Submitted:
13 December 2023
Posted:
14 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
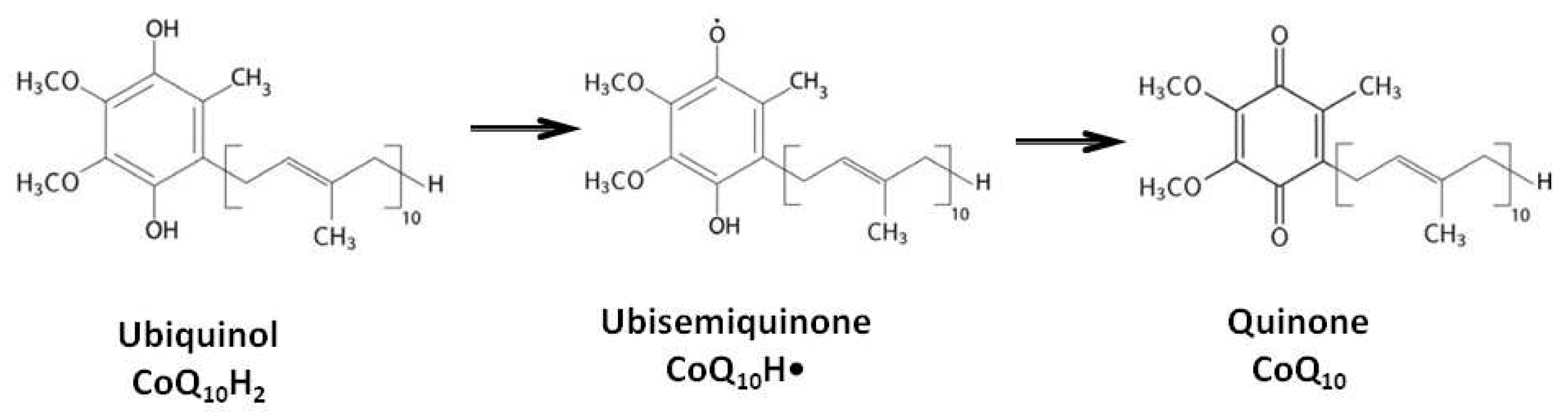
2. Biological Functions of Coenzyme Q10
3. Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 Therapy When Administered Orally
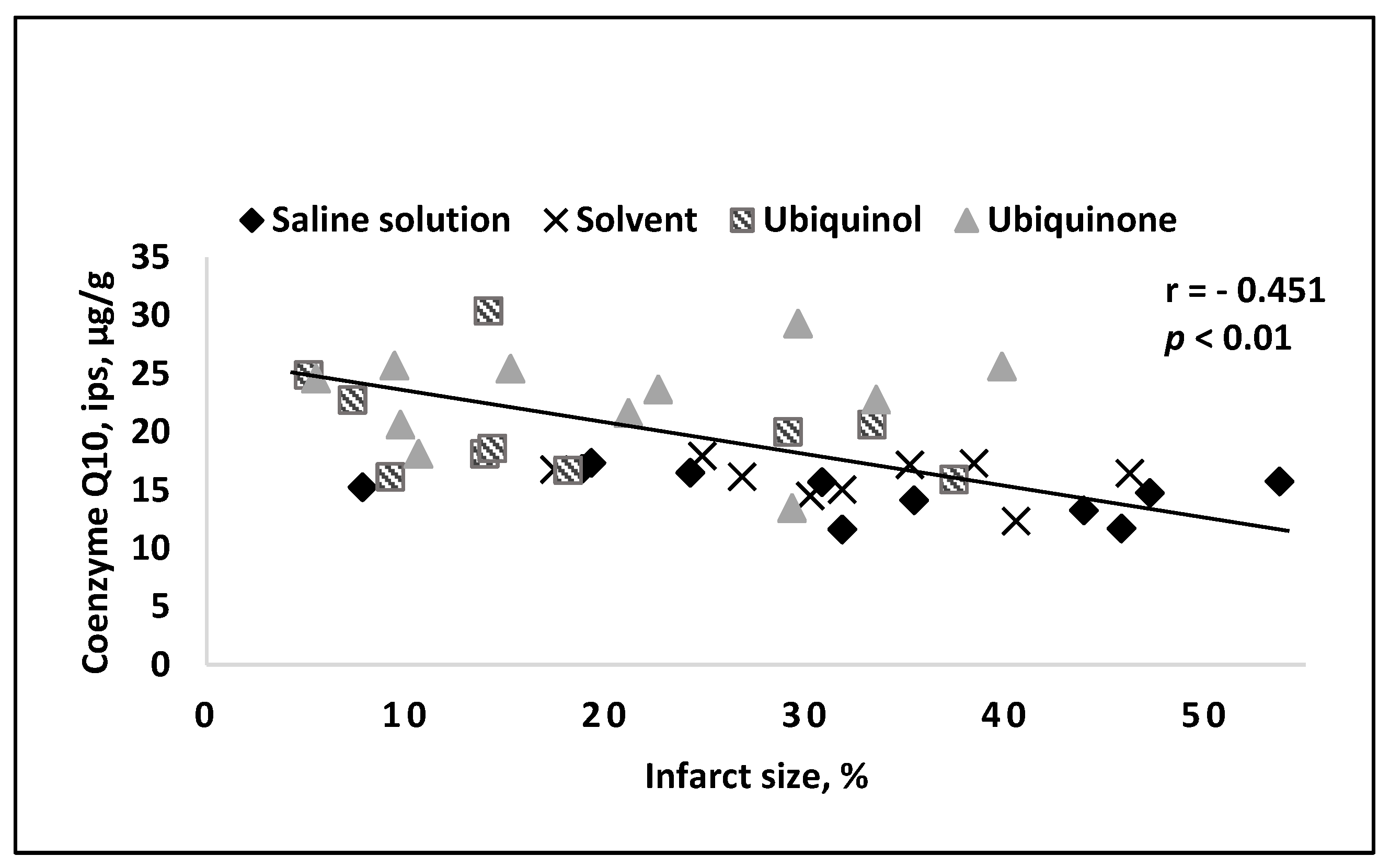
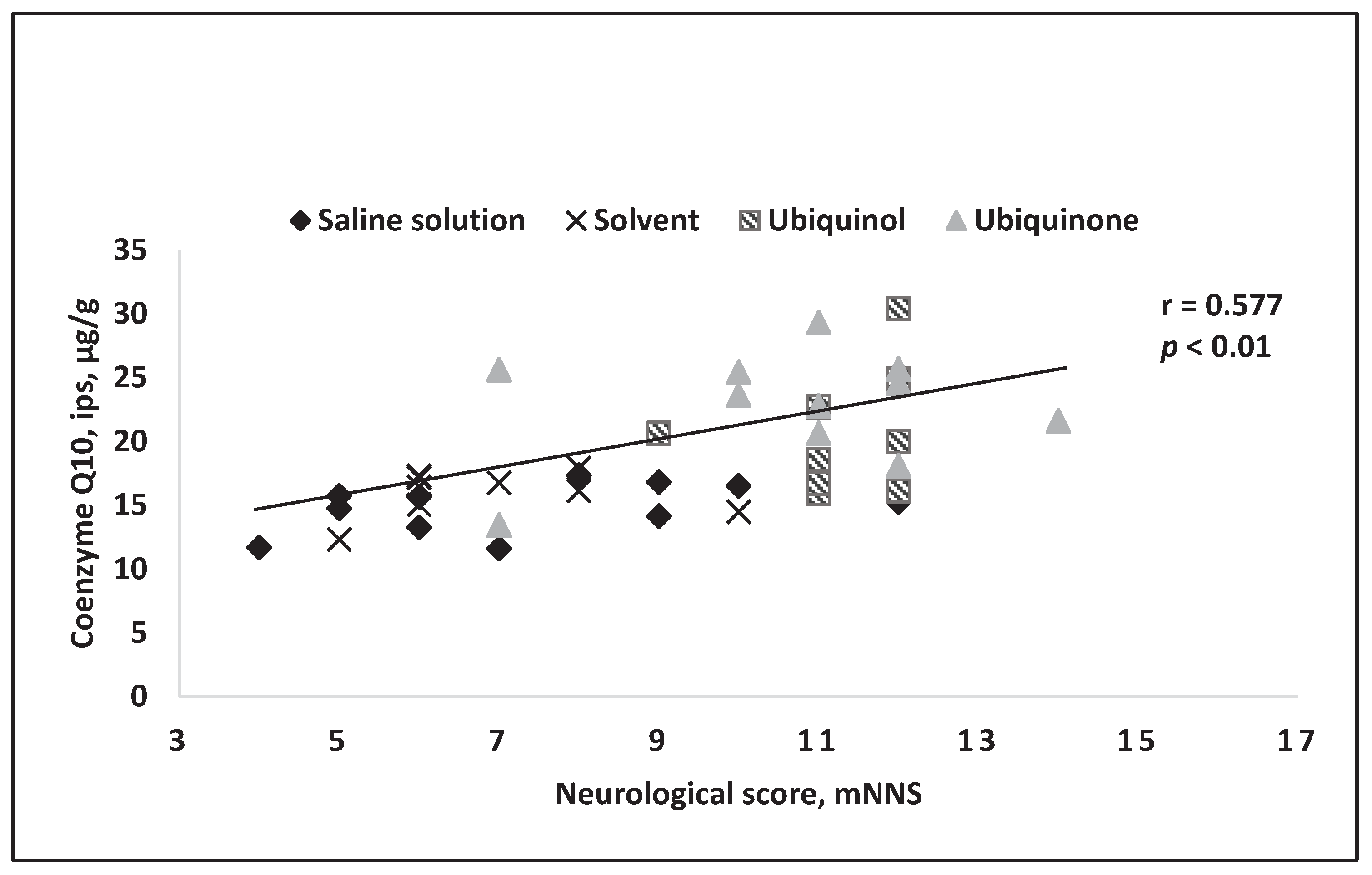
4. Results of Intravenous Coenzyme Q10 Administration in Experimental Models In Vivo
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crane, F.L.; Hatef, Y.; Lester, R.L.; Widmer, C. Isolation of quinine from beef heart mitochondria. BiochimBiophysActa 1957, 25, 220–221. [Google Scholar]
- Raizner, A. E. Coenzyme Q10. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2019, 15, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.N.; Zimmerman, M.; Milledge, G.Z.; Hou, X.L.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, P.A. Water-Soluble Coenzyme Q10 Reduces Rotenone-Induced Mitochondrial Fission. Neurochem Res. 2017, 42, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, S.; Haddadi, R.; Saki, S.; Kourosh-Arami, M.; Rashno, M.; Mojaver, A.; Komaki, A. Neuroprotective effects of coenzyme Q10 on neurological diseases: a review article. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1188839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povarova, O.; Balatsky, A.; Gusakov, V.; Medvedev, O. Effect of coenzyme Q10 on expression of UbiAd1 gene in rat model of local cerebral ischemia. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med 2018, 165, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erol, B.; Bozlu, M.; Hanci, V.; Tokgoz, H.; Bektas, S.; Mungan, G. Coenzyme Q10 treatment reduces lipid peroxidation, inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthases, and germ cell-specific apoptosis in a rat model of testicular ischemia/reperfusion injury. Fertil Steril. 2010, 93, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattarinezhad, E.; Shafaroodi, H.; Sheikhnouri, K.; Mousavi, Z.; Moezi, L. The effects of coenzyme Q10 on seizures in mice: the involvement of nitric oxide. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 37, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, W.Q.; Gong, H. Effects of milk and coenzyme Q10 on the interference of acrylonitrile on vascular endothelial functions. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. Chinese. 2011, 91, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Arenas-de Larriva, A.P.; Limia-Perez, L.; Romero-Cabrera, J.L.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; López-Miranda, J. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation for the Reduction of Oxidative Stress: Clinical Implications in the Treatment of Chronic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Moreno, J.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Camargo, A.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Tinahones, F.J.; Striker, G.E.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Villalba, J.M.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M. Mediterranean Diet Supplemented With Coenzyme Q10 Modulates the Postprandial Metabolism of Advanced Glycation End Products in Elderly Men and Women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2018, 73, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuneki, H.; Sekizaki, N.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Wada, T.; Okamoto, T.; Kimura, I.; Sasaoka, T. Coenzyme Q10 prevents high glucose-induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 566, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.-L.; Chen, L.-H.; Chiou, S.-H.; Chiou, G.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chou, H.-Y.; Chen, L.-K.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chiu, T.-H.; Tsai, C.-S.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 suppresses oxLDL-induced endothelial oxidative injuries by the modulation of LOX-1-mediated ROS generation via the AMPK/PKC/NADPH oxidase signaling pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, S227–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozaeva, L.P.; Gorodetskaya, E.A.; Ruuge, E.K.; Kalenikova, E.I.; Medvedev, O.S. Beneficial effect of coenzyme Q10 injection on nitric oxide -related dilation of the rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017, 794, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; de la Cruz-Ares, S.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Alcalá-Diaz, J.F.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; López-Miranda, J. Coenzyme Q10 and Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, A.Y.; Shirokov, I.V.; Toshchakov SV, Kozlova AD, Obolenskaya ON, Mariasina SS, Ivlev VA, Gartseev IB, Medvedev OS. Effects of Coenzyme Q10 on the Biomarkers (Hydrogen, Methane, SCFA and TMA) and Composition of the Gut Microbiome in Rats. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023, 16, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargreaves, I.; Heaton, R.A.; Mantle, D. Disorders of Human Coenzyme Q10 Metabolism: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Maraver, J.; Cordero, M.D.; Oropesa-Avila, M.; Vega, A.F.; de la Mata, M.; Pavon, A.D.; Alcocer-Gomez, E.; Calero, C.P.; Paz, M.V.; Alanis, M.; de Lavera, I.; Cotan, D.; Sanchez-Alcazar, J.A. Clinical applications of coenzyme Q10. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2014, 19, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testai, L.; Martelli, A.; Flori, L.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Colletti, A. Coenzyme Q10: Clinical Applications beyond Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadian, M.; Sharma, G.; Pandita, S.; et al. The Impact of Coenzyme Q10 on Neurodegeneration: a Comprehensive Review. Curr Pharmacol Rep 2022, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Aberg, F. .; Appelkvist, E.L.; Dallner, G.; Ernster, L. Uptake of dietary coenzyme Q supplement is limited in rats. J Nutr. 1995, 125, 446–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepal, P.R.; Han, H.K.; Choi, H.K. Enhancement of solubility and dissolution of coenzyme Q10 using solid dispersion formulation. Int J Pharm. 2010, 383, 147–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Lluch, G.; Del Pozo-Cruz, J.; Sánchez-Cuesta, A.; Cortés-Rodríguez, A.B.; Navas, P. Bioavailability of coenzyme Q10 supplements depends on carrier lipids and solubilization. Nutrition. 2019, 57, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas-Jal, M.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; García-Montoya, E. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation: Efficacy, safety, and formulation challenges. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2020, 19, 574–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor-Maldonado, C.J.; Suárez-Rivero, J.M.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Álvarez-Córdoba, M.; Villalón-García, I.; Munuera-Cabeza, M.; Suárez-Carrillo, A.; Talaverón-Rey, M.; Sánchez-Alcázar, J.A. Coenzyme Q10: Novel Formulations and Medical Trends. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pravst, I.; Aguilera, J.C.R.; Rodriguez, A.B.C.; Jazbar, J.; Locatelli, I.; Hristov, H.; Žmitek, K. Comparative Bioavailability of Different Coenzyme Q10 Formulations in Healthy Elderly Individuals. Nutrients 2020, 12, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalenikova, E.I.; Kharitonova, E.V.; Gorodetskaya, E.A.; Tokareva, O.G.; Medvedev, O.S. Redox status and pharmacokinetics of coenzyme Q10 in rat plasma after its single intravenous administration. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. B 2014, 8, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.L.; Rosenfeldt, F.; Filipiak, K.J. Effect of coenzyme Q10 in Europeans with chronic heart failure: A sub-group analysis of the Q-SYMBIO randomized double-blind trial. Cardiol J. 2019, 26, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Saadi, T.; Assaf, Y.; Farwati, M.; Turkmani, K.; Al-Mouakeh, A.; Shebli, B.; Khoja, M.; Essali, A.; Madmani, M.E. Coenzyme Q10 for heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021, 2, CD008684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu Z, Tian Z, Zhao D, Liang Y, Dai S, Liu M, Hou S, Dong X, Zhaxinima, Yang Y. Effects of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Lipid Profiles in Adults: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022, 108, 232–249. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorat MV, Tabrizi R, Mirhosseini N, Lankarani KB, Akbari M, Heydari ST, Mottaghi R, Asemi Z. The effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on lipid profiles among patients with coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 230. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou. S.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, D.; Liang, Y.; Dai, S.; Ji, Q.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Yang., Y. Efficacy and Optimal Dose of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Inflammation-Related Biomarkers: AGRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 220800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Guo, M.; Chai, H.; Wang, W.T.; Gao, Z.Y.; Shi, D.Z. Effects of Coenzyme Q10 on Statin-Induced Myopathy: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, C.; Köller, Y.; Surkova, E. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on statin-associated myalgia and adherence to statin therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2020, 299, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeldt, F.L.; Haas, S.J.; Krum, H.; Hadj, A.; Ng, K.; Leong, J.Y.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 in the treatment of hypertension: a meta-analysis of the clinical trials. J Hum Hypertens. 2007, 21, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabrizi, R.; Akbari, M.; Sharifi, N.; Lankarani, K. B.; Moosazadeh, M.; Kolahdooz, F.; Taghizadeh, M.; Asemi, Z. . The Effects of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Blood Pressures Among Patients with Metabolic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, M.; Sahraei, Z.; Simani, L.; Heydari, K.; Shahidi, F. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation in acute ischemic stroke: Is it beneficial in short-term administration? Nutr Neurosci. 2020, 23, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazali, S.; Badrin, S.; Norhayati, M.N.; Idris, N.S. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation for prophylaxis in adult patients with migraine-a meta-analysis. BMJ 2021, 11, e039358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane Library. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/advanced-search/search-manager. (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- World Health Organisation. International Clinical Trial Registry Platform. Available online: https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=IRCT20210907052400N1 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- World Health Organisation. International Clinical Trial Registry Platform. Available online: https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ChiCTR1900025513 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- World Health Organisation. International Clinical Trial Registry Platform. Available online: https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ACTRN12605000545662 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Ali, S.H.; Dizaye, K.F. Influence of ubiquinol on angina severity and dyspnea in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol, 2023, 30, e405–e414. [Google Scholar]
- Sangouni, A.A.; Taghdir., M.; Mirahmadi, J.; Sepandi, M.; Parastouei, K. Effects of curcumin and/or coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic control in subjects with metabolic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Nutr J. 2022, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. International Clinical Trial Registry Platform. Available online: https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ChiCTR2100045256 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Samuel, T.Y.; Hasin, T.; Gotsman, I.; Weitzman, T.; Ben Ivgi, F.; Dadon, Z.; Asher, E.; Amir, O.; Glikson, M.; Alcalai, R.; Leibowitz, D. Coenzyme Q10 in the Treatment of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Drugs R D. 2022, 22, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. International Clinical Trial Registry Platform. Available online: https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ChiCTR2100053923 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- ClinicalTrial.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05871086#study-plan https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05984745 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- ClinicalTrial.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05731596 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Zhang, P.; Chen, K.; He, T.; Guo, H.; Chen, X. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation improves adipokine profile in dyslipidemic individuals: a randomized controlled trial. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2022, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golmohammadi, S. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on renal function parameters in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Kidney international reports 2022, 7, S226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrial.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT0598 Registry Platform. Available online: https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=CTRI/2023/07/055198 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- ClinicalTrial.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05871086#study-plan (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Karamali, M.; Gholizadeh, M. The effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic profiles and parameters of mental health in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2022, 38, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, A.; Begue, G.; Valencia, A.P.; Norman, J.E.; Lidgard, B.; Bennett, B.J.; Van Doren, M.P.; Marcinek, D.J.; Fan, S.; Prince, D.K.; Gamboa, J.L.; Himmelfarb, J.; de Boer, I.H.; Kestenbaum, B.R.; Roshanravan, B. Randomized crossover clinical trial of coenzyme Q10 and nicotinamide ribosome in chronic kidney disease. JCI insight 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, P.; Sajedi, F.; Mirjalili, M.; Mohammadi, Y.; Mehrpooya, M. Coenzyme Q10 as a potential add-on treatment for patients suffering from painful diabetic neuropathy: results of a placebo-controlled randomized trial. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmberg, M.J.; Andersen, L.W.; Moskowitz, A.; Berg, K.M.; Cocchi, M.N.; Chase, M.; Liu, X.; Kuhn, D.M.; Grossestreuer, A.V.; Hoeyer-Nielsen, A.K.; Kirkegaard, H.; Donnino, M.W. Ubiquinol (reduced coenzyme Q10) as a metabolic resuscitator in post-cardiac arrest: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Resuscitation. 2021, 162, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.J.; Li, E.C.; Wright, J.M. Blood pressure lowering efficacy of coenzyme Q10 for primary hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016, 3, CD007435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantle, D.; Lopez-Lluch, G.; Hargreaves, I.P. Coenzyme Q10 Metabolism: A Review of Unresolved Issues. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hekimi, S. Micellization of coenzyme Q by the fungicide caspofungin allows for safe intravenous administration to reach extreme supraphysiological concentrations. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honardoust, P.; Najafpour, A.; Mohammadi, R. Influence of Systemic Administration of Coq10 Nanoparticles on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury on Ovaries in Rat. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021, 2021, 2303417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemloo, E.; Oryan, S.; Bigdeli, M.R.; Mostafavi, H.; Eskandari, M. The neuroprotective effect of MicroRNA-149-5p and coenzymeQ10 by reducing levels of inflammatory cytokines and metalloproteinases following focal brain ischemia in rats. Brain Res Bull. 2021, 169, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niibori, K.; Yokoyama, H.; Crestanello, J.A.; Whitman, G.J. Acute administration of liposomal coenzyme Q10 increases myocardial tissue levels and improves tolerance to ischemia reperfusion injury. J Surg Res. 1998, 79, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, M.; Watanabe, J. A possible mode of solubilization of coenzyme Q10 with HCO-60. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1987, 10, 124–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadali, Yu.V. .; Fomichev, Yu.S..; Gorodetskaya, E.A..; Kalenikova E.I..; Karlina M.V.; Makarov, V.G.; Makarova, M.N.; Medvedev O.S.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N. Ubiquinol composition for parenteral administration and method for its. production. Patent RU2635993-C1, 17 November 2017. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Kalenikova, E.I.; Gorodetskaya, E.A.; Obolenskaya, O.N.; Shapavo, N. S.; Medvedev, O. S. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Oxidized and Reduced Coenzyme Q10 Upon Intravenous Administration. Pharm Chem J 2021, 55, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.; Gorodetskaya, E.; Kalenikova, E.; Medvedev, O. Single intravenous injection of CoQ10 reduces infarct size in a rat model of ischemia and reperfusion injury. World Journal of Cardiovascular Diseases, 2013, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Gorodetskaya, E.A.; Kalenikova, E.I.; Medvedev, O.S. Single intravenous injection of coenzyme Q10 protects the myocardium after irreversible ischemia. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 155, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Tokareva, O.G.; Gorodetskaya, E.A.; Kalenikova, E.I.; Medvedev, O.S. Cardioprotection with Intravenous Injection of Coenzyme Q10 is limited by Time of Administration after Onset of Myocardial Infarction in Rats. J. Clin. Exp. Cardiolog. 2014, 5, 299. [Google Scholar]
- Kulyak, O. Y.; Gorodetskaya E., A.; Kalenikova, E. I.; Makarova, M. N.; Pozharitskaya O., N.; Medvedev, O. S. Evaluation of cardioprotective efficacy of innovative dosage form of ubiqinol for intravenous administration. Eksp Klin Farmakol. 2018, 81, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, M.; Tokareva, O.G.; Gorodetskaya, E.A.; Kalenikova, E.I.; Medvedev, O.S. Intravenous Treatment With Coenzyme Q10 Improves Neurological Outcome and Reduces Infarct Volume After Transient Focal Brain Ischemia in Rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belousova, M.A.; Tokareva, O.G.; Gorodetskaya, E.A.; Kalenikova, E.I.; Medvedev, O.S. Neuroprotective Effectiveness of Intravenous Ubiquinone in Rat Model of Irreversible Cerebral Ischemia. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 161, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obolenskaia, O. N.; Gorodetskaya, E. A.; Kalenikova, E. I.; Belousova, M. A.; Gulyaev, M.V.; Makarov, V. G.; Pirogov, Y.A.; Medvedev, O. S. Intravenous Administration of Coenzyme Q10 in Acute Period of Cerebral Ischemia Decreases Mortality by Reducing Brain Necrosis and Limiting its Increase within 4 Days in Rat Stroke Model. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | Name of Study | Country, year of Registration |
Daily Dose of CoQ10, Duration of Administration |
Results for Completed Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ischemic stroke | Evaluation of the effects of coenzyme Q10 on stroke | Iran, 2021 | 200 mg of CoQ10 3 times a day for 30 days [39] |
|
| Children with tetralogy of fallot | The safety and efficacy of preoperative oral supplementation of coenzyme Q10 in improving postoperative cardiac function in children with tetralogy of fallot (pulmonary atresia): a preliminary study | China, 2019 | Orally in different dosages before surgery: coenzyme Q10, 2.5mg;03:Oral coenzyme Q10, 5mg;04:Oral coenzyme Q10, 10mg.;05:Oral coenzyme Q10, 20mg. Duration not specified[40] | |
| Statin-induced myalgia | Coenzyme Q10 and tolerability of simvastatin in subjects with a history of statin-induced myalgia | New Zealand, since 2005 (update 2020) | 200 mg/day of CoQ10 - with simvastatin dose titration for about 3 months [41] |
|
| Acute coronary syndrome | Influence of ubiquinol on angina severity and dyspnea in patients with acute coronary syndrome | Iraq, 2023 | 200 mg of ubiquinol for 8 weeks [42] | Ubiquinol addition to OMT after ACS has a highly significant effect on improving clinical outcomes and patients’ quality of life through greater reductions in angina frequency, physical limitations and dyspnea severity. This suggests an effective and safe strategy for optimizing therapeutic outcomes and secondary prevention |
| Metabolic syndrome | Effects of curcumin and/or coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic control in subjects with metabolic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial | Iraq, 2021 | 60 mg of CoQ10 daily for 12 weeks and/or curcumin [43] |
СoQ10 showed no therapeutic effects |
| Acute Myocardial Infarction | A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Vascular Endothelial and Cardiac Function after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Therapy for Acute Myocardial Infarction | China, 2021 | Dose and duration of administration not specified [44] | |
| Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction | Coenzyme Q10 in the Treatment of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: a Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial | Israel, 2021 | 300 mg of ubiquinol for 4 months [45] | In this pilot trial in elderly patients with HFpEF, treatment with CoQ10 did not significantly affect echocardiographic indices of diastolic function and serum NT-proBNP levels. |
| Prevention of high altitude heart disease | Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on prevention of high altitude heart disease and improvement of cardiac function | China, 2021 | High and low doses of CoQ10, dose and duration not specified [46] | |
| MAFLD | Effect of CoQ10 on the Outcome of MAFLD Patients | Egypt, 2023 | 200 mg/day of CoQ10 for 12 weeks [47] | |
| Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis | Comparative Clinical Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Rosuvastatin Vs CoQ10 on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis | Egypt, 2023 | 100 mg/day of CoQ10 for 3 months [48] | |
| Dyslipidemia | Coenzyme Q10 supplementation improves adipokine profile in dyslipidemic individuals: a randomized controlled trial | China, 2022 | 120 mg CoQ10 на 24 недели [49] |
This study shows that CoQ10 ameliorates glucolipid profile and adipokines dysfunction in dyslipidemic patients in 24 weeks’ intervention. The beneficial effect of CoQ10 on glucolipid profile was mediated by adiponectin. |
| Diabetic nephropathy | Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on renal function parameters in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial | Iran, 2022 | 100 mg CoQ10 for 6 months [50] |
This study found that daily administration of 100 mg CoQ10 improved the mean proteinuria, GFR and creatinine levels in patients with diabetic nephropathy. |
| Acute Herpes Zoster | To Evalute the Analgesic effect of Coenzyme Q10 in Acute Herpes Zoster | India, 2023 | Coenzyme Q10 (100mg) given daily for 4 weeks [51] | |
| Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis | Coenzyme Q10 in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients | Egypt, 2023 | Coenzyme Q10 100 mg daily for 3 months. [52] |
|
| Polycystic ovary syndrome |
The effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic profiles and parameters of mental health in women with polycystic ovary syndrome | Iran, 2021 | CoQ10 100 mg/day for 12 weeks [53] |
12-week supplementation of CoQ10 to PCOS women showed beneficial impact on BDI, BAI, hs-CRP, total testosterone, DHEAS, hirsutism, SHBG, TAC and MDA levels |
| Chronic kidney disease | Randomized crossover clinical trial of coenzyme Q10 and nicotinamide ribosome in chronic kidney disease |
USA, 2023 | CoQ10 (1200 mg/day) for 6 weeks [54] |
Six-weeks of treatment with NR or CoQ10 improved markers of systemic mitochondrial metabolism and lipid profiles but did not improve VO2 peak or total work efficiency. CoQ10 increased free fatty acids and decreased complex medium/long chain triglycerides. |
| Diabetic neuropathy | Coenzyme Q10 as a potential add-on treatment for patients suffering from painful diabetic neuropathy: results of a placebo-controlled randomized trial |
Iran, 2021 | CoQ10 at a dosage of 100 mg every 8 h for 8 consecutive weeks [55] |
This trial support the idea that diabetic patients suffering from painful diabetic neuropathy may benefit from using antioxidant and anti-inflammatory supplements like CoQ10. However, further studies are required before supplementation with CoQ10 can be recommended for treating painful diabetic neuropathy. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




