1. Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is a condition in which the blood level of circulating lipid become elevated. This condition occurs due to a disturbance in lipid metabolism and become a major cause of death worldwide [
1]. The occurrence of this condition is mostly related to the increased consumption of high-fat diets and lifestyle [
2]. Hyperlipidemia is directly connected to the progression of cardiovascular diseases, obesity as well as metabolic syndromes [
3]. Thus, it is essential to regulate the lipid level in the blood for the prevention and regulation of hyperlipidemia and related disorders.
Several anti-hyperlipidemic drugs have been identified to cure hyperlipidemia. Lovastatin is an anti-hyperlipidemic drug that inhibits β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase and lowers cholesterol levels. This enzyme facilitates the transformation of HMG-CoA into mevalonic acid, which plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of cholesterol [
4]. However, lovastatin is linked with several adverse outcomes in human beings such as rhabdomyolysis, myositis, muscle cramps and weakness [
5,
6]. Such unfavourable consequences of available anti-hyperlipidemic drugs motivate researchers to seek novel anti-hyperlipidemic agents with greater potency and safety.
Plant-based medicines are a rich source of bioactive molecules which are essential for human health. Thus, the search for a new metabolome from a plant having lipid-lowering property will be a useful strategy. The anti-hyperlipidemic property of several plant extracts or purified active compounds have been reported which includes
Pandanus tectorius fruits extract and 2, 4, 6-trihydroxyacetophenone from
Myrcia multiflora activity against hypolipidemia test [
7,
8]. Triterpenoids are the most important class of chemical compounds. It has been reported that triterpenoids exhibited several biological activities. Among these activities include the inhibition of HIV proteases, antibacterial and anticancer activity [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. Methyl-3β-hydroxylanosta-9, 24-dien-21-oate a triterpenoid isolated from
Protorhus longifolia exhibited significant hypolipidemic activity in high-fat diet (HFD) induced hyperlipidemic rats [
17]. The present research work was designed to evaluate in a better way the hypolipidemic effect of isolated pentacyclic triterpene, 15-oxoursolic acid, isolated from stem and bark of
Rhododendron arboreum, against hyperlipidemic rats using
in-vivo HFD- induced hyperlipidemia model and
in-silico molecular docking assessments.
2. Results
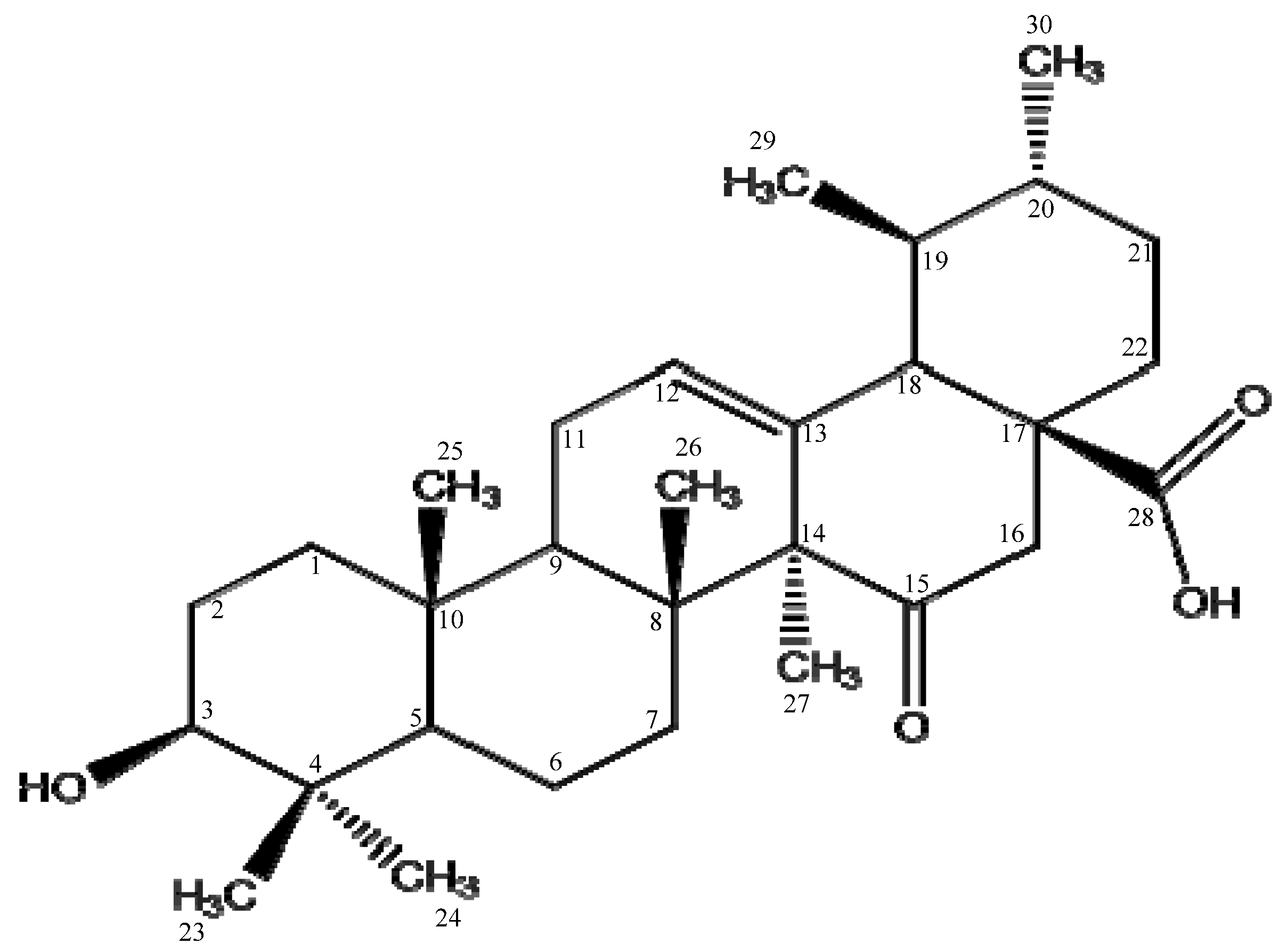
The 15-oxoursolic acid was isolated as amorphous powder from stem bark of
Rhododendron arboreum. The molecular formula of the title compound was developed as C
30H
46O
4 using different characterization techniques (
Figure 1) [
18]. The hypolipidemic potential of newly isolated pentacyclic triterpenoid (15-oxorsolic aid) was examined in high fat diet induced hyperlipidemic model. It is evident from the results (
Table 1) that the animals received HFD (Positive control) showed a marked increase in the total cholesterol (TC) (58.34 ± 0.21 mg/dl), triglycerides (TG) (45.45 ± 0.39 mg/dl), low density lipoprotein (LDL-c) (66.12 ± 0.10 mg/dl), very low density lipoprotein (VLDL-c) (19.34 ± 0.16 mg/dl) and decreased in high density lipoprotein (HDL-c) (10.34 ± 0.18 mg/dl) compared to the control group where the lipid profile was 37.90 ± 0.45 mg/dl (TC), 28.56 ± 0.15 mg/dl (TG), 37.11 ± 0.11 mg/dl (LDL-c), 12.45 ± 0.22 mg/dl (VLDL-c) and 19.78 ± 0.34 mg/dl (HDL-c), respectively. The animal’s group that received HFD fortified with test compound (15-oxorsolic aid) at a concentration of 30 mg/ kg b.w had significantly decreased the bad lipids and increased the HDL-c. In the test group the TC level, TG, LDL and very VLDL were 42.65 ± 0.54, 32.33 ± 0.16, 50.34 ± 0.15 and 13.15 ± 0.45 mg/dl, respectively while that of HDL was 18.56 ± 0.34 mg/dl. These values are comparable with the standard drug (Lovastatin) which showed that 15-oxoursolic acid can exert a significant anti-hyperlipidemic effect in HFD induced lipidemia.
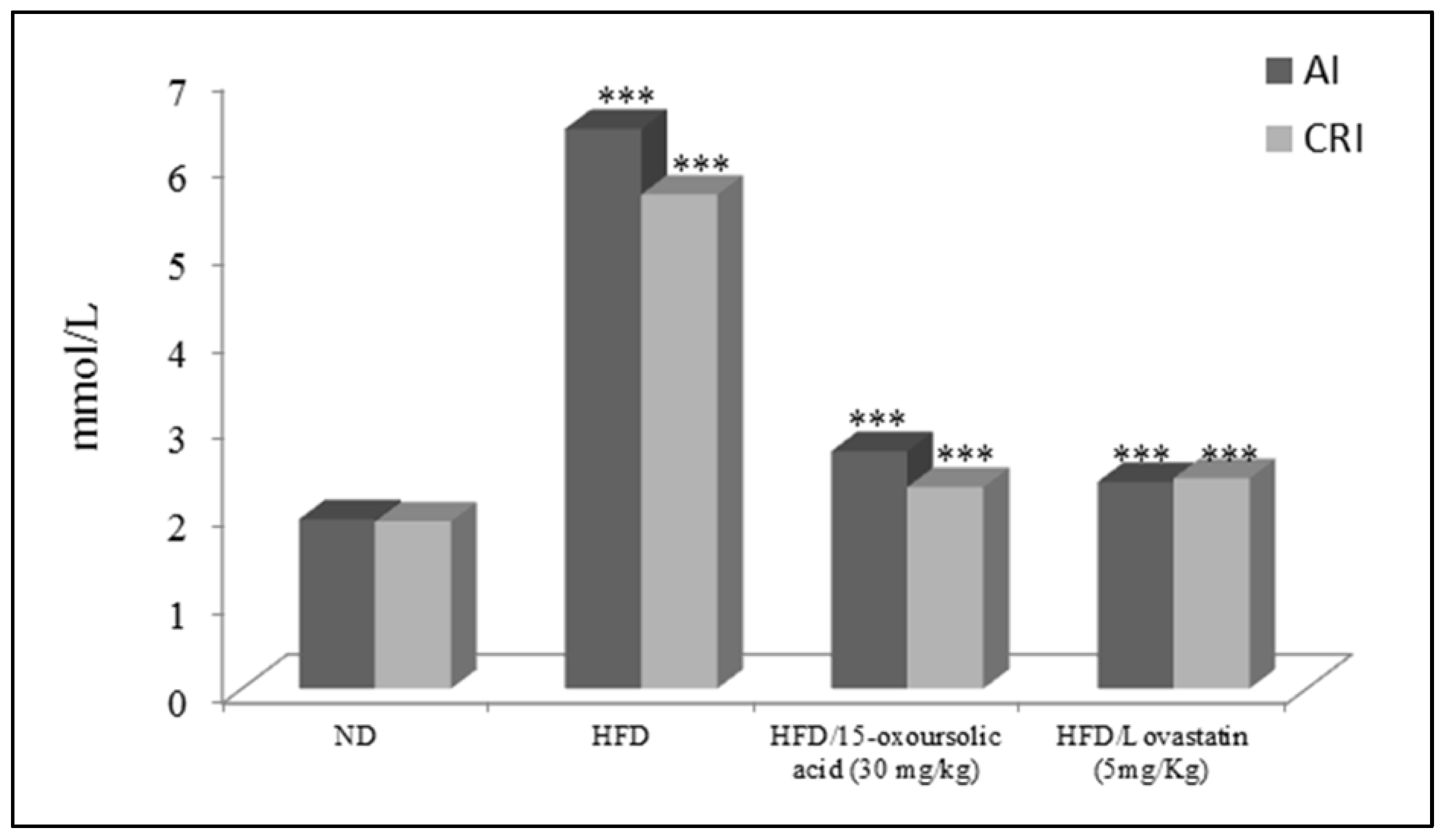
The effect of 15-oxoursolic acid on the AI and CRI in the HFD initiated hyperlipidemia in rates was also evaluated (
Figure 2). The results showed that HFD significantly increased the AI and CRI in animal model. The 15-oxoursolic acid at a concentration of 30 mg/kg b.w has significantly reduced the AI and CRI in HFD induced hyperlipidemic animals for 36 days (
Figure 2). The effect of HFD and HFD fortified with 15-oxoursolic acid and standard drug on the liver enzymes i.e., AST, ALT and ALP were also determined as shown in
Table 2. It is evident from the results that HFD significantly elevated the serum level of liver enzymes compared to the normal diet group. The animal group treated with HFD fortified with 15-oxoursolic acid at a concentration of 30 mg/kg of b.w showed a marked decrease in the liver enzymes and brought them to the level as that of the ND group.
2.1. In Silico Study
2.1.1. Ligand preparation
In the current study, isolated triterpene 15-oxoursolic acid from the stem bark of
Rhododendron arboreum were chosen as ligand to use as inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. The selection of ligand helps in subsequent stages of investigation by enabling the evaluation of ligand binding affinity and their attachment to the target. The chemical structure of isolated ligand were created using ChemBioDraw Ultra (14.0) and [
19] saved in .mol format for compatibility with MOE software to promote the ligand binding affinities and their interaction with target protein.
2.1.2. Receptor protein Refinement
The obtained 3D structure of HMG-CoA reductase with PDB ID: 1HWK was refined using MOE 2015.10. Using the geometry optimization and energy minimization, the structure of receptor protein was refined. In this process of preparation, the protonate 3D option of MOE was used and the parameter for energy minimization was carry through the Force Field: AMBER12EHT, chiral constrain, Gradient: 0.05 and current geometry. The prepared structure of receptor was subjected to CASTp server for active site prediction.
2.1.3. Active site determination
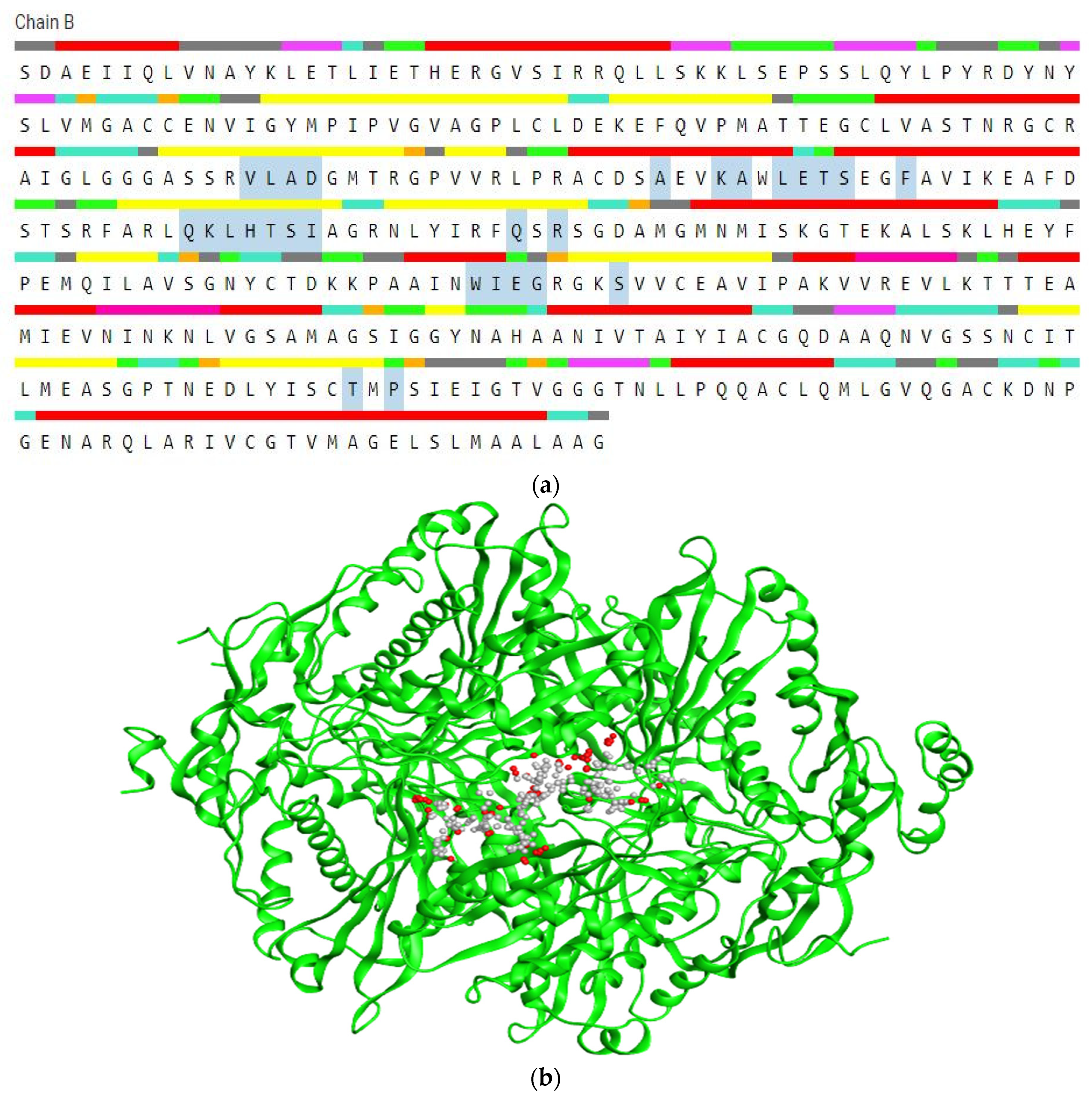
The generated structure was evaluated by using CASTp 3.0 and MOE 2015.10 software that determine the amino acids within the active site region. The identification and characterization of active site compound is important step in the development of an inhibitor. The CASTp evaluation observed the active domain, surface region (995.248), volume (1254.994) of HMG-CoA reductase shown in
Figure 3a. All the binding cavities were arranged to findout the residues with probe 1.4Å radius in the selected protein. The site finder option of MOE was employed to detect and evaluate active region based on 3D structure of the receptor protein as shown in
Figure 3b. These potential binding sites used for docking analysis of HMG-CoA reductase.
2.1.4. Molecular docking
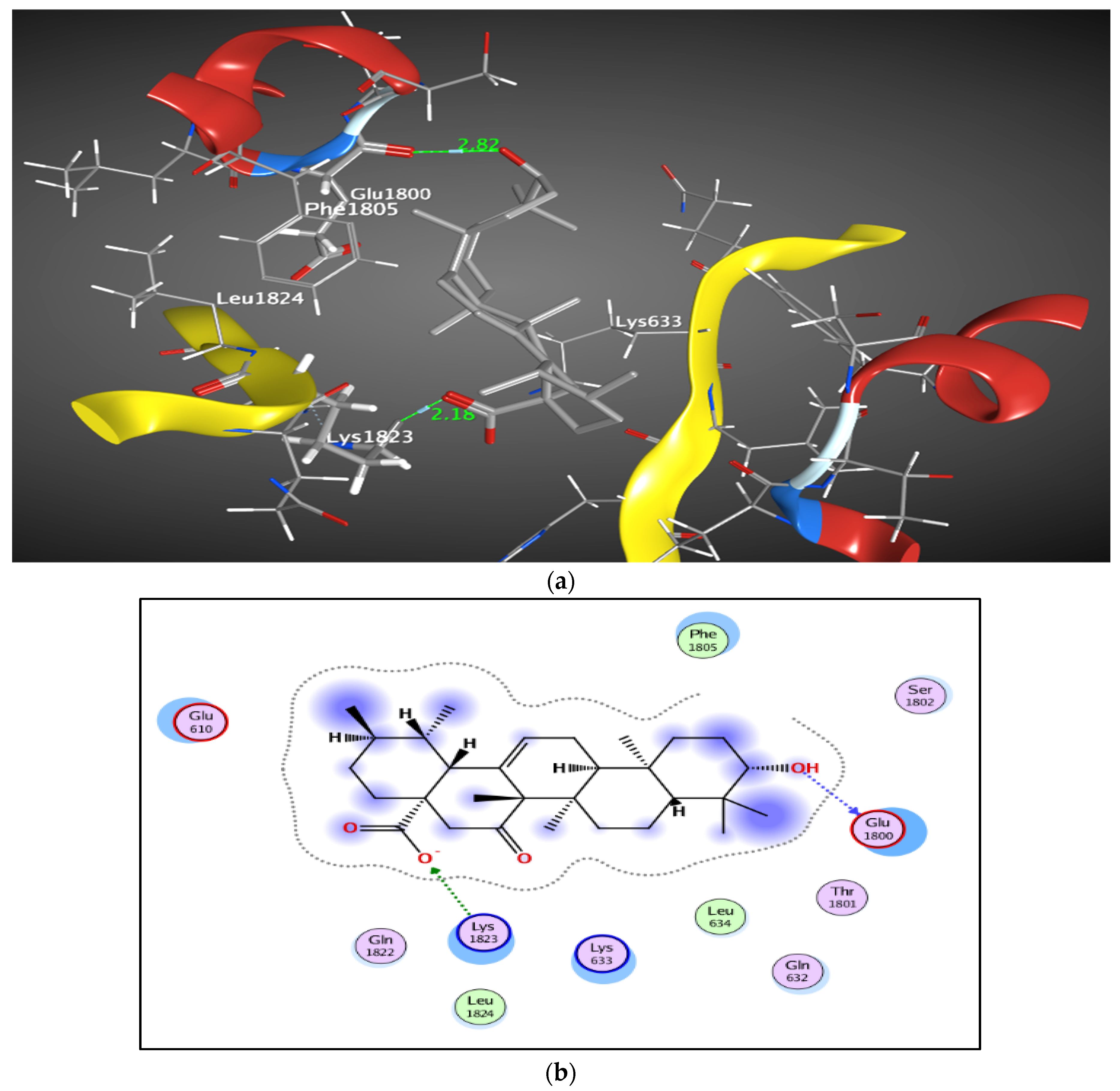
Docking analysis was performed by MOE 2015.10 between HMG-CoA reductase and the ligand 15-oxoursolic acid. A strong binding affinity was found by the ligand within the active site of selected protein. The binding energy obtained up to −9.26805 Kcal/mol by 15-oxoursolic acid against the target HMG CoA reductase. More negative binding score indicate stronger binding to the receptor. Amino acid Glu-1800 bind with the OH- group of 15-oxoursolic acid with a distance of 2.82Å while Lys-1823 attach to the O- group of the ligand showing distance of 2.18Å in the active site of receptor protein, depicted by 2D and 3D structures (
Figure 4a,b). This represents that the ligand molecules at the active site exhibit a greater binding affinity and therefore hold a favorable place as an effective inhibitor for HMG-CoA reductase.
3. Discussion
Use of high fat diet resulted in the elevation of serum lipid level causing hyperlipidemia. A number of abnormal conditions such as cardiac diseases, obesity and a number of other disorders are associated with abnormal lipid metabolism [
19]. Thus, to prevent and treat cardiovascular events it is necessary to regulate dyslipidemia [
20,
21].
In the present study, the anti-hyperlipidemic potential of the 15-oxoursolic acid, a penta cyclic triterpene isolated from the stem bark of
Rhododendron arboreum was evaluated in the high fat diet induced hyperlipidemia model in rats. It is evident from the results that newly isolated pentacyclic triterpene has anti-hyperlipidemic properties. As it is clear from the results that HFD significantly increases the serum level of TC, TG, LDL-c and VLDL-c and decreases the serum concentration of HDL-c compared to the normal diet group. However, HFD supplemented with 15-oxoursolic acid has significantly lowered the serum level of TC, TG, LDL-c and VLDL-c and increased the serum level of HDL-c which suggested that the 15-oxoursolic acid had potent hypolipidemic effect. The results obtained are in accordance with literature reported on the hypolipidemic effect of other plant derived compounds. A triterpenoid (Methyl-3β-hydroxylanosta-9,24-diene-21-oate) isolated from the stem bark of
Protorhus longifolia have been reported to possess significant anti-hyperlipidemic activity in HFD induced hyperlipidemia model [
17]. Similarly a mixture of triterpene including α,β-amyrin isolated from
Protium heptaphyllum and lanostane terpenoide isolated from
Prosthechea michuacana have been reported to having significant anti-hyperlipidemic activity [
22,
23]. Plant sterol and their ester are reported to have lowering of the intestinal cholesterol absorption as well as decrease the level of LDL-c [
24,
25]. As HDL protect from the incidence of atherosclerosis and related abnormalities, so a hypolipidemic agent with the ability of increasing blood HDL-c are of great interest [
26].
Consequently,
in-silico analysis showed the compatibility between the active sites of target enzyme and functional parts of leading compounds as ligand which resulted in HMG-CoA reductase inhibition [
27]. The ligand-protein interaction analysis shows binding energy −9.26805 Kcal/mol near to reference drug (Lovastatin) and occupy similar binding sites in the catalytic domain and form H-bonds, electrostatic interactions, and hydrophobic interaction with the residues at the binding site of HMG-CoA reductase [
28]. The enzyme inhibition capacity of selected compounds can be checked by interactions with the target through binding energies [
29]. The lower protein-ligand complex’s binding energy, the higher is its stability [
30]. From the interaction, the catalytic center of HMG-CoA reductase would undergo a conformational change and suppress the enzyme activity [
31].
As observed in the
in-vivo study, 15-oxoursolic acid compound has significantly reduced the AI and CRF in the HFD elevated hyperlipidemia in rats and inhibition of HMG-CoA from
in-
silico molecular docking suggested the cardiovascular protection of the 15-oxoursolic acid. Arteriosclerosis and plaque formation in the arteries due to high blood cholesterol and LDL-c could cause several complications in the form of stroke, heart attack, and even death [
17]. It is apparent in the present study that 15-oxoursolic acid exerted its therapeutic effect by lowering the atherogenic cholesterol and TG.
Consumption of HFD for a long period causes an increase inTG biosynthesis and stops the β-oxidation of fatty acids which increases the liver TG. Deposition of the excess amount of TG in the liver results in raising the liver weight and adipose tissues [
19,
32,
33]. Interestingly 15-oxoursolic acid, a new pentacyclic triterpene isolated from the stem bark of
Rhododendron arboreum not only inhibit HMG-CoA reductase enzyme and reduces the TG level but can also reduce the liver enzymes. An elevated level of liver enzymes is a clear indication of the liver inflammation or damage to the hepatic cells [
34]. Therefore, the normal level of liver enzymes is an indication of normal liver function.
4. Materials and methods
4.1. Plant materials
An authenticated Rhododendron arboreum, stem bark was obtained from Dr. Abdul Rasheed, Department of Botany, University of Peshawar Pakistan, and a voucher sample was submitted to the department.
4.2. Extraction and isolation
The powdered plant material (10 KG) was successively extracted with methanol (3x20L) at room temperature. The filtrate was concentrated through rotary evaporator to afford a gummy brownish methanolic extract (1.2 Kg). The methanolic extract was fractionated with different solvents in increasing order of polarity. The fraction ethyl acetate (50 g) was purified through column chromatography to afford a white amorphous compound 15-oxoursolic acid.
4.3. Physical data of 15-Oxoursolic acid
White amorphous powder with molecular formula C30H46O4 (15mg), Rf value¼0.35 (methanol: chloroform; 2:8), m.p. = 288–290°C, UV (kmax) 280nm. IR (KBr) kmax cm
-1: 3430, 1740, 1720 and 1650cm
-1. HREIMS m/z 470.0320 (calculated 470.3396 for C30H46O4) [
18].
4.4. In Vivo Study
4.4.1. Animals
For the present study, male BALB/c mice (weight: 18–22 g) were used. The animals were maintained under stabilized ambient conditions (22 ± 2°C and light/dark cycles, i.e. 12/12 h) and sustained with standard food and water ad libitum. All ethical principles regarding the laboratory animals were strictly observed. All the animals were acclimatized to the laboratory conditions for 7 days before the commencement of the experiments. Once the animals had adapted to the experimental conditions the animals were randomly divided into different groups.
4.4.2. Anti-hyperlipidemic activity
The anti-hyperlipidemic activity was determined following the reported procedure [
35]. The HFD contained about 4.8kcal/g while the normal chow contained 3.1kcal/g. The overnight fasted animals were divided into four groups each group having six animals, respectively.
- 1)
NC: Normal control diet and vehicle throughout the study
- 2)
HFD: High-fat diet and vehicle throughout the study
- 3)
Test drug: High fat diet + test drug (30mg/kg)
- 4)
Lovastatin: High fat diet + Lovastatin (5 mg/kg)
During the investigation, animals had unrestricted access to water only. The HFD preparation was pelleted each weighting 3g per pellet and were fed daily to the animals for 36 days to prompt hyperlipidemia. Blood samples were collected under light ether anesthesia using the retro-orbital plexus process. The samples of blood were centrifuged at 6000 rpm/10min and the serum obtained were employed in the analysis of lipid.
4.4.3. Biochemical analysis/Screening
The serum obtained from blood samples was used to investigate TC, TG, HDL-c, LDL-c, VLDL-c, AST and ALT. LDL-cholesterol was estimated in the serum through the Friedwald’s equation [
36].
LDL-c = [TC-(HDL-c+ (TG/5)]
Further lipid indexes such as VLDL-c, coronary risk index (CDI) and atherogenic index (AI) were measured as follows/proceeds [
19].
LDL-c =[TC-(HDL-c+ (TG/5)]
VLDL-c = [TG - (HDL-c+ LDL-c]
Atherogenic index (AI) = LDL-c/HDL-c (mg/dl)
CRI= TC/HDL-c (mg/dl)
4.5. Molecular Docking
4.5.1. Ligand Preparation
The isolated chemical compound 15-oxoursolic acid from stem bark of
Rhododendron arboreum was selected as ligand [
18]. The structure of ligand was generated by using ChemBioDraw Ultra (14.0) and saved in
.mol for compatibility with molecular operating environment (MOE). The 15-oxoursolic acid were then subjected to MOE 2015.10 software for 3D protonation [
37].
4.5.2. Preparation of protein
The 3-dimensional structure of HMG-CoA reductase with PDB ID: 1HWK was obtained from the Protein Data Bank (
https://www.rcsb.org/search) [
38]. The obtained 3D structure of protein was prepared in the Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) 2015.10 for molecular docking [
39]. In the preparation process, water molecules were excluded, hydrogen atoms were added, bond orders were carefully corrected, and the ionization states of the receptor protein were correctly determined. The optimization of the structure was conducted by applying restrained minimization with the AMBER12EHT force field. The determined structure of HMG-CoA reductase was subjected to CASTp server for active site prediction [
40].
4.5.3. Active Site Prediction
The CASTp 3.0 online server (
http://sts.bioe.uic.edu/cast p/) and MOE 2015.10 active site prediction tool was employed to identify the active site of selected protein that contains important amino acid residues. Computational analysis of the active pockets situated both on the external surface and within the interior of protein 3D structure was accurately determined and measured precisely by using CASTp web server [
41,
42]. Additionally, active site prediction tool of MOE software was employed to describe the active region within the 3D structure of HMG-CoA reductase.
4.5.4. Molecular docking Process
MOE docking software provides an appropriate conformation (with bond rotation, the structure of the molecule is not rigid) of the ligand in order to attain the minimal amount of energy structure [
43]. Molecular docking was conducted using molecular operating environment (MOE) 2015.10 to analyze the interaction between target protein HMG-CoA reductase and the ligand, 15-oxoursolic acid [
44]. The parameters for docking to ensure the precise results were set as “London dG 1” scoring function and “Triangle Matcher” for better position strategy. The “Induced fit” of refinement force field were selected to find out the ligand and receptor binding within the selected active site. In addition, the Generalized Born solvation model (known as GBVI/WSA dG) was used to calculate scoring function [
45,
46]. Other parameters were set as defaults. The docking outcomes were stored in .mdb and further visualized using Discovery Studio Visualizer.
4.6. Statistical analysis
The obtained results/outcomes were presented as mean +SEM. ANOVA was used for statistical interpretation, followed by post hoc Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons. Values were considered to be substantial at p < 0.05 (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p< 0.001).
5. Conclusion
It can be concluded that newly isolated pentacyclic triterpene 15-oxoursolic acid has in-vivo lipid reducing ability in HFD animal model and also exhibited significant interaction capabilities with HMG-CoA reductase as confirmed by in-silico molecular docking assessments. It is evident from in-vivo study that reduction in TC and LDL- c with increase in the HDL-c. The 15-oxoursolic acid causes a significant reduction in the risk of atherosclerosis through decreasing AI and CRI. In addition, the test compound can decrease the serum lipid profile but can also cause a dramatic decrease in the liver enzymes. As confirmed from in-silico study, 15-oxoursolic acid has the capabilities to interact, inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, and can serve as a potent lipid-lowering drug. Therefore, 15-oxoursolic acid could be employed as a new candidate for controlling the conditions associated with hyperlipidimia as confirmed by in-vivo and in-silico results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.A., Methodology: U.A.; Investigation: M.I.J.; Data curation: M.I.J. Validation: U.A.; Writing – original draft: S.A., Writing – review & editing: U.A.; Formal analysis: M.I.J.; Supervision: S.A.
References
- Thayyil, A.H.; Surulivel, M.K.M.; Ahmed, M.F.; Ahamed, G.S.S.; Sidheeq, A.; Rasheed, A.; Ibrahim, M. Hypolipidemic Activity of Luffa Aegiptiaca Fruits in Cholesterol Fed Hypercholesterolemic Rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. Appl. 2011, 2, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, T.A.; Miller, M.; Schaefer, E.J. Hypertriglyceridemia and Cardiovascular Risk Reduction. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adisakwattana, S.; Moonrat, J.; Srichairat, S.; Chanasit, C.; Tirapongporn, H.; Chanathong, B.; Ngamukote, S.; Mäkynen, K.; Sapwarobol, S. Lipid-Lowering Mechanisms of Grape Seed Extract (Vitis Vinifera L) and Its Antihyperlidemic Activity. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Stancu, C.; Sima, A. Statins: Mechanism of Action and Effects. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2001, 5, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.D.; Clarkson, P.; Karas, R.H. Statin-Associated Myopathy. Jama 2003, 289, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hor, S.Y.; Farsi, E.; Yam, M.F.; Nuyah, N.M.; Asmawi, M.Z. Lipid-Lowering Effects of Coriolus Versicolor Extract in Poloxamer 407-Induced Hypercholesterolaemic Rats and High Cholesterol-Fed Rats. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 2261–2266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Wu, H.; Sheng, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luan, H.; Sun, G.; Sun, X.; Tian, Y.; et al. Anti-Hyperlipidemic Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Action of the Caffeoylquinic Acid-Rich Pandanus Tectorius Fruit Extract in Hamsters Fed a High Fat-Diet. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, E.A.; Gris, E.F.; Rebello, J.M.; Correia, J.F.G.; De Oliveira, L.F.S.; Filho, D.W.; Pedrosa, R.C. The 2′,4′,6′-Trihydroxyacetophenone Isolated from Myrcia Multiflora Has Antiobesity and Mixed Hypolipidemic Effects with the Reduction of Lipid Intestinal Absorption. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayaux, J.F.; Bousseau, A.; Pauwels, R.; Huet, T.; Hénin, Y.; Dereu, N.; Evers, M.; Soler, F.; Poujade, C.; De Clercq, E.; et al. Triterpene Derivatives That Block Entry of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 into Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3564–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwada, Y.; Nagao, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Ikeshiro, Y.; Okabe, H.; Cosentino, L.M.; Lee, K.H. Anti-AIDS Agents 38. Anti-HIV Activity of 3-O-Acyl Ursolic Acid Derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1619–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Shen, J.K.; Wang, H.K.; Cosentino, L.M.; Lee, K.H. Synthesis and Anti-HIV Activity of Oleanolic Acid Derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 3115–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Nakamura, N.; Miyashiro, H.; Hattori, M.; Shimotohno, K. Inhibitory Effects of Constituents from Cynomorium Songaricum and Related Triterpene Derivatives on HIV-1 Protease. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska, K.I.; Grudniak, A.M.; Fiecek, B.; Kraczkiewicz-Dowjat, A.; Kurek, A. Antibacterial Activity of Oleanolic and Ursolic Acids and Their Derivatives. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2010, 5, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lin, Y.M.; Wu, T.S.; Zhang, D.C.; Yamagishi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Hall, I.H.; Chang, J.J.; Wu, R.Y.; Yang, T.H. The Cytotoxic Principles of Prunella Vulgaris, Psychotria Serpens, and Hyptis Capitata: Ursolic Acid and Related Derivatives. Planta Med. 1988, 54, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.N.; Lu, C.M.; Cheng, M.K.; Gan, K.H.; Won, S.J. The Cytotoxic Principles of Solanum Incanum. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Pharmacology of Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 49, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaba, K.E.; Cobongela, S.Z.Z.; Mosa, R.A.; Oladipupo, L.A.; Djarova, T.G.; Opoku, A.R. In Vivo Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activity of the Triterpene from the Stem Bark of Protorhus Longifolia (Benrh) Engl. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Nisar, M.; Qaisar, M.; Khan, A.; Khan, A.A. Evaluation of the Cytotoxic Potential of a New Pentacyclic Triterpene from Rhododendron Arboreum Stem Bark. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1927–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, H.S.; Bhandari, U.; Khanna, G. Preventive Effect of Embelin from Embelia Ribes on Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, G.; Salvadeo, S.; Cicero, A.F.G. Prospects for the Development of Novel Anti-Hyperlipidemic Drugs. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 7, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karalis, D.G.; Victor, B.; Ahedor, L.; Liu, L. Use of Lipid-Lowering Medications and the Likelihood of Achieving Optimal LDL-Cholesterol Goals in Coronary Artery Disease Patients. Cholesterol 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.A.; Frota, J.T.; Arruda, B.R.; De Melo, T.S.; Da Silva, A.A.D.C.A.; Brito, G.A.D.C.; Chaves, M.H.; Rao, V.S. Antihyperglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of A,β-Amyrin, a Triterpenoid Mixture from Protium Heptaphyllum in Mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.M.P. Evaluation of the Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Triterpenoids from Prosthechea Michuacana in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Pharmacologia 2013, 4, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhahar, V.; Kumar, S.A.; Sudharsan, P.T.; Varalakshmi, P. Protective Effect of Lupeol and Its Ester on Cardiac Abnormalities in Experimental Hypercholesterolemia. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2007, 46, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.W.; Hang, J.; Dussault, P.H.; Carr, T.P. Plant Sterol and Stanol Substrate Specificity of Pancreatic Cholesterol Esterase. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, B.J.; Watson, K.E.; Fogelman, A.M.; Navab, M.; Fonarow, G.C. High-Density Lipoprotein Function: Recent Advances. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Eckert, A.O.; Schrey, A.K.; Preissner, R. ProTox-II: A Webserver for the Prediction of Toxicity of Chemicals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W257–W263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.H.; Huang, K.J.; Weng, C.F.; Shiuan, D. Exploration of Natural Product Ingredients as Inhibitors of Human HMG-CoA Reductase through Structure-Based Virtual Screening. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 3313–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatriansyah, J.F.; Rizqillah, R.K.; Yandi, M.Y.; Fadilah; Sahlan, M. Molecular Docking and Dynamics Studies on Propolis Sulabiroin-A as a Potential Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2. J. King Saud Univ. - Sci. 2022, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgonosov, A.M. The Universal Relationship between the Energy and Length of a Covalent Bond Derived from the Theory of Generalized Charges. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 62, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, G.; Li, G.; Yan, J.; Yi, J.; Zhang, G. Discovery and Identification of 2-Phenylethyl 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoate as a Natural Lipid-Lowering Lead. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 2047–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durendić-Brenesel, M.; Popović, T.; Pilija, V.; Arsić, A.; Milić, M.; Kojić, D.; Jojić, N.; Milić, N. Hypolipidemic and Antioxidant Effects of Buckwheat Leaf and Flower Mixture in Hyperlipidemic Rats. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2013, 13, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imafidon, K.E.; Okunrobo, L.O. Study on Biochemical Indices of Liver Function Tests of Albino Rats Supplemented with Three Sources of Vegetable Oils. Niger. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 19, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rasekh, H.R.; Khoshnood-Mansourkhani, M.J.; Kamalinejad, M. Hypolipidemic Effects of Teucrium Polium in Rats. Fitoterapia 2001, 72, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the Concentration of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Plasma, without Use of the Preparative Ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.; Ismatullah, H.; Rauf, S.; Niazi, U.H.K. Identification of Bioflavonoid as Fusion Inhibitor of Dengue Virus Using Molecular Docking Approach. Informatics Med. Unlocked 2016, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.; Khan, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Hussain, M.S.; Ali, M. Bioactivity Guided Fractionation and Hypolipidemic Property of a Novel HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor from Ficus Virens Ait. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marahatha, R.; Basnet, S.; Bhattarai, B.R.; Budhathoki, P.; Aryal, B.; Adhikari, B.; Lamichhane, G.; Poudel, D.K.; Parajuli, N. In-Silico Analysis of Secondary Metabolites That Modulates Enzymes of Cholesterol Target. bioRxiv, 2020; 2020.07.24.219998. [Google Scholar]
- Punetha, A.; Muthukumaran, J.; Hemrom, A.J.; Arumugam, N.; Jayakanthan, M. Sundar Durai Towards Understanding the Regulation of Rubber Biosynthesis: Insights into the Initiator and Elongator Enzymes. J. Bioinforma. Seq. Anal. 2010, 2, 001–010. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W.; Chen, C.; Lei, X.; Zhao, J.; Liang, J. CASTp 3.0: Computed Atlas of Surface Topography of Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W363–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, M.F.; Akter, S.A.; Hasan, M.J.; Amin, A. In Silico Characterization of a Hypothetical Protein from Shigella Dysenteriae ATCC 12039 Reveals a Pathogenesis-Related Protein of the Type-VI Secretion System. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, N.R.; Singh, V.; Marla, S.S.; Chandra, R.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A. Molecular Docking Studies with Rabies Virus Glycoprotein to Design Viral Therapeutics. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Rauf, A.; Rashid, U.; Bawazeer, S.; Khan, K.; Mubarak, M.S.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Khan, H.; El-Saber Batiha, G.; El-Esawi, M.A.; et al. In Vivo and in Silico Studies of Flavonoids Isolated from Pistacia Integerrima as Potential Antidiarrheal Agents. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 15617–15624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Rashid, U.; Shah, Z.A.; Rauf, A.; Muhammad, N.; Al-Awthan, Y.S.; Bahattab, O.S. In Vivo Antinociceptive, Muscle Relaxant, Sedative, and Molecular Docking Studies of Peshawaraquinone Isolated from Fernandoa Adenophylla (Wall. Ex G. Don) Steenis. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, F.; Yaqoob, F.; Tabassum, N.; Jan, M.S.; Sadiq, A.; Tahir, S.; Batool, T.; Niaz, B.; Ansari, F.L.; Choudhary, M.I.; et al. Design, Synthesis, in-Vitro Thymidine Phosphorylase Inhibition, in-Vivo Antiangiogenic and in-Silico Studies of C-6 Substituted Dihydropyrimidines. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).