Submitted:
19 December 2023
Posted:
19 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Biology of Rheb1 and Rheb2
2.1. Structure of Rheb1 and Rheb2
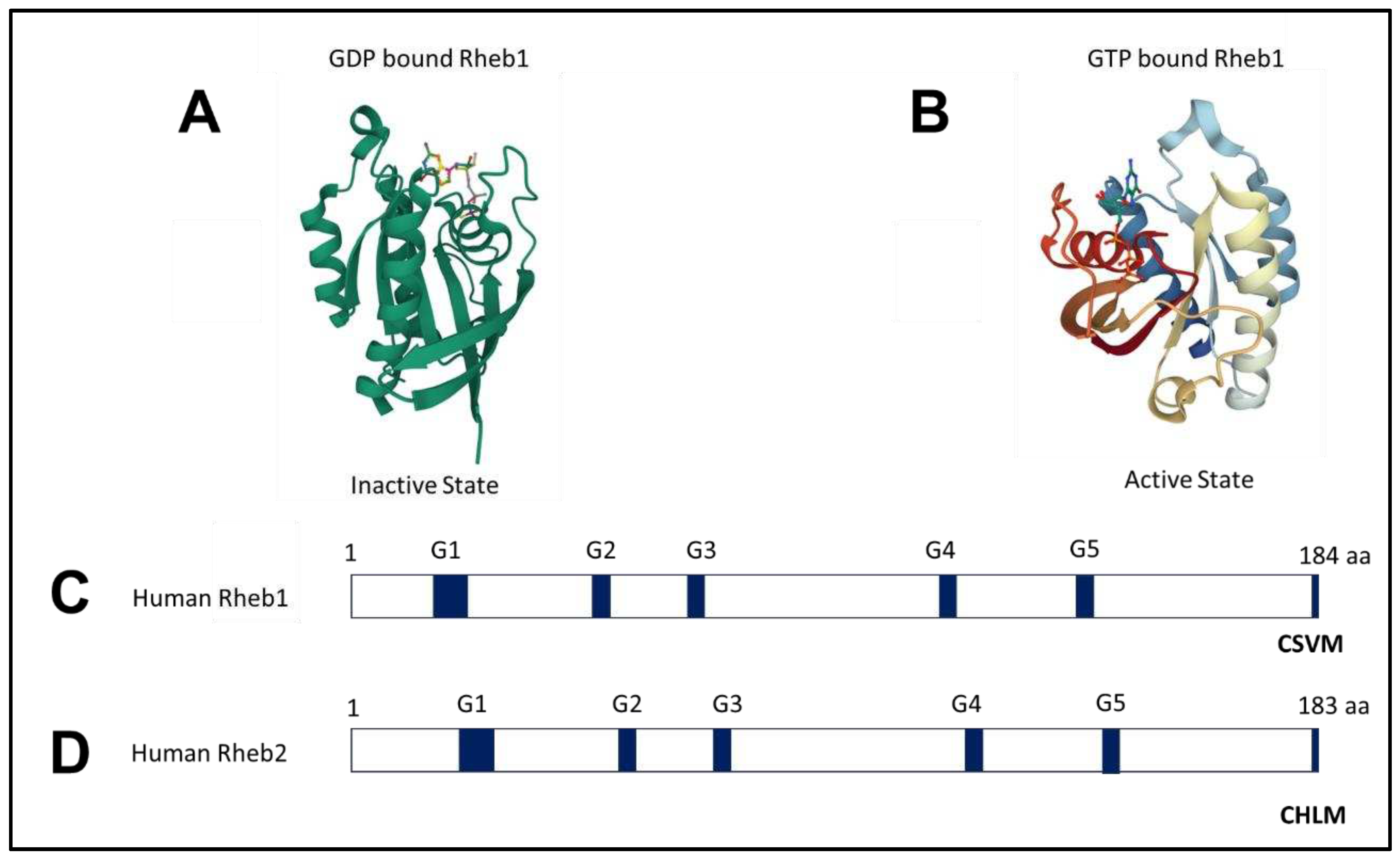
2.2. Rheb1 expression
2.3. Mutation of Rheb1
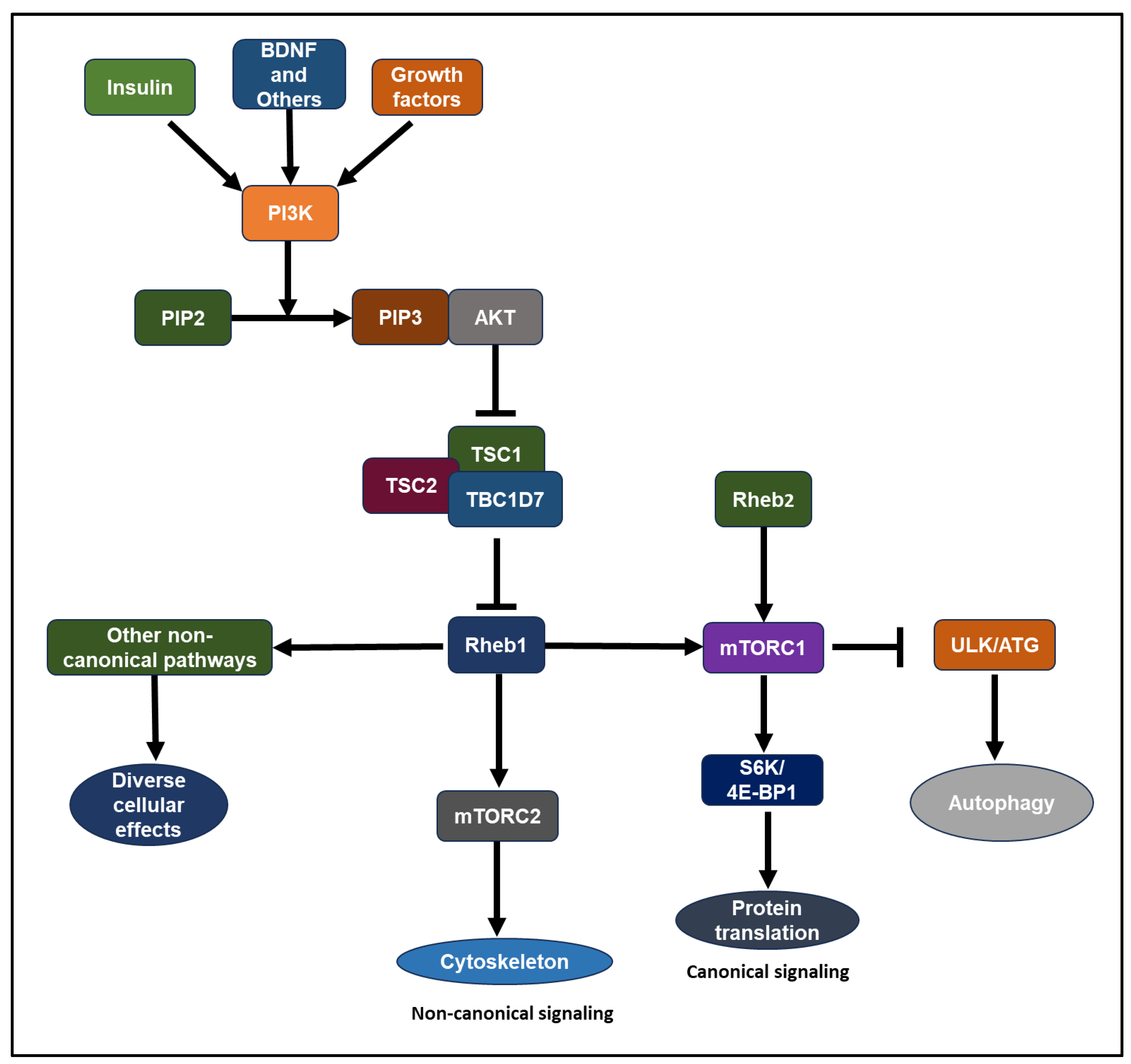
2.4. Rheb1 and Rheb2 signaling pathways
- Growth hormones, such as insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and insulin, stimulate the lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) through receptor tyrosine kinases or G-protein coupled receptors [50,51]. Akt, a serine/threonine kinase, stands as one of the key downstream mediators of PI3K signaling [47,50,51,52,53]. Akt-mTOR signaling involves the TSC complex protein and Rheb1 GTPase. The TSC complex, comprising TSC1 (hamartin), TSC2 (tuberin), and TBC1D7, acts as a GAP (GTPase-activating protein) towards Rheb1, suppressing its activity [1,45,52,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63]. Akt inhibits TSC2 GAP activity by phosphorylating it at conserved consensus phosphorylation sites in vitro [59,60]. Reduced GAP activity of the TSC complex leads to the accumulation of GTP-bound Rheb1 over GDP-bound Rheb1 [45,58,63,64]. Compared to other Ras-related small G proteins, Rheb1 exhibits low intrinsic GTPase activity[60,65]. Consequently, Rheb1’s GTP/GDP loading state is tightly regulated by its GAP, influenced by the presence of growth factors. Rheb1 binds to its effector, mTOR, where GTP-loaded Rheb1 is essential for mTOR activation [47,51,59,66]. The biochemical and physiological significance of a GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) for Rheb1 remains to be determined [6,65]. Elevated expression of the Rheb2 transgene results in heightened mTORC1 activity in HepG2 cells [67].
2.5. Binding partners of Rheb1
3. Role of Rheb1 and Rheb2 in Neurons
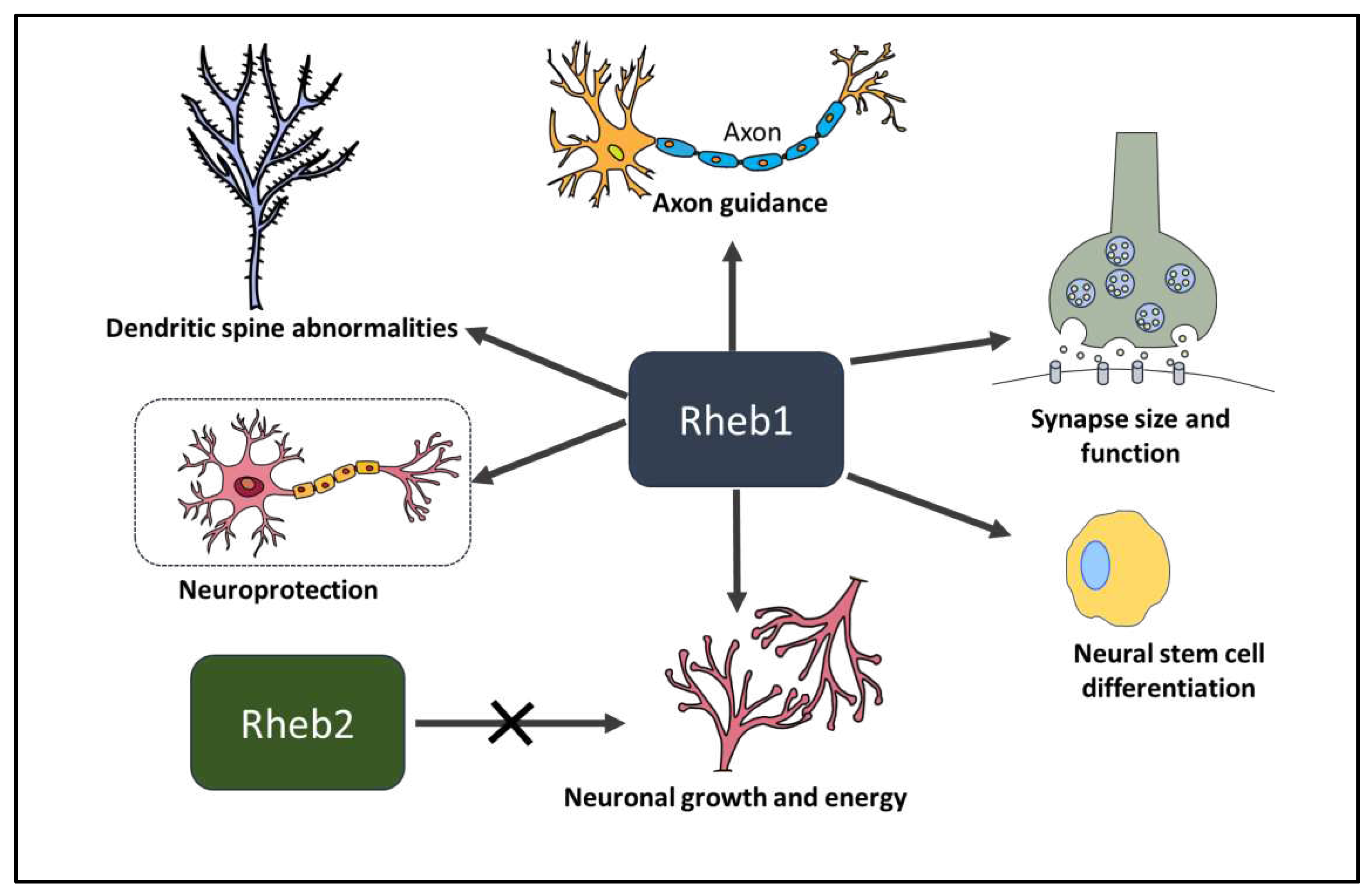
3.1. Rheb1 in neural stem cell differentiation.
3.2. Rheb1 and Rheb2 in neuronal growth and energy
3.3. Rheb1 in synapse size and function
3.4. Rheb1 in spine morphology and function
3.5. Rheb1 in axon guidance
3.6. Rheb1 in neuroprotection and axon regeneration
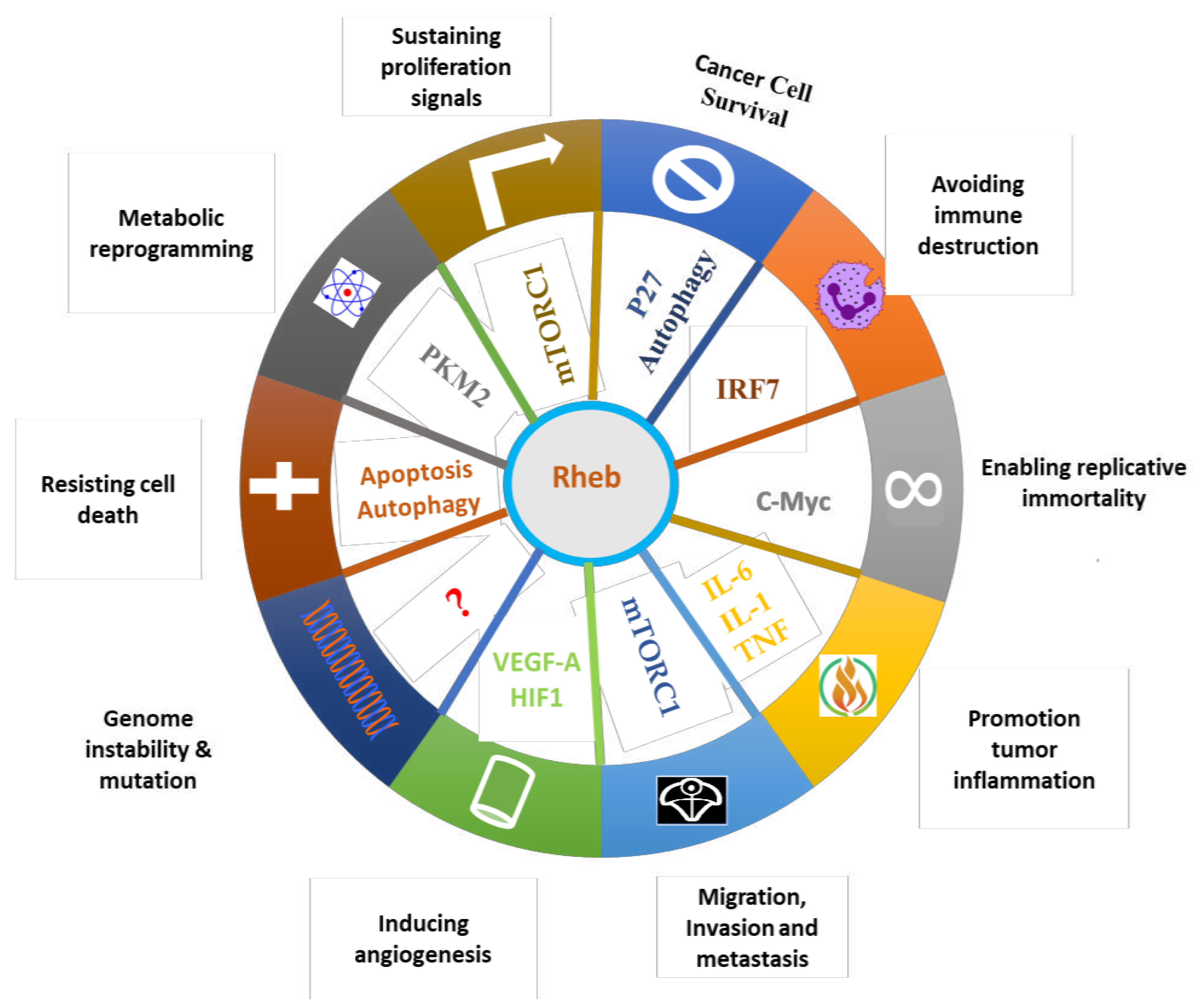
4. Role of Rheb1 and Rheb2 in Cancer
4.1. Effects of Rheb1 and Rheb2 on cancer hallmarks from tumor itself
4.1.1. Effect of Rheb1 and Rheb2 on proliferation
4.1.2. Effect of Rheb1 on cancer cell survival
4.1.3. Effect of Rheb1 and Rheb2 on migration, invasion, and metastasis
4.1.4. Rheb1 on genomic instability and mutation
4.1.5. Effect of Rheb1 on resisting cell death
4.1.6. Effect of Rheb1 on cancer metabolism
4.1.7. Effect of Rheb1 on enhancing replicative immortality
4.2. Effects of Rheb1 on Tumor Microenvironments
4.2.1. Effect of Rheb1 on angiogenesis
4.2.2. Effect of Rheb1 on inflammation
4.2.3. Effect of Rheb1 on avoiding immune destruction
4.2.4. Effect of Rheb1 on nerve and cancer connection
5. Potential Therapeutic Options
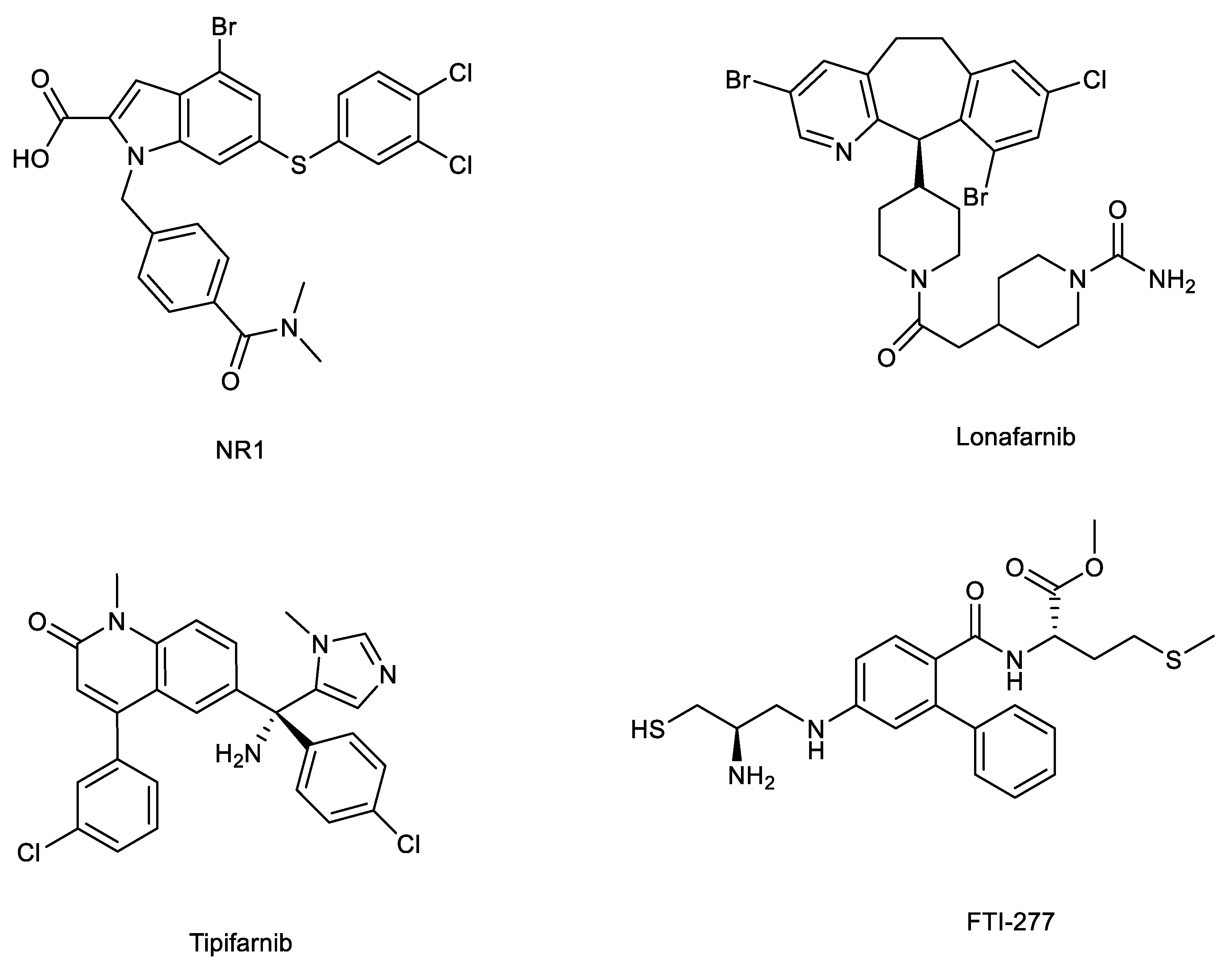
5.1. Direct binders: NR1 inhibitors
5.2. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors
6. Future perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aspuria, P.-J.; Tamanoi, F. The Rheb family of GTP-binding proteins. Cell. Signal. 2004, 16, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromov, P.S.; Madsen, P.; Tomerup, N.; Celis, J.E. A novel approach for expression cloning of small GTPases: identification, tissue distribution and chromosome mapping of the human homolog of rheb. FEBS Lett. 1995, 377, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, K.; Sanders, L.K.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Yee, W.; Barnes, C.A.; Nathans, D.; Worley, P.F. rheb, a growth factor-and synaptic activity-regulated gene, encodes a novel Ras-related protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16333–16339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urano, J.; Tabancay, A.P.; Yang, W.; Tamanoi, F. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rheb G-protein is involved in regulating canavanine resistance and arginine uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11198–11206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasper, R.; Wittinghofer, F. The Ras switch in structural and historical perspective. Biol. Chem. 2019, 401, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehmann, H.; Brüning, M.; Berghaus, C.; Schwarten, M.; Köhler, K.; Stocker, H.; Stoll, R.; Zwartkruis, F.J.; Wittinghofer, A. Biochemical characterisation of TCTP questions its function as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rheb. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3005–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Li, N.; Li, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X. IPP5, a novel protein inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1, promotes G1/S progression in a Thr-40-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12076–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiling, J.; Sabatini, D. Stress and mTORture signaling. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6373–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradetti, M.; Guan, K. Upstream of the mammalian target of rapamycin: do all roads pass through mTOR? Oncogene 2006, 25, 6347–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avruch, J.; Hara, K.; Lin, Y.; Liu, M.; Long, X.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Yonezawa, K.J.O. Insulin and amino-acid regulation of mTOR signaling and kinase activity through the Rheb GTPase. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6361–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Manning, B.D. The TSC1–TSC2 complex: a molecular switchboard controlling cell growth. Biochem. J. 2008, 412, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabancay, A.P.; Gau, C.-L.; Machado, I.M.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Gutmann, D.H.; Guo, L.; Tamanoi, F. Identification of dominant negative mutants of Rheb GTPase and their use to implicate the involvement of human Rheb in the activation of p70S6K. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39921–39930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.R.; Sampson, J.R.; Whittemore, V.H. Tuberous sclerosis complex. Oxford University Press 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Roach, E.; Gomez, M.R.; Northrup, H. Tuberous sclerosis complex consensus conference: revised clinical diagnostic criteria. J. Child Neurol. 1998, 13, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.J.; Kinch, M.S.; Rogers-Graham, K.; Sebti, S.M.; Hamilton, A.D.; Der, C.J. The Ras-related protein Rheb is farnesylated and antagonizes Ras signaling and transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 10608–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuki, N.; Kimura, M.; Ohno, S.; Miyata, S.; Sato, M.; Ando, H.; Ishihara, M.; Goto, K.; Watanabe, S.; Yamazaki, M. Isolation of cDNA and genomic clones of a human Ras-related GTP-binding protein gene and its chromosomal localization to the long arm of chromosome 7, 7q36. Genomics 1996, 34, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Araki, Y.; Kontani, K.; Nishina, H.; Katada, T. Novel role of the small GTPase Rheb: its implication in endocytic pathway independent of the activation of mammalian target of rapamycin. J. Biochem. 2005, 137, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Shan, Y.; Chen, X.; Tang, W.; Luo, K.; Ni, J.; Wan, B.; Yu, L. Identification and characterization of RHEBL1, a novel member of Ras family, which activates transcriptional activities of NF-kappa B. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2005, 32, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanker, A.B.; Mitin, N.; Wilder, R.S.; Henske, E.P.; Tamanoi, F.; Cox, A.D.; Der, C.J. Differential requirement of CAAX-mediated posttranslational processing for Rheb localization and signaling. Oncogene 2010, 29, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Nakashima, A.; Guo, L.; Tamanoi, F. Specific activation of mTORC1 by Rheb G-protein in vitro involves enhanced recruitment of its substrate protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12783–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.H.; Thapar, N.; Guo, L.; Martinez, M.; Maris, J.; Gau, C.-L.; Lengyel, J.A.; Tamanoi, F. Drosophila Rheb GTPase is required for cell cycle progression and cell growth. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3601–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, N.; Tamanoi, F. Rheb G-Proteins and the Activation of mTORC1. Enzymes 2010, 27, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Guan, K.; Arnold, E.; Ding, J. Structural basis for the unique biological function of small GTPase RHEB. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17093–17100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, S.; Shannon, K.M.; Bollag, G. GTPase activating proteins: critical regulators of intracellular signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002, 1602, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernards, A.; Settleman, J. GAP control: regulating the regulators of small GTPases. Trends Cell Biol. 2004, 14, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Hall, A. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rho GTPases: turning on the switch. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1587–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, B. Rho guanine dissociation inhibitors: pivotal molecules in cellular signalling. Cell. Signal. 1999, 11, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-K.; Zeng, K.; Wilson, I.A.; Balch, W.E. Structural insights into the function of the Rab GDI superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhab-Jafari, M.T.; Marshall, C.B.; Ishiyama, N.; Ho, J.; Di Palma, V.; Stambolic, V.; Ikura, M. An autoinhibited noncanonical mechanism of GTP hydrolysis by Rheb maintains mTORC1 homeostasis. Structure 2012, 20, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, C.B.; Ho, J.; Buerger, C.; Plevin, M.J.; Li, G.-Y.; Li, Z.; Ikura, M.; Stambolic, V. Characterization of the intrinsic and TSC2-GAP–regulated GTPase activity of Rheb by real-time NMR. Sci Signal 2009, 2, ra3–ra3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karassek, S.; Berghaus, C.; Schwarten, M.; Goemans, C.G.; Ohse, N.; Kock, G.; Jockers, K.; Neumann, S.; Gottfried, S.; Herrmann, C. Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb) enhances apoptotic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33979–33991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Young, S.G.; Yamanaka, S. Differential membrane localization of ERas and Rheb, two Ras-related proteins involved in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mTOR pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 32768–32774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.H.; Shvartsman, M.B.; Lee, A.Y.; Shao, J.M.; Murray, M.M.; Kladney, R.D.; Fan, D.; Krajewski, S.; Chiang, G.G.; Mills, G.B. Mammalian target of rapamycin activator RHEB is frequently overexpressed in human carcinomas and is critical and sufficient for skin epithelial carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3287–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Vogt, P.K. Constitutively active Rheb induces oncogenic transformation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5729–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Xu, L.; Mao, J.; Li, J.; Fang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; He, W.; Zhao, A.Z.; Yang, J. Rheb/mTORC1 signaling promotes kidney fibroblast activation and fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, K.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lai, X.; Chen, T.; Feng, L.; Li, M.; Huang, C. MicroRNA-155 promotes autophagy to eliminate intracellular mycobacteria by targeting Rheb. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, M.; Li, M.; Li, D.; Peng, A.; Nie, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Q. miR-155 Suppresses Bacterial Clearance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa–Induced Keratitis by Targeting Rheb. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.K.; Shrivastava, S.; Meyer, K.; Ray, R.B.; Ray, R.J.J.o.v. Hepatitis C virus activates the mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway in inhibiting IRS-1 function for insulin resistance. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6315–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.; Kim, S.K.; Byun, Y.J.; Oh, E.; Jeong, S.-W.; Chae, G.T.; Lee, S.-B. Hydrogen peroxide induces Beclin 1-independent autophagic cell death by suppressing the mTOR pathway via promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of Rheb in GSH-depleted RAW 264.7 cells. Free Radic. Res. 2011, 45, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heard, J.J.; Fong, V.; Bathaie, S.Z.; Tamanoi, F. Recent progress in the study of the Rheb family GTPases. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1950–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Findlay, G.M.; Jones, R.; Procter, J.; Cao, Y.; Lamb, R.F. Hyperactivation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling by a gain-of-function mutant of the Rheb GTPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 19793–19797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabiner, B.C.; Nardi, V.; Birsoy, K.; Possemato, R.; Shen, K.; Sinha, S.; Jordan, A.; Beck, A.H.; Sabatini, D.M. A diverse array of cancer-associated MTOR mutations are hyperactivating and can predict rapamycin sensitivity. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhab-Jafari, M.T.; Marshall, C.B.; Ho, J.; Ishiyama, N.; Stambolic, V.; Ikura, M. Structure-guided mutation of the conserved G3-box glycine in Rheb generates a constitutively activated regulator of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12195–12201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Inoki, K.; Guan, K.-L. Biochemical and functional characterizations of small GTPase Rheb and TSC2 GAP activity. Molecular and cellular biology 2004, 24, 7965–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urano, J.; Comiso, M.J.; Guo, L.; Aspuria, P.J.; Deniskin, R.; Tabancay Jr, A.P.; Kato-Stankiewicz, J.; Tamanoi, F. Identification of novel single amino acid changes that result in hyperactivation of the unique GTPase, Rheb, in fission yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 58, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Lin, Y.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Yonezawa, K.; Avruch, J. Rheb binds and regulates the mTOR kinase. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Lin, Y.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Busch, S.; Avruch, J. The Rheb switch 2 segment is critical for signaling to target of rapamycin complex 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18542–18551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.S.; Stojanov, P.; Mermel, C.H.; Robinson, J.T.; Garraway, L.A.; Golub, T.R.; Meyerson, M.; Gabriel, S.B.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types. Nature 2014, 505, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Dey, C.S. PTEN, a widely known negative regulator of insulin/PI3K signaling, positively regulates neuronal insulin resistance. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 3882–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, C.C.; Cantley, L.C. Regulation of mTORC1 by PI3K signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, N.; Sonenberg, N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1926–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoncu, R.; Efeyan, A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR: from growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2011, 12, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, C.C.; Elis, W.; Menon, S.; Qin, W.; Klekota, J.; Asara, J.M.; Finan, P.M.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Murphy, L.O.; Manning, B.D. TBC1D7 is a third subunit of the TSC1-TSC2 complex upstream of mTORC1. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Pan, D. TSC1 and TSC2 tumor suppressors antagonize insulin signaling in cell growth. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.J.; Huang, H.; Xu, T. Drosophila Tsc1 functions with Tsc2 to antagonize insulin signaling in regulating cell growth, cell proliferation, and organ size. Cell 2001, 105, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapon, N.; Ito, N.; Dickson, B.J.; Treisman, J.E.; Hariharan, I.K. The Drosophila tuberous sclerosis complex gene homologs restrict cell growth and cell proliferation. Cell 2001, 105, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoki, K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wu, J.; Guan, K.-L. TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoki, K.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Guan, K.-L. Rheb GTPase is a direct target of TSC2 GAP activity and regulates mTOR signaling. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. Rheb fills a GAP between TSC and TOR. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, A.R.; Manning, B.D.; Roux, P.P.; Cantley, L.C.; Blenis, J. Tuberous sclerosis complex gene products, Tuberin and Hamartin, control mTOR signaling by acting as a GTPase-activating protein complex toward Rheb. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo, L.J.; Gao, X.; Chiarelli, D.A.; Li, L.; Pan, D.; Edgar, B.A. Rheb promotes cell growth as a component of the insulin/TOR signalling network. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Saucedo, L.J.; Ru, B.; Edgar, B.A.; Pan, D. Rheb is a direct target of the tuberous sclerosis tumour suppressor proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, A.R.; Blenis, J.; Proud, C.G. Analysis of mTOR signaling by the small G-proteins, Rheb and RhebL1. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 4763–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöpel, M.; Potheraveedu, V.N.; Al-Harthy, T.; Abdel-Jalil, R.; Heumann, R.; Stoll, R. The small GTPases Ras and Rheb studied by multidimensional NMR spectroscopy: structure and function. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Dibble, C.C.; Talbott, G.; Hoxhaj, G.; Valvezan, A.J.; Takahashi, H.; Cantley, L.C.; Manning, B.D. Spatial control of the TSC complex integrates insulin and nutrient regulation of mTORC1 at the lysosome. Cell 2014, 156, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Pang, D.; Chen, M.; Du, C.; Jia, L.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Jiang, W.; Luo, L.; Yu, Z.; et al. Rheb mediates neuronal-activity-induced mitochondrial energetics through mTORC1-independent PDH activation. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, A.; García-Álvarez, B.; Arias-Palomo, E.; Barford, D.; Llorca, O. Structure of TOR and its complex with KOG1. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiech, L.; Perycz, M.; Malik, A.; Jaworski, J. Role of mTOR in physiology and pathology of the nervous system. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008, 1784, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewith, R.; Jacinto, E.; Wullschleger, S.; Lorberg, A.; Crespo, J.L.; Bonenfant, D.; Oppliger, W.; Jenoe, P.; Hall, M.N. Two TOR complexes, only one of which is rapamycin sensitive, have distinct roles in cell growth control. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Inoki, K.; Kim, E.; Guan, K.-L. TSC1/TSC2 and Rheb have different effects on TORC1 and TORC2 activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2006, 103, 6811–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, P.E.; Barrow, R.K.; Cohen, N.A.; Snyder, S.H.; Sabatini, D.M. RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences 1998, 95, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganley, I.G.; Lam, D.H.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Chen, S.; Jiang, X. ULK1· ATG13· FIP200 complex mediates mTOR signaling and is essential for autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12297–12305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, N.; Hara, T.; Kaizuka, T.; Kishi, C.; Takamura, A.; Miura, Y.; Iemura, S.-i.; Natsume, T.; Takehana, K.; Yamada, N. Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the ULK1–Atg13–FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.H.; Jun, C.B.; Ro, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Otto, N.M.; Cao, J.; Kundu, M.; Kim, D.-H. ULK-Atg13-FIP200 complexes mediate mTOR signaling to the autophagy machinery. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 1992–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Lao, U.; Edgar, B.A. TOR-mediated autophagy regulates cell death in Drosophila neurodegenerative disease. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, J.L.; Hall, M.N. Elucidating TOR signaling and rapamycin action: lessons from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2002, 66, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkogkas, C.; Sonenberg, N.; Costa-Mattioli, M. Translational control mechanisms in long-lasting synaptic plasticity and memory. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31913–31917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avruch, J.; Long, X.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Rapley, J.; Papageorgiou, A.; Dai, N. Amino acid regulation of TOR complex 1. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E592–E602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, E.; Loewith, R.; Schmidt, A.; Lin, S.; Rüegg, M.A.; Hall, A.; Hall, M.N. Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Ali, S.M.; Kim, D.-H.; Guertin, D.A.; Latek, R.R.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Sabatini, D.M. Rictor, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowniczek, M.; Robertson, G.P.; Henske, E.P. Rheb inhibits C-raf activity and B-raf/C-raf heterodimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25447–25456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ikenoue, T.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Inoki, K.; Guan, K.-L. Rheb controls misfolded protein metabolism by inhibiting aggresome formation and autophagy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2009, 106, 8923–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, N.A.; Henske, E.P. Non-canonical functions of the tuberous sclerosis complex-Rheb signalling axis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, S.; Sugiura, H.; Katsurabayashi, S.; Shimada, T.; Tanaka, H.; Takasaki, K.; Iwasaki, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Hino, O.; Yamagata, K. Activation of Rheb, but not of mTORC1, impairs spine synapse morphogenesis in tuberous sclerosis complex. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöpel, M.; Jockers, K.F.; Düppe, P.M.; Autzen, J.; Potheraveedu, V.N.; Ince, S.; Yip, K.T.; Heumann, R.; Herrmann, C.; Scherkenbeck, J.r. Bisphenol A binds to Ras proteins and competes with guanine nucleotide exchange: implications for GTPase-selective antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9664–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbowniczek, M.; Zitserman, D.; Khabibullin, D.; Hartman, T.; Yu, J.; Morrison, T.; Nicolas, E.; Squillace, R.; Roegiers, F.; Henske, E.P. The evolutionarily conserved TSC/Rheb pathway activates Notch in tuberous sclerosis complex and Drosophila external sensory organ development. The Journal of clinical investigation 2010, 120, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, E.; Von Lintig, F.C.; Chen, J.; Zhuang, S.; Qui, W.; Chowdhury, S.; Worley, P.F.; Boss, G.R.; Pilz, R.B. Rheb is in a high activation state and inhibits B-Raf kinase in mammalian cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 6356–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbowniczek, M.; Cash, T.; Cheung, M.; Robertson, G.P.; Astrinidis, A.; Henske, E.P. Regulation of B-Raf kinase activity by tuberin and Rheb is mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-independent. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29930–29937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Bai, X.; Zou, H.; Lai, Y.; Jiang, Y. Rheb GTPase controls apoptosis by regulating interaction of FKBP38 with Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 8621–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melser, S.; Chatelain, E.H.; Lavie, J.; Mahfouf, W.; Jose, C.; Obre, E.; Goorden, S.; Priault, M.; Elgersma, Y.; Rezvani, H.R. Rheb regulates mitophagy induced by mitochondrial energetic status. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, N.; Clark, G.J. Rheb may complex with RASSF1A to coordinate Hippo and TOR signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Akasu, H.; Shimono, W.; Matsu, C.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shibagaki, Y.; Heard, J.J.; Tamanoi, F.; Hattori, S. Rheb protein binds CAD (carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2, aspartate transcarbamoylase, and dihydroorotase) protein in a GTP-and effector domain-dependent manner and influences its cellular localization and carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (CPSase) activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, H.; Yasuda, S.; Katsurabayashi, S.; Kawano, H.; Endo, K.; Takasaki, K.; Iwasaki, K.; Ichikawa, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Hino, O. Rheb activation disrupts spine synapse formation through accumulation of syntenin in tuberous sclerosis complex. Nature Communications 2015, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahani, N.; Pryor, W.; Swarnkar, S.; Kholodilov, N.; Thinakaran, G.; Burke, R.E.; Subramaniam, S. Rheb GTPase regulates β-secretase levels and amyloid β generation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5799–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, R.; Shahani, N.; Gorgen, L.; Ferretti, M.; Pryor, W.; Chen, P.Y.; Swarnkar, S.; Worley, P.F.; Karbstein, K.; Snyder, S.H. Rheb inhibits protein synthesis by activating the PERK-eIF2α signaling cascade. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kim, E.; Beemiller, P.; Wang, C.-Y.; Swanson, J.; You, M.; Guan, K.-L. Bnip3 mediates the hypoxia-induced inhibition on mammalian target of rapamycin by interacting with Rheb. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35803–35813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yoon, M.-S.; Zhang, C.; Roccio, M.; Zwartkruis, F.; Armstrong, M.; Brown, H.; Chen, J. Phospholipase D1 is an effector of Rheb in the mTOR pathway. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105, 8286–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ma, D.; Liu, A.; Shen, X.; Wang, Q.J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y. Rheb activates mTOR by antagonizing its endogenous inhibitor, FKBP38. Science 2007, 318, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potheraveedu, V.N.; Schöpel, M.; Stoll, R.; Heumann, R. Rheb in neuronal degeneration, regeneration, and connectivity. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goorden, S.M.; Abs, E.; Bruinsma, C.F.; Riemslagh, F.W.; van Woerden, G.M.; Elgersma, Y.J.H.m.g. Intact neuronal function in Rheb1 mutant mice: implications for TORC1-based treatments. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 3390–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, J.M.; McNeill, H.J.C. Temporal control of differentiation by the insulin receptor/tor pathway in Drosophila. Cell 2004, 119, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloëtta, D.; Thomanetz, V.; Baranek, C.; Lustenberger, R.M.; Lin, S.; Oliveri, F.; Atanasoski, S.; Rüegg, M.A.J.J.o.N. Inactivation of mTORC1 in the developing brain causes microcephaly and affects gliogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 7799–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafourcade, C.A.; Lin, T.V.; Feliciano, D.M.; Zhang, L.; Hsieh, L.S.; Bordey, A. Rheb activation in subventricular zone progenitors leads to heterotopia, ectopic neuronal differentiation, and rapamycin-sensitive olfactory micronodules and dendrite hypertrophy of newborn neurons. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, U.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Park, R.; Cho, J.Y.; Hughes, L.J.; McKenna III, J.; Goetzl, L.; Cho, S.-H.; Crino, P.B.; Gambello, M.J. Impaired Reelin-Dab1 signaling contributes to neuronal migration deficits of tuberous sclerosis complex. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angliker, N.; Burri, M.; Zaichuk, M.; Fritschy, J.M.; Rüegg, M.A.J.E.J.o.N. m TORC 1 and m TORC 2 have largely distinct functions in Purkinje cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 42, 2595–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhou, L.; Du, X.-X.; Ji, Y.; Xu, J.; Tian, J.; Jiang, W.; Zou, Y.; Yu, S.; Gan, L. Rheb1 is required for mTORC1 and myelination in postnatal brain development. Dev. Cell 2011, 20, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Mattioli, M.; Sossin, W.S.; Klann, E.; Sonenberg, N. Translational control of long-lasting synaptic plasticity and memory. Neuron 2009, 61, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavazoie, S.F.; Alvarez, V.A.; Ridenour, D.A.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Sabatini, B.L. Regulation of neuronal morphology and function by the tumor suppressors Tsc1 and Tsc2. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Zhang, M.-X.; Swank, M.W.; Kunz, J.; Wu, G.-Y. Regulation of dendritic morphogenesis by Ras–PI3K–Akt–mTOR and Ras–MAPK signaling pathways. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 11288–11299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitroff, B.; Howe, K.; Watson, A.; Campion, B.; Lee, H.-G.; Zhao, N.; O'Connor, M.B.; Neufeld, T.P.; Selleck, S.B. Diet and energy-sensing inputs affect TorC1-mediated axon misrouting but not TorC2-directed synapse growth in a Drosophila model of tuberous sclerosis. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, S.; Ge, H.; Dimitroff, B.D.; Ren, Y.; Howe, K.A.; Arsham, A.M.; Easterday, M.C.; Neufeld, T.P.; O'Connor, M.B.; Selleck, S.B. Mechanisms of TSC-mediated control of synapse assembly and axon guidance. PLoS One 2007, 2, e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, R.; Trivedi-Vyas, D.; Wairkar, Y.P. Tuberous sclerosis complex regulates Drosophila neuromuscular junction growth via the TORC2/Akt pathway. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2010–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Locke, C.; Davis, G.W.J.J.o.C.B. S6 kinase localizes to the presynaptic active zone and functions with PDK1 to control synapse development. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeffer, C.A.; Klann, E. mTOR signaling: at the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherill, D.B.; Dyer, J.; Sossin, W.S. Ribosomal protein S6 kinase is a critical downstream effector of the target of rapamycin complex 1 for long-term facilitation in Aplysia. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12255–12267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antion, M.D.; Hou, L.; Wong, H.; Hoeffer, C.A.; Klann, E.J.M.; biology, c. mGluR-dependent long-term depression is associated with increased phosphorylation of S6 and synthesis of elongation factor 1A but remains expressed in S6K-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28, 2996–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, C.-H.; Luikart, B.W.; Powell, C.M.; Zhou, J.; Matheny, S.A.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Baker, S.J.; Parada, L.F. Pten regulates neuronal arborization and social interaction in mice. Neuron 2006, 50, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.-T.; Nam, J.H.; Shin, W.-H.; Leem, E.; Jeong, K.H.; Jung, U.J.; Bae, Y.-S.; Jin, Y.-H.; Kholodilov, N.; Burke, R.E. In vivo AAV1 transduction with hRheb (S16H) protects hippocampal neurons by BDNF production. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimura, N.; Kaibuchi, K.J.N.R.N. Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradke, F.; Dotti, C.G.J.S. The role of local actin instability in axon formation. Science 1999, 283, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Di Nardo, A.; Kramvis, I.; Meikle, L.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Sahin, M.; He, X.H. Tuberous sclerosis complex proteins control axon formation. Genes Dev 2008, 22, 2485–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, L.A.; Smith, N.; Bowser, M.; Niida, Y.; Murthy, V.; Gonzalez-Agosti, C.; Ramesh, V. The TSC1 tumor suppressor hamartin interacts with neurofilament-L and possibly functions as a novel integrator of the neuronal cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44180–44186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Di Nardo, A.; Han, J.M.; Baharanyi, H.; Kramvis, I.; Huynh, T.; Dabora, S.; Codeluppi, S.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Pasquale, E.B. Tsc2-Rheb signaling regulates EphA-mediated axon guidance. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracias, N.G.; Shirkey-Son, N.J. , Hengst, Ulrich Local translation of TC10 is required for membrane expansion during axon outgrowth. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Werner, H.; Püschel, A.W. Rheb and mTOR regulate neuronal polarity through Rap1B. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33784–33792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.L.; Kaun, K.R.; Edgar, B.A. The small GTPase Rheb affects central brain neuronal morphology and memory formation in Drosophila. PLoS One 2012, https. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, I.P.; Koh, Y.-H.; Lee, W.-C.M.; Slind, J.; Fergestad, T.; Littleton, J.T.; Ganetzky, B.J.N. Nervous wreck, an SH3 adaptor protein that interacts with Wsp, regulates synaptic growth in Drosophila. Neuron 2004, 41, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L. Actin cytoskeleton regulation in neuronal morphogenesis and structural plasticity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2002, 18, 601–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebl, E.C.; Forsthoefel, D.J.; Franco, L.S.; Sample, S.H.; Hess, J.E.; Cowger, J.A.; Chandler, M.P.; Shupert, A.M.; Seeger, M.A. Dosage-sensitive, reciprocal genetic interactions between the Abl tyrosine kinase and the putative GEF trio reveal trio's role in axon pathfinding. Neuron 2000, 26, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Klaw, M.C.; Kholodilov, N.; Burke, R.E.; Detloff, M.R.; Côté, M.-P.; Tom, V.J. Expressing constitutively active Rheb in adult dorsal root ganglion neurons enhances the integration of sensory axons that regenerate across a chondroitinase-treated dorsal root entry zone following dorsal root crush. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, M.T.; Kim, S.R. Roles of Rheb (S16H) in substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons in vivo. Biomed Rep 2015, 3, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.H.; Leem, E.; Jeon, M.-T.; Jeong, K.H.; Park, J.-W.; Jung, U.J.; Kholodilov, N.; Burke, R.E.; Jin, B.K.; Kim, S.R. Induction of GDNF and BDNF by hRheb (S16H) transduction of SNpc neurons: neuroprotective mechanisms of hRheb (S16H) in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.K.; Liu, K.; Hu, Y.; Smith, P.D.; Wang, C.; Cai, B.; Xu, B.; Connolly, L.; Kramvis, I.; Sahin, M. Promoting axon regeneration in the adult CNS by modulation of the PTEN/mTOR pathway. Science 2008, 322, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.R.; Kareva, T.; Yarygina, O.; Kholodilov, N.; Burke, R.E.J.M.T. AAV transduction of dopamine neurons with constitutively active Rheb protects from neurodegeneration and mediates axon regrowth. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.R.; Chen, X.; Oo, T.F.; Kareva, T.; Yarygina, O.; Wang, C.; During, M.; Kholodilov, N.; Burke, R.E. Dopaminergic pathway reconstruction by Akt/Rheb-induced axon regeneration. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kelamangalath, L.; Kim, H.; Han, S.B.; Tang, X.; Zhai, J.; Hong, J.W.; Lin, S.; Son, Y.-J.; Smith, G.M. NT-3 promotes proprioceptive axon regeneration when combined with activation of the mTor intrinsic growth pathway but not with reduction of myelin extrinsic inhibitors. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 283, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, S.P.; Issman-Zecharya, N.; Oren-Suissa, M.; Podbilewicz, B.; Schuldiner, O. Axon regrowth during development and regeneration following injury share molecular mechanisms. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsztein, D.C. The roles of intracellular protein-degradation pathways in neurodegeneration. Nature 2006, 443, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Small molecule enhancers of autophagy for neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Biosyst. 2008, 4, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broertjes, J. The Ten Hallmarks of Cancer in Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma. UNAV Journal for Medical Students 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey, I.; Manning, B.D. mTORC1 status dictates tumor response to targeted therapeutics. Sci Signal 2013, 6, pe31–pe31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Terada, N.; Yamasaki, T.; Nakamura, E.; Toda, Y.; Nishiyama, H.; Kamoto, T.; Ogawa, O.; Inoue, T. Regulation of androgen receptor transactivity and mTOR–S6 kinase pathway by Rheb in prostate cancer cell proliferation. Prostate 2010, 70, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ni, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Gu, F.; Dong, W.; Zhou, W.; Liu, H. Overexpression of RHEB is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3838–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrakis, K.J.; Zhu, H.; Silva, R.L.; Mills, J.R.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Lowe, S.W.; Tam, W.; Pelletier, J.; Wendel, H.-G. Tumorigenic activity and therapeutic inhibition of Rheb GTPase. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 2178–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, A.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Luo, X. Ras homologue enriched in brain is a critical target of farnesyltransferase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 297, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, T.; Ziehe, J.; Palma, M.; Escobar, D.; Tapia, J.C.; Pincheira, R.; Castro, A.F. Rheb promotes cancer cell survival through p27Kip1-dependent activation of autophagy. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wazir, U.; Newbold, R.; Jiang, W.G.; Sharma, A.; Mokbel, K. Prognostic and therapeutic implications of mTORC1 and Rictor expression in human breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1969–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. mTOR signaling in cancer and mTOR inhibitors in solid tumor targeting therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armijo, M.E.; Campos, T.; Fuentes-Villalobos, F.; Palma, M.E.; Pincheira, R.; Castro, A.F. Rheb signaling and tumorigenesis: mTORC1 and new horizons. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Yoshida, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamasaki, T.; Toda, Y.; Segawa, T.; Kamoto, T.; Nakamura, E.; Ogawa, O. Requirement of androgen-dependent activation of protein kinase Cζ for androgen-dependent cell proliferation in LNCaP cells and its roles in transition to androgen-independent cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 3053–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, H.; Radimerski, T.; Schindelholz, B.; Wittwer, F.; Belawat, P.; Daram, P.; Breuer, S.; Thomas, G.; Hafen, E. Rheb is an essential regulator of S6K in controlling cell growth in Drosophila. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guertin, D.A.; Sabatini, D.M. Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zuo, D.; Hirukawa, A.; Cardiff, R.D.; Lamb, R.; Sonenberg, N.; Muller, W.J. Rheb1-Independent Activation of mTORC1 in Mammary Tumors Occurs through Activating Mutations in mTOR. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.B.; Dimos, J.T.; Schaniel, C.; Hackney, J.A.; Moore, K.A.; Lemischka, I.R. A stem cell molecular signature. Science 2002, 298, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.B.; Basu, S.; Hangoc, G.; Tao, W.; Broxmeyer, H.E. Overexpression of Rheb2 enhances mouse hematopoietic progenitor cell growth while impairing stem cell repopulation. Blood 2009, 114, 3392–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.B.; Hangoc, G.; Tao, W.; Broxmeyer, H.E. Overexpression of Rheb2 Has Diverse Effects on Hematopoietic Progenitor and Stem Cell Functions. Blood 2007, 110, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardella, C.; Chen, Z.; Salmena, L.; Carracedo, A.; Alimonti, A.; Egia, A.; Carver, B.; Gerald, W.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Pandolfi, P.P. Aberrant Rheb-mediated mTORC1 activation and Pten haploinsufficiency are cooperative oncogenic events. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Wan, X.; Ouyang, M. Silencing of RHEB inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells via inhibition of the mTOR signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Mao, L.; Shi, R.; Wang, W.; Cheng, J. circRNA MYLK accelerates cervical cancer via Up-Regulation of RHEB and activation of mTOR signaling. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; White, E. Autophagy, stress, and cancer metabolism: what doesn't kill you makes you stronger. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2011, 76, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacher, M.; Pincheira, R.; Zhu, Z.; Camoretti-Mercado, B.; Matli, M.; Warren, R.; Castro, A. Rheb activates AMPK and reduces p27Kip1 levels in Tsc2-null cells via mTORC1-independent mechanisms: implications for cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6543–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Wyckoff, J.; Condeelis, J. Cell migration in tumors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Song, Z. Over-expressed RHEB promotes the progression of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KIM, H.; LEE, C. Abstract 2023: RhebL1 is involved in epithelial mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2023–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Halazonetis, T.D. Genomic instability—an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2010, 11, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Vassetzky, Y.; Dokudovskaya, S. mTORC1 pathway in DNA damage response. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2018, 1865, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadysirisack, D.D.; Baenke, F.; Ory, B.; Lei, K.; Ellisen, L.W. Feedback control of p53 translation by REDD1 and mTORC1 limits the p53-dependent DNA damage response. Molecular and cellular biology 2011, 31, 4356–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Hu, H.; Tong, X.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Yuan, H.; Xie, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. The mTOR–S6K pathway links growth signalling to DNA damage response by targeting RNF168. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, J.J.; Phung, I.; Potes, M.I.; Tamanoi, F. An oncogenic mutant of RHEB, RHEB Y35N, exhibits an altered interaction with BRAF resulting in cancer transformation. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, H.-G.; Silva, R.L.; Malina, A.; Mills, J.R.; Zhu, H.; Ueda, T.; Watanabe-Fukunaga, R.; Fukunaga, R.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Pelletier, J. Dissecting eIF4E action in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 2007, 21, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirane, M.; Nakayama, K.I. Inherent calcineurin inhibitor FKBP38 targets Bcl-2 to mitochondria and inhibits apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Bai, X.; Guo, S.; Jiang, Y. The switch I region of Rheb is critical for its interaction with FKBP38. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25963–25970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlich, F.; Weiwad, M.; Erdmann, F.; Fanghänel, J.; Jarczowski, F.; Rahfeld, J.U.; Fischer, G. Bcl-2 regulator FKBP38 is activated by Ca2+/calmodulin. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2688–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, B.C.; Yeung, R.S. The tuberous sclerosis complex genes in tumor development. Cancer Invest. 2004, 22, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, M.; Gui, Y.; Hou, Q.; Gu, M.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, B.; Zhao, A.Z.; Dai, C. Rheb1 protects against cisplatin-induced tubular cell death and acute kidney injury via maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; De Poi, S.P.; Humphrey, S.J.; Hein, L.K.; Bruning, J.; Pan, W.; Sargeant, T.J.; Proud, C.G. TSC-insensitive Rheb mutations induce oncogenic transformation through a combination of hyperactive mTORC1 signalling and metabolic reprogramming. Cell Mol Life Sci 2020, https. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racker, E. Bioenergetics and the problem of tumor growth: an understanding of the mechanism of the generation and control of biological energy may shed light on the problem of tumor growth. Am. Sci. 1972, 60, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.; Lin, A.W.; McCurrach, M.E.; Beach, D.; Lowe, S.W. Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell 1997, 88, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggero, D.; Montanaro, L.; Ma, L.; Xu, W.; Londei, P.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Pandolfi, P.P. The translation factor eIF-4E promotes tumor formation and cooperates with c-Myc in lymphomagenesis. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Trotman, L.C.; Shaffer, D.; Lin, H.-K.; Dotan, Z.A.; Niki, M.; Koutcher, J.A.; Scher, H.I.; Ludwig, T.; Gerald, W.J.N. Crucial role of p53-dependent cellular senescence in suppression of Pten-deficient tumorigenesis. Nature 2005, 436, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, A.; Harris, A.W.; Bath, M.L.; Cory, S. Novel primitive lymphoid tumours induced in transgenic mice by cooperation between myc and bcl-2. Nature 1990, 348, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.A.; Fridman, J.S.; Yang, M.; Baranov, E.; Hoffman, R.M.; Lowe, S.W. Dissecting p53 tumor suppressor functions in vivo. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, H.-G.; Stanchina, E.d.; Fridman, J.S.; Malina, A.; Ray, S.; Kogan, S.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Pelletier, J.; Lowe, S.W. Survival signalling by Akt and eIF4E in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nature 2004, 428, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5904–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.; Sharma, D.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Tumor microenvironment targeted nanotherapeutics for cancer therapy and diagnosis: A review. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, C.; Erez, N. From sentinel cells to inflammatory culprits: cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumour-related inflammation. The Journal of pathology 2013, 229, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allinen, M.; Beroukhim, R.; Cai, L.; Brennan, C.; Lahti-Domenici, J.; Huang, H.; Porter, D.; Hu, M.; Chin, L.; Richardson, A. Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, N.; Truitt, M.; Olson, P.; Hanahan, D. Cancer-associated fibroblasts are activated in incipient neoplasia to orchestrate tumor-promoting inflammation in an NF-κB-dependent manner. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, S.C.; Tee, A.R. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α is regulated by the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) via an mTOR signaling motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20534–20543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of bladder cancer. Medical sciences 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kim, S.; Lin, P.C. Interleukin-33 and ST2 signaling in tumor microenvironment. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ouyang, W.; Huang, C. Inflammation, a key event in cancer development. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Qiao, F.; Huang, D.; Wu, Q.; Chen, T.; Badawy, S.; Cheng, G.; Hao, H.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.J.F.; et al. MiR-155-5p plays as a “janus” in the expression of inflammatory cytokines induced by T-2 toxin. Food Chem Toxicol 2020, 140, 111258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barral, Y.; Mermall, V.; Mooseker, M.S.; Snyder, M.J.M.c. Compartmentalization of the cell cortex by septins is required for maintenance of cell polarity in yeast. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaijmakers, J.H.; Bos, J.L. Specificity in Ras and Rap signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 10995–10999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangoiti, P.; Arana, L.; Ouro, A.; Granado, M.H.; Trueba, M.; Gómez-Muñoz, A.J.C.s. Activation of mTOR and RhoA is a major mechanism by which Ceramide 1-phosphate stimulates macrophage proliferation. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Yin, A. MicroRNA-194 overexpression protects against hypoxia/reperfusion-induced HK-2 cell injury through direct targeting Rheb. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 8311–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Cui, L. MicroRNA-199a-5p induced autophagy and inhibits the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis by modulating the mTOR signaling via directly targeting Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb). Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Luo, Z.; Zhong, C.; Pan, X.; Xu, X. Influence of miR-155 on cell apoptosis in rats with ischemic stroke: role of the ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb)/mTOR pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinay, D.S.; Ryan, E.P.; Pawelec, G.; Talib, W.H.; Stagg, J.; Elkord, E.; Lichtor, T.; Decker, W.K.; Whelan, R.L.; Kumara, H.S. Immune evasion in cancer: Mechanistic basis and therapeutic strategies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S185–S198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitsky, D.; Tamura, T.; Yanai, H.; Taniguchi, T. Regulation of immunity and oncogenesis by the IRF transcription factor family. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2010, 59, 489–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Pagano, J.; Barber, G. IRF7: activation, regulation, modification and function. Genes Immun 2011, 12, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-I-and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.; Heit, A.; Dreher, S.; Eisenächer, K.; Mages, J.; Haas, T.; Krug, A.; Janssen, K.P.; Kirschning, C.J.; Wagner, H. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) orchestrates the defense program of innate immune cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 2981–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makovski, V.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Gefen-Dor, C.; Shai, B.; Ehrlich, M.; Rechavi, G.; Kloog, Y. Analysis of gene expression array in TSC2-deficient AML cells reveals IRF7 as a pivotal factor in the Rheb/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1557–e1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Cho, J.; Lee, K. Tumour regression via integrative regulation of neurological, inflammatory, and hypoxic tumour microenvironment. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2020, 28, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataramani, V.; Tanev, D.I.; Strahle, C.; Studier-Fischer, A.; Fankhauser, L.; Kessler, T.; Körber, C.; Kardorff, M.; Ratliff, M.; Xie, R. Glutamatergic synaptic input to glioma cells drives brain tumour progression. Nature 2019, 573, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arese, M.; Bussolino, F.; Pergolizzi, M.; Bizzozero, L.; Pascal, D. Tumor progression: the neuronal input. Annals of translational medicine 2018, 6, https. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.W.; Nagaraja, A.S.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Green, P.A.; Sood, A.K. Sympathetic nervous system regulation of the tumour microenvironment. Nature Reviews Cancer 2015, 15, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makale, M.T.; McDonald, C.R.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.A.; Kesari, S. Mechanisms of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability in patients with brain tumours. Nature Reviews Neurology 2017, 13, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquier, E.; Street, J.; Pouchy, C.; Carre, M.; Gifford, A.; Murray, J.; Norris, M.; Trahair, T.; Andre, N.; Kavallaris, M. β-blockers increase response to chemotherapy via direct antitumour and anti-angiogenic mechanisms in neuroblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Gao, D. Role of the nervous system in cancer metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, M.; Couillard, J.; Belanger, S.; St-Pierre, Y. New roles for matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 25, https. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryugina, E.I.; Quigley, J.P. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, K.H.; Nam, J.H.; Jin, B.K.; Kim, S.R. Activation of CNTF/CNTFRα signaling pathway by hRheb (S16H) transduction of dopaminergic neurons in vivo. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0121803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grondin, R.; Gash, D.M. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF): a drug candidate for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 1998, 245, P35–P42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Eibl, G.; Duffy, J.P.; Reber, H.A.; Hines, O.J. Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor upregulates the expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human pancreatic cancer. Surgery 2003, 134, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, A.D.; Mirza, A.; Liu, G.; Long, B.J.; Bishop, W.R.; Kirschmeier, P. The farnesyl transferase inhibitor (FTI) SCH66336 (lonafarnib) inhibits Rheb farnesylation and mTOR signaling: role in FTI enhancement of taxane and tamoxifen anti-tumor activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31101–31108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; McDonald, J.S.; Yun, S.; Schneider, P.A.; Peterson, K.L.; Flatten, K.S.; Loegering, D.A.; Oberg, A.L.; Riska, S.M.; Huang, S. Farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib inhibits Rheb prenylation and stabilizes Bax in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Haematologica 2014, 99, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, S.J.; Narayan, S.; Molz, L.; Berstler, L.A.; Kang, S.A.; Vlasuk, G.P.; Saiah, E. A small molecule inhibitor of Rheb selectively targets mTORC1 signaling. Nature communications 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goorden, S.M.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; Cheng, C.; van Woerden, G.M.; Mozaffari, M.; Post, L.; Duckers, H.J.; Nellist, M.; Elgersma, Y. Rheb is essential for murine development. Mol Cell Biol 2011, 31, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenewoud, M.J.; Goorden, S.M.; Kassies, J.; Pellis-van Berkel, W.; Lamb, R.F.; Elgersma, Y.; Zwartkruis, F.J. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex I (mTORC1) activity in ras homologue enriched in brain (Rheb)-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts. PLoS One 2013, 8, e81649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoroge, F.G.; Taveras, A.G.; Kelly, J.; Remiszewski, S.; Mallams, A.K.; Wolin, R.; Afonso, A.; Cooper, A.B.; Rane, D.F.; Liu, Y.-T. (+)-4-[2-[4-(8-Chloro-3, 10-dibromo-6, 11-dihydro-5 H-benzo [5,6] cyclohepta [1, 2-b]-pyridin-11 (R)-yl)-1-piperidinyl]-2-oxo-ethyl]-1-piperidinecarboxamide (SCH-66336): A Very Potent Farnesyl Protein Transferase Inhibitor as a Novel Antitumor Agent. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 4890–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, W.R.; Bond, R.; Petrin, J.; Wang, L.; Patton, R.; Doll, R.; Njoroge, G.; Catino, J.; Schwartz, J.; Windsor, W.; et al. Novel tricyclic inhibitors of farnesyl protein transferase. Biochemical characterization and inhibition of Ras modification in transfected Cos cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 30611–30618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, R.J.; Kirschmeier, P.; Bishop, W.R. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors as anticancer agents: critical crossroads. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel 2004, 7, 478–486. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J. Ding C Batorsky R. Discovery of (R)-7-cyano-2, 3, 4, 5-tetrahydro-1-(1H-imidazol-4-ylmethyl)-3-(phenylmethyl)-4-(2-thienylsulfonyl)-H-1, 4-benzodiazepine (BMS-214662), A farnesyltransferase inhibitor with potentpreclinical antitumor activity. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.F.; Rebhun, J.F.; Clark, G.J.; Quilliam, L.A. Rheb binds tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2) and promotes S6 kinase activation in a rapamycin-and farnesylation-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32493–32496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mutation Type | Amino Acid Position | Mutation(s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activating | 16 | S16H | [42] |
| 35 | Y35N/C/H | [43] | |
| 63 | G63A | [44] | |
| 64 | Q64L | [45] | |
| 153 | N153T/S | [42,46] | |
| Loss of function | 35 | Y35A | [30,46] |
| 36 | D36A | [21] | |
| 37 | P37A | [21,46] | |
| 38 | T38A | [21,46,47] | |
| 39 | I39A, K | [47,46] | |
| 41 | N41A | [21,47] | |
| 65 | D65A | [30] | |
| 67,69 | Y67A/I69A | [48] | |
| 76,77 | I76A/D77A | [48] | |
| Activating Mutations Found in Cancer Database | 35 | Y35N (5x) | [43,49] |
| 139 | E139K/D/G/* (2X) | [43] | |
| Loss of Membrane Association | 181 | C181S | [20,33] |
| Dominant Negative | 20 | S20N | [12,21] |
| 60 | D60I/K/V | [12,21] |
| Proteins involved in canonical signaling pathway | |
| TSC complex | In the exclusion of growth hormones or insulin, the TSC complex increases Rheb1's intrinsic GTPase activity on the lysosomal surface and forms a complex with Rheb1 at the lysosomal membranes by converting Rheb1-GDP. |
| Bnip3 | Bnip3 interacts with Rheb1 in hypoxia as well as suppresses its function via preventing Rheb1 contact with downstream targets or interfering with Rheb1 GTP loading [98]. |
| mTOR | Rheb1 binding to mTOR is independent of its GTP-bound state, yet GTP-bound state is required for mTORC1 activation, boosting growth, cell cycle advancement, and autophagy suppression. |
| GAPDH | GAPDH interacts with Rheb1 in the absence of glucose, regardless of Rheb1's guanyl nucleotide loaded condition. |
| PLD1 | In a GTP-dependent way, Rheb1 binds to and activates phospholipase D1 (PLD1) , Rheb1 stimulates PLD1 to create phosphatidic acid, which activates mTORC1 indirectly [99]. |
| Proteins involved in non-canonical signaling pathway | |
| RASSF1 | By limiting mTORC1 signaling, RASSF1 interacts with Rheb1 to promote autophagy. |
| LC3 | Rheb1 physically interacts with the mitochondrial autophagic receptor Nix and the autophagosomal protein LC3-II. The recruitment of Rheb1 to mitochondria leads to the activation of mitophagy. |
| NIX | Rheb1 is recruited to the mitochondrial outer membrane in response to strong oxidative phosphorylation activity. Rheb1 stimulates mitophagy by interacting physically with Nix, the mitochondrial autophagic receptor, and LC3-II, the autophagosomal protein. |
| Syntenin | Rheb1-GDP regulates spine development by binding syntenin. |
| FKBP38 | FKBP38 belongs to the FK506-binding protein family and functions as a mTOR antagonist [100]. Rheb1, which interacts with FKBP38 in a GTP-dependent way and hinders it from interacting with mTOR, counteracts the inhibitory effect of FKBP38. Rheb1 and the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 attach to the same area on FKBP38, therefore Rheb1 displaces Bcl-2, allowing Bcl-2 to interact to pro-apoptotic proteins [91]. |
| PERK | Rheb1 forms a GTP-dependent association with PERK to limit protein synthesis via eIF2 signaling during ER stress. |
| CAD | Rheb1 regulates pyrimidine synthesis via binding to CAD at its C-terminal carbamoyl phosphate synthetase domain in a GTP-dependent manner. This connection is reliant on Rheb1's effector domain. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





