Submitted:
12 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction:
MATERIAL AND METHODS
| Group | Flours |
|---|---|
| A | Wheat |
| B | Rice, Chickpeas, Moong dal, Black gram |
| C | Toor dal, Horse gram, Black sesame, Broad beans |
Result and Discussion:
Conclusion:
References
- Navathaniyam. (2022, May 28). Tamil Wikipedia.
- India, K. A. (2023, December 12). 10 Secrets You Didn't Know About Navadhanyam | Kerela Ayurveda India. Kerala Ayurveda. Available online: https://www.keralaayurveda.biz/blog/navadhanyam-a-healthy-mix-of-9-grains.
- Shewry, Peter R, and Sandra J Hey. “The contribution of wheat to human diet and health.” Food and energy security vol. 4,3 (2015): 178-202. [CrossRef]
- Rd, K. A. J. M. (2023, July 17). 9 Health Benefits of Eating Whole Grains. Healthline. Available online: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/9-benefits-of-whole-grains.
- Gaesser, Glenn A. “Perspective: Refined Grains and Health: Genuine Risk, or Guilt by Association?.” Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.) vol. 10,3 (2019): 361-371. [CrossRef]
- Roszkowska, Anna et al. “Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity: A Review.” Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) vol. 55,6 222. 28 May. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, Gopika et al. “A Narrative Review on Rice Proteins: Current Scenario and Food Industrial Application.” Polymers vol. 14,15 3003. 25 Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Oghbaei M., Prakash J. Effect of primary processing of cereals and legumes on its nutritional quality: A comprehensive review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016;2:1136015. [CrossRef]
- Wang N., Cui X., Duan Y., Yang S., Wang P., Saleh A.S., Xiao Z. Potential health benefits and food applications of rice bran protein: Research advances and challenges. Food Rev. Int. 2021:1–24. [CrossRef]
- Yu Y., Zhang J., Wang J., Sun B. The anti-cancer activity and potential clinical application of rice bran extracts and fermentation products. RSC Adv. 2019;9:18060–18069. [CrossRef]
- Kawakatsu T., Takaiwa F. Rice proteins and essential amino acids. In: Bao J., editor. Rice. 4th ed. AACC International Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2019. pp. 109–130.
- Hossny E., Ebisawa M., El-Gamal Y., Arasi S., Dahdah L., El-Owaidy R., Galvan C.A., Lee B.W., Levin M., Martinez S., et al. Challenges of managing food allergy in the developing world. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019;12:100089. [CrossRef]
- Kaur R., Prasad K. Nutritional characteristics and value-added products of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum)—A review. J. Postharvest Technol. 2021;9:1–13.
- Jukanti, A. K., Gaur, P. M., Gowda, C. L. L., and Chibbar, R. N. (2012). Nutritional quality and health benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A review. Br. J. Nutr. 108(Suppl. 1), S11–S26. [CrossRef]
- Madurapperumage, A., Tang, L., Thavarajah, P., Bridges, W., Shipe, E., Vandemark, G., & Thavarajah, D. (2021, October 12). Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) as a Source of Essential Fatty Acids – A Biofortification Approach. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12. [CrossRef]
- Albete I., Astrup A., Martinez J.A., Martinez J.A., Thorsdottir I., Zulet M.A. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome: Role of different dietary macronutrient distribution patterns and specific nutritional components on weight loss and maintenance. Nutr. Rev. 2010;68:214–231. [CrossRef]
- Jukanti A.K., Gaur P.M., Gowda C.L., Chibbar R.N. Nutritional quality and health benefits of chickpea (Cicerarietinum L.): A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2012;108:S11–S26. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y., Zhou L., Gu Y., Zhang Y., Tang J., Li F., Shang W., Jiang B., Yue X., Chen M. Dietary chickpeas reverse visceral adiposity, dyslipidemia and insulin resistance in rats induced by a chronic high-fat diet. Br. J. Nutr. 2007;98:720–726. [CrossRef]
- Pittway J.K., Ahuja K.D., Cehun M., Chronopoulos A., Robertson I.K., Nestel P.J., Ball M.J. Dietary supplementation with chickpeas for at least five weeks results in small but significant reductions in serum total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterols in adult women and men. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2006;50:512–518. [CrossRef]
- Pittaway J.K., Robertson I.K., Ball M.J. Chickpeas may influence fatty acid and fiber intake in an ad libitum diet, leading to small improvements in serum lipid profile and glycemic control. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008;108:1009–1013. [CrossRef]
- Murty C.M., Pittaway J.K., Ball M.J. Chickpea supplementation in an Australian diet affects food choice, satiety and bowel health. Appetite. 2010;54:282–288. [CrossRef]
- Momaya, A. (2023, April 5). Moong Dal (Green Gram): 6 Amazing Health Benefits, Nutrition & Recipes. HealthifyMe. Available online: https://www.healthifyme.com/blog/many-benefits-moong-dal/.
- N. R. Reddy , D. K. Salunkhe , S. K. Sathe & Samuel Kon (1982) Biochemistry of black gram (phaseolus mungo L.): A review, C R C Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 16:1, 49-114. [CrossRef]
- Duraiswamy, Aishwarya et al. “Genetic manipulation of anti-nutritional factors in major crops for a sustainable diet in future.” Frontiers in plant science vol. 13 1070398. 15 Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Roosdiana A, Fitri Hendrawan V, Wulandari M, Ariviani S, Affandi DR, Listyaningsih E, et al. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science The potential of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) beverage as an anti-diabetic functional drink The potential of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) beverage as an anti-diabetic functional drink. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 2018;102:12054. [CrossRef]
- Saxena KB, Kumar RV, Sultana R, Saxena KB, Kumar RV, Sultana R. Quality nutrition through pigeonpea-a review. Health 2010;2:1335–44. [CrossRef]
- Motiwala MN, Gupta RA, Dumore NG, Danao KR. In vivo wound healing activity of Cajanus cajan on burn wound model in mice by regulating antioxidant and inflammatory mediators. Journal of Pharmaceutical Care & Health Systems 2015;02:5. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Saroj Kumar, and Manoj Kumar Singh. “Horse gram- an underutilized nutraceutical pulse crop: a review.” Journal of food science and technology vol. 52,5 (2015): 2489-99. [CrossRef]
- Narasimhulu C.A., Selvarajan K., Litvinov D., Parthasarathy S. Anti-atherosclerotic and Anti-inflammatory actions of sesame oil. J. Med. Food. 2015;18:11–20. [CrossRef]
- Namiki M. Nutraceutical Functions of sesame: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2007;47:651–673. [CrossRef]
- Gouveia L.D.V., Cardoso C.A., de Oliveira G.M.M., Rosa G., Moreira A.S.B. Effects of the intake of sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum L.) and derivatives on oxidative stress: A systematic review. J. Med. Food. 2016;19:337–345. [CrossRef]
- Majdalawieh A.F., Massri M., Nasrallah G.K. A comprehensive review on the anti-cancer properties and mechanisms of action of sesamin, a lignan in sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017;815:512–521. [CrossRef]
- Puertollano, María A et al. “Dietary antioxidants: immunity and host defense.” Current topics in medicinal chemistry vol. 11,14 (2011): 1752-66. [CrossRef]
- Martineau-Côté, Delphine et al. “Faba Bean: An Untapped Source of Quality Plant Proteins and Bioactives.” Nutrients vol. 14,8 1541. 7 Apr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M, R. Valorisation of Orange and Banana Peel: Formulation of Fibre Loaded Biscuits. Preprints 2023, 2023051809. [CrossRef]
- Colla K, Costanzo A, Gamlath S (2018) Fat replacers in baked food products. Foods 7(1):192. [CrossRef]
- Investigations on the Maillard Reaction in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Seeds Induced by Roasting. Ecem Berk, Aytül Hamzalıoğlu, and Vural Gökmen. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2019 67 (17), 4923-4930. [CrossRef]
- Laguna L, Salvador A, Sanz T, Fiszman SM (2011) Performance of a resistant starch rich ingredient in the baking and eating quality of short-dough biscuits. LWT Food Sci Technol 44:737–746. [CrossRef]
- Kweon M, Slade L, Levine H (2011) Solvent retention capacity (SRC) testing of wheat flour: Principles and value in predicting flour functionality in different wheat-based food processes, as well as in wheat breeding—a review. Cereal Chem 88:537–552. [CrossRef]
- Sharma P, Gujral HS (2013) Extrusion of hulled barley affecting β-glucan and properties of extrudates. Food Bioproc Tech 6:1374–1389. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, Homi & Awasthi, Pratima. (2020). Evaluation of physical properties and sensory attributes of biscuits developed from whole wheat flour supplemented with horse gram flour.
- Arab, Radia et al. “Effects of Seed Roasting Temperature on Sesame Oil Fatty Acid Composition, Lignan, Sterol and Tocopherol Contents, Oxidative Stability and Antioxidant Potential for Food Applications.” Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 27,14 4508. 14 Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Wheat (g) |
Rice (g) |
Chickpeas (g) |
Moong dal (g) |
Black gram (g) |
Toor dal (g) |
Horse gram (g) |
Black sesame (g) |
Broad beans (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| T1 | 50 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| T2 | 50 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| T3 | 50 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 |
| Treatment | Palm jaggery (g) |
Butter (g) |
Milk powder (g) | Salt (g) | Baking powder (g) | Vanilla essence (drops) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 60 | 20 | 5 | 1 | .5 | 2 |
| T1 | 60 | 20 | 5 | 1 | .5 | 2 |
| T2 | 60 | 20 | 5 | 1 | .5 | 2 |
| T3 | 60 | 20 | 5 | 1 | .5 | 2 |
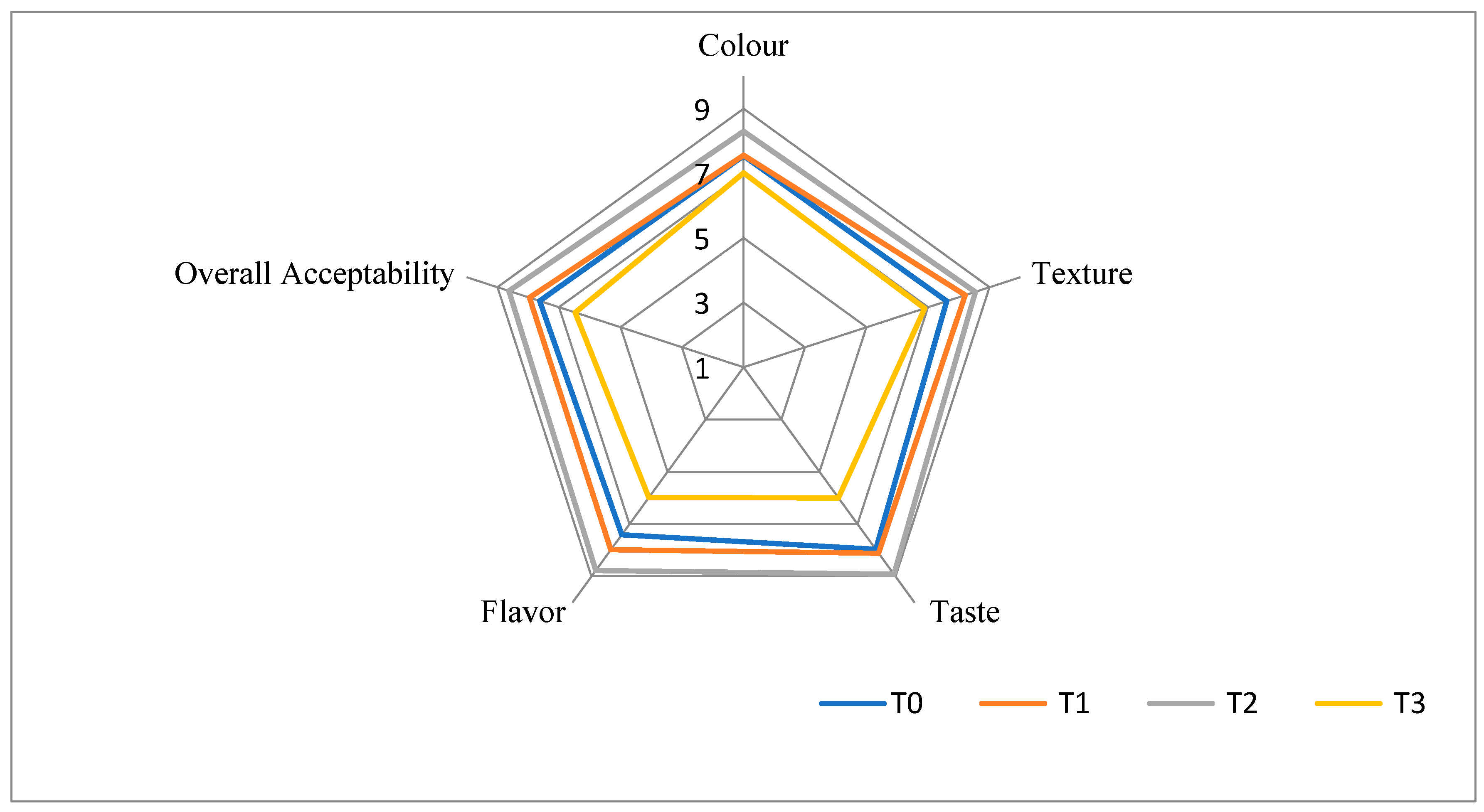
| Treatment | Colour | Texture | Taste | Flavour | Overall acceptability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 7.54 | 7.61 | 7.96 | 7.41 | 7.63 |
| T1 | 7.56 | 8.21 | 8.11 | 7.98 | 7.96 |
| T2 | 8.3 | 8.54 | 8.92 | 8.77 | 8.63 |
| T3 | 7.01 | 6.89 | 6 | 5.98 | 6.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




