1. Introduction
Fibrogenesis is a key pathomechanism in various pulmonary diseases, particularly idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) [
1,
2,
3] and non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP); but occurs also in end-stage disease lungs of patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or sarcoidosis (SAR). Fibrogenesis leads to a remodelling of the delicate lung micro-architecture into compact and rigid connective tissue. Due to the severe loss of lung function and the lack of an effective therapeutic option in IPF [
4], the mean survival time has been ranging between 2.5 and 3.5 years after diagnosis [
1,
5,
6] but some improvement is achieved with newly approved therapeutics like nintedanib and pirfenidone targeting signalling in FGF, PDGF and TGFβ pathways [
7,
8,
9]. The prognosis of non-IPF pulmonary fibrosis is in most cases more favourable compared with IPF although no approved therapeutics exists [
10,
11].
Current hypotheses on the onset of fibrosis postulate epithelial damage with ongoing repair processes either due to recurrent inflammation or repeated injuries. Thus, fibrosis is regarded a result from an abnormal wound-healing process in which aberrant cross-talk between fibroblasts and epithelial cells promotes chronic fibroblast proliferation [
12,
13,
14,
15]. This causes the release of several growth factors and cytokines resulting in an increased migration and proliferation of fibroblasts. Thus, fibroblasts are the key players in pulmonary fibrosis and their enhanced extracellular matrix deposition is a hallmark in pulmonary fibrosis [
12,
16].
Therapeutic options are rare as anti-inflammatory therapeutic approaches like steroids or cyclophosphamide have only little impact on fibrotic processes of the lung. While these drugs are of value in distinct forms of pulmonary fibrosis characterized by an inflammatory cell composition, e.g. non-specific-interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) [
6,
17], they are hardly effective in IPF the most common form of pulmonary fibrosis. Currently, two new drugs are approved for the therapy of mild to moderate fibrosis in IPF which, however, slow down disease progression but do not induce a “restitutio ad integrum” [
7,
8].
CC-chemokine 18 (CCL18) is a chemokine with chemotactic and immuno-regulatory functions mainly released by alternatively activated macrophages [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. Interestingly, CCL18 is unique in the chemokine system as it is present only in humans and there is currently no comparable chemokine known in rodents [
23,
24]. We found elevated CCL18 serum levels and increased CCL18 release by alveolar macrophages from patients suffering from pulmonary fibrosis [
25]. Moreover, we could demonstrate that both, CCL18 production by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells and serum CCL18 concentrations reflect pulmonary fibrotic activity [
26] and is a prognostic marker in IPF [
27].
The importance of CCL18 in fibrotic diseases is obvious by its collagen inducing properties [
28]. High levels of CCL18 are directly linked to the increased matrix deposition in pulmonary fibrosis [
25]. Vice versa, we could demonstrate that collagen recognition via CD204 increases CCL18 release by alveolar macrophages [
29] inducing a vicious cycle in IPF [
25]. Although the pro-fibrotic properties of CCL18 are already known, the transmission of the CCL18 signals are not clear as for long time CCL18 was one of the few chemokines with unknown receptor(s).
CCL18 signalling is inhibited by pertussis toxin pointing to a conventional G-protein coupled chemokine receptor [
28]. In addition, the induction of matrix production by CCL18 in human fibroblasts is triggered via the ERK-pathway [
28] and PKCα [
30], two signal transduction molecules which are known to be triggered by other chemokines like CCL2 or other CC chemokines via G-protein coupled chemokine receptors [
31,
32]. We therefore aimed to identify the receptor for CCL18 responsible for its pro-fibrotic properties. The identification of such a receptor would provide a new therapeutic target in disorders with increased levels of CCL18 like fibrosis [
25] and cancer [
33]. Our data suggest that the CC-chemokine Receptor 6 (CCR6) expressed on fibroblasts mediates the pro-fibrotic activity of CCL18.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phage display peptide library screenings
A cyclic random phage display peptide library with seven random residues (CX
7C; C = cysteine; X = random amino acid) was cloned and generated as described previously for phage [
34] and for plasmid libraries in the context of the adeno-associated viral genome [
35,
36]. The library was screened on recombinant CCL18 as described previously for epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies [
37,
38] after two-fold negative selection on irrelevant control proteins BSA and casein. The screening was done for three selection rounds. Randomly selected clones from the third panning round were sequenced (GATC, Konstanz, Germany).
2.2. Patients
Fibroblast lines were established either from surgical material, from explanted lungs (n=13), pneumectomies or lobectomies from patients suffering from squamous carcinoma (n=19) or from remaining material obtained from left-over of diagnostic biopsies of fibrotic lungs (video-assisted thoracoscopy (VATS, n=4), transbronchial biopsies (TBB, n=4) from patients suffering from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF, n=13), non-specific interstitial pneumonitis (NSIP, n=3), sarcoidosis, (n=3) or hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP, n=2). All of of NSIP are “non-classified NSIP” as no underlying diseases could be detected.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University Medical Centre Freiburg (vote number 276/02, renewed in 2007).
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
Tumour free lung tissues were obtained from surgery (lobectomy or pneumonectomy) due to non-small cell lung cancer; only specimens at least 7cm away from the tumour were selected as tumour free and only those confirmed by microscopy entered the study. Tissues were fixed and embedded in paraffin using the HOPE-technique [
39]. Immunohistochemical detection of CC-chemokine receptor 6 (CCR6) was performed as previously described [
39,
40]. Primary antibody (anti hCCR-6 mouse monoclonal IgG, clone 53103, 500 µg/mL, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minnesota) was applied after de-paraffinization in a dilution of 1/100 for 1h at ambient temperature. Detection of signals was achieved by application of ZytoChem Plus HRP polymer system (Zytomed Systems, Berlin, Germany) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. Aminoethylcarbazole (permanent AEC, Zytomed Systems, Berlin) was used as a chromogen.
2.3. Isolation of primary fibroblasts
Lung tissue was cut in small pieces (app. 0.5 cm edge length) and placed in 6-well plates containing 1mL Quantum 333 (PAA, Pasching, Austria) with 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Quantum 333 is a fibroblast selection medium to allow the growth of the cells without the addition of foetal calf serum. Outgrowing fibroblasts were harvested by trypsinisation when they reached approximately 80% confluence, cultured in 75cm2 cell culture flasks (NUNC Thermo Fisher, Roskilde, Denmark) in Quantum 333 or DMEM with 10% FCS and subsequently split (1:3 to 1:5). The established lines were enrolled in our studies from passages 3 to ensure that no other cells (e.g. macrophages) are in our culture to 8 to prevent senescence of the cells. Phase contrast microscopy photographs of three different cell lines are depicted in
Figure S1.
2.4. Cell lines
Rat lung epithelial cells were obtained from ATCC (Teddington, Middlesex, UK) and cultured in HAM-F12 (Lonza, Verviers, Belgium) containing 10% foetal bovine serum (FCS gold, PAA, Pasching, Austria), 10 µg/mL bovine pituitary extract (Gibco, Invitrogen, Paisley, UK), 5 µg/mL insulin (Sigma, Taufkirchen, Germany), 2.5 ng/mL insulin-like growth factor (ImmunoTools, Friesoythe, Germany), 1.25 µg/mL transferrin (Gibco, Invitrogen, Paisley, UK), and 2.5 ng/mL EGF (ImmunoTools, Friesoythe, Germany).
U937 cells are a pro-monocytic lymphoma cell line originally derived from a male patient. We found that in our laboratory cell line a large percentage of cells express CCR6. We therefore used anti-CCR6 antibodies (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minnesota) and anti-mouse IgG microbeads (Miltenyi. Bergisch-Gladbach, Germany) and MACS cell enrichment columns (Miltenyi) to enrich CCR6 positive U937 cells in order to establish a “U937*CCR6+” cell line (
Figure S2). The cells were cultured in DMEM (Gibco, Invitrogen, Paisley, UK), containing 10% foetal bovine serum (FCS gold, PAA, Pasching, Austria) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco, Invitrogen, Paisley, UK).
The mouse embryonal fibroblast line NIH/3T3 was obtained from ATCC and cultured in DMEM (Gibco, Invitrogen, Paisley, UK), containing 10% foetal bovine serum (FCS gold, PAA, Pasching, Austria) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco, Invitrogen, Paisley, UK). All cells are incubated at 37°C at 5% CO2.
2.5. Flow cytometry
Fibroblasts populations were gated by forward/sideward scatter and surface expression of CCR6 was estimated using a FITC-labelled anti-human CCR6 antibody (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) and a suitable IgG control. As CCR6 is a trypsin-sensitive molecule, trypsinized cells were allowed to recover in medium in polystyrene tubes (to avoid adhesion) for at least 3h at 37°C before staining.
2.6. FGF2-Determination
Fibroblasts were seeded at a density of 300.000 cells per well in a 6-well cell culture plate in Quantum 333 medium. Cells were allowed to attach overnight and the medium was replaced with 1 mL of DMEM plus 10% FCS. Cells were either left non-stimulated or were stimulated with 10 ng/mL of CCL18. To block CCR6/CCL18 interaction a blocking antibody against CCR6 (R&D systems, Wiesbaden, FRG) or an irrelevant antibody (mouse anti human IgG, R&D Systems) was added to a final concentration of 20 µg/mL in parallel cultures. After 24h of culture the supernatant was harvested and stored at -80°C until FGF2 determination. FGF2 was measured using an ELISA development kit (R&D) and performed as suggested by the supplier.
2.7. Real-time PCR
After the indicated culture period total RNA was extracted using TRIzol Reagent according to the manufacturer's protocol (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany). Total RNA was reverse-transcribed with StrataScript RT (Stratagene, CA) using oligo (dT)12-18 primers to produce cDNA according to the manufacturer's protocol. Specific primers for human CCR6, collagen 1, alpha-smooth muscle actin and GAPDH were designed using AmplifX 1.7.0 (
https://inp.univ-amu.fr/en/amplifx-manage-test-and-design-your-primers-for-pcr) [
41] using LocusLink and GenBank databases (National Center for Biotechnology Information;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/LocusLink/index.html). Accession code numbers for the nucleotide sequences used to generate the respective primers and the primer sequences are depicted in
Table 1.
All primers were intron-spanning and synthesized by biomers (
https://www.biomers.net/). Real time PCR was performed with the iQ SYBR Green SuperMix, iCycler thermocycler, and iCycler iQ 3.0 software (Bio-Rad Laboratories GmbH, Germany) according to the manufacturer's protocol. After initial denaturation (10 minutes, 95°C) PCR was performed using an annealing time of 30 seconds at 57°C, amplification for 30 seconds, and 15 seconds at 94°C for denaturation for 45 cycles. To control for specificity of the amplification products, a melting curve analysis was performed. No amplification of nonspecific products was observed in any of the reactions. A threshold cycle value (Ct) was calculated and used to compute the relative level of specific mRNA by the following formula:
2.8. Stable transfection of RLE-6TN
As the human CCR6 vector (pORF9-hCCR6, InvivoGen, San Diego, California) does not have a Sal I or Sma I cleavage site, the vector was first cut with EcoRV and a Sal I linker was integrated into the cleavage site. In order to create a GFP fusion protein, a part of the coding sequence of CCR6 was re-synthesized together with a Sma I cleavage site, the stop codon at the C-terminal end was removed and ligated back into the original vector. Only then the cleavage was carried out with Sal I and Sma I.
3-5x105 293T-cells were transfected with pCDNL B**, pLTR VSVG and pNL CEV CCR6*GFP using FuGeneHD (Roche Diagnostics, Penzberg). After 24h the medium was replaced and after 48h virus supernatant was used to infect RLE-6TN.
Stable transfected RLE-CCR6*GFP cells were separated from wild-type cells by fluorescence activated cell sorting and limiting dilution. The purity of the cells was 99% and was stable during the culture periods.
2.9. Knock-down of CCR6 in NIH/3T3 cells by CRISPR/Cas9
Primer sequences for the generation of CRISPR/Cas9 were selected from the gRNA design tool by ThermoFischer (ThermoFisher, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) (thermofisher.com/crisprdesign) and synthesized by biomers (
https://www.biomers.net/). The following primer sequences were used: ATAATCATCCGTTCCAAAGT and GTAGACGTCAGTCATGGATC. The gRNA was then synthesized and transcribed using the GeneArt Precision gRNA Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen/ThermoFisher, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). GeneArt Platinum Cas9 Nuclease protein (Invitrogen/ThermoFisher) and the gRNAs were then used to transfect the cells using the Lipofectamine™ CRISPRMAX™ Transfection Reagent (Invitrogen/ThermoFisher) according to the protocol provided by the manufacturer. After transfection the cells were cultured for two days, harvested and cloned by limiting dilution. Clones were picked and expanded and analysed for CCR6 expression. CCR6-negative clones were expanded and used for the experiments.
2.10. Receptor internalization
Receptor internalization was estimated using flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy. CCR6 is a trypsin-sensitive receptor thus, it is lost during the detachment of adherent cells using trypsin. To avoid artefacts by damaging CCR6 by trypsinization, we used the non-adherent U967*CCR6+ cell line. The cells were incubated with CCL18 or CCL20 in varying concentrations ranging from 0.03 to 1000 nM in 30µl of culture medium containing 100,00 cells for 20 minutes and immediately fixed by addition of 200µl of cold paraformaldehyde (4%, Sigma, Taufkirchen, Germany) for 5 minutes on ice. The cells were then washed by the addition of 1 mL PBS and centrifugation. This step was performed twice. Subsequently the cells were stained with a FITC-labelled anti-human CCR6 antibody (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) and analysed using a FACS Calibur (Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany) and FlowJo for data analysis (Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany).
For fluorescence microscopy RLE-CCR6*GFP were seeded on chamber slides and cultured over night at 37°C and 5% CO2 to allow to adhere. The next day the medium was discarded and replaced by medium containing 10 ng/mL of CCL18. As control we added CXCL10 in the same concentration. After the indicated time points, the cells were fixed and embedded in Vecta shield containing DAPI (Vector Laboratories, Newark, CA, United States) and analysed using a fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Hamburg, Germany).
2.11. Co-immunoprecipitation
For co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) 107 RLE-6TN CCR6*GFP cells were cultured overnight in a petri dish to let them adhere and subsequently loaded with 500ng/mL recombinant human CCL18 (Immunotools, Friesoyte, Germany) for 10 and 30 minutes. After incubation loaded cells were gently lysed using the lysing buffer provided by the manufacturer and CCR6*GFP was isolated using the isolation kit for GFP-tagged proteins according the manufacturers protocol (Miltenyi, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany). The isolated CCR6*GFP and CCR6*GFP/CCL18 complexes were analysed by routine western blot. In brief: isolated proteins were boiled at 95°C for 5 minutes in equal volumes of loading buffer (0,5M Tris-HCl pH 6.8, 2% SDS, 0,05% bromophenol blue, 20% 2-mercaptoethanol, 10% Glycerol) and subjected to 12% sodium dodecyl-sulphate–PAGE, separated by electrophoresis and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (PVDF). After blocking for 2h in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) containing 5% non-fat dry milk, the membranes were incubated with primary antibody against CCR6 (CKR6/C20, Santa Cruz, California) and anti-CCL18 (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) both diluted 1:700 with TBS at 4°C overnight. Visualization was performed using appropriate secondary antibodies labelled with IRDye 800CW or IRDye 700CW (Li-COR Bioscience, Bad Homburg, Germany) diluted 1:10000-1:20000 for 2 h and scanned using Odyssey system (Li-COR Bioscience) according to the manufactures instructions.
2.12. Statistical analysis
Data are shown as median, box plots or bar charts. For comparison of independent samples Mann-Whitney test were performed using StatView for Windows (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Values of p≤0.05 were considered statistically significant.
4. Discussion
CCL18 was identified as a structural homolog of MIP1α (CCL3) and is primarily released by alternatively activated macrophages [
44]. Just three years later it was found that CCL18 mRNA is up-regulated in the lungs of patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis [
45]. CCL18 gained interest as it stimulates collagen production in lung fibroblasts [
28,
43]. We demonstrated that CCL18 and collagen production are strongly connected [
25,
29] and that CCL18 is of prognostic usefulness in IPF [
26,
27]. However, although these results point to an important role of CCL18 in lung fibrosis, no information was available on the receptor responsible for its pro-fibrotic properties. Here we demonstrate that the pro-fibrotic effects of CCL18 are based on the expression of and the signal transduction by CCR6 in lung fibroblasts.
The role of CCR6 as a CCL18 receptor in fibrotic lung diseases was demonstrated by different approaches. Immunohistochemistry revealed CCR6 expression in human lung tissue from patients suffering from fibrotic lung diseases but not in tissue from lung cancer patients. The data show that different cells are affected including fibroblast as well as alveolar type II cells. Likewise, CCR6 was only expressed on fibroblasts from lungs of patients suffering from fibrotic lung diseases. In contrast, lung fibroblasts from lungs of controls (i.e. tumour free tissue from cancer patients) did not express CCR6. Thus, CCR6 expression in lung tissue might be a marker for an ongoing fibrotic process. In the current manuscript we focus on fibroblasts as these cells are the main drivers of pulmonary fibrosis by their capability to release large amount of matrix protein. In addition, expression of α-smooth muscle protein turns the fibroblasts into contractible so called myofibroblasts, a cell type frequently found in pulmonary fibrosis.
CCR6 was first described as a receptor for the chemokine CCL20 [
46]. Our data demonstrate that indeed CCL18 and CCL20 both down-regulate CCR6 receptor expression in a dose dependent manner. However, the concentration required to reach a 50% downregulation are 10-fold higher for CCL18 compared with CCL20. It has been hypothesized that the binding of CCL20 is dependent on a “DCCL” motive present in the receptor binding region of CCL20 [
47]. With a sequence of “LCCL” in this motive is different in CCL18 which might result in weaker binding of CCL18 to CCR6.
In fibroblast lines derived from fibrotic lungs CCL18 induces FGF2 release and increases collagen and αSMA expression which is inhibited by anti-CCR6 antibodies. This is of interest as current drugs like pirfenidone or nintedanib inhibit either the up-regulated release of FGF2 [
48] or inhibit signal transduction of the FGF2-receptor [
9]. As FGF2 release is upregulated by CCL18 it is tempting to speculate whether or not a therapy targeting CCL18/CCR6 is of additive value.
CCR6-dependent up-regulation of Col1A or αSMA was demonstrated by the fact that primary human fibroblasts without CCR6 did not react to CCL18 whereas CCR6 positive fibroblast lines up-regulate Col1A and αSMA after CCL18 stimulation. Blockade of CCR6 inhibited this up-regulation of both molecules.
Likewise, NIH 3T3 cells expressing high levels of CCR6 are comparable to human CCR6 positive fibroblast lines as they show a clear and dose dependent up-regulation of Col1A and αSMA after CCL18 stimulation. In contrast, upregulation of both markers is lost after knock-down of CCR6 on these cells. However, stimulation of the CCR6 KO cells with TGFβ induced a robust increase in αSMA and Col1A expression indicating that despite the CCR6 knock-down these cells are still able to increase αSMA and Col1A using other stimuli. These results strongly suggest that CCR6 expression on fibroblasts is crucial for the pro-fibrotic effects of CCL18.
Most interestingly, a mouse model of bleomycin-induced fibrosis showed that the administration of human CCL18 via an adenoviral vector increased TNF-, IFNγ-, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and increased lymphocytosis but attenuated unexpectedly the bleomycin induced collagen deposition [
49]. However, our own preliminary analyses indicated that in the bleomycin model CCR6 is not expressed on lung tissue cells (data not shown) and thus, the responsible, pro-fibrotic receptor is missing. Moreover, the loss of CCR6 resulted in a dose dependent down-regulation of αSMA expression in NIH 3T3 cells. This might be an explanation for the more or less protective activity of CCL18 in the experiments presented by Pochetuhen and colleagues [
49].
CCR6 is known to be expressed by CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells, by TNF activated granulocytes, immature dendritic cells, as well as by B cells and human intestinal cells but neither by macrophages nor by freshly isolated monocytes (summarized in [
50]). CCR6 gained interest because it was found to be highly expressed on IL-17 producing cells [
51] and on FoxP3 expressing IL-17 releasing regulatory T-cells [
52]. Thus, the expression on fibroblasts and alveolar epithelial cells is remarkable. The reason for this expression currently is unknown, however, it has been reported, that in human umbilical vein vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC) CCR6 expression is up-regulated by the combined stimulation with HGF and VEGF [
53]. In fibroblast-like synovial cells stimulation with IL-1β induced an up-regulation of CCR6 expression [
54]. In our experiments, upregulation of CCR6 in normal human lung fibroblasts using IL-4, IL-10, IL-13 and TGFβ in various combinations failed (
Figure S7). It is noteworthy that the increased CCR6 expression found in fibroblasts from patients suffering from IPF is stable over several culture passages of the fibroblast lines. Therefore, we conclude that the increased expression of CCR6 by fibroblast lines is not transiently induced by the surrounding cytokine milieu in the fibrotic lung but seems to be a key characteristic of fibroblasts from IPF lungs which is acquired during patho-mechanistic differentiation.
We found a concordant expression of CCR6 on lung fibroblasts demonstrated by immunohistochemistry of fibrotic lung and by flow cytometric analysis of fibroblast lines isolated from lungs of patients suffering from IPF and NSIP. The fact that not all fibroblast lines from IPF lungs express CCR6 might be caused by the heterogeneity of fibroblasts in fibrotic lungs as described earlier [
55]. In addition, lung remodelling in IPF is not homogeneously distributed. Severely destructed areas with massive accumulation of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix build a patchwork with areas of almost normal or even completely normal lung histology [
56]. In addition, evaluation of our fibroblast lines by the sampling source (explant, VATS, TBB) revealed a clear but insignificant difference between the different sampling methods. Explanted tissue derives from patients with a widely remodelled and dysfunctional end stage lung. In contrast VATS and TBB are diagnostic procedures and performed at less advanced lung remodelling. Thus, it is conceivable that fibroblasts although grown from an IPF lung sample might be CCR6 negative if this sample has been taken from a region of more or less normal histology. However, high CCR6 expression might also be a feature of an advanced disease reflecting the tremendous remodelling of the lung.
Lung tissue from patients with sarcoidosis and HP were used in the experiments described here and derived from explanted lungs after lung transplantation due to massive pulmonary fibrosis. Both diseases are based on an inflammatory background and are different from IPF/UIP [
10]. Despite the fact that these patients suffered from lung fibrosis, the fibroblast lines isolated from these lungs showed no CCR6 expression. Although based on a small number of cell lines, this lack of expression is remarkable. Even though these diseases are also associated with increased CCL18 levels [
25,
45] a clear correlation of CCL18 levels with the natural course of the disease has not been shown. In contrast, in IPF CCL18 is a prognostic marker and phases of acute exacerbations are accompanied with increasing CCL18 levels [
27]. Thus, we speculate that the interaction of CCR6 and CCL18 might be pivotal for the progress of IPF whereas in fibrosis due to sarcoidosis or HP these processes are obviously driven by other factors.
We used fibroblast lines established from lungs of patients with squamous carcinoma as controls. The tissue was harvested far from the tumour and was therefore considered to be normal. It is of interest that in sera from patients with squamous carcinoma CCL18 levels are also increased, however, theses CCL18 levels have no impact on the survival time of these patients [
33].
In summary, we conclude that CCR6 is an important receptor involved in pro-fibrotic activities of CCL18 and blocking of CCL18/CCR6 interaction or the signalling cascade induced by this interaction is an interesting therapeutic option for IPF.
Figure 1.
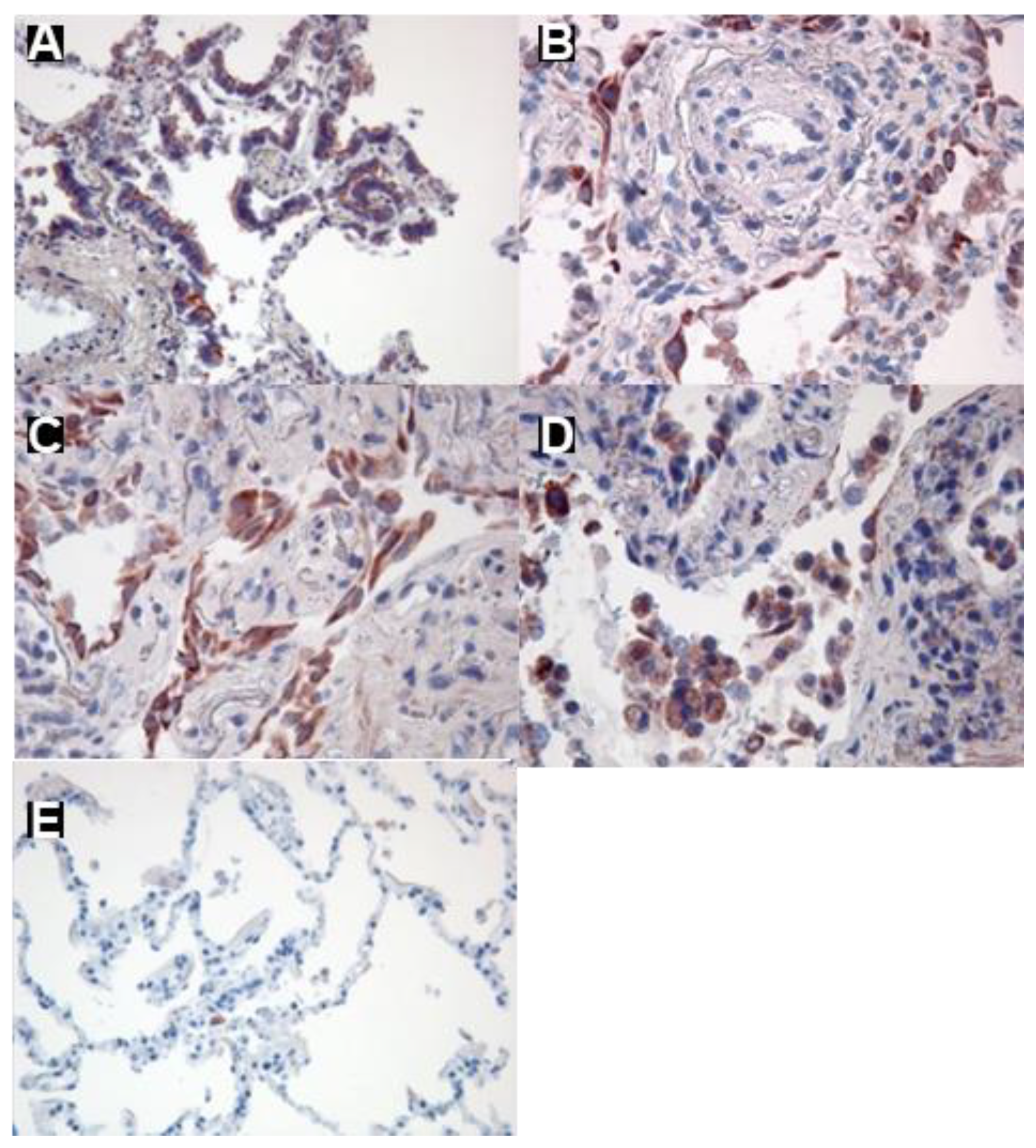
Expression of CCR6 in human lung tissue and lung fibroblast lines: A-E: Immunohistochemical staining of CCR6. CCR6 expression (red) is visible in bronchial epithelia (A), hyperplastic alveolar epithelial cells type II (B), fibroblasts (C) and probably macrophages (D) in a lung section from an IPF patient. In contrast, in a tumour-free lung from a cancer patient without COPD only a few cells, possibly macrophages, were found to express CCR6 (E) Magnifications A, B, and C: 200x, B and C: 400x.
Figure 1.
Expression of CCR6 in human lung tissue and lung fibroblast lines: A-E: Immunohistochemical staining of CCR6. CCR6 expression (red) is visible in bronchial epithelia (A), hyperplastic alveolar epithelial cells type II (B), fibroblasts (C) and probably macrophages (D) in a lung section from an IPF patient. In contrast, in a tumour-free lung from a cancer patient without COPD only a few cells, possibly macrophages, were found to express CCR6 (E) Magnifications A, B, and C: 200x, B and C: 400x.
Figure 2.
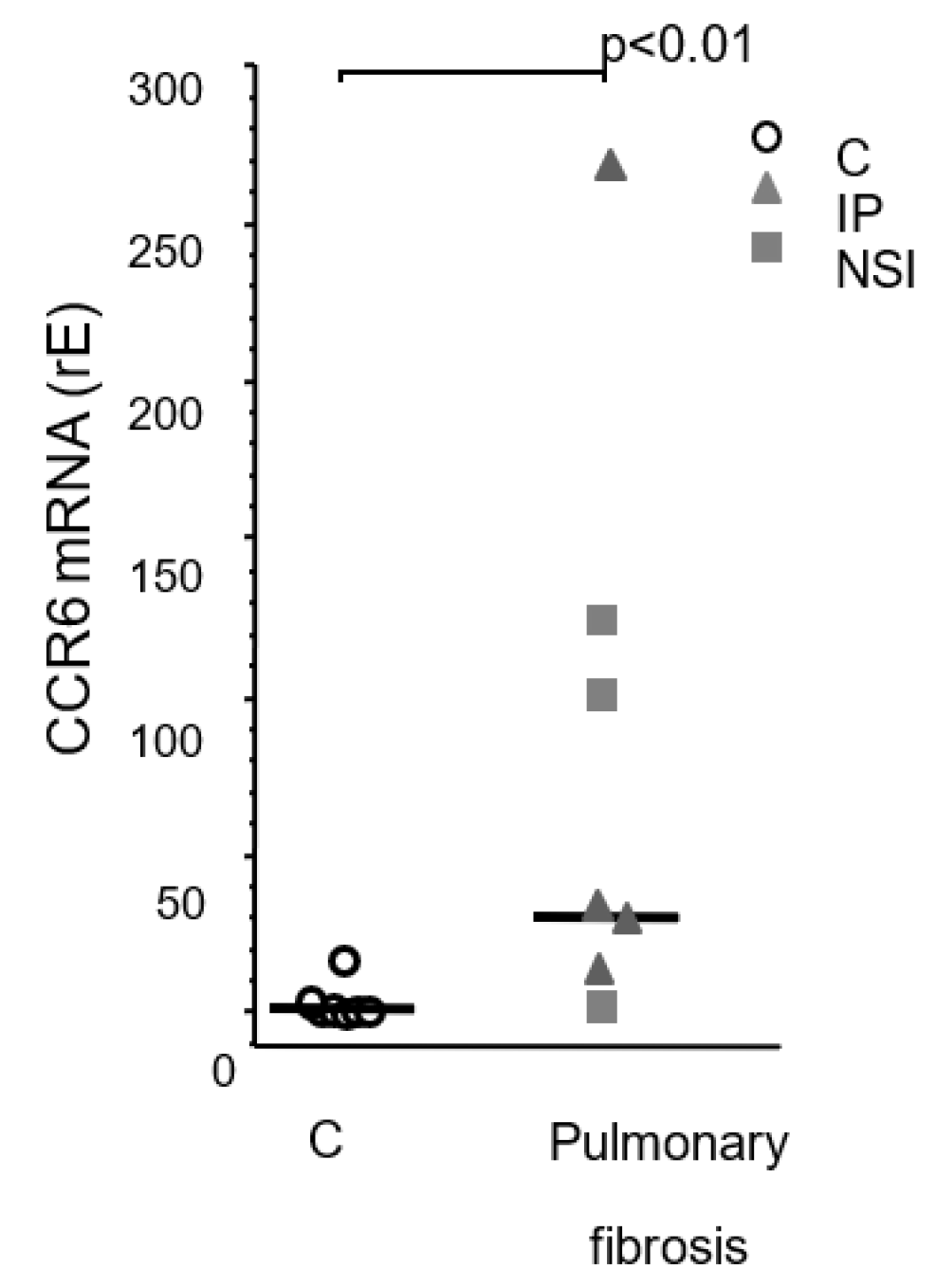
CCR6 mRNA in human primary fibroblast lines. Quantitative PCR analysis of CCR6 expression by different fibroblast lines from patients suffering from squamous carcinoma (control; n=7) and pulmonary fibrosis (UIP: n=4, NSIP: n=3). Control fibroblasts did.
Figure 2.
CCR6 mRNA in human primary fibroblast lines. Quantitative PCR analysis of CCR6 expression by different fibroblast lines from patients suffering from squamous carcinoma (control; n=7) and pulmonary fibrosis (UIP: n=4, NSIP: n=3). Control fibroblasts did.
Figure 3.
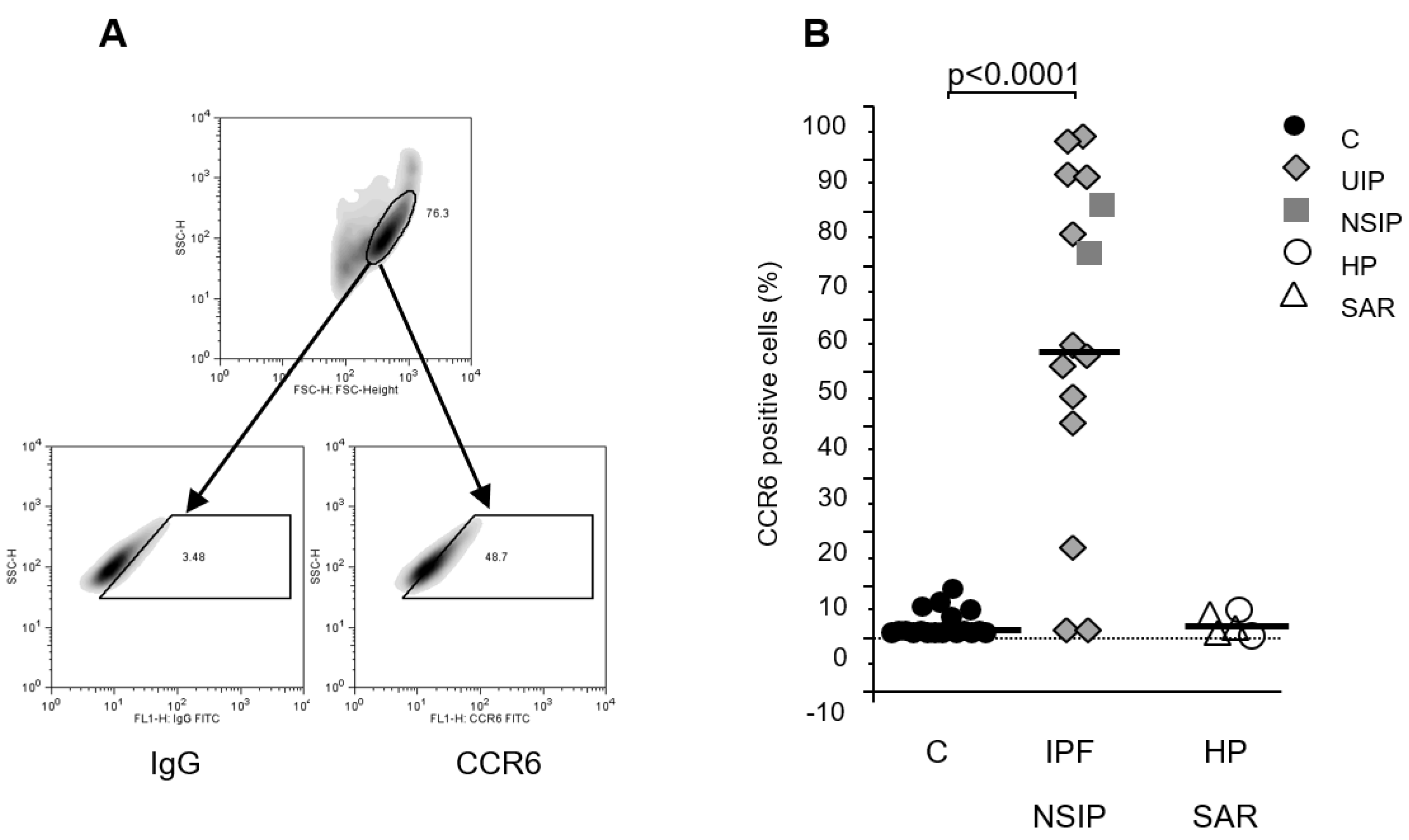
CCR6 protein expression in human primary fibroblast lines. Figure A depicts flow cytometry strategy: the cells were plotted in the forward/sideward scatter (SSC/FSC) and the population with the highest density was gated. Within this gate a second gate was defined using an isotype control IgG (left panel) and CCR6-stained cells within this gate were regarded as positive (right panel). (B) Analysis of the flow cytometry revealed a clear up regulation of CCR6 in fibroblasts lines established from pulmonary fibrosis patients (IPF and NSIP) compared to our controls (p<0.0001) but not in patients suffering from fibrosis due to sarcoidosis (SAR) or hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP).
Figure 3.
CCR6 protein expression in human primary fibroblast lines. Figure A depicts flow cytometry strategy: the cells were plotted in the forward/sideward scatter (SSC/FSC) and the population with the highest density was gated. Within this gate a second gate was defined using an isotype control IgG (left panel) and CCR6-stained cells within this gate were regarded as positive (right panel). (B) Analysis of the flow cytometry revealed a clear up regulation of CCR6 in fibroblasts lines established from pulmonary fibrosis patients (IPF and NSIP) compared to our controls (p<0.0001) but not in patients suffering from fibrosis due to sarcoidosis (SAR) or hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP).
Figure 4.
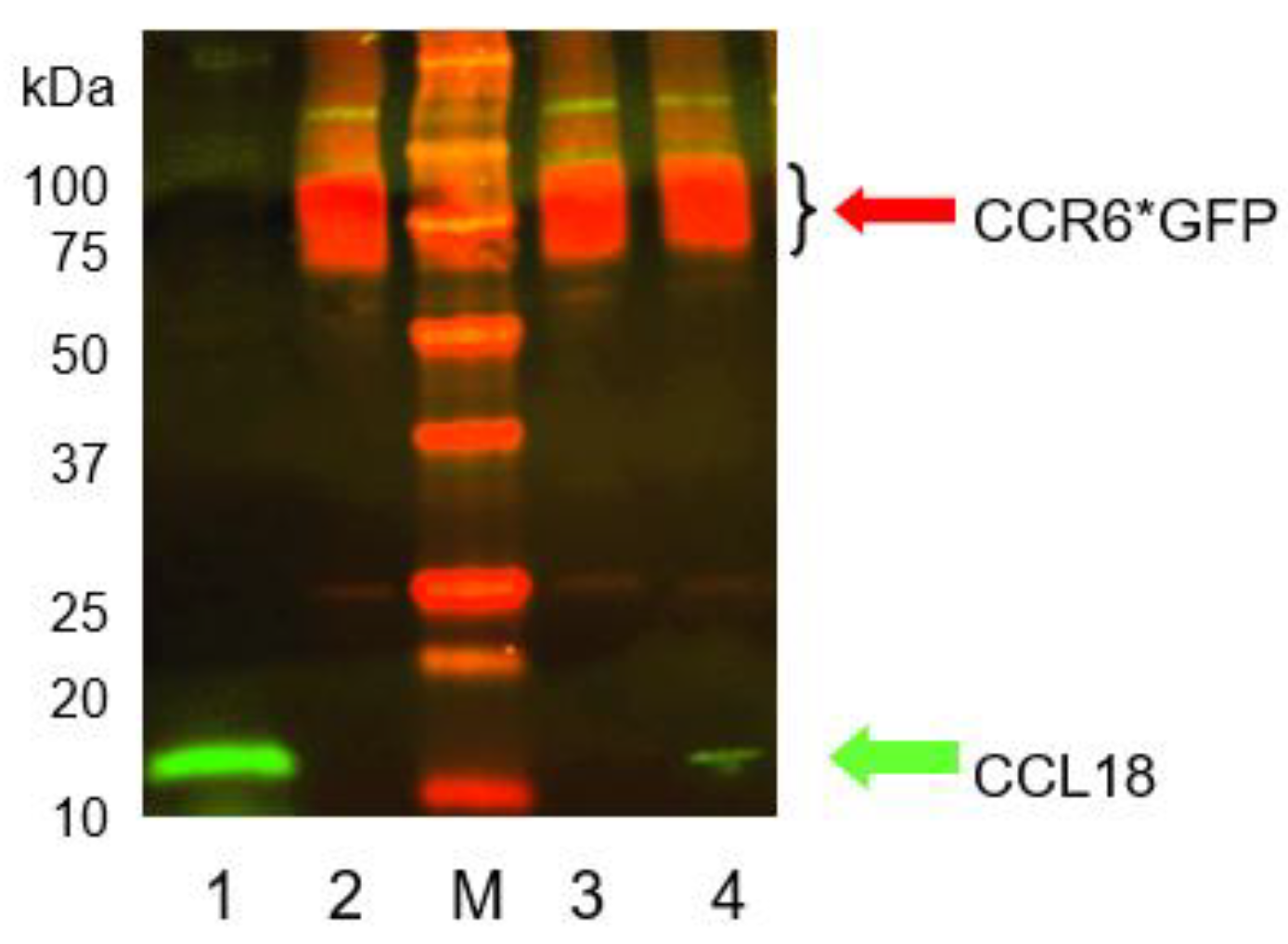
Co-immunoprecipitation of CCR6*GFP (red) and CCL18 (green). RLE-6TN cells were loaded with 500 ng/mL recombinant CCL18 and the receptor/ligand complex was gently isolated from the membranes using anti-GFP beads. Lane 1: CCL18 (20ng); lane 2: lysed RLE-6TN cells only; M: marker; lane 3: CoIP after 10 minutes of CCL18 incubation; lane 4: CoIP after 30 minutes of incubation. CCR6*GFP is visible in all RLE-6TN preparations irrespective of the addition of CCL18 (lane 2, 3, and 4). CCL18 loaded directly on the gel forms a bright band at the lower end of lane 1 (green). CoIP after 10 minutes of CCL18 incubation did not reveal a visible CCL18 band. However, after 30minutes of incubation CoIP disclosed a small but visible CCL18 band (lane 4 bottom). The figure depicts one gel out of two independent experiments.
Figure 4.
Co-immunoprecipitation of CCR6*GFP (red) and CCL18 (green). RLE-6TN cells were loaded with 500 ng/mL recombinant CCL18 and the receptor/ligand complex was gently isolated from the membranes using anti-GFP beads. Lane 1: CCL18 (20ng); lane 2: lysed RLE-6TN cells only; M: marker; lane 3: CoIP after 10 minutes of CCL18 incubation; lane 4: CoIP after 30 minutes of incubation. CCR6*GFP is visible in all RLE-6TN preparations irrespective of the addition of CCL18 (lane 2, 3, and 4). CCL18 loaded directly on the gel forms a bright band at the lower end of lane 1 (green). CoIP after 10 minutes of CCL18 incubation did not reveal a visible CCL18 band. However, after 30minutes of incubation CoIP disclosed a small but visible CCL18 band (lane 4 bottom). The figure depicts one gel out of two independent experiments.
Figure 5.
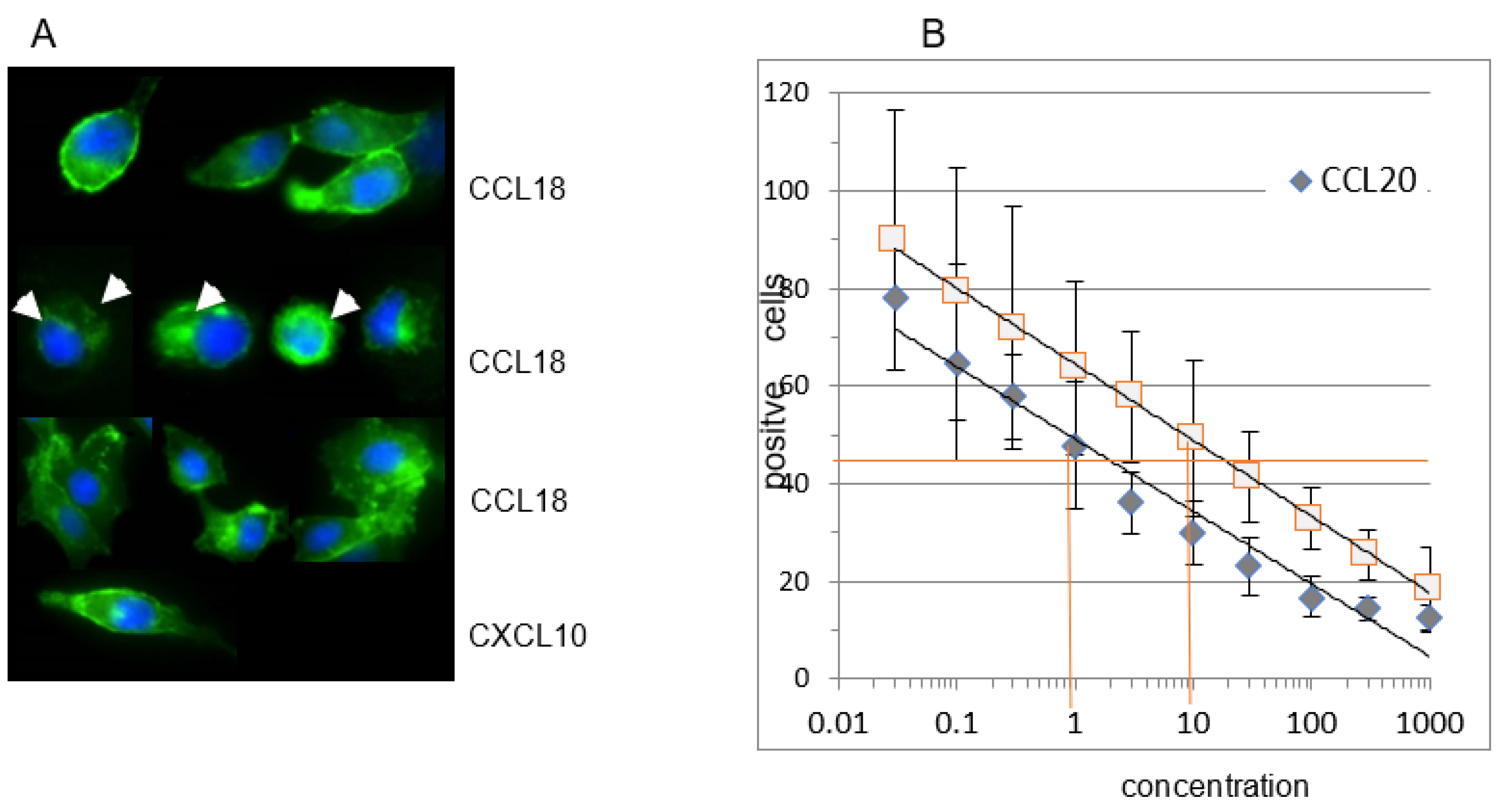
A) CCL18 induces receptor internalization in CCR6*GFP transfected RLE-6TN cells. At time point 0 the receptor is located at the outer rim of the cells. Incubation with rhCCL18 (10 ng/mL) for 5 minutes induces receptor internalization visible as a ring or as bright dots within the cells (white arrows). After 20min of incubation with rhCCL18 the CCR6*GFP distribution is merely diffuse. In contrast, incubation with the irrelevant chemokine CXCL10 for 20min does not induce receptor internalization (magnification 10x40; 1 of 3 replicates). (B) Loading CCR6+ U937 cells with a wide concentration range of CCL18 or CCL20 reveals a clear dose-dependent internalization of CCR6. It is obvious that for the same effect approx. 10-fold more CCL18 is necessary compared with CCL20. The figure shows one illustrative series out of three.
Figure 5.
A) CCL18 induces receptor internalization in CCR6*GFP transfected RLE-6TN cells. At time point 0 the receptor is located at the outer rim of the cells. Incubation with rhCCL18 (10 ng/mL) for 5 minutes induces receptor internalization visible as a ring or as bright dots within the cells (white arrows). After 20min of incubation with rhCCL18 the CCR6*GFP distribution is merely diffuse. In contrast, incubation with the irrelevant chemokine CXCL10 for 20min does not induce receptor internalization (magnification 10x40; 1 of 3 replicates). (B) Loading CCR6+ U937 cells with a wide concentration range of CCL18 or CCL20 reveals a clear dose-dependent internalization of CCR6. It is obvious that for the same effect approx. 10-fold more CCL18 is necessary compared with CCL20. The figure shows one illustrative series out of three.
Figure 6.
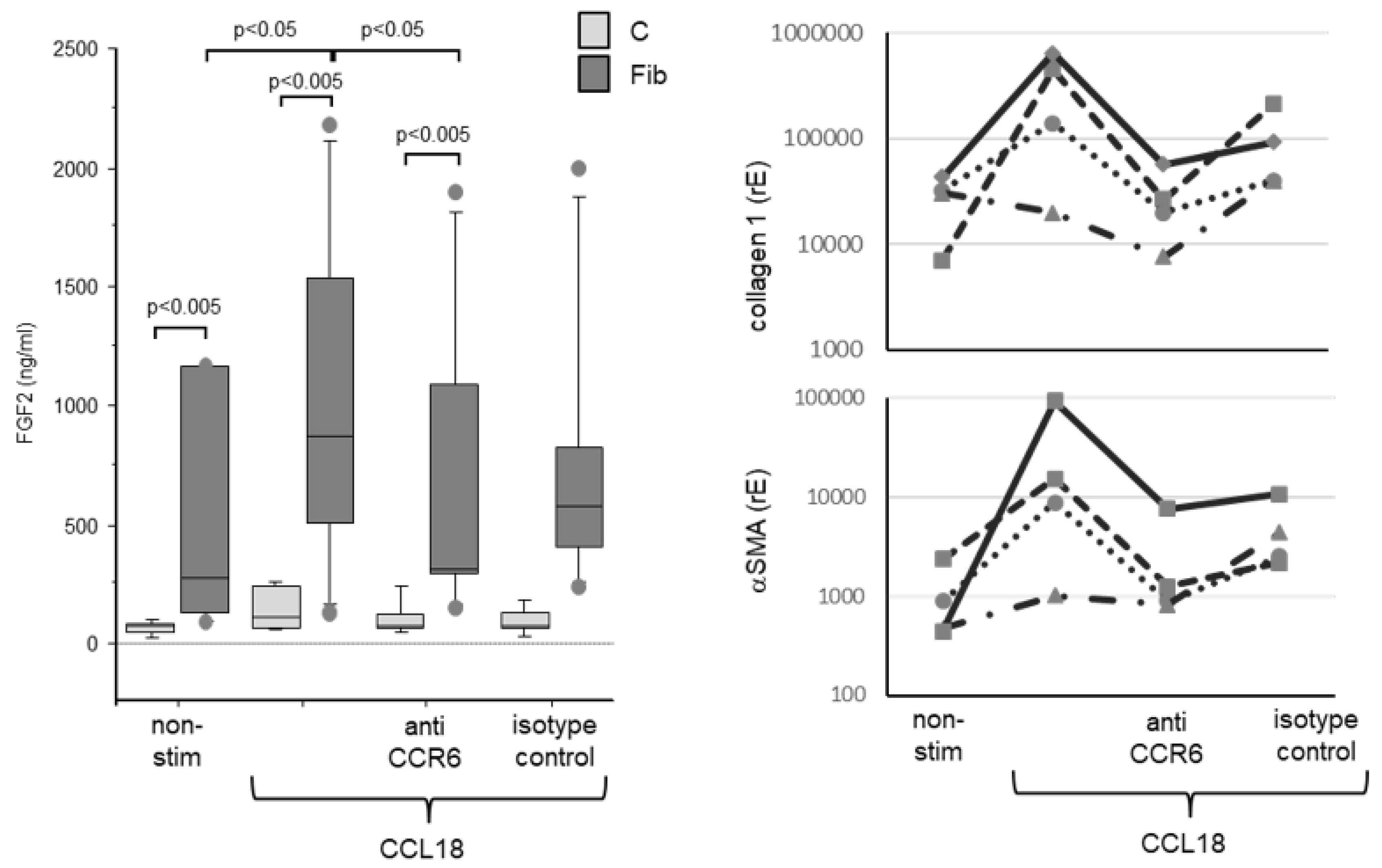
A FGF2 release of human lung fibroblasts. Fibroblasts from fibrotic tissue (dark bars) release significantly higher levels of FGF2 compared with control fibroblasts (light bars). CCL18 significantly increases FGF2 release in fibrotic fibroblasts but barely in control fibroblasts. The CCL18 induced up-regulation of FGF2 release is abrogated by the addition of an anti-CCR6 antibody. The isotype control induced an insignificant reduction of the FGF2 release (C = control: n=6; Fib = fibrosis: n=6). B CCL18 induced collagen 1 (upper panel) and alpha-smooth muscle actin (αSMA, (lower panel)) mRNA expression by human lung fibroblasts is blocked by anti-CCR6 (rE = relative Expression; n=4).
Figure 6.
A FGF2 release of human lung fibroblasts. Fibroblasts from fibrotic tissue (dark bars) release significantly higher levels of FGF2 compared with control fibroblasts (light bars). CCL18 significantly increases FGF2 release in fibrotic fibroblasts but barely in control fibroblasts. The CCL18 induced up-regulation of FGF2 release is abrogated by the addition of an anti-CCR6 antibody. The isotype control induced an insignificant reduction of the FGF2 release (C = control: n=6; Fib = fibrosis: n=6). B CCL18 induced collagen 1 (upper panel) and alpha-smooth muscle actin (αSMA, (lower panel)) mRNA expression by human lung fibroblasts is blocked by anti-CCR6 (rE = relative Expression; n=4).
Figure 7.
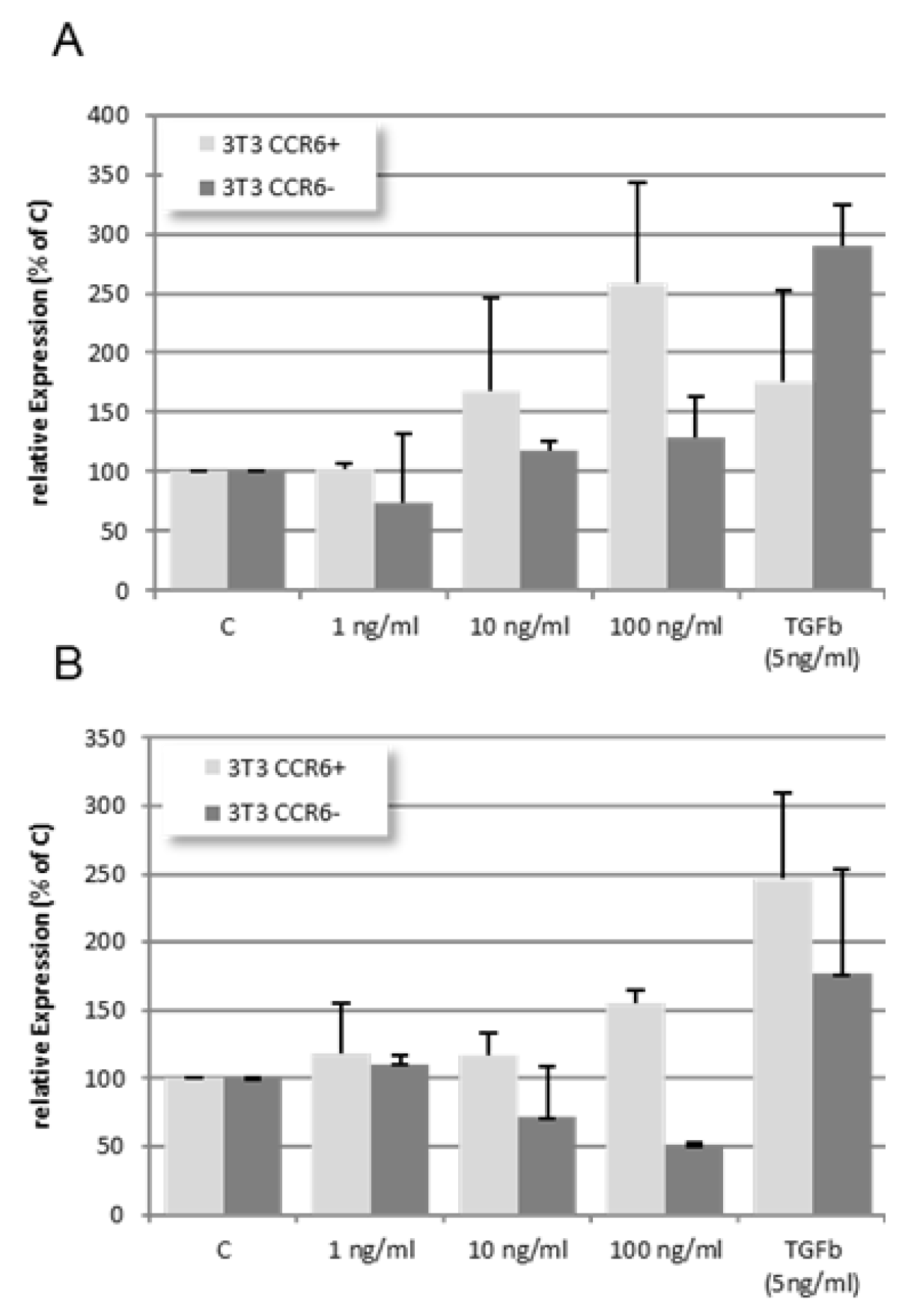
In wild type NIH 3T3 cells CCL18 induces a dose dependent increase in Col1A and αSMA mRNA expression. TGFβ induced less Col1A but more αSMA mRNA expression compared with the highest dose of CCL18. In contrast, in the CCR6 KO clone no up-regulation of Col1A mRNA expression was seen. Interestingly, αSMA mRNA expression is down-regulated in this clone (rE = relative Expression; n=4).
Figure 7.
In wild type NIH 3T3 cells CCL18 induces a dose dependent increase in Col1A and αSMA mRNA expression. TGFβ induced less Col1A but more αSMA mRNA expression compared with the highest dose of CCL18. In contrast, in the CCR6 KO clone no up-regulation of Col1A mRNA expression was seen. Interestingly, αSMA mRNA expression is down-regulated in this clone (rE = relative Expression; n=4).
Figure 8.
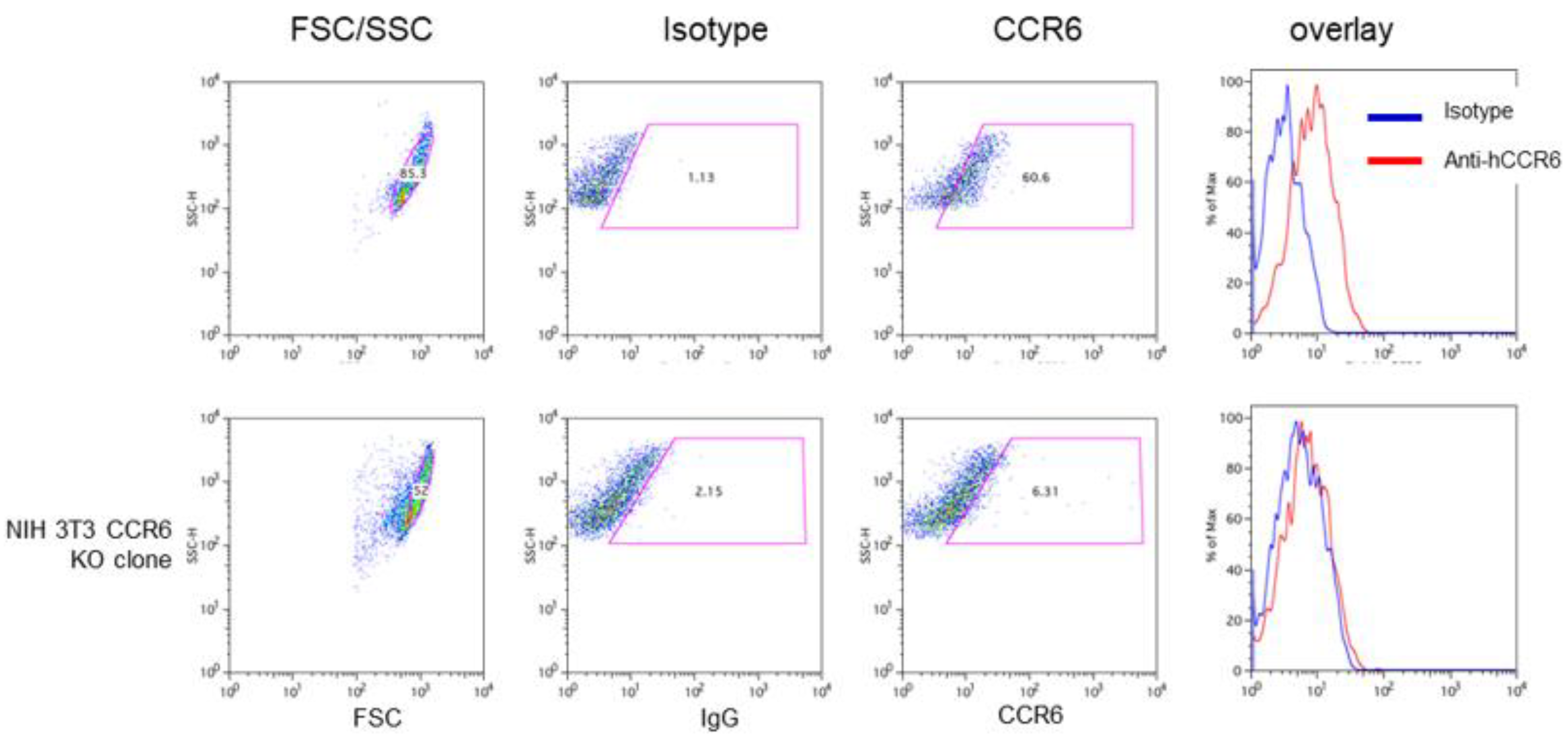
Wild type and CCR6 KO NIH 3T3 cells were harvested and stained using isotype and anti-CCR6 antibodies as described. Gating as well as overlay of the flow cytometric analyses demonstrate that wild type NIH 3T3 cells clearly express CCR6 on the surface (upper panel). In contrast, the 3T3 CCR6 KO clone does not express CCR6 anymore (lower panel).
Figure 8.
Wild type and CCR6 KO NIH 3T3 cells were harvested and stained using isotype and anti-CCR6 antibodies as described. Gating as well as overlay of the flow cytometric analyses demonstrate that wild type NIH 3T3 cells clearly express CCR6 on the surface (upper panel). In contrast, the 3T3 CCR6 KO clone does not express CCR6 anymore (lower panel).
Table 1.
List of primers used in qPCR together with the accession numbers used for generating the primers.
Table 1.
List of primers used in qPCR together with the accession numbers used for generating the primers.
| Gene |
accession
number |
forward primer |
reverse primer |
| hGAPDH |
NM_002046 |
CACCAGGGCTGCTTTTAACT |
GATCTCGCTCCTGGAAGATG |
| hCCR6 |
NM_004367
NM_031409 |
GCACAAAATGATGGCAGTGG |
CCGAAGCACTTCCAGGTTGT |
| hCollagen 1A1 |
NM_000088 |
CCCTGTCTGCTTCCTGTAAACT |
CATGTTCGGTTGGTCAAAGATA |
| hαSMA |
NM_001141945 |
CATCATGCGTCTGGATCTGG |
GGACAATCTCACGCTCAGCA |
| mGAPDH |
NM_001289726 |
GCGAGACCCCACTAACATCAAA |
cttttggctccacccttcaagt |
| mCollagen 1A1 |
NM_007742 |
TGCTGGGAAACATGGAAACCGA |
AGGTTCTCCTTTGTCACCTCGGAT |
| mαSMA |
NM_007392 |
cacccagcaccatgaagatcaagA |
CCTGTTTGCTGATCCACATCTGCT |