Submitted:
15 December 2023
Posted:
15 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
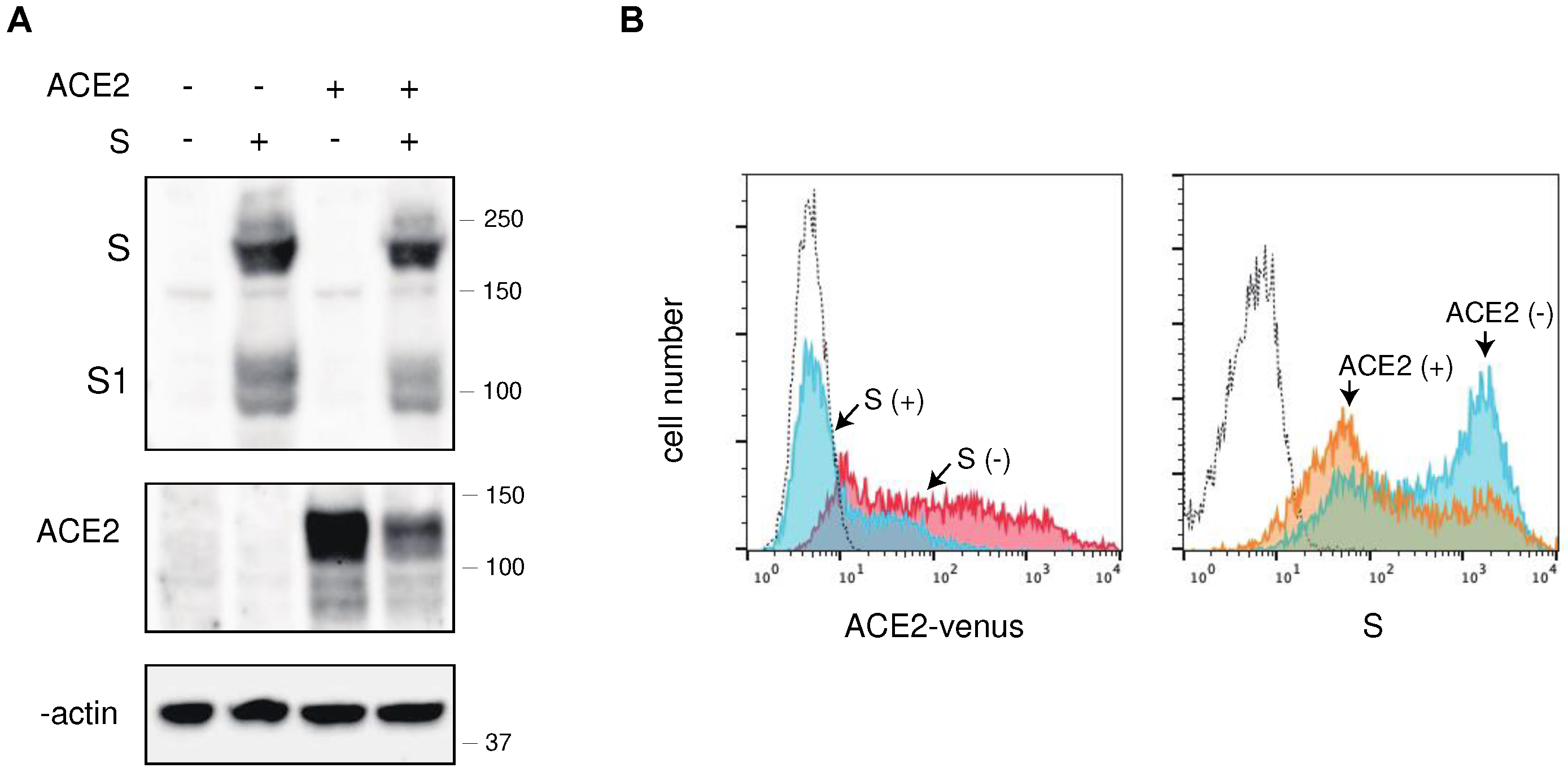
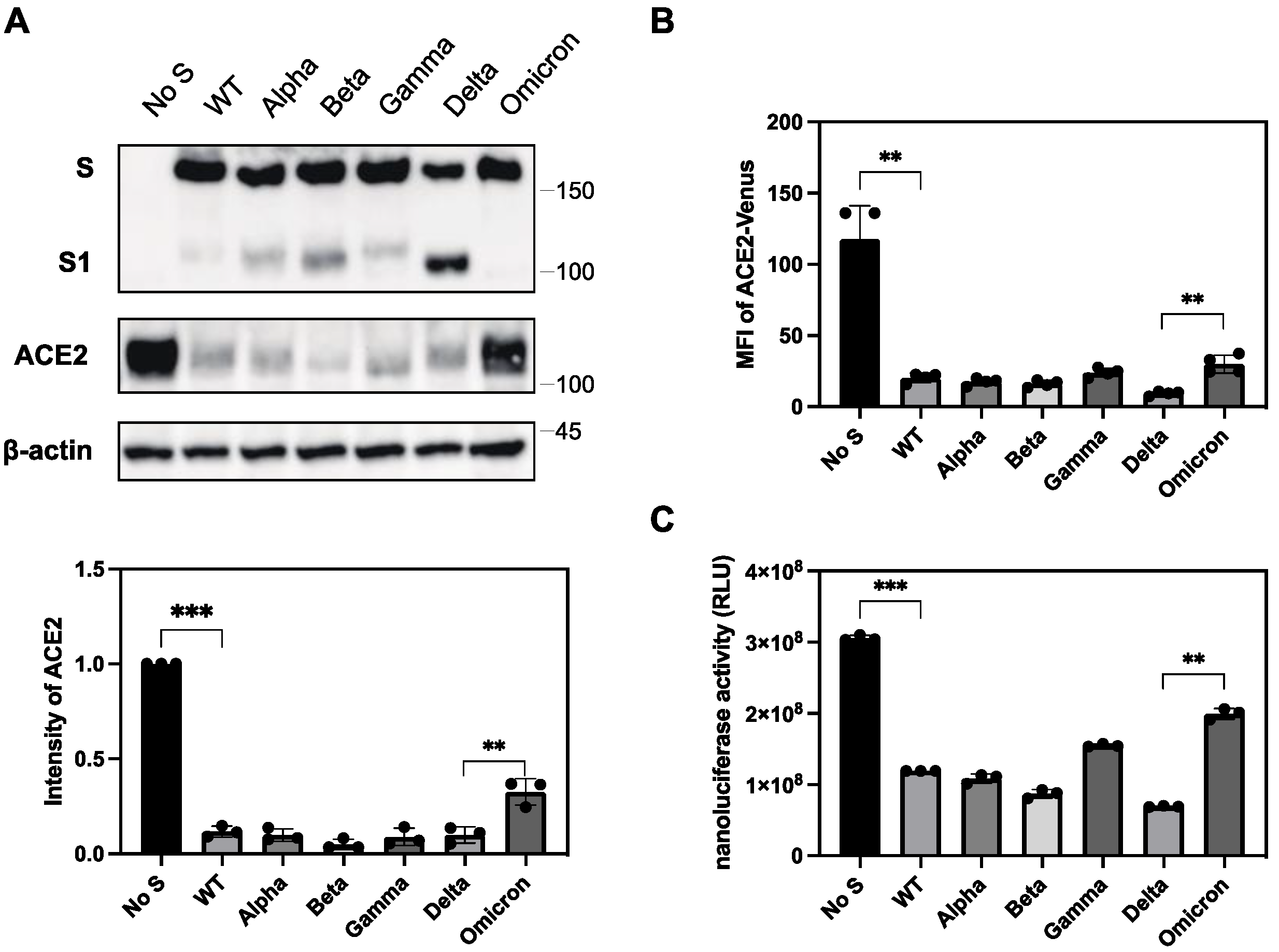
2.1. The S protein of SARS-CoV-2 downregulates ACE2
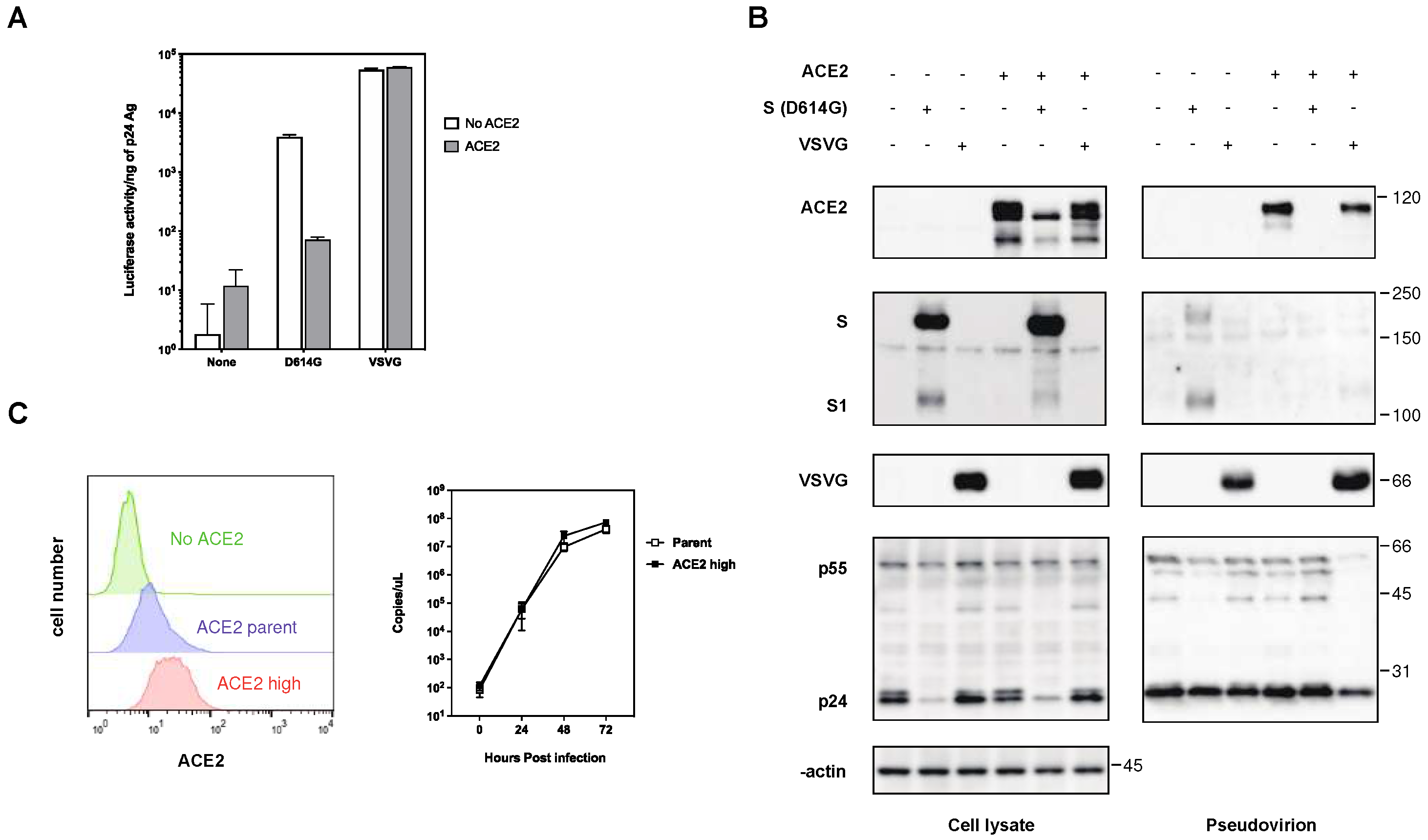
2.2. The expression of ACE2 impeded the infectivity of pseudovirus with the S protein of SARS-CoV-2
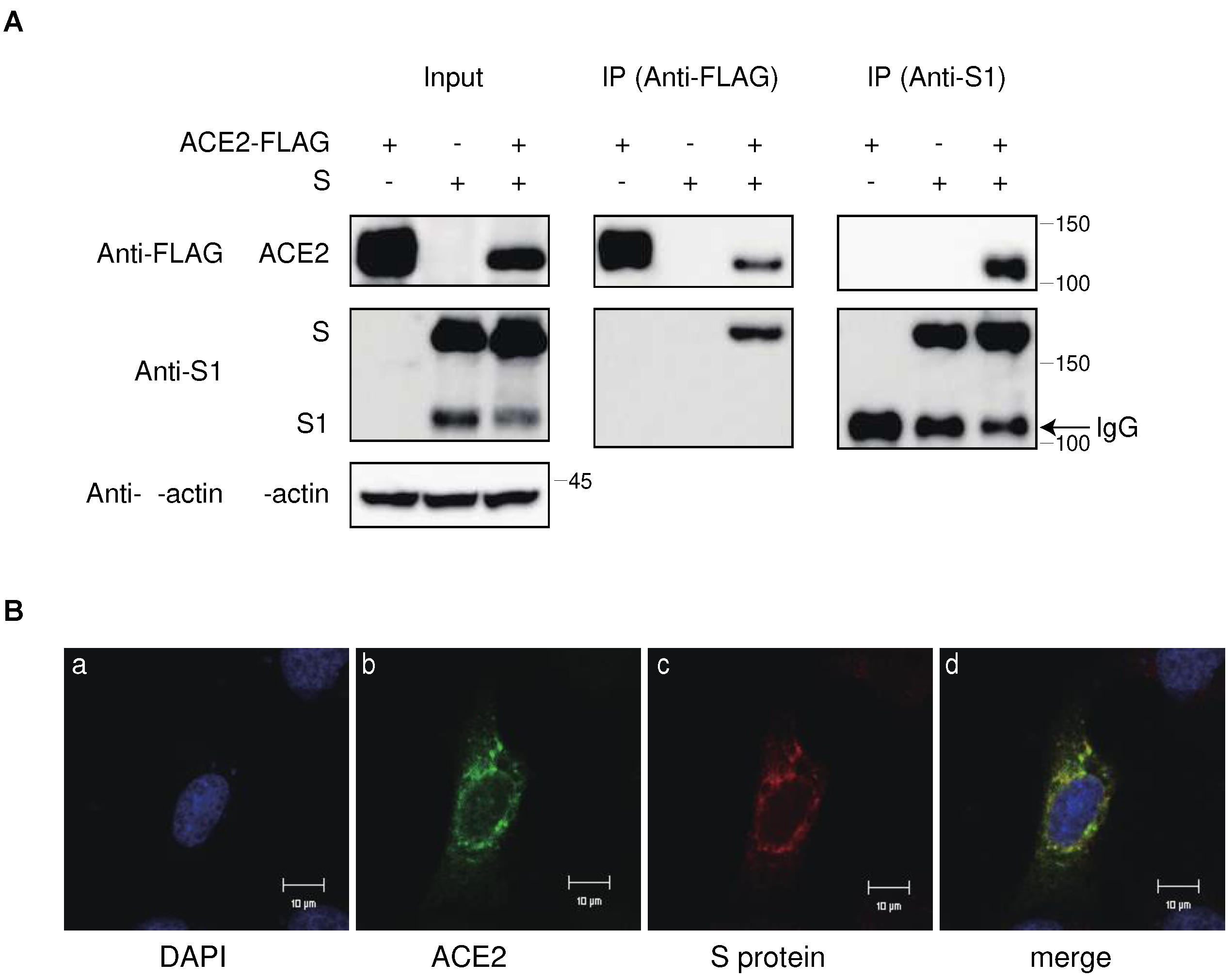
2.3. Interaction of ACE2 with the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 in the cytoplasmic compartment of the cells
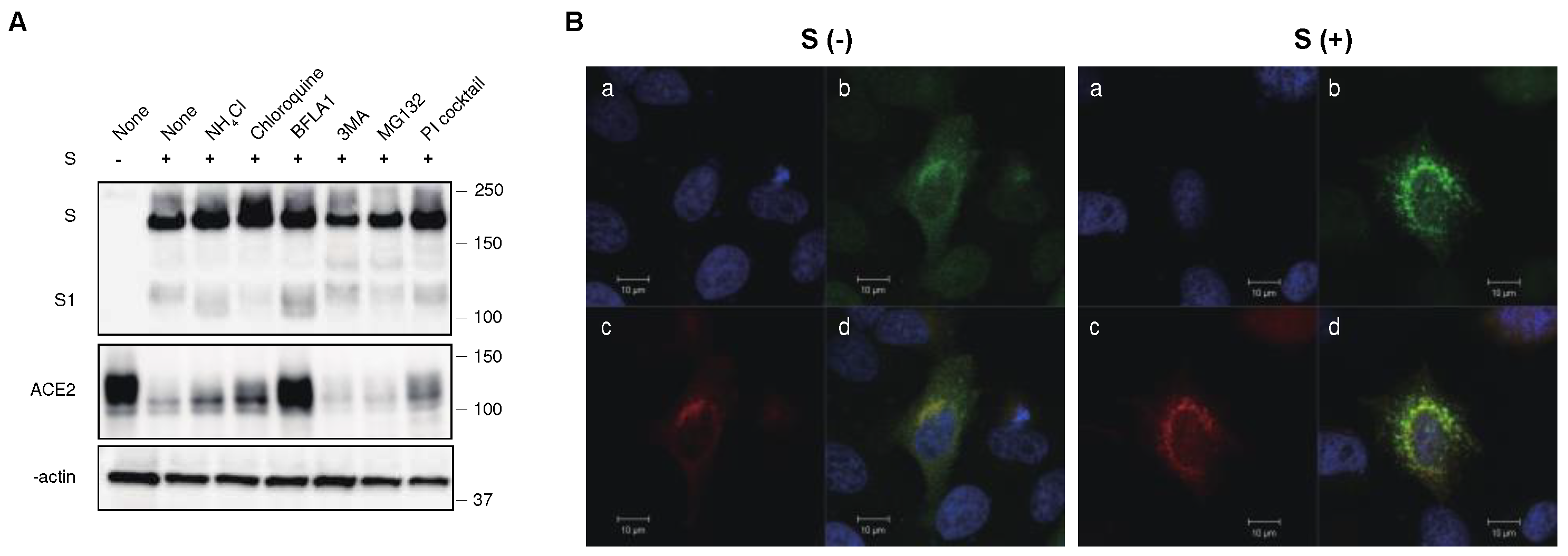
2.4. The S protein degrades ACE2 in the lysosomal compartment through the endocytic pathway
2.5. Cytoplasmic domains of ACE2 and S protein are not essential for the downregulation of ACE2
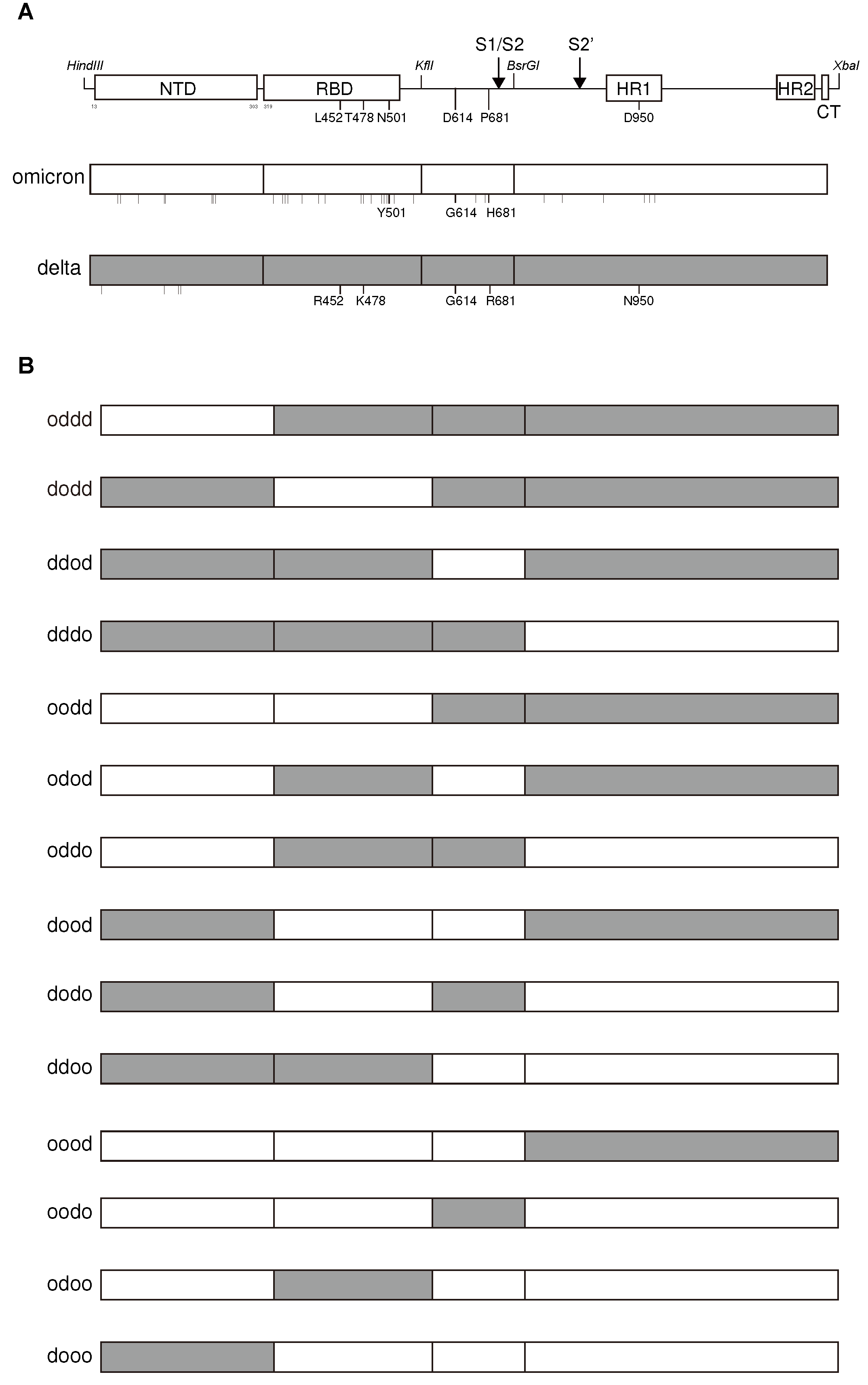
2.6. Differential ability of S protein from SARS-CoV-2 variants to downregulate ACE2
2.7. Determination of the lower ability of ACE2 downregulation in Omicron variants by Receptor Binding Domain and Heptad Repeat domains of S the protein
2.8. The determination of higher ability of ACE2 downregulation in the Delta variants by the combination of three substitutions in L452R/P681R/D950N of the S protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell lines, reagents, and viruses
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Infection experiments
4.4. Real-time RT-PCR
4.5. Flow cytometry
4.6. Quantitative measurement of ACE2 downregulation activity by the S protein from VOCs and its chimeras
4.7. Measurement of fusion activity of S protein with ACE2
4.8. Immunoprecipitation and western blotting
4.9. Laser Scanning Confocal microscopic analysis
4.10. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bager, P.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Bhatt, S.; Stegger, M.; Legarth, R.; Moller, C. H.; Skov, R. L.; Valentiner-Branth, P.; Voldstedlund, M.; Fischer, T. K.; Simonsen, L.; Kirkby, N. S.; Thomsen, M. K.; Spiess, K.; Marving, E.; Larsen, N. B.; Lillebaek, T.; Ullum, H.; Molbak, K.; Krause, T. G.; Omicron-Delta study, g. , Risk of hospitalisation associated with infection with SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant versus delta variant in Denmark: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 2022, 22, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, F. B.; Talisa, V. B.; Castro, A. D.; Shaikh, O. S.; Omer, S. B.; Butt, A. A. , COVID-19 disease severity in US Veterans infected during Omicron and Delta variant predominant periods. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, T.; Ferguson, N. M.; Nash, S. G.; Webster, H. H.; Flaxman, S.; Andrews, N.; Hinsley, W.; Bernal, J. L.; Kall, M.; Bhatt, S.; Blomquist, P.; Zaidi, A.; Volz, E.; Aziz, N. A.; Harman, K.; Funk, S.; Abbott, S.; Nyberg, T.; Ferguson, N. M.; Nash, S. G.; Webster, H. H.; Flaxman, S.; Andrews, N.; Hinsley, W.; Lopez Bernal, J.; Kall, M.; Bhatt, S.; Blomquist, P.; Zaidi, A.; Volz, E.; Abdul Aziz, N.; Harman, K.; Funk, S.; Abbott, S.; Hope, R.; Charlett, A.; Chand, M.; Ghani, A. C.; Seaman, S. R.; Dabrera, G.; De Angelis, D.; Presanis, A. M.; Thelwall, S.; Hope, R.; Charlett, A.; Chand, M.; Ghani, A. C.; Seaman, S. R.; Dabrera, G.; De Angelis, D.; Presanis, A. M.; Thelwall, S. , Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B. 1.1.529) and delta (B.1.617.2) variants in England: a cohort study. Lancet 2022, 399, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Sigal, A.; Milo, R.; Jassat, W. , Estimating disease severity of Omicron and Delta SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nature Rev Immunol 2022, 22, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silhol, F.; Sarlon, G.; Deharo, J.-C.; Vaïsse, B. , Downregulation of ACE2 induces overstimulation of the renin–angiotensin system in COVID-19: should we block the renin–angiotensin system? Hypertens Res 2020, 43, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Moniwa, N.; Takizawa, H.; Ura, N.; Shimamoto, K. , Potential differential effects of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on SARS-CoV-2 infection and lung injury in COVID-19. Hypertens Res 2020, 43, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrell, L. M.; Johnston, C. I.; Tikellis, C.; Cooper, M. E. , ACE2, a new regulator of the renin–angiotensin system. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2004, 15, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, M. K.; Karnik, S.; Saef, J.; Bergmann, C.; Barnard, J.; Lederman, M. M.; Tilton, J.; Cheng, F.; Harding, C. V.; Young, J. B.; Mehta, N.; Cameron, S. J.; McCrae, K. R.; Schmaier, A. H.; Smith, J. D.; Kalra, A.; Gebreselassie, S. K.; Thomas, G.; Hawkins, E. S.; Svensson, L. G. , SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2: The biology and clinical data settling the ARB and ACEI controversy. eBioMedicine 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S. G.; Rattis, B. A. d. C.; Ottaviani, G.; Celes, M. R. N.; Dias, E. P. , ACE2 down-regulation may act as a transient molecular disease causing RAAS dysregulation and tissue damage in the microcirculatory environment among COVID-19 patients. Am J Pathol 2021, 191, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Bao, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Chappell, M.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Leibbrandt, A.; Wada, T.; Slutsky, A. S.; Liu, D.; Qin, C.; Jiang, C.; Penninger, J. M. , A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat Med 2005, 11, 875–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowacka, I.; Bertram, S.; Herzog, P.; Pfefferle, S.; Steffen, I.; Muench, M. O.; Simmons, G.; Hofmann, H.; Kuri, T.; Weber, F.; Eichler, J.; Drosten, C.; Pöhlmann, S. , Differential downregulation of ACE2 by the spike proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and human coronavirus NL63. J Virol 2010, 84, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniloski, Z.; Jordan, T. X.; Ilmain, J. K.; Guo, X.; Bhabha, G.; tenOever, B. R.; Sanjana, N. E. , The Spike D614G mutation increases SARS-CoV-2 infection of multiple human cell types. Elife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ozono, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ode, H.; Sano, K.; Tan, T. S.; Imai, K.; Miyoshi, K.; Kishigami, S.; Ueno, T.; Iwatani, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Tokunaga, K. , SARS-CoV-2 D614G spike mutation increases entry efficiency with enhanced ACE2-binding affinity. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliche, J.; Kuss, H.; Ali, M.; Ivarsson, Y. , Cytoplasmic short linear motifs in ACE2 and integrin β(3) link SARS-CoV-2 host cell receptors to mediators of endocytosis and autophagy. Sci Signal 2021, 14, (665).
- Pang, X. C.; Zhang, H. X.; Zhang, Z.; Rinkiko, S.; Cui, Y. M.; Zhu, Y. Z. , The two-way switch role of ACE2 in the treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia and underlying comorbidities. Molecules 2021, 26, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser, H.; Shimizu, R.; Ito, J.; Saito, A.; Sato, K.; Ikeda, T. , Monitoring fusion kinetics of viral and target cell membranes in living cells using a SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein-mediated membrane fusion assay. STAR Protoc 2022, 3, 101773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kiso, M.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Imai, M.; Takeda, M.; Kinoshita, N.; Ohmagari, N.; Gohda, J.; Semba, K.; Matsuda, Z.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kawaoka, Y.; Inoue, J. I. , The anticoagulant nafamostat potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated fusion in a cell fusion assay system and viral infection in vitro in a cell-type-dependent manner. Viruses 2020, 12, (6).
- Motozono, C.; Toyoda, M.; Zahradnik, J.; Saito, A.; Nasser, H.; Tan, T. S.; Ngare, I.; Kimura, I.; Uriu, K.; Kosugi, Y.; Yue, Y.; Shimizu, R.; Ito, J.; Torii, S.; Yonekawa, A.; Shimono, N.; Nagasaki, Y.; Minami, R.; Toya, T.; Sekiya, N.; Fukuhara, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Schreiber, G.; Ikeda, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Ueno, T.; Sato, K. , SARS-CoV-2 spike L452R variant evades cellular immunity and increases infectivity. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1124–1136.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, Y.; Kiso, M.; Iida, S.; Uraki, R.; Hirata, Y.; Imai, M.; Suzuki, T.; Yamayoshi, S.; Kawaoka, Y. , In SARS-CoV-2 delta variants, Spike-P681R and D950N promote membrane fusion, Spike-P681R enhances spike cleavage, but neither substitution affects pathogenicity in hamsters. EBioMedicine 2023, 91, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Irie, T.; Suzuki, R.; Maemura, T.; Nasser, H.; Uriu, K.; Kosugi, Y.; Shirakawa, K.; Sadamasu, K.; Kimura, I.; Ito, J.; Wu, J.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Ito, M.; Yamayoshi, S.; Loeber, S.; Tsuda, M.; Wang, L.; Ozono, S.; Butlertanaka, E. P.; Tanaka, Y. L.; Shimizu, R.; Shimizu, K.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Kawabata, R.; Sakaguchi, T.; Tokunaga, K.; Yoshida, I.; Asakura, H.; Nagashima, M.; Kazuma, Y.; Nomura, R.; Horisawa, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Imai, M.; Tanaka, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Ikeda, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Kawaoka, Y.; Sato, K. , Enhanced fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Delta P681R mutation. Nature 2022, 602, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. , Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Ye, G.; Shi, K.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Aihara, H.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. , Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 581, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A. C.; Park, Y. J.; Tortorici, M. A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A. T.; Veesler, D. , Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K. S.; Goldsmith, J. A.; Hsieh, C. L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B. S.; McLellan, J. S. , Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama, J.; Mangasarian, A.; Trono, D. , Cell-surface expression of CD4 reduces HIV-1 infectivity by blocking Env incorporation in a Nef- and Vpu-inhibitable manner. Curr Biol 1999, 9, 622–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildum, S.; Schindler, M.; Münch, J.; Kirchhoff, F. , Contribution of Vpu, Env, and Nef to CD4 down-modulation and resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected T cells to superinfection. J Virol 2006, 80, 8047–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque, K.; Zhao, Y. S.; Cohen, E. A. , Vpu exerts a positive effect on HIV-1 infectivity by down-modulating CD4 receptor molecules at the surface of HIV-1-producing cells. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 28346–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, M.; Ogata, Y.; Mahiti, M.; Maeda, Y.; Kuang, X. T.; Miura, T.; Jessen, H.; Walker, B. D.; Brockman, M. A.; Brumme, Z. L.; Ueno, T. , Differential ability of primary HIV-1 Nef isolates to downregulate HIV-1 entry receptors. J Virol 2015, 89, 9639–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welstead, G. G.; Hsu, E. C.; Iorio, C.; Bolotin, S.; Richardson, C. D. , Mechanism of CD150 (SLAM) down regulation from the host cell surface by measles virus hemagglutinin protein. J Virol 2004, 78, 9666–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Fox, D. M.; Gao, C.; Stanley, S. A.; Luo, K. , SARS-CoV-2 down-regulates ACE2 through lysosomal degradation. Mol Biol Cell 2022, 33, ar147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stertz, S.; Reichelt, M.; Spiegel, M.; Kuri, T.; Martínez-Sobrido, L.; García-Sastre, A.; Weber, F.; Kochs, G. , The intracellular sites of early replication and budding of SARS-coronavirus. Virology 2007, 361, 304–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klumperman, J.; Locker, J. K.; Meijer, A.; Horzinek, M. C.; Geuze, H. J.; Rottier, P. J. , Coronavirus M proteins accumulate in the Golgi complex beyond the site of virion budding. J Virol 1994, 68, 6523–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujike, M.; Huang, C.; Shirato, K.; Makino, S.; Taguchi, F. , The contribution of the cytoplasmic retrieval signal of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus to intracellular accumulation of S proteins and incorporation of S protein into virus-like particles. J Gen Virol 2016, 97, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y.; Terasawa, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Mitsuura, C.; Nakashima, K.; Yusa, K.; Harada, S. , Separate cellular localizations of human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1) Env and glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) are required for HTLV-1 Env-mediated fusion and infection. J Virol 2015, 89, 502–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, Z. H.; Greifer, N.; Hadavand, A.; Murphy, S. N.; Estiri, H. , Estimates of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 2 subvariant severity in New England. JAMA Netw Open 2022, 5, e2238354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaku, Y.; Kuwata, T.; Zahid, H. M.; Hashiguchi, T.; Noda, T.; Kuramoto, N.; Biswas, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimizu, M.; Kawanami, Y.; Shimura, K.; Onishi, C.; Muramoto, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sasaki, J.; Nagasaki, Y.; Minami, R.; Motozono, C.; Toyoda, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kishi, H.; Fujii, K.; Tatsuke, T.; Ikeda, T.; Maeda, Y.; Ueno, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Iwagoe, H.; Matsushita, S. , Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by antibodies induced in convalescent patients with COVID-19. Cell Rep 2021, 36, 109385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y.; Foda, M.; Matsushita, S.; Harada, S. , Involvement of both the V2 and V3 regions of the CCR5-tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope in reduced sensitivity to macrophage inflammatory protein 1 α. J Virol 2000, 74, 1787–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y.; Takemura, T.; Chikata, T.; Kuwata, T.; Terasawa, H.; Fujimoto, R.; Kuse, N.; Akahoshi, T.; Murakoshi, H.; Tran, G. V.; Zhang, Y.; Pham, C. H.; Pham, A. H. Q.; Monde, K.; Sawa, T.; Matsushita, S.; Nguyen, T. V.; Nguyen, K. V.; Hasebe, F.; Yamashiro, T.; Takiguchi, M. , Existence of replication-competent minor variants with different coreceptor usage in plasma from HIV-1-infected individuals. J Virol 2020, 94, (12).
| ACE2 downregulation activity (%)a | Fusion activity (%)b | |
|---|---|---|
| S wild | 100.0 ± 0.4 c | 100.0 ± 8.2 |
| Delta | 142.3 ± 0.5 | 257.7 ± 6.3 |
| Omicron | 75.4 ± 3.5 | 13.3 ± 1.6 |
| oddd | 134.8 ± 1.1 | 212.8 ± 8.6 |
| dodd | 93.5 ± 1.9 | 176.8 ± 5.8 |
| ddod | 113.3 ± 1.2 | 95.6 ± 4.8 |
| dddo | 110.2 ± 2.7 | 127.9 ± 5.2 |
| oodd | 111.7 ± 3.3 | 184.9 ± 9.0 |
| odod | 104.1 ± 2.4 | 71.1 ± 5.8 |
| oddo | 107.0 ± 3.7 | 117.3 ± 3.9 |
| dood | 104.6 ± 2.2 | 83.7 ± 9.8 |
| dodo | 47.8 ± 3.9 | 48.4 ± 2.6 |
| ddoo | 88.5 ± 3.1 | 26.2 ± 0.7 |
| oood | 117.4 ± 3.0 | 67.5 ± 3.7 |
| oodo | 67.7 ± 1.2 | 46.7 ± 4.7 |
| odoo | 77.5 ± 2.0 | 24.5 ± 3.1 |
| dooo | 75.9 ± 2.2 | 13.4 ± 1.1 |
| ACE2 downregulation activity (%)a | Fusion activity (%)b | |
|---|---|---|
| S wild (Wuhan) | 100.0 ± 5.9 | 100.0 ± 5.7 |
| Delta | 156.4 ± 4.8 | 196.5 ± 18.3 |
| Omicron | 71.0 ± 7.7 | 14.3 ± 2.6 |
| L452R | 107.6 ± 5.5 | 97.0 ± 9.3 |
| P681R | 95.3 ± 11.4 | 166.5 ± 12.1 |
| D950N | 117.1 ± 4.4 | 124.2 ± 10.2 |
| L452R/P681R | 120.6 ± 6.4 | 170.8 ± 12.9 |
| L452R/D950N | 111.8 ± 5.7 | 122.2 ± 5.2 |
| P681R/D950N | 133.5 ± 4.8 | 196.6 ± 10.7 |
| L452R/P681R/D950N | 156.6 ± 5.9 | 187.5 ± 6.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





