Submitted:
15 December 2023
Posted:
18 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Inducing wt-APC Expression
2.2. Cell Proliferation
2.3. WNT/β-Catenin Activity
2.4. NanoString Profiling
2.5. Western Blotting & Densitometry
2.6. Flow Cytometry and Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting
2.7. Determining synergistic, Additive, or Antagonistic Anti-Proliferative Effects of CYP26A1 and WNT Signaling Inhibitors
2.8. Patient Survival Studies
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
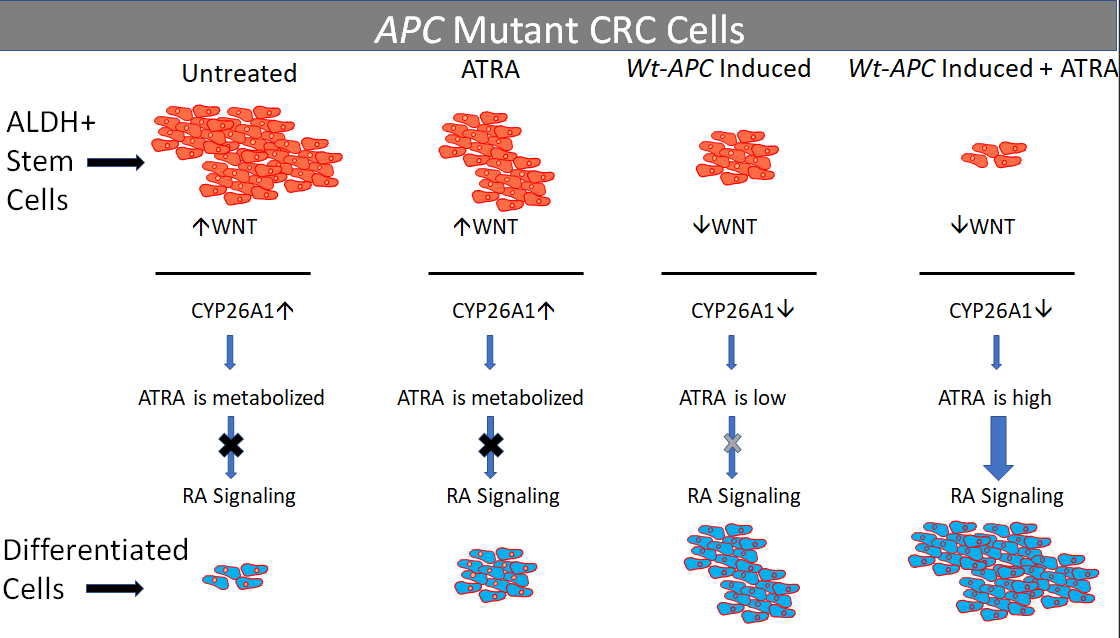
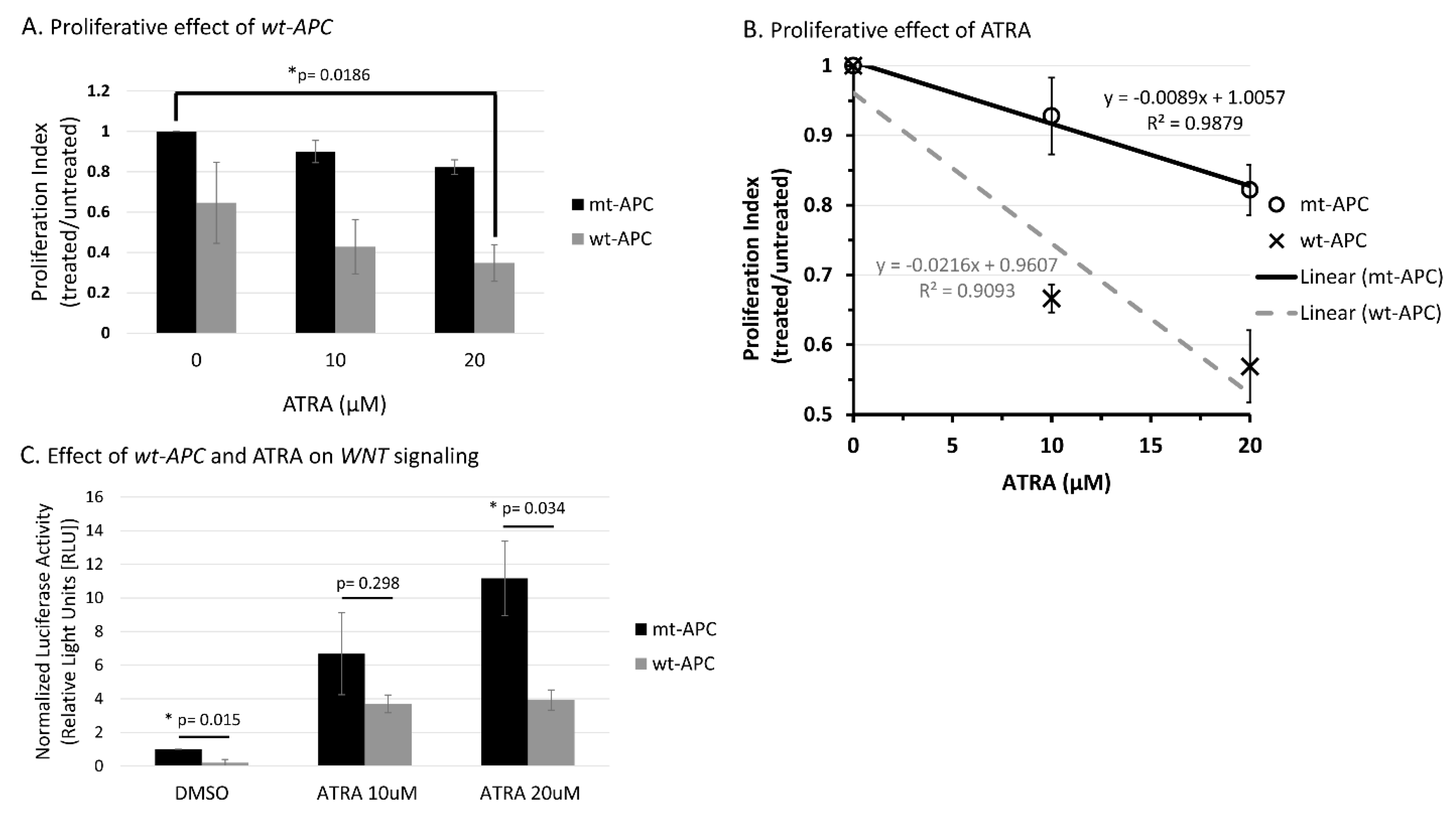
3.1. Inducing wt-APC Decreases WNT Signaling and Reduces Expression of WNT Target Genes
3.2. ATRA Promotes WNT/β-Catenin Activity, wt-APC Attenuates ATRA’s Effect
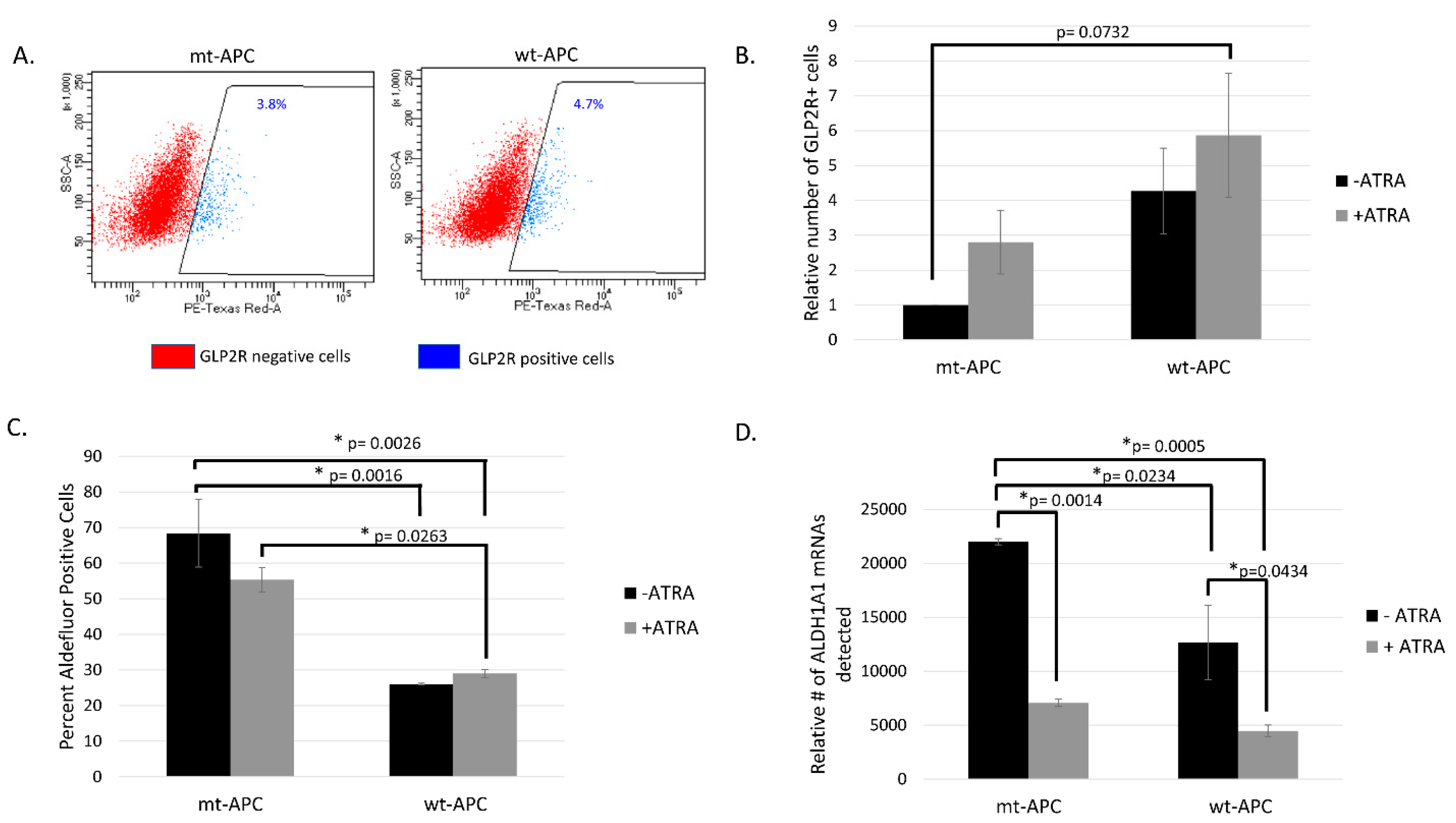
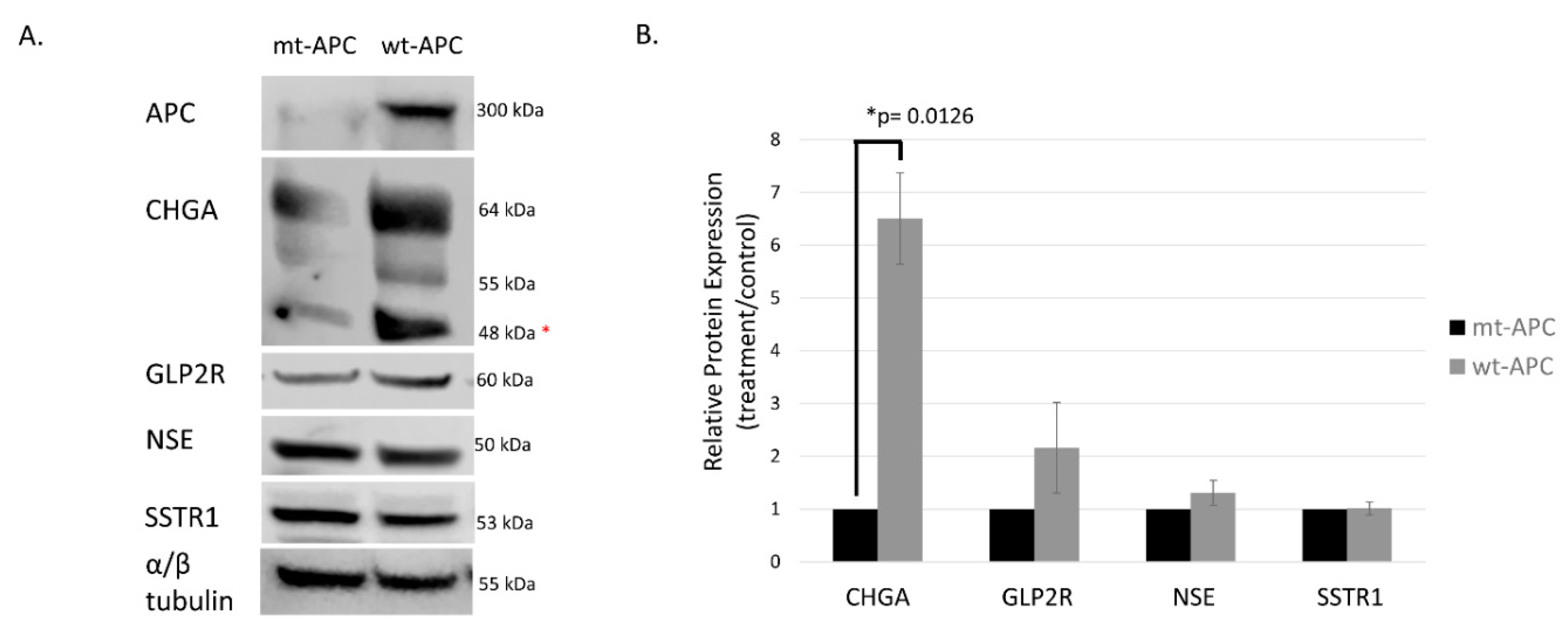
3.3. Inducing wt-APC Decreases ALDH+ Stem Cells and Increases NEC Differentiation
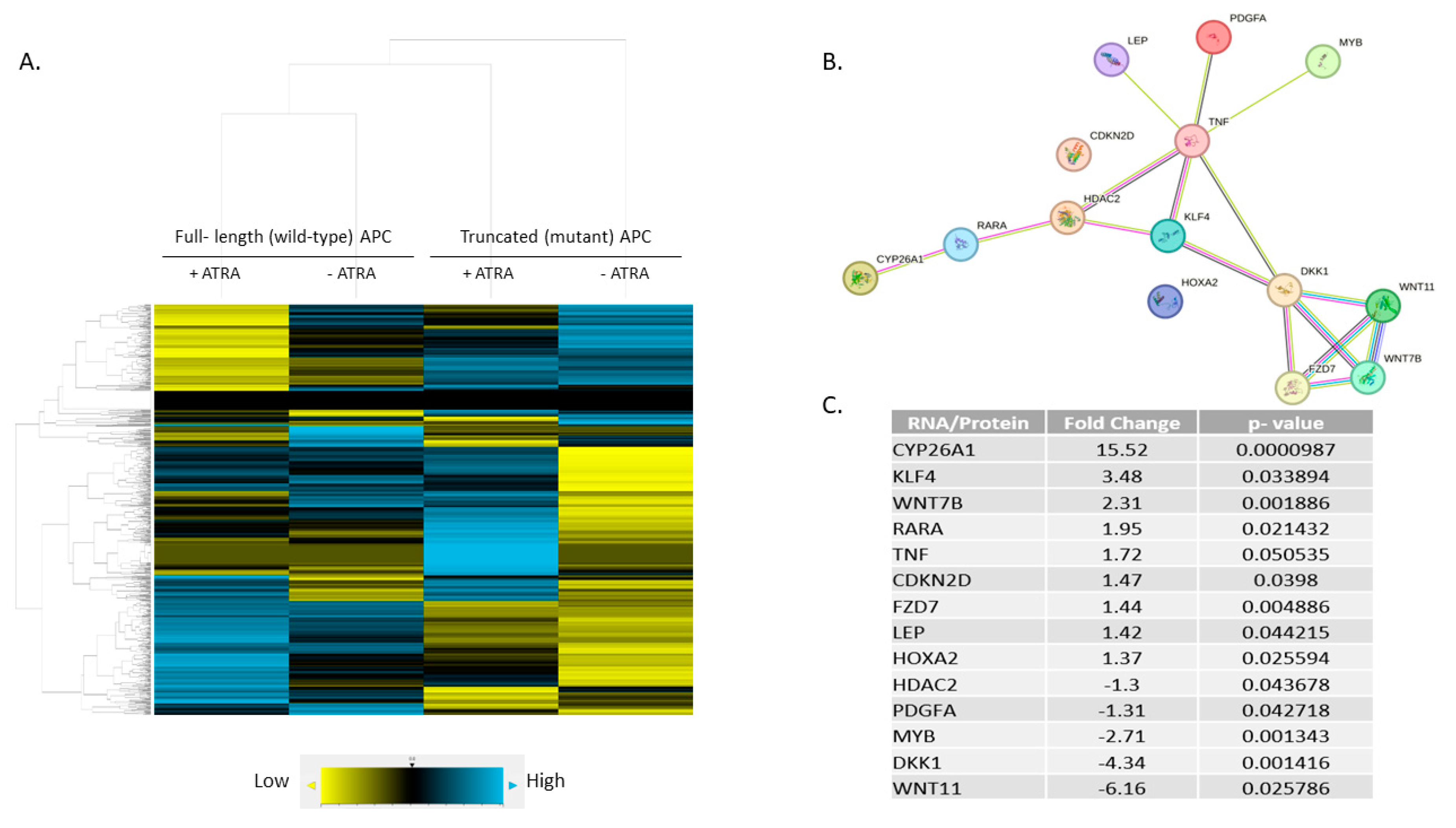
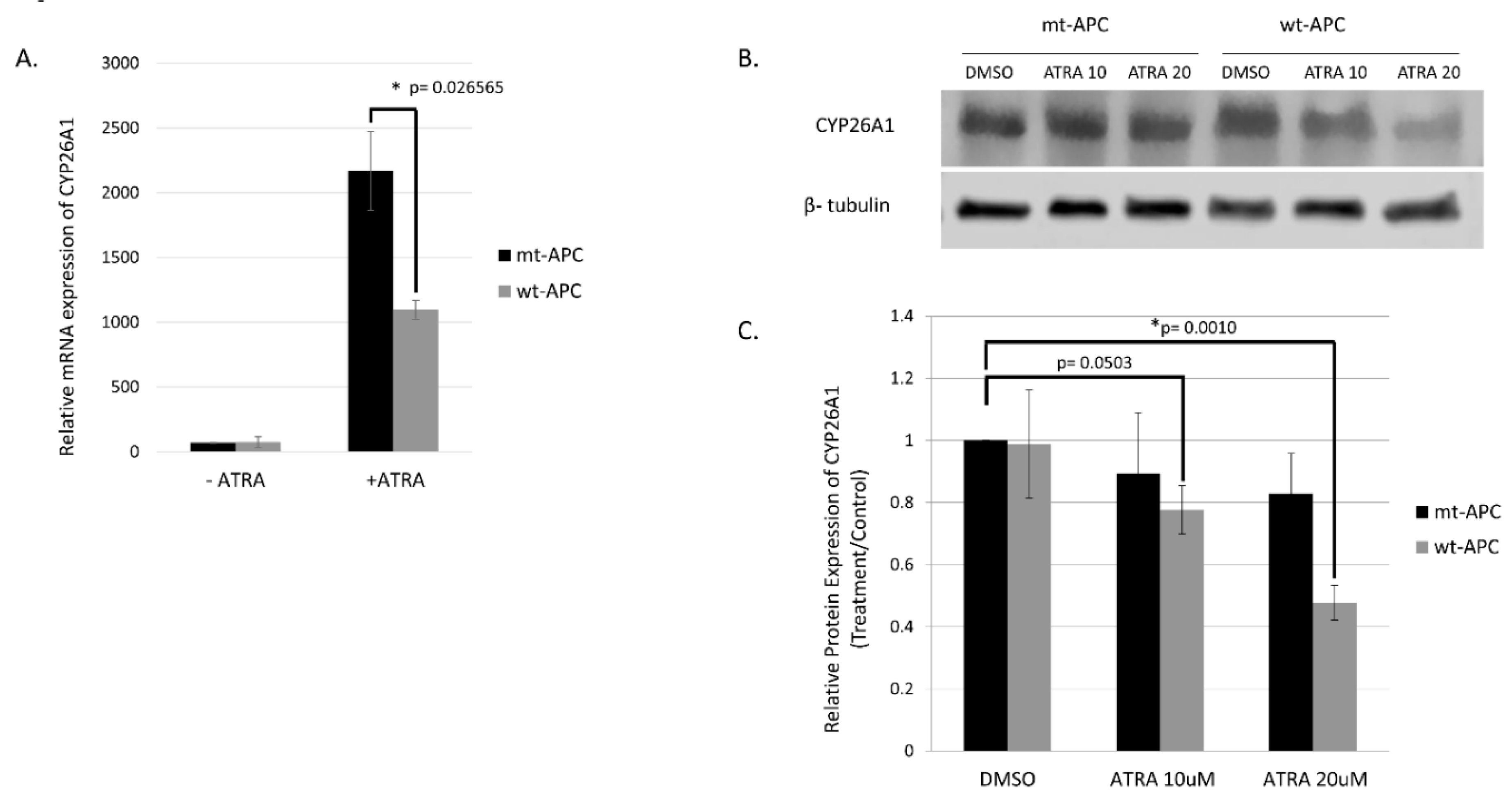
3.4. Expression Profiling Identified CYP26A1 as a Link between WNT and RA Signaling Pathways
3.5. CYP26A1 Inhibitor Agents Sensitize CRC Cells to the Anti-Proliferative Effect of Drugs That Downregulate WNT Signaling.
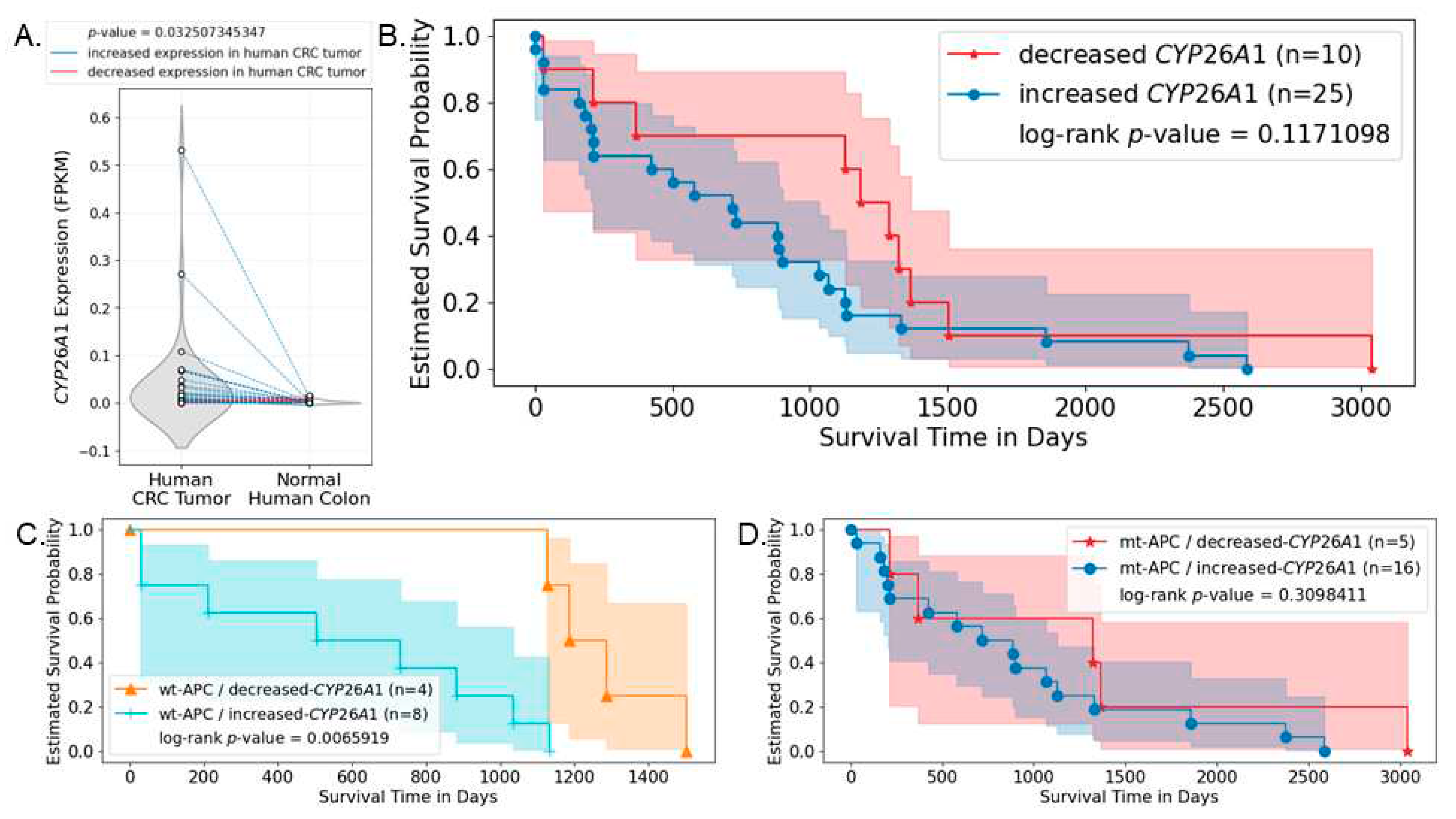
3.6. Analysis of Human CRC Cases Indicates CYP26A1 Predicts Survival of Patients with Wild-type APC Tumors
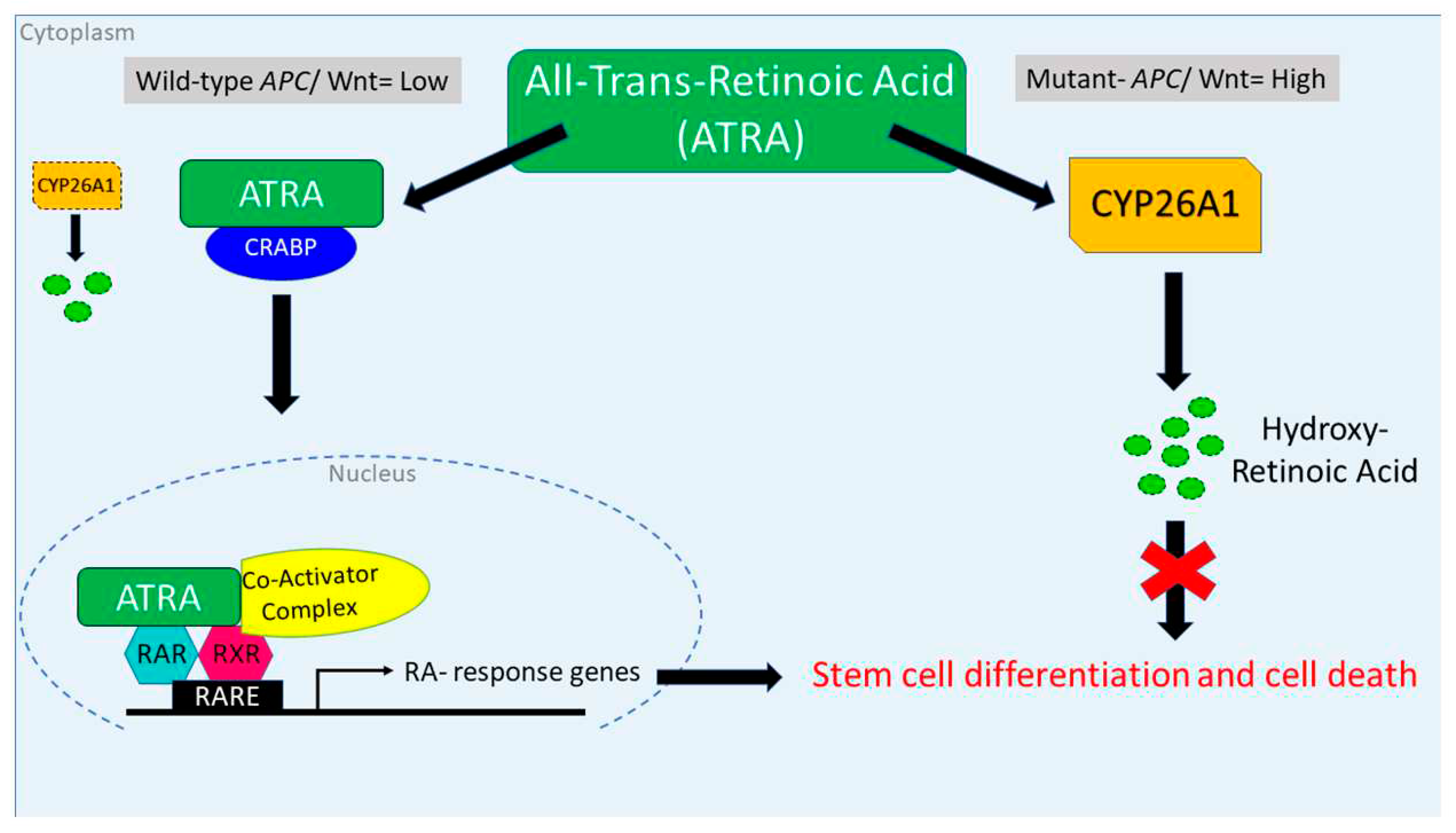
4. Discussion
- Q1 How is RA signaling regulated in ALDH+ SCs?
- Q2 How does dysregulation of RA signaling due to APC mutation contribute to overpopulation of ALDH+ SCs that drives development of CRC?
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Huang, E.H.; Hynes, M.J.; Zhang, T.; Ginestier, C.; Dontu, G.; Appelman, H.; Fields, J.Z.; Wicha, M.S.; Boman, B.M. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1 Is a Marker for Normal and Malignant Human Colonic Stem Cells (SC) and Tracks SC Overpopulation during Colon Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 3382–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boman, B.M.; Walters, R.; Fields, J.Z.; Kovatich, A.J.; Zhang, T.; Isenberg, G.A.; Goldstein, S.D.; Palazzo, J.P. Colonic Crypt Changes during Adenoma Development in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. Am J Pathol 2004, 165, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, I.; Allan, A.L. The Role of Human Aldehyde Dehydrogenase in Normal and Cancer Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep 2010, 7, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchitti, S.A.; Brocker, C.; Stagos, D.; Vasiliou, V. Non-P450 Aldehyde Oxidizing Enzymes: The Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Superfamily. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2008, 4, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M., A.; Bagirova, M.; Nehir, O.; Yaman, S.; Sefik, E.; Cakir, R.; Canim, S.; Elcicek, S.; Yesilkir, S. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase: Cancer and Stem Cells. In Dehydrogenases; InTech, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, W.J.; Stagos, D.; Marchitti, S.A.; Nebert, D.W.; Tipton, K.F.; Bairoch, A.; Vasiliou, V. Human Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Genes: Alternatively Spliced Transcriptional Variants and Their Suggested Nomenclature. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2009, 19, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.C.; Thapa, P.; Karki, R.; Das, S.; Mahapatra, S.; Liu, T.-C.; Torregroza, I.; Wallace, D.P.; Kambhampati, S.; Veldhuizen, P. Van; et al. Retinoic Acid Signaling Pathways in Development and Diseases. Bioorg Med Chem 2014, 22, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ahn, K.; Emerick, B.; Modarai, S.R.; Opdenaker, L.M.; Palazzo, J.; Schleiniger, G.; Fields, J.Z.; Boman, B.M. APC Mutations in Human Colon Lead to Decreased Neuroendocrine Maturation of ALDH+ Stem Cells That Alters GLP-2 and SST Feedback Signaling: Clue to a Link between WNT and Retinoic Acid Signalling in Colon Cancer Development. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0239601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, P.J.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Apoptosis and APC in Colorectal Tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996, 93, 7950–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Fields, J.Z.; Opdenaker, L.; Otevrel, T.; Masuda, E.; Palazzo, J.P.; Isenberg, G.A.; Goldstein, S.D.; Brand, M.; Boman, B.M. Survivin-Induced Aurora-B Kinase Activation. Am J Pathol 2010, 177, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Otevrel, T.; Gao, Z.; Gao, Z.; Ehrlich, S.M.; Fields, J.Z.; Boman, B.M. Evidence That APC Regulates Survivin Expression: A Possible Mechanism Contributing to the Stem Cell Origin of Colon Cancer. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 8664–8667. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, N.; Ridgway, R.A.; van Es, J.H.; van de Wetering, M.; Begthel, H.; van den Born, M.; Danenberg, E.; Clarke, A.R.; Sansom, O.J.; Clevers, H. Crypt Stem Cells as the Cells-of-Origin of Intestinal Cancer. Nature 2008, 457, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, L.E.; O’Rourke, K.P.; Simon, J.; Tschaharganeh, D.F.; van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H.; Lowe, S.W. APC Restoration Promotes Cellular Differentiation and Reestablishes Crypt Homeostasis in Colorectal Cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarai, S.R.; Gupta, A.; Opdenaker, L.M.; Kowash, R.; Masters, G.; Viswanathan, V.; Zhang, T.; Fields, J.Z.; Boman, B.M. The Anti-Cancer Effect of Retinoic Acid Signaling in CRC Occurs via Decreased Growth of ALDH Colon Cancer Stem Cells and Increased Differentiation of Stem Cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34658–34669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.W.; Palle, K. Aldehyde Dehydrogenases in Cancer Stem Cells: Potential as Therapeutic Targets. Ann Transl Med 2016, 4, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsu, V.O.; Facey, C.O.B.; Fields, J.Z.; Boman, B.M. Retinoids as Chemo-Preventive and Molecular-Targeted Anti-Cancer Therapies. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facey COB, Boman BM. Retinoids in Treatment of Colorectal Cancer [Online First], IntechOpen. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/online-first/retinoids-in-treatment-of-colorectal-cancerRetinoids. [CrossRef]
- Modarai, S.R.; Opdenaker, L.M.; Viswanathan, V.; Fields, J.Z.; Boman, B.M. Somatostatin Signaling via SSTR1 Contributes to the Quiescence of Colon Cancer Stem Cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boman, B.M.; Fields, J.Z. An APC:WNT Counter-Current-Like Mechanism Regulates Cell Division Along the Human Colonic Crypt Axis: A Mechanism That Explains How APC Mutations Induce Proliferative Abnormalities That Drive Colon Cancer Development. Front Oncol 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://Nanostring.Com/Products/Ncounter-Assays-Panels/Oncology/Ncounter-Pancancer-Pathways-Panel/.
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein–Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu Q, Yin X, Languino LR. Evaluation of drug combination effect using a Bliss independence dose-response surface model. Stat Biopharm Res 2018, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://Web.Stanford.Edu/Group/Nusselab/Cgi-Bin/Wnt/Target_genes.
- Boon, E.M.J.; van der Neut, R.; van de Wetering, M.; Clevers, H.; Pals, S.T. Wnt Signaling Regulates Expression of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Met in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 5126–5128. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, B.; Gelos, M.; Siedow, A.; Hanski, M.L.; Gratchev, A.; Ilyas, M.; Bodmer, W.F.; Moyer, M.P.; Riecken, E.O.; Buhr, H.J.; et al. Target Genes of β-Catenin–T Cell-Factor/Lymphoid-Enhancer-Factor Signaling in Human Colorectal Carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999, 96, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wielenga, V.J.M.; Smits, R.; Korinek, V.; Smit, L.; Kielman, M.; Fodde, R.; Clevers, H.; Pals, S.T. Expression of CD44 in APC and Tcf Mutant Mice Implies Regulation by the WNT Pathway. Am J Pathol 1999, 154, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.-C.; Sparks, A.B.; Rago, C.; Hermeking, H.; Zawel, L.; da Costa, L.T.; Morin, P.J.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Identification of C- MYC as a Target of the APC Pathway. Science 1998, 281, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedenmann, B.; Franke, W.W.; Kuhn, C.; Moll, R.; Gould, V.E. Synaptophysin: A Marker Protein for Neuroendocrine Cells and Neoplasms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986, 83, 3500–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://David.Ncifcrf.Gov/.
- Shelton, D.N.; Sandoval, I.T.; Eisinger, A.; Chidester, S.; Ratnayake, A.; Ireland, C.M.; Jones, D.A. Up-Regulation of CYP26A1 in Adenomatous Polyposis Coli-Deficient Vertebrates via a WNT-Dependent Mechanism: Implications for Intestinal Cell Differentiation and Colon Tumor Development. Cancer Res 2006, 66, 7571–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozpolat B, Mehta K, Lopez-Berestein G. Regulation of a highly specific retinoic acid-4-hydroxylase (CYP26A1) enzyme and all-trans-retinoic acid metabolism in human intestinal, liver, endothelial, and acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Leuk Lymphoma 2005, 46, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmer JE, Blomhoff R. Gene expression regulation by retinoic acid. J Lipid Res 2002, 43, 1773–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhinn M, Dollé P. Retinoic acid signalling during development. Development 2012, 139, 843–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadauld LD, Sandoval IT, Chidester S. Adenomatous polyposis coli control of retinoic acid biosynthesis is critical for zebrafish intestinal development and differentiation. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 51581–51589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadauld LD, Chidester S, Shelton DN. Dual roles for adenomatous polyposis coli in regulating retinoic acid biosynthesis and Wnt during ocular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006, 103, 13409–13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.; Buttrick, B.; Isoherranen, N. Therapeutic Potential of the Inhibition of the Retinoic Acid Hydroxylases CYP26A1 and CYP26B1 by Xenobiotics. Curr Top Med Chem 2013, 13, 1402–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penny, H.L.; Prestwood, T.R.; Bhattacharya, N.; Sun, F.; Kenkel, J.A.; Davidson, M.G.; Shen, L.; Zuniga, L.A.; Seeley, E.S.; Pai, R.; et al. Restoring Retinoic Acid Attenuates Intestinal Inflammation and Tumorigenesis in ApcMin/ Mice. Cancer Immunol Res 2016, 4, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idres, N.; Benoı̂t, G.; Flexor, M.A.; Lanotte, M.; Chabot, G.G. Granulocytic Differentiation of Human NB4 Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells Induced by All-Trans Retinoic Acid Metabolites. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.-W.; Shi, X.G.; Chu, H.Y.; Tong, J.H.; Wang, Z.; Naoe, T.; Waxman, S.M.; Chen, S.; Chen, Z. Effect of retinoic acid isomers on proliferation, differentiation and PML relocalization in the APL cell line NB4. Leukemia 1995, 9, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Chen, S.-J.; Tong, J.-H.; Wang, Z.-G.; Chen, G.-Q. Treatment of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with ATRA and As2O3: A Model of Molecular. Cancer Biol Ther 2002, 1, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Kantarjian, H.; Ravandi, F. Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Current Treatment Algorithms. Blood Cancer J 2021, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, M.; Tallman, M.S. Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL): Remaining Challenges towards a Cure for ALL. Leuk Lymphoma 2019, 60, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudas, L.J.; Wagner, J.A. Retinoids Regulate Stem Cell Differentiation. J Cell Physiol 2011, 226, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phi, L.T.H.; Sari, I.N.; Yang, Y.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Jun, N.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y. Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) in Drug Resistance and Their Therapeutic Implications in Cancer Treatment. Stem Cells Int 2018, 2018, 5416923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Vila, M.; Takahashi, R.; Usuba, W.; Kohama, I.; Ochiya, T. Drug Resistance Driven by Cancer Stem Cells and Their Niche. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boman, B.M.; Wicha, M.S. Cancer Stem Cells: A Step Toward the Cure. J Clin Oncol 2008, 26, 2795–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




