1. Introduction
Water shortages due to climate change are becoming more common and significantly affect agricultural production [
1]. In arid farming regions, and during times of low rainfall, irrigation is the process of adding water to the soil to increase crop growth and replant degraded soil [
2]. Irrigation depends on regional climatic conditions; however, as climate change begins to affect new regions that were not affected by drought in the past, the need for irrigation also arises in these regions. According to research and current practices, some farmers are increasingly using irrigation, even in northern EU countries. In countries where irrigation is widely used, irrigation water is still applied at appropriate rates and using the best technologies. Consequently, it is reasonable to assume that irrigation will receive greater attention in parts of the world where it was not a priority before. Precision irrigation is necessary because of the rising demand for water to combat climate concerns. To achieve higher agricultural yields and water savings, it is crucial to choose when and how much to irrigate. The four most popular methods of operation for irrigation scheduling, namely, evapotranspiration and water balance (ET-WB), soil moisture status, plant water status, and models, along with their advantages and disadvantages, are introduced and contrasted in order to better understand their fundamental processes and principles [
3]. Future irrigation scheduling methods should focus on the management of soil moisture based on an advanced understanding of its effects on crop growth, either by integrating existing irrigation scheduling methods or developing new models using intelligent algorithms. This is because all four types of scheduling methods focus on soil water content, which acts as a bridge between irrigation management and crop water requirements for growth [
3]. It is necessary to have knowledge of the soil's properties, including texture, water-holding capacity (WHC), wetness, and crop water requirements at different growth stages [
4]. With the advancement of contemporary sensors and sensing technology, a variety of technologies, such as wireless network sensors (WSNs), remote sensing (RS), global positioning systems (GPS), geographic information systems (GIS), LoRaWAN, and Bluetooth could be used to collect field data for precision irrigation. WSNs have been widely used in agriculture for automated irrigation management because they are cost-effective and have low energy consumption [
5,
6,
7,
8]. In addition to wired solutions, wireless sensor technologies have been gaining move importance and broadening their use [
9], particularly in weather forecasting, early warning systems, soil and crop monitoring, and automated and smart irrigation [
10,
11,
12]. Wireless sensor networks with cloud capabilities are promising because the end-user does not have to tackle collecting and storing the data.
It has been well documented that parameters affecting the yield of any crop exhibit spatial and temporal variations [
13,
14,
15,
16]. Despite the awareness of this known fact, the great majority of farmers today are known to apply a constant rate over the field while they vary the total amount of water from one irrigation to another during the irrigation season depending on the soil, plant, and weather conditions. Already a limited number of farmers seem to determine irrigation needs based on climate data and some sensor data, if any. One of the most important factors affecting the adoption of precision or smart irrigation technologies is that the accuracy of the moisture sensor changes with time in the field, which requires occasional calibration. Other factors include cost, installation, data collection, and interpretation issues, which cause difficulties for an average end user. Although the advantages of variable rate irrigation have been documented, the adoption rate of this technology has been low; however, the effort to develop the technology should continue for several reasons, including climate change, declining water resources, nutrient management regulations, and water management policies [
17].
The development of variable-rate irrigation control systems has attracted considerable attention since the early 2000s. Some of these studies focused on center-pivot and linearly moving irrigation systems [
18,
19,
20]. Smart irrigation systems development has been of the utmost interest and requires the accurate determination of all parameters requiring irrigation [
10,
21]. Smart systems require not only sensor-based monitoring but also the integration of internet of things (IoT) and Cloud technologies [
10,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. [
27] reviewed various water management techniques and the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning (DL), along with the IoT network and case studies. Although previous studies have covered new techniques to apply irrigation water more intelligently, there is still a need to improve the current applications by considering the dynamic variations in irrigation needs within fields more precisely. There have been studies focusing on variable rate irrigation (VRI) using hose-reel machines, but they usually use the full-swath width as the lateral resolution. There appears to be a research gap in improving the lateral and longitudinal resolutions of VRI applications using hose-reel machines. Furthermore, spatial and temporal changes during the irrigation period should be addressed in a VRI management.
It is hypothesized in this study that by using cloud-based wireless soil moisture sensors, dynamic spatiotemporal variations in irrigation requirements can be determined during the growing season of a given crop. The general objective of this study was to simulate spatiotemporal variations in irrigation needs based on dynamic irrigation management zones of maize crops using a wireless soil moisture sensor network and GIS capabilities. This study compared the constant user rates of irrigation water on different irrigation dates with that of the sensor-based simulated variable irrigation rate. It assesses the right time and rate for irrigation, determines the accuracy of user rate applications, and analyses the dynamic irrigation management zones to be applied by VRFM.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site and irrigation system
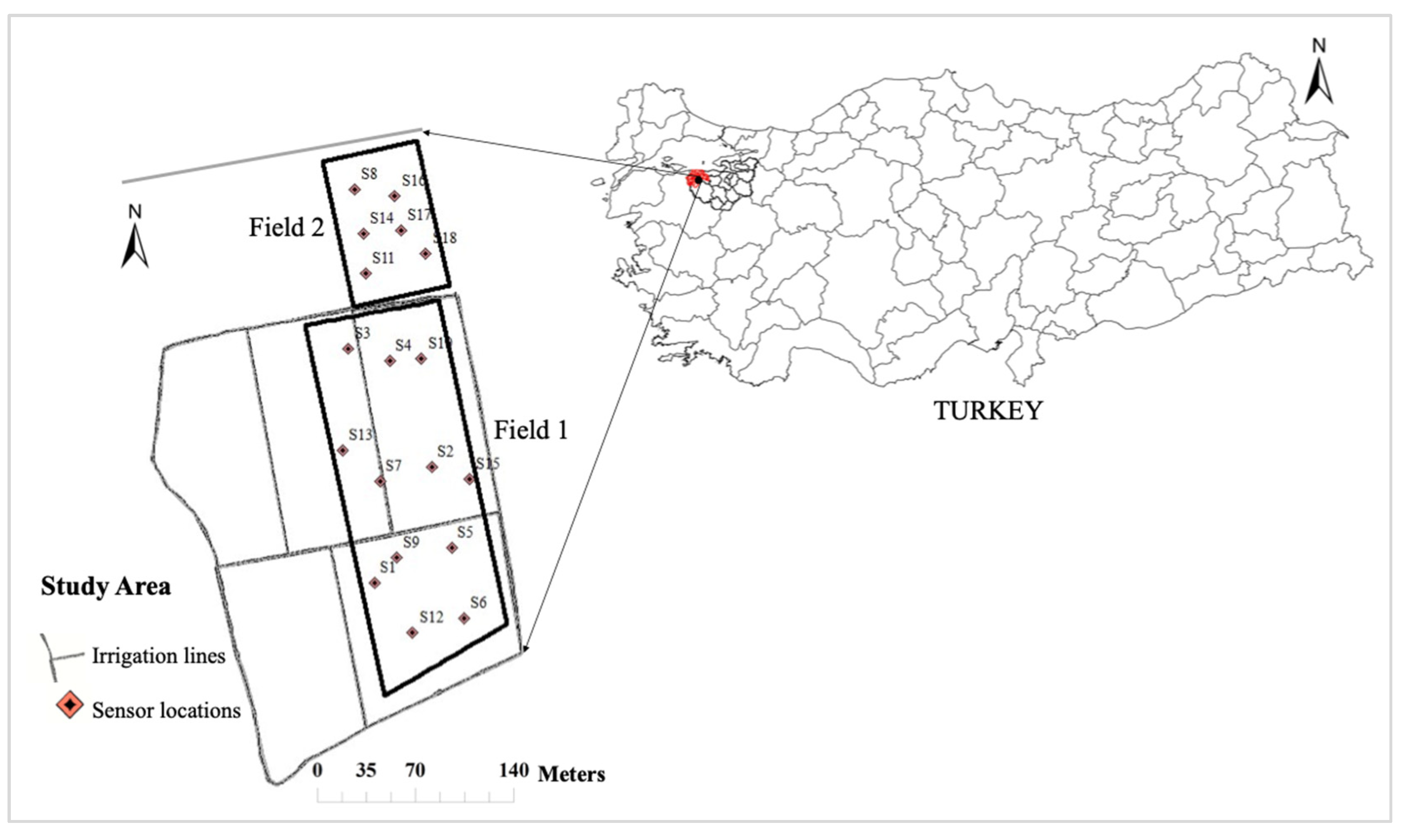
The experimental maize fields were located in Bakırköy village of Karacabey, Turkey (40°08’22.61”N, 28°22’58.7″ E). An 8.2-ha field named Field 1 (F1) and a 2.5-ha field named Field 2 (F2) were selected for the experiment (
Figure 1). The soil type in these fields varies between sandy clay and loamy clay. The fields have approximately rectangular shapes and are irrigated using a closed-loop pressurized wide-area drip irrigation system operated by an irrigation union in the district. The field experiment was conducted during the 2022 growing season. Maize seeds were planted on the 16th of May 2022 for Field 1, and on the 11th of May 2022 for Field 2, and the first drip irrigation was done on July 2 for both fields.
The drip irrigation system was used in the growing season in 2022 with drippers delivering 28.8 t/h-ha irrigation water at an operating pressure of 0.3 MPa (3 bar). The main and secondary plastic pipes were 20 cm in diameter each. The main field (22 ha) was divided into approximately 4.0 ha sections. About 8.2 ha of the main field was used for F1 in this study, as shown in
Figure 1. F2 lies at the corner of the second field north of F1. Undisturbed soil samples were taken at 80 and 30 locations from F1 and F2, respectively, to determine the soil properties pertinent to the determination of irrigation needs.
2.2. Wireless soil moisture sensor system
A cloud based LoRaWAN wireless network was used with soil moisture sensors to collect soil moisture data continuously (
Figure 2). Dragino LSE01 sensors were used to collect soil moisture data continuously at a depth of 300 mm. The gateway was approximately 800 m away from the sensors with a clear view of sight.
2.3. Methods
The variable irrigation needs were determined by monitoring the water status using soil moisture content (MC) sensors by previous researchers [
29,
30] and the same method was used in this study in the experimental fields. Field capacity (FC), permanent wilting point (PWP), and volumetric weight (VW) were determined under laboratory conditions for each soil sample at each sensor location. Undisturbed soil samples were collected. VV were determined by drying them in an oven for 24 hours at 105°C. The Sand/Kaolin Box instrument (Eijkelkamp, the Netherlands) was used to determine field capacity at 2.54 pF (1/3 atm). The permanent wilting point at a pressure of 4.2 pF (15 atm) was determined using the Pressure Membrane Apparatus (Eijkelkamp, the Netherlands). Available water (AW), management allowable depletion (MAD), and amount of irrigation water (irrigation need, IN) were determined based on laboratory analyses of the soil samples. IN was calculated based on the moisture content (MC) value of the soil to reach the FC values at a given location in the field. Twelve and six MC sensors were installed at depth of 300 mm for F1 and F2, respectively, and the following formulae were used to determine the aforementioned parameters:
Management allowable depletion was calculated to be 50% of the available water (Eq. 4), and the irrigation efficiency (EF) was taken as 0.9 (Eq. 6) for the drip irrigation system to calculate sensor-based irrigation needs based on field capacity and moisture measurement.
The dates and constant application rates of irrigation were determined by the farmer. Before each irrigation date, sensor data were retrieved from the cloud-based portal and processed. Ordinary Kriging (OK) interpolation method were applied using ArcGIS ArcMap v10.8 (ESRI ArcGIS version 10.8, CA, USA) software to generate the spatial variation of soil moisture content in each trial field. Three- and five-zone irrigation application rates were generated using soil moisture sensor data for each irrigation date: July 2-5-7-13-17-21-25 and August 04. During this period, constant-rate irrigation was applied eight times using a drip irrigation system. The irrigations started before the sensors were ready to collect real-time MC data. After processing the sensor data, only eight irrigation applications were considered for the analyses.
2.3.1. Water use comparison between user- and sensor-based constant irrigation rates
The farmer applied a constant flow rate of 28.8 t/h-ha during irrigation at a known operating pressure of 3 bar. The pressure at the end of each secondary line was measured using a handheld analogue pressure gauge (Pakkens 0-6 bar) so that the flow rate was the same and the water distribution was uniform in each irrigation plot. For each irrigation, the farmer changed the irrigation time from 6 to 10 h per irrigation, depending on the job and employee status. The user irrigation rate was determined by the experience of the farmer, crop water demands given in the irrigation guide for the Bursa-Karacabey district, and evapotranspiration values provided by the farmer’s weather station (Metos IMT280).
Wireless MC sensors were configured to deliver MC data every 20 min in this study. To make a sensor-based constant irrigation recommendation on a given irrigation day, the MC value measured just before irrigation was taken from each sensor, and the average of all sensor readings was used as the sensor-based field-scale soil MC value. Equation 6 was used to determine the amount of water to be applied (irrigation need) to bring the moisture content of the field to the field capacity for a given irrigation date. The differences among the soil moisture sensor measurements for each irrigation date were calculated to reveal the range of soil moisture content within the field. Within-field soil moisture content variations were evaluated to assess the accuracy of uniform irrigation in the trial fields.
2.3.2. Variable Rate Irrigation recommendations
The Ordinary Kriging (OK) interpolation method were implemented using ArcGIS ArcMap v10.8 (ESRI ArcGIS version 10.8, CA, USA) software to generate variable rate irrigation (VRI) maps. The irrigation needs (IN, mm/da) were mapped with three and five management zones (MZs) for each field to compare the effects of different resolutions for irrigation. Three and five MZs were selected to as to see the effects of the number of MZs on the variability in irrigation needs.
First, a theoretical application map was produced for the irrigation dates (July 2-5-7-13-17-21-25 and August 04) for F1 and F2, resulting in 32 maps (8 days × 2 different zone maps × 2 fields). The amount of water to be applied in each irrigation MZ was tabulated based on the irrigation rate and the total area of each irrigation management zone in each field. The user-applied uniform rates and variable-rate irrigation recommendations were then compared to meet the irrigation demands of the soil based on the postulated irrigation zones.
Then, the theoretical 3- and 5-zone irrigation need maps were further processed for VRI application to be applied by using a variable rate hose-reel fertigation system being developed as a part of the project. The VRFM has a working width of 46 m, and it is proposed to have four sections, each to be individually controlled for VRI applications. Thus, using theoretical maps, applicable irrigation maps were obtained for cell sizes of 11.5 m x 1 m. Applicable maps were presented for the irrigation dates July 7-17-25 and August 04 to discuss the effect of management zones on the water distribution within the fields and were compared with theoretical IN maps.
Sentinel 2A satellite data were used to generate the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) maps corresponding to the nearest irrigation dates. Additionally, the texture (clay, silt, and sand) was mapped for F1 and F2 in an attempt to find a potential cause and effect of NDVI and soil texture on the spatiotemporal variations in irrigation water needs across the fields studied.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. User-rate and sensor-based constant irrigation comparisons
Nine out of twelve sensors could be utilized for soil moisture measurements due to unexpected weak signals, battery, or installation problems in three of the sensors installed in F1, and four of the six sensors were operable in F2 (
Table 1). The average FC, PWP, and MAD values in F1 were approximately 139, 66, and 37 mm, respectively. The volumetric weight of the soil samples had an average of 1.45 (g/cm3) with a small coefficient of variation (CV) value (1.82%). Other parameters included in Table 3 had variations, with CV values ranging from approximately 4.4 to 7.3%. In F2, based on measurements performed by the four soil moisture sensors, the FC was smaller, and VW was higher than that of F1. The MAD values were also greater than those of F1. The coefficient of variation of the measured parameters in F2 ranged from 2.02 to 8.29%, except for PWP. The high CV value of PWP may be attributed to fewer sensors, and hence, to fewer data points to be averaged.
The irrigation duration determined by the farmer varied from 7 to 10 h depending on the weather, crop conditions, and labor availability (
Table 2). More water should have been applied throughout the season to bring soil MC to the FC. For instance, on July 7, the applied user rate was 23.04 t/da as a result of 8 h irrigation, which was 14.7% less than the recommended rate based on the average of the soil MC measurements. The overall average of user rates was 22.68 mm/da while the sensor-based application rate was calculated to be 29.83 mm/da. The overall difference between the user and sensor-based rates was -22.76% whereas the differences ranged from − 4.6% to -35.9% on specific dates. This means that the soil received a smaller amount of water than it should have if the moisture sensor data would have been used to calculate the irrigation rate. It can be concluded that the irrigation duration could be adjusted more accurately by the farmer if moisture sensor data were used to bring the available MC to the FC level.
In F2, the ranges of irrigation rates for the user- and sensor-based irrigations were 17.28-28.80 mm/da and 27.0-47.19 mm/da, respectively (
Table 2). On average, throughout the irrigation season, the user-rate of irrigation water application was 45.09% less than the recommended IN. In this case, the difference was more significant than that for F1.
Although the farmer intended to apply water every 3-4 days after July 7, due to labor shortage, an irrigation was skipped between July 7 and July 13. Automated irrigation systems can reduce the dependency on workers to accomplish time-dependent tasks.
It should be noted that the above discussion does not account for spatial variations in irrigation needs within a field. Even for a constant irrigation rate at the whole-field scale, the use of soil moisture sensors showed opportunities for implementing irrigation at more accurate times and rates. [
31] concluded that the total profit was the same when sensor-based irrigation scheduling was compared with the user application, but the sensor-based application was found to be promising in terms of water and financial savings.
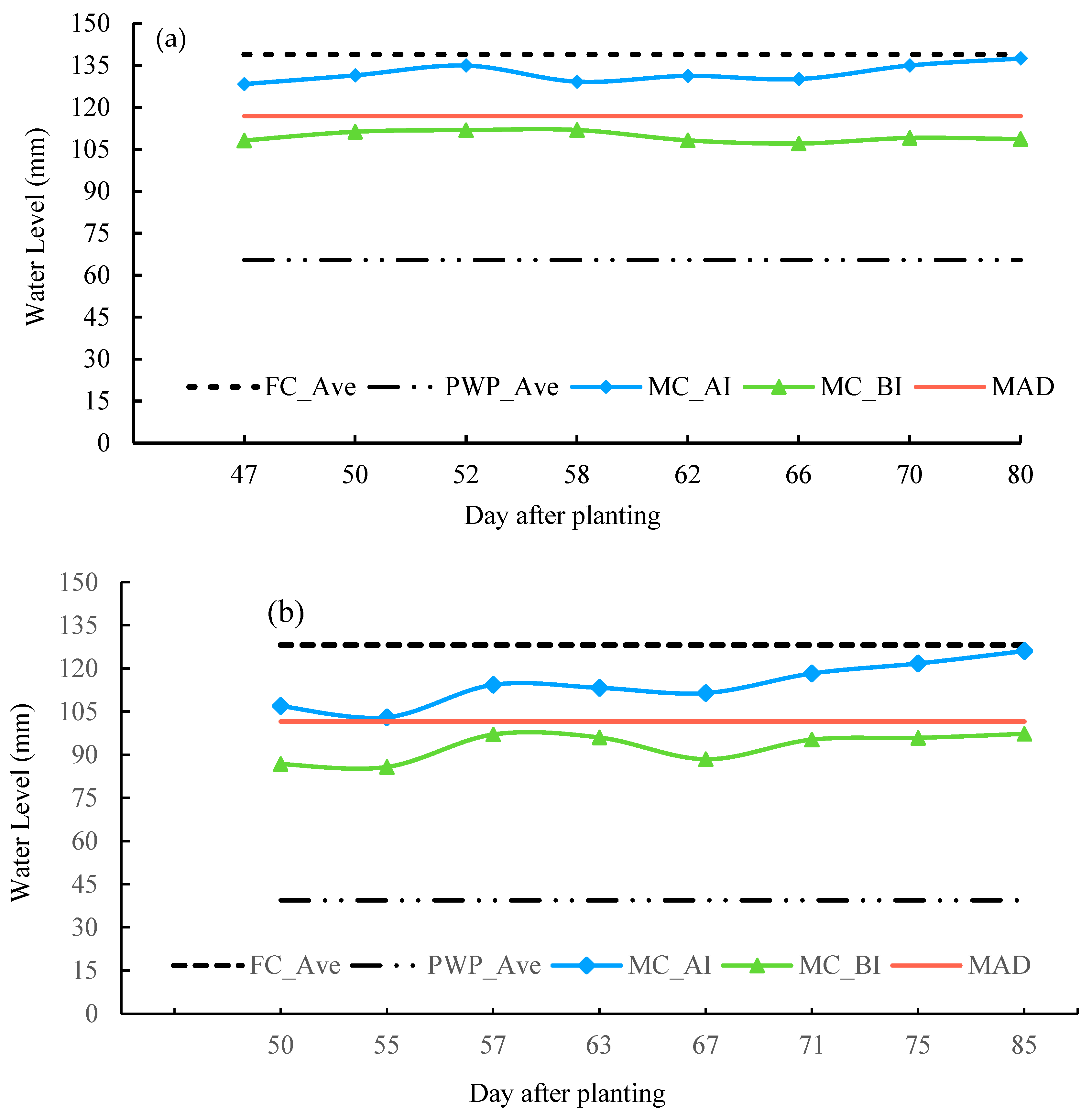
The variations in the measured MC values on specific irrigation dates were shown in
Figure 3 for F1 and F2.
Figure 3 also presents the average FC, PWP, and MAD values to visualize when irrigation had to be started and terminated.
The MC values were expected to be around the MAD line before the irrigation started and near the FC line after the irrigation was completed. The farmer always started irrigation at a soil moisture content slightly lower than the MAD value in F1 (
Figure 3a). The irrigation timings were slightly later than the right irrigation times. After irrigation, the soil MC was always lower than the FC. The farmer applied irrigation water that never exceeded the FC for the entire field. However, the timing and duration of the user rate can be improved by using the average soil moisture readings made by the sensors so that the soil MC values reach FC. In the first part of the graph in
Figure 3a, it was observed that irrigation started late and was terminated early because the soil moisture after irrigation was lower than the MAD value.
In the rest of the season (after day 50), irrigation seemed to be done at about the right time, but stopped somewhat early, before the soil moisture reached the FC value. At the early growth stages of maize plants, the penetration of the maize roots is shallower than in the later stages [
32]; thus, maintaining the topsoil moisture should be more important to avoid water stress. The soil tended to generate cracks owing to the lack of moisture, especially during windy periods that are common in the region. Therefore, it may be recommended to start irrigation earlier than was actually done because the measured MC values before irrigation were lower than the MAD values. MC values below the MAD value in
Figure 3a and 3b suggest that plants might have experienced water stress during the early growth stages. To prevent this, frequent and sufficient irrigation could have been done using the sensor-based data.
Figure 3b suggests that the timing of irrigation was not accurate for some irrigation dates in Field 2. The MAD line shows the lower limit of the soil moisture value at which the irrigation system should start. This limit was taken to be 30% of the difference between the FC and MAD values. The farmer started irrigating the field at a soil MC level lower than the MAD value. Furthermore, irrigation was terminated too early since the after-irrigation soil MC values were just above the MAD values, not reaching the targeted FC values. As demonstrated in
Figure 3b, real-time data could be used to accurately determine the right time and right amount of irrigation, either done manually or automatically.
FC and after-irrigation MC values were compared on each irrigation day (
Table 3). The MC of the soil was approximately 110 mm before irrigation and increased to 128.2-137.5 mm while the average FC was 138.9 mm for the field. The percent user difference in irrigation needs between the user and the average sensor readings varied from 1% to 7.6%, implying that the user had to apply slightly more water to bring the MC values to the FC level at the field scale.
Table 3 shows the user applications compared with the after-irrigation MC-based measurements for F1 and F2. The user started irrigation when the soil MC value was between 86 mm and 97 mm in the field, depending on the irrigation date. The resulting MC values following irrigations were between 107 and 126 mm. The applied water was less than the amount of water necessary to increase the soil MC values up to an average FC level of 128 mm in Field 2. Up to 17% more water should have been applied in Field 2 on July 2 and 5, corresponding to the early growth stages of plants.
The spatial variation in the before-irrigation MC values for each irrigation day is shown in
Table 4, where the first column shows the sensors installed in both fields. On average, the IN was between 30 and 35.5 mm before irrigation in F1. However, the IN was calculated to range from 35.94 to 47.19 mm for F2, which was a wider range compared to F1.
The average irrigation need for each irrigation date was greater in F2 than in F1, probably because of the different ranges between the FC and PWP, and hence the MAD values in the two fields. The average MAD value of F2 (44.39 mm) was greater than that of F1 (36.58 mm), requiring more water delivery to irrigate the field up to field capacity.
3.2. Constant vs variable rate irrigation
As discussed in the previous subsection, irrigation scheduling based on soil moisture sensors has the potential to improve the timing and amount of irrigation water required. However, the above discussion was based on the average of all readings from the soil moisture sensors. As the sensors were in different parts of the field, it would be more useful to determine the spatial irrigation needs on a given irrigation day.
Table 5 shows the difference between the average before-irrigation MC values and point-based MC values on each irrigation day. The data show that some parts of the field required more or less water than the previously calculated average IN. For instance, on July 13, 11.5% more water would have been applied at S2, whereas 12.1% less water would have been applied at S10 if the average before-irrigation MC values had been used. Similarly, in F2, a maximum of 12.7% more and 11.5% less water would have been applied on July 25 at S8 and August 4 at S14, respectively, if the average of all MC sensors were to be used to determine the irrigation need.
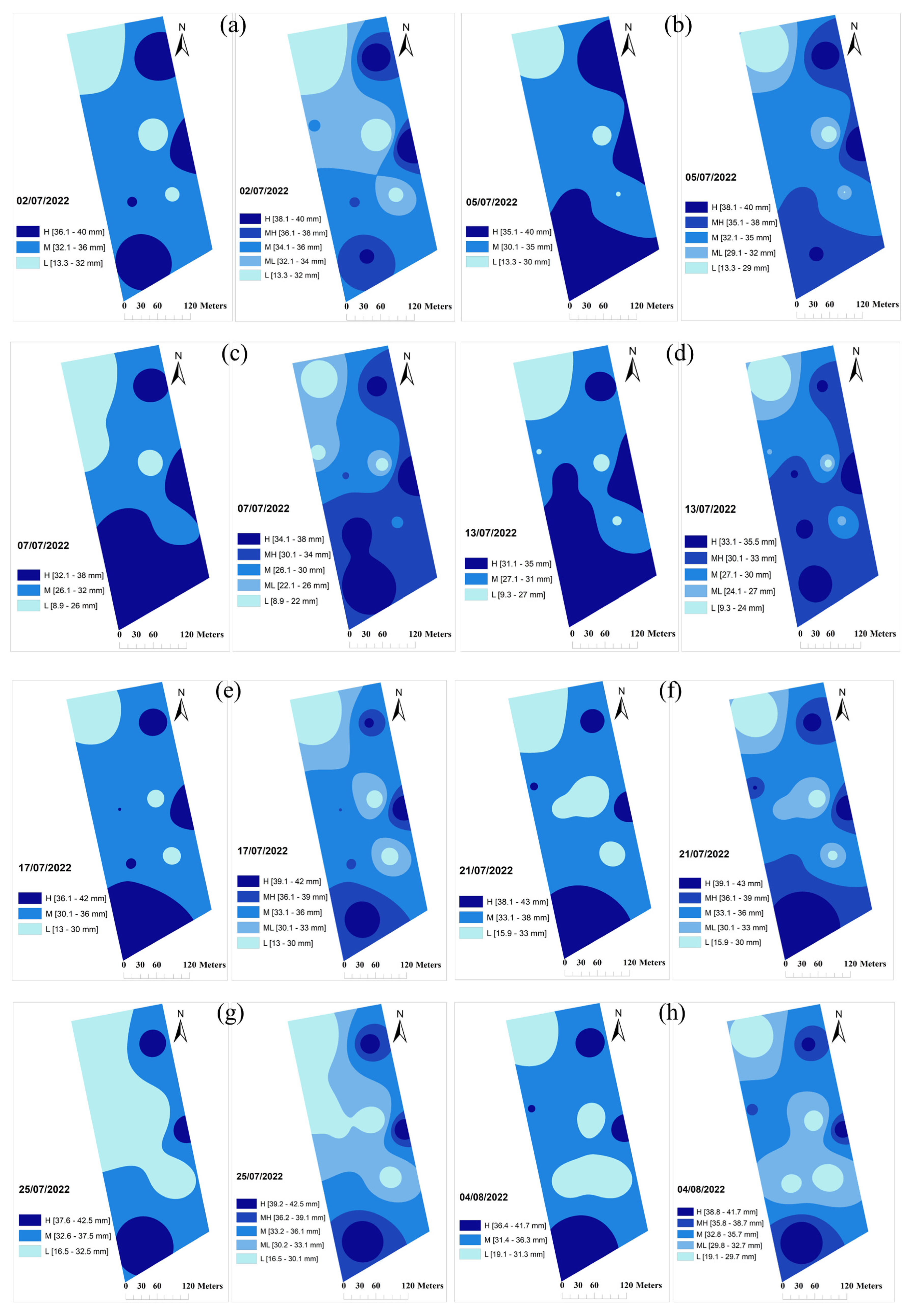
The spatiotemporal changes in the soil MC values show that the irrigation needs vary within the fields; hence, appropriate precision application technologies should be developed to account for these variations (
Figure 4).
The variations in the soil MC in F1 during the monitoring period showed that the upper-left corner of the field always had lower moisture content values and the lower-left corner had the greatest measured MC values. Other parts of the field showed varying degrees of change in the level of water requirements.
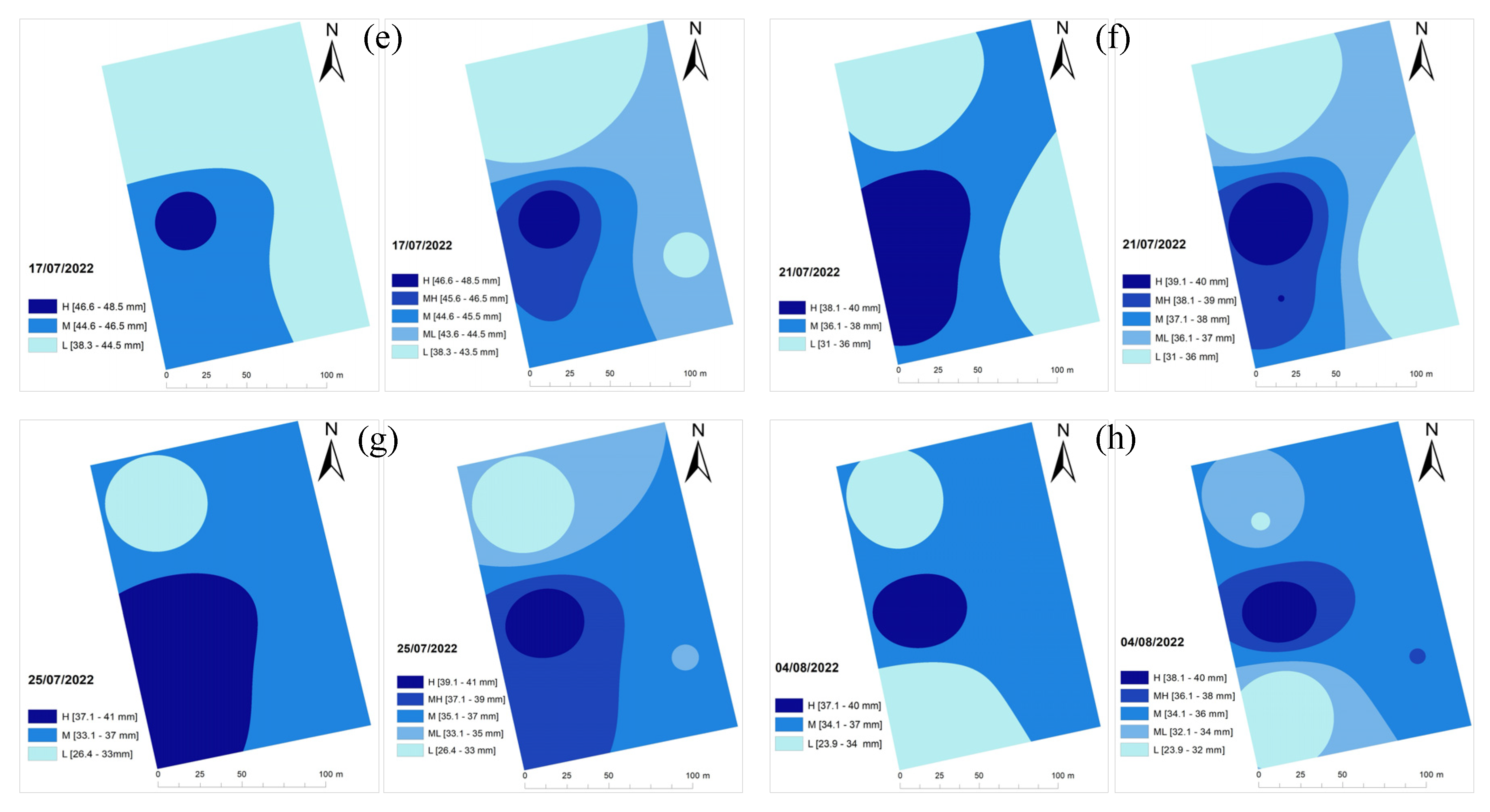
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 show the three- and five-zone irrigation management zones for F1, and F2. These figures show the same patterns in irrigation needs with different precisions with low (L), medium low (ML), medium (M), medium high (MH), and high (H) application rates.
Analysis of five irrigation management zones suggests that irrigation water can be delivered more precisely to areas needing different irrigation rates, for example, M, ML, L, MH, and H levels. However, accurately applying five different application rates based on the management zones is unlikely considering the layout of the current drip irrigation systems in use. Thus, it may be concluded that the maps obtained by the OK method are useful for revealing the spatiotemporal variabilities within the fields but need to be processed for use with the most appropriate irrigation technology available, for example, hose-reel or pivot systems with at least section control mechanisms.
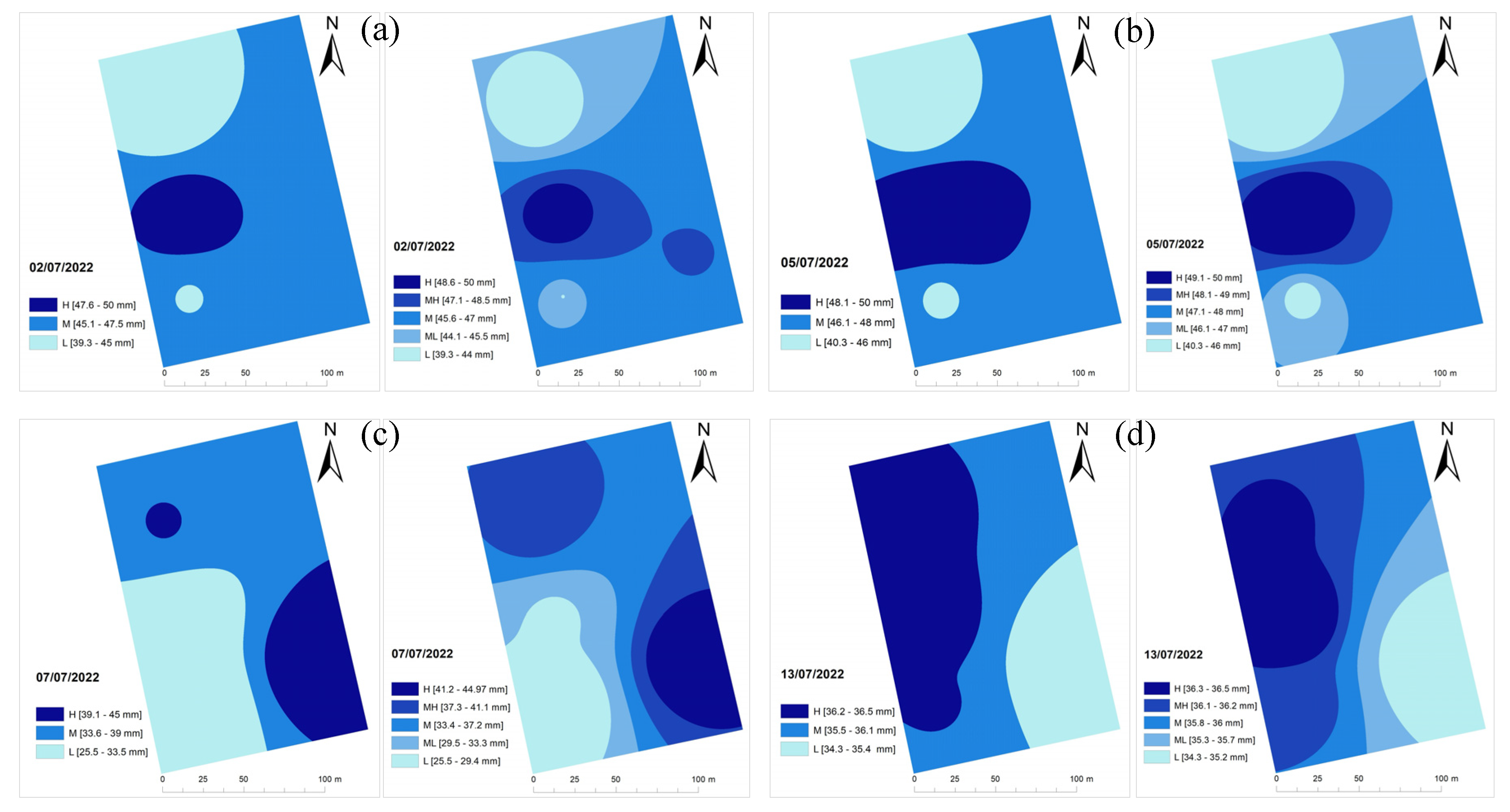
The irrigation maps for F2 in
Figure 5 show that the areas requiring the least amount of water moved from the top-left corner (July 2 and July 5) to the bottom-left (July 7) and bottom-right (July 13) sides of the field.
The locations of the areas needing the least amount of water kept changing for the remaining F2 during the irrigation season. The irrigation simulation maps in Figures 7 and 8 show a different behavior compared to F1, in that the dynamic changes in the spatial IN requirements can be prominent over time.
Table 6 shows the partitioning of the sub-section areas of the three- and five-zone irrigation maps for F1 and F2 derived from the maps in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, respectively.
The H level irrigation rate corresponded to areas from 0.89 ha to 32.6 ha with 3-zone analysis in F1 whereas 5-zone analysis resulted in 0.14 ha to 14.3 ha for H level rates on different irrigation days. Dividing the field into management zones shows that different parts of the field require different application rates to bring the soil MC to the FC. Five zones depicted the distribution of the rates more precisely for each irrigation date. In F2, the zone areas were smaller due to the smaller field size compared to that of F1. The CV values from about 45-65% both for F1 and F2 also show that the application rates for each zone need to be changed significantly over time. For instance, the CV level of 46.7% for M level area with 5-zone analysis was found from areas ranging from 3.0 ha (July 21) to 13.87 ha (August 4). The IN maps shown in
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7 and
Figure 8 are not readily applicable because of the lack of precise application technologies that can deliver irrigation water based on contour maps. The length of the lateral pipes in a drip irrigation system is designed to have the same length for each management zone in sub-plot areas up to four hectares in the current practices in the Karacabey district, intersecting with the simulated IN maps. Furthermore, the dynamic variation of the irrigation management zone from one irrigation to the next requires an irrigation system to respond accordingly.
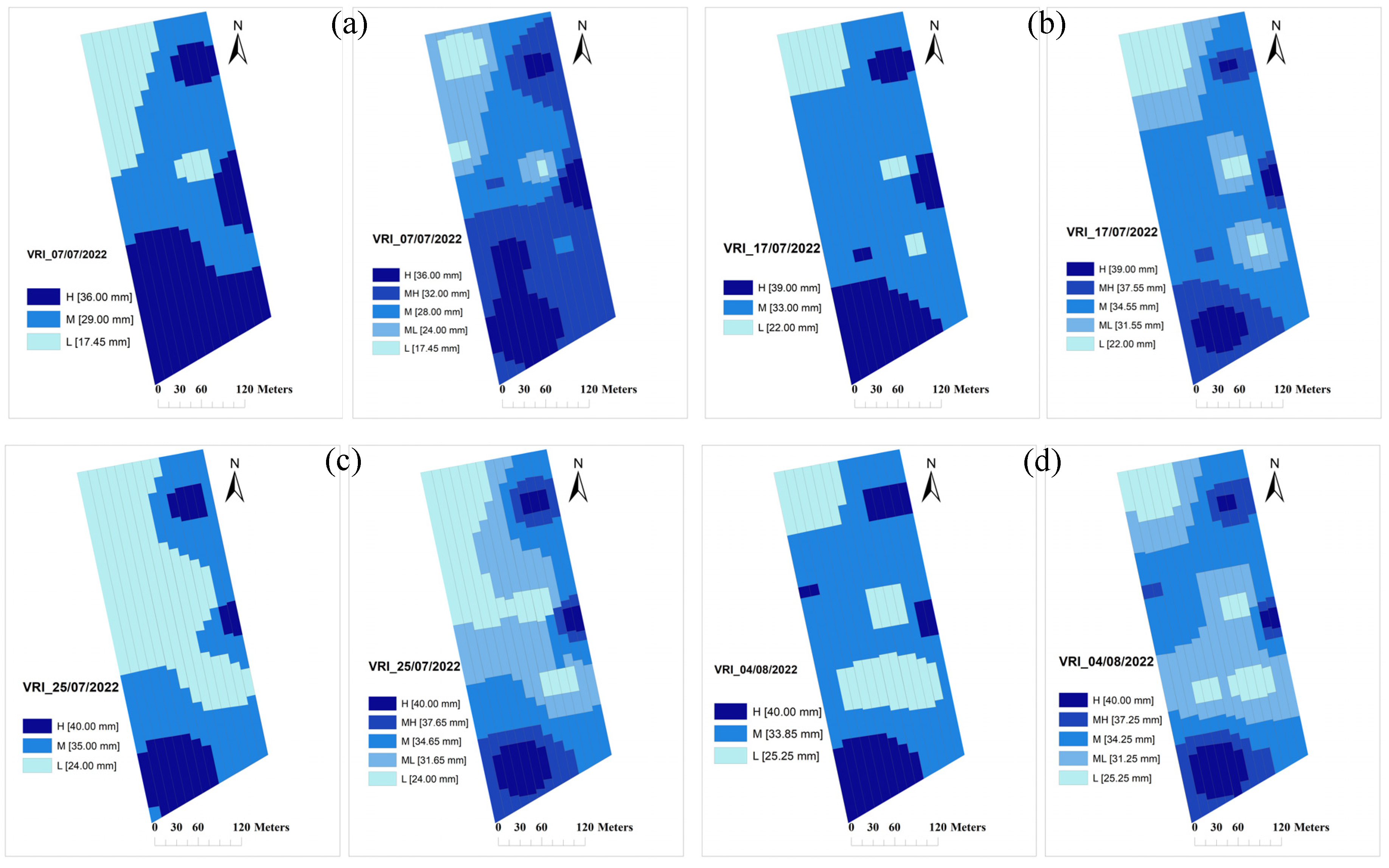
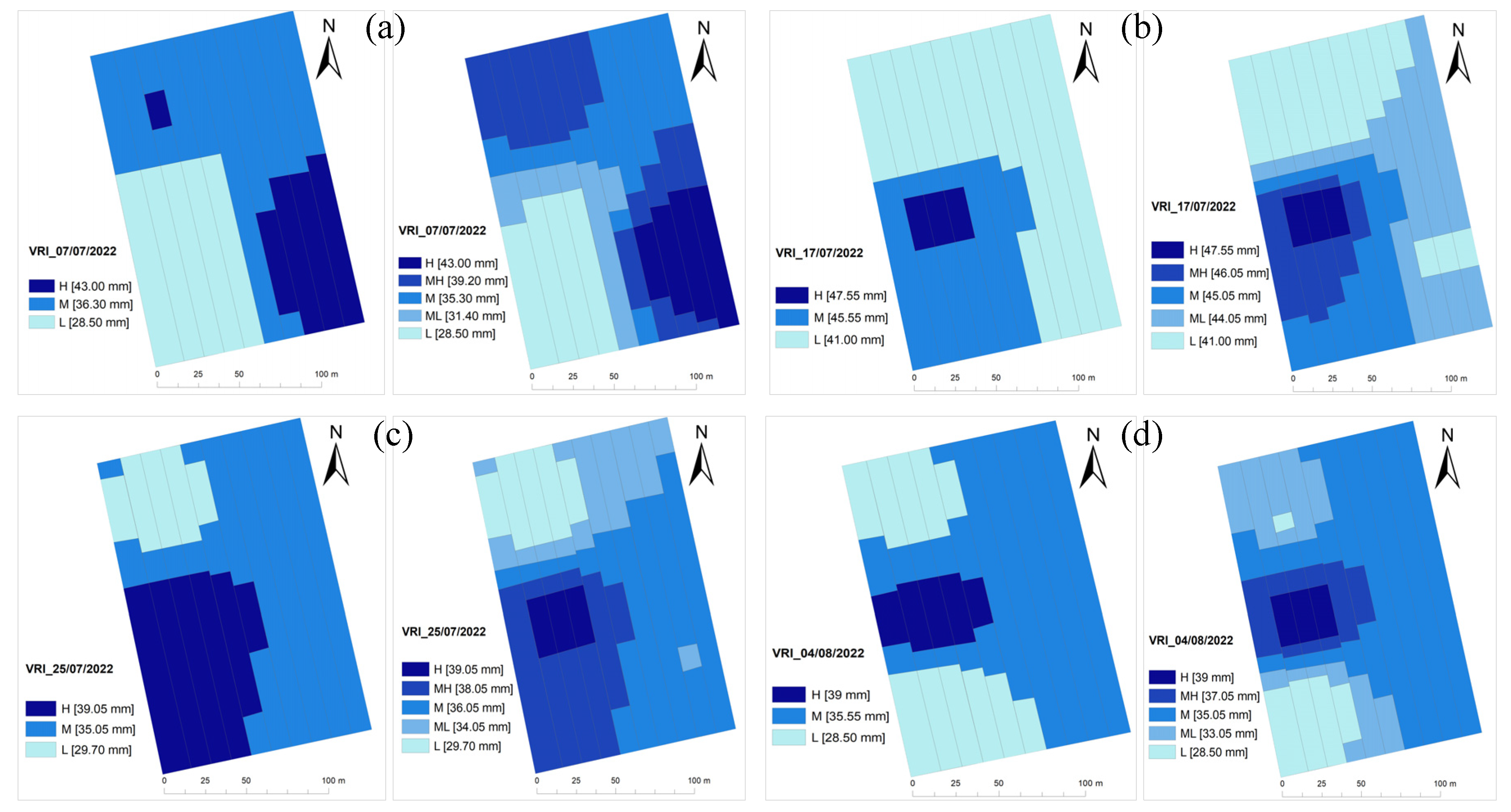
3.3. VRI maps for hose-reel irrigation machine
Since an irrigation system in a fixed-size management zone is unlikely to accurately respond to spatiotemporal irrigation needs, a linearly moving hose-reel irrigation system with section control was proposed as a solution in this study. For a four-section control machine, the IN maps were translated into grid maps so that the hose-reel irrigation machine can have a lateral application resolution of 11.5 m (with a working width of 46 m) and a longitudinal resolution with sub-meters due to the low ground speeds (30-80 m/h). Management zones with appropriate section widths that can be utilized by the VRFM are shown in
Figure 6 for four selected irrigation days, both with three- and five-zone mapping.
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 show that the ideal irrigation management zones showed in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 respectively, have to be changed due to the overlaps among the intersecting management zones when cells are formed with a width of 11.5 m with varying lengths. The lateral and longitudinal resolutions of the machine and the number of zones will be the initial determinants for the overall precision of the variable-rate irrigation application.
Table 7 provides the updated sub-areas of each management zone after the maps were fitted to the widths of the sections of the VRFM. When rectangular cells with fixed widths and varying lengths were used, the total area of each management zone changed accordingly. For instance, 3-zone H-level application areas for F1 ranged from 1.22 ha to 3.67 ha for different irrigation dates, which were 0.90 ha to 3.26 ha in
Table 6. For F2, L-level areas with 5-zone analysis ranged from 0.29 ha (August 4) to 0.98 ha (July 21) in
Table 7, whereas these areas were 0.27 ha and 0.99 ha, respectively for August 4 and July 21 in
Table 6. In terms of the variations among irrigation days, the CV values were high in the application maps fitted to the VRF machine, ranging from 25.77 to 67.4%.
The means of 3-zone areas for H, M, and L levels in Field 1 were 2.22, 4.34, and 1.71 ha and 0.50, 1.24, 1.24, and 0.75 ha in Field 2. The large area differences among the zones point out that the constant-rate applications would introduce large errors in the application rates. Similar evaluations can be performed for a specific irrigation date. For instance, 5-zone areas corresponding to July 17 in F1 range from 0.53 ha (H level) to 4.1 ha (M level) with the largest area, showing up to eight-fold area difference between different zones. It is documented in the literature that precision agriculture has the potential to reduce the excess amount of inputs in production agriculture, along with an increase in profit and energy saving [
33,
34]. [
35] found large irrigation need differences within a study field, with up to 26% less water requirement in the management zones compared to user-rate applications and suggested that sensor-based variable-rate irrigation scheduling would prevent users from applying over- or under-irrigation.
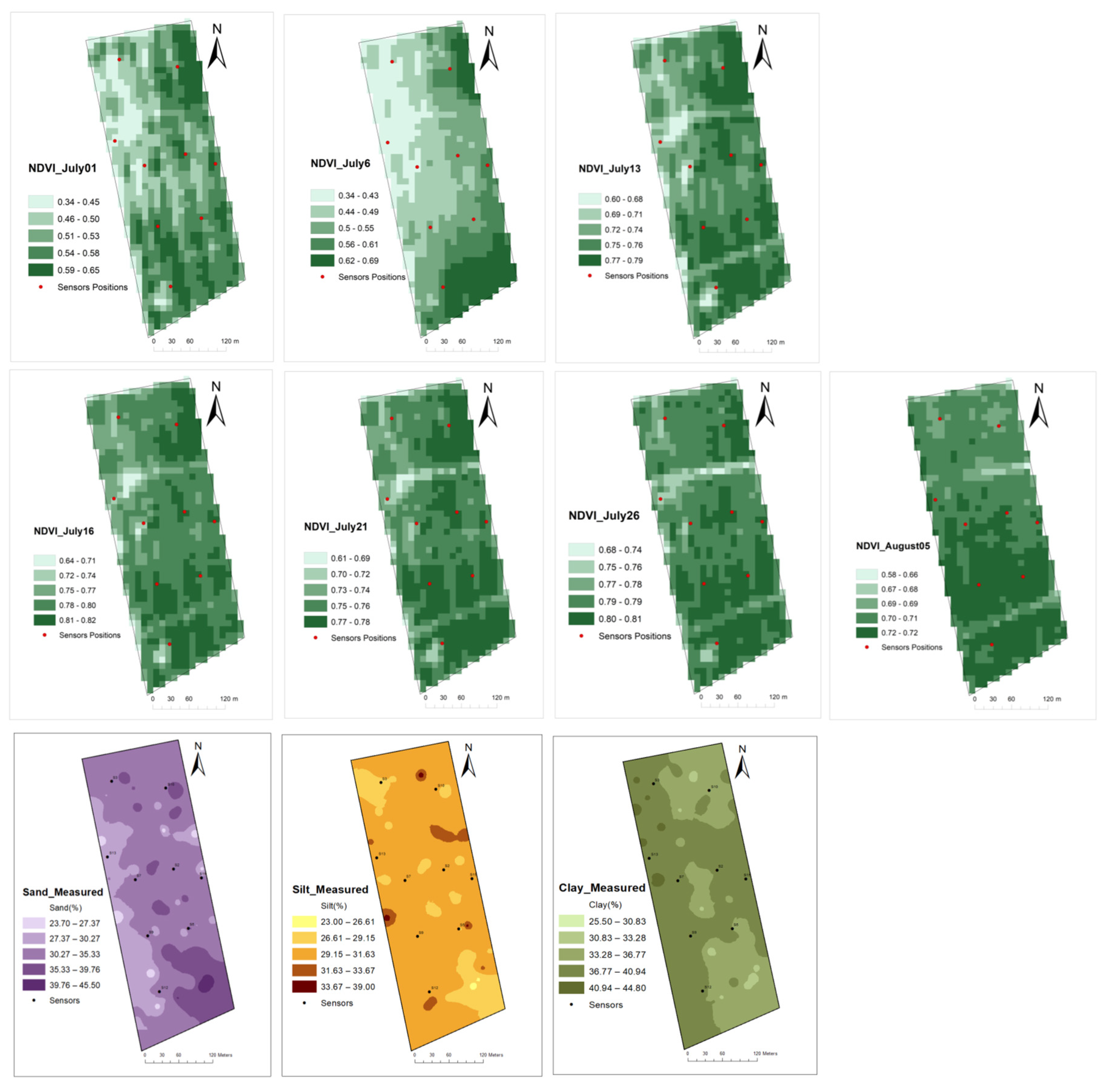
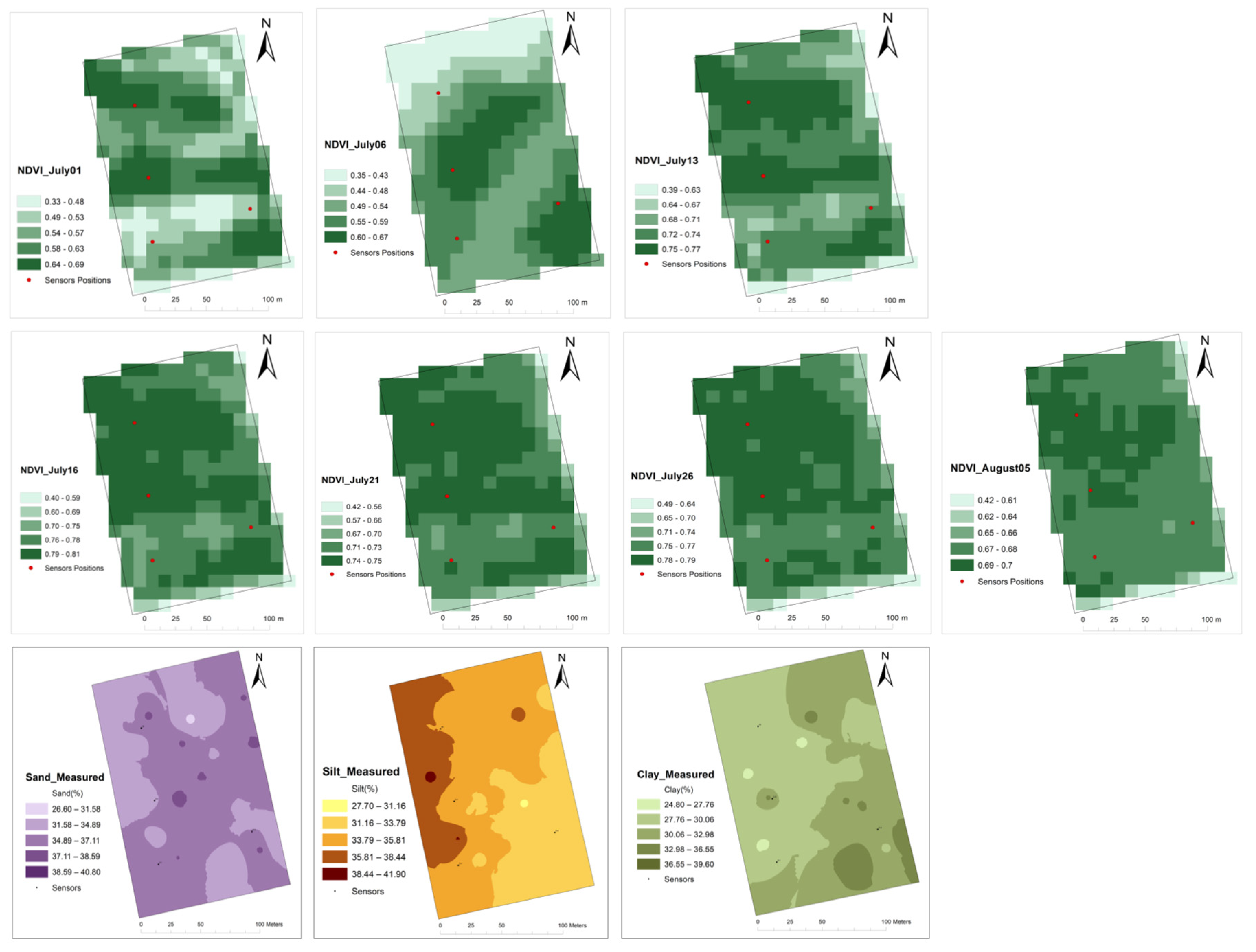
Neither the variations in NDVI nor the soil texture seemed to explain the sharp spatial or temporal changes in irrigation needs in this study.
Figure 8 and
Figure 9 could not reveal insight about the reasons for varying irrigation MZs within the field since there was no sign of correlation between the variations in MZs and NDVI or soil texture. Previous research has also concluded that NDVI data alone are not sufficient to make decisions in irrigation management [
36]. More data, such as spatial emergence rate, plant density, leaf area index, and pest (weed and disease) pressure on plant growth, may reveal the necessary information to explain the cause of varying irrigation management zones.
The application rates associated with the dynamic management zones simulated in this study were based on measurements using multiple number of soil moisture sensors installed in fields integrated with a cloud-based wireless system. A greater number of sensors may improve the accuracy of application maps, albeit at a higher cost. Data from sources other than soil moisture sensors have been used by researchers. Some researchers have utilized areal measurements, particularly NDVI, to reduce the daily soil moisture variance [
20,
37] and/or to develop a smart system for linear irrigation systems, whereas others have focused on individual sprinkler control in continuously moving irrigation systems [
38,
39,
40,
41].
Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques have been used to improve the decision-support process in irrigation scheduling [
42,
43,
44,
45]. Other data sources for irrigation decision-making can be weather stations, satellites, drones, soil electrical conductivity (EC) sensors, and leaf area index (LAI) sensors [
46,
47,
48,
49,
50]. Therefore, future studies should adopt data fusion of weather station data, electrical conductivity (EC), leaf area index (LAI), and satellite thermal and NDVI data to improve the irrigation management zones for a hose reel irrigation/fertigation system.
4. Conclusion
In this study, the irrigation needs of two maize fields were determined based on spatiotemporal soil moisture content variations using LoRaWAN-based soil moisture sensor technology in an attempt to simulate the dynamic irrigation management zones to be used with a hose reel irrigation machine. In this study, it was found that more water than that actually applied by the farmer using traditional methods had to be applied in all irrigations throughout the season. Based on constant user-rate applications and sensor-based irrigation recommendations, 1-7% and 2-17% more water should have been applied in Fields 1 and 2, respectively. Wireless soil MC technology with instantaneous data allowed to determine that the farmer had to start irrigation earlier and irrigate for a longer duration to meet the field capacity requirement. In addition, simulations of the irrigation management zones showed that the management zone was not fixed over time (particularly in F2); rather, the management zones changed temporally within the fields, requiring an update in the irrigation map for the next irrigation. The maps with contours generated using the raw data show the best approximation of spatial variability. However, the application technology for irrigation requires certain lateral and longitudinal resolutions imposing that the theoretical (contour) irrigation maps be converted to applicable grids or cells. Sensor-based 3- and 5-zone irrigation application maps fitted to the section controlled VRFM showed that uniform rates deviated significantly from site-specific irrigation needs. Determining the dynamic irrigation management zones, and hence the instantaneous irrigation needs in a given field, is of utmost importance to meet spatial and temporal water needs and optimize water use within the fields. Future work should adopt data fusion of weather, electrical conductivity (EC), leaf area index (LAI), and satellite thermal and NDVI data in an attempt to improve irrigation management zones for a variable rate hose reel fertigation system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A., and B.B.B.; methodology, B.B.B., S.A., and K.S.G; software, B.B.B.; validation, Y.T., and K.S.G.; formal analysis, B.B.B., and S.A.; investigation, B.B.B., S.A., Y.T., Y.U., and K.S.G.; resources, B.B.B., S.A., and Y.U.; data curation, B.B.B., and M.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, S.A., and B.B.B.; writing—review and editing, Y.T., A.M.M., X.E.P., M.Q., K.D., C.P., and G.T.; visualization, B.B.B., and S.A.; supervision, S.A., Y.T., and K.S.G; project administration, A.M.M.; funding acquisition, A.M.M., and Y.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was founded by ICT-AGRI-FOOD 2019 Joint Call (European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme), for “A Data-Driven Platform for Site-Specific Fertigation” (ADDFerti) Project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that has been used during this study is confidential.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support received from the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBITAK), Contract no. 120N787, Fonds Weten-schappelijk Onderzoek (FWO), contract no. S007621N, General Secretariat for Research and Innovation (GSRI), contract no. Τ12ΕΡA5-00048, for “A Data-Driven Platform for Site-Specific Fertigation” (ADDFerti) Project. The authors would like to thank Karaca Farm for their cooperation with this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Kalboussi, N.; Biard, Y.; Pradeleix, L.; Rapaport, A.; Sinfort, C.; Ait-Mouheb, N. Life cycle assessment as decision support tool for water reuse in agriculture irrigation. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 836, 155486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrinmayi, G.; Bhagyashri, D.; Atul, V. A Smart Irrigation System for Agriculture Based on Wireless Sensors. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol 2016, 5(5), 6893–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Qi, Z.; Burghate, R.; Yuan, S.; Jiao, X.; & Xu, J. Irrigation scheduling approaches and applications: A review. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering 2020, 146(6), 04020007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaščak, I.; Jurišić, M.; Radočaj, D.; Vujić, M.; & Zimmer, D. An overview of precision irrigation systems used in agriculture. Tehnički glasnik 2021, 15(4), 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, L.; Di Gioia, F.; Choi, D.; Elia, A.; & Heinemann, P. LoRaWAN based internet of things (IoT) system for precision irrigation in plasticulture fresh-market tomato. Smart Agricultural Technology 2022, 2, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davcev, D.; Mitreski, K.; Trajkovic, S.; Nikolovski, V.; & Koteli, N. IoT agriculture system based on LoRaWAN. In 2018 14th IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems (WFCS) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.; & Tian, L. A promising trend for field information collection: An air-ground multi-sensor monitoring system. Information processing in agriculture 2018, 5(2), 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haule, J., Michael, K. Deployment of wireless sensor networks (WSN) in automated irrigation management and scheduling systems: a review. In Proceedings of the 2nd Pan African international conference on science, computing and telecommunications (PACT 2014) (pp. 86-91). IEEE. 2014.
- Hamami, L.; Nassereddine, B. Application of wireless sensor networks in the field of irrigation: A review. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2020, 179, 105782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Riaz, S.; Abid, A.; Umer, T.; & Zikria, Y.B. Role of IoT technology in agriculture: A systematic literature review. Electronics 2020, 9(2), 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblete-Echeverría, C.; & Fuentes, S. Special Issue “Emerging Sensor Technology in Agriculture”. Sensors 2020, 20(14), 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. A.; Ilango, P. The impact of wireless sensor network in the field of precision agriculture: A review. Wireless Personal Communications 2018, 98, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaynes, D. B.; Colvin, T. S. Spatiotemporal variability of corn and soybean yield. Agronomy Journal 1997, 89(1), 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.X.; Whelan, B.M.; & Shatar, T.M. Variability and uncertainty in spatial, temporal and spatiotemporal crop-yield and related data. In Ciba Foundation Symposium 210-Precision Agriculture: Spatial and Temporal Variability of Environmental Quality (pp. 141-160). Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 2007.
- Cao, J.; Leng, G.; Yang, P.; Zhou, Q.; & Wu, W. Variability in Crop Response to Spatiotemporal Variation in Climate in China, 1980–2014. Land 2022, 11(8), 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Martelli, R.; Scudiero, E.; Lupia, F.; Falsone, G.; Rondelli, V.; & Barbanti, L. Soil and climate factors drive spatio-temporal variability of arable crop yields under uniform management in Northern Italy. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 2023, 69(1), 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, S.A.; Evett, S. R.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Andrade, M.A.; Marek, T.H.; Heeren, D.M.; ... & LaRue, J.L. Identifying advantages and disadvantages of variable rate irrigation: An updated review. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 2019, 35(6), 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.; Podcknee, S. Development of a Variable-Rate Pivot Irrigation Control System. In Proceedings of the 2003 Georgia Water Resources Conference at the University of Georgia, Georgia, USA, 23 – 24 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vellidis, G.; Liakos, V.; Porter, W; Tucker, M; Liang, Xi. A Dynamic Variable Rate Irrigation Control System. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Precision Agriculture, St. Louis, Missouri, USA, July 31 – August 4, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aleotti, J.; Amoretti, M.; Nicoli, A.; Caselli, S. A Smart Precision-Agriculture Platform for Linear Irrigation Systems. IEEE 2022.
- David, H.; & Rakesh, V.S. Smart Irrigation Management System Using Lora Wan Based Sensor Nodes. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research 2020, 15(11), 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifnasab, H.; Mahrokh, A.; Dehghanisanij, H.; Łazuka, E.; Łagód, G.; & Karami, H. Evaluating the Use of Intelligent Irrigation Systems Based on the IoT in Grain Corn Irrigation. Water 2023, 15(7), 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briciu-Burghina, C.; Zhou, J.; Ali, M. I.; & Regan, F. Demonstrating the potential of a low-cost soil moisture sensor network. Sensors 2020, 22(3), 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, F.F.; Messenger, R.; Captain, G.L.; Ekin, S.; Jacob, J.D.; Taghvaeian, S.; O’Hara, J.F. Soil moisture monitoring through UAS-assisted internet of things LoRaWAN wireless underground sensors. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 102107–102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froiz-Míguez, I.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Celaya-Echarri, M.; Blanco-Novoa, Ó.; Azpilicueta, L.; ... & Fernández-Caramés, T. M. Design, implementation, and empirical validation of an IoT smart irrigation system for fog computing applications based on Lora and Lorawan sensor nodes. Sensors 2020, 20(23), 6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sutil, F.; & Cano-Ortega, A. Smart control and energy efficiency in irrigation systems using LoRaWAN. Sensors 2021, 21(21), 7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.R.; Nallakaruppan, M.K.; Chengoden, R.; Koppu, S.; Iyapparaja, M.; Sadhasivam, J.; Sethuraman, S. Smart Water Resource Management Using Artificial Intelligence—A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14(20), 13384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragino LSE01-LoRaWAN Soil Moisture & EC Sensor User Manual. Available online: https://www.dragino.com/products/agriculture-weather-station/item/277-se01-lb.html (accessed on 17/06/2023).
- El-Naggar, A.G.; Hedley, C.B.; Horne, D.; Roudier, P.; & Clothier, B. E.; & Clothier, B. E. Soil sensing technology improves application of irrigation water. Agricultural Water Management 2020, 228, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, S.; Rees, J.M.; Zoubek, G.L.; van DeWalle, B.S.; Rathje, W.R.; DeBuhr, R.; Leininger, D.; Siekman, D.D.; Schneider, J.W.; Christiansen, A.P. Nebraska agricultural water management demonstration network (NAWMDN): Integrating research and extension/outreach. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 2010, 26(4), 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha Leme Filho, J.F.; Ortiz, B.V.; Damianidis, D.; Balkcom, K.S.; Dougherty, M.; & Poschel, T. Irrigation scheduling to promote corn productivity in central Alabama. Journal of Agricultural Science 2020, 12, No. 9. 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Duan, A.; Qiu, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Distribution of roots and root length density in a maize/soybean strip intercropping system. Agricultural Water Management 2010, 98(1), 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, S. A.; & Rodrigues, L. N. Increased profitability and energy savings potential with the use of precision irrigation. Agricultural Water Management 2022, 270, 107730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vories, E.; O’Shaughnessy, S.; Sudduth, K.; Evett, S.; Andrade, M.; & Drummond, S. Comparison of precision and conventional irrigation management of cotton and impact of soil texture. Precision Agriculture 2021, 22, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondesan, L.; Ortiz, B.V.; Morlin, F.; Morata, G.; Duzy, L.; van Santen, E.; ... & Vellidis, G. A comparison of precision and conventional irrigation in corn production in Southeast Alabama. Precision Agriculture 2023, 24(1), 40–67. [Google Scholar]
- Quebrajo, L.; Perez-Ruiz, M.; Perez-Urrestarazu, L.; Martinez, G.; Egea, G. Linking thermal imaging and soil remote sensing to enhance irrigation management of sugar beet. Biosystems Engineering 2017, 165, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanet, M.; Scudiero, E.; Skaggs, T.H.; Fernàndez-Garcia, D.; Ferrer, F.; Rodrigo, G.; & Bellvert, J. Dynamic management zones for irrigation scheduling. Agricultural water management 2020, 238, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, A.F.; Cardenas, P.F.; Canales, A.; Jimenez, F.; & Portacio, A. A survey on intelligent agents and multi-agents for irrigation scheduling. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2020, 176, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, J.; Wendroth, Ole.; Matocha, C.; Zhu, J. Delineating Site-Speciic Management Zones and Evaluating Soil Water Temporal Dynamics in a Farmer’s Field in Kentucky. Vadose Zone Journal | Advancing Critical Zone Science 2019, 15391663. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Evans, R.G.; & Iversen, W.M. Remote sensing and control of an irrigation system using a distributed wireless sensor network. IEEE transactions on instrumentation and measurement 2008, 57(7), 1379–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, J.L.; Pierce, F.J.; Elliott, T.V.; & Evans, R.G. A remote irrigation monitoring and control system for continuous move systems. Part A: Description and development. Precision Agriculture 2010, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qammaz, A.; Darabkh, K.A.; Abualigah, L.; Khasawneh, A.M.; & Zinonos, Z. An AI-based irrigation and weather forecasting system utilizing LoraWAN and cloud computing technologies. In 2021 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (ElConRus) (pp. 443-448). IEEE 2021.
- Talaviya, T.; Shah, D.; Patel, N.; Yagnik, H.; & Shah, M. Implementation of artificial intelligence in agriculture for optimisation of irrigation and application of pesticides and herbicides. Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture 2020, 4, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangprathub, J.; Boonnam, N.; Kajornkasirat, S.; Lekbangpong, N.; Wanichsombat, A.; & Nillaor, P. IoT and agriculture data analysis for smart farm. Computers and electronics in agriculture 2019, 156, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, R.G.; Poyato, E.C.; Montesinos, P.; & Díaz, J.R. Prediction of applied irrigation depths at farm level using artificial intelligence techniques. Agricultural Water Management 2018, 206, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbedo, J.G. A. Data Fusion in Agriculture: Resolving Ambiguities and Closing Data Gaps. Sensors 2022, 22(6), 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaideen, K.; Yousef, B.A.; AlMallahi, M.N.; Tan, Y. C.; Mahmoud, M.; Jaber, H.; & Ramadan, M. An overview of smart irrigation systems using IoT. Energy Nexus 2022, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y.; An, J.; He, L.; Zheng, L.; & Zou, Z. An IoT-based intelligent irrigation system with data fusion and a self-powered wide-area network. Journal of Industrial Information Integration 2022, 29, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, T.; Ma, H.; He, C.; Xu, F.; Malone, R.W.; ... & He, J. Dynamic within-season irrigation scheduling for maize production in Northwest China: A Method Based on Weather Data Fusion and yield prediction by DSSAT. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2020, 285, 107928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, E.; Castrignanò, A.; Arvanitis, K.; Fountas, S. A multi-source data fusion approach to assess spatial-temporal variability and delineate homogeneous zones: A use case in a table grape vineyard in Greece. Science of the Total Environment 2019, 684, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Study site (Field 1 and Field 2) with irrigation main lines and sub-plots for the drip-irrigation.
Figure 1.
Study site (Field 1 and Field 2) with irrigation main lines and sub-plots for the drip-irrigation.
Figure 2.
LoRaWAN used for continuous soil moisture data collection [
28].
Figure 2.
LoRaWAN used for continuous soil moisture data collection [
28].
Figure 3.
The soil moisture content (MC) before irrigation (BI) and after irrigation (AI) and their relationship with field capacity average (FC_Ave) permanent point average (PWP_Ave), and Management Allowable Depletion (MAD) for Field 1 (a) and Field 2 (b).
Figure 3.
The soil moisture content (MC) before irrigation (BI) and after irrigation (AI) and their relationship with field capacity average (FC_Ave) permanent point average (PWP_Ave), and Management Allowable Depletion (MAD) for Field 1 (a) and Field 2 (b).
Figure 4.
Three and five irrigation management zones maps for Field 1 for different irrigation dates; (a), July 2; (b), July 5; (c), July 7; (d), July 13; (e), July 17; (f), July 21; (g), July 25; and (h), August 4, 2022.
Figure 4.
Three and five irrigation management zones maps for Field 1 for different irrigation dates; (a), July 2; (b), July 5; (c), July 7; (d), July 13; (e), July 17; (f), July 21; (g), July 25; and (h), August 4, 2022.
Figure 5.
Three and five irrigation management zones maps for Field 2 for different irrigation dates; (a), July 2; (b), July 5; (c), July 7; (d), July 13; (e), July 17; (f), July 21; (g), July 25; and (h), August 4, 2022.
Figure 5.
Three and five irrigation management zones maps for Field 2 for different irrigation dates; (a), July 2; (b), July 5; (c), July 7; (d), July 13; (e), July 17; (f), July 21; (g), July 25; and (h), August 4, 2022.
Figure 6.
Three and five-MZs maps for VRI using VRFM for Field 1 for selected irrigation days; (a), July 7; (b), July 17; (c), July 25; and (d), August 4, 2022.
Figure 6.
Three and five-MZs maps for VRI using VRFM for Field 1 for selected irrigation days; (a), July 7; (b), July 17; (c), July 25; and (d), August 4, 2022.
Figure 7.
Three- and five-MZs maps for VRI using VRFM for Field 2 for selected irrigation days (a), July 7; (b), July 17; (c), July 25; and (d), August 4, 2022.
Figure 7.
Three- and five-MZs maps for VRI using VRFM for Field 2 for selected irrigation days (a), July 7; (b), July 17; (c), July 25; and (d), August 4, 2022.
Figure 8.
NDVI and soil texture (Sand, Silt, and Clay maps for Field 1.
Figure 8.
NDVI and soil texture (Sand, Silt, and Clay maps for Field 1.
Figure 9.
NDVI and soil texture (Sand, Silt, and Clay) maps for Field 2.
Figure 9.
NDVI and soil texture (Sand, Silt, and Clay) maps for Field 2.
Table 1.
Laboratory results for soil samples taken at the sensor locations for Field 1 and Field 2.
Table 1.
Laboratory results for soil samples taken at the sensor locations for Field 1 and Field 2.
| |
Sensor
No |
FC
(% w/w) |
PWP
(% w/w) |
VW
(g/cm3) |
FC
(mm) |
PWP
(mm) |
AW
(mm) |
MAD
(mm) |
| F1 |
S2 |
32.49 |
14.80 |
1.45 |
141.10 |
64.27 |
76.84 |
38.42 |
| S3 |
29.17 |
14.38 |
1.47 |
128.41 |
63.28 |
65.13 |
32.57 |
| S5 |
32.88 |
15.28 |
1.42 |
139.72 |
64.94 |
74.78 |
37.39 |
| S7 |
31.66 |
15.99 |
1.44 |
137.10 |
69.24 |
67.86 |
33.93 |
| S9 |
32.96 |
16.36 |
1.43 |
141.50 |
70.25 |
71.25 |
35.63 |
| S10 |
29.12 |
12.92 |
1.50 |
131.11 |
58.19 |
72.92 |
36.46 |
| S12 |
34.03 |
15.74 |
1.42 |
144.51 |
66.82 |
77.70 |
38.85 |
| S13 |
32.21 |
16.09 |
1.44 |
139.28 |
69.56 |
69.71 |
34.86 |
| S15 |
33.86 |
15.01 |
1.45 |
147.68 |
65.47 |
82.21 |
41.11 |
| Ave. |
32.04 |
15.17 |
1.45 |
138.94 |
65.78 |
73.16 |
36.58 |
| Std |
1.80 |
1.07 |
0.03 |
6.07 |
3.78 |
5.32 |
2.66 |
| CV (%) |
5.62 |
7.03 |
1.82 |
4.37 |
5.75 |
7.28 |
7.28 |
| F2 |
S8 |
28.07 |
9.87 |
1.56 |
131.58 |
46.27 |
85.31 |
42.66 |
| S11 |
28.79 |
11.10 |
1.52 |
130.91 |
50.47 |
80.44 |
40.22 |
| S14 |
27.40 |
6.61 |
1.56 |
127.92 |
30.87 |
97.05 |
48.52 |
| S18 |
28.00 |
6.87 |
1.46 |
122.38 |
30.05 |
92.33 |
46.17 |
| Ave. |
28.06 |
8.61 |
1.52 |
128.20 |
39.41 |
88.78 |
44.39 |
| Std |
0.57 |
2.22 |
0.05 |
4.19 |
10.49 |
7.36 |
3.68 |
| CV (%) |
2.02 |
25.77 |
3.18 |
3.27 |
26.61 |
8.29 |
8.29 |
Table 2.
Irrigation needs to reach field capacity for each irrigation date based on average MC from all sensors for Field 1 and Field 2.
Table 2.
Irrigation needs to reach field capacity for each irrigation date based on average MC from all sensors for Field 1 and Field 2.
Irrigation
date |
MC_BI
(mm) |
Irrigation duration(h) |
User rate
(mm/da) |
Recommended
(mm/da) |
% difference
(mm/da) |
| F1 |
July 2 |
108.17 |
7 |
20.16 |
30.73 |
-34.4 |
| July 5 |
111.3 |
7 |
20.16 |
27.6 |
-26.9 |
| July 7 |
111.9 |
8 |
23.04 |
27.0 |
-14.7 |
| July 13 |
111.93 |
6 |
17.28 |
26.97 |
-35.9 |
| July 17 |
108.23 |
8 |
23.04 |
30.7 |
-24.9 |
| July 21 |
107.1 |
8 |
23.04 |
31.8 |
-27.6 |
| July 25 |
109.07 |
9 |
25.92 |
29.83 |
-13.1 |
| August 4 |
108.7 |
10 |
28.8 |
30.2 |
-4.6 |
| Average |
109.55 |
7.9 |
22.68 |
32.65 |
-22.76 |
| F2 |
July 2 |
86.78 |
7 |
20.16 |
46.03 |
-56.20 |
| July 5 |
85.73 |
6 |
17.28 |
47.19 |
-63.38 |
| July 7 |
97.05 |
6 |
17.28 |
34.61 |
-50.07 |
| July 13 |
96.00 |
6 |
17.28 |
35.78 |
-51.70 |
| July 17 |
88.43 |
8 |
23.04 |
44.19 |
-47.86 |
| July 21 |
95.25 |
8 |
23.04 |
36.61 |
-37.06 |
| July 25 |
95.85 |
9 |
25.92 |
35.94 |
-27.88 |
| August 4 |
97.28 |
10 |
28.80 |
34.36 |
-16.18 |
| Average |
92.79 |
7.50 |
21.60 |
39.34 |
-45.09 |
Table 3.
Percent user difference between after-irrigation moisture content and field capacity (FC) for Field 1 and Field 2.
Table 3.
Percent user difference between after-irrigation moisture content and field capacity (FC) for Field 1 and Field 2.
| F1 |
|
F2 |
| Irrigation date |
FC_Ave
(mm) |
MC_BI (mm) |
MC_AI
(mm) |
Diff. (mm) |
%User diff. |
|
FC_Ave
(mm) |
MC_BI
(mm) |
MC_AI
(mm) |
Diff. (mm) |
%User diff. |
| July 2 |
138.9 |
108.2 |
128.3 |
10.6 |
-7.6 |
|
128 |
87 |
107 |
21 |
-17 |
| July 5 |
138.9 |
111.3 |
131.5 |
7.5 |
-5.4 |
|
128 |
86 |
106 |
22 |
-17 |
| July 7 |
138.9 |
111.9 |
134.9 |
4 |
-2.9 |
|
128 |
97 |
120 |
8.1 |
-6.3 |
| July 13 |
138.9 |
111.9 |
129.2 |
9.7 |
-7 |
|
128 |
96 |
113 |
15 |
-12 |
| July 17 |
138.9 |
108.2 |
131.3 |
7.7 |
-5.5 |
|
128 |
88 |
112 |
17 |
-13 |
| July 21 |
138.9 |
107.1 |
130.1 |
8.8 |
-6.3 |
|
128 |
95 |
118 |
9.9 |
-7.7 |
| July 25 |
138.9 |
109.1 |
135 |
4 |
-2.8 |
|
128 |
96 |
122 |
6.4 |
-5 |
| August 4 |
138.9 |
108.7 |
137.5 |
1.4 |
-1 |
|
128 |
97 |
126 |
2.1 |
-1.7 |
Table 4.
Average irrigation needs (mm/da) per irrigation and maximum differences among sensors for Field 1 and Field 2.
Table 4.
Average irrigation needs (mm/da) per irrigation and maximum differences among sensors for Field 1 and Field 2.
| |
|
Sensor No |
July 2 |
July 5 |
July 7 |
July 13 |
July 17 |
July 21 |
July 25 |
August 4 |
| |
|
S2 |
18.12 |
12.12 |
10.12 |
18.12 |
19.78 |
19.45 |
19.45 |
19.78 |
| |
S3 |
12.68 |
8.01 |
8.35 |
8.68 |
12.35 |
15.35 |
16.01 |
18.68 |
| |
S5 |
28.25 |
27.58 |
27.58 |
23.58 |
22.25 |
25.58 |
22.25 |
20.25 |
| |
S7 |
34.00 |
31.33 |
31.33 |
35.33 |
36.67 |
30.00 |
28.67 |
35.33 |
| |
S9 |
37.22 |
41.89 |
41.56 |
36.22 |
37.22 |
37.56 |
35.22 |
24.56 |
| F1 |
S10 |
47.34 |
41.67 |
41.67 |
36.34 |
42.67 |
45.01 |
48.01 |
43.67 |
| |
S12 |
40.24 |
40.24 |
40.24 |
36.57 |
47.57 |
52.90 |
51.90 |
52.90 |
| |
S13 |
34.75 |
19.09 |
15.42 |
26.09 |
35.09 |
40.42 |
24.09 |
38.09 |
| |
S15 |
55.09 |
54.42 |
54.09 |
49.09 |
53.42 |
52.09 |
53.09 |
49.09 |
| |
Ave |
34.2 |
30.7 |
30.0 |
30.0 |
34.1 |
35.4 |
33.2 |
33.6 |
| |
Std |
13.3 |
15.4 |
16.0 |
12.1 |
13.5 |
13.6 |
14.5 |
13.3 |
| |
% CV |
39 |
50 |
53 |
40 |
40 |
39 |
44 |
40 |
| |
Max diff (%) |
0.77 |
0.85 |
0.85 |
0.82 |
0.77 |
0.71 |
0.70 |
0.65 |
| |
|
S8 |
39.20 |
40.20 |
39.20 |
36.20 |
38.20 |
32.20 |
26.20 |
30.86 |
| |
S11 |
43.79 |
44.12 |
25.46 |
36.12 |
45.79 |
39.12 |
37.79 |
23.79 |
| |
S14 |
53.80 |
57.13 |
28.80 |
36.46 |
50.13 |
44.13 |
45.46 |
46.46 |
| F2 |
S18 |
47.32 |
47.32 |
44.98 |
34.32 |
42.65 |
30.98 |
34.32 |
36.32 |
| |
Ave |
46.03 |
47.19 |
34.61 |
35.78 |
44.19 |
36.61 |
35.94 |
34.36 |
| |
Std |
6.2 |
7.2 |
9.1 |
1.0 |
5.0 |
6.2 |
8.0 |
9.6 |
| |
% CV |
13.4 |
15.3 |
26.2 |
2.7 |
11.4 |
16.8 |
22.2 |
27.8 |
| |
Max diff (%) |
0.27 |
0.30 |
0.43 |
0.06 |
0.24 |
0.30 |
0.42 |
0.49 |
Table 5.
The percent difference between the average sensor readings to point-based moisture content (MC) reading for each irrigation date for Field 1 and Field 2.
Table 5.
The percent difference between the average sensor readings to point-based moisture content (MC) reading for each irrigation date for Field 1 and Field 2.
| |
Sensor No |
July 2 |
July 5 |
July 7 |
July 13 |
July 17 |
July 21 |
July 25 |
August 4 |
| F1 |
S2 |
15.4 |
17.0 |
18.0 |
11.5 |
13.9 |
15.4 |
13.3 |
13.4 |
| S3 |
8.2 |
8.9 |
8.0 |
7.7 |
8.4 |
7.0 |
4.5 |
2.7 |
| S5 |
5.7 |
3.2 |
2.7 |
5.9 |
10.6 |
9.0 |
9.7 |
11.8 |
| S7 |
-1.5 |
-2.2 |
-2.7 |
-5.9 |
-3.8 |
2.8 |
2.0 |
-3.1 |
| S9 |
-0.2 |
-6.7 |
-7.0 |
-2.7 |
-0.2 |
0.6 |
0.7 |
9.8 |
| S10 |
-18.2 |
-15.9 |
-16.4 |
-12.1 |
-14.4 |
-15.4 |
-19.4 |
-15.5 |
| S12 |
0.1 |
-2.7 |
-3.2 |
-0.3 |
-6.0 |
-9.5 |
-10.3 |
-10.9 |
| S13 |
-0.2 |
9.7 |
12.1 |
3.5 |
-0.5 |
-3.9 |
7.8 |
-3.4 |
| S15 |
-9.3 |
-11.3 |
-11.5 |
-7.5 |
-8.0 |
-5.9 |
-8.4 |
-4.8 |
| F2 |
S8 |
11.0 |
11.3 |
-0.8 |
3.1 |
9.9 |
7.7 |
12.7 |
6.7 |
| S11 |
5.4 |
6.4 |
11.3 |
2.5 |
1.4 |
0.5 |
1.1 |
12.6 |
| S14 |
-8.4 |
-10.8 |
5.1 |
-0.9 |
-6.4 |
-7.4 |
-9.2 |
-11.5 |
| S18 |
-8.0 |
-6.9 |
-15.6 |
-4.7 |
-5.0 |
-0.8 |
-4.5 |
-7.8 |
Table 6.
Variation of area (ha) of each management zone over time for variable irrigation based on OK for Field 1 and Field 2.
Table 6.
Variation of area (ha) of each management zone over time for variable irrigation based on OK for Field 1 and Field 2.
| |
|
3- MZs |
|
5-MZs |
| |
Irrigation date/rate |
H |
M |
L |
|
H |
MH |
M |
ML |
L |
| F1 |
July 2 |
1.60 |
5.36 |
1.32 |
|
0.41 |
1.18 |
3.06 |
2.58 |
1.05 |
| July 5 |
0.90 |
4.26 |
3.12 |
|
0.14 |
0.75 |
2.82 |
1.97 |
2.60 |
| July 7 |
3.26 |
3.45 |
1.57 |
|
1.44 |
3.28 |
2.00 |
1.11 |
0.46 |
| July 13 |
3.56 |
3.58 |
1.14 |
|
0.72 |
4.26 |
2.17 |
0.55 |
0.59 |
| July 17 |
1.80 |
5.53 |
0.95 |
|
0.49 |
1.31 |
4.09 |
1.44 |
0.95 |
| July 21 |
1.54 |
4.95 |
1.79 |
|
1.20 |
1.76 |
3.53 |
1.11 |
0.68 |
| July 25 |
1.20 |
3.08 |
4.00 |
|
0.65 |
1.06 |
2.08 |
2.51 |
1.98 |
| August 4 |
1.35 |
4.93 |
2.01 |
|
0.40 |
1.20 |
3.07 |
2.65 |
0.97 |
| Ave. |
1.90 |
4.39 |
1.99 |
|
0.68 |
1.85 |
2.85 |
1.74 |
1.16 |
| Std dev. |
0.98 |
0.94 |
1.06 |
|
0.43 |
1.24 |
0.74 |
0.80 |
0.74 |
| %CV |
51.31 |
21.28 |
53.11 |
|
63.67 |
67.24 |
26.10 |
45.94 |
64.21 |
| F2 |
July 2 |
0.27 |
1.69 |
0.54 |
|
0.13 |
0.38 |
1.24 |
0.48 |
0.28 |
| July 5 |
0.52 |
1.50 |
0.49 |
|
0.29 |
0.23 |
0.96 |
0.53 |
0.49 |
| July 7 |
0.49 |
1.21 |
0.80 |
|
0.33 |
0.69 |
0.69 |
0.30 |
0.49 |
| July 13 |
0.94 |
1.01 |
0.56 |
|
0.32 |
0.93 |
0.50 |
0.30 |
0.46 |
| July 17 |
0.11 |
0.83 |
1.56 |
|
0.11 |
0.32 |
0.51 |
0.99 |
0.57 |
| July 21 |
0.56 |
0.96 |
0.99 |
|
0.21 |
0.34 |
0.30 |
0.66 |
0.99 |
| July 25 |
0.78 |
1.43 |
0.29 |
|
0.16 |
0.62 |
0.97 |
0.46 |
0.29 |
| August 4 |
0.22 |
1.55 |
0.74 |
|
0.13 |
0.24 |
1.39 |
0.47 |
0.27 |
| Ave. |
0.49 |
1.27 |
0.75 |
|
0.21 |
0.47 |
0.82 |
0.52 |
0.48 |
| Std dev. |
0.28 |
0.31 |
0.39 |
|
0.09 |
0.25 |
0.38 |
0.22 |
0.23 |
| %CV |
57.97 |
24.64 |
52.65 |
|
43.69 |
53.08 |
46.66 |
42.57 |
48.91 |
Table 7.
Area (ha) of each variable rate irrigation (VRI) management zone for VRFM for Field 1 and Field 2.
Table 7.
Area (ha) of each variable rate irrigation (VRI) management zone for VRFM for Field 1 and Field 2.
| |
|
3-MZs |
|
5-MZs |
| |
Irrigation date/rate |
H |
M |
L |
|
H |
MH |
M |
ML |
L |
| F1 |
July 2 |
1.61 |
5.35 |
1.32 |
|
0.41 |
1.16 |
3.05 |
2.35 |
1.32 |
| July 5 |
3.16 |
4.31 |
0.82 |
|
0.49 |
2.68 |
3.78 |
0.67 |
0.66 |
| July 7 |
3.25 |
3.44 |
1.60 |
|
1.49 |
3.24 |
1.98 |
1.13 |
0.45 |
| July 13 |
3.67 |
3.44 |
1.18 |
|
0.81 |
4.11 |
2.18 |
0.55 |
0.64 |
| July 17 |
1.88 |
5.46 |
0.94 |
|
0.53 |
1.30 |
4.08 |
1.42 |
0.95 |
| July 21 |
1.60 |
4.84 |
1.85 |
|
1.22 |
1.77 |
3.48 |
1.11 |
0.70 |
| July 25 |
1.22 |
3.04 |
4.03 |
|
0.67 |
1.08 |
2.10 |
2.41 |
2.02 |
| August 4 |
1.44 |
4.84 |
2.00 |
|
0.62 |
1.02 |
2.96 |
2.65 |
1.02 |
| Ave. |
2.23 |
4.34 |
1.72 |
|
0.78 |
2.05 |
2.95 |
1.54 |
0.97 |
| Std dev. |
0.96 |
0.93 |
1.02 |
|
0.38 |
1.16 |
0.80 |
0.83 |
0.50 |
| %CV |
43.32 |
21.54 |
59.59 |
|
48.84 |
56.80 |
27.21 |
53.71 |
52.15 |
| F2 |
July 2 |
0.28 |
1.68 |
0.54 |
|
0.12 |
0.41 |
1.23 |
0.42 |
0.33 |
| July 5 |
0.53 |
1.49 |
0.49 |
|
0.29 |
0.24 |
0.94 |
0.55 |
0.49 |
| July 7 |
0.49 |
1.22 |
0.80 |
|
0.35 |
0.71 |
0.62 |
0.29 |
0.53 |
| July 13 |
1.05 |
0.86 |
0.60 |
|
0.58 |
0.70 |
0.49 |
0.28 |
0.45 |
| July 17 |
0.12 |
0.86 |
1.52 |
|
0.11 |
0.34 |
0.53 |
0.77 |
0.76 |
| July 21 |
0.57 |
0.96 |
0.98 |
|
0.23 |
0.32 |
0.30 |
0.67 |
0.98 |
| July 25 |
0.79 |
1.38 |
0.33 |
|
0.14 |
0.64 |
0.97 |
0.42 |
0.33 |
| August 4 |
0.25 |
1.50 |
0.76 |
|
0.12 |
0.26 |
1.35 |
0.48 |
0.29 |
| Ave. |
0.51 |
1.24 |
0.75 |
|
0.24 |
0.45 |
0.80 |
0.49 |
0.52 |
| Std dev. |
0.30 |
0.32 |
0.37 |
|
0.16 |
0.20 |
0.38 |
0.17 |
0.24 |
| %CV |
59.82 |
25.77 |
49.26 |
|
67.40 |
44.30 |
46.99 |
35.12 |
46.14 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).