Submitted:
20 December 2023
Posted:
21 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
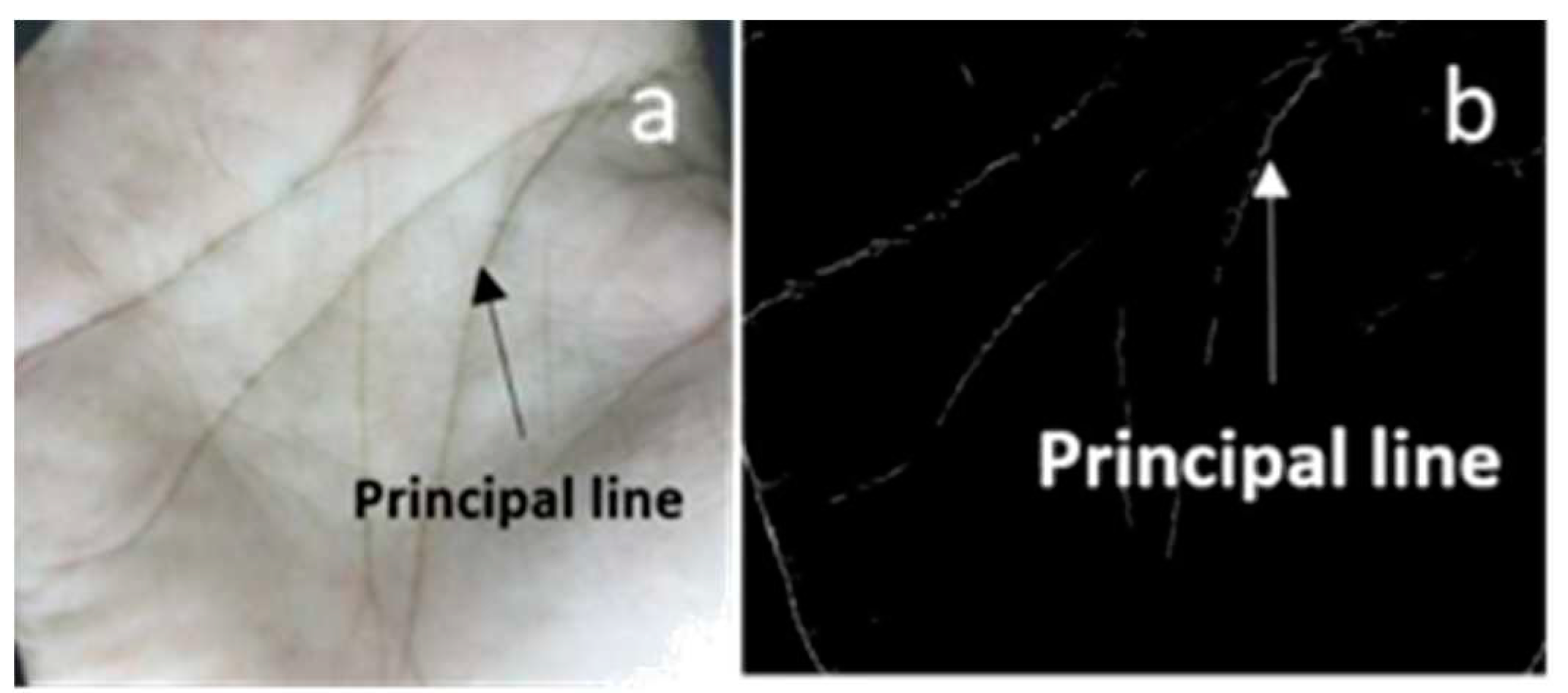
Methodology
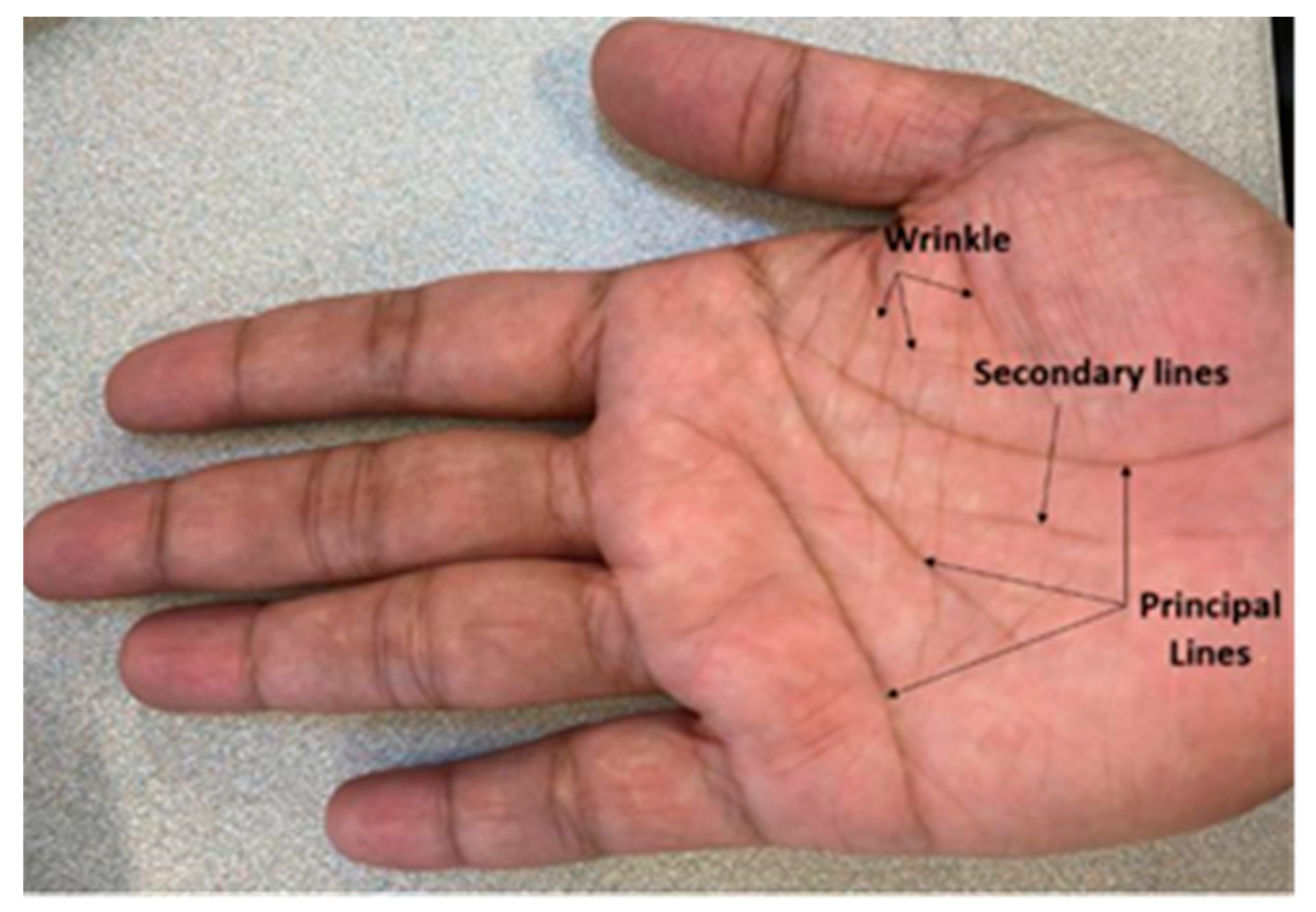
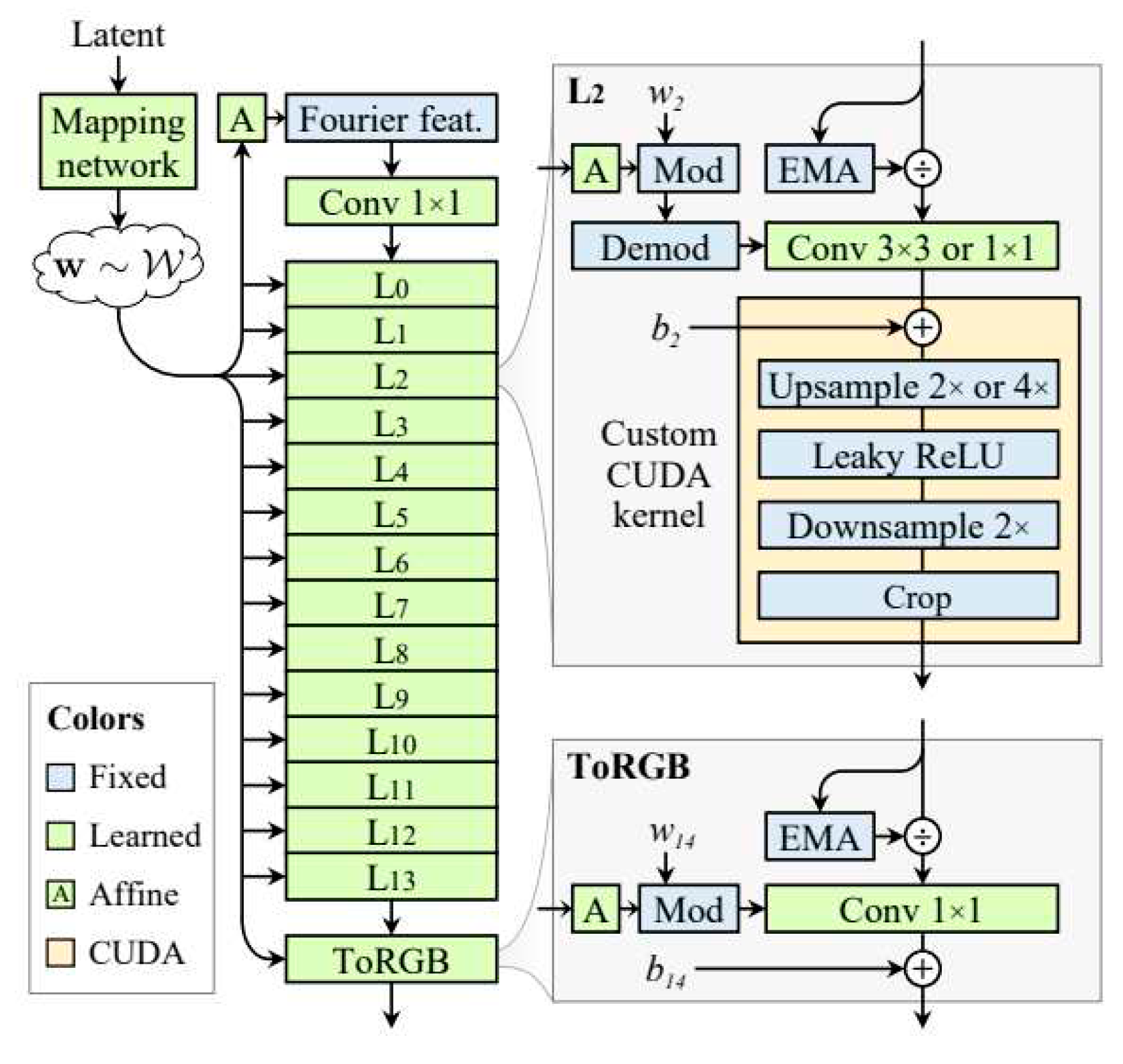
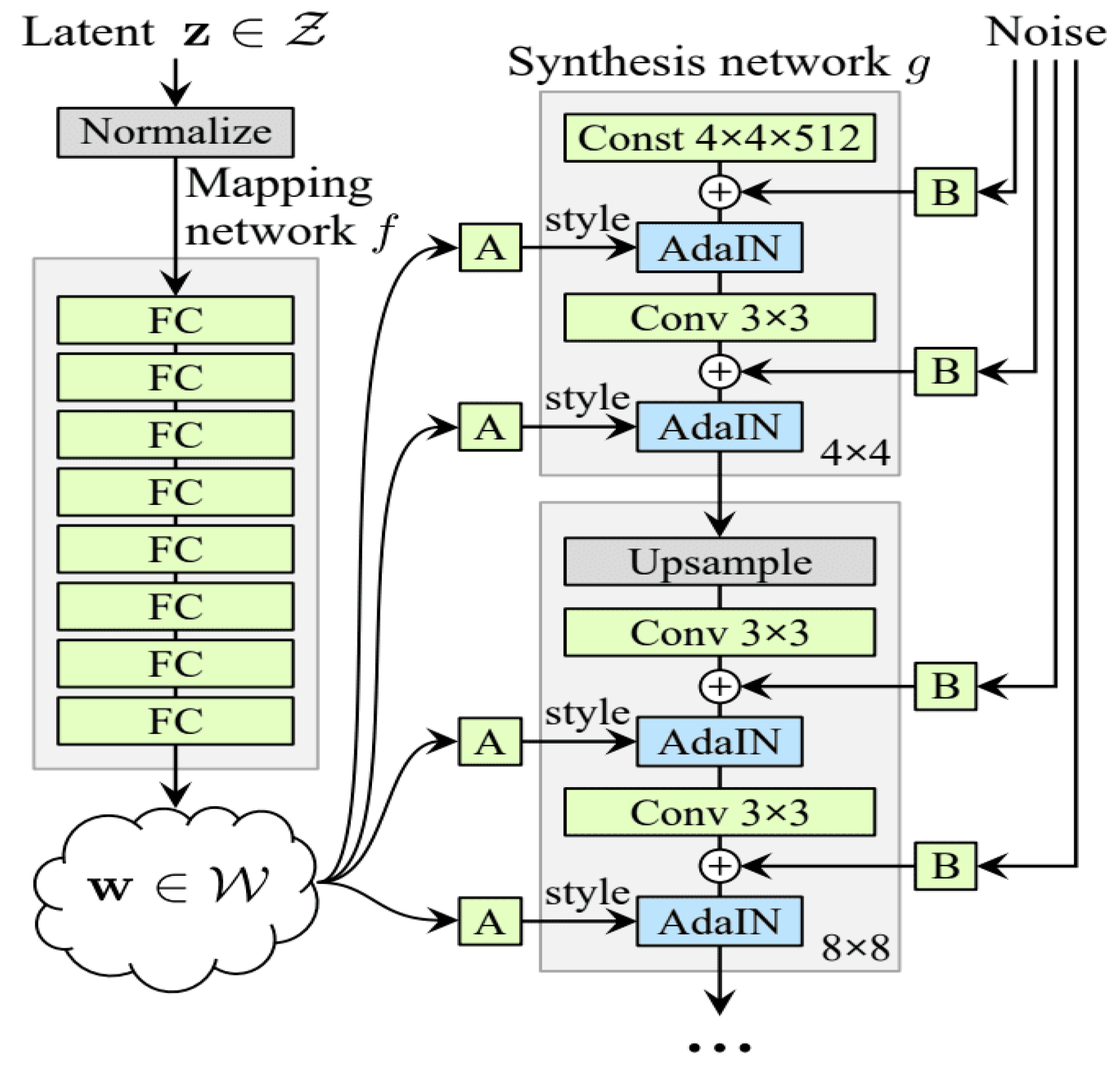
A. StyleGAN-2-ADA Architechture Overview
B. StyleGAN3 Architecture Overview
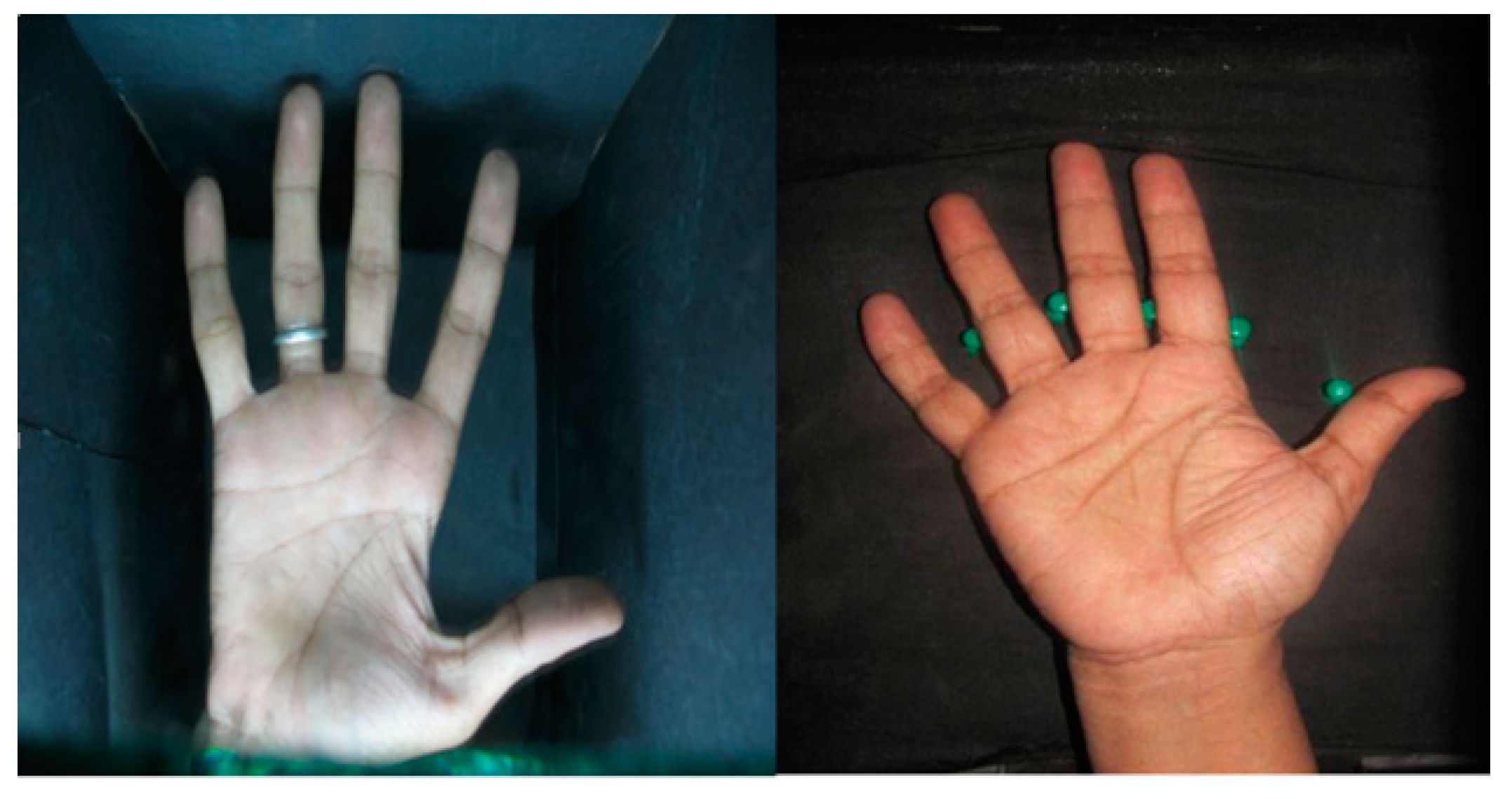
Dataset
Training the Model with StyleGAN2-ADA
A. Preparing Datasets
B Training StyleGAN2-ADA
C Training StyleGAN3
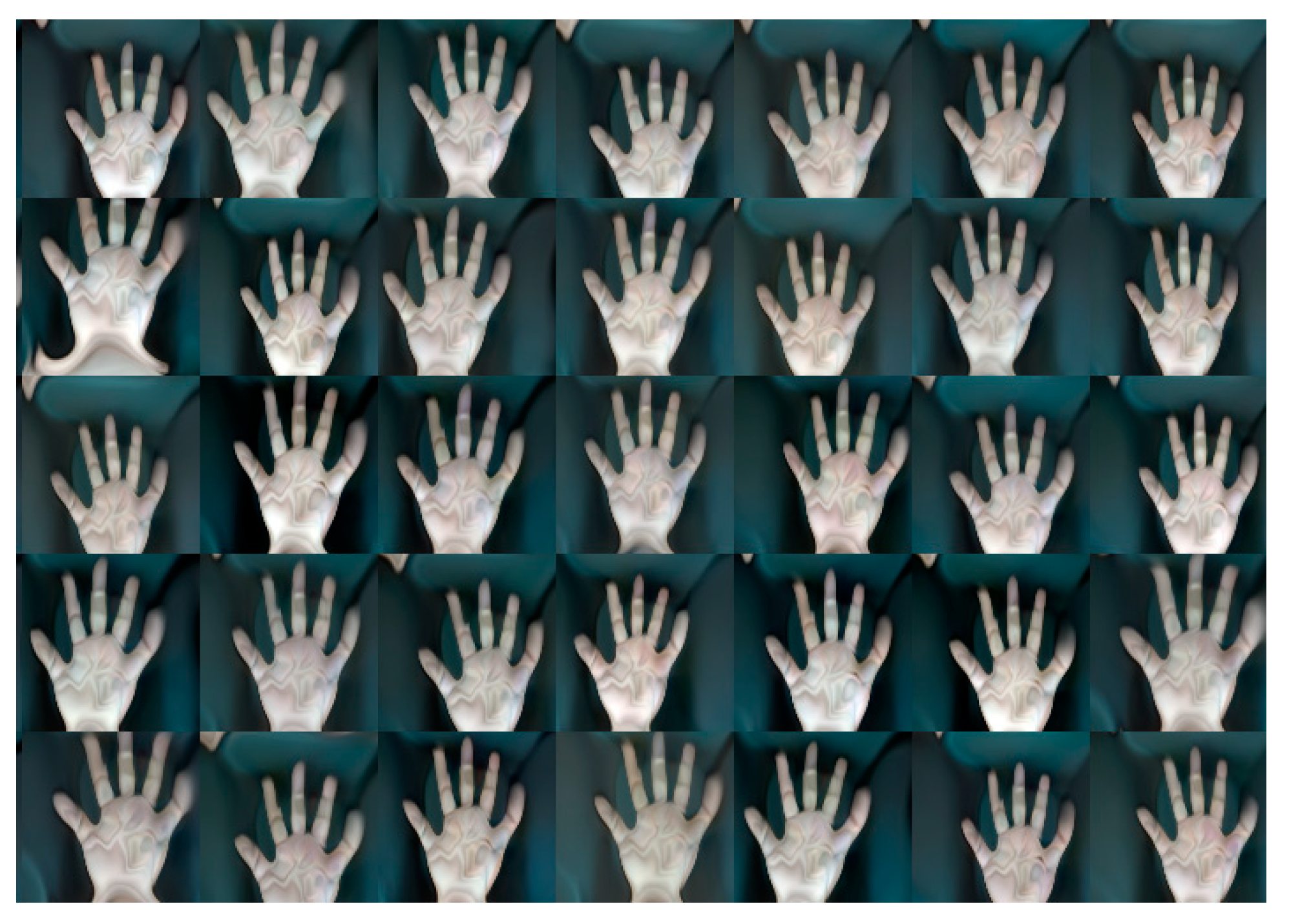
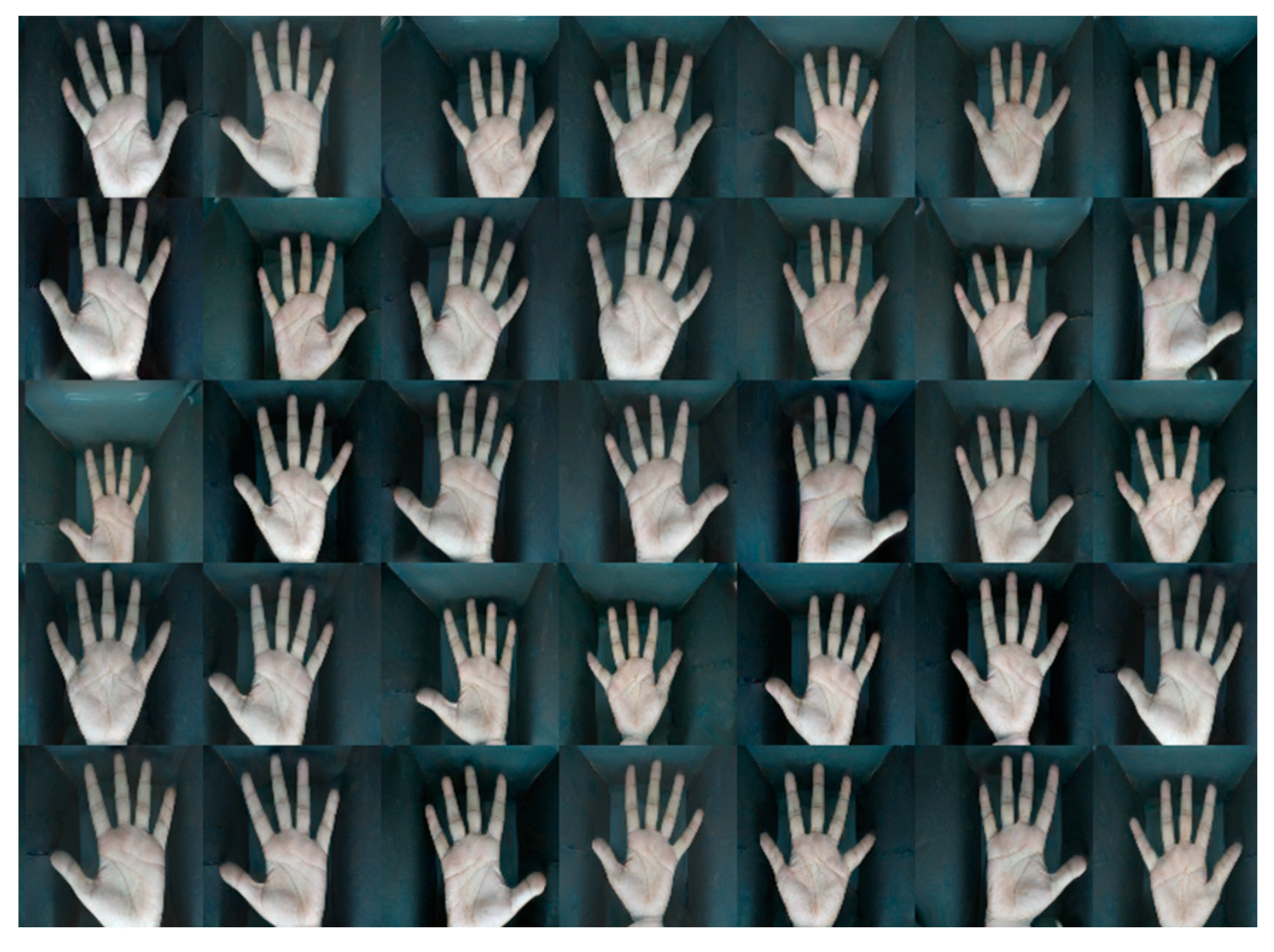
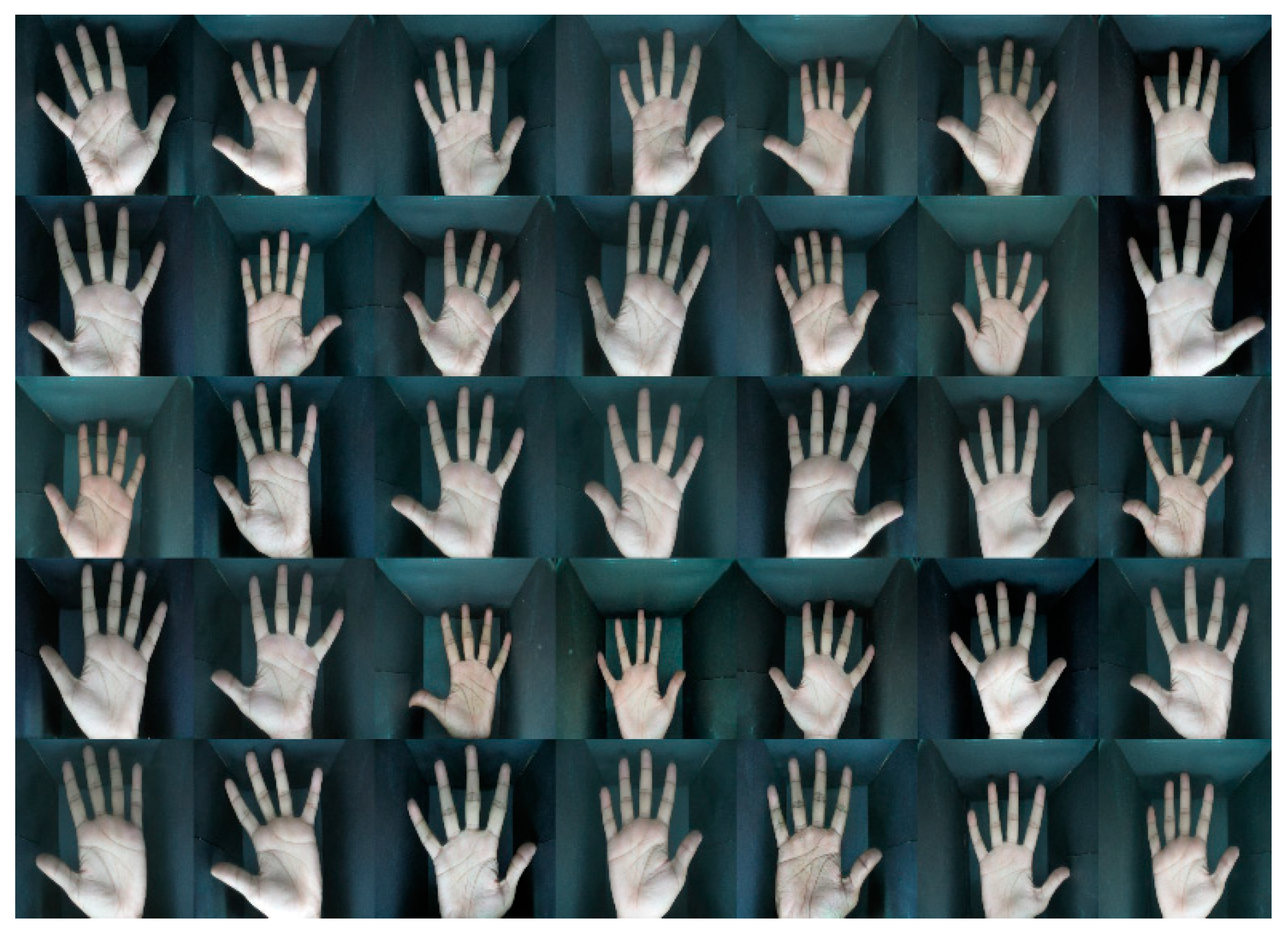



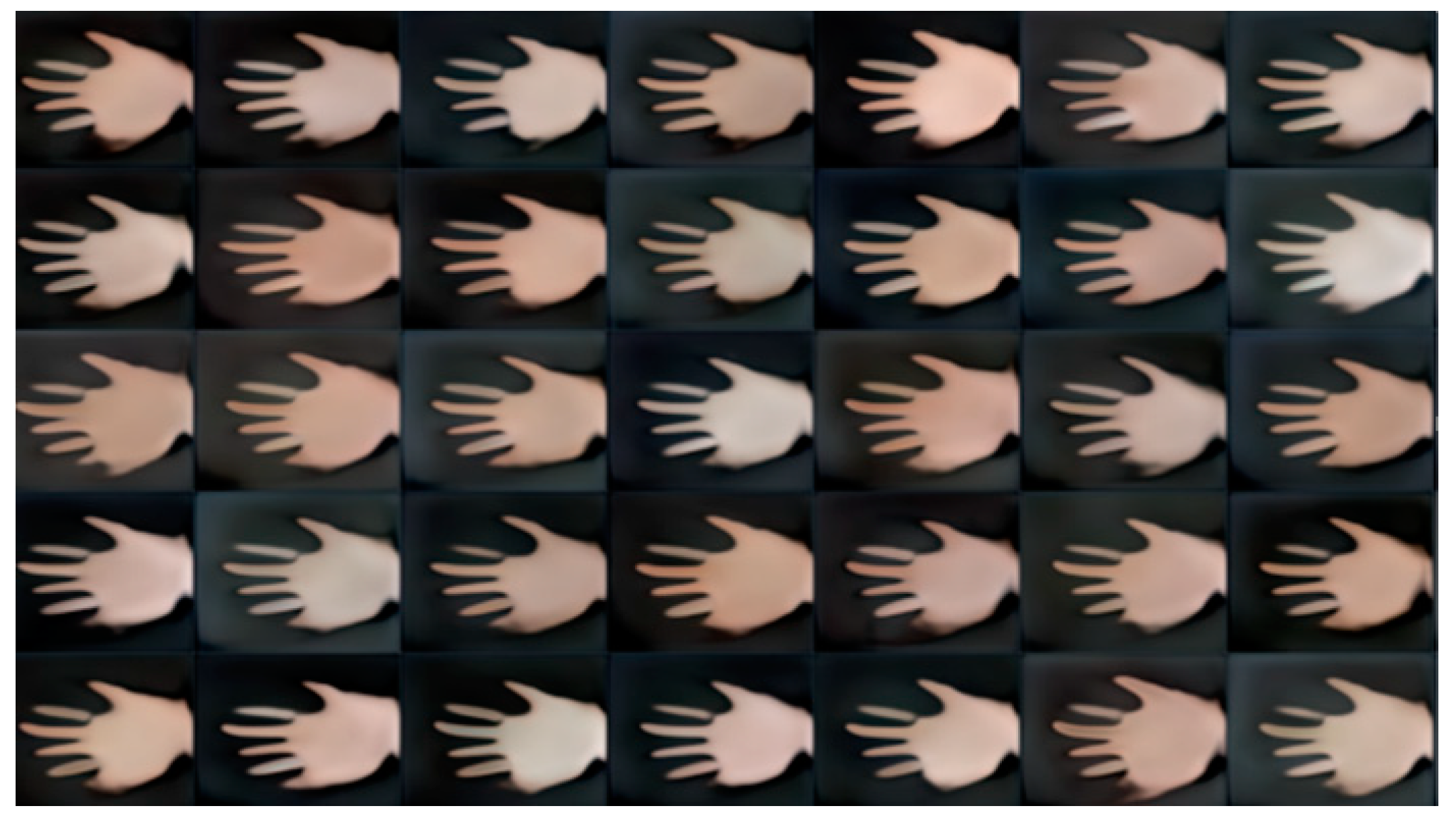
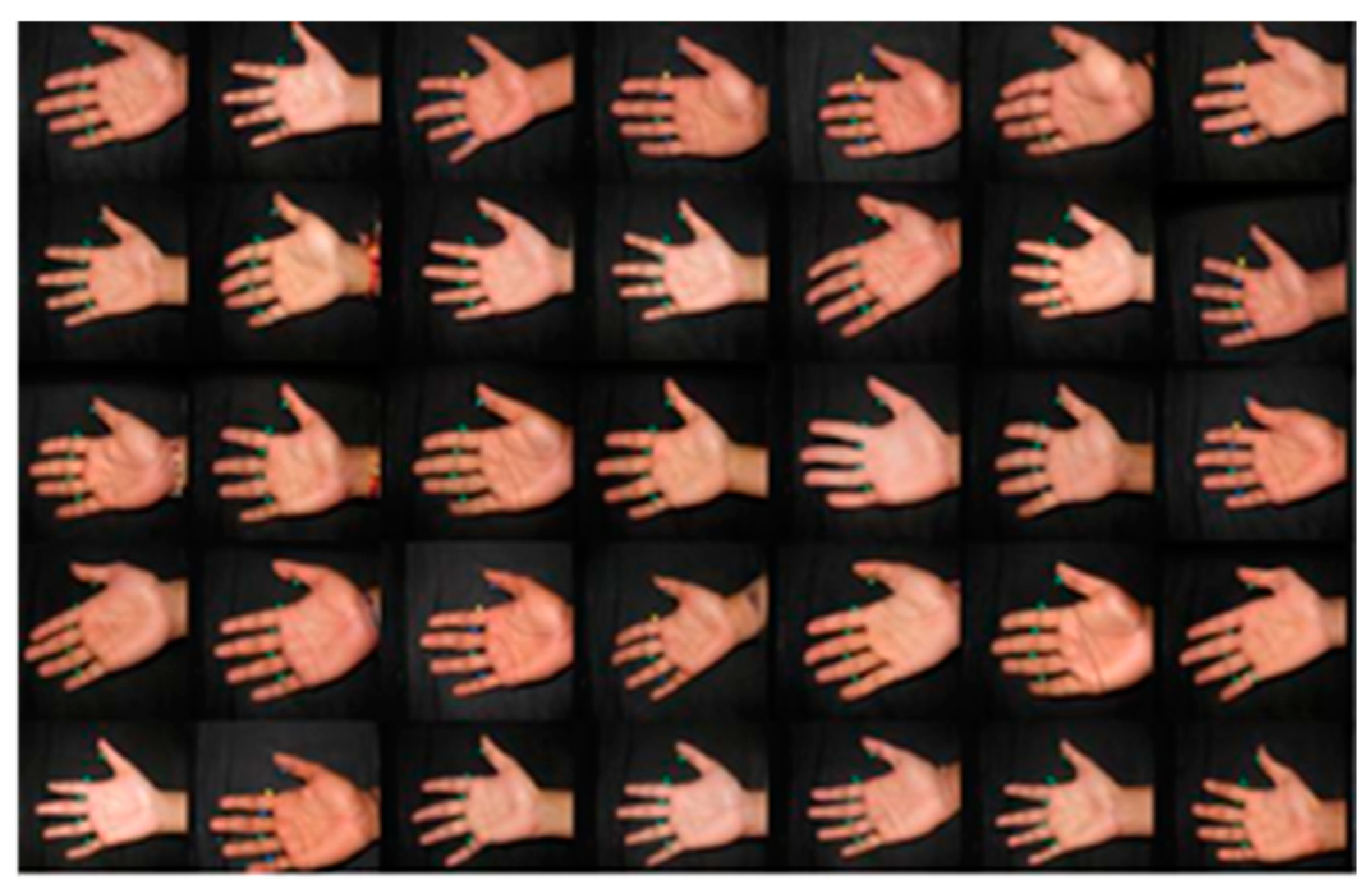
Experimental Results
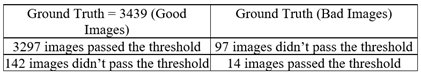
A. Filter out Unwanted Images
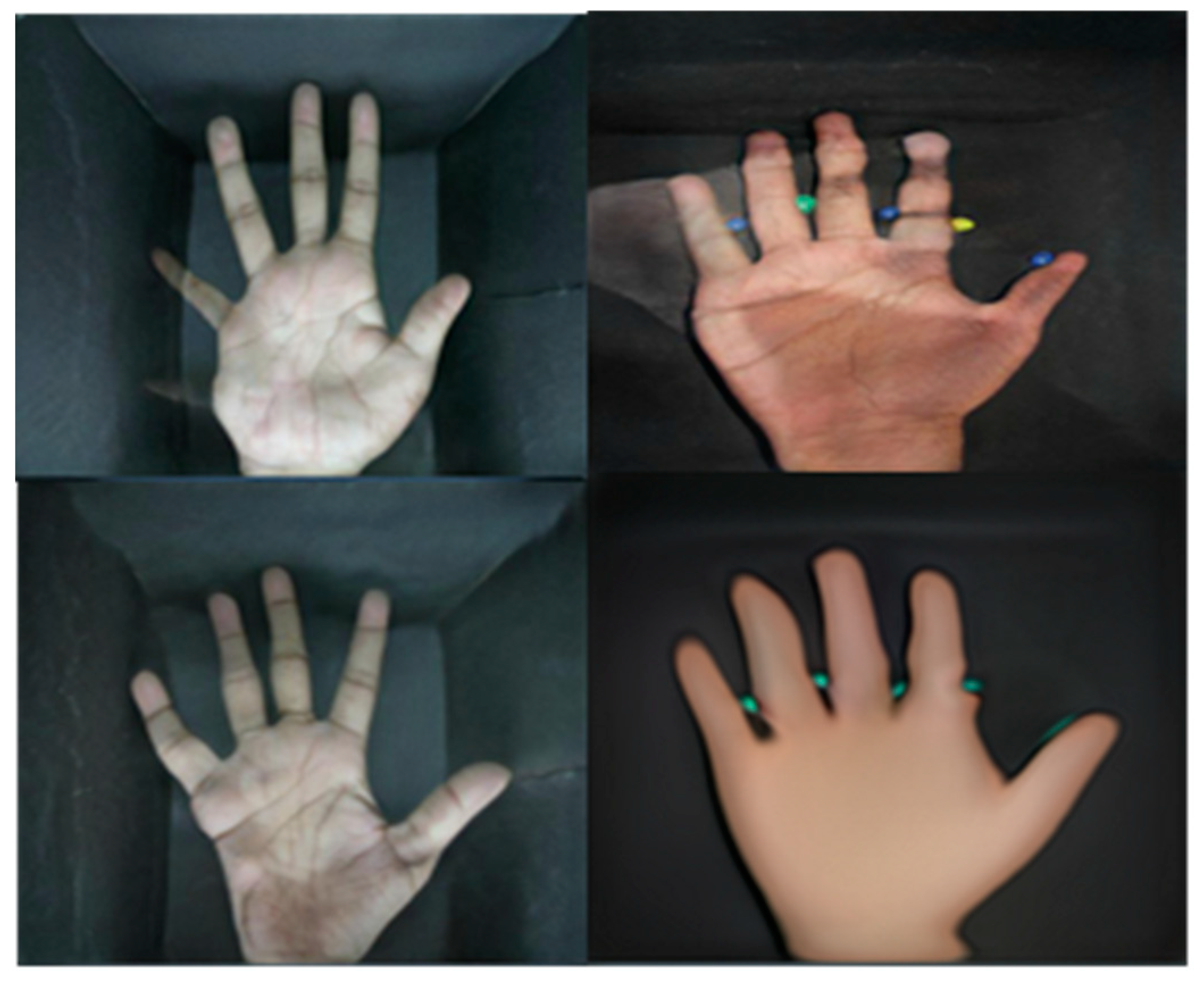
B. Elimination Method to Remove Unwanted Images
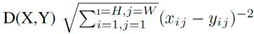
Performance Measurement
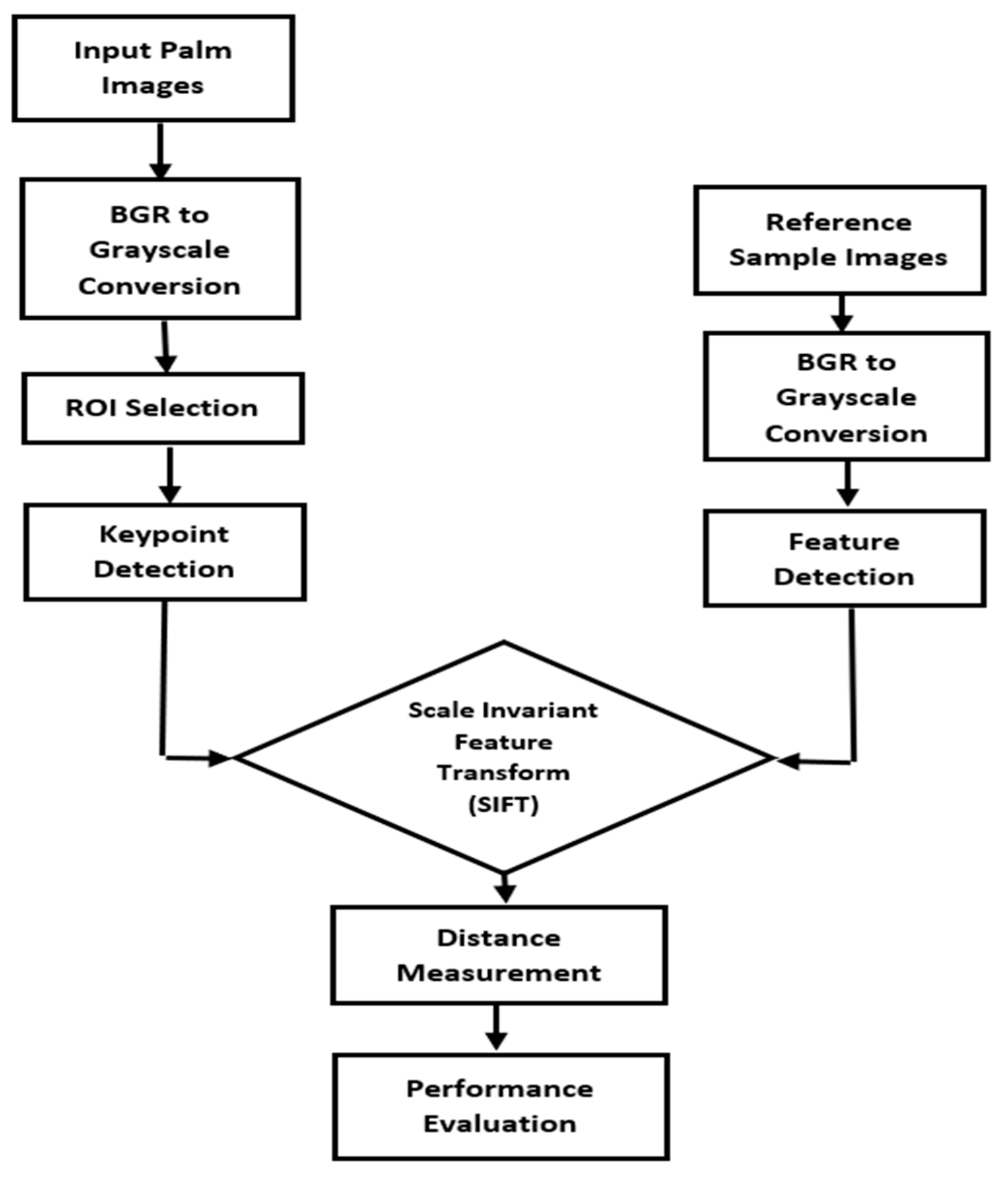
| Tests | Pairs | Similarity Score | Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 112, 106 | 39.58% | 19.55% |
| 2 | 35,84 | 10.20% | |
| 3 | 77, 96 | 14.29% | |
| 4 | 2,21 | 3.84% | |
| 5 | 27,119 | 35.22% | |
| 6 | 54,57 | 0.00% | |
| 7 | 5,3 | 8.33% | |
| 8 | 88,52 | 9.86% | |
| 9 | 90,76 | 31.70% | |
| 10 | 24,67 | 42.5% |
Conclusion
References
- H. K. Kalluri, M. V. Prasad, and A. Agarwal, “Dynamic roi extraction algorithm for palmprints,” in International Conference in Swarm Intelligence, pp. 217–227, Springer, 2012.
- Joshi, D.G.; Rao, Y.V.; Kar, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, R. Computer- vision-based approach to personal identification using finger crease pattern. Pattern Recognit. 1998, 31, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.; Zhang, D.; Kong, W.-K.; Lu, G. Real-time palmprint acquisition system design. IEE Proc. -Vis. Image Signal Process. 2005, 152, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Kong, W.-K.; You, J.; Wong, M. Online palmprint identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Bhanu, A. Kumar, et al., Deep learning for biometrics, vol. 7. Springer, 2017.
- Ozdenizci, O.; Wang, Y.; Koike-Akino, T.; Erdogmus, D. Adversarial deep learning in eeg biometrics. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Lu, G.; Luo, N. A novel 3-d palmprint acquisition system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. -Part A Syst. Hum. 2011, 42, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishneswari, K.; Arumugam, S. A review on palm print verification system. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. Ind. Manag. Appl. (IJCISIM) 2010, 2150–7988. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.S.; Haffari, G. A statistically efficient and scalable method for exploratory analysis of high-dimensional data. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Huang, D.-S.; Zhang, D. Palmprint verification based on robust line orientation code. Pattern Recognit. 2008, 41, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-T.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Zhang, B.; Jia, W.; Xue, F.; Lu, J.-T.; Zhu, Y.-H.; Xu, B.-Q. Local line directional pattern for palmprint recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 50, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronthaler, H.; Kollreider, K.; Bigun, J. Automatic image quality assessment with application in biometrics. in 2006 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (CVPRW’06), pp. 30–30, IEEE, 2006.
- Kalka, N.D.; Zuo, J.; Schmid, N.A.; Cukic, B. Image quality assessment for iris biometric,” in Biometric technology for human identification III, vol. 6202, pp. 124–134, SPIE, 2006.
- F. Mokhayeri, E. Granger, and G.-A. Bilodeau, “Synthetic face generation under various operational conditions in video surveillance,” in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 4052–4056, IEEE, 2015.
- K. Bahmani, R. Plesh, P. Johnson, S. Schuckers, and T. Swyka, “High fidelity fingerprint generation: Quality, uniqueness, and privacy,” in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3018–3022, IEEE, 2021.
- E. Tabassi and C. L. Wilson, “A novel approach to fingerprint image quality,” in IEEE International Conference on Image Processing 2005, vol. 2, pp. II–37, IEEE, 2005.
- Bharadwaj, S.; Vatsa, M.; Singh, R. Biometric quality: a review of fingerprint, iris, and face. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2014, 2014, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Karras, S. Laine, M. Aittala, J. Hellsten, J. Lehtinen, and T. Aila, “Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 8110–8119, 2020.
- Kim, J.; Hong, S.-A.; Kim, H. A stylegan image detection model based on convolutional neural network. J. Korea Multimed. Soc. 2019, 22, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Patashnik, O.; Wu, Z.; Shechtman, E.; Cohen-Or, D.; Lischinski, D. Styleclip: Text-driven manipulation of stylegan imagery. in Proceed-ings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2085–2094, 2021.
- S. Minaee, M. Minaei, and A. Abdolrashidi, “Palm-gan: Generating realistic palmprint images using total-variation regularized gan,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.10834, 2020.
- T. Karras, T. Aila, S. Laine, and J. Lehtinen, “Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196, 2017.
- T. Karras, S. Laine, and T. Aila, “A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 4401–4410, 2019.
- D. P. Kingma and J. Ba, “Adam: A method for stochastic optimization,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980, 2014.
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Kurach, M. Lucic, X. Zhai, M. Michalski, and S. Gelly, “The gan landscape: Losses, architectures, regularization, and normalization,” 2018.
- G. Liu, L. F. Schneider, and S. Yuan, “Pianogan-generating piano music from magnitude matrices (generative modeling),”.
- Jain, Y.; Juneja, M. Ridge energy based human verification using iris. Int. J. Trend Res. Dev. 2018, 5, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- G. Chaudhary, S. Srivastava, and S. Bhardwaj, “Multi-level fusion of palmprint and dorsal hand vein,” in Information Systems Design and Intelligent Applications, pp. 321–330, Springer, 2016.
- Coelho, L.P.; Kangas, J.D.; Naik, A.W.; Osuna-Highley, E.; Glory-Afshar, E.; Fuhrman, M.; Simha, R.; Berget, P.B.; Jarvik, J.W.; Murphy, R.F. Determining the subcellular location of new proteins from microscope images using local features. Bioinformatics, 2013, 29, 2343–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R. K. Saha, A. Chowdhury, K.-S. Na, G. D. Hwang, Y. Eom, J. Kim, H.-G. Jeon, H. S. Hwang, and E. Chung, “Ai-based automated meibomian gland segmentation, classification and reflection correction in infrared meibography,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.15543, 2022.
- A. M. M. Chowdhury and M. Imtiaz, “Computational Intelligence for Solving the Biometric Enrollment Issue”. Mathematics Conference and Competition of Northern New York (MCCNNY2022).
- A. M. Chowdhury, F. B. Kashem, A. Hossan, and M. M. Hasan, “Brain controlled assistive buzzer system for physically impaired people,” in 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), pp. 666–669, IEEE, 2017.
- A. Hossan and A. M. Chowdhury, “Real time eeg based automatic brainwave regulation by music,” in 2016 5th international conference on informatics, electronics and vision (iciev), pp. 780–784, IEEE, 2016.
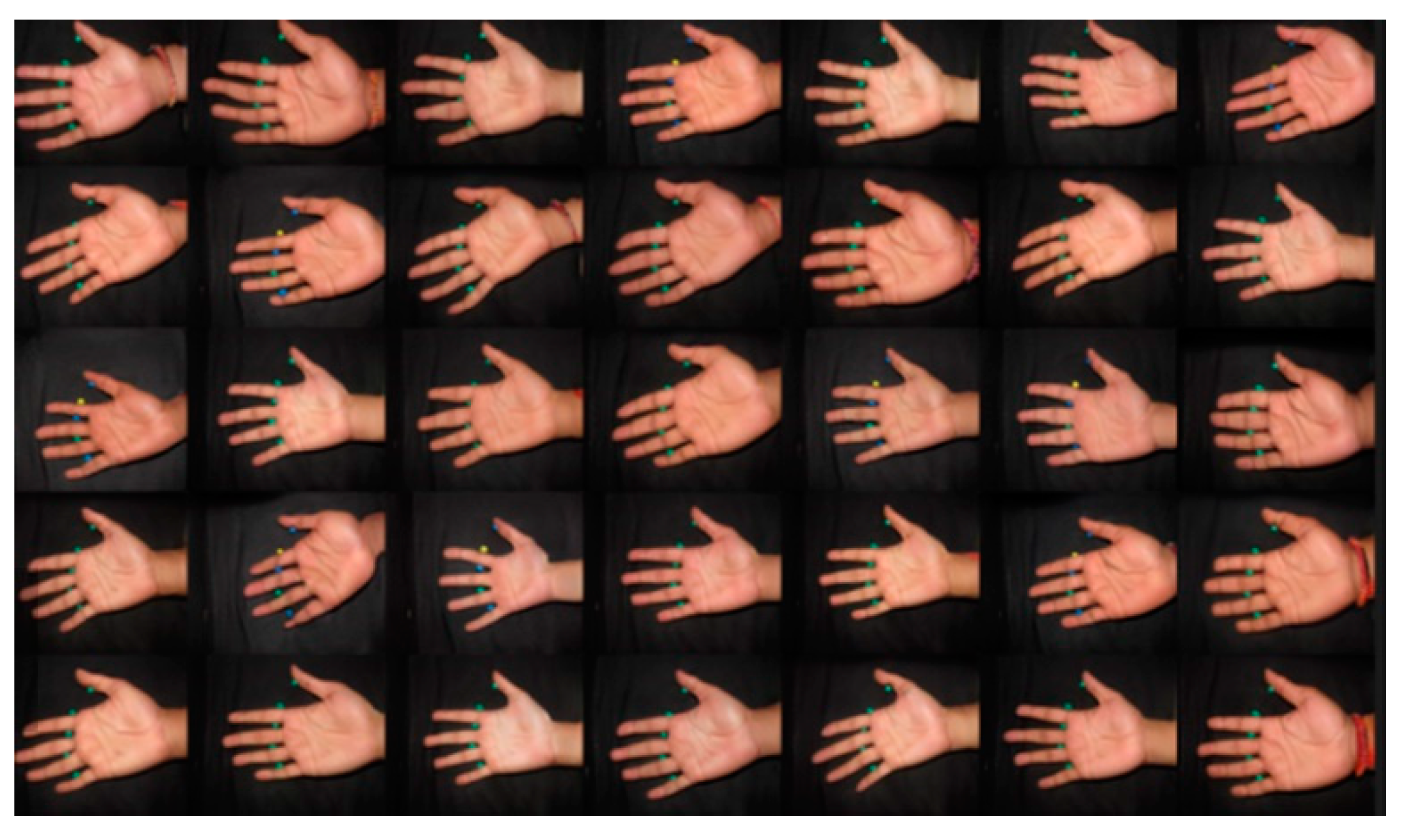

| Training Steps | Datasets |
|---|---|
| 1. DB1 Right Hand | 960 Images |
| 2. DB1 Left Hand | 960 Images |
| 3. DB1(Right Hand) + DB2 | 2304 Images |
| 4. DB1(Left Hand) + DB2 | 2304 Images |
| 5. DB1+DB2 | 2954 ges |
| Name of the Images | Numbers |
|---|---|
| 1. Shadow on the palm | 41 |
| 2. Total Imbalance | 23 |
| 3. Overlap with two palms | 21 |
| 4. Finger Issue | 15 |
| 5. No palm marker | 11 |
| 6. Total | 111 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).