Submitted:
19 December 2023
Posted:
21 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiefari J, Chong Y K, Ercole F, et al. Living Free-Radical Polymerization by Reversible Addition−Fragmentation Chain Transfer: The Raft Process [J]. Macromolecules, 1998, 31(16): 5559-5562. [CrossRef]
- Moad G, Rizzardo E, Thang S H. Living Radical Polymerization by the Raft Process – a Third Update [J]. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 2012, 65. [CrossRef]
- Hu W, Ren Z, Li J, et al. New Dielectric Elastomers with Variable Moduli [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(30): 4827-4836. [CrossRef]
- Molev G, Lu Y, Kim K S, et al. Organometallic–Polypeptide Diblock Copolymers: Synthesis by Diels–Alder Coupling and Crystallization-Driven Self-Assembly to Uniform Truncated Elliptical Lamellae [J]. Macromolecules, 2014, 47(8): 2604-2615. [CrossRef]
- Chang H, Kim M S, Huber G W, et al. Design of Closed-Loop Recycling Production of a Diels-Alder Polymer from a Biomass-Derived Difuran as a Functional Additive for Polyurethanes [J]. Green Chem, 2021, 23(23): 9479-9488. [CrossRef]
- Bowman C, Du Prez F, Kalow J. Introduction to Chemistry for Covalent Adaptable Networks [J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2020, 11(33): 5295-5296. [CrossRef]
- Xu X, Ma S, Wang S, et al. Fast-Reprocessing, Postadjustable, Self-Healing Covalent Adaptable Networks with Schiff Base and Diels-Alder Adduct [J]. Macromol Rapid Commun, 2022, 43(13): e2100777. [CrossRef]
- Rinehart J M, Reynolds J R, Yee S K. Limitations of Diels–Alder Dynamic Covalent Networks as Thermal Conductivity Switches [J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2022, 4(2): 1218-1224. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Yu R, He Y, et al. Four-Dimensional Printing of Shape Memory Polyurethanes with High Strength and Recyclability Based on Diels-Alder Chemistry [J]. Polymer, 2020, 200. [CrossRef]
- Hirschbiel A F, Konrad W, Schulze-Sunninghausen D, et al. Access to Multiblock Copolymers Via Supramolecular Host-Guest Chemistry and Photochemical Ligation [J]. ACS Macro Lett, 2015, 4(10): 1062-1066. [CrossRef]
- Hu Y, Zhang J, Miao Y, et al. Enzyme-Mediated in Situ Self-Assembly Promotes in Vivo Bioorthogonal Reaction for Pretargeted Multimodality Imaging [J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2021, 60(33): 18082-18093. [CrossRef]
- Masson G, Lalli C, Benohoud M, et al. Catalytic Enantioselective [4 + 2]-Cycloaddition: A Strategy to Access Aza-Hexacycles [J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2013, 42(3): 902-923. [CrossRef]
- Knall A C, Slugovc C. Inverse Electron Demand Diels-Alder (Iedda)-Initiated Conjugation: A (High) Potential Click Chemistry Scheme [J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2013, 42(12): 5131-5142. [CrossRef]
- Geng Z, Shin J J, Xi Y, et al. Click Chemistry Strategies for the Accelerated Synthesis of Functional Macromolecules [J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 2021, 59(11): 963-1042. [CrossRef]
- Espinosa E, Glassner M, Boisson C, et al. Synthesis of Cyclopentadienyl Capped Polyethylene and Subsequent Block Copolymer Formation Via Hetero Diels-Alder (Hda) Chemistry [J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2011, 32(18): 1447-1453. [CrossRef]
- Nebhani L, Schmiedl D, Barner L, et al. Quantification of Grafting Densities Achieved Via Modular ’Grafting-to’ Approaches onto Divinylbenzene Microspheres [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(12): P.2010-2020. [CrossRef]
- Tischer T, Goldmann A S, Linkert K, et al. Modular Ligation of Thioamide Functional Peptides onto Solid Cellulose Substrates [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(18): 3853-3864. [CrossRef]
- Kaupp M, Vogt A P, Natterodt J C, et al. Modular Design of Glyco-Microspheres Via Mild Pericyclic Reactions and Their Quantitative Analysis [J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2012, 3(9): 2605-2614. [CrossRef]
- Inglis A J, Sinnwell S, Davis T P, et al. Reversible Addition Fragmentation Chain Transfer (Raft) and Hetero-Diels?Alder Chemistry as a Convenient Conjugation Tool for Access to Complex Macromolecular Designs [J]. MACROMOLECULES, 2008, 41(12): 4120-4126. [CrossRef]
- Sinnwell S, Inglis A J, Davis T P, et al. An Atom-Efficient Conjugation Approach to Well-Defined Block Copolymers Using Raft Chemistry and Hetero Diels–Alder Cycloaddition [J]. Chemical Communications, 2008, 19(17): 2052-2054. [CrossRef]
- Sinnwell S, Inglis A J, Stenzel M H, et al. Access to Three-Arm Star Block Copolymers by a Consecutive Combination of the Copper(I)-Catalyzed Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition and the Raft Hetero Diels–Alder Concept [J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2008, 29(12-13). [CrossRef]
- Bousquet A, Barner-Kowollik C, Stenzel M H. Synthesis of Comb Polymers Via Grafting-onto Macromolecules Bearing Pendant Diene Groups Via the Hetero-Diels-Alder-Raft Click Concept [J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A Polymer Chemistry, 2010, 48(8): 1773-1781. [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, Sinnwell, Mieke, et al. Efficient Access to Multi-Arm Star Block Copolymers by a Combination of Atrp and Raft-Hdaclickchemistry [J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Beloqui A, Mane S R, Langer M, et al. Hetero-Diels–Alder Cycloaddition with Raft Polymers as Bioconjugation Platform [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Inglis A J, Paulöhrl T, Barner-Kowollik C. Ambient Temperature Synthesis of a Versatile Macromolecular Building Block: Cyclopentadienyl-Capped Polymers [J]. Macromolecules, 2009, 43(1): 33-36. [CrossRef]
- Inglis A J, Stenzel M H, Barner-Kowollik C. Ultra-Fast Raft-Hda Click Conjugation: An Efficient Route to High Molecular Weight Block Copolymers [J]. Macromol Rapid Commun, 2009, 30(21): 1792-1798. [CrossRef]
- Langer M, Brandt J, Lederer A, et al. Amphiphilic Block Copolymers Featuring a Reversible Hetero Diels-Alder Linkage [J]. Polym Chem, 2014, 5(18): 5330-5338. [CrossRef]
- Dürr C J, Hlalele L, Kaiser A, et al. Mild and Efficient Modular Synthesis of Poly(Acrylonitrile-Co-Butadiene) Block and Miktoarm Star Copolymer Architectures [J]. Macromolecules, 2012, 46(1): 49-62. [CrossRef]
- Zydziak N, Hübner C, Bruns M, et al. One-Step Functionalization of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (Swcnts) with Cyclopentadienyl-Capped Macromolecules Via Diels−Alder Chemistry [J]. Macromolecules, 2011, 44(9): 3374-3380. [CrossRef]
- Zydziak N, Preuss C M, Winkler V, et al. Hetero Diels-Alder Chemistry for the Functionalization of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Cyclopentadienyl End-Capped Polymer Strands [J]. Macromol Rapid Commun, 2013, 34(8): 672-680. [CrossRef]
- Guimard N K, Ho J, Brandt J, et al. Harnessing Entropy to Direct the Bonding/Debonding of Polymer Systems Based on Reversible Chemistry [J]. Chemical Science, 2013, 4(7). [CrossRef]
- Schenzel A M, Klein C, Rist K, et al. Reversing Adhesion: A Triggered Release Self-Reporting Adhesive [J]. Advanced Science, 2016, 3(3): 1500361. [CrossRef]
- Glassner M, Kempe K, Schubert U S, et al. One-Pot Synthesis of Cyclopentadienyl Endcapped Poly(2-Ethyl-2-Oxazoline) and Subsequent Ambient Temperature Diels-Alder Conjugations [J]. Chem Commun (Camb), 2011, 47(38): 10620-10622. [CrossRef]
- Brandt J, Lenz J, Pahnke K, et al. Investigation of Thermoreversible Polymer Networks by Temperature Dependent Size Exclusion Chromatography [J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2017, 8(43): 6598-6605. [CrossRef]
- Oehlenschlaeger K K, Mueller J O, Brandt J, et al. Adaptable Hetero Diels-Alder Networks for Fast Self-Healing under Mild Conditions [J]. Adv Mater, 2014, 26(21): 3561-3566. [CrossRef]
- Mutlu H, Schmitt C W, Wedler-Jasinski N, et al. Spin Fluorescence Silencing Enables an Efficient Thermally Driven Self-Reporting Polymer Release System [J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2017, 8(40): 6199-6203. [CrossRef]
- Oh J K, Drumright R, Siegwart D J, et al. The Development of Microgels/Nanogels for Drug Delivery Applications [J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2008, 33(4): 448-477. [CrossRef]
- Oh J K, Lee D I, Park J M. Biopolymer-Based Microgels/Nanogels for Drug Delivery Applications [J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2009, 34(12): 1261-1282. [CrossRef]
- Wiemer K, Dormbach K, Slabu I, et al. Hydrophobic Superparamagnetic Fept Nanoparticles in Hydrophilic Poly(N-Vinylcaprolactam) Microgels: A New Multifunctional Hybrid System [J]. J Mater Chem B, 2017, 5(6): 1284-1292. [CrossRef]
- Karg M. Multifunctional Inorganic/Organic Hybrid Microgels [J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 2012, 290(8): 673-688. [CrossRef]
- Peng L, Feng A, Liu S, et al. Electrochemical Stimulated Pickering Emulsion for Recycling of Enzyme in Biocatalysis [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016, 8(43): 29203-29207. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Niu C, Zhang Y, et al. A Mechanically Strong Polyvinyl Alcohol/Poly(2-(N,N′-Dimethyl Amino) Ethyl Methacrylate)-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel with Ph-Responsiveness [J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 2020, 298(6): 619-628. [CrossRef]
- Sasaki Y, Akiyoshi K. Nanogel Engineering for New Nanobiomaterials: From Chaperoning Engineering to Biomedical Applications [J]. Chem Rec, 2010, 10(6): 366-376. [CrossRef]
- Rossow T, Heyman J A, Ehrlicher A J, et al. Controlled Synthesis of Cell-Laden Microgels by Radical-Free Gelation in Droplet Microfluidics [J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134(10): 4983-4989. [CrossRef]
- Li B, Jiang X, Yin J. Multi-Responsive Microgel of Hyperbranched Poly(Ether Amine) (Hpea-Mgel) for the Selective Adsorption and Separation of Hydrophilic Fluorescein Dyes [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(34). [CrossRef]
- Steinhilber D, Rossow T, Wedepohl S, et al. A Microgel Construction Kit for Bioorthogonal Encapsulation and Ph-Controlled Release of Living Cells [J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2013, 52(51): 13538-13543. [CrossRef]
- Bahadur K C R, Xu P. Multicompartment Intracellular Self-Expanding Nanogel for Targeted Delivery of Drug Cocktail [J]. Adv Mater, 2012, 24(48): 6479-6483. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Yang F, Shen H, et al. Controlled Formation of Microgels/Nanogels from a Disulfide-Linked Core/Shell Hyperbranched Polymer [J]. ACS Macro Lett, 2012, 1(11): 1295-1299. [CrossRef]
- Yan L, Tao W. One-Step Synthesis of Pegylated Cationic Nanogels of Poly(N,N′-Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate) in Aqueous Solution Via Self-Stabilizing Micelles Using an Amphiphilic Macroraft Agent [J]. Polymer, 2010, 51(10): 2161-2167. [CrossRef]
- Heller D A, Levi Y, Pelet J M, et al. Modular ’Click-in-Emulsion’ Bone-Targeted Nanogels [J]. Adv Mater, 2013, 25(10): 1449-1454. [CrossRef]
- Tan H, Jin H, Mei H, et al. Peg-Urokinase Nanogels with Enhanced Stability and Controllable Bioactivity [J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8(9). [CrossRef]
- Kim K, Bae B, Kang Y J, et al. Natural Polypeptide-Based Supramolecular Nanogels for Stable Noncovalent Encapsulation [J]. Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14(10): 3515-3522. [CrossRef]
- Nakai T, Hirakura T, Sakurai Y, et al. Injectable Hydrogel for Sustained Protein Release by Salt-Induced Association of Hyaluronic Acid Nanogel [J]. Macromol Biosci, 2012, 12(4): 475-483. [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa U, Sawada S, Shimizu T, et al. Raspberry-Like Assembly of Cross-Linked Nanogels for Protein Delivery [J]. J Control Release, 2009, 140(3): 312-317. [CrossRef]
- Hirakura T, Yasugi K, Nemoto T, et al. Hybrid Hyaluronan Hydrogel Encapsulating Nanogel as a Protein Nanocarrier: New System for Sustained Delivery of Protein with a Chaperone-Like Function [J]. J Control Release, 2010, 142(3): 483-489. [CrossRef]
- Sasaki Y, Asayama W, Niwa T, et al. Amphiphilic Polysaccharide Nanogels as Artificial Chaperones in Cell-Free Protein Synthesis [J]. Macromol Biosci, 2011, 11(6): 814-820. [CrossRef]
- Sekine Y, Moritani Y, Ikeda-Fukazawa T, et al. A Hybrid Hydrogel Biomaterial by Nanogel Engineering: Bottom-up Design with Nanogel and Liposome Building Blocks to Develop a Multidrug Delivery System [J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2012, 1(6): 722-728. [CrossRef]
- Siegwart D J, Srinivasan A, Bencherif S A, et al. Cellular Uptake of Functional Nanogels Prepared by Inverse Miniemulsion Atrp with Encapsulated Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Gold Nanoparticles [J]. Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10(8): 2300-2309. [CrossRef]
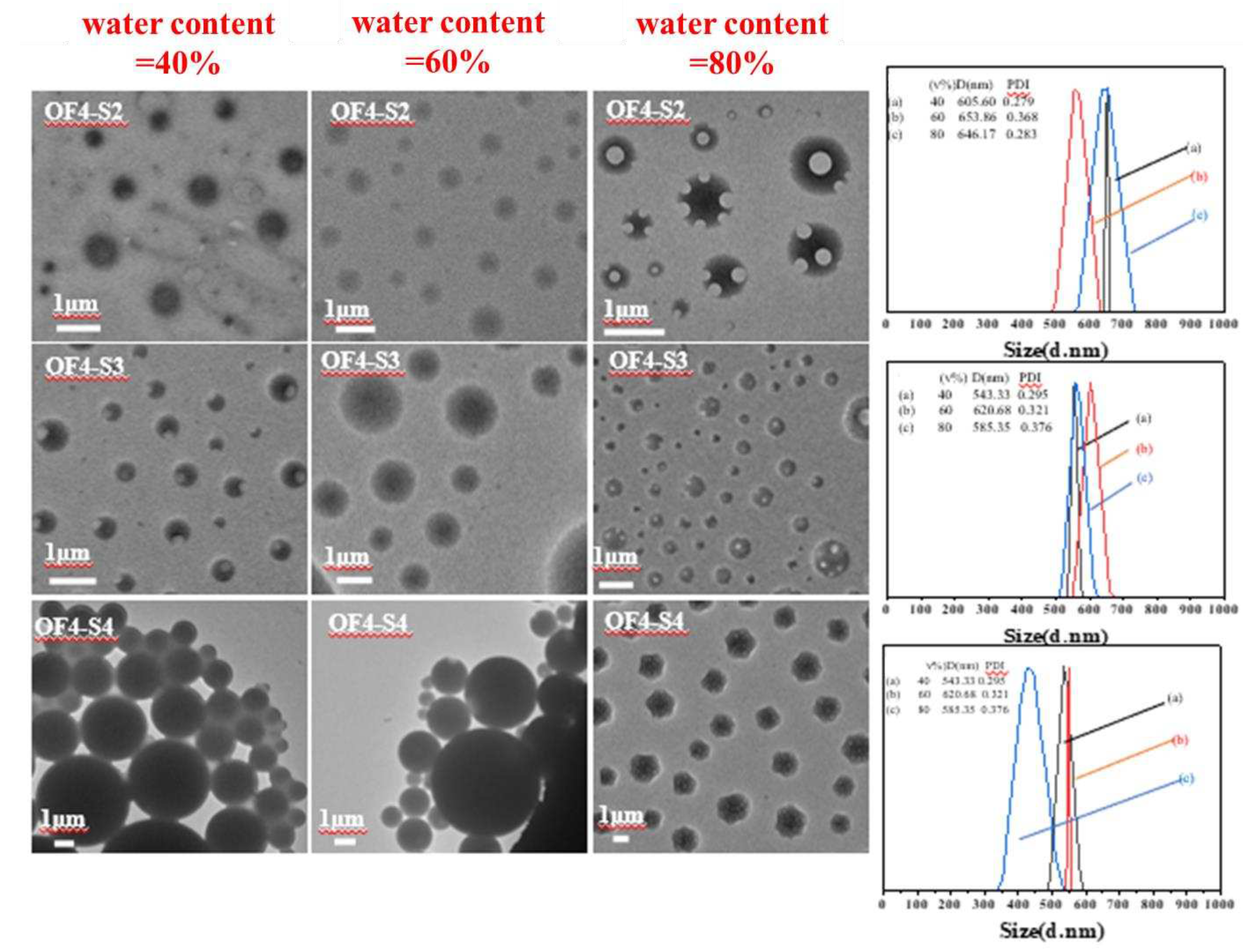
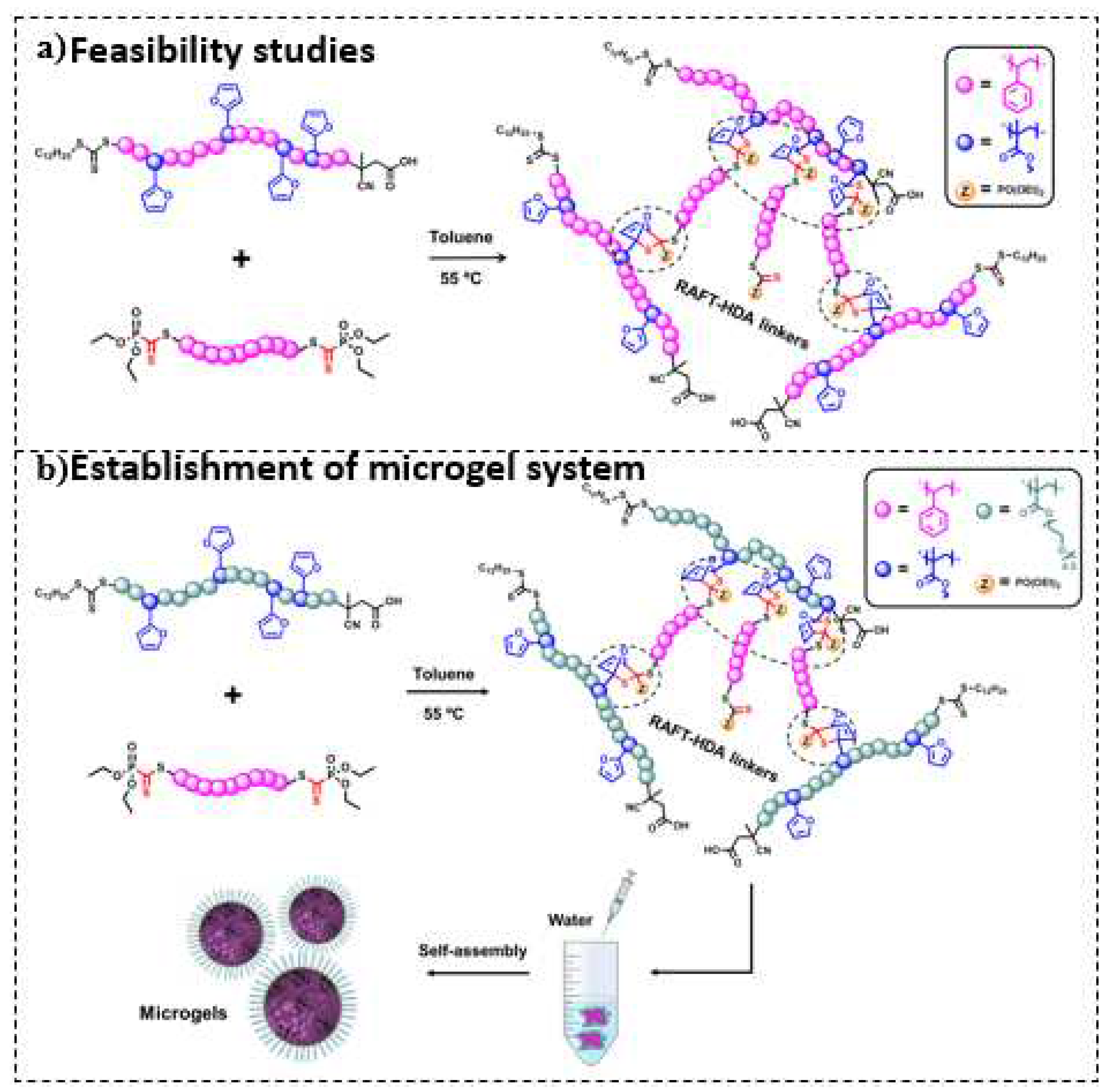
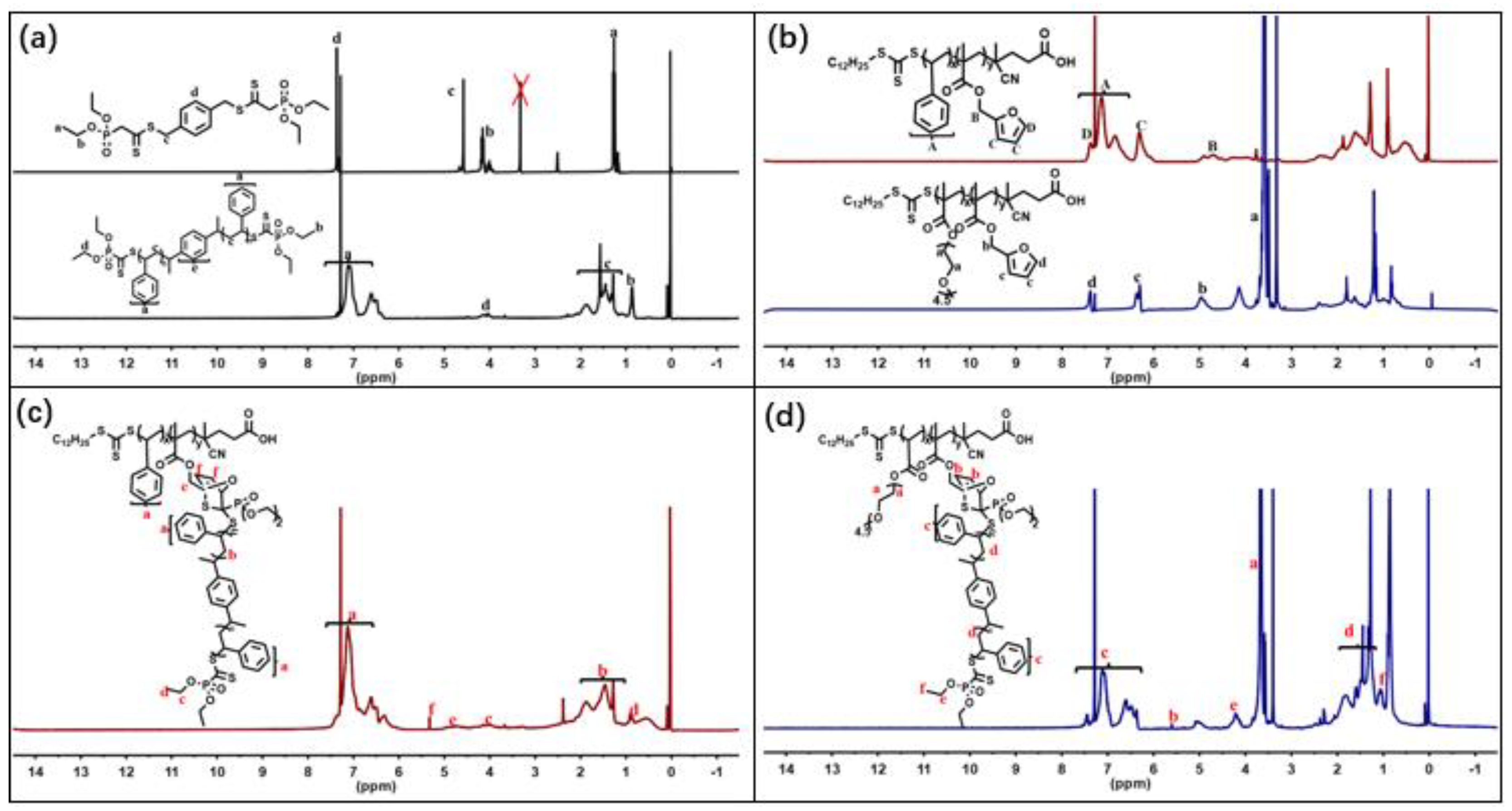
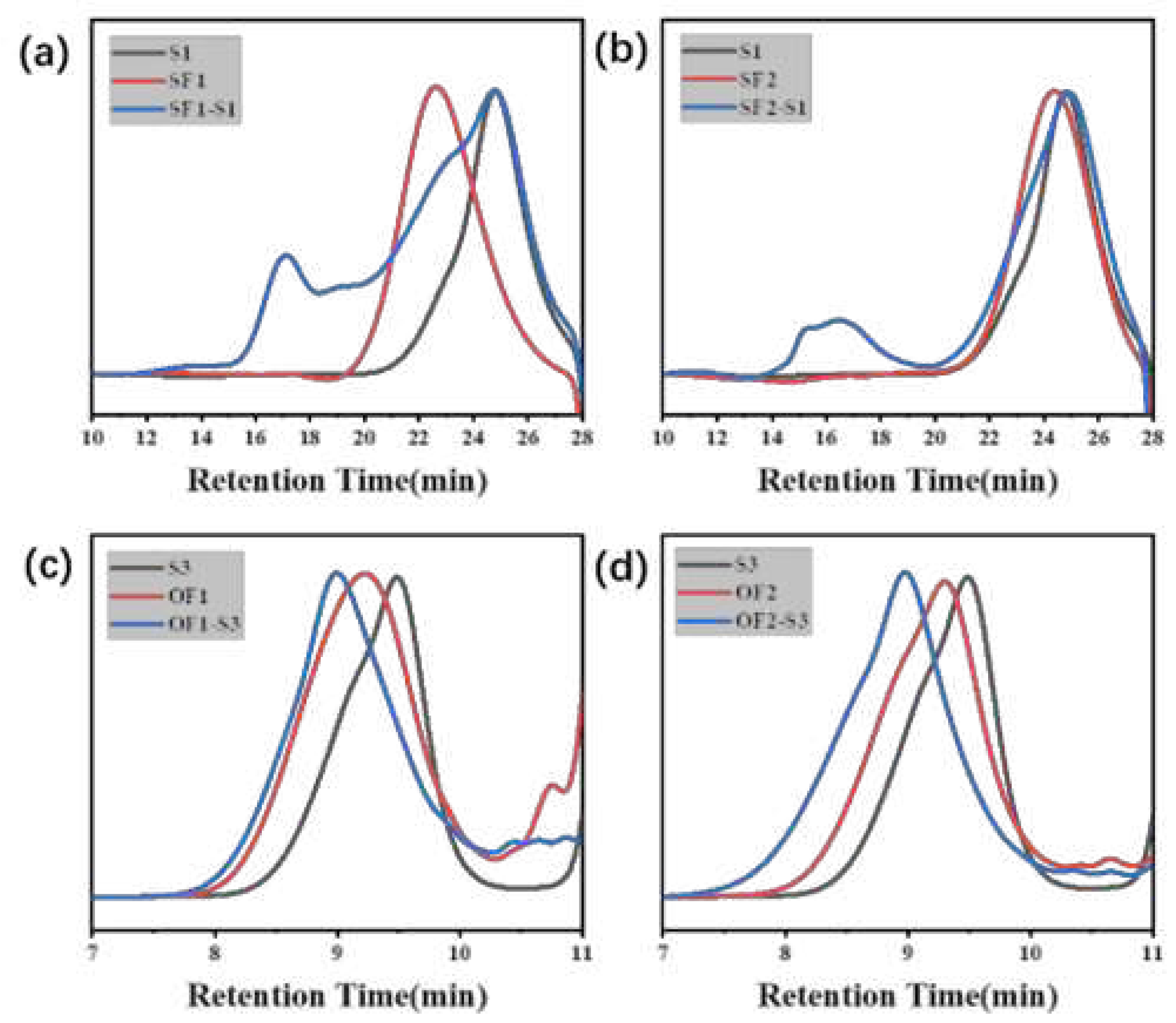
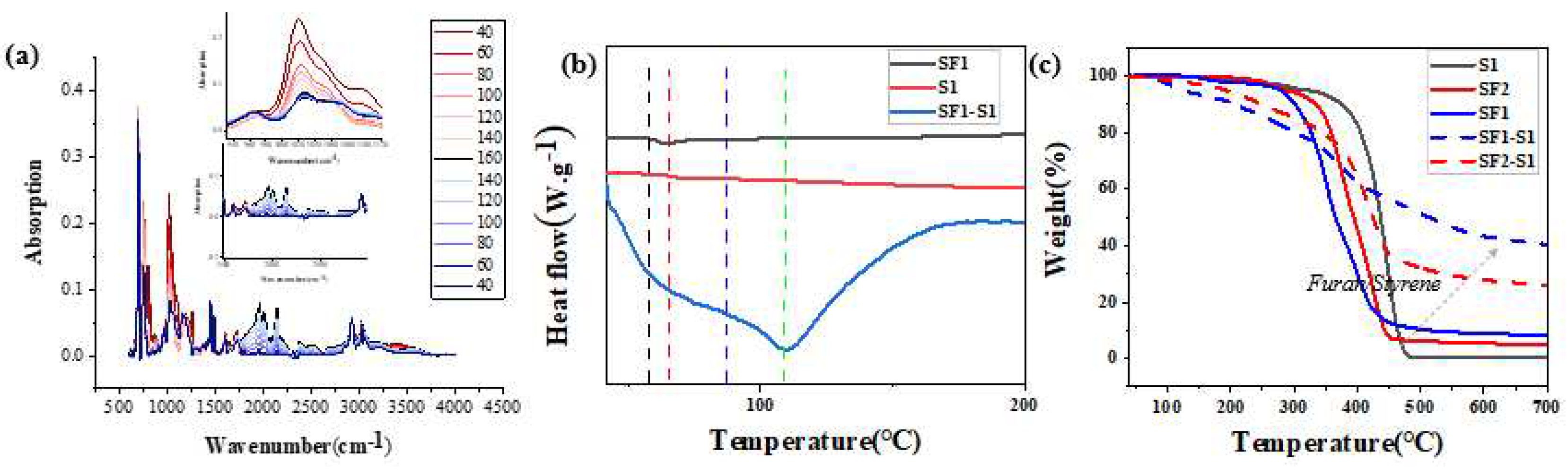
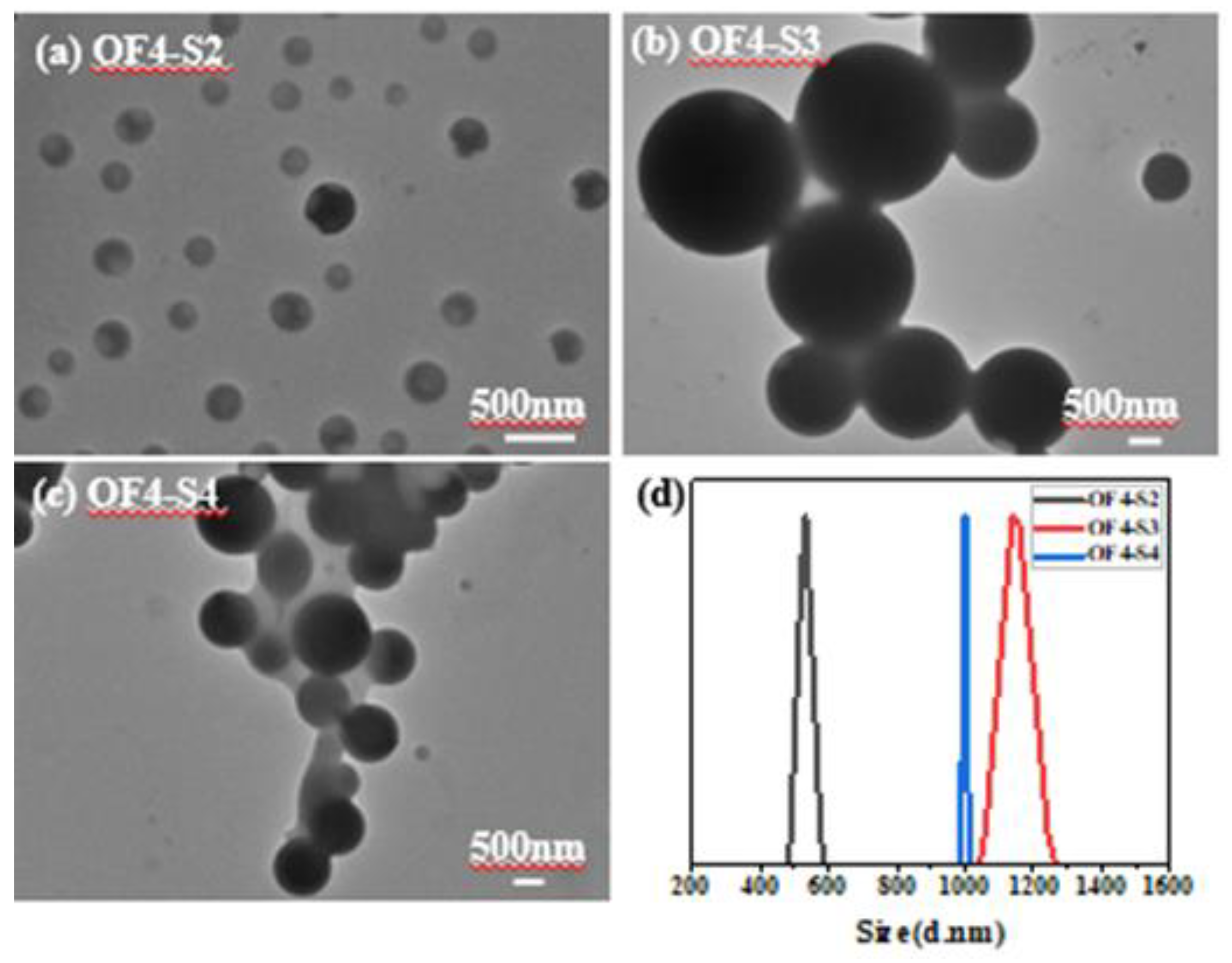

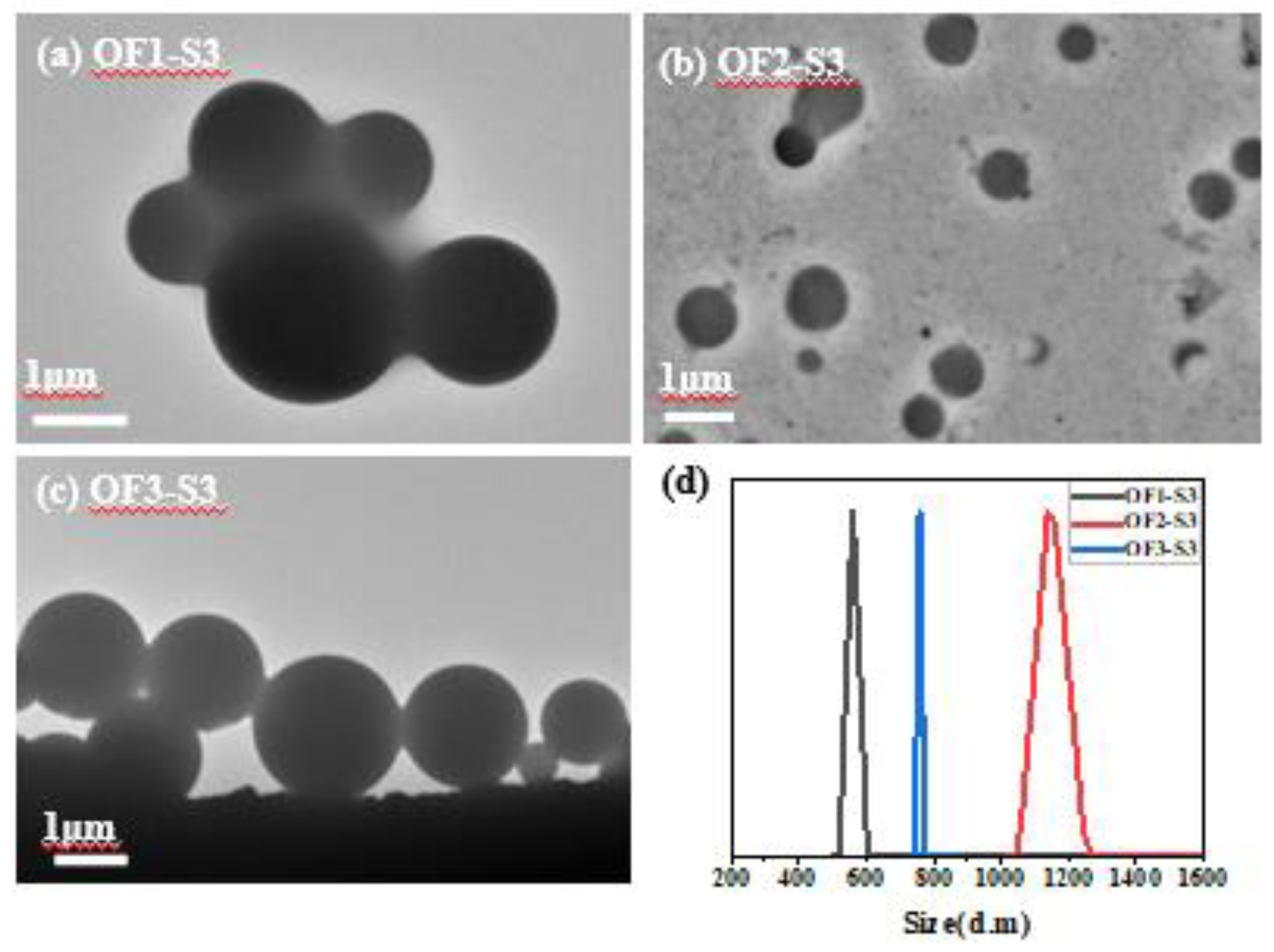
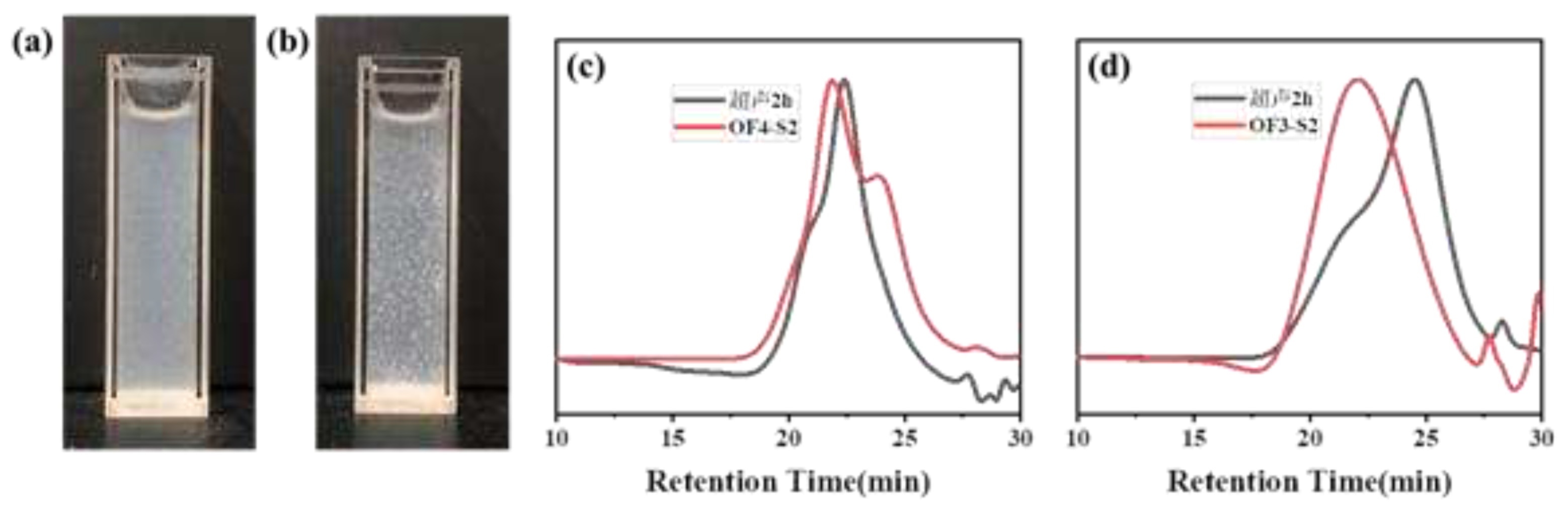
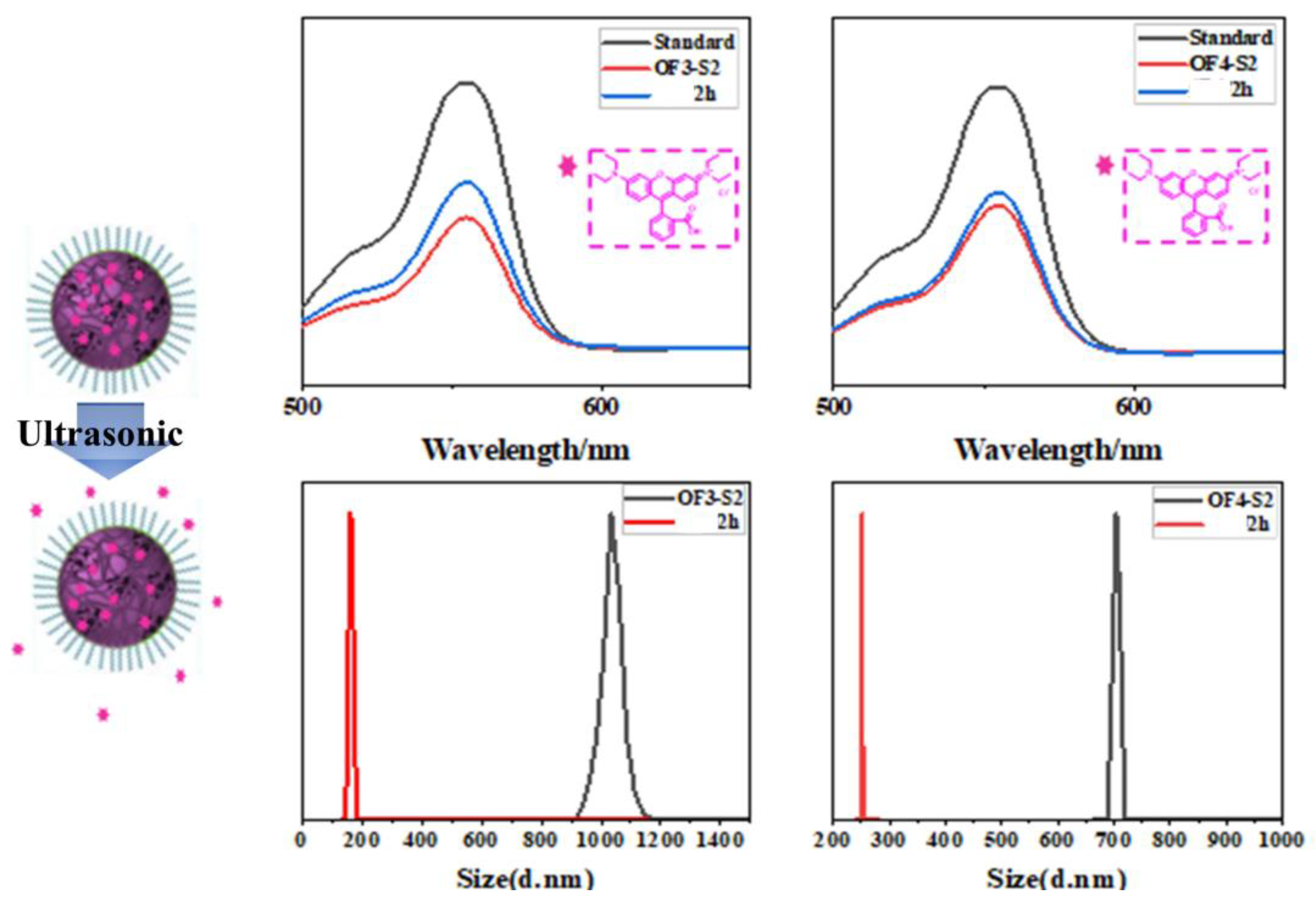
| Component | ƒ | M/ƒ (g.mol-1) |
DPa | Mna | Mnb | Đb | Blocks | r ([F]0/[S]0) |
[F]0 (mol.ML-1) |
[S]0 (mol.ML-1) |
T (ºC) |
Mnb | Đb |
| PSt1(S1) | 2 | 3344 | 66 | 6689 | 6838 | 1.15 | |||||||
| PSt2(S2) | 2 | 1416 | 28 | 2832 | 2765 | 1.15 | OF4-S2 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 55 | 8696 | 1.11 |
| PSt3(S3) | 2 | 1993 | 39 | 3987 | 3767 | 1.4 | OF4-S3 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 55 | 12586 | 1.33 |
| PSt4(S4) | 2 | 3781 | 75 | 7563 | 7209 | 1.13 | OF4-S4 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 55 | 15428 | 1.33 |
| P(St60-co-FMA35)(SF1) | 35 | 351 | 95 | 10473 | 12289 | 1.19 | SF1-S1 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 55 | 154080 | 1.18 |
| P(St43-co-FMA17)(SF2) | 17 | 443 | 60 | 7531 | 7483 | 1.15 | SF2-S1 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 55 | 213879 | 1.52 |
| P(OEGMA45-co-FMA2)(OF1) | 2 | 2566 | 47 | 5133 | 4743 | 1.54 | OF1-S3 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 55 | 10434 | 1.4 |
| P(OEGMA45-co-FMA4)(OF2) | 4 | 1375 | 49 | 5501 | 5498 | 1.26 | OF2-S3 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 55 | 19380 | 1.14 |
| P(OEGMA45-co-FMA7)(OF3) | 7 | 860 | 52 | 6021 | 7902 | 1.03 | OF3-S3 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 55 | 3162 | 1.03 |
|
P(OEGMA40-co-FMA5)(OF4) |
5 |
952 |
42 |
4763 |
4477 |
1.38 |
OF4-S2 OF4-S3 OF4-S4 |
2 |
0.12 |
0.06 |
55 |
gel |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




