Submitted:
08 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
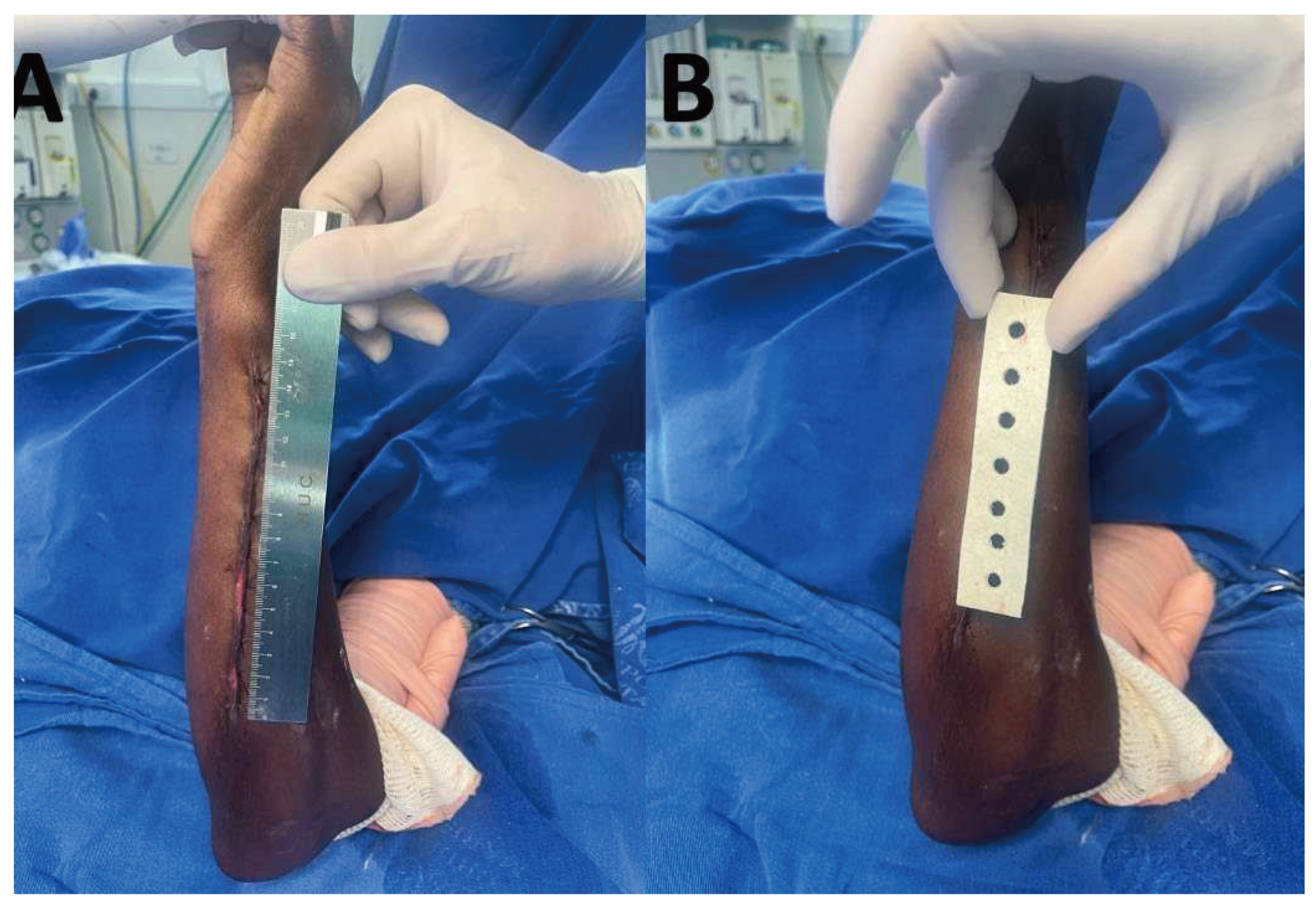
2.1. Dressing development
2.2. Study design and sample size
2.3. Ethical aspects
2.4. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.5. Randomization
2.6. Intervention and outcome
2.7. Statistical analysis
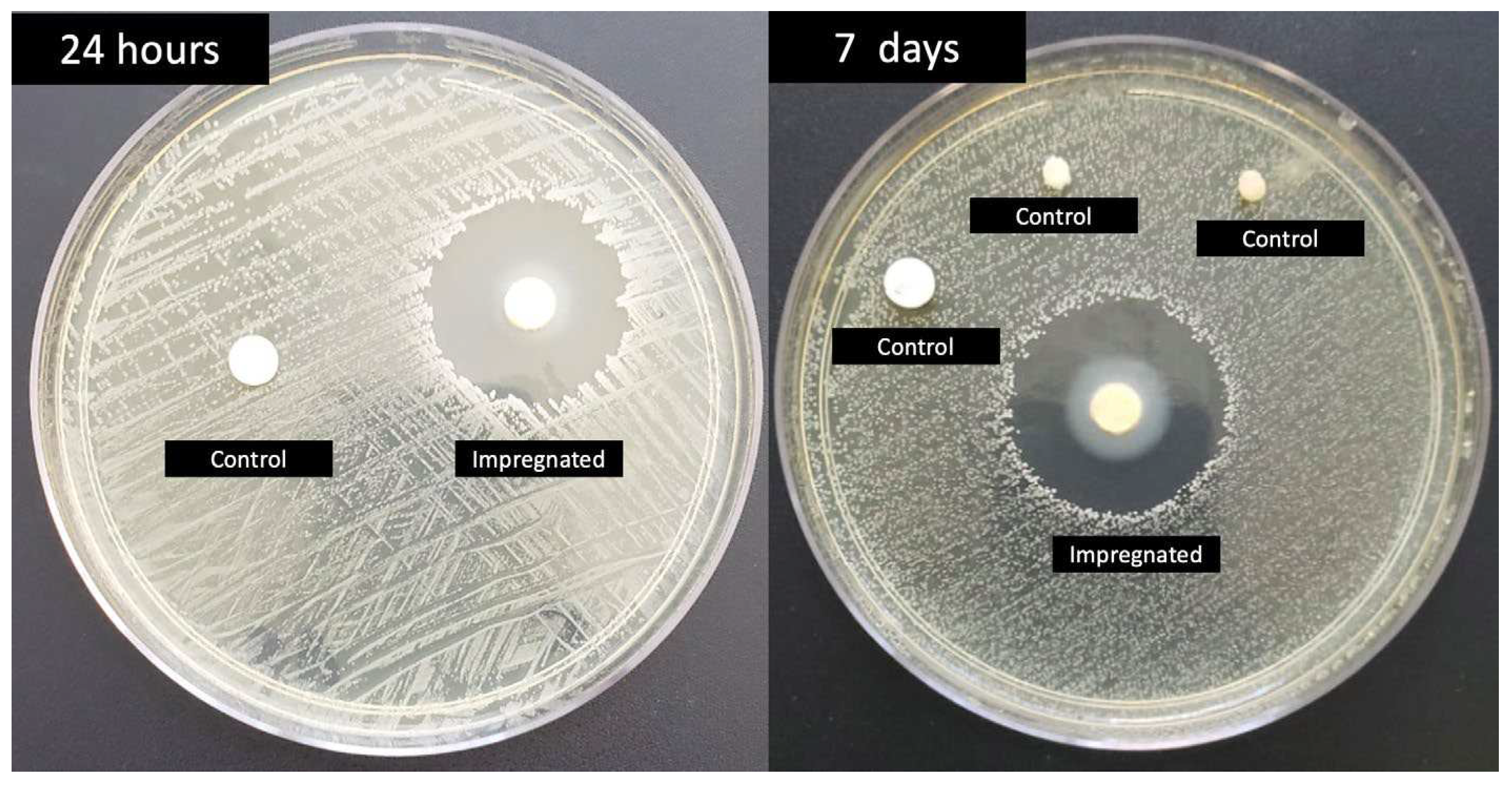
3. Results
3. Materials and Methods
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sartelli M, Labricciosa FM, Coccolini F, Coimbra R, Abu-Zidan FM, Ansaloni L, et al. It is time to define an organizational model for the prevention and management of infections along the surgical pathway: a worldwide cross-sectional survey. World J Emerg Surg. 2022;17(1):17. [CrossRef]
- Tao J, Yan Z, Bai G, Zhang H, Li J. Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Rehabilitation Protocol in the Perioperative Period of Orthopedics: A Systematic Review. J Pers Med. 2023;13(3). [CrossRef]
- Rousseau T, Plomion C, Sandy-Hodgetts K. An advanced transparent hydropolymer wound dressing for undisturbed post-op management of surgical wounds following hip and knee replacement: A prospective observational series. Int Wound J. 2022;19(6):1456-62. [CrossRef]
- Birhanu A, Amare HH, M GM, Girma T, Tadesse M, Assefa DG. Magnitude of surgical site infection and determinant factors among postoperative patients, A cross sectional study. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022;83:104324. [CrossRef]
- Wolfe PN, Campfield BD, Crist BD, Keeney JA, Smith MJ, Cook JL, et al. Bacterial DNA screening to characterize surgical site infection risk in orthopaedic patients. J Orthop. 2021;27:56-62. [CrossRef]
- Tuon FF, Suss PH, Telles JP, Dantas LR, Borges NH, Ribeiro VST. Antimicrobial Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023;12(1). [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro VST, Cieslinski J, Bertol J, Schumacher AL, Telles JP, Tuon FF. Detection of Microorganisms in Clinical Sonicated Orthopedic Devices Using Conventional Culture and qPCR. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2022;57(4):689-96. [CrossRef]
- Tuon FF, Dantas LR, Suss PH, Tasca Ribeiro VS. Pathogenesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm: A Review. Pathogens. 2022;11(3). [CrossRef]
- da Rocha L, Ribeiro VST, de Andrade AP, Goncalves GA, Kraft L, Cieslinski J, et al. Evaluation of Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans biofilms adherence to PEEK and titanium-alloy prosthetic spine devices. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022;32(5):981-9. [CrossRef]
- Cieslinski J, Ribeiro VST, Kraft L, Suss PH, Rosa E, Morello LG, et al. Direct detection of microorganisms in sonicated orthopedic devices after in vitro biofilm production and different processing conditions. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021;31(6):1113-20. [CrossRef]
- Tuon FF, Cieslinski J, Ono AFM, Goto FL, Machinski JM, Mantovani LK, et al. Microbiological profile and susceptibility pattern of surgical site infections related to orthopaedic trauma. Int Orthop. 2019;43(6):1309-13. [CrossRef]
- Worldwide Antimicrobial Resistance National/International Network Group C. Ten golden rules for optimal antibiotic use in hospital settings: the WARNING call to action. World J Emerg Surg. 2023;18(1):50. [CrossRef]
- Cruz JAW, da Cunha M, de Moraes TP, Marques S, Tuon FF, Gomide AL, et al. Brazilian private health system: history, scenarios, and trends. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):49. [CrossRef]
- Loesch GH, Cruz JAW, Gasparetto J, Oliveira DDS, Telles JP, Tuon FF. Cost minimization analysis of outpatient parenteral/oral antibiotic therapy at a trauma hospital: Public health system. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2021;42(12):1445-50. [CrossRef]
- Motelica L, Vasile BS, Ficai A, Surdu AV, Ficai D, Oprea OC, et al. Antibacterial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Essential Oils. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(10). [CrossRef]
- Aldakheel FM, Mohsen D, El Sayed MM, Fagir MH, El Dein DK. Employing of Curcumin-Silver Nanoparticle-Incorporated Sodium Alginate-Co-Acacia Gum Film Hydrogels for Wound Dressing. Gels. 2023;9(10). [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro CT, Dias FA, Fregonezi GA. Hydrogel dressings for venous leg ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;8(8):CD010738. [CrossRef]
- Arend L, Bergamo R, Rocha FB, Bail L, Ito C, Baura VA, et al. Dissemination of NDM-producing bacteria in Southern Brazil. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2023;106(2):115930. [CrossRef]
- Chaiben V, Yamada CH, Telles JP, de Andrade AP, Arend L, Ribeiro VST, et al. A carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak associated with a polymyxin shortage during the COVID pandemic: an in vitro and biofilm analysis of synergy between meropenem, gentamicin and sulbactam. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022;77(6):1676-84. [CrossRef]
- Telles JP, Yamada CH, Dario TM, Miranda AN, Pacheco A, Tuon FF. Impact of an antimicrobial stewardship program in a COVID-19 reference hospital according to the AWaRe classification. Am J Infect Control. 2022;50(10):1182-4. [CrossRef]
- Ito CAS, Bail L, Arend L, Nogueira KDS, Tuon FF. The activity of ceftazidime/avibactam against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Dis (Lond). 2021;53(5):386-9. [CrossRef]
- Bail L, Ito CAS, Arend L, Pilonetto M, Nogueira KDS, Tuon FF. Distribution of genes encoding 16S rRNA methyltransferase in plazomicin-nonsusceptible carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales in Brazil. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021;99(2):115239. [CrossRef]
- Zequinao T, Telles JP, Gasparetto J, Tuon FF. Carbapenem stewardship with ertapenem and antimicrobial resistance-a scoping review. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53:e20200413. [CrossRef]
- Tuon FF, Cieslinski J, Rodrigues SDS, Serra FB, Paula MD. Evaluation of in vitro activity of ceftolozane-tazobactam against recent clinical bacterial isolates from Brazil - the EM200 study. Braz J Infect Dis. 2020;24(2):96-103. [CrossRef]
- Zequinao T, Gasparetto J, Oliveira DDS, Silva GT, Telles JP, Tuon FF. A broad-spectrum beta-lactam-sparing stewardship program in a middle-income country public hospital: antibiotic use and expenditure outcomes and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles. Braz J Infect Dis. 2020;24(3):221-30. [CrossRef]
- Chiquin CA, Silva JH, Ciruelos MJ, Lemes MC, Penteado-Filho SR, Tuon FF. Postdischarge surveillance system for nontuberculous mycobacterial infection at a Brazilian regional referral hospital after an outbreak. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009;30(4):399-401. [CrossRef]
- Oprica GM, Panaitescu DM, Usurelu CD, Vlasceanu GM, Stanescu PO, Lixandru BE, et al. Nanocellulose Sponges Containing Antibacterial Basil Extract. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(14). [CrossRef]
- Suneetha M, Won SY, Zo SM, Han SS. Fungal Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Impregnated Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel as Wound-Dressing Agent. Gels. 2023;9(3). [CrossRef]
- Awasthi A, Gulati M, Kumar B, Kaur J, Vishwas S, Khursheed R, et al. Recent Progress in Development of Dressings Used for Diabetic Wounds with Special Emphasis on Scaffolds. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:1659338. [CrossRef]
- Wali N, Wajid N, Shabbir A, Ali F, Shamim S, Abbas N, et al. Safety Considerations for Lyophilized Human Amniotic Membrane Impregnated with Colistin and Silver Nanoparticles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Xu H, Hyun A, Mihala G, Rickard CM, Cooke ML, Lin F, et al. The effectiveness of dressings and securement devices to prevent central venous catheter-associated complications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2023;149:104620. [CrossRef]
- Cerchiara T, Abruzzo A, Nahui Palomino RA, Vitali B, De Rose R, Chidichimo G, et al. Spanish Broom (Spartium junceum L.) fibers impregnated with vancomycin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles as new antibacterial wound dressing: Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activity. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;99:105-12. [CrossRef]
- de Andrade AP, Arend L, Ribeiro VST, Tuon FF. Resistance of clinical and environmental Acinetobacter baumannii against quaternary ammonium. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2022;43(4):527-30. [CrossRef]
- Mendonca JR, Dantas LR, Tuon FF. Activity of multipurpose contact lens solutions against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens and Candida albicans biofilms. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2023;43(5):1092-9. [CrossRef]
- Pedroni MA, Ribeiro VST, Cieslinski J, Lopes APA, Kraft L, Suss PH, et al. Different concentrations of vancomycin with gentamicin loaded PMMA to inhibit biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus and their implications. J Orthop Sci. 2022;14(14):S0949-2658(22)00336-0. [CrossRef]
- Jiang N, Rao F, Xiao J, Yang J, Wang W, Li Z, et al. Evaluation of different surgical dressings in reducing postoperative surgical site infection of a closed wound: A network meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2020;82:24-9. [CrossRef]
- Mana TSC, Donskey C, Carty N, Perry L, Leaper D, Edmiston CE, Jr. Preliminary analysis of the antimicrobial activity of a postoperative wound dressing containing chlorhexidine gluconate against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vivo porcine incisional wound model. Am J Infect Control. 2019;47(9):1048-52. [CrossRef]
- Safdar N, O'Horo JC, Ghufran A, Bearden A, Didier ME, Chateau D, et al. Chlorhexidine-impregnated dressing for prevention of catheter-related bloodstream infection: a meta-analysis*. Crit Care Med. 2014;42(7):1703-13. [CrossRef]
- Buetti N, Rickard CM, Timsit JF. Catheter dressings. Intensive Care Med. 2022;48(8):1066-8. [CrossRef]
- Kalalinia F, Taherzadeh Z, Jirofti N, Amiri N, Foroghinia N, Beheshti M, et al. Evaluation of wound healing efficiency of vancomycin-loaded electrospun chitosan/poly ethylene oxide nanofibers in full thickness wound model of rat. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;177:100-10. [CrossRef]
| Impregnated dressing (n=12) | % | Control (n=9) | % | total | % | ||
| Aging (years/SD) | 42.91+/-17.46 | 34.77+/-9.41 | 39.42+/-14.84 | ||||
| Male sex | 11 | 91.66 | 8 | 88.88 | 19 | 90.47 | |
| Comobidities | 1 | 11.11 | 1 | 4.76 | |||
| SAH | 3 | 25 | 1 | 11.11 | 4 | 19.04 | |
| DM | 2 | 16.67 | 1 | 11.11 | 3 | 14.28 | |
| Smoking | 2 | 16.67 | 2 | 22.22 | 4 | 19.04 | |
| Trauma | |||||||
| Lower limbs | 9 | 75 | 6 | 66.67 | 15 | 71.42 | |
| Upper limbs | 3 | 25 | 3 | 33.33 | 6 | 28.57 | |
| Infection | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11.11 | 1 | 4.76 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





