Submitted:
20 December 2023
Posted:
20 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
3. Methodolgy
- 1.
- General approach
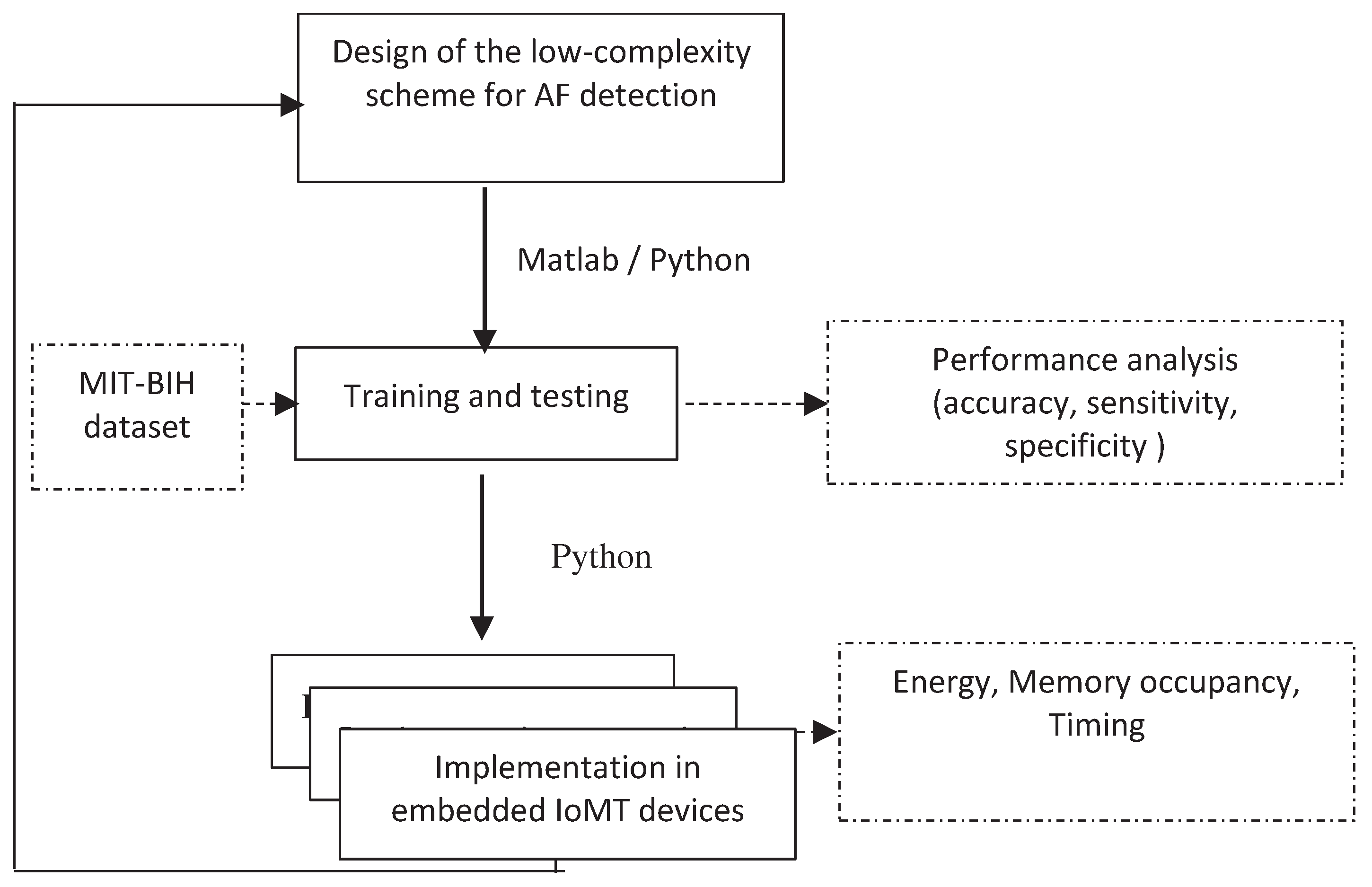
- 2.
- Structure of the proposed scheme
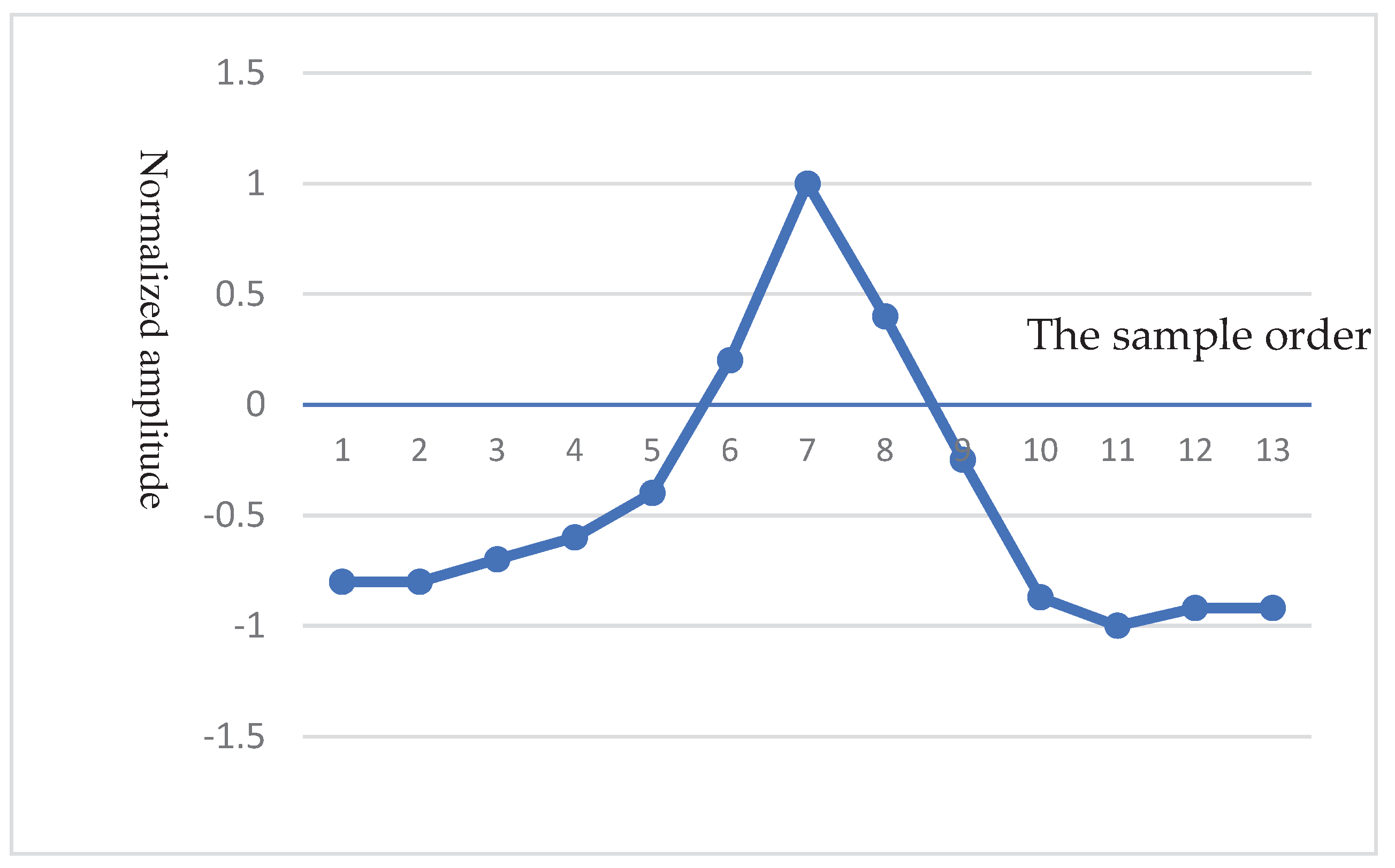
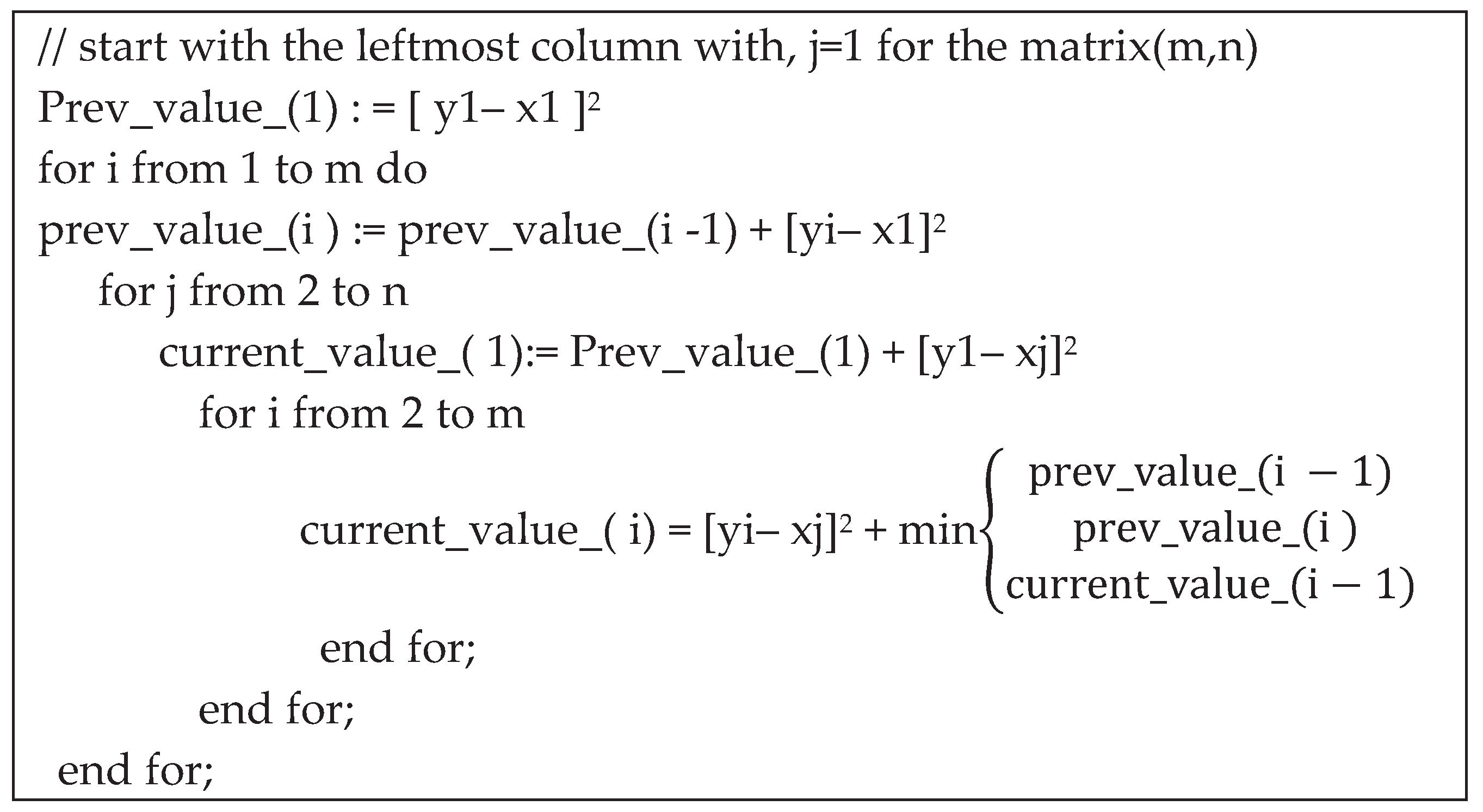
- QRS complex detection
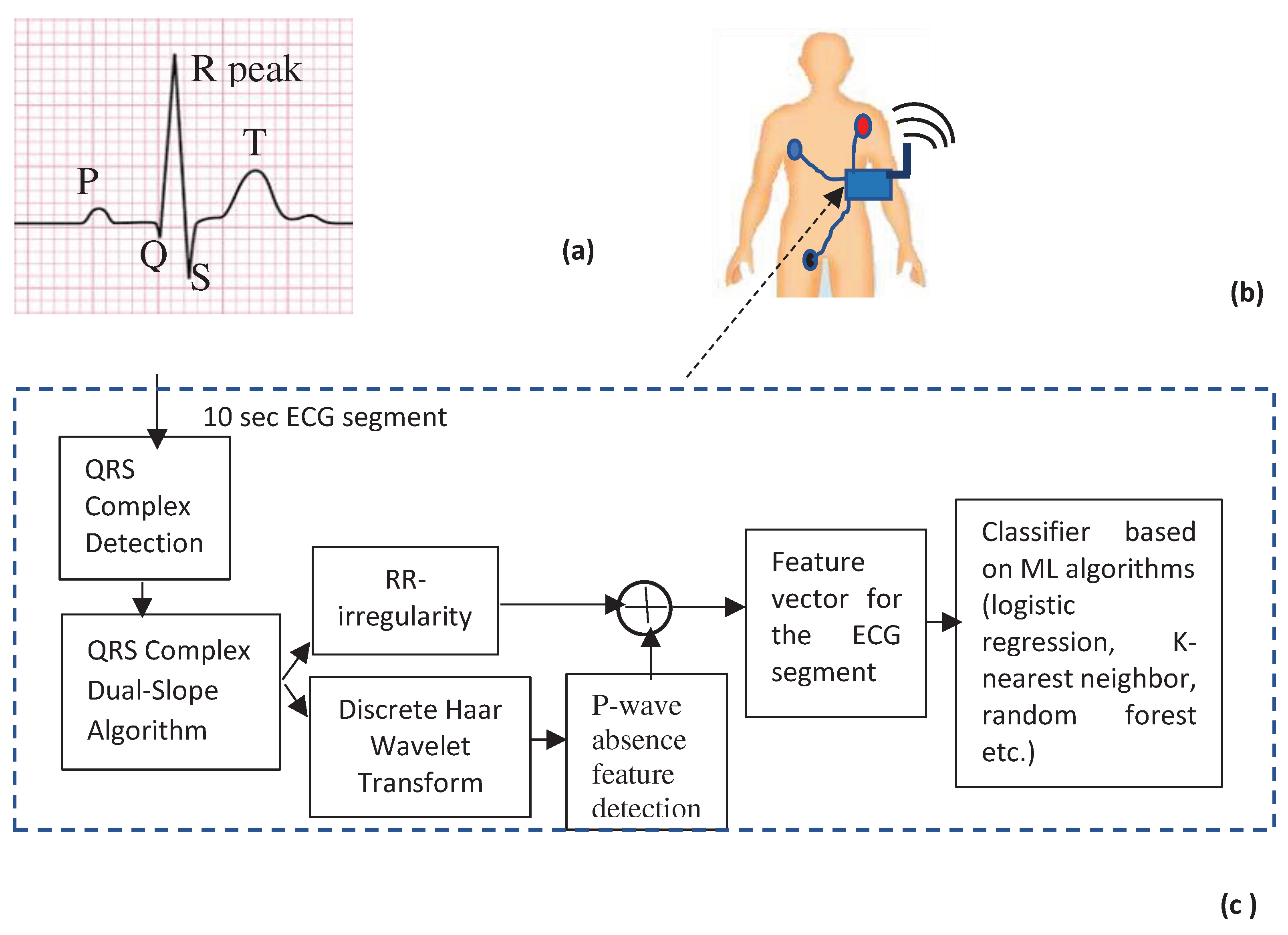
- Haar Discrete Wavelet Transformation (HDWT)
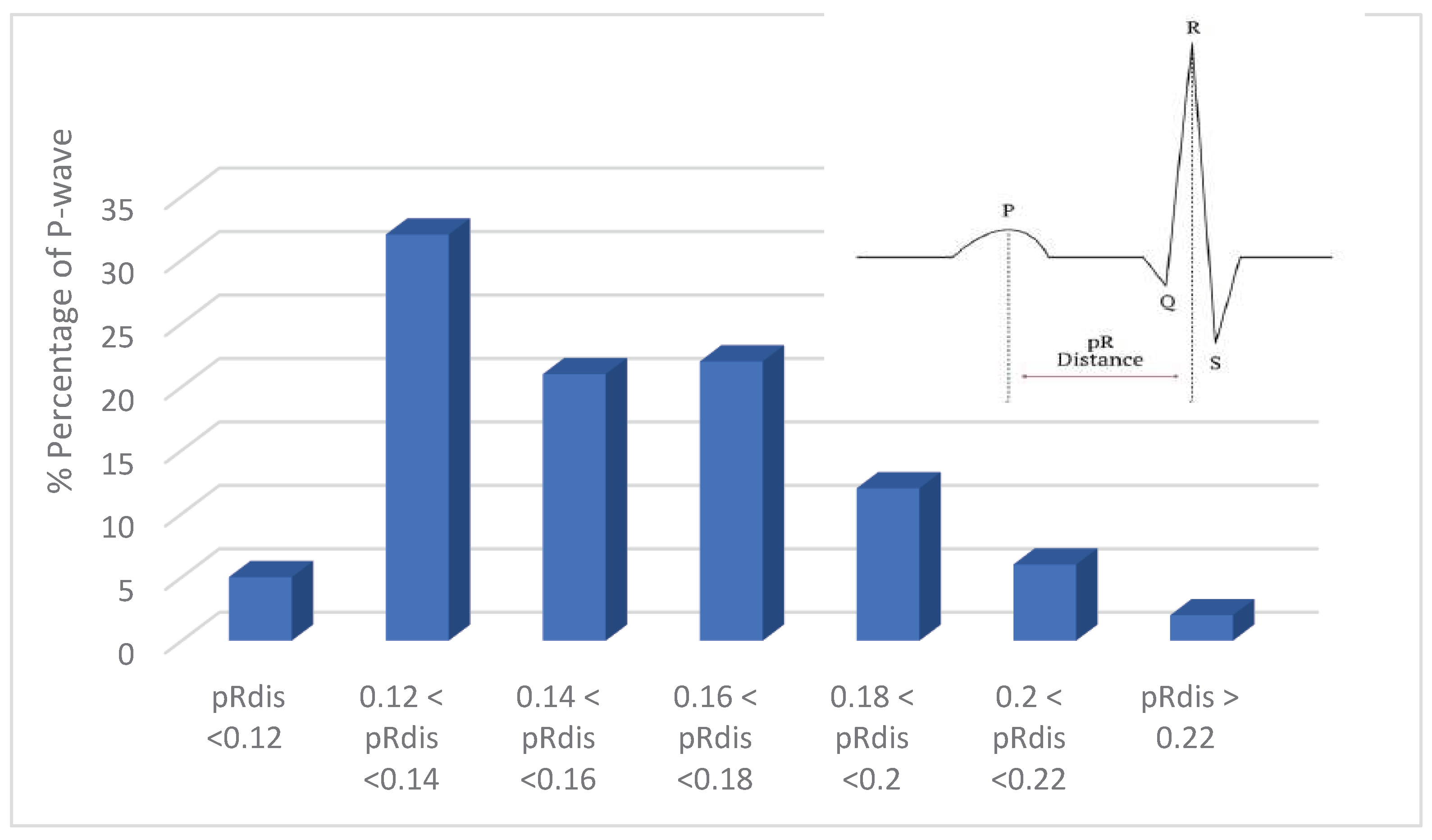
- P-wave absence detection
| Sel16265 | Sel16272 | Sel16273 |
| Sel16420 | Sel16773 | Sel16939 |
| sel117 | sel123 | Sel213 |
| Sel16786 | Sel17152 | Sel17453 |
- 3.
- AF detection using machine learning classifiers
4. Result and Discussion
4.2. AF detection and accuracy
- The number of false positives (FP) is the number of non-AF segments that were missclassified as AF segments.
- The number of false negatives (FN) is the number of AF segments that were missclassified as non-AF segments.
- The number of true negatives (TN) is the number of non-AF segments that were correctly classified as non-AF segments.
- The number of true positives (TP) is the number of AF segments that were correctly classified as AF segments.
- The sensitivity estimates the ability of the scheme to classify correctly subjects with AF disease.
- The specificity, defines the percentage of non-AF segments that were correctly classified
- The accuracy the prediction ability oof the scheme
- The positive Predictive Value, It provides the probability of how likely is that the subject has AF
- F1-score (F1): It combines both sensitivity and PPV in a single metric.
| Classifier | Sen % | Spec % | Acc % | F1 % | |
| Our proposed scheme | SVM | 96.7 | 94.4 | 94.8 | 92.3 |
| Logistic Regression | 100 | 94.5 | 97.4 | 95.2 | |
| Decision tree | 98.2 | 95.4 | 95.2 | 94 | |
| Marsili et al. [25] | Threshold based classifer using only RR interval | 96, 13 |
97.9 |
97.6 |
--- |
| Huerta et al. [1]
FFT, Pantompkins |
SVM | -- | -- | 71.2 | 78 |
| Logistic regression | -- | -- | 70.8 | 70 | |
| Ahsanuzzaman et al. [26] | Neural Network | -- | -- | 97.5 | -- |
| Kim et al. [27] | K-NN | 91.1 | -- | 83.7 | -- |
| Decision Tree | 88.2 | -- | 83.7 | -- | |
| Ma et al [28] | SVM | 89.2 | 96.8 | 93.8 | -- |
4.2. IoT-based device implementation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liaqat, S.; Dashtipour, K.; Zahid, A.; Assaleh, K.; Arshad, K.; Ramzan, N. Detection of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Machine Learning Approach. Information 2020, 11, 549. [CrossRef]
- Wegner, F.K.; Plagwitz, L.; Doldi, F.; Ellermann, C.; Willy, K.; Wolfes, J.; Sandmann, S.; Varghese, J.; Eckardt, L. Machine learning in the detection and management of atrial fibrillation. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2022, 111, 1010–1017. [CrossRef]
- Rienstra, M.; Lubitz, S.A.; Mahida, S.; Magnani, J.W.; Fontes, J.D.; Sinner, M.F.; Ellinor, P.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Benjamin, E.J. Response to Letter Regarding Article, “Symptoms and Functional Status of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: State of the Art and Future Research Opportunities”. Circulation 2012, 126, 2933-2943. [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, S.; Soudani, A.; Almusallam, M. Energy-Efficient EEG-Based Scheme for Autism Spectrum Disorder Detection Using Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 2228. [CrossRef]
- Alsaleem, M.N.; Islam, S.; Al-Ahmadi, S.; Soudani, A. Multiscale Encoding of Electrocardiogram Signals with a Residual Network for the Detection of Atrial Fibrillation. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 480. [CrossRef]
- Almarshad, M.A.; Al-Ahmadi, S.; Islam, S.; BaHammam, A.S.; Soudani, A. Adoption of Transformer Neural Network to Improve the Diagnostic Performance of Oximetry for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sensors 2023, 23, 7924. [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.S.; Mansourvar, M.; Puthusserypady, S.; Wiil, U.K.; Peimankar, A. Short-term atrial fibrillation detection using electrocardiograms: A comparison of machine learning approaches. Int. J. Med Informatics 2022, 163, 104790. [CrossRef]
- Mäkynen, M.; Ng, G.A.; Li, X.; Schlindwein, F.S. Wearable Devices Combined with Artificial Intelligence—A Future Technology for Atrial Fibrillation Detection? Sensors 2022, 22, 8588. [CrossRef]
- Lown, M.; Brown, M.; Brown, C.; Yue, A.M.; Shah, B.N.; Corbett, S.J.; Lewith, G.; Stuart, B.; Moore, M.; Little, P. Machine learning detection of Atrial Fibrillation using wearable technology. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0227401. [CrossRef]
- Parmar, R.; Janveja, M.; Pidanic, J.; Trivedi, G. Design of DNN-Based Low-Power VLSI Architecture to Classify Atrial Fibrillation for Wearable Devices. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (vlsi) Syst. 2023, 31, 320–330. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.J.; Chon, S.; Kim, S.; Jang, J.; Kim, J.-K.; Jang, S.; Gil, Y.; et al. Compressed Deep Learning to Classify Arrhythmia in an Embedded Wearable Device. Sensors 2022, 22, 1776. [CrossRef]
- Almusallam, M.; Soudani, A. Embedded Solution for Atrial Fibrillation Detection Using Smart Wireless Body Sensors. IEEE Sensors J. 2019, 19, 5740–5750. [CrossRef]
- Saadatnejad, S.; Oveisi, M.; Hashemi, M. LSTM-Based ECG Classification for Continuous Monitoring on Personal Wearable Devices. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.04818. [CrossRef]
- J. Pan and J. T. Willis, “A Real-Time QRS Detection Algorithm,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. BME-32, no. 3, pp. 230–236, 1985.
- Faust, O.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R. A Review of Atrial Fibrillation Detection Methods as a Service. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 3093. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.; Oh, K.; Kwon, S.; Son, H.; Yun, Y.; Jung, E.-S.; Kim, M.S. A Lightweight Deep Learning Model for Fast Electrocardiographic Beats Classification With a Wearable Cardiac Monitor: Development and Validation Study. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 8, e17037. [CrossRef]
- Rincón, F.; Grassi, P.R.; Khaled, N.; Atienza, D.; Sciuto, D. Automated real-time atrial fibrillation detection on a wearable wireless sensor platform. 2012 34th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 2472–2475.
- Laguna, P.; Mark, R.G.; Goldberg, A.; Moody, G.B. A database for evaluation of algorithms for measurement of QT and other waveform intervals in the ECG. In Proceedings of the Computers in Cardiology 1997, Lund, Sweden, 7–10 September 2002; pp. 673–676.
- Li, H.; Wang, C. Similarity Measure Based on Incremental Warping Window for Time Series Data Mining. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 3909–3917. [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, A.U.; Sahabudin, N.A.; Remli, M.A.; Ismail, N.S.N.; Mohamad, M.S.; Nies, H.W.; Warif, N.B.A. A Review on Recent Progress in Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods for Cancer Classification on Gene Expression Data. Processes 2021, 9, 1466. [CrossRef]
- Bashar, S.K.; Han, D.; Zieneddin, F.; Ding, E.; Fitzgibbons, T.P.; Walkey, A.J.; McManus, D.D.; Javidi, B.; Chon, K.H. Novel Density Poincaré Plot Based Machine Learning Method to Detect Atrial Fibrillation From Premature Atrial/Ventricular Contractions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 448–460. [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, H. Derksen, J. Gryak, H. Ghanbari, P. Gunaratne and K. Najarian, "A Novel Atrial Fibrillation Prediction Algorithm Applicable to Recordings from Portable Devices," 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 2018, pp. 4034-4037.
- Z. Li, H. Derksen, J. Gryak, H. Ghanbari, P. Gunaratne and K. Najarian, "A Novel Atrial Fibrillation Prediction Algorithm Applicable to Recordings from Portable Devices," 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 2018, pp. 4034-4037.
- Narin, A.; Isler, Y.; Ozer, M.; Perc, M. Early prediction of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation based on short-term heart rate variability. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. its Appl. 2018, 509, 56–65. [CrossRef]
- Marsili, I.A.; Mase, M.; Pisetta, V.; Ricciardi, E.; Andrighetti, A.O.; Ravelli, F.; Nollo, G. Optimized algorithms for atrial fibrillation detection by wearable tele-holter devices. 2016 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, ItalyDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–4.
- Ahsanuzzaman, S.; Ahmed, T.; Rahman, A. Low Cost, Portable ECG Monitoring and Alarming System Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5–7 June 2020; pp. 316–319. [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wei, S.; Chen, T.; Zhong, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C. Integration of Results From Convolutional Neural Network in a Support Vector Machine for the Detection of Atrial Fibrillation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- K, S.R.S.; Martis, R.J. Machine Learning Based Decision Support System for Atrial Fibrillation Detection using Electrocardiogram. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing, VLSI, Electrical Circuits and Robotics (DISCOVER). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, IndiaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 263–266.
- Kurniawan, A. “Practical Contiki-NG”; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-4842-3407-5.
- Titzer, B.L.; Lee, D.K.; Palsberg, J. Avrora: Scalable sensor network simulation with precise timing. In Proceedings of the IPSN 2005, Fourth International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Boise, ID, USA, 15 April 2005; pp. 477–482.
- N. R. Hendrawan and I. G. N. W. Arsa, "Zolertia Z1 energy usage simulation with Cooja simulator," 2017 1st International Conference on Informatics and Computational Sciences (ICICoS), Semarang, Indonesia, 2017, pp. 147-152.
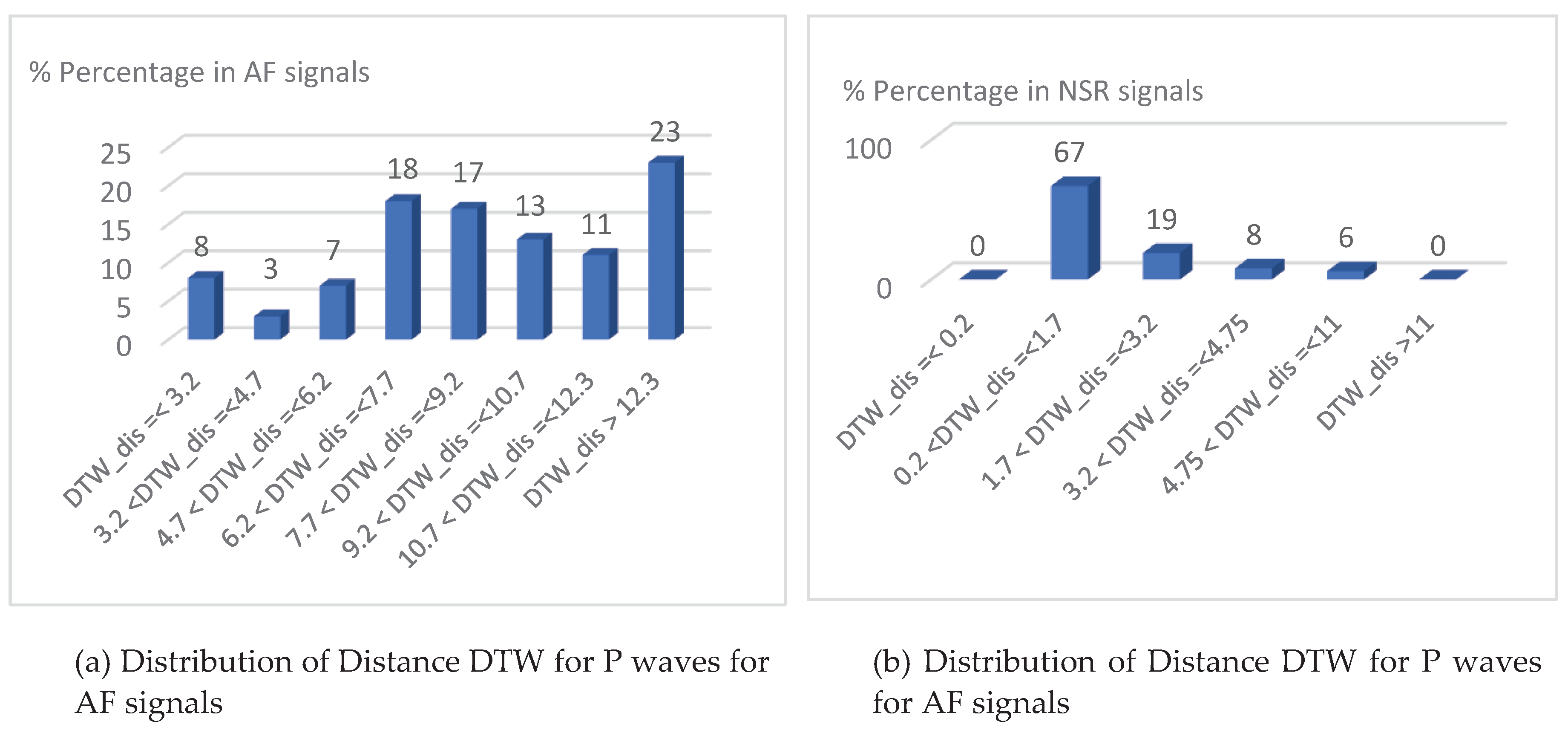
| Dual-Slope (DS) | Pan Tompkins algorithm (PT) | |
| Flash Memory KBytes | 7,4 | 15.6 |
| Estimated execution time (ms) | 17,2 | 30.7 |
| sel100 | sel102 | sel103 |
| sel104 | sel114 | sel116 |
| sel117 | sel123 | Sel213 |
| Sel223 | Sel230 | Sel231 |
| Sel232 | Sel233 |
| Number evaluate distances | ||
| AF signals | 04048, 05121, 08215, 04043, 04746, 06453 | 690 |
| NSR signals | 19830,16483, 16795 | 830 |
| Signals | 04048, 04015, 07910, 04126, 04908, 18177,
18184, 19090, 19093, 19140 |
580 AF segments |
| 472 NSR segments | ||
| Number of segments 10 sec | 1052 |
| IoMT plateform | Zolertia Z1 | Waspmote | |
| (a) | CPU | MSP430 | ATmega1281 |
| Processing frequency (MHz) | 8 | 14.7 | |
| Flash | 98 KB | 128 KB | |
| Battery | 2AA (3.3 V) ( or USB 5V) | ||
| (b) | Energy Consumption related to the processing of the scheme | 405.2 mJ | 422.2 mJ |
| Notification to a remote base station | 0.16 mJ | ||
| Execution time | 80 ms | 45.5 ms | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





