Submitted:
15 December 2023
Posted:
15 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Statement of problem
1.2. Justification for the study
1.3. Significance of the study
1.4. Aim
1.5. Objective
1.6. Research question
1.7. Null hypothesis
1.8. Research gap/Novelty
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
| Age group (years) | N | % |
| 0-10 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 11-20 | 7 | 4.0 |
| 21-30 | 28 | 16.0 |
| 31-40 | 32 | 18.3 |
| 41-50 | 65 | 37.1 |
| 51-60 | 24 | 13.7 |
| 61 and above | 19 | 10.9 |
| Total | 175 | 100.0 |
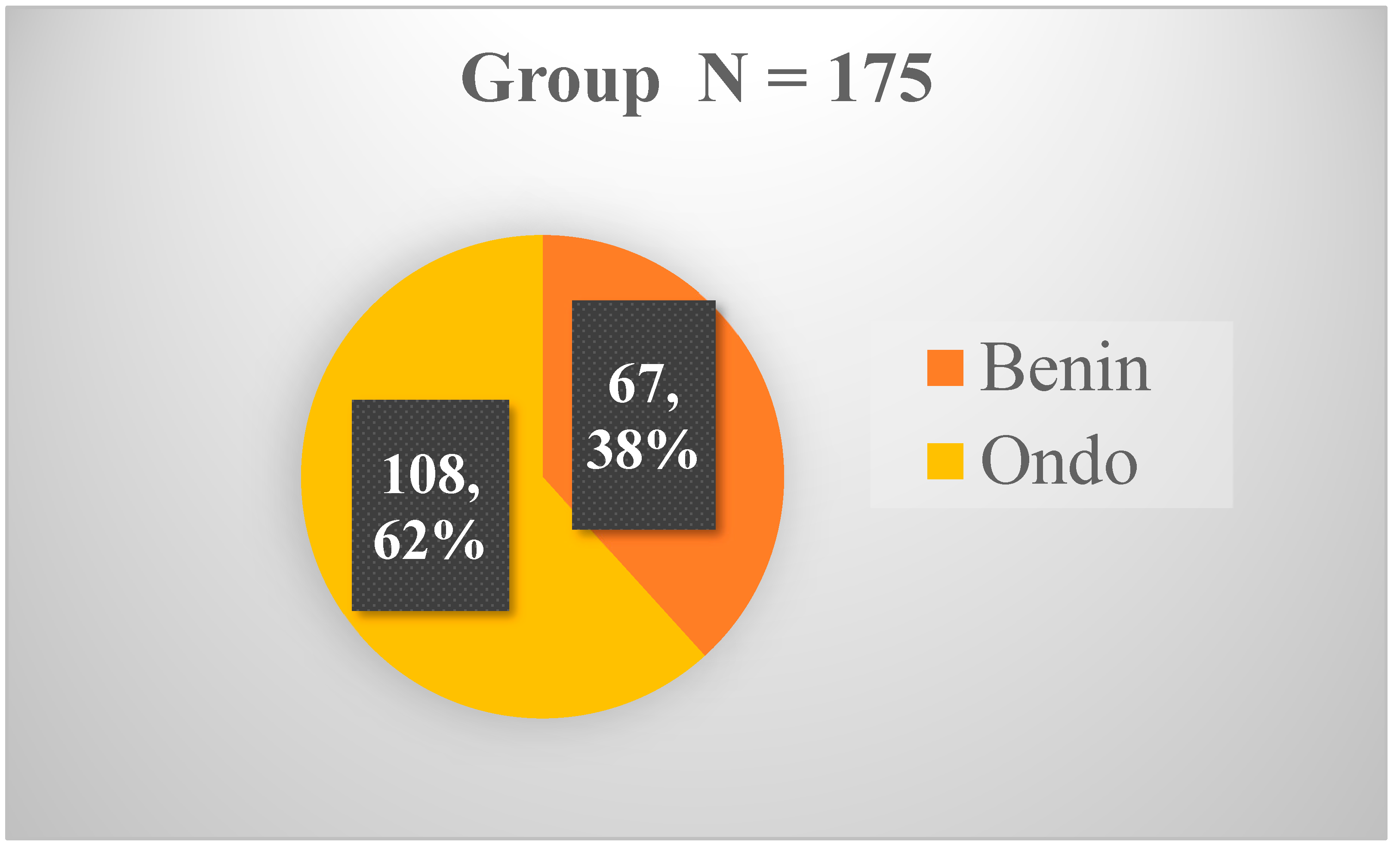
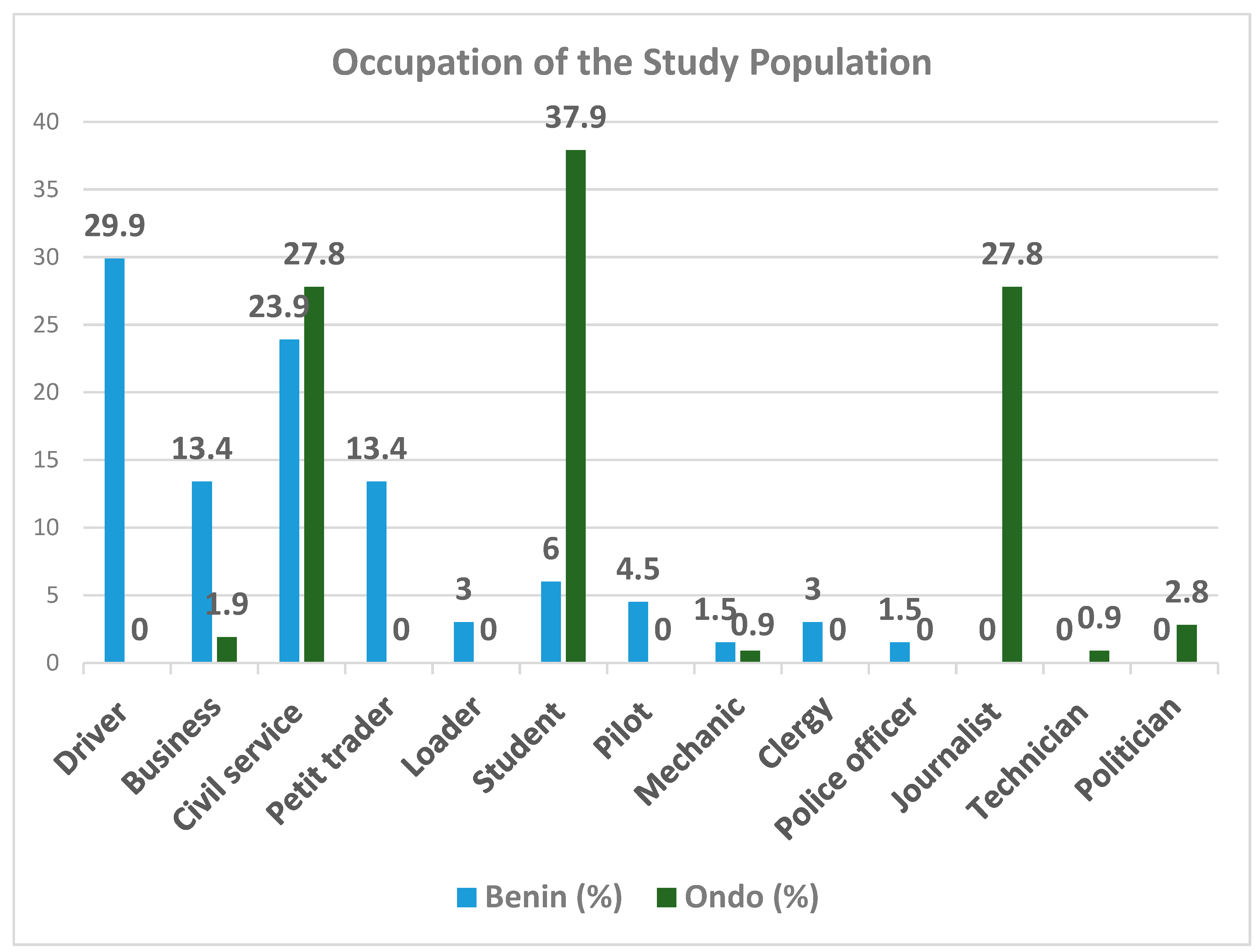
| Occupation | Benin N (%) |
Ondo N (%) |
Total N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driver | 20 (29.9) | 0 (0.0) | 20 (11.4) |
| Business | 9 (13.4) | 2 (1.9) | 11 (6.3) |
| Civil service | 16 (23.9) | 30 (27.8) | 46 (26.3) |
| Petit Trader | 9 (13.4) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (5.1) |
| Loader | 2 (3.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.1) |
| Student | 4 (6.0) | 41 (37.9) | 45 (25.7) |
| Pilot | 3 (4.5) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.7) |
| Mechanic | 1 (1.5) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (1.1) |
| Clergy | 2 (3.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.1) |
| Police officer | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.6) |
| Journalist | 0 (0.0) | 30 (27.8) | 30 (17.1) |
| Technician | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | 1 (0.6) |
| Politician | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.8) | 3 (1.7) |
| Total | 67 (100) | 108 (100) | 175 (100) |
| HearWho App Values | BENIN | ONDO |
TOTAL N=350 ears |
Grading | Interpretation | ||
|
RIGHT (N=67) |
LEFT (N=67) |
RIGHT (N=108) |
LEFT (N=108) |
||||
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| 0 – 49 | 55 (82.1) | 56 (83.6) | 86 (79.6) | 74 (68.5) | 271 (77.4) | Abnormal hearing | Hearing loss |
| 50 - 69 | 7 (10.4) | 8 (11.9) | 10 (9.3) | 16 (14.8) | 41 (11.7) | Good | Normal hearing |
| 70 – 100 | 5 (7.5) | 3 (4.5) | 12 (11.1) | 18 (16.7) | 38 (10.9) | Excellent | Normal hearing |
| Total | 67 (100.0) | 67 (100.0) | 108 (100.0) | 108 (100.0) | 350 (100.0) | ||
| Variables | BENIN | ONDO | TOTAL N=350 ears | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIGHT (N=67) |
LEFT (N=67) |
RIGHT (N=108) |
LEFT (N=108) |
||
| Characteristics | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) |
| Shiny | 16 (23.9) | 23 (34.3) | 42 (38.9) | 42 (38.9) | 123 (35.0) |
| Wax | 4 (6.0) | 2 (3.0) | 15 (13.9) | 20 (18.5) | 41 (11.7) |
| Dull | 2 (3.0) | 39 (58.2) | 41 (38.0) | 38 (35.2) | 120 (34.3) |
| Scar | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.3) |
| Retracted | 43 (64.2) | 1 (1.5) | 6 (5.6) | 4 (3.7) | 54 (15.4) |
| Perforated TM | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.5) | 1(0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.6) |
| Narrow Canal | 1 (1.5) | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.6) |
| Foreign body | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.8) | 3 (0.9) |
| Fungal debris | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9)) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (0.6) |
| Aural polyp | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.3) |
| Inflamed canal | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.3) |
| Total | 67 (100.0) | 67 (100.0) | 108 (100.0) | 108 (100.0) | 350 (100.0) |
| Chi square | 0.940 | 0.027 | 0.030 | 0.022 | |
| Characteristics | Otoscopy | X2 Value | df | Sig. | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Age |
Right Ear | 21.666 | 25 | .655 | Not significant |
| Left Ear | 42.577 | 25 | .016 | Significant | |
|
Sex Male/Female |
Right Ear | 3.883 | 5 | .566 | Not significant |
| Left Ear | 5.537 | 5 | .354 | Not significant | |
| Occupation | Right Ear | 39.410 | 45 | .707 | Not significant |
| Left Ear | 41.003 | 45 | .642 | Not significant |
| Characteristics | X2 Value | Df | Sig. | Remark |
| Location | 37.158 | 12 | .000 | Significant |
| Age | 22.633 | 20 | .307 | Not significant |
| Sex | .676 | 4 | .954 | Not significant |
| Occupation | 33.618 | 36 | .582 | Not significant |
| Characteristics | X2 Value | Df | Sig. | Remark |
| Location | 25.199 | 12 | .014 | Significant |
| Age | 27.474 | 20 | .122 | Not significant |
| Sex | 4.361 | 4 | .359 | Not significant |
| Occupation | 41.134 | 36 | .256 | Not significant |
| N = 350 | TOTAL (N = 350) | |||
| FINDINGS | RIGHT (N-175) | LEFT (N-175) | ||
|
HEARWHO APP Normal findings Abnormal findings |
N (%) | N (%) | ||
| 34 (19.4) | 45 (25.7) | 79 (22.6) | Normal hearing | |
| 141 (80.6) | 130 (74.3) | 271 (77.4) | Hearing loss | |
| TOTAL | 175 (100.0) | 175 (100.0) | 350 (100.0) | |
|
OTOSCOPY Normal findings Abnormal findings |
N (%) | N (%) | ||
| 58 (33.1)) | 65 (37.1) | 123 (35.0) | Normal ear | |
| 117 (66.9) | 110 (62.9) | 227 (65.0) | Ear pathology | |
| TOTAL | 175 (100.0) | 175 (100.0) | 350 (100.0) | |
| KAPPA | 0.914 | 0.000 | ||
| S/N | Treatment Rendered | N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ear syringing | 43 (12.3_ |
| 2 | Foreign body removal | 3 (0.86) |
| 3 | Ear dressing | 3 (0.86) |
| 4 | Ear toileting | 1 (0.29) |
| 5 | Counselling | 9 (2.57) |
| 6 | Reassurance | 35 (10.0) |
| 7 | Referrals for follow up and further evaluations | |
| Otological conditions | 350 (100.0) | |
| Others (Nasal polyps, sore throat, Non otorhinolaryngological conditions) |
9 (2.57) |
4. Discussion
4.1. Demography
4.2. Challenges
4.3. Discrepancy between HearWHO App findings and Otoscopic findings
4.4. Solutions proffered
5. Conclusion
6. Recommendations
References
- Emmett SD, Platt A, Gallo JJ, Labrique AB, Wang NY, Inglis-Jenson M, Jenson CD, Hofstetter P, Hicks KL, Ross AA, Egger JR. Prevalence of Childhood Hearing Loss in Rural Alaska. Ear and Hearing. 2023 Jun 8:10-97. [CrossRef]
- Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al.; GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016. October 8;388(10053):1545–1602.
- Resolution WHA70.13. Prevention of deafness and hearing loss. In: Seventieth World Health Assembly, Geneva, 31 May 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Available from: http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA70/A70_R13-en.pdf?ua=1.
- Wilson BS, Tucci DL, Merson MH, O’Donoghue GM. Global hearing health care: new findings and perspectives. Lancet. 2017. December 2;390(10111):2503–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]. [CrossRef]
- WHO. Deafness and Hearing loss: Key facts. Newsroom. 27 February, 2023.
- Shan A, Ting JS, Price C, Goman AM, Willink A, Reed NS, Nieman CL. Hearing loss and employment: a systematic review of the association between hearing loss and employment among adults. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology. 2020 May; 134(5):387-97. [CrossRef]
- Kodiya AM, Afolabi OA, Ahmad BM. The burden of hearing loss in Kaduna, Nigeria: a 4-year study at the National Ear Care Centre. Ear Nose Throat J. 2012 Apr; 91(4):156-63. [CrossRef]
- Akpalaba I.O, Onyeagwara C.N., Community Otorhinolaryngological service in a group of Schools in South- South Nigeria. Nigerian journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 2010 - 2015; 8-12.
- Tamblay N, Torrente MC, Huidobro B, Tapia-Mora D, Anabalon K, Polack S, Bright T. Prevalence, risk factors and causes of hearing loss among adults 50 years and older in Santiago, Chile: Results from a rapid assessment of hearing loss survey. International journal of audiology. 2023 Jan 3; 62(1):53-61. [CrossRef]
- Khan, SA. Importance of hearing and hearing loss treatment & recovery. IJSA. 2022; 3(1):14-6.
- De Raeve L, Cumpăt MC, van Loo A, Costa IM, Matos MA, Dias JC, Mârțu C, Cavaleriu B, Gherguț A, Maftei A, Tudorean OC. Quality Standard for Rehabilitation of Young Deaf Children Receiving Cochlear Implants. Medicina. 2023 Jul 24;59(7):1354. [CrossRef]
- Swanepoel DW, De Sousa KC, Smits C, Moore DR. Mobile applications to detect hearing impairment: opportunities and challenges. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2019: 10; 97(10):717. [CrossRef]
- Yousuf Hussein S, Swanepoel W, Mahomed F, Biagio de Jager L. Community-based hearing screening for young children using an mHealth service-delivery model. Glob Health Action. 2018;11(1):1467077. [CrossRef]
- Case study by UNESCO-Pearson initiative for literacy: improved livelihoods in a digital World. Paris: United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization; 2017.
- Mobile industry impact report: sustainable development goals. London: Groupe Spéciale Mobile Association; 2018. Available from: https://www.gsmaintelligence.com/research/?file=ecf0a523bfb1c9841147a335cac9f6a7&download.
- Oluwakemi Ololade Odukoya, Adebola A Adejimi, Brenda Isikekpei, Chris S Jim, Akin Osibogun, Folasade Tolulope Ogunsola. Epidemiological trends of coronavirus disease 2019 in Nigeria; 2020 : 27 (4): 271 – 279. [CrossRef]
- Hansson I, Buratti S, Allwood CM. Experts' and Novices' Perception of Ignorance and Knowledge in Different Research Disciplines and Its Relation to Belief in Certainty of Knowledge. Front Psychol. 2017; 8:377. Published 2017 Mar 17. [CrossRef]
- Singh KP, Prasad A. A Study of Different Parameters In Complicated Versus Uncomplicated Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. Int J Acad Med Pharm. 2023; 5(4):1695-7. [CrossRef]
- Więckowska B, Kubiak KB, Jóźwiak P, Moryson W, Stawińska-Witoszyńska B. Cohen’s Kappa Coefficient as a Measure to Assess Classification Improvement following the Addition of a New Marker to a Regression Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022 Aug 17;19(16):10213. [CrossRef]
- Cathy R. Balsom, Alison Farrell, Deborah V Kelly et al. Barriers and Enablers to Testing for Hepatitis C Infection in People Who Inject Drugs – A Scoping Review of the Qualitative Evidence, 14 February 2023, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square. [CrossRef]
- Pratten, Susan; Schindel Martn, Lori Dr.; Ryan, Ellen Dr.; Anas, Ann; Spadafora, Pat; and Hart, Rebecca, "Older Adults Embracing Technology: Leave No One Behind" (2005). Publications and Scholarship. 15. https://source.sheridancollege.ca/centres_elder_publ/15.
- Mustafa MW, Abdelrahim AG, Khodary MM, Aref ZF. Restoration of quality of life in elderly with hearing loss. International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery. 2023 Jan;9(1):1.
- Agarwal S, LeFevre AE, Lee J, L’Engle K, Mehl G, Sinha C, et al.; WHO mHealth Technical Evidence Review Group. Guidelines for reporting of health interventions using mobile phones: mobile health (mHealth) evidence reporting and assessment (mERA) checklist. BMJ. 2016. March 17;352:i1174. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim RL, Ajide KB, Olatunde Julius O. Easing of lockdown measures in Nigeria: Implications for the healthcare system. Health Policy Technol. 2020;9(4):399-404. [CrossRef]
- Phillips OR, Baguley DM, Pearson SE, Akeroyd MA. The long-term impacts of hearing loss, tinnitus and poor balance on the quality of life of people living with and beyond cancer after platinum-based chemotherapy: a literature review. Journal of Cancer Survivorship. 2023 Jan 13:1-9.
- Sarah M. Theodoroff, M. Samantha Lewis, Robert L. Folmer, James A. Henry, Kathleen F. Carlson, Hearing Impairment and Tinnitus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes in US Service Members and Veterans Deployed to the Iraq and Afghanistan Wars, Epidemiologic Reviews, Volume 37, Issue 1, 2015, Pages 71–85. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, F. , Abdulkareem J.H., Chowdhury A.A. Major public health problems in Nigeria: a review. Southeast Asia J Public Health. 2017;7(1):6–11. [CrossRef]
- Dillard LK, Nelson-Bakkum ER, Walsh MC, Schultz A. Self-reported hearing loss is associated with poorer perceived health care access, timeliness, satisfaction, and quality: Findings from the Survey of the Health of Wisconsin. Disability and Health Journal. 2023; 1;16(1):101394. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




