Submitted:
13 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
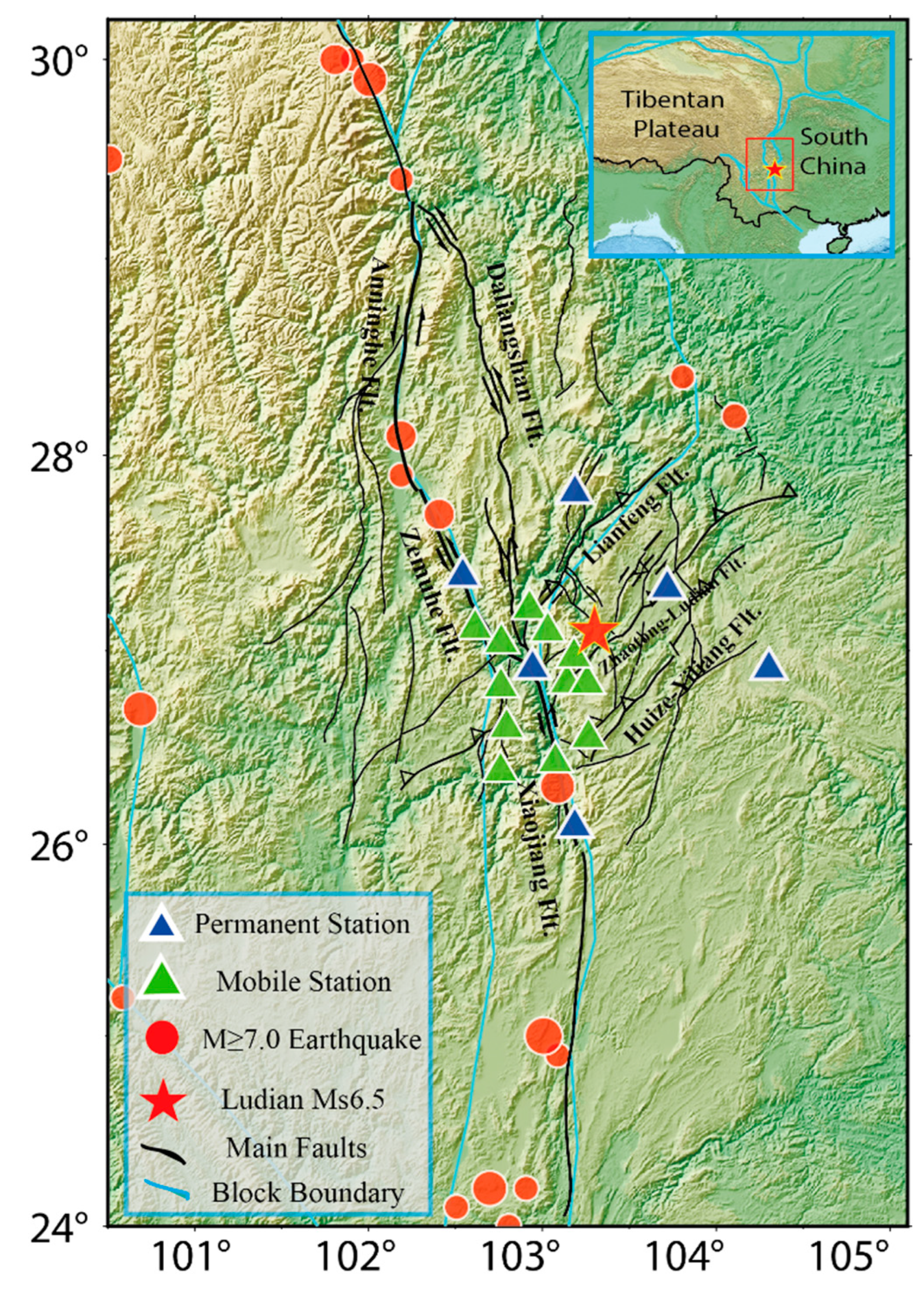
2. Tectonic Background
3. Data and Methods
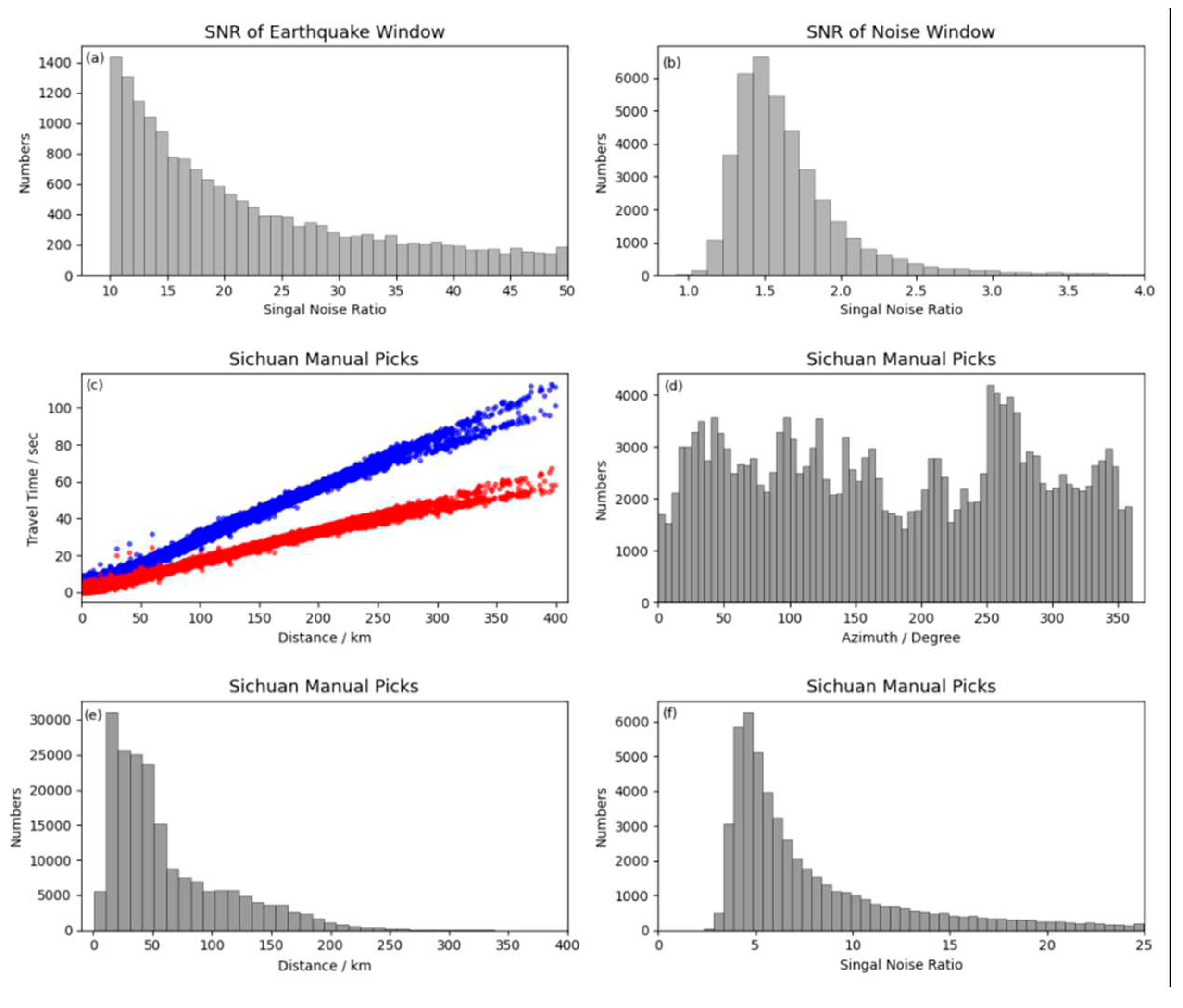
3.1. Seismic data
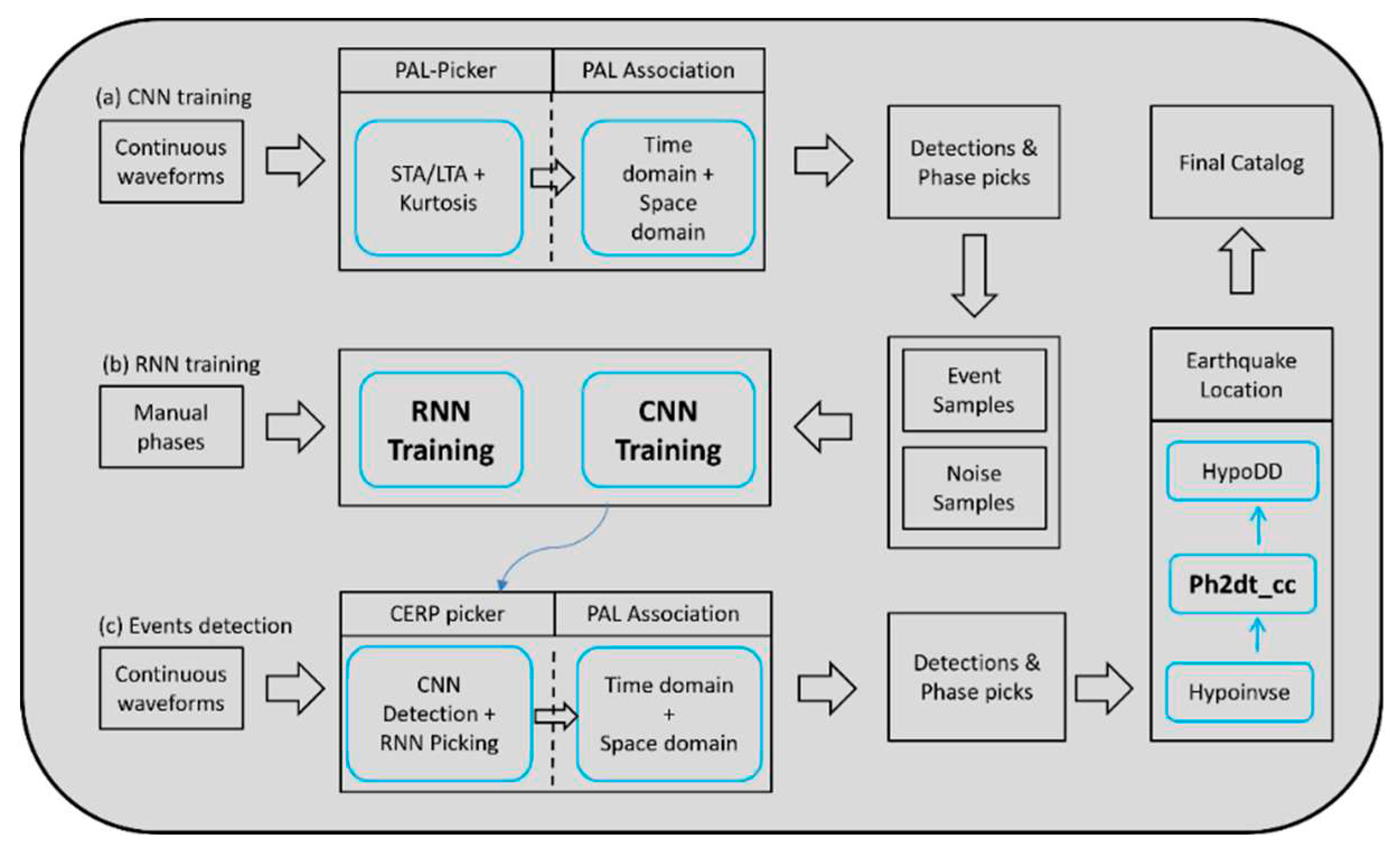
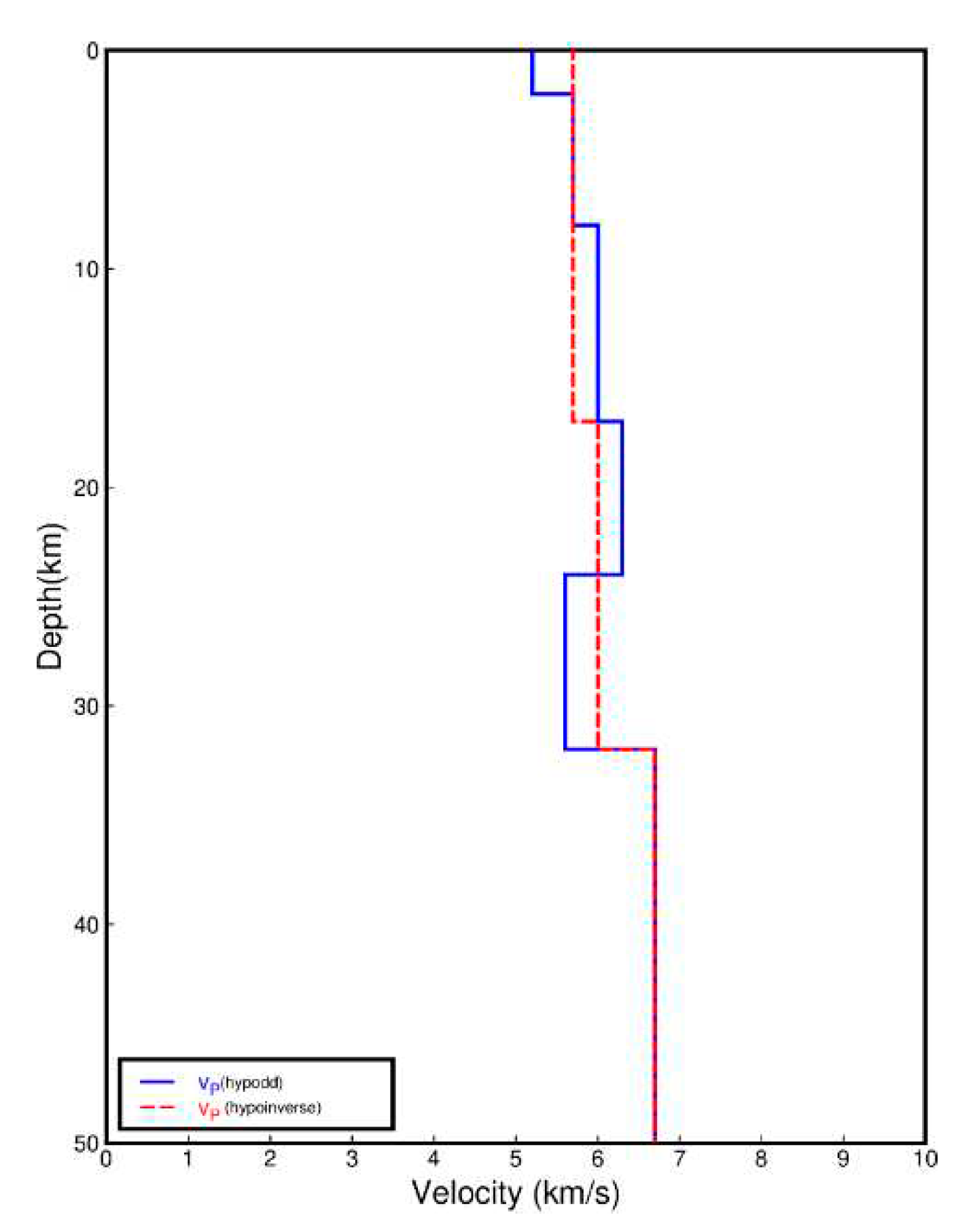
3.2. Methods
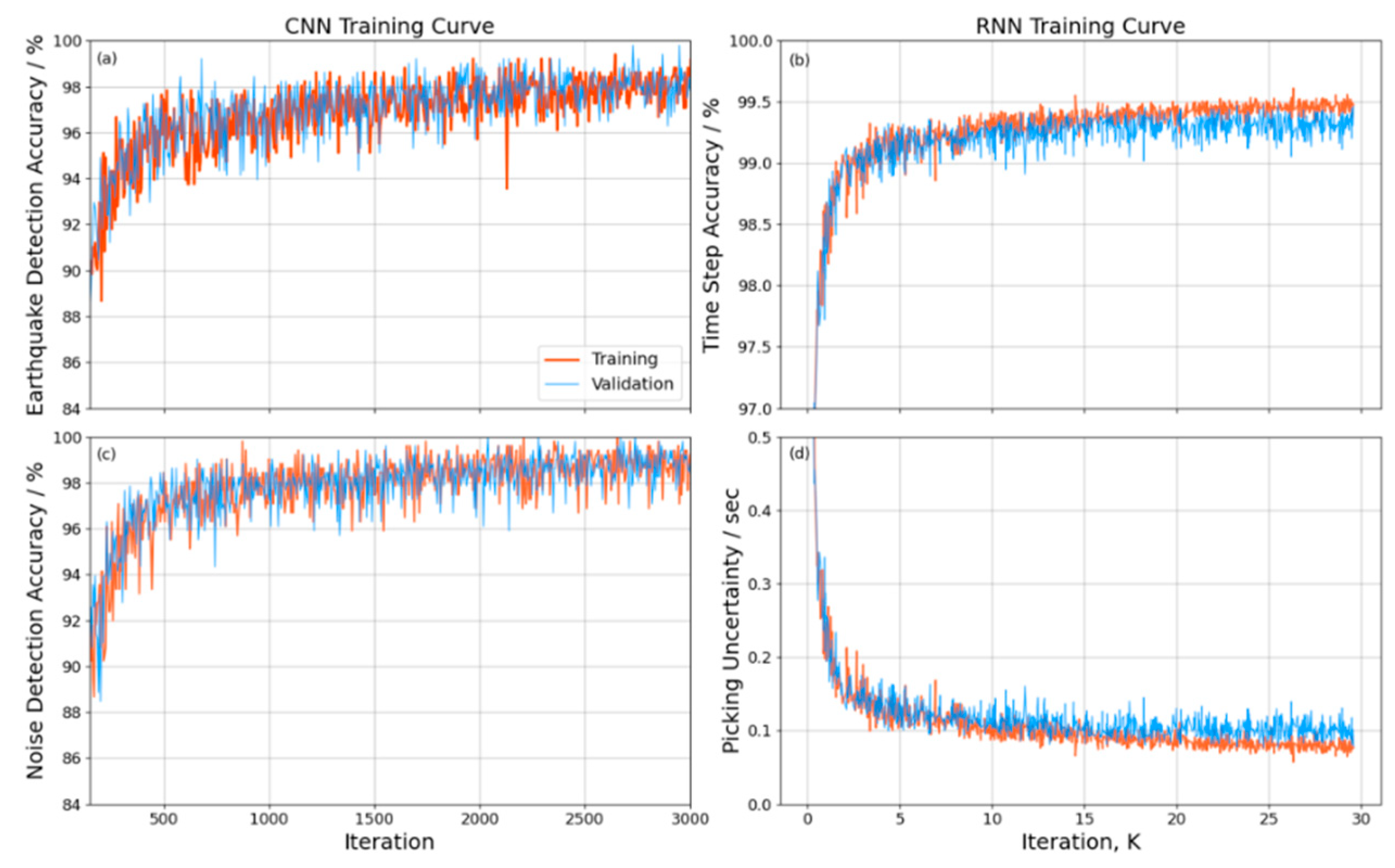
3.3. AI model training
3.4. Earthquake detection, phase picking, association and location
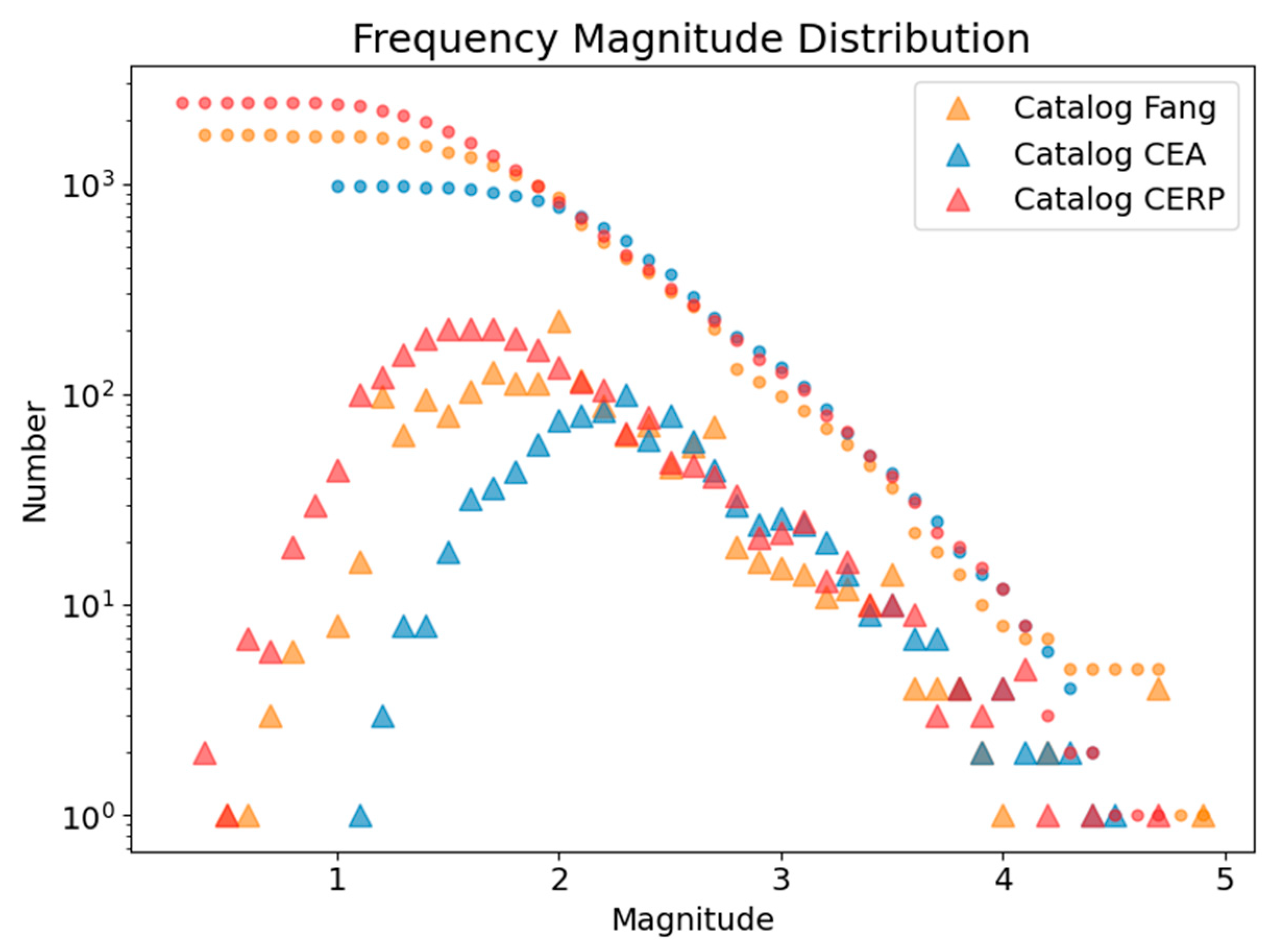
4. Results and Discussion
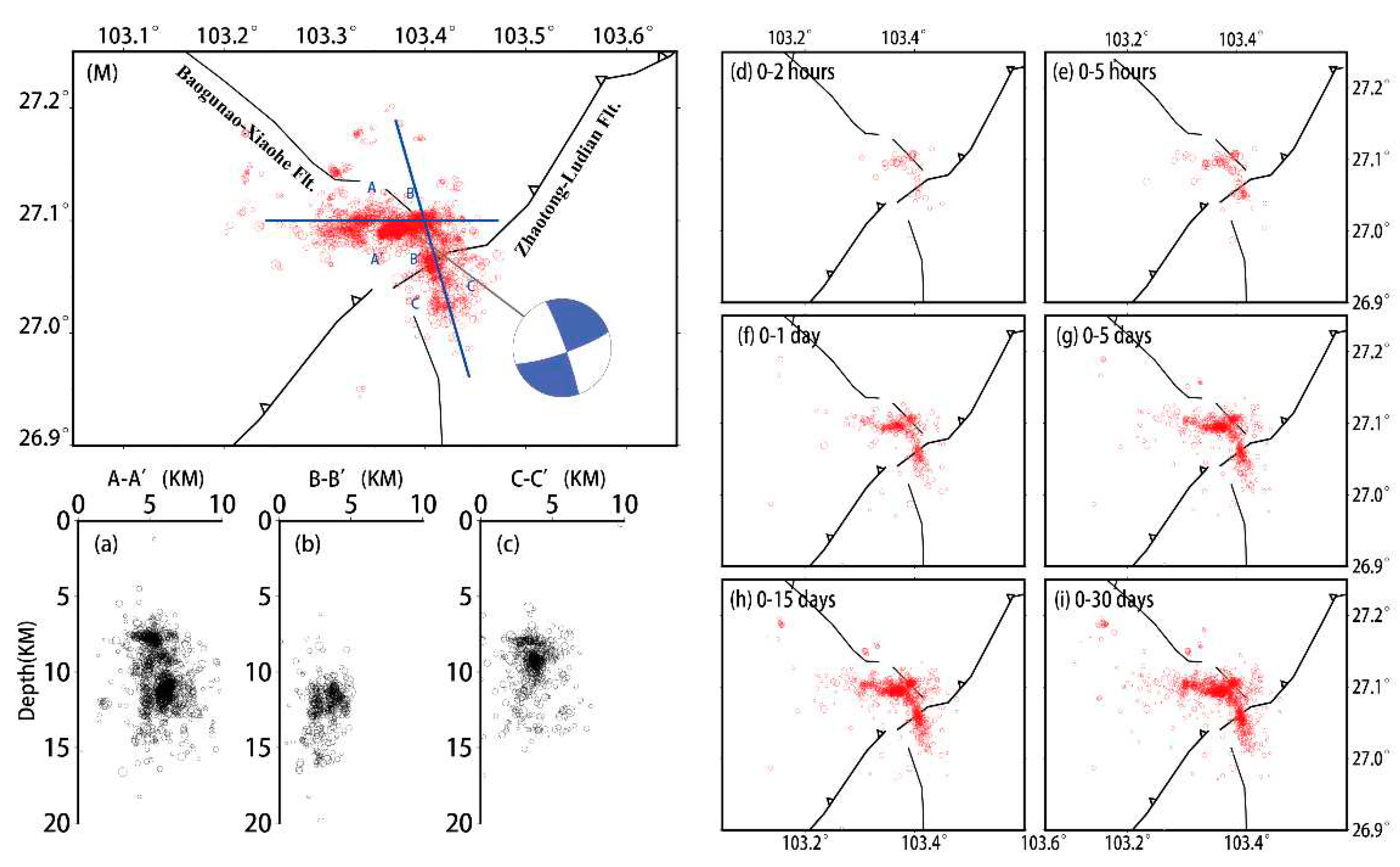
4.1. Aftershocks space distribution, temporal evolution and focal mechanism
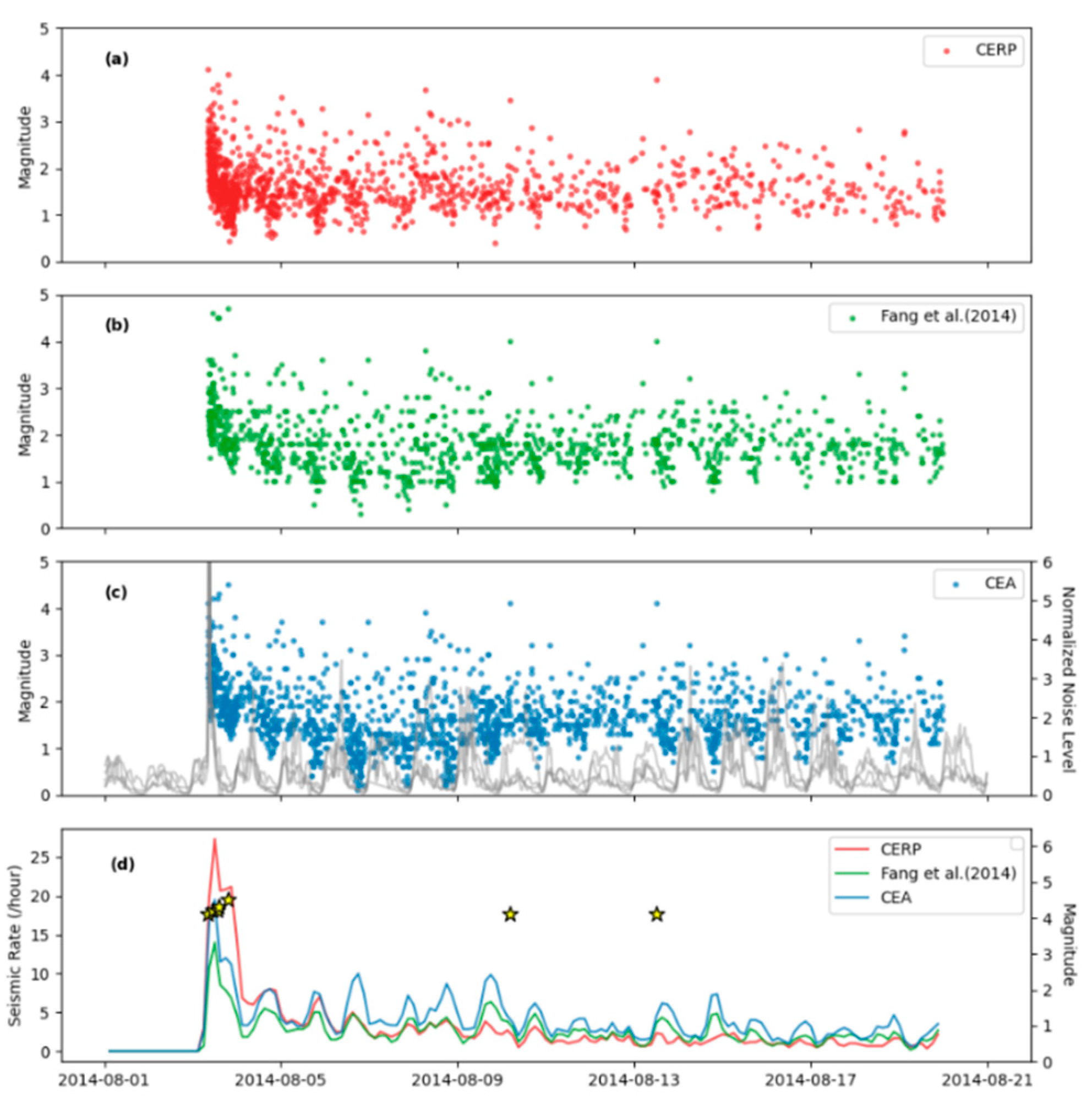
4.2. Seismic rate evolution
4.3. Seismogenic fault
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shelly, D.R. A High-Resolution Seismic Catalog for the Initial 2019 Ridgecrest Earthquake Sequence: Foreshocks, Aftershocks, and Faulting Complexity. Seismological Research Letters 2020, 91, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, Z.E. , Idini, B., Jia, Z., Stephenson, O.L., Zhong, M.Y., Wang, X., Zhan, Z.W., Simons, M., Fielding, E.J., Yun, S.H., Hauksson, E., Moore, A.W., Liu, Z., and Jung, J. Hierarchical interlocked orthogonal faulting in the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquake sequence. Science 2019, 366, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, Z.E. , Trugman, D.T., Hauksson, E., and Shearer, P.M. Searching for hidden earthquakes in Southern California. Science 2019, 364, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.J. , Yue, H., Kong, Q.K., and Zhou, S.Y. Hybrid Event Detection and Phase-Picking Algorithm Using Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks. Seismological Research Letters, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y. , Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.Q. and Beroza, G.C. PhaseNet: A Deep-Neural-Network-Based Seismic Arrival Time Picking Method. Geophysical Journal International 2018. [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M., Zhu, W.Q., Sheng, Y.X., and Beroza, G.C. CRED: A Deep Residual Network of Convolutional and Recurrent Units for Earthquake Signal Detection. Scientific Reports 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M., Ellsworth, W.L., Zhu, W.Q., Chuang, L.Y., and Beroza, G.C. Earthquake transformer—an attentive deep-learning model for simultaneous earthquake detection and phase picking. Nature Communications 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Perol, T. , Gharbi, M., and Denolle, M. Convolutional neural network for earthquake detection and location. Science Advances 2018, 4, e1700578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, Z.E. , Meier, M.A., Hauksson, E., and Heaton, T.H. Generalized Seismic Phase Detection with Deep Learning. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 2018, 108, 2894–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Xiao, Z.W., Liu, C., Zhao, D.P., and Yao, Z.X. Deep Learning for Picking Seismic Arrival Times. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2019, 124, 6612-6624.
- Park, Y., Mousavi, S.M., Zhu, W.Q., Ellsworth, W.L., and Beroza, G.C. Machine-Learning-Based Analysis of the Guy-Greenbrier, Arkansas Earthquakes: A Tale of Two Sequences. Geophysical Research Letters 2020, 47.
- Liu, M., Zhang, M., Zhu, W.Q., Ellsworth, W.L., and Li, H.Y. Rapid Characterization of the July 2019 Ridgecrest, California, Earthquake Sequence From Raw Seismic Data Using Machine-Learning Phase Picker. Geophysical Research Letters 2020, 47.
- Zhao, M., Xiao, Z.W., Chen, S., and Fang, L.H. DiTing: A large-scale Chinese seismic benchmark dataset for artificial intelligence in seismology. Earthquake Science 2022, 35, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M., Sheng, Y.X., Zhu, W.Q., and Beroza, G.C. STanford EArthquake Dataset (STEAD): A Global Data Set of Seismic Signals for AI. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 179464-179476. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C. , Fang, L.H., Fan, L.P., and Li, B.R. Comparison of the earthquake detection abilities of PhaseNet and EQTransformer with the Yangbi and Maduo earthquakes. Earthquake Science 2021, 34, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.V. Automatic earthquake recognition and timing from single traces. Bulletin of the seismological society of America 1978, 68, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J., Yue, H., Fang, L.H., Zhou, S.Y., Zhao, L., and Ghosh, A. An Earthquake Detection and Location Architecture for Continuous Seismograms: Phase Picking, Association, Location, and Matched Filter (PALM). Seismological Research Letters 2021, 93, 413-425. [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.H., Wu, J.P., Wang, W.L., Lv, Z.Y., Wang, C.Z., Yang, T., and Zhong, S.J. Relocation of the aftershock sequence of the M S 6.5 Ludian earthquake and its seismogenic structure. Seismology and Geology 2014, 36(4): 1173-1185.
- Wen, X.Z., Du, F., Yi, G.X., Long, F., Fan, J., Yang, F.X., Xiong, R.W., Liu, Q.X., and Liu, Q. Earthquake potential of the Zhaotong and Lianfeng fault zones of the eastern Sichuan-Yunnan border region. Chinese Journal of Geophysics 2013, 56(10):3361-3372.
- He, H.L., Ikeda, Y., He, Y.L., Togo, M., Chen, J., Chen, C.Y., Tajikara, M., Echigo, T., and Okada, S. Newly-generated Daliangshan fault zone — Shortcutting on the central section of Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault system. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences 2008, 51, 1248-1258. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W., Wen, X.Z., Zheng, R.Z., Ma, W.T., Song, F.M., and Yu, G.H. Pattern of latest tectonic motion and its dynamics for active blocks in Sichuan-Yunnan region, China. Science in China Series D Earth Sciences 2003, 46, 210-226. [CrossRef]
- Baillard, C., Crawford, W.C., Ballu, V., Hibert, C., and Mangeney, A. An Automatic Kurtosis-Based P- and S-Phase Picker Designed for Local Seismic Networks. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 2013, 104, 394-409. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y., Ghosh, A., Fang, L.H., Yue, H., Zhou, S.Y., and Su, Y.J. A high-resolution seismic catalog for the 2021 MS6.4/MW6.1 Yangbi earthquake sequence, Yunnan, China: Application of AI picker and matched filter. Earthquake Science 2021, 34, 390-398. [CrossRef]
- Klein, F.W., User's Guide to HYPOINVERSE-2000, a Fortran Program to Solve for Earthquake Locations and Magnitudes, in Open-File Report. 2002.
- Waldhauser, F. and Ellsworth, W. A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: Method and application to the northern Hayward fault, California. Bulletin of the seismological society of America 2000, 90, 1353-1368.
- Waldhauser, F. and Ellsworth, W.L. Fault structure and mechanics of the Hayward Fault, California, from double-difference earthquake locations. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2002, 107.
- Dziewonski, A.M., Chou, T.A., and Woodhouse, J.H. Determination of earthquake source parameters from waveform data for studies of global and regional seismicity. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 1981, 86, 2825-2852. [CrossRef]
- Ekström, G., Nettles, M., and Dziewoński, A.M. The global CMT project 2004–2010: Centroid-moment tensors for 13,017 earthquakes. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 2012, 200-201, 1-9.
- Wang, W., Wu, J., Fang, L., and Juan, L. Double difference location of the Ludian MS6.5 earthquake sequences in Yunnan province in 2014. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese) 2014, 57, 3042-3051.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



