a concentration of 1228.8 μg/mL. Moreover, RHL in combination with AMX eliminated over 90% of
H. pylori biofilm, which was better than the combination of RHL + CLR + AMX. Lansoprazole (used as PPI) + RHL + AMX resulted in a 95% reduction of
H. pylori biofilm.
Nakase et al. [
32] studied the interactions of modified Gingyo-san and clarithromycin, amoxicillin, metronidazole, minocycline, and sitafloxacin against reference (ATCC 700392) and 2 clinical strains of planktonic
H. pylori at pH 7.0 and 5.0. Two types of interactions were found: additive and indifferent; the pH slightly influenced the changes in interactions.
Krzyżek et al. [
9] investigated interaction activity of myricetin (MYR) with the classically used antibiotics amoxicillin, clarithromycin, tetracycline, metronidazole, and levofloxacin. They used the checkerboard assay. Three selected concentrations of MYR (1/4 ×, 1/8 ×, and 1/16 × MIC) and antibiotics at the range of concentrations 0.0015 to 16 μg/mL were incubated in 1 mL of BHI broth with 7% serum at 37°C for 72 h, in microaerophilic conditions, with shaking (100 rpm). Their research results showed that 1/4 × MIC of MYR is able to decrease the MICs of all tested antibiotics by 4–16 times its potential to synergistically enhance the action of the antibiotics ( FICI = 0.31–0.5). The 1/8 × MIC of MYR also increased the activity of all tested antibiotics; most of the interactions were additive (FICI = 0.625). The 1/16 × MIC of MYR additively increased only the activity of amoxicillin, metronidazole, and levofloxacin (FICI = 0.56), but not clarithromycin and tetracycline (FICI = 2.0). The viability of
H. pylori was examined by staining bacterial cells with the LIVE/DEAD kit and analyzing them by fluorescence microscopy.
Park et al. [
19] studied the interaction of
Rubus crataegifolius (RF) and
Ulmus macrocarpa (UL) extracts in concentrations of 150 and 200 µg/mL, respectively, using the in vitro method from dilutions in agar. UL extract did not show any inhibition at 150 μg/mL, RF or UL did not show anti-
H. pylori effect at 50 or 75 μg/mL, while RF in combination with UL at 75 and 50 μg/ml showed a strong synergistic effect. Combination of RF and UL at 75 μg/mL each showed complete inhibition of
H. pylori colonization. All 11
H. pylori clinical strains and 2 reference strains were tested for the synergistic effect of RF and UL on amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and omeprazole and showed similar inhibitory effects on
H. pylori colony formation. Park et al. [
19] studied an extract from
R. crataegifolius that contained polyphenols including sanguine, coreanoside-F1, nigaichigoside, gallic acid, and ellagic acid. According to the authors, the strong anti-
H. pylori properties of the extract were indicated by the presence of ellagic acid (14.2 mg/g of dry extract) and catechin (30.5 mg/g of dry extract).
Krzyżek et al. [
11] cited that the presence of
H. pylori in the biofilm in coccoid forms only indicates a mature form of the biofilm created by this bacteria. This form results in physiological changes in the bacteria, including tolerance to variable environmental factors. Transformation may lead to the development of a viable but non-culturable (VBNC) phenotype by spherical
H. pylori forms, but still metabolically active.
Martini et al. [
18] studied the effect of the extract from
R. ulmifolius and the isolated compounds ellagic acid, gallic rutin (quercetin-3-rutinoside), and kaempferol — effective anti-
H. pylori agents. Rutin (quercetin-3-rutinoside) is known to possess antimicrobial activity against some gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, and ellagic acid kills
H. pylori by inhibiting arylamine
N-acetyltransferase activity. Kaempferol induces a significant decrease in the number of colonies of
H. pylori in gerbils’ stomachs after oral treatment. They hypothesize that the target of the antibacterial action of
R. ulmifolius and its extracts, which are polyphenols, could be one or more bacterial ion pumps. To support such conjecture, they compared the structure of the gastric proton pump with those of
H. pylori ion pumps and found significant linear homologies. The researchers suggested that blackberry polyphenols kill
H. pylori because of inactivation of its ion pumps, i.e., enzymes that regulate the flux of copper and metal cations through membranes. The authors noted that the extract appears to be much less effective after 24 h of exposure than the isolated compounds. This behavior, which is more evident after 24 h of incubation, may be explained by the low concentration of single compounds in the extract and the presence of other constituents that may lack antibacterial activity.
Studies conducted by Krazue Baranowska et al. [
20,
21] on the planktonic form of
H. pylori showed the activity of ellagic acid against the cells of these bacteria (MIC 0.125 mg/mL). In contrast, dimeric sanguine H-6 had no antimicrobial activity against
H. pylori. Researchers cited the view that among hydrolysable tannins only monomeric forms are the most effective and promising
H. pylori inhibitors. The inhibiting effect of raspberry fruit extracts against
H. pylori was on the same level for all the analyzed varieties (MIC 8 mg/mL). The inhibitory activity of the fruit extracts towards
H. pylori may be connected with their content of free ellagic acid. However, the extract from
R. occidentalis ‘Litacz’ was found to contain about 5 times more anthocyanins than the fruit extracts of red ‘Ljulin’ and ‘Veten’. In turn, in the fruits of
R. occidentalis ‘Litacz’,
R. idaeus ‘Ljulin’ and ‘Veten’ the cyanidin glycosides dominated. The fruits of ‘Litacz’, ‘Poranna Rosa’, and ‘Ljulin’ have similar levels of sanguiin H-6, but the ‘Veten’ has 3 to 5 times higher concentrations of sanguiin H-6. A similar situation is the content of free ellagic acid in fruits extracts from ‘Litacz’‘Poranna Rosa’, and 'Ljulin' varieties, in which the discussed compound occurs at the same level, and in 'Veten' it was approximately 2 times higher. The extract from
R. idaeus ‘Willamette’ shoot contained about 5% sanguiin H-6 and about 1% free ellagic acid [
21]. According to the authors, ellagic acid is mentioned among the compounds that might contribute to the antimicrobial activity of raspberries. It has been proposed that by binding to the bacterial membrane, ellagic acid can destabilize its structure, thus disrupting cell functionality. The authors cited research to support this theory, in which alcoholic beverages enriched with raspberries had a greater potential against
H. pylori than pure alcohol. The authors suggested that this effect is due to raspberry extracts damaging bacterial cell membranes and thus making them more sensitive to alcohol. The researchers concluded that the raspberry shoot extract (MIC for
H. pylori – 7.4 mg/mL) is a prospective source of sanguiin H-6 and ellagic acid; these 2 components are believed to be responsible for its antimicrobial properties.
In the presented studies, the extract from R. idaeus ‘Willamette’ shoots transpired to be more active in preventing biofilm formation on intravenous infusions compared to fruit extracts. Perhaps antibacterial activity was demonstrated not only by sanguiin H-6 and free ellagic acid, but also by isoquercetin, quercetin 3-Oglucuronide, epicatechin, and catechin contained in this extract. However, on the already formed biofilm on fragments of the intravenous infusion, the following agents had the best effect; for the fruit extracts from R. idaeus 'Poranna Rosa' and extract from R. idaeus 'Willamette' shoots, the activity was at the same level. In this case, in our opinion, the main role against H. pylori biofilm was played by sanguiin H-6 and free ellagic acid, which are the only biologically active compounds detected so far in fruit extracts from ‘Poranna Rosa’, and the extract from the shoot contains a high concentration of them. It would be worth examining the mechanism of action of both compounds on bacteria.
There are various theories cited by Krauze-Baranowska et al. [
20] regarding the absorption of anthocyanins from the gastrointestinal tract, suggest that they are poorly absorbed and excreted unmetabolized. Ellagitannins are reported not to be absorbed in the intestine, but instead are metabolized by colonic microflora to form urolithins. Therefore, the authors believe it is difficult to predict and estimate whether the compounds will be able to reach the infection sites at a desired concentration.
Krauze-Baranowska et al. [
21] proposed the use of raspberry extracts, e.g. in the form of lozenges, to prevent or limit infections with various pathogens of infectious diseases of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract. An advantage that should be added here is wide access to the fruits of various varieties of raspberry plants consumed as part of the daily diet in various forms. But it should also be noted that the current active compounds isolated and identified in extracts from raspberry fruit, leaves, and shoots may provide a starting point for the synthesis of derivatives with much greater antibacterial properties. The synergism of extracts form
Rubus sp. fruit with doxycycline and
R. idaeus 'Willamette' shoot with doxycycline and levofloxacin, as well as the additivity of amoxicillin, which we have demonstrated, may provide a basis for the use of extracts in combination with antibiotics in clinical trials to combat
H. pylori infections. In our research, we have shown that
H. pylori can form a biofilm on medical materials used in the treatment of patients. These results suggest that the presence of artificial materials in the human body, e.g., stents, may make it possible to colonize them with
H. pylori. Additionally, the use of treated water, used, e.g., for artificial respiration in hospitals, in which
H. pylori has already been detected, in our opinion, expands the ways of spreading
H. pylori infections. Our demonstration of the activity of the tested extracts from
Rubus sp. against
H. pylori biofilm on fragments of infusions may provide a new option for covering artificial surfaces used in hospital treatments with compounds of natural origin.