Submitted:
18 December 2023
Posted:
19 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the idea of hydrogen vitamin C combination therapy
1.2. Hydrogen and Vitamin C Combination Therapy Method
1.3. Home therapy
1.4. Anti-cancer effects of hydrogen and vitamin C combination therapy
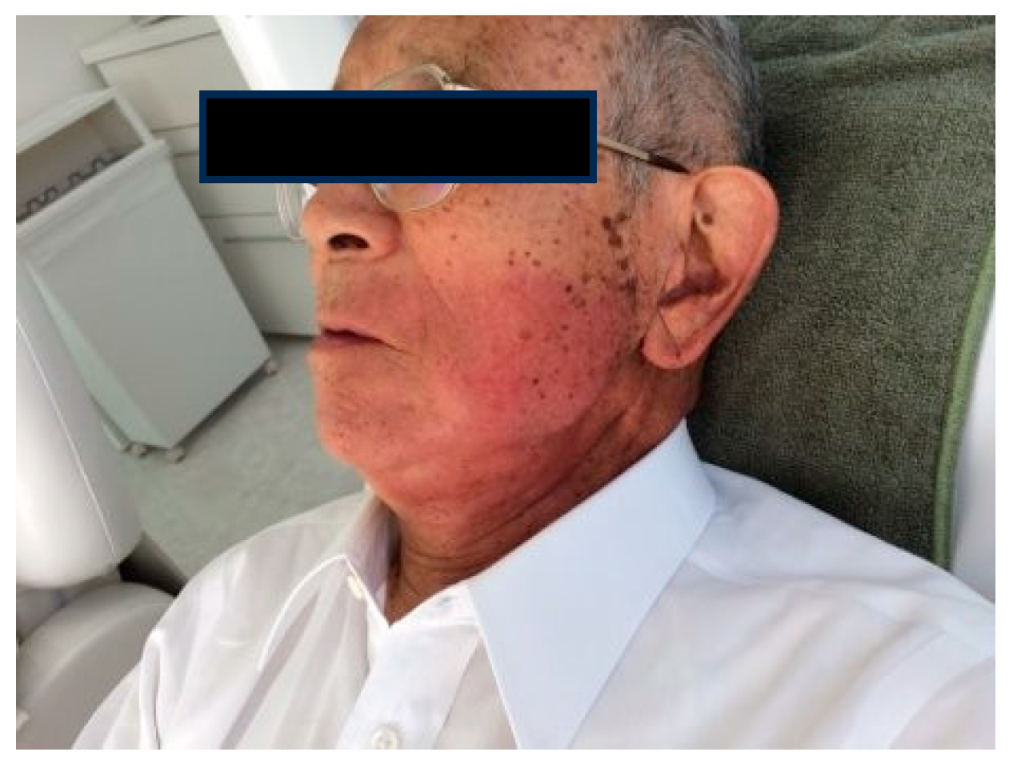
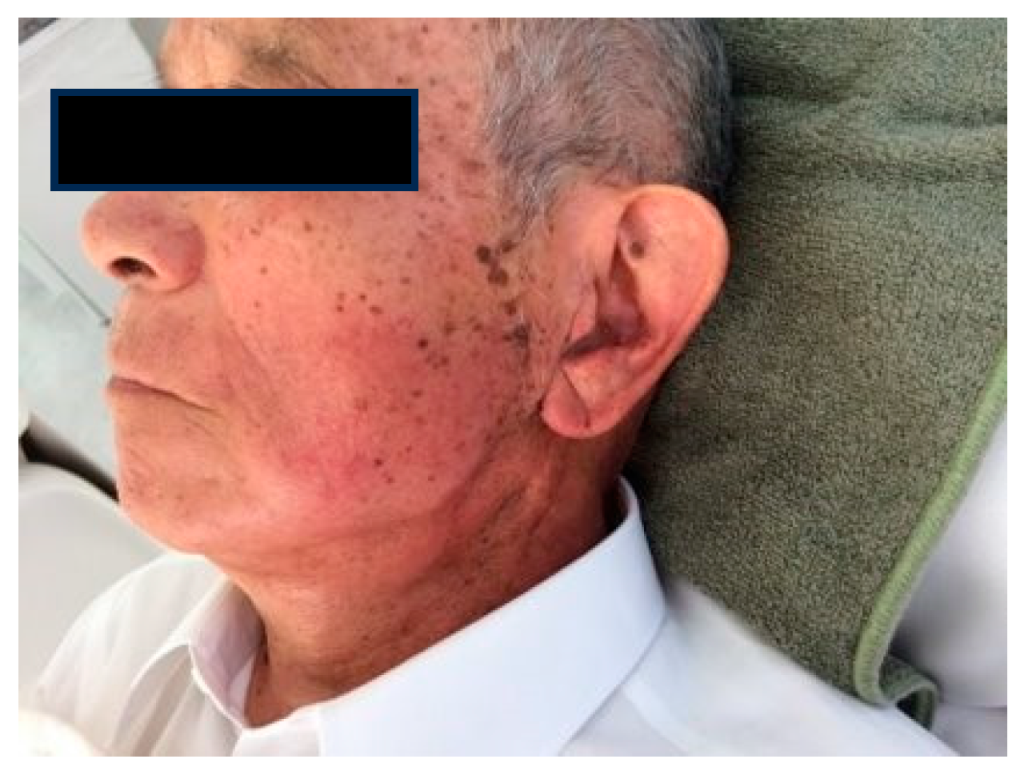
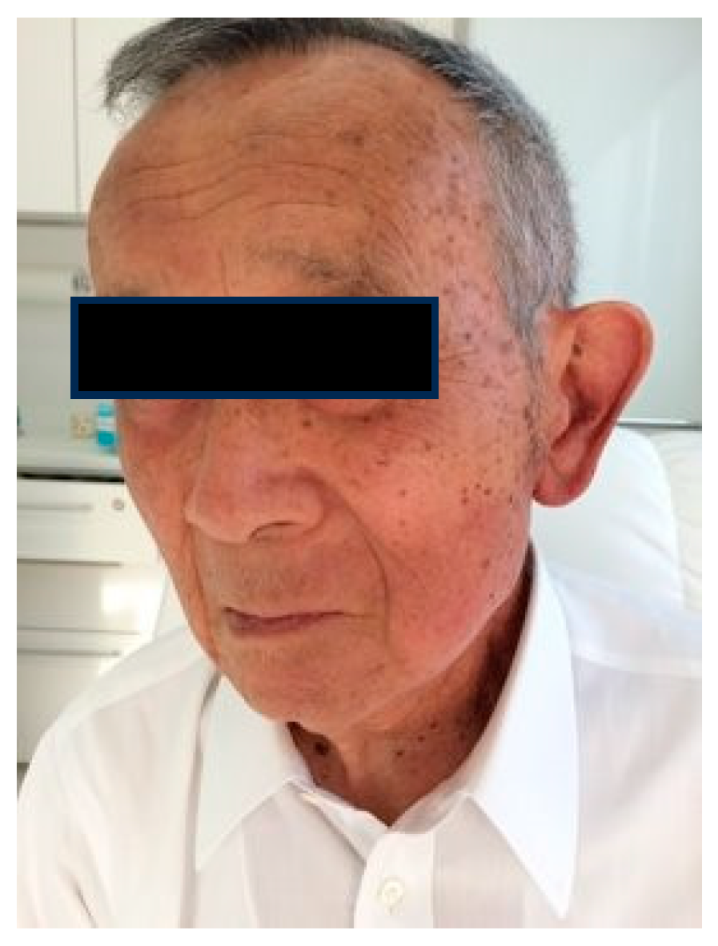
1.5. Radioprotection Case
Case1: 85-year-old male
Case 2: 47-year-old female
1.6. The hypothesis
2. Material and method
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Vitamin C and hydrogen treatment
2.3. Radiation treatment
2.4. Fluorescent detection of ROS
2.5. Confirmation of apoptosis
2.6. EMT gene expression
| Gene name | Accession number |
| SNAI1 | Hs_SNAI1_1_SG |
| SNAI2 | Hs_SNAI2_1_SG |
| CDH1 | Hs_CDH1_1_SG |
| TWIST1 | Hs_TWIST1_1_SG |
| TGFB1 | Hs_TGFB1_1_SG |
| STAT3 | Hs_STAT3_1_SG |
| VIM | Hs_VIM_1_SG |
| CD248 | Hs_CD248_1_SG |
| GAPDH | Hs_GAPDH_1_SG |
| ACTB | Hs_ACTB_1_SG |
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparative experiments of cell viability
3.2. Confirmation of apoptosis (Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12)
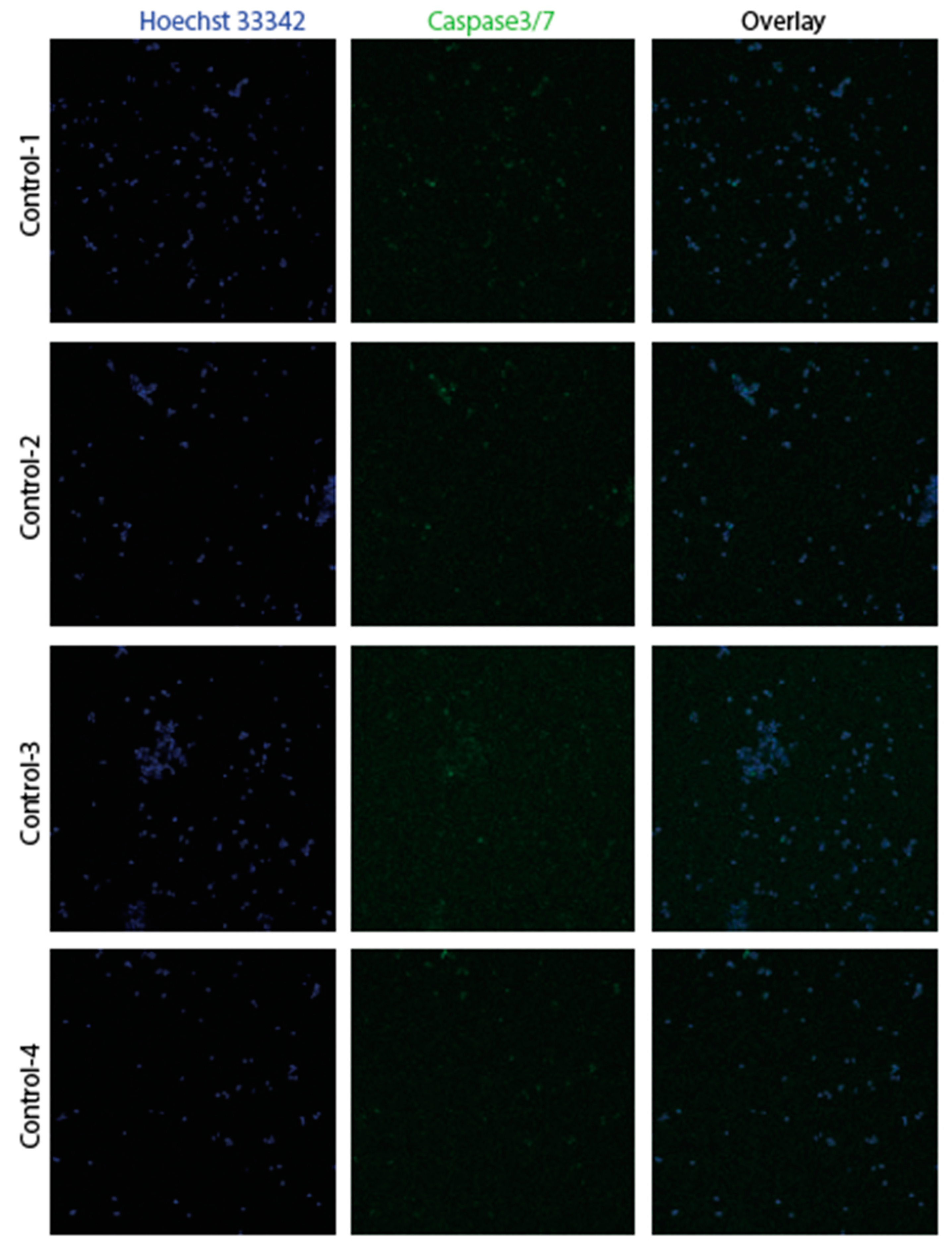
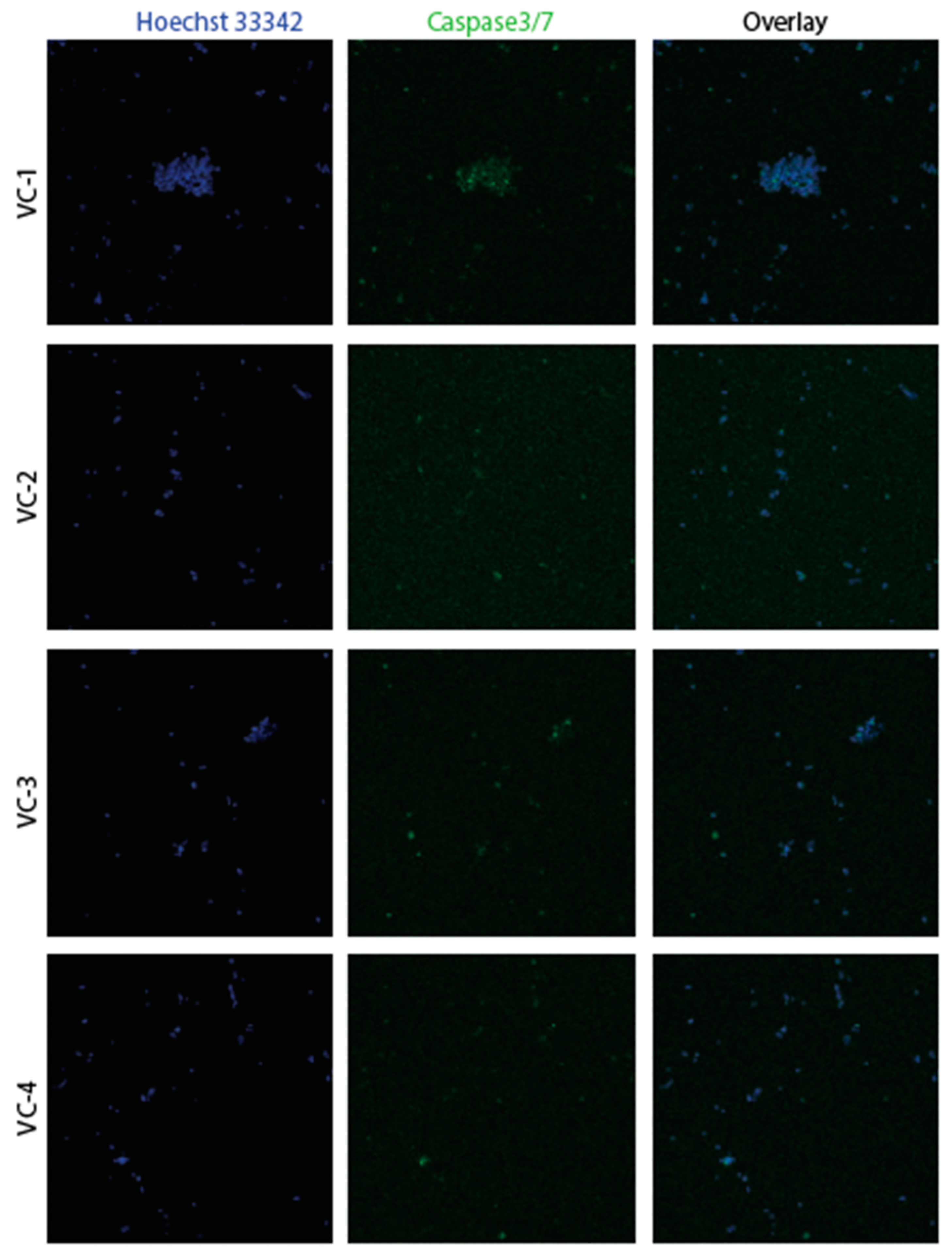
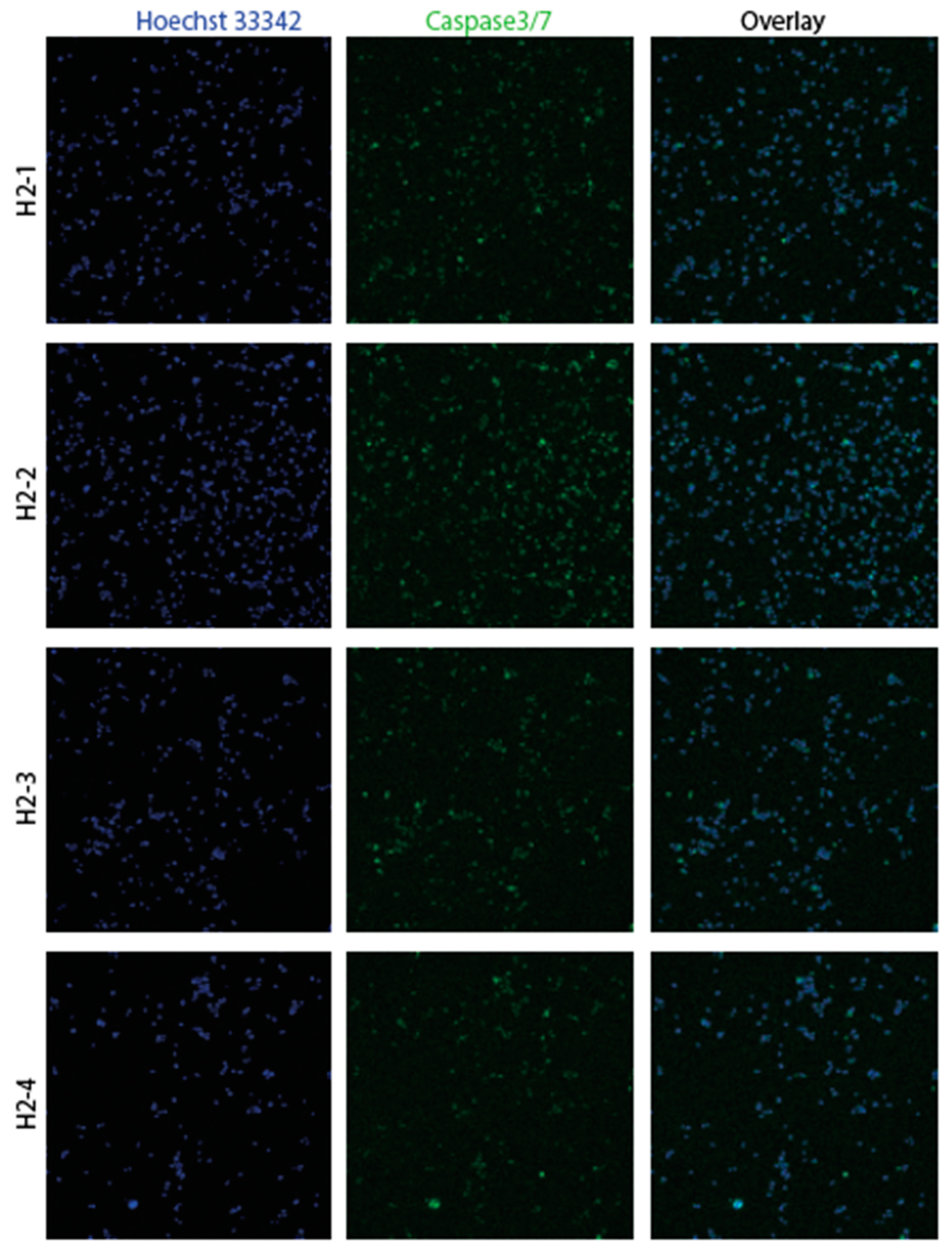
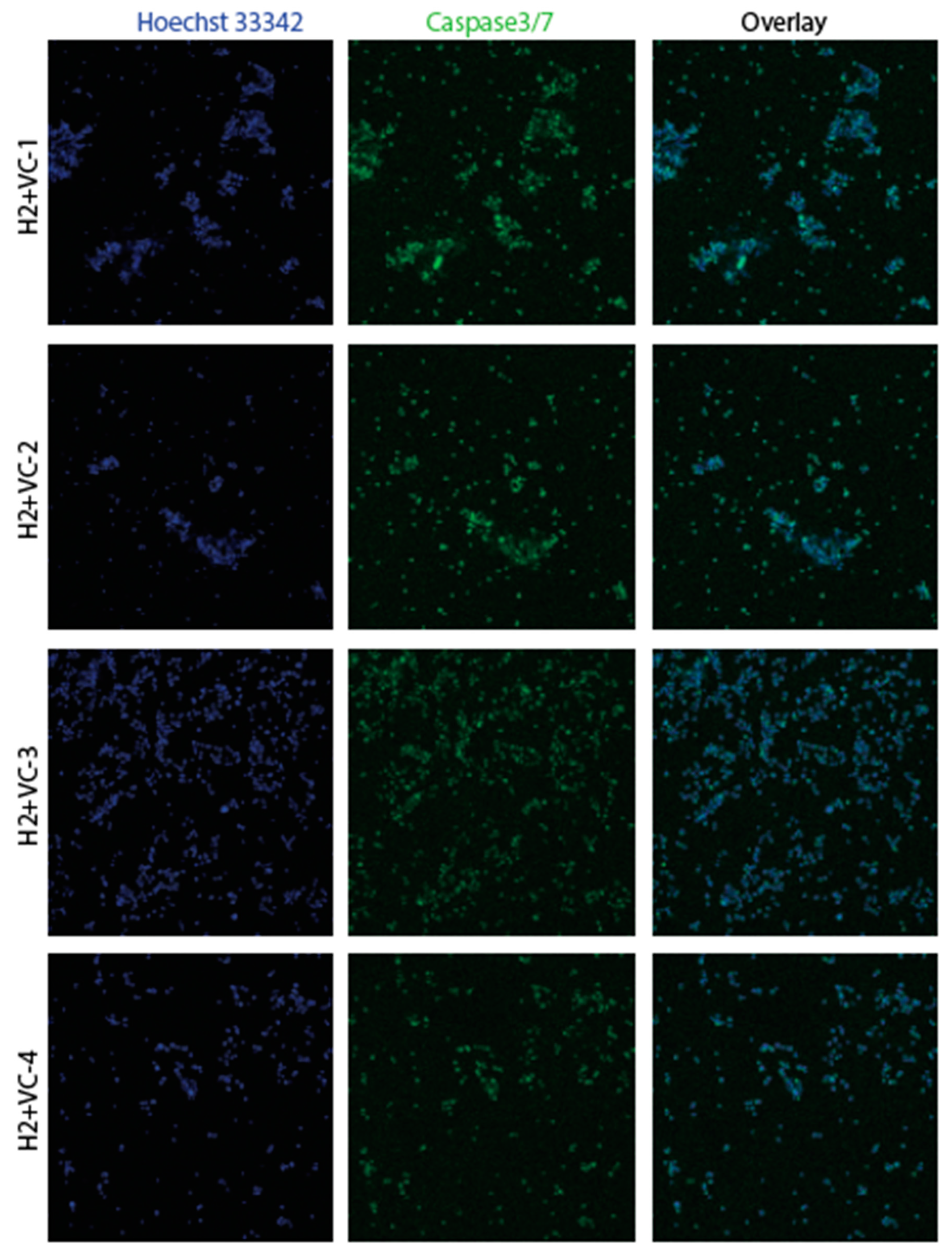
3.3. The EMT signature in GBM
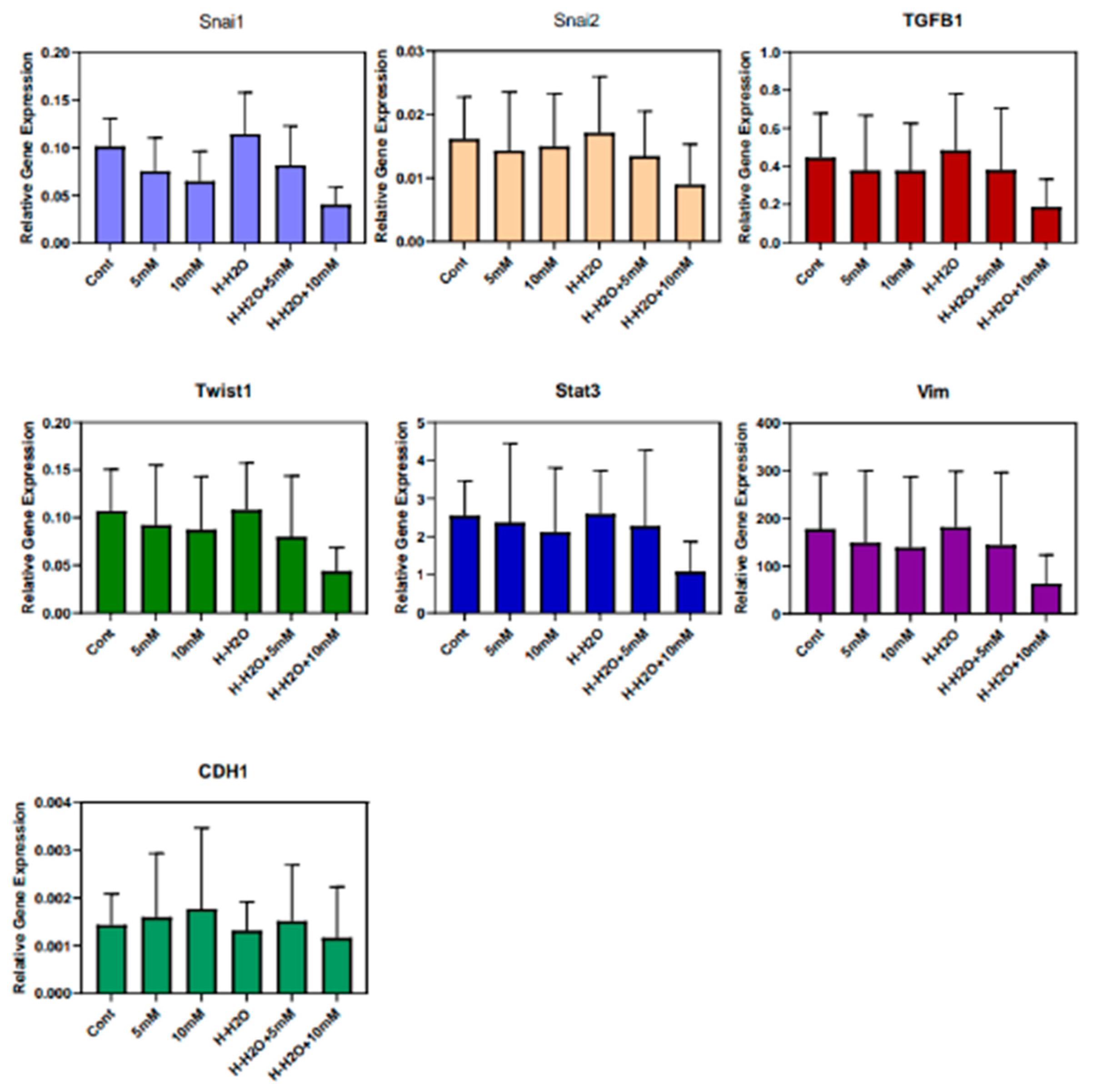
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of vitamin C and Hydrogen Peroxide(H2O2)
4.2. The effects of hydrogen
4.3. Expected benefits of hydrogen and vitamin C combination therapy
4.4. Hydrogen and vitamin C combination therapy in health and disease
4.5. Limitations and issues to be solved
5. Conclusion
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest statement
References
- Berrington de González A, Mahesh M, Kim KP, Bhargavan M, Lewis R, Mettler F, Land C. Projected cancer risks from computed tomographic scans performed in the United States in 2007. Arch Intern Med. 2009 Dec 14;169(22):2071-7. [CrossRef]
- Fischer N, Seo EJ, Efferth T. Prevention from radiation damage by natural products. Phytomedicine. 2018; Aug 1;47:192-200. [CrossRef]
- Yahyapour R, Shabeeb D, Cheki M, Musa AE, Farhood B, Rezaeyan A, Amini P, Fallah H, Najafi M. Radiation Protection and Mitigation by Natural Antioxidants and Flavonoids: Implications to Radiotherapy and Radiation Disasters. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018;11(4):285-304. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saif-Elnasr M, Abdel-Aziz N, Ibrahim EL-Batal A. Ameliorative effect of selenium nanoparticles and fish oil on cisplatin and gamma irradiation-induced nephrotoxicity in male albino rats. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2018; Sep 11:1-10. [CrossRef]
- Nukala U, Thakkar S, Krager KJ, Breen PJ, Compadre CM. Aykin-Burns N. Antioxidant Tocols as Radiation Countermeasures (Challenges to be Addressed to Use Tocols as Radiation Countermeasures in Humans). Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Feb 23;7(2). pii: E33. [CrossRef]
- Camphausen K, Citrin D, Krishna MC, Mitchell JB. Implications for tumor control during protection of normal tissues with antioxidants. J Clin Oncol. 2005 Aug 20;23(24):5455-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawk MA, McCallister C, Schafer ZT. Antioxidant Activity during Tumor Progression: A Necessity for the Survival of Cancer Cells? Cancers. 2016 Oct; 8(10): 92. [CrossRef]
- Bairati I, Meyer F, Gélinas M, Fortin A, Nabid A, Brochet F, Mercier JP, Têtu B, Harel F, Abdous B, Vigneault E, Vass S, Del Vecchio P, Roy J. Randomized trial of antioxidant vitamins to prevent acute adverse effects of radiation therapy in head and neck cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2005 Aug 20;23(24):5805-13. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer F, Bairati I, Fortin A, Gélinas M, Nabid A, Brochet F, Têtu B. Interaction between antioxidant vitamin supplementation and cigarette smoking during radiation therapy in relation to long-term effects on recurrence and mortality: a randomized trial among head and neck cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2008 Apr 1;122(7):1679-83. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud C. Meta-regression analyses, meta-analyses, and trial sequential analyses of the effects of supplementation with beta-carotene, vitamin A, and vitamin E singly or in different combinations on all-cause mortality: do we have evidence for lack of harm? PLoS One. 2013 Sep 6;8(9):e74558. [CrossRef]
- Orditura M, De Vita F, Roscigno A, Infusino S, Auriemma A, Iodice P, Ciaramella F, Abbate G, Catalano G. Amifostine: A selective cytoprotective agent of normal tissues from chemo-radiotherapy induced toxicity (Review). Oncol Rep. 1999 Nov-Dec;6(6):1357-62. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukourakis, MI. Radiation damage and radioprotectants: new concepts in the era of molecular medicine. Br J Radiol. 2012 Apr;85(1012):313-30. [CrossRef]
- Ferraiolo DM, Veits-keenan A. Insufficient evidence for interventions to prevent dry mouth and salivary gland dysfunction post head and neck radiotherapy. Evid Based Dent. 2018 Mar 23;19(1):30-31. [CrossRef]
- Ito Y, Kinoshita M, Yamamoto T, Sato T, Obara T, Saitoh D, Seki S, Takahashi Y. A combination of pre- and post-exposure ascorbic acid rescues mice from radiation-induced lethal gastrointestinal damage. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Sep 27;14(10):19618-35. [CrossRef]
- Jafari E, Alavi M, Zal F. The evaluation of protective and mitigating effects of vitamin C against side effects induced by radioiodine therapy. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2018 Aug;57(36):233-240. [CrossRef]
- Velauthapillai N, Barfett J, Jaffer H, Mikulis D, Murphy K. Antioxiants taken orally prior to diagnostic radiation exposure can prevent DNA injury. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017 Mar;28(3):406-411. [CrossRef]
- Kennedy M, Bruninga K, Mutlu EA, Losurdo J, Choudhary S, Keshavarzian A. Successful and sustained treatment of chronic radiation proctitis with antioxidant vitamins E and C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Apr;96(4):1080-4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato T, Kinoshita M, Yamamoto T, Ito M, Nishida T, Takeuchi M, Saitoh D, Seki S, Mukai Y. Treatment of irradiated mice with high-dose ascorbic acid reduced lethality. PLoS One. 2015 Feb 4;10(2):e0117020. [CrossRef]
- Saga R, Uchida T, Takino Y, Kondo Y, Kobayashi H, Kinoshita M, Saitoh D, Ishigami A, Makishima M. Radiation-induced gastrointestinal syndrome is exacerbated in vitamin C-insufficient SMP30/GNL knockout mice. Nutrition. 2021 Jan;81:110931. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu C, Cui J, Sun Q, Cai J. Hydrogen therapy may be an effective and specific novel treatment for acute radiation syndrome. Med Hypotheses. 2010 Jan;74(1):145-6. [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld MP, Ansari RR, Zakrajsek JF, Billiar TR, Toyoda Y, Wink DA, Nakao A. Hydrogen therapy may reduce the risks related to radiation-induced oxidative stress in space flight. Med Hypotheses. 2011 Jan;76(1):117-8. [CrossRef]
- Qian L, Shen J, Chuai Y, Cai J. Hydrogen as a New Class of Radioprotective Agent. Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Sep 14;9(9):887-94. [CrossRef]
- Terasaki Y, Ohsawa I, Terasaki M, Takahashi M, Kunugi S, Dedong K, Urushiyama H, Amenomori S, Kaneko-Togashi M, Kuwahara N, Ishikawa A, Kamimura N, Ohta S, Fukuda Y. Hydrogen therapy attenuates irradiation-induced lung damage by reducing oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):L415-26. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slezák J, Kura B, Frimmel K, Zálešák M, Ravingerová T, Viczenczová C, Okruhlicová Ľ, Tribulová N. Preventive and therapeutic application of molecular hydrogen in situations with excessive production of free radicals. Physiol Res. 2016 Sep 19;65 Suppl 1:S11-28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu Q, Zhou Y, Wu S, Wu W, Deng Y, Shao A. Molecular hydrogen: A potential radioprotective agent. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Oct;130:110589. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Hamdan M, Gardette B, Cadet J, Gharib B, De Reggi M, Douki T, Triantaphylides C. Molecular hydrogen attenuates radiation-induced nucleobase damage to DNA in aerated aqueous solutions. Int J Radiat Biol. 2016 Sep;92(9):536-41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang KM, Kang YN, Choi IB, et al. Effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water on the quality of life of patients treated with radiotherapy for liver tumors. Med Gas Res. 2011 Jun 7;1(1):11. [CrossRef]
- Chuai Y, Gao F, Li B, Zhao L, Qian L, Cao F, Wang L, Sun X, Cui J, Cai J. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates radiation-induced male germ cell loss in mice through reducing hydroxyl radicals. Biochem J. 2012 Feb 15;442(1):49-56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao L, Zhou C, Zhang J, Gao F, Li B, Chuai Y, Liu C, Cai J. Hydrogen protects mice from radiation induced thymic lymphoma in BALB/c mice. Int J Biol Sci. 2011 Mar 25;7(3):297-300. [CrossRef]
- Chen P, Reed G, Jiang J, Wang Y, Sunega J, Dong R, Ma Y, Esparham A, Ferrell R, Levine M, Drisko J, Chen Q. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Intravenous Vitamin C: A Classic Pharmacokinetic Study. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022 Sep;61(9):1237-1249. [CrossRef]
- Stephenson CM, Levin RD, Spector T, Lis CG. Phase I clinical trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of high-dose intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Jul;72(1):139-46. [CrossRef]
- Hoffer LJ, Levine M, Assouline S, Melnychuk D, Padayatty SJ, Rosadiuk K, Rousseau C, Robitaille L, Miller WH Jr. Phase I clinical trial of i.v. ascorbic acid in advanced malignancy. Ann Oncol. 2008 Nov;19(11):1969-74. Erratum in: Ann Oncol. 2008 Dec;19(12):2095. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh JL, Wagner BA, van’t Erve TJ, Zehr PS, Berg DJ, Halfdanarson TR, Yee NS, Bodeker KL, Du J, Roberts LJ 2nd, Drisko J, Levine M, Buettner GR, Cullen JJ. Pharmacological ascorbate with gemcitabine for the control of metastatic and node-positive pancreatic cancer (PACMAN): results from a phase I clinical trial. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;71(3):765-75. [CrossRef]
- Böttger F, Vallés-Martí A, Cahn L, Jimenez CR. High-dose intravenous vitamin C, a promising multi-targeting agent in the treatment of cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Oct 30;40(1):343. [CrossRef]
- Tamura T, Hayashida K, Sano M, Suzuki M, Shibusawa T, Yoshizawa J, Kobayashi Y, Suzuki T, Ohta S, Morisaki H, Fukuda K, Hori S. Feasibility and Safety of Hydrogen Gas Inhalation for Post-Cardiac Arrest Syndrome - First-in-Human Pilot Study. Circ J. 2016 Jul 25;80(8):1870-3. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole AR, Sperotto F, DiNardo JA, Carlisle S, Rivkin MJ, Sleeper LA, Kheir JN. Safety of Prolonged Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas in Air in Healthy Adults. Crit Care Explor. 2021 Oct 8;3(10):e543. [CrossRef]
- Vollbracht C, Schneider B, Leendert V, Weiss G, Auerbach L, Beuth J. Intravenous vitamin C administration improves quality of life in breast cancer patients during chemo-/radiotherapy and aftercare: results of a retrospective, multicentre, epidemiological cohort study in Germany. In Vivo. 2011 Nov-Dec;25(6):983-90. [PubMed]
- Shinozaki K, Hosokawa Y, Hazawa M, Kashiwakura I, Okumura K, Kaku T, Nakayama E. Ascorbic acid enhances radiation-induced apoptosis in an HL60 human leukemia cell line. J Radiat Res. 2011;52(2):229-37. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runtuwene J, Amitani H, Amitani M, Asakawa A, Cheng KC, Inui A. Hydrogen-water enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced inhibition of colon cancer. Peer J. 2015 Apr 7;3:e859. [CrossRef]
- Du J, Cieslak JA 3rd, Welsh JL, Sibenaller ZA, Allen BG, Wagner BA, Kalen AL, Doskey CM, Strother RK, Button AM, Mott SL, Smith B, Tsai S, Mezhir J, Goswami PC, Spitz DR, Buettner GR, Cullen JJ. Pharmacological Ascorbate Radiosensitizes Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015 Aug 15;75(16):3314-26. [CrossRef]
- Alexander MS, Wilkes JG, Schroeder SR. Pharmacological ascorbate reduces radiation-induced normal tissue toxicity and enhances tumor radiosensitization in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2018 Dec 15;78(24):6838-6851. [CrossRef]
- Herst PM, Broadley KW, Harper JL, McConnell MJ. Pharmacological concentrations of ascorbate radiosensitize glioblastoma multiforme primary cells by increasing oxidative DNA damage and inhibiting G2/M arrest. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Apr 15;52(8):1486-93. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro ML, McConnell MJ, Herst PM. Radiosensitisation by pharmacological ascorbate in glioblastoma multiforme cells, human glial cells, and HUVECs depends on their antioxidant and DNA repair capabilities and is not cancer specific. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Sep;74:200-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvissers MCM, Das AB. Potential Mechanisms of Action for Vitamin C in Cancer: Reviewing the Evidence. Front Physiol. 2018 Jul 3;9:809. [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo D, Pelosi E, Castelli G, Lo-Coco F, Testa U. Mechanisms of anti-cancer effects of ascorbate: Cytotoxic activity and epigenetic modulation. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2018 Mar;69:57-64. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agathocleous M, Meacham CE, Burgess RJ, Piskounova E, Zhao Z, Crane GM, Cowin BL, Bruner E, Murphy MM, Chen W, Spangrude GJ, Hu Z, DeBerardinis RJ, Morrison SJ. Ascorbate regulates haematopoietic stem cell function and leukaemogenesis. Nature. 2017 Sep 28;549(7673):476-481. [CrossRef]
- Mikirova N, Casciari J, Rogers A, Taylor P. Effect of high-dose intravenous vitamin C on inflammation in cancer patients. J Transi Med. 2012 Sep 11;10:189. [CrossRef]
- Chen Q, Espey MG, Krishna MC, Mitchell JB, Corpe CP, Buettner GR, Shacter E, Levine M. Pharmacologic ascorbic acid concentrations selectively kill cancer cells: action as a pro-drug to deliver hydrogen peroxide to tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 20;102(38):13604-9. [CrossRef]
- Yun J, Mullarky E, Lu C, Bosch KN, Kavalier A, Rivera K, Roper J, Chio II, Giannopoulou EG, Rago C, Muley A, Asara JM, Paik J, Elemento O, Chen Z, Pappin DJ, Dow LE, Papadopoulos N, Gross SS, Cantley LC. Vitamin C selectively kills KRAS and BRAF mutant colorectal cancer cells by targeting GAPDH. Science. 2015 Dec 11;350(6266):1391-6. [CrossRef]
- Cimmino L, Dolgalev I, Wang Y, Yoshimi A, Martin GH, Wang J, Ng V, Xia B, Witkowski MT, Mitchell-Flack M, Grillo I, Bakogianni S, Ndiaye-Lobry D, Martín MT, Guillamot M, Banh RS, Xu M, Figueroa ME, Dickins RA, Abdel-Wahab O, Park CY, Tsirigos A, Neel BG, Aifantis I. Restoration of TET2 Function Blocks Aberrant Self-Renewal and Leukemia Progression. Cell. 2017 Sep 7;170(6):1079-1095.e20. [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld JD, Sibenaller ZA, Mapuskar KA, Wagner BA, Cramer-Morales KL, Furqan M, Sandhu S, Carlisle TL, Smith MC, Abu Hejleh T, Berg DJ, Zhang J, Keech J, Parekh KR, Bhatia S, Monga V, Bodeker KL, Ahmann L, Vollstedt S, Brown H, Shanahan Kauffman EP, Schall ME, Hohl RJ, Clamon GH, Greenlee JD, Howard MA, Schultz MK, Smith BJ, Riley DP, Domann FE, Cullen JJ, Buettner GR, Buatti JM, Spitz DR, Allen BG. O2⋅- and H2O2-Mediated Disruption of Fe Metabolism Causes the Differential Susceptibility of NSCLC and GBM Cancer Cells to Pharmacological Ascorbate. Cancer Cell. 2017 Apr 10;31(4):487-500.e8. Erratum in: Cancer Cell. 2017 Aug 14;32(2):268. [CrossRef]
- Carosio R, Zuccari G, Orienti I, Mangraviti S, Montaldo PG. Sodium ascorbate induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cell lines by interfering with iron uptake. Mol Cancer. 2007 Aug 30;6:55. [CrossRef]
- Saitoh Y, Okayasu H, Xiao L, Harata Y, Miwa N. Neutral pH hydrogen-enriched electrolyzed water achieves tumor-preferential clonal growth inhibition over normal cells and tumor invasion inhibition concurrently with intracellular oxidant repression. Oncol Res. 2008;17(6):247-55. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh Y, Yoshimura Y, Nakano K, Miwa N. Platinum nanocolloid-supplemented hydrogendissolved water inhibits growth of human tongue carcinoma cells preferentially over normal cells. Exp Oncol. 2009 Sep;31(3):156-62. [PubMed]
- Runtuwene J, Amitani H, Amitani M, Asakawa A, Cheng KC, Inui A. Hydrogen-water enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced inhibition of colon cancer. PeerJ. 2015 Apr 7;3:e859. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Liu YP, Bao W, Chen JS, Xi XW. RNA sequencing analysis reveals apoptosis induction by hydrogen treatment in endometrial cancer via TNF and NF-κB pathways. Transl Cancer Res. 2020 May;9(5):3468-3482. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Liu PY, Bao W, Chen SJ, Wu FS, Zhu PY. Hydrogen inhibits endometrial cancer growth via a ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated pyroptotic pathway. BMC Cancer. 2020 Jan 10;20(1):28. [CrossRef]
- Liu MY, Xie F, Zhang Y, Wang TT, Ma SN, Zhao PX, Zhang X, Lebaron TW, Yan XL, Ma XM. Molecular hydrogen suppresses glioblastoma growth via inducing the glioma stem-like cell differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 ;10(1):145. 21 May. [CrossRef]
- Akagi J, Baba H. Hydrogen gas restores exhausted CD8+ T cells in patients with advanced colorectal cancer to improve prognosis. Oncol Rep. 2019 Jan;41(1):301-311. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen JB, Kong XF, Mu F, Lu TY, Lu YY, Xu KC. Hydrogen therapy can be used to control tumor progression and alleviate the adverse events of medications in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Med Gas Res. 2020 Apr-Jun;10(2):75-80. [CrossRef]
- Mohd Noor MNZ, Alauddin AS, Wong YH, Looi CY, Wong EH, Madhavan P, Yeong CH. A Systematic Review of Molecular Hydrogen Therapy in Cancer Management. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Jan 1;24(1):37-47. [CrossRef]
- https://riordanclinic.org/what-we-do/high-dose-iv-vitamin-c/ Last accessed on October 28, 2023.
- Ngo B, Van Riper JM, Cantley LC, Yun J. Targeting cancer vulnerabilities with high-dose vitamin C. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 May;19(5):271-282. [CrossRef]
- Mahabir R, Tanino M, Elmansuri A, Wang L, Kimura T, Itoh T, Ohba Y, Nishihara H, Shirato H, Tsuda M, Tanaka S. Sustained elevation of Snail promotes glial-mesenchymal transition after irradiation in malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16:671–685. [CrossRef]
- E Cameron, L Pauling Supplemental ascorbate in the supportive treatment of cancer: Prolongation of survival times in terminal human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1976 Oct;73(10):3685-9. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad IM, Aykin-Burns N, Sim JE, Walsh SA, Higashikubo R, Buettner GR, Venkataraman S, Mackey MA, Flanagan SW, Oberley LW, Spitz DR. Mitochondrial O2*- and H2O2 mediate glucose deprivation-induced stress in human cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4254-63. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, D. Levitt Production and Excretion of Hydrogen Gas in Man. N Engl J Med 1969; 281:122-127. [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S, Ohta S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 2007 Jun;13(6):688-94. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radyuk, SN. Mechanisms Underlying the Biological Effects of Molecular Hydrogen. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(5):626-735. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Z, Xu X, Leng X. Roles of reactive oxygen species in cell signaling pathways and immune responses to viral infections. Arch Virol. 2016 Mar;162(3):603-610. [CrossRef]
- Ichihara M, Sobue S, Ito M, Ito M, Hirayama M, Ohno K. Beneficial biological effects and the underlying mechanisms of molecular hydrogen - comprehensive review of 321 original articles. Med Gas Res. 2015 Oct 19;5:12. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Yu H, Tu Q, He Q, Huang N. New Approaches for Hydrogen Therapy of Various Diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(5):636-649. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;144(1):1-11. [CrossRef]
- Podmore ID, Griffiths HR, Herbert KE, Mistry N, Mistry P, Lunec J. Vitamin C exhibits pro-oxidant properties. Nature. 1998 Apr 9;392(6676):559. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee SH, Oe T, Blair IA. Vitamin C-induced decomposition of lipid hydroperoxides to endogenous genotoxins. Science. 2001 Jun 15;292(5524):2083-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte TL, Lunec J. Review: When is an antioxidant not an antioxidant? A review of novel actions and reactions of vitamin C. Free Radic Res. 2005 Jul;39(7):671-86. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu Y, Zhow BP. Inflammation is a driving force of cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle. 2009 Oct 15;8(20):3267-73.
- Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002 Dec 19;420(6917):860-7.
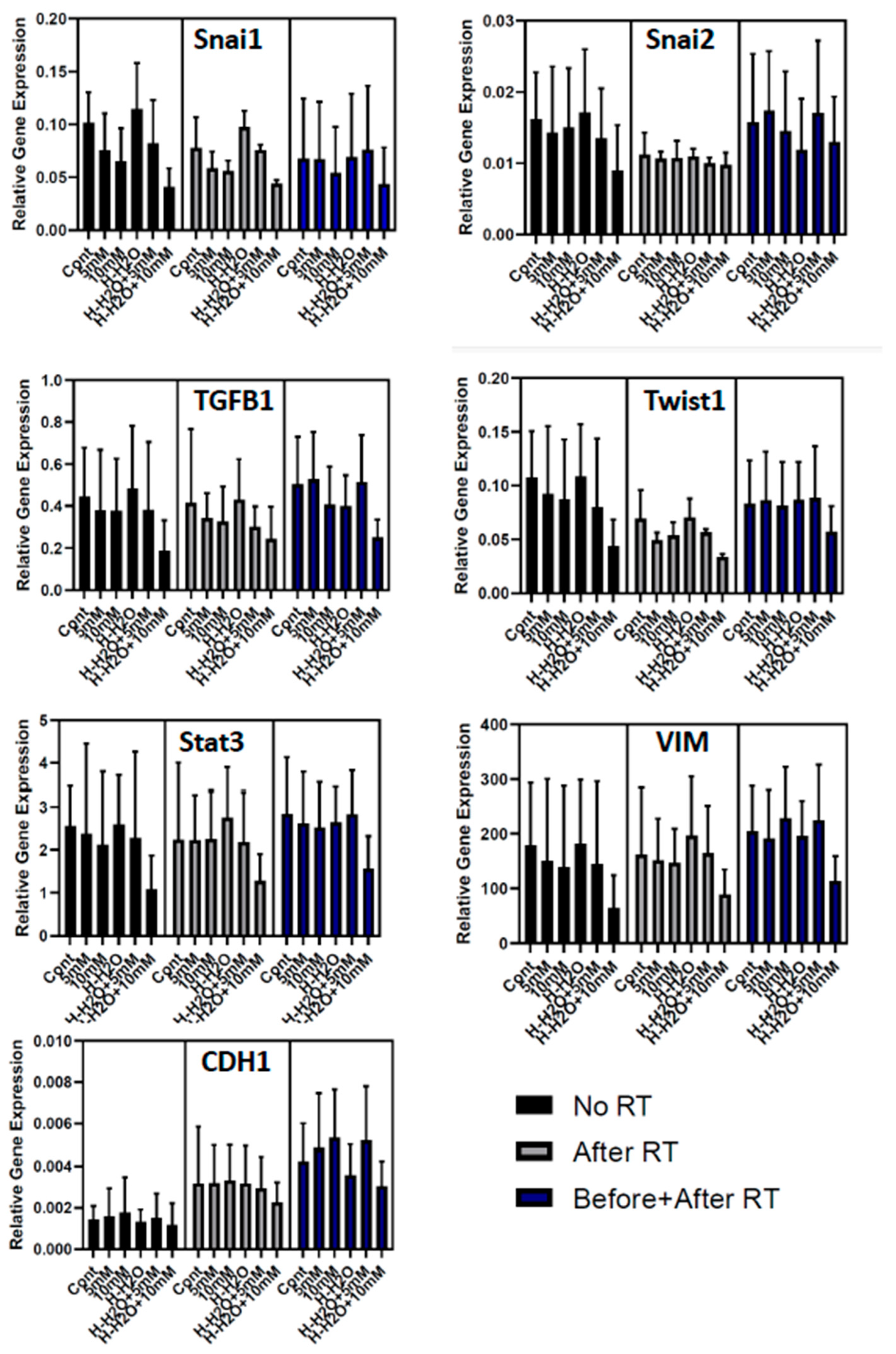
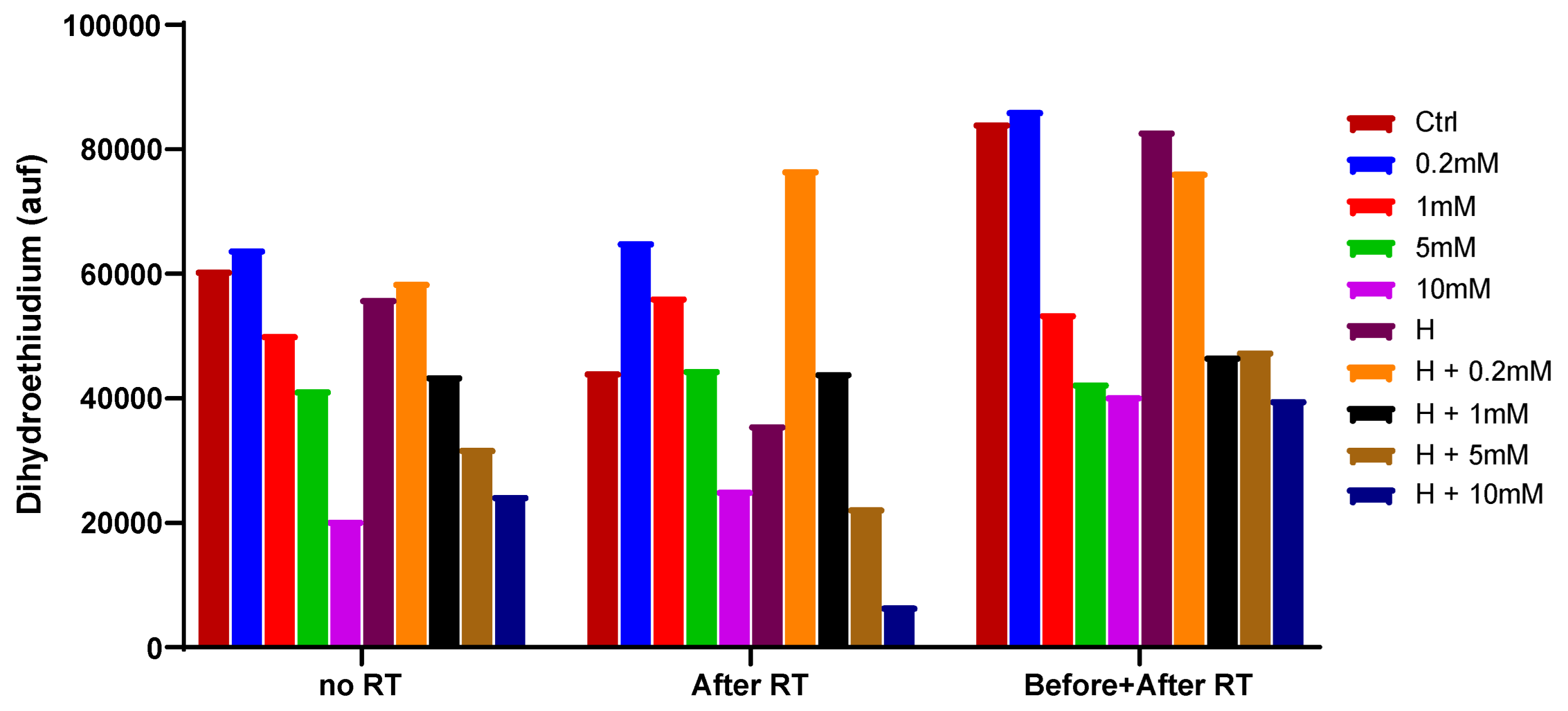
| control | VC0.2mM | VC1mM | H2 | H2+VC0.2mM | H2+VC1mM | |
| Without RD | 1 | 1.31 | 1.35 | 1.21 | 1.03 | 1.14 |
| Before RD | 1 | 1.37 | 1.34 | 1.27 | 1.31 | 1.56 |
| After RD | 1 | 1.47 | 1.47 | 1.14 | 1.37 | 1.52 |
| Before and After RD | 1 | 1.52 | 1.58 | 1.09 | 1.61 | 1.8* |
| control | VC0.2mM | VC1mM | H2 | H2+VC0.2mM | H2+VC1mM | |
| Without RD | 1 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.85 |
| Before RD | 1 | 1.09 | 0.75 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.63* |
| After RD | 1 | 0.74 | 0.62* | 0.81 | 0.65* | 0.44** |
| Before and After RD | 1 | 0.72* | 0.62** | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.44 *** |
| control | VC0.2mM | VC1mM | H2 | H2+VC0.2mM | H2+VC1mM | |
| Without RD | 1 | 0.85 | 0.72 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.54* |
| Before RD | 1 | 0.89 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.8 | 0.73* |
| After RD | 1 | 0.86 | 0.61* | 0.83 | 0.71* | 0.71* |
| Before and After RD | 1 | 0.9 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




