1. Introduction
Decision-making systems continue to be used in the analysis of maintenance activities and, in particular, in the risks of their tasks. Planning maintenance tasks can detect failures in advance and avoid production stops, and this objective has been considered in the development of strategic, tactical and operational systems due to their influence on long, medium and short-term decisions respectively. At a strategic level, Al-Turki [
1] concludes that planning should ensure alignment with other areas of the organization and the definition of a structured plan; in this line, systems that integrate strategic functions with Balanced Score-Card (BSC), using the Analytic Hierarchy Process, allow associated the Key Performance Indicators (KPI) to goals of company [
2]. Regarding tactical level, models based on BSC, capable of discovering structures and behavior patterns that are relatively hidden in work orders, using machining learning have been analyzed [
3]. Regarding operational level, a computer application has been designed, implemented and validated through the incorporation of RCM (Reliability Centered Maintenance) cases successfully carried out on an equipment [
4] or on a productive process [
5].
Thus, proposals that integrate maintenance plans oriented to reliability, risk, and cost have been defined [
6]. In circumstances when there are not training data, tools as a general mechanical functional modeling approach have been developed [
7]. Particular cases, as multistage industrial machines have been analyzed, concluding that for a preventive maintenance strategy, the study of individual maintenance times allow defining the KPIs [
8], while that a predictive maintenance strategy should be used when an unexpected failure occurs [
9]. Song et al. [
10] establishes a framework based on RCM that allow automatically evaluating the consequences of all equipment failures that are predefined, considering data from a multilevel flow modeling.
The application of methodologies such as RCM and Failure Modes, Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) allow knowing the Risk Priority Number (RPN); this number is a combination of the probability of severity, occurrence and detectability of risks. This indicator has been used to validate decision-making models and with different scales, for example [
11,
12] have propose a calculation for FMECA based on four fuzzy logic systems.
As has been seen, there are numerous proposals in the field of maintenance planning, some innovative and others with improvements in existing systems.
This article aims to provide the assisted system with a more consistent calculation of the RPN, considering the way in which the defining risk factors are introduced. The intention is to address two shortcomings present in the classic method: the numerical scoring of risk factors by experts does not necessitate a language closer to human understanding, and the assumption that risk factors are treated with the same importance for all proposed failure modes. From this point, the article attempts to analyze alternative methods to the classic RPN calculation and select those that more efficiently resolve both shortcomings.
The decision has been made to employ the fuzzy logic methodology due to its proven success in utilizing natural language. Additionally, various works have used fuzzy logic in Failure Modes, Effects, and Criticality Analysis (FMECA), including the calculation of RPN, with real case studies conducted in industrial production environments, as evidenced by works employing the Fuzzy FMECA approach compiled by Kabir and Papadopoulos [
13].
Once suitable methods are identified, efforts will be made to incorporate them into the assisted system through implementation in its source code. The final objective of the article is to validate the newly proposed RPN method and subsequently address specific cases using the new score derived from the refined RPN calculation.
2. Methodology
2.1. Fundamentals
The previously work presented by Rodríguez-Padial et al. [
5] was based on a system for decision-making regarding the design of customized maintenance plans, within a production plant, whose general objective is the proposal of an expert system that assists in decision-making for the design of maintenance plans tailored to the real productive context of an industrial plant, based on the alignment of the company's strategic objectives, those tactical and maintenance operations. In summary, it tries to solve a reliability problem posed by the proven success methodology of Reliability-Centered Maintenance, RCM, and driven by Case-Based Reasoning algorithms, CBR, to offer an optimized maintenance solution adapted to a new problem presented, such as a new case. The goal pursued in that work was to help in the design of maintenance plans in a real environment of a plant's productive context, in a driven way, that is, to guide the expert in the efficient application of the RCM method. As result three advantages are achieved by apply proposed methodology: human error is minimized as Rahman et al. [
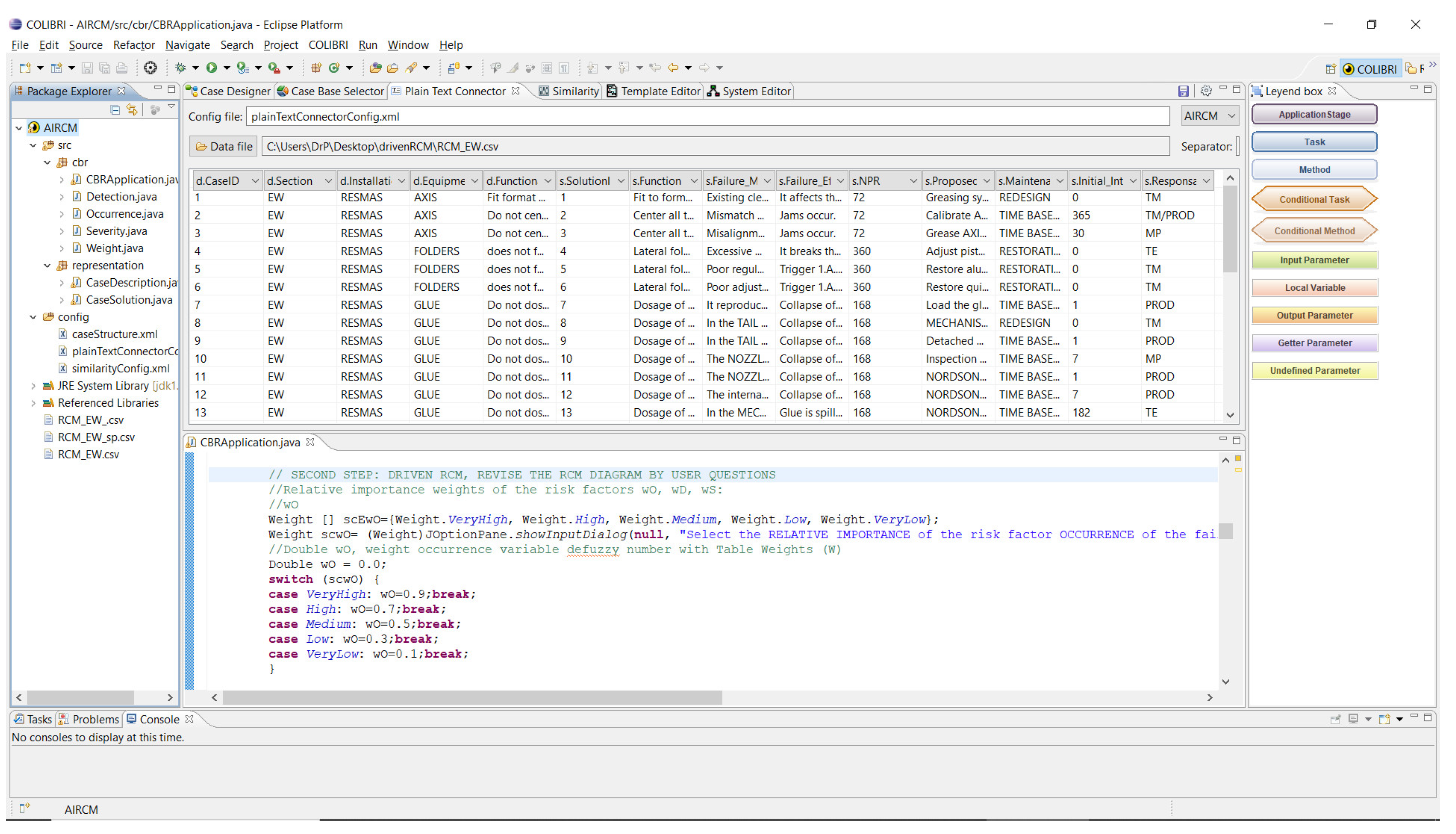
14], an adequate level of excellence is ensured, and the devoted time by the expert is drastically reduced. For this purpose, a software application was developed that, when a new reliability problem arises to carried out automatically a recovery, analysis and adaptation of the same. A fundamental advantage resides in the fact of having a large number of historical cases and the expert will only consider the most similar k-cases, kNN, where k limits the number of similar cases that will be displayed by the application, in this work the system will propose the three most similar cases (k=3) to the new one proposed. Integrating the RCM method with the CBR methodology allowing the expert to be efficiently conducted in the RCM method, with great savings in devoted time, specifically on the part of the method where failure modes, effects and criticalities, FMECA. This integration of both methodologies, implemented in the Java programming language, results in obtaining an independent computer RCM application, designed to the effect to be applied in any industrial environment.
In particular, the driven-RCM application has been conceived in two stages; In the first stage, FMECA has been implemented with the CBR method using the jCOLIBRI environment,
Figure 1, Recio-García et al. [
15,
16], and the second stage, where the maintenance policy has been implemented according to the decisional flow chart on the operating context of the new case raised, and therefore the maintenance policy adopted for recovered case is discarded. This is because the maintenance policy depend/s more on the operational context where the equipment is located, that is, its effects and not with the failure mode, as this is more related to the type of equipment and the maintenance policy with the productive context.
The first stage applies the flow of CBR on the FMECA part of the RCM method, this is recovery of failure modes within the cases base, comparing them with the new problem raised through queries. The second stage (conductive RCM decision flow diagram within CBR cycle review activity) attempts to reapply the maintenance actions, re-evaluating the Risk Priority Number (RPN), the maintenance task instruction, the maintenance class, the interval and the assigned workshop responsible.
The purpose of this article is to improve the second stage method -conductive RCM-, only and exclusively the calculation of RPN, where it is about improving its approximation using another evaluation methodology, through the adjustment and weighting of the risk factors that compose it. The attributes whose values have been reviewed through the implementation of the second stage are: Risk Priority Number (RPN) -through its occurrence, severity and detection risk factors-, Proposed Task (PT), Initial Interval (II), Responsible (R), and finally, the new maintenance policy or Maintenance Classification (MC) has been applied, obeying the RCM decision diagram and leading the user through the questions to obtain the maintenance action to be applied in this context. The final part of the CBR cycle is the retained activity, where the new reviewed case has been stored in the cases base by adding one more instance in the RCM data base cases file. The previous work showed a use of the application to resolve a new failure case by the assistant. In the first stage (CBR-RCM) the input information of the new problem posed on the query window, same as
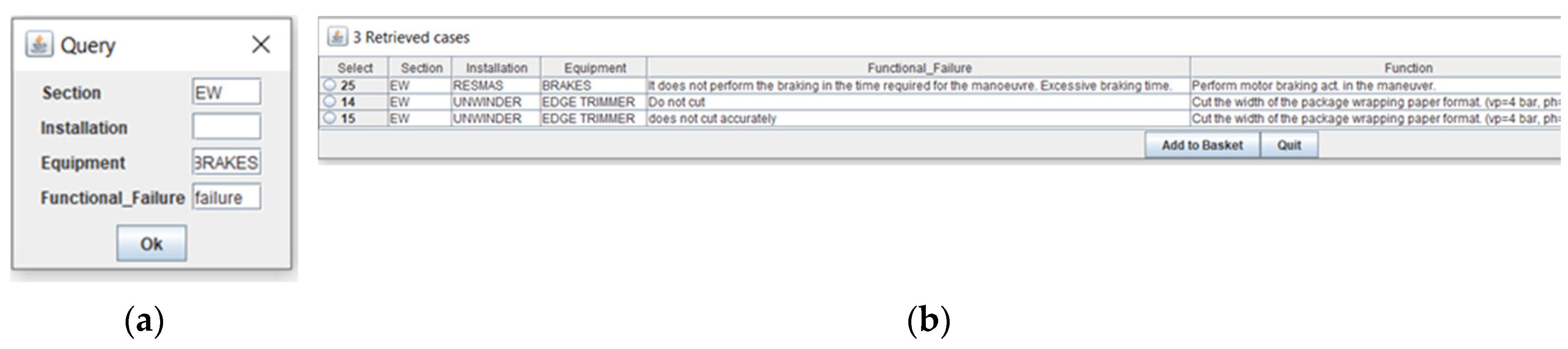
Figure 2 has been entered, describing the problem as a Functional Failure: "Do not center the axes" for the Section: "EW", within Installation: "RESMAS" and Equipment: "AXIS". The three recovered similar cases to the problem raised have been obtained and showed in descending order of similarity, as table in
Figure 2. The application user can choose the case that best suits from the three presented, since it also allows him to see other variables such as failure modes or failure effects that complete the FMECA. The second stage of the driven RCM process reviewing the contextual information of the new problem, as shown in
Figure 2. With the occurrence, O, severity, S, and detection, D, data entered by user, the new Risk Priority Number (RPN) is automatically calculated, as classical method RPN=OxSxD. Finally redefining the new maintenance class following the RCM diagram in a guided way, that is, the user has been guided through the questions in the diagram, and the new revised case is added as last case in the cases base.
2.2. Improved RPN Methodology
In the design of this assisted system, the RCM methodology was implemented integrated into a CBR cycle, resulting in a conductive RCM method, directing or conducting the RCM methodology in order to assist an expert efficiently from the beginning to the end of it, through all intermediate stages. During an RCM process, specifically within the FMECA analysis, each failure mode analyzed is classified by risk, evaluated by the Risk Priority Number or RPN, to be subsequently prioritized. Although the classic RPN calculation method was implemented in the original design of the assisted system, it has certain disadvantages that will be mentioned later. This work attempts to correct them, implementing fuzzy logic (FL) techniques in the source code of the assisted system to make up for the aforementioned deficiencies with the current method. The following subsections briefly describe fuzzy logic and its use for calculating RPN, hereinafter referred as fuzzy RPN or fRPN.
2.2.1. Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic developed by Zadeh [
17] to deal with imprecise information expressed in human language. The fuzzy process consists of transforming a set of numerical variables into a fuzzy set of values. A fuzzy set, A, in the discourse universe, U, is characterized by a membership function μ
A(x), where the membership function μ
A(x), which assigns a degree of membership of an element x to the fuzzy set A, in a range between 0 and 1. The fuzzy set A is mathematically defined according to Eq. (1),
A special case of fuzzy sets are fuzzy numbers where they are characterized by being represented by an interval of real numbers, and are usually denoted by them. (a, b, c), Ɐ a,b,c ϵ ℝ, for the case of triangular fuzzy numbers, like those used in this work, and its membership function is:
The inverse operation, which makes it possible to convert a fuzzy number, A, into a real number, x, is called the defuzzification process, x(A), and there are various methods to calculate it, the most used being the centroid:
Due to its simplicity, and its proven usefulness, the method of converting linguistic variables to fuzzy numbers used will be the L-R fuzzy method used by Baghbani et al. [
18], the total score of a fuzzy number is
2.2.2. Fuzzy Logic Applied in the Calculation of RPN (Fuzzy RPN)
The classic calculation of the Risk Priority Number is obtained by Eq. (7),
Where O, S, D, are, respectively, the risk factors that represent the probabilities of occurrence, severity and detection respectively, of each failure mode evaluated. Each risk factor is evaluated within the numerical range of 1 to 10, so the RPN value is limited within the range of 0 to 1000.
As mentioned above, the classic RPN calculation, although it is a widely used method, presents certain weaknesses and its calculation method has been questioned in some application environments, as cited by Ben-Daya and Raouf [
19], Bowles [
20], Braglia et al. [
21], Chang et al. [
22], Gilchrist [
23], Pillay and Wang [
24], Sankar and Prabhu [
25]. The disadvantages of this calculation, although several authors list several, all basically agree on two; On the one hand, risk factors are evaluated numerically, from 0 to 10, by experts, and therefore natural language is not used, such as the use of linguistic variables that including values as “low”, “medium” or “high”, more comfortable or close expressions for the human evaluator. On the other hand, as can be seen in equation (7), the classic method of calculating RPN presents the same relative importance for the three risk factors O, S and D. This is not always the case, depending on the criticality of each operational context, so the relative importance of each factor must be weighted. To correct these weaknesses, fuzzy logic is used to calculate the Risk Priority Number, RPN, through its three risk factors, O, S, D.
The methodology used by Baghbani et al. [
18] tries to integrate expert judgment through fuzzy triangular membership functions, associated with each risk factor, instead of “crisp” numerical values of the classic method.
Table 1,
Table 2 and
Table 3 show the linguistic variables to evaluate the risk factors occurrence (O), severity (S) and detection (D), and their respective fuzzy numbers fNO, fNS and fND. In the following columns the values of the parameters are obtained α y β, and left μ
L(A), right μ
R(A) and total score μ
T(A), using the L-R defuzzification method used by Baghbani et al. [
18], according to equations (4), (5) and (6) for each of the three risk factors, as defuzzified triangular fuzzy numbers, resulting μ
O, as μ
T(O), μ
S as μ
T(S), μ
D as μ
T(D), these numerical values can be seen in the last columns of
Table 1,
Table 2 and
Table 3, respectively, for each linguistic term.
The classic RPN calculation method assigns the same relative importance to each risk factor. Although many authors decide to use fuzzy IF-THEN rules as Renjith et al. [
26], building the rule base becomes very tedious due to the huge number of judgments issued by experts, which results in in a lot of devoted time, even when rule reduction methods have been applied, as proposed by Cao et al. [
27]. Francis and Colli [
28] try to weight the severity risk factor, despite their attempt, only one of the three risk factors is pre-weighted, so it is not considered a complete solution. Wang et al. [
29] aims to correct this effect, without using fuzzy rules, avoiding asking the experts too much, proposes to calculate RPN using fuzzy logic and fuzzy weighted geometric mean and thus avoid the weakness that fairness entails in the relative importance of risk factors in the classic calculation of RPN calculation. The relative importance of each risk factor is considered as a weight factor, W, and evaluated in linguistic terms using a triangular fuzzy function, whose fuzzy numbers are shown in
Table 4.
It should be noted that the input values, triangular fuzzy numbers fNO, fNS, fND, used in
Table 1,
Table 2 and
Table 3, respectively, have been taken because they are consistent with the "crisp" scores of the classic RPN calculation method and because they have been used and validated for case studies in real production environments. Although [
29] uses trapezoidal functions to evaluate fNO, it is possible to find the equivalence in a triangular membership function, as shown in Mentes et al. [
30] and is used and adapted to the equivalent values "crisp" 1-10 in [
18]. As for the values taken by different authors, they vary slightly; those of [
18] have been chosen for two reasons; the first because the triangular fuzzy numbers validated in a productive system contextualized in factories similar to those considered in the case base of this work are considered, and secondly because it has been based on the tables of [
29] main and contrasted source of the previously cited articles. Reason why the values of triangular fuzzy numbers of fNW from [
29] have also been taken for
Table 4.
Using the L-R defuzzification methodology of Baghbani et al. [
18] the weighted numbers can be obtained μ
W, as μ
T(W) over reached weight factor μ
WO, μ
WS, μ
WD, according to five linguistic terms W such as can be seen in
Table 5, which extends
Table 4 above.
Finally, once the defuzzified numbers of each risk factor μ
O, μ
S μ
D and their relative importance through their weight factors μWO, μWS, μWD have been obtained, the Risk Priority Number can be calculated using logic. fuzzy, fRPN, like:
Adapted from the formula by Wang et al. [
29]
In summary, a new RPN calculation is obtained, in which the weaknesses of the classical method are resolved, and this new calculation will be implemented in the source code of the software application of the assisted system.
3. Application and Results
In the previous work, the pursued objective of integrating Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) and Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) methodologies was implemented in the Java programming language, the result of which is an independent computer application for the conductive RCM model, called driven-RCM.
This section has been divided into 3 phases, according to chronological order: the preparation of the cases base used, the design and implementation of the CBR-RCM application and its use to solve a new case raised, enabling the applicability of the conductive RCM method through the execution of the CBR-RCM application.
3.1. Cases Base
The cases base is made up of a total of 35 cases, related in the Appendix, through easy data dumping from the worksheets corresponding to 35 problems that actually occurred and were successfully resolved under the RCM methodology on a machine identified according to a machine tree in hierarchy format (Section S, Installation I, Equipment E), to locate the area where the failure FF occurs for the function F. These cases pertain to papermaking industry, where maintenance is essential because it is a continuous process and because a malfunction can have environmental consequences [
31].
3.2. Design and Implementation of Conductive RCM: Application
Once a database from cases base with structured attributes (appendix) has been established, the implementation of the computer application begins, using the Java programming language under the eclipse environment. However, the corresponding logical functioning flow of the CBR method is executed through queries. This cycle presents two stages, the first one applies the flow of CBR on the FMECA part of the RCM method, this is recovery of failure modes within the cases base, comparing them with the new problem raised through consultation. The second stage attempts to reapply the maintenance actions, re-evaluating the Risk Priority Number (RPN), the maintenance task instruction, the maintenance class, the interval and the assigned workshop responsible.
The objective of this work focuses on the modification of the second stage, in particular in the RPN calculation, replacing the classic calculation with the fuzzy RPN or fRPN methodology seen in
Section 2 of this work. Therefore, focusing on the second stage, driven-RCM within the CBR Cycle Review Activity, the code has been implemented to modify Risk Priority Number (RPN) -through its occurrence, severity and detection factors- as fuzzy RPN.
3.3. Study Cases: Resolution of a New Failure Case Conducted By an Improved Assisted-Driven System
The design assistance system has been launched in a machine (Section) to which the RCM design must be applied to improve its reliability and maintainability. At this moment the use of driven RCM is made possible through the application designed and modified in previous section for this purpose, with the advantages of minimizing devoted time by users responsible for the design and human errors inherent in handling extensive case databases.
To evaluate the improvement in the assisted system, another case has been evaluated, different from the one studied in the previous publication, where the classic RPN calculation method was used. The input information of the new problem posed on the query window of
Figure 2 has been introduced, describing the problem as a Functional Failure: "failure", on the Section: "EW" without data entry in Installation, for the Equipment: "BRAKES". The robustness of the application is noted, in case of missing input data that locates the problem, you can even describe only the problem, without recording S/I/E data.
The three recovered cases similar to the problem raised have been obtained in descending order of similarity. The first identified case ID = 25 is the most similar to the problem posed, as can be seen in
Figure 2, then cases ID = 14 and ID = 15 will be the second and third most similar among those found in the cases base.
Once, the user has chosen the case that best suits the needs of the new case or problem raised, in this work he has chosen ID = 25, since it is the most similar to the problem posed.
Continuing with the review process, the second stage of the driven RCM process begins immediately, by reviewing the contextual information of the new problem. This time, with the new RPN calculation method, the risk factors associated with Occurrence, Severity and Detection, the new Risk Priority Number (RPN) is calculated automatically using linguistic terms through fuzzy logic.
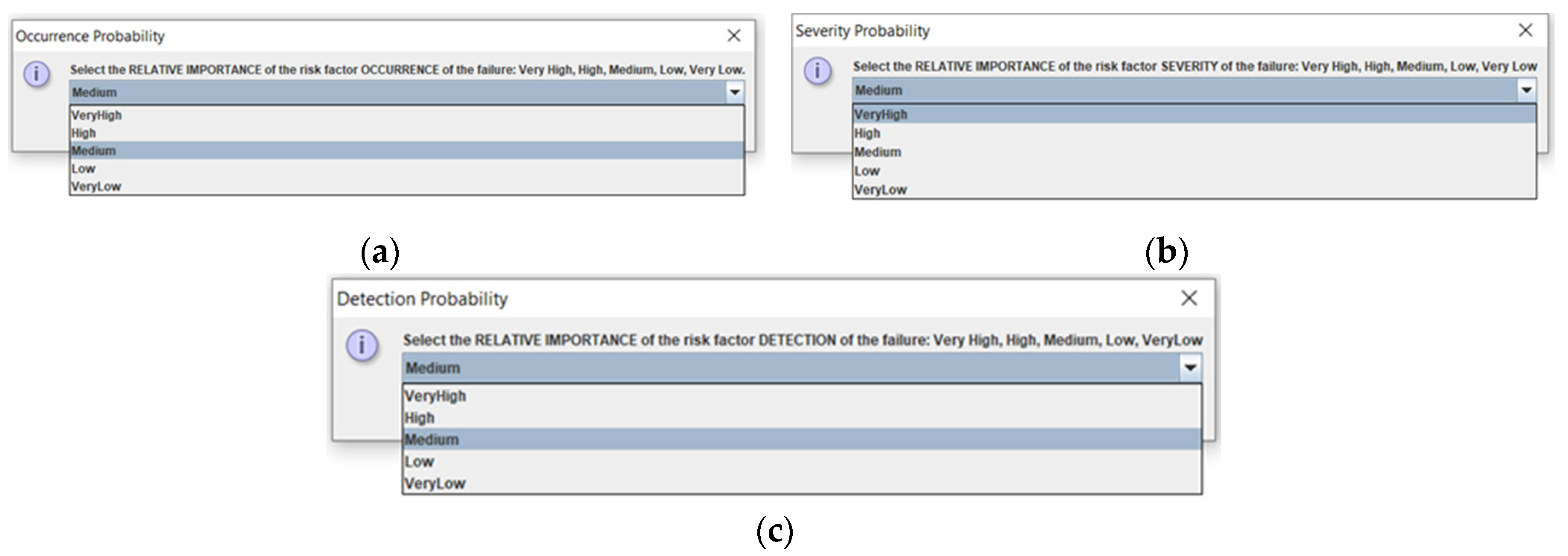
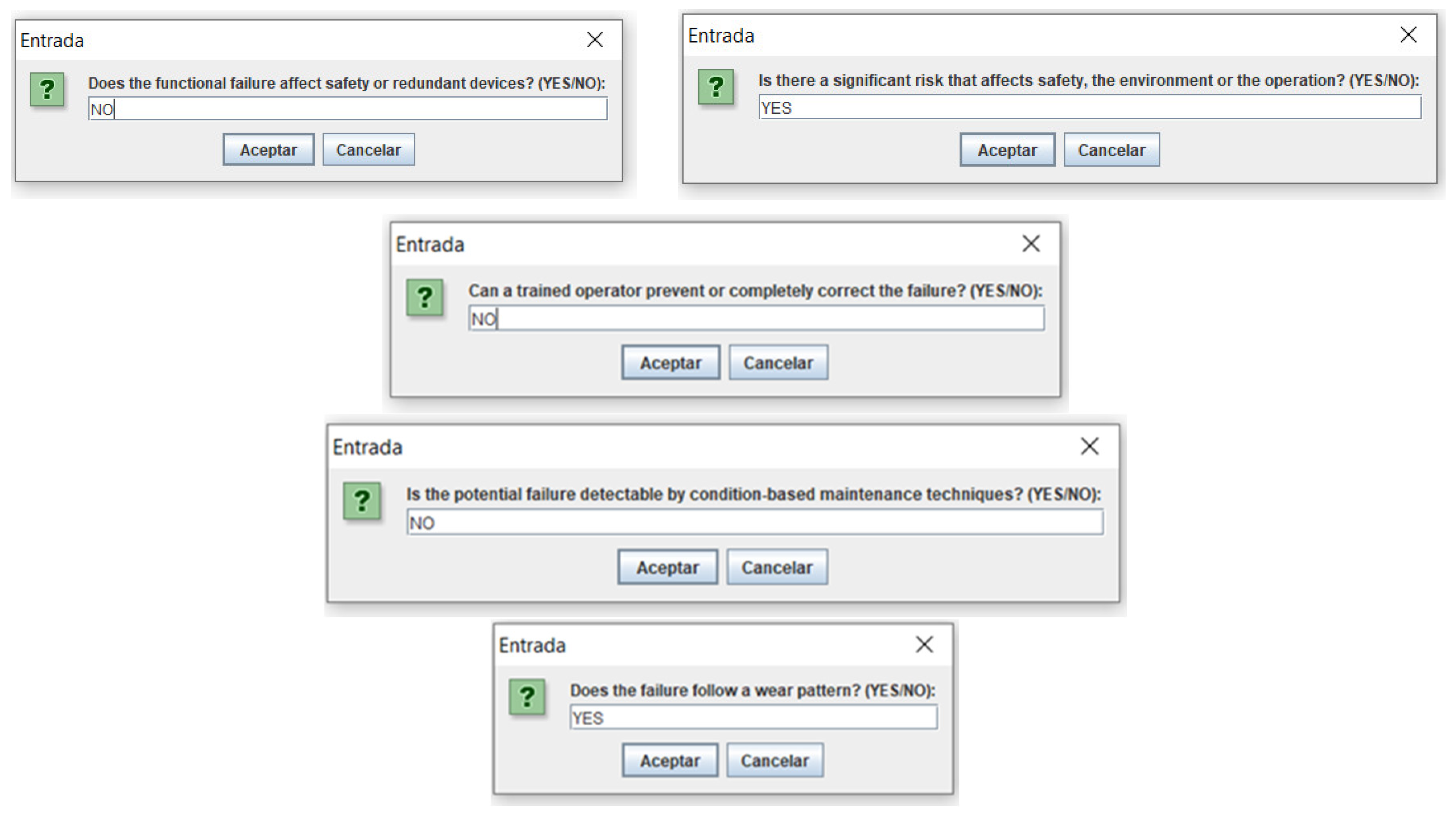
As can be seen, unlike the previous RPN method, the information entered is not numerical from 1 to 10, but rather linguistic expressions, such as low, medium, high, etc. Likewise, as seen in the first three pop-up windows in
Figure 3, new dialog boxes appear asking for information on the relative importance of each of the risk factors, using a drop-down list of terms. This represents a novelty compared to the previous calculation, where it was not evaluated.
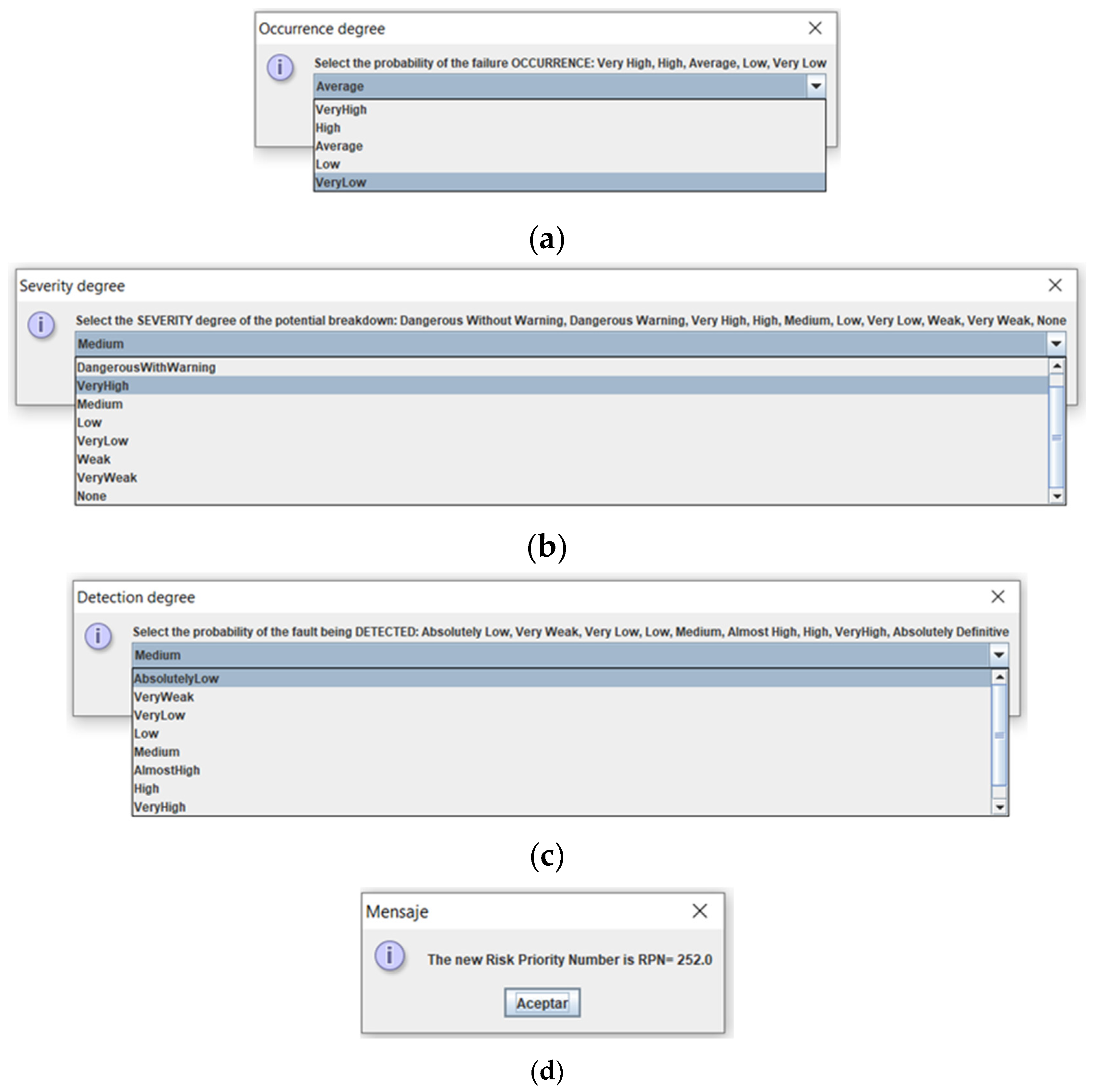
In
Figure 4, data on the values of the three risk factors, occurrence, severity and detection, are entered, choosing from a drop-down list the most appropriate term that defines each of them, for the functional failure analyzed. In this way, the expert goes from trying to evaluate precisely and numerically to using a more natural language with human tolerance. As a result of the calculation, an information box appears with the new RPN value calculated with the new methodology implemented, in this case it can be seen in the last figure in
Figure 4.
At this point, It should be noted that previously, the new method was validated with extreme and average values for the weights and risk factors, verifying RPN results in accordance with them. Finally, similar input data for both classical/fuzzy-weighted methodologies, RPN values are obtained, 300 vs 336, respectively, resulting in a discrepancy of 1.78%, which indicates that the method It has been well adjusted.
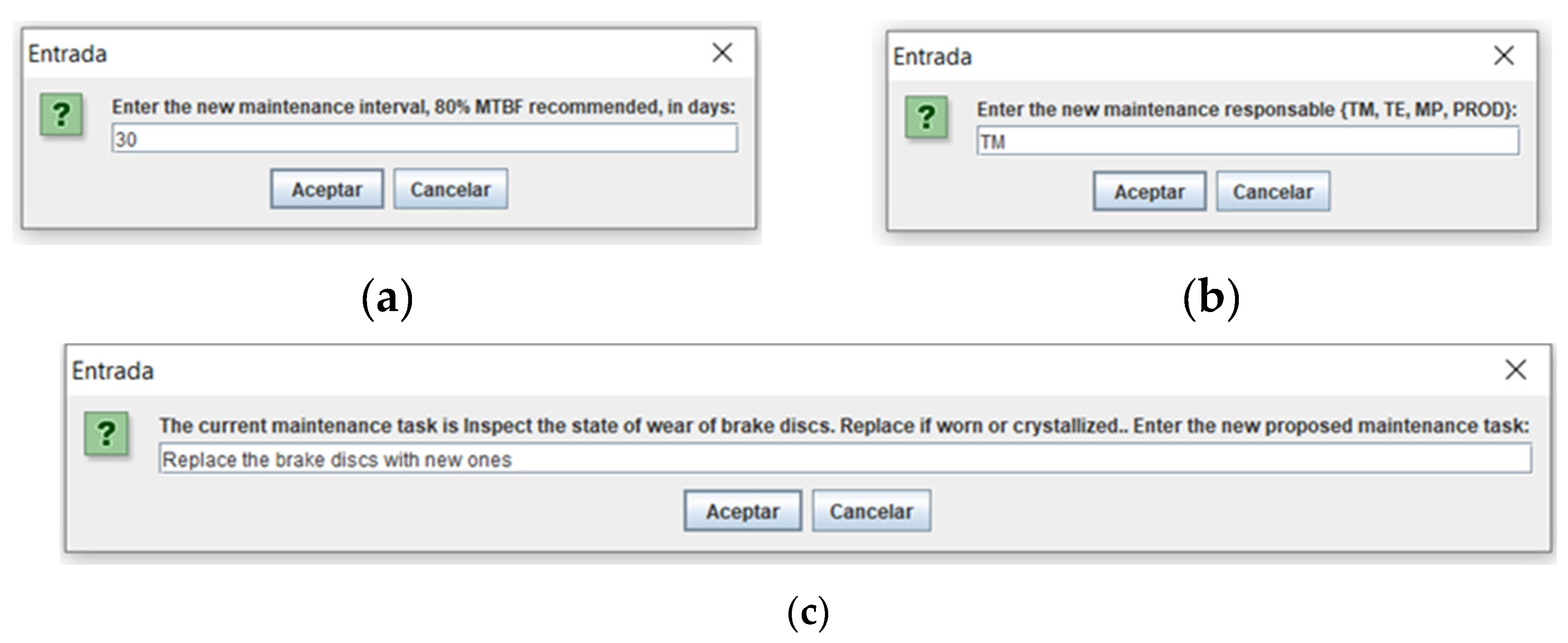
Continuing with the review process, in the same way as in the previous work, the source code implementation from now on until the completion of the program has not been modified, therefore, by reviewing the contextual information of the new problem, as shown in
Figure 5, for the new data recorded: interval (periodicity), responsible and proposed maintenance task, respectively.
The second revision stage comprises redefining the new maintenance policy or class following the RCM diagram, where the user has been guided through the questions in the diagram, as seen in
Figure 6. The maintenance policy is obtained as an output. In this work, the maintenance classification obtained is Maintenance by Operator, thus completing the solution of the chosen case, see the last case in
Figure 7 (a), split for better display.
Finally, the retention activity is checked by verifying the persistence, that is, that the new case is stored in the database, RCM_EW.CSV file. The new added case is also shown highlighted in
Figure 7 (b), where it can be seen how the case number 36, consecutive number to the last existing case in the original cases base, contain all the values obtained in the solution process of the driven process according to
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7.
The rest of the cases studied have been collected in the
Table 7, where the attributes are presented in
Table 6, and the values that can be selected in some of them. The previously solved problem has been presented as IDC=E in
Table 7. Note that the acronyms used are: OM = Operator Maintenance, RD= Redesign, CBM= Condition Based Maintenance, TBM= Time Based Maintenance, CM= Corrective Maintenance, PFF= Periodic Failure Finding, for Maintenance Classify (MC), and TM = Mechanical workshop, TE= Electrical workshop, PROD= Production operator, MP= Preventive workshop, for Responsible (R).
4. Discussion
The objective of this work is to improve the calculation of the Risk Priority Number (RPN) in the assisted system already presented to design maintenance plans driven by CBR algorithms integrated into the RCM methodology. The classic RPN calculation method based on independently evaluating the three risk factors (Occurrence, Severity and Detection) is replaced by a weighted defuzzification method to calculate the same, using linguistic terms.
As a result, it has been found that the environment implemented in the Java application is much friendlier to the expert personnel it assists, since evaluating them through a list of linguistic terms is closer to human natural language and more easily quantifiable. Likewise, the expert's assessment of the relative importance of each risk factor has also been introduced with fuzzy logic, before assessing each one individually.
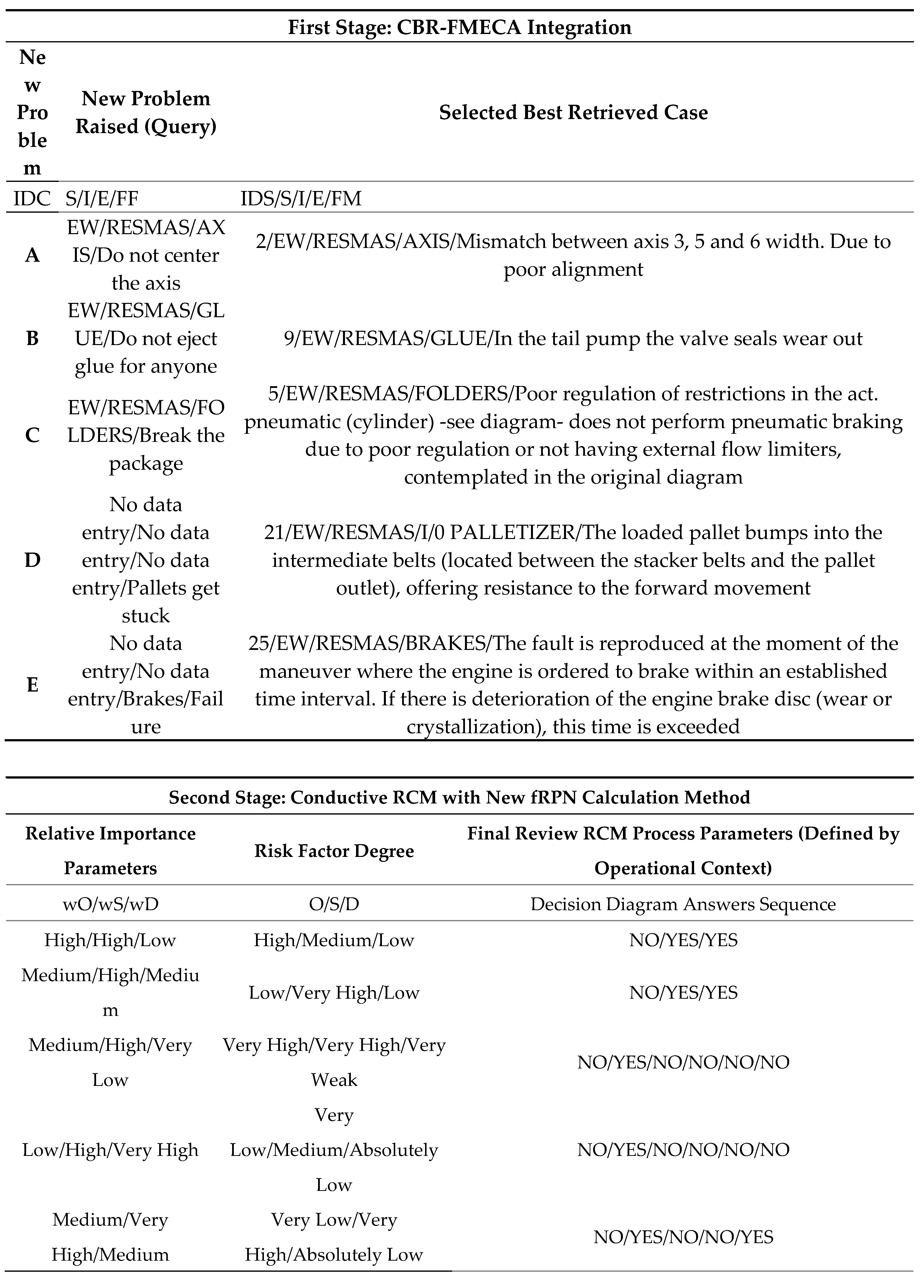
The same new case to be solved, case IDC=A from
Table 7, has been presented again as in the previous work of Rodríguez-Padial et al. [
5] on the new improved system, in such a way that when the second stage of the conductive RCM begins, the data inputs and the automatic calculation differs substantially, although this is not the case with the result, which as has been verified shows a discrepancy of 1.78%, which ensures a good fit of the new method used. This highlights the different implemented methodology, that is, classical RPN versus the new defuzzy-RPN methodology.
The rest of the problems resolved by the improved application have been registered as IDC=B,C,D, E. These new problems have been raised because they presented greater criticality in the RCM work groups that were carried out to create the case base. Therefore, they are three of the problems where the highest number of risk priorities were evaluated and that have now been re-evaluated with the new RPN calculation methodology.
The application of the assisted driven RCM system has been validated taking comparable extreme and intermediate cases and obtaining the expected results.
5. Conclusions
For the implemented software application, as a result of previous work, a conductive assisted system was achieved that helps a person responsible for the maintenance of a plant develop a maintenance plan ensuring ideal management of the intellectual capital stored in the cases base.
In this work, the objective is to improve the assisted system developed previously. A new methodology for automatically calculating the Risk Priority Number (RPN) has been implemented, replacing it with the classic RPN calculation method, because it has several weaknesses, two of them common in most of the authors' publications. who criticize the classic method of calculating the RPN.
To achieve this, fuzzy logic has been used in such a way that it is simultaneously possible to improve two aspects that the classical methodology considered questionable by various authors: the first is to take into account a prior evaluation by experts or maintenance responsible of the relative importance of the three risk factors (Occurrence, Severity and Detection), the second is to use linguistic terms, as "Low", "Medium" or "High", instead of numerical scores (from 1 to 10) used to evaluate the three previous factors.
The novelty introduced in this work consists of ideally combining two methods used successfully in fuzzy logic to improve the calculation of the Risk Priority Number, RPN, on the one hand the fuzzy weighted geometric mean method developed by Wang et al. [
29] and on the other hand the defuzzification method used by Baghbani et al. [
18] for RPN calculation. The advantage achieved is that it is not necessary to use tedious IF-THEN inference rules. In this work, the combination of both fuzzy logic methods, weighted L-R defuzzification, has been used to efficiently calculate RPN in a more natural language and prioritizing the risk factors necessary to assess RPN.
The result obtained has substantially improved the application, modifying an extract of its source code in Java, so that the automatic RPN calculation routine has been improved, implementing the new weighted L-R defuzzification methodology. Once the validation of the new improved application has been verified, it has been possible to measure how its precision is preserved. A final improvement achieved is the fact that the way of entering the information in this second stage, by using linguistic terms instead of specifying them through numerical values, in addition to comfort for the human expert to whom the system leads, therefore represents a savings in devoted time.
Finally, five problems have been presented to be solved by the improved application of the assisted system, while one of the cases has made it possible to compare the discrepancy between the RPN according to the new and classical methods, posing the same problem as in the previous work, the rest of resolved cases have been chosen as those with the highest initial risk value, and in this work they have been re-evaluated by the application using the new fRPN calculation method. It can be seen that the values obtained by the new method are slightly lower than those by the classic RPN method and vice versa, suggesting that the new method allows the RPN to be more homogenized.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.R.-P. and R.D.; methodology, N.R.-P.; software, N.R.-P.; validation, N.R.-P.; formal analysis, N.R.-P., M.M.M. and R.D.; investigation, N.R.-P.; resources, N.R.-P., M.M.M. and R.D; writing—original draft preparation, N.R.-P. and R.D.; writing—review and editing, N.R.-P., M.M.M. and R.D.; supervision, M.M.M. and R.D.; project administration, M.M.M. and R.D.; funding acquisition, M.M.M and R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by College of Industrial Engineers of UNED, grant number 2023-ETSII-UNED-05.
Data Availability Statement
Nor applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix
Records on the CSV file that make up the Cases Base. Note: Cases from 26 to 32 omitted by simplicity
| IDP |
S |
I |
E |
FF |
F |
| 1 |
EW |
Resmas |
Axis |
Fit format out of range |
Fit to format width |
| 2 |
EW |
Resmas |
Axis |
Do not center the axis with each other |
Center all the axes respect to each other on the machine axis |
| 3 |
EW |
Resmas |
Axis |
Do not center any axis on the rest |
Center all the axes with respect to each other on the machine axis |
| 4 |
EW |
Resmas |
Folders |
Does not fold |
Lateral folding of the package v=15 folded/min |
| 5 |
EW |
Resmas |
Folders |
Does not fold |
Lateral folding of the package v=15 folded/min |
| 6 |
EW |
Resmas |
Folders |
Does not fold |
Lateral folding of the package v=15 folded/min |
| 7 |
EW |
Resmas |
Glue |
Do not dose the glue through any nozzle |
Dosage of glue for gluing the package dc/dt=15 lines/minute x 3 nozzles |
| 8 |
EW |
Resmas |
Glue |
Do not dose the glue through any nozzle |
Dosage of glue for gluing the package dc/dt=15 lines/minute x 3 nozzles |
| 9 |
EW |
Resmas |
Glue |
Do not dose the glue through any nozzle |
Dosage of glue for gluing the package dc/dt=15 lines/minute x 3 nozzles |
| 10 |
EW |
Resmas |
Glue |
Do not dose the glue through any nozzle |
Dosage of glue for gluing the package dc/dt=15 lines/minute x 3 nozzles |
| 11 |
EW |
Resmas |
Glue |
Do not dose the glue through any nozzle |
Dosage of glue for gluing the package dc/dt=15 lines/minute x 3 nozzles |
| 12 |
EW |
Resmas |
Glue |
Do not dose the glue through any nozzle |
Dosage of glue for gluing the package dc/dt=15 lines/minute x 3 nozzles |
| 13 |
EW |
Resmas |
Glue |
Do not dose the glue through any nozzle |
Dosage of glue for gluing the package dc/dt=15 lines/minute x 3 nozzles |
| 14 |
EW |
Unwinder |
Edge Trimmer |
Do not cut |
Cut the width of the package wrapping paper format. (vp=4 bar, ph=2 bar) |
| 15 |
EW |
Unwinder |
Edge Trimmer |
does not cut accurately |
Cut the width of the package wrapping paper format. (vp=4 bar, ph=2 bar) |
| 16 |
EW |
Unwinder |
Edge Trimmer |
does not cut accurately |
Cut the width of the package wrapping paper format. (vp=4 bar, ph=2 bar) |
| 17 |
EW |
Unwinder |
Edge Trimmer |
does not cut accurately |
Cut the width of the package wrapping paper format. (vp=4 bar, ph=2 bar) |
| 18 |
EW |
I/0 Palletizer |
Palletizer |
During loading, the pallet turns as it passes through the intermediate belt |
Automatic loading and positioning of empty pallets |
| 19 |
EW |
I/0 Palletizer |
Palletizer |
It does not position the pallet correctly |
Automatic loading and positioning of empty pallets |
| 20 |
EW |
I/0 Palletizer |
Palletizer |
It does not position the pallet correctly |
Automatic loading and positioning of empty pallets |
| 21 |
EW |
I/0 Palletizer |
Palletizer |
Do not transfer the loaded pallet |
Transfer loaded pallets by belt to the transport line |
| 22 |
EW |
I/0 Palletizer |
Palletizer |
Do not transfer the loaded pallet |
Transfer loaded pallets by belt to the transport line |
| 23 |
EW |
Resmas |
Pads |
Not adequacy of the minimum pressure according to the optimum operating value |
The pads must be adjusted to the height of the package and introduce a pressure between a minimum and a maximum to achieve adequate quality in the wrapped package. 1st PRESS p1(min=1_max=2.5) bar. 2nd PRESS p2(min=0_max=1.5) bar. 3rd PRESS p3(min=1_max=2) bar |
| 24 |
EW |
Resmas |
Pads |
Not adequacy of the minimum pressure according to the optimum operating value |
The pads must be adjusted to the height of the package and introduce a pressure between a minimum and a maximum to achieve adequate quality in the wrapped package. 1st PRESS p1(min=1_max=2.5) bar. 2nd PRESS p2(min=0_max=1.5) bar. 3rd PRESS p3(min=1_max=2) bar |
| 25 |
EW |
Resmas |
Brakes |
It does not perform the braking in the time required for the maneuvre. Excessive braking time |
Perform motor braking act. in the maneuver |
| … |
… |
… |
… |
… |
… |
| 33 |
EW |
Unwinder |
Loading of Coils |
Partial cargo handling assistance |
Assist in the loading of packaging reels to the operator in the form of ergonomic loading |
| 34 |
EW |
Despalletizer |
Protection |
Uncontrolled rise |
Package Feeding Lift Platform Rise |
| 35 |
EW |
Despalletizer |
Protection |
Uncontrolled rise |
Package Feeding Lift Platform Rise |
References
- Al-Turki, U.M. A framework for strategic planning in maintenance. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2011, 17(2), 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Padial, N.; Marín, M.M.; Domingo, R. Strategic framework to maintenance decision support systems. Procedia Eng. 2015, 132, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Padial, N.; Marín, M.M.; Domingo, R. Managing Information Uncertainty and Complexity in Decision-Making. Complexity 2017, 2017, 3759514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitak, P.; Belak, L.; Pihler, J.; Ribič, J. Maintenance Management of a Transmission Substation with Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Padial, N.; Marín, M.M.; Domingo, R. Assisted-Driven Design of Customized Maintenance Plans for Industrial Plants. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12(14), 7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.F.; Melani, A.H.d.A.; Michalski, M.A.d.C.; de Souza, G.F.M. Reliability and Risk Centered Maintenance: A Novel Method for Supporting Maintenance Management. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Santos, I.F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Lind, M. Explicit Representation of Mechanical Functions for Maintenance Decision Support. Electronics 2023, 12, 4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, F.J.A.; Salgado, D.R. Analysis of the Influence of Component Type and Operating Condition on the Selection of Preventive Maintenance Strategy in Multistage Industrial Machines: A Case Study. Machines 2022, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, F.J.A.; Salgado, D.R. An Approach for Predictive Maintenance Decisions for Components of an Industrial Multistage Machine That Fail before Their MTTF: A Case Study. Systems 2022, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhang, X.; Lind, M. Automatic identification of maintenance significant items in reliability centered maintenance analysis by using functional modeling and reasoning. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 182, 109409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivančan, J.; Lisjak, D. New FMEA Risks Ranking Approach Utilizing Four Fuzzy Logic Systems. Machines 2021, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeri, A.; Naderikia, R. A new fuzzy approach to identify the critical risk factors in maintenance management. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 3749–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.; Papadopoulos, Y. A review of applications of fuzzy sets to safety and reliability engineering. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2018, 100, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Pasaribu, E.; Nugraha, Y.; Khair, F.; Soebandrija, K.E.N.; Wijaya, D.I. Industry 4.0 and society 5.0 through lens of condition based maintenance (CBM) and machine learning of artificial intelligence (MLAI). IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 852, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio-García, J.A.; González-Calero, P.A.; Díaz-Agudo, B. jcolibri2: A framework for building Case-based reasoning systems. Sci. Comput. Program. 2014, 79, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio-García, J.A. jCOLIBRI: Una plataforma multi-nivel para la construcción y generación de sistemas de Razonamiento Basado en Casos. Doctoral Thesis, Departamento de Ingeniería del Software e Inteligencia Artificial, Facultad de Informática, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghbani, M.; Iranzadeh, S.; Khajeh, M.B. Investigating the relationship between RPN parameters in fuzzy PFMEA and OEE in a sugar factory. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 60, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Daya, M.; Raouf, A. A revised failure mode and effects analysis model. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 1996, 13(1), 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, J.B. An assessment of PRN prioritization in a failure modes effects and criticality analysis. J. IEST. 2004, 47, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braglia, M.; Frosolini, M.; Montanari, R. Fuzzy criticality assessment model for failure modes and effects analysis. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2003, 20(4), 503–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.L.; Liu, P. H.; Wei, C.C. Failure mode and effects analysis using grey theory. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2001, 12(3), 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, W. Modelling failure modes and effects analysis. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 1993, 10(5), 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, A.; Wang, J. Modified failure mode and effects analysis using approximate reasoning. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2003, 79, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, N.R.; Prabhu, B.S. Modified approach for prioritization of failures in a system failure mode and effects analysis. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2001, 18(3), 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renjith, V.R.; Kalathil, M.J.; Kumar, P.H.; Madhavan, D. Fuzzy FMECA (failure mode effect and criticality analysis) of LNG storage facility. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2018, 56(2018), 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Dvořák, A.; Štěpnička, M.; Valášek, R. Redundancy criteria for linguistic fuzzy rules. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 214(15), 119112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R. S.; Colli, A. Information-based reliability weighting for failure mode prioritization in photovoltaic (PV) module design. In Proceedings of the Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM 12), Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 22-27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Chin, K.S.; Poon, G.K.K.; Yang, J.B. Risk evaluation in failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy weighted geometric mean. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36(2), 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentes, A.; Akyildiz, H.; Yetkin, M.; Turkoglu, N. A FSA based fuzzy DEMATEL approach for risk assessment of cargo ships at coasts and open seas of Turkey. Saf. Sci. 2015, 79, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, L.M.; Domingo, R. CO2 Emissions Reduction and Energy Efficiency Improvements in Paper Making Drying Process Control by Sensors. Sustainability 2017, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).