Submitted:
18 December 2023
Posted:
19 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Cellular m6A regulating proteins and their functions
3. Mapping m6A modification sites on HIV-1 RNA
4. HIV-1 infection modulates the cellular RNA m6A profile
5. HIV-1 m6A suppresses the induction of type I interferon (IFN-I) in macrophages
6. m6A reader proteins negatively impact HIV-1 reverse transcription
7. m6A regulates HIV-1 RNA splicing and nuclear export
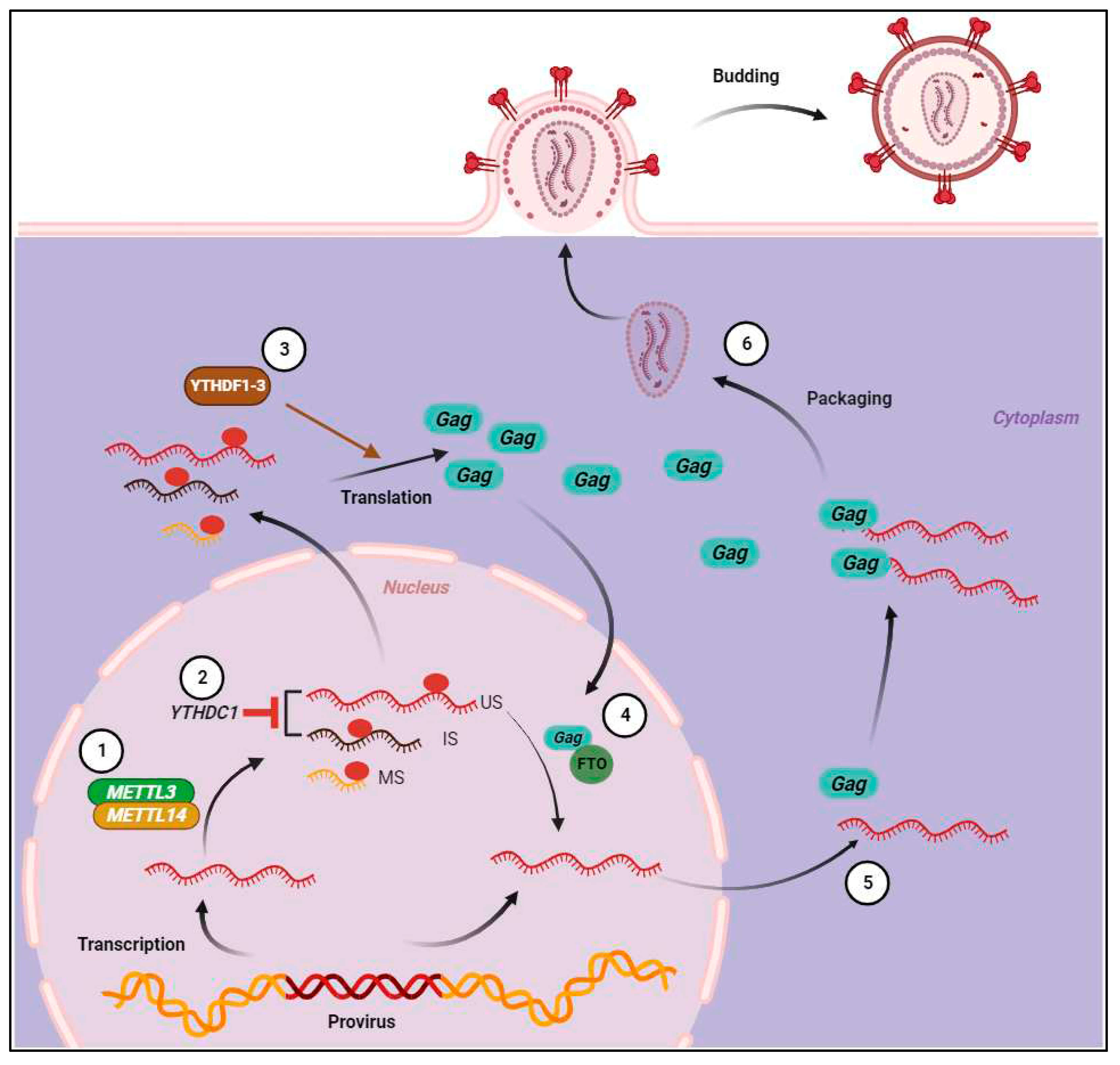
8. m6A enhances post-integration HIV-1 RNA abundance, stability, and translation
9. m6A inhibits HIV-1 RNA packaging and reduces virion infectivity
10. m6A modulation may have therapeutic potential for HIV-1-infected individuals
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B. S.; Roundtree, I. A.; Lu, Z.; Han, D.; Ma, H.; Weng, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, H.; He, C., N(6)-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, (6), 1388-99. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G. C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; Ren, B.; Pan, T.; He, C., N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2014, 505, (7481), 117-20. [CrossRef]
- Roundtree, I. A.; Luo, G. Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, T.; Cui, Y.; Sha, J.; Huang, X.; Guerrero, L.; Xie, P.; He, E.; Shen, B.; He, C., YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N(6)-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. Elife 2017, 6. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, B. F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiao, W.; Hao, Y. J.; Ping, X. L.; Chen, Y. S.; Wang, W. J.; Jin, K. X.; Wang, X.; Huang, C. M.; Fu, Y.; Ge, X. M.; Song, S. H.; Jeong, H. S.; Yanagisawa, H.; Niu, Y.; Jia, G. F.; Wu, W.; Tong, W. M.; Okamoto, A.; He, C.; Rendtlew Danielsen, J. M.; Wang, X. J.; Yang, Y. G., FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell Res 2014, 24, (12), 1403-19. [CrossRef]
- Lavi, S.; Shatkin, A. J., Methylated simian virus 40-specific RNA from nuclei and cytoplasm of infected BSC-1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1975, 72, (6), 2012-6. [CrossRef]
- Williams, G. D.; Gokhale, N. S.; Horner, S. M., Regulation of Viral Infection by the RNA Modification N6-Methyladenosine. Annu Rev Virol 2019, 6, (1), 235-253. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, G.; Yu, M.; Lu, Z.; Deng, X.; Dai, Q.; Chen, W.; He, C., A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol 2014, 10, (2), 93-5. [CrossRef]
- Ping, X. L.; Sun, B. F.; Wang, L.; Xiao, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, W. J.; Adhikari, S.; Shi, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Y. S.; Zhao, X.; Li, A.; Yang, Y.; Dahal, U.; Lou, X. M.; Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Yuan, W. P.; Zhu, X. F.; Cheng, T.; Zhao, Y. L.; Wang, X.; Rendtlew Danielsen, J. M.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y. G., Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res 2014, 24, (2), 177-89. [CrossRef]
- Patil, D. P.; Chen, C. K.; Pickering, B. F.; Chow, A.; Jackson, C.; Guttman, M.; Jaffrey, S. R., m(6)A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature 2016, 537, (7620), 369-373. [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; Cui, X.; Cao, J.; Luo, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, T.; Gao, M.; Shu, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Shen, B.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; He, C.; Liu, J., VIRMA mediates preferential m(6)A mRNA methylation in 3'UTR and near stop codon and associates with alternative polyadenylation. Cell Discov 2018, 4, 10. [CrossRef]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Schwartz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Ungar, L.; Osenberg, S.; Cesarkas, K.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Kupiec, M.; Sorek, R.; Rechavi, G., Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 2012, 485, (7397), 201-6. [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y. G.; He, C., N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol 2011, 7, (12), 885-7.
- Zheng, G.; Dahl, J. A.; Niu, Y.; Fedorcsak, P.; Huang, C. M.; Li, C. J.; Vagbo, C. B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W. L.; Song, S. H.; Lu, Z.; Bosmans, R. P.; Dai, Q.; Hao, Y. J.; Yang, X.; Zhao, W. M.; Tong, W. M.; Wang, X. J.; Bogdan, F.; Furu, K.; Fu, Y.; Jia, G.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Krokan, H. E.; Klungland, A.; Yang, Y. G.; He, C., ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell 2013, 49, (1), 18-29. [CrossRef]
- Mauer, J.; Luo, X.; Blanjoie, A.; Jiao, X.; Grozhik, A. V.; Patil, D. P.; Linder, B.; Pickering, B. F.; Vasseur, J. J.; Chen, Q.; Gross, S. S.; Elemento, O.; Debart, F.; Kiledjian, M.; Jaffrey, S. R., Reversible methylation of m(6)A(m) in the 5' cap controls mRNA stability. Nature 2017, 541, (7637), 371-375. [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, B. S.; Ma, H.; Hsu, P. J.; Liu, C.; He, C., YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N(6)-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res 2017, 27, (3), 315-328. [CrossRef]
- Zaccara, S.; Jaffrey, S. R., A Unified Model for the Function of YTHDF Proteins in Regulating m(6)A-Modified mRNA. Cell 2020, 181, (7), 1582-1595 e18. [CrossRef]
- Zaccara, S.; Ries, R. J.; Jaffrey, S. R., Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2019, 20, (10), 608-624.
- Meyer, K. D.; Jaffrey, S. R., Rethinking m(6)A Readers, Writers, and Erasers. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2017, 33, 319-342.
- Zou, Z.; Sepich-Poore, C.; Zhou, X.; Wei, J.; He, C., The mechanism underlying redundant functions of the YTHDF proteins. Genome Biol 2023, 24, (1), 17. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. M.; Zhou, J.; Mao, Y.; Ji, Q.; Qian, S. B., Programmable RNA N(6)-methyladenosine editing by CRISPR-Cas9 conjugates. Nat Chem Biol 2019, 15, (9), 865-871. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, F.; Xie, G.; Ling, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Luo, N.; Chiang, C. M.; Wang, H., Targeted mRNA demethylation using an engineered dCas13b-ALKBH5 fusion protein. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, (10), 5684-5694. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Chen, P. J.; Miao, Z.; Liu, D. R., Programmable m(6)A modification of cellular RNAs with a Cas13-directed methyltransferase. Nat Biotechnol 2020, 38, (12), 1431-1440. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Ma, G.; Cheung, E.; Hutchins, A. P., A programmable system to methylate and demethylate N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) on specific RNA transcripts in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 2022, 298, (11), 102525. [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, Y.; Tian, N.; Yang, M.; Liang, F. S., Inducible and reversible RNA N(6)-methyladenosine editing. Nat Commun 2022, 13, (1), 1958. [CrossRef]
- Lichinchi, G.; Gao, S.; Saletore, Y.; Gonzalez, G. M.; Bansal, V.; Wang, Y.; Mason, C. E.; Rana, T. M., Dynamics of the human and viral m(6)A RNA methylomes during HIV-1 infection of T cells. Nat Microbiol 2016, 1, 16011. [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E. M.; Bogerd, H. P.; Kornepati, A. V.; Kang, D.; Ghoshal, D.; Marshall, J. B.; Poling, B. C.; Tsai, K.; Gokhale, N. S.; Horner, S. M.; Cullen, B. R., Posttranscriptional m(6)A Editing of HIV-1 mRNAs Enhances Viral Gene Expression. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, (5), 675-85.
- Tirumuru, N.; Zhao, B. S.; Lu, W.; Lu, Z.; He, C.; Wu, L., N(6)-methyladenosine of HIV-1 RNA regulates viral infection and HIV-1 Gag protein expression. eLife 2016, 5.
- Courtney, D. G.; Tsai, K.; Bogerd, H. P.; Kennedy, E. M.; Law, B. A.; Emery, A.; Swanstrom, R.; Holley, C. L.; Cullen, B. R., Epitranscriptomic Addition of m(5)C to HIV-1 Transcripts Regulates Viral Gene Expression. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, (2), 217-227 e6. [CrossRef]
- Cristinelli, S.; Angelino, P.; Janowczyk, A.; Delorenzi, M.; Ciuffi, A., HIV Modifies the m6A and m5C Epitranscriptomic Landscape of the Host Cell. Frontiers in Virology 2021, 1. [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Montecinos, C.; Toro-Ascuy, D.; Ananias-Saez, C.; Gaete-Argel, A.; Rojas-Fuentes, C.; Riquelme-Barrios, S.; Rojas-Araya, B.; Garcia-de-Gracia, F.; Aguilera-Cortes, P.; Chnaiderman, J.; Acevedo, M. L.; Valiente-Echeverria, F.; Soto-Rifo, R., Epitranscriptomic regulation of HIV-1 full-length RNA packaging. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, (4), 2302-2318. [CrossRef]
- Baek, A.; Lee, G.; Golconda, S.; Rayhan, A.; Manganaris, A.; Chen, S.; Tirumuru, R.; Yu, H.; Shihyoung, K.; Kimmel, C.; Zablocki, O.; Sullivan, M.; Addepalli, B.; Wu, L.; Kim, S., Single-RNA-level analysis of full-length HIV-1 RNAs reveals functional redundancy of m6As. Research Square 2023.
- Chen, K.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Luo, G. Z.; Liu, N.; Han, D.; Dominissini, D.; Dai, Q.; Pan, T.; He, C., High-resolution N(6) -methyladenosine (m(6) A) map using photo-crosslinking-assisted m(6) A sequencing. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2015, 54, (5), 1587-90.
- Fu, Y.; Zorman, B.; Sumazin, P.; Sanna, P. P.; Repunte-Canonigo, V., Epitranscriptomics: Correlation of N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation and pathway dysregulation in the hippocampus of HIV transgenic rats. PLoS One 2019, 14, (1), e0203566. [CrossRef]
- Reid, W.; Sadowska, M.; Denaro, F.; Rao, S.; Foulke, J., Jr.; Hayes, N.; Jones, O.; Doodnauth, D.; Davis, H.; Sill, A.; O'Driscoll, P.; Huso, D.; Fouts, T.; Lewis, G.; Hill, M.; Kamin-Lewis, R.; Wei, C.; Ray, P.; Gallo, R. C.; Reitz, M.; Bryant, J., An HIV-1 transgenic rat that develops HIV-related pathology and immunologic dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, (16), 9271-6. [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, A. B. R.; Gokhale, N. S.; Cerchietti, L.; Jaffrey, S. R.; Horner, S. M.; Mason, C. E., Limits in the detection of m(6)A changes using MeRIP/m(6)A-seq. Sci Rep 2020, 10, (1), 6590. [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Behrens, R.; Wiggins, J.; Sherer, N.; Liu, S. L.; Xiong, Y.; Xiang, S. H.; Wu, L., The Polar Region of the HIV-1 Envelope Protein Determines Viral Fusion and Infectivity by Stabilizing the gp120-gp41 Association. J Virol 2019, 93, (7). [CrossRef]
- Tirumuru, N.; Wu, L., HIV-1 envelope proteins up-regulate N (6)-methyladenosine levels of cellular RNA independently of viral replication. J Biol Chem 2019, 294, (9), 3249-3260. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Qiao, J.; Li, W.; You, Q.; Hu, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Hu, K.; Sun, B., Global m6A methylation and gene expression patterns in human microglial HMC3 cells infected with HIV-1. Heliyon 2023, 9, (11), e21307. [CrossRef]
- Selberg, S.; Zusinaite, E.; Herodes, K.; Seli, N.; Kankuri, E.; Merits, A.; Karelson, M., HIV Replication Is Increased by RNA Methylation METTL3/METTL14/WTAP Complex Activators. ACS Omega 2021, 6, (24), 15957-15963.
- Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Dai, Q.; Natchiar, S. K.; Lv, R.; Chen, K.; Lu, Z.; Chen, H.; Shi, Y. G.; Lan, F.; Fan, J.; Klaholz, B. P.; Pan, T.; Shi, Y.; He, C., N(6-)Methyladenosine methyltransferase ZCCHC4 mediates ribosomal RNA methylation. Nat Chem Biol 2019, 15, (1), 88-94. [CrossRef]
- van Tran, N.; Ernst, F. G. M.; Hawley, B. R.; Zorbas, C.; Ulryck, N.; Hackert, P.; Bohnsack, K. E.; Bohnsack, M. T.; Jaffrey, S. R.; Graille, M.; Lafontaine, D. L. J., The human 18S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 is stabilized by TRMT112. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, (15), 7719-7733. [CrossRef]
- Rong, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, J.; Xing, S.; Dai, R.; Li, Y.; Cai, J.; Xie, J.; Song, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Yan, G.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Han, J. J.; Qu, Q.; Ma, H.; Tian, Y.; Lan, F., Ribosome 18S m(6)A Methyltransferase METTL5 Promotes Translation Initiation and Breast Cancer Cell Growth. Cell Rep 2020, 33, (12), 108544. [CrossRef]
- Ringeard, M.; Marchand, V.; Decroly, E.; Motorin, Y.; Bennasser, Y., FTSJ3 is an RNA 2'-O-methyltransferase recruited by HIV to avoid innate immune sensing. Nature 2019, 565, (7740), 500-504. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Kumar, S.; Espada, C. E.; Tirumuru, N.; Cahill, M. P.; Hu, L.; He, C.; Wu, L., N6-methyladenosine modification of HIV-1 RNA suppresses type-I interferon induction in differentiated monocytic cells and primary macrophages. PLoS Pathog 2021, 17, (3), e1009421. [CrossRef]
- Rehwinkel, J.; Gack, M. U., RIG-I-like receptors: their regulation and roles in RNA sensing. Nat Rev Immunol 2020, 20, (9), 537-551. [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, M.; Zhao, B. S.; Harder, O.; Li, A.; Liang, X.; Gao, T. Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Z.; Niewiesk, S.; Peeples, M. E.; He, C.; Li, J., N(6)-methyladenosine modification enables viral RNA to escape recognition by RNA sensor RIG-I. Nat Microbiol 2020, 5, (4), 584-598.
- Lu, M.; Xue, M.; Wang, H. T.; Kairis, E. L.; Ahmad, S.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Garcin, D.; Peeples, M. E.; Sharma, A.; Hur, S.; He, C.; Li, J., Nonsegmented Negative-Sense RNA Viruses Utilize N(6)-Methyladenosine (m(6)A) as a Common Strategy To Evade Host Innate Immunity. J Virol 2021, 95, (9).
- Qiu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, X.; Cui, G.; Sun, B.; Peng, Y.; Deng, H.; Peng, H.; Yang, A.; Yang, Y. G.; Yang, P., N(6)-methyladenosine RNA modification suppresses antiviral innate sensing pathways via reshaping double-stranded RNA. Nat Commun 2021, 12, (1), 1582. [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Hui, H.; Bray, B.; Gonzalez, G. M.; Zeller, M.; Anderson, K. G.; Knight, R.; Smith, D.; Wang, Y.; Carlin, A. F.; Rana, T. M., METTL3 regulates viral m6A RNA modification and host cell innate immune responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep 2021, 35, (6), 109091.
- Burdick, R. C.; Li, C.; Munshi, M.; Rawson, J. M. O.; Nagashima, K.; Hu, W. S.; Pathak, V. K., HIV-1 uncoats in the nucleus near sites of integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, (10), 5486-5493. [CrossRef]
- Selyutina, A.; Persaud, M.; Lee, K.; KewalRamani, V.; Diaz-Griffero, F., Nuclear Import of the HIV-1 Core Precedes Reverse Transcription and Uncoating. Cell Rep 2020, 32, (13), 108201. [CrossRef]
- Dharan, A.; Bachmann, N.; Talley, S.; Zwikelmaier, V.; Campbell, E. M., Nuclear pore blockade reveals that HIV-1 completes reverse transcription and uncoating in the nucleus. Nat Microbiol 2020, 5, (9), 1088-1095. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Burdick, R. C.; Nagashima, K.; Hu, W. S.; Pathak, V. K., HIV-1 cores retain their integrity until minutes before uncoating in the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118, (10). [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tirumuru, N.; St Gelais, C.; Koneru, P. C.; Liu, C.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; He, C.; Wu, L., N(6)-Methyladenosine-binding proteins suppress HIV-1 infectivity and viral production. J Biol Chem 2018, 293, (34), 12992-13005. [CrossRef]
- Jurczyszak, D.; Zhang, W.; Terry, S. N.; Kehrer, T.; Bermudez Gonzalez, M. C.; McGregor, E.; Mulder, L. C. F.; Eckwahl, M. J.; Pan, T.; Simon, V., HIV protease cleaves the antiviral m6A reader protein YTHDF3 in the viral particle. PLoS Pathog 2020, 16, (2), e1008305. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.; Bogerd, H. P.; Kennedy, E. M.; Emery, A.; Swanstrom, R.; Cullen, B. R., Epitranscriptomic addition of m(6)A regulates HIV-1 RNA stability and alternative splicing. Genes Dev 2021, 35, (13-14), 992-1004. [CrossRef]
- Knuckles, P.; Carl, S. H.; Musheev, M.; Niehrs, C.; Wenger, A.; Buhler, M., RNA fate determination through cotranscriptional adenosine methylation and microprocessor binding. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2017, 24, (7), 561-569. [CrossRef]
- Malim, M. H.; Hauber, J.; Le, S. Y.; Maizel, J. V.; Cullen, B. R., The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature 1989, 338, (6212), 254-7. [CrossRef]
- Chu, C. C.; Liu, B.; Plangger, R.; Kreutz, C.; Al-Hashimi, H. M., m6A minimally impacts the structure, dynamics, and Rev ARM binding properties of HIV-1 RRE stem IIB. PLoS One 2019, 14, (12), e0224850. [CrossRef]
- Shima, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Ishigami, Y.; Ebina, M.; Muto, A.; Sato, Y.; Kumagai, S.; Ochiai, K.; Suzuki, T.; Igarashi, K., S-Adenosylmethionine Synthesis Is Regulated by Selective N(6)-Adenosine Methylation and mRNA Degradation Involving METTL16 and YTHDC1. Cell Rep 2017, 21, (12), 3354-3363. [CrossRef]
- Kasowitz, S. D.; Ma, J.; Anderson, S. J.; Leu, N. A.; Xu, Y.; Gregory, B. D.; Schultz, R. M.; Wang, P. J., Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates alternative polyadenylation and splicing during mouse oocyte development. PLoS Genet 2018, 14, (5), e1007412. [CrossRef]
- N'Da Konan, S.; Segeral, E.; Bejjani, F.; Bendoumou, M.; Ait Said, M.; Gallois-Montbrun, S.; Emiliani, S., YTHDC1 regulates distinct post-integration steps of HIV-1 replication and is important for viral infectivity. Retrovirology 2022, 19, (1), 4.
- Emery, A.; Swanstrom, R., HIV-1: To Splice or Not to Splice, That Is the Question. Viruses 2021, 13, (2). [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, B., Multiple biological roles associated with the repeat (R) region of the HIV-1 RNA genome. Adv Pharmacol 2000, 48, 29-73.
- D'Souza, V.; Summers, M. F., How retroviruses select their genomes. Nat Rev Microbiol 2005, 3, (8), 643-55. [CrossRef]
- Tuffy, K. M.; Maldonado, R. J. K.; Chang, J.; Rosenfeld, P.; Cochrane, A.; Parent, L. J., HIV-1 Gag Forms Ribonucleoprotein Complexes with Unspliced Viral RNA at Transcription Sites. Viruses 2020, 12, (11). [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Meng, H.; Yi, C., m(6)Am-seq reveals the dynamic m(6)Am methylation in the human transcriptome. Nat Commun 2021, 12, (1), 4778. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Campos, M. A.; Edelheit, S.; Toth, U.; Safra, M.; Shachar, R.; Viukov, S.; Winkler, R.; Nir, R.; Lasman, L.; Brandis, A.; Hanna, J. H.; Rossmanith, W.; Schwartz, S., Deciphering the "m(6)A Code" via Antibody-Independent Quantitative Profiling. Cell 2019, 178, (3), 731-747 e16.
- Flexner, C. W.; Hildreth, J. E.; Kuncl, R. W.; Drachman, D. B., 3-Deaza-adenosine and inhibition of HIV. Lancet 1992, 339, (8790), 438. [CrossRef]
- Selberg, S.; Blokhina, D.; Aatonen, M.; Koivisto, P.; Siltanen, A.; Mervaala, E.; Kankuri, E.; Karelson, M., Discovery of Small Molecules that Activate RNA Methylation through Cooperative Binding to the METTL3-14-WTAP Complex Active Site. Cell Rep 2019, 26, (13), 3762-3771 e5. [CrossRef]
- Yankova, E.; Blackaby, W.; Albertella, M.; Rak, J.; De Braekeleer, E.; Tsagkogeorga, G.; Pilka, E. S.; Aspris, D.; Leggate, D.; Hendrick, A. G.; Webster, N. A.; Andrews, B.; Fosbeary, R.; Guest, P.; Irigoyen, N.; Eleftheriou, M.; Gozdecka, M.; Dias, J. M. L.; Bannister, A. J.; Vick, B.; Jeremias, I.; Vassiliou, G. S.; Rausch, O.; Tzelepis, K.; Kouzarides, T., Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2021, 593, (7860), 597-601. [CrossRef]
- Guirguis, A. A.; Ofir-Rosenfeld, Y.; Knezevic, K.; Blackaby, W.; Hardick, D.; Chan, Y. C.; Motazedian, A.; Gillespie, A.; Vassiliadis, D.; Lam, E. Y. N.; Tran, K.; Andrews, B.; Harbour, M. E.; Vasiliauskaite, L.; Saunders, C. J.; Tsagkogeorga, G.; Azevedo, A.; Obacz, J.; Pilka, E. S.; Carkill, M.; MacPherson, L.; Wainwright, E. N.; Liddicoat, B.; Blyth, B. J.; Albertella, M. R.; Rausch, O.; Dawson, M. A., Inhibition of METTL3 Results in a Cell-Intrinsic Interferon Response That Enhances Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Discov 2023, 13, (10), 2228-2247. [CrossRef]
- Cully, M., Chemical inhibitors make their RNA epigenetic mark. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, (12), 892-894. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Lai, J.; Wang, Q.; Lin, J.; Ao, W.; Ye, H.; Han, X., Expression of RNA-m6A-related genes correlates with the HIV latent reservoir level and the CD4+ and CD8+T cell profiles of patients with AIDS. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2023, 69, (4), 125-132. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.; Baek, A.; Kim, S.; Chen, S.; Wu, L., Protocol for the generation of HIV-1 genomic RNA with altered levels of N (6)-methyladenosine. STAR Protoc 2022, 3, (3), 101616. [CrossRef]
- Linder, B.; Grozhik, A. V.; Olarerin-George, A. O.; Meydan, C.; Mason, C. E.; Jaffrey, S. R., Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods 2015, 12, (8), 767-72. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, L. Q.; Zhao, Y. L.; Yang, C. G.; Roundtree, I. A.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, J.; Xie, W.; He, C.; Luo, G. Z., Single-base mapping of m(6)A by an antibody-independent method. Sci Adv 2019, 5, (7), eaax0250.
- Roberts, J. T.; Porman, A. M.; Johnson, A. M., Identification of m(6)A residues at single-nucleotide resolution using eCLIP and an accessible custom analysis pipeline. RNA 2021, 27, (4), 527-541. [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, S.; Peng, Y.; Ge, R.; Su, R.; Senevirathne, C.; Harada, B. T.; Dai, Q.; Wei, J.; Zhang, L.; Hao, Z.; Luo, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, M.; Chen, M.; Chen, J.; He, C., m(6)A RNA modifications are measured at single-base resolution across the mammalian transcriptome. Nat Biotechnol 2022, 40, (8), 1210-1219.
- Liu, X. M.; Qian, S. B., Targeted RNA m(6)A Editing Using Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 Conjugates. Methods Mol Biol 2021, 2298, 399-414.
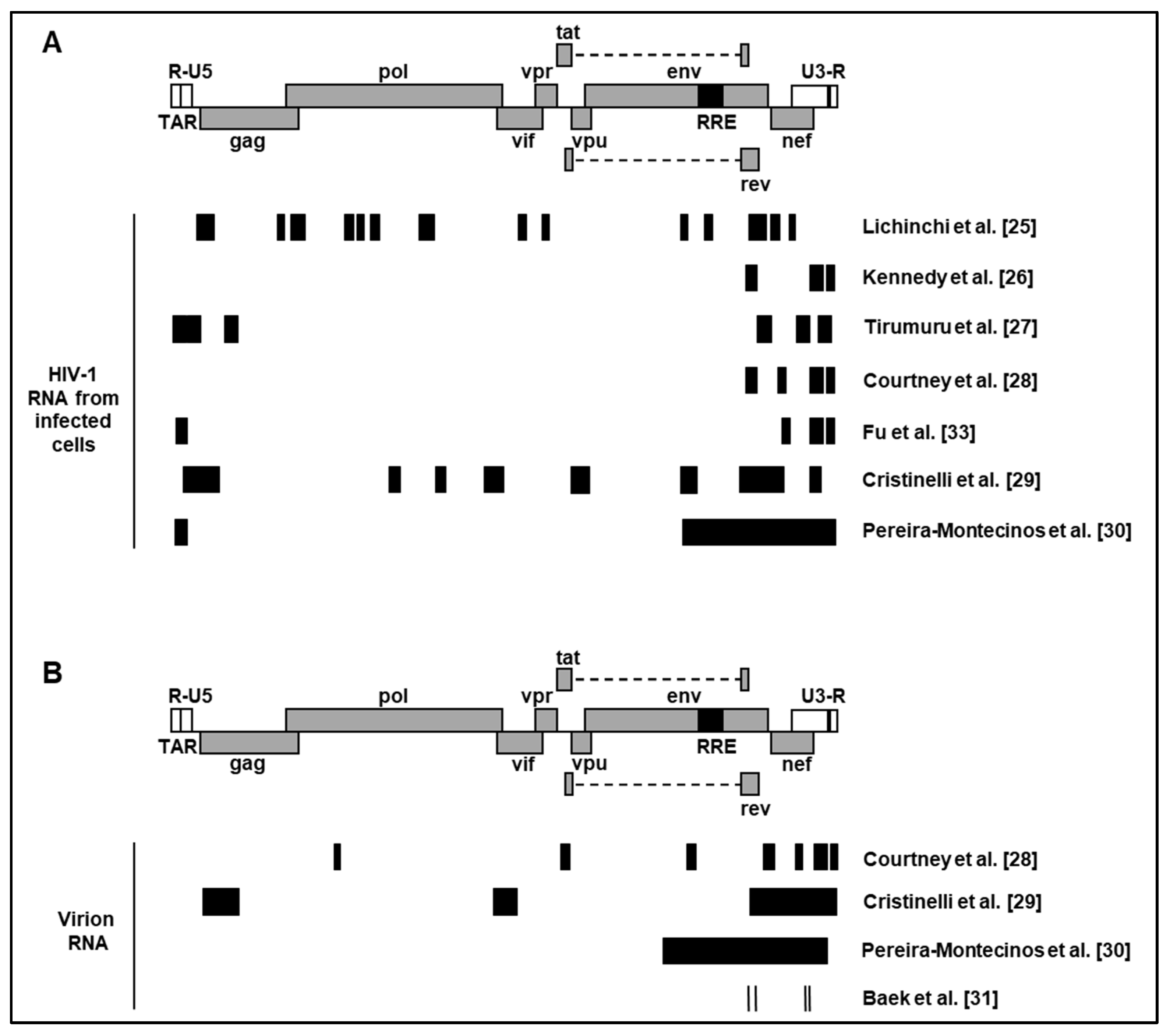
| HIV-1 Strain | Cell type | Sequencing method | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| LAI | MT4 | meRIP-seq3 | [25] |
| NL4-3 ΔEnv VSV-G1 | CEM | PA-m6A-seq | [26] |
| NL4-3 | Jurkat$Primary CD4+ T cells | meRIP-seq | [27] |
| NL4-3 | CEM | PA- m6A-seq4 | [28] |
| NL4-3 GFP ΔEnv VSV-G2 | SupT1 | meRIP-seq | [29] |
| NL4-3 ΔEnv VSV-G | HEK293T | meRIP-seq | [30] |
| NL4-3 | HEK293T | Direct RNA sequencing | [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





