1. Introduction
G-quadruplexes (G4s) are higher-order structures formed by Guanine-rich DNA or RNA sequences.
In silico analyses of the human genome have identified over 376 000 putative quadruplex sequences that harbor a specific consensus motif (G
≥3N
1‒7G
≥3N
1‒7G
≥3N
1‒7G
≥3) [
1,
2]. Similarly, extensive experimental evidence has demonstrated the existence of G4s in a variety of nucleic acid regions, including the telomeric regions of chromosomes, the promotor regions of proto-oncogenes, 5′- and 3′-UTRs of mRNAs, tRNA fragments, the telomerase RNA component (TERC), and telomeric repeat-containing RNA (TERRA) [
1,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. The four-stranded G4s form protrusions on the nucleic acid structures and play important roles in a series of key biological processes including DNA replication, transcription and translation, and telomere maintenance [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14].
Stabilization of G4s formed in the promotor regions of proto-oncogenes, such as
c-MYC, has attracted considerable interest as a promising anticancer strategy [
13,
15]. Human
c-MYC oncogene is located on chromosome 8 and involves in regulating gene expressions of ~15% of all genes through binding on enhancer boxes (E-boxes) [
16,
17]. A 27-mer G4-forming sequence (5′-TGGGGAGGGTGGGGAGGGTGG-GGAAGG-3′) has been identified in the nuclease hypersensitive element III1 of the
c-MYC promoter region. This sequence regulating up to 90% of
c-MYC transcription exists in equilibrium between its double-helical or single-stranded active form and the transcriptionally inactive G4 form [
18]. A stable G4 structure has been determined by using the four consecutive 3′ runs of guanines within the 27-mer sequence [
18]. The G4 has four loop isomers with dual G-to-T substitutions occurred at (14, 23), (11, 23), (14, 20), and (11, 20) positions, respectively [
19]. The major (14, 23) substituted loop isomer with the sequence of 5′-TGAGGGTGGGTAGGGTGGGTAA-3′ (
c-MYC14/23), forms the same structure as that of the WT
c-MYC G4 [
18,
19]. All of the loop isomers show the same parallel conformation and contribute to the silencing of
c-MYC in vivo [
19].
Small molecules that stabilize the
c-MYC G4 and down-regulate the expression of
c-MYC oncogene have been shown to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cell [
20,
21]. The most effective
c-MYC G4 stabilizers have been shown to be compounds capable of forming π–π stacking interactions with the exposed G-tetrad layers, including berberines [
22], carbazoles [
23], naphthopyrones [
24], porphyrins [
5], and quindolines molecules [
25]. These stabilizers are not selective enough for the
c-MYC G4, however, and this lack of specificity has hampered their development into clinical treatments. Novel molecules with higher binding specificity as well as bioavailability are urgently needed.
A series of crescent-shaped cell-penetrating thiazole peptides (
TH1,
TH2, and
TH3) have been found to act as stabilizers of G4 structures. Intriguingly, one of these peptides,
TH3, preferentially stabilizes the
c-MYC G4 structure over other promotor G4s and thus specifically inhibits the expression of the
c-MYC oncogene.
TH3 was found to exhibit antiproliferative activities by inducing S phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [
26] (
Figure 1,
Table S1). However, mechanism leading to the selective binding of the thiazole peptides remains obscure.
In the current study, in order to gain atomic-level insight into this selective binding, molecular docking and explicit-solvent molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed on the binding of the c-MYC G4-selective peptide TH3 and the less selective peptide TH1 to multiple promotor G4 structures, including those associated with the promotors of c-MYC, c-KIT1, c-KIT2, and BCL2. We further characterized key binding features by performing combined analyses with information from principal component analysis (PCA), analyses of non-covalent interaction (NCI) and intermolecular hydrogen bonds, molecular mechanics/generalized Born surface area (MM/GBSA) calculations, and per-nucleotide binding free energy decompositions.
2. Results and Discussion
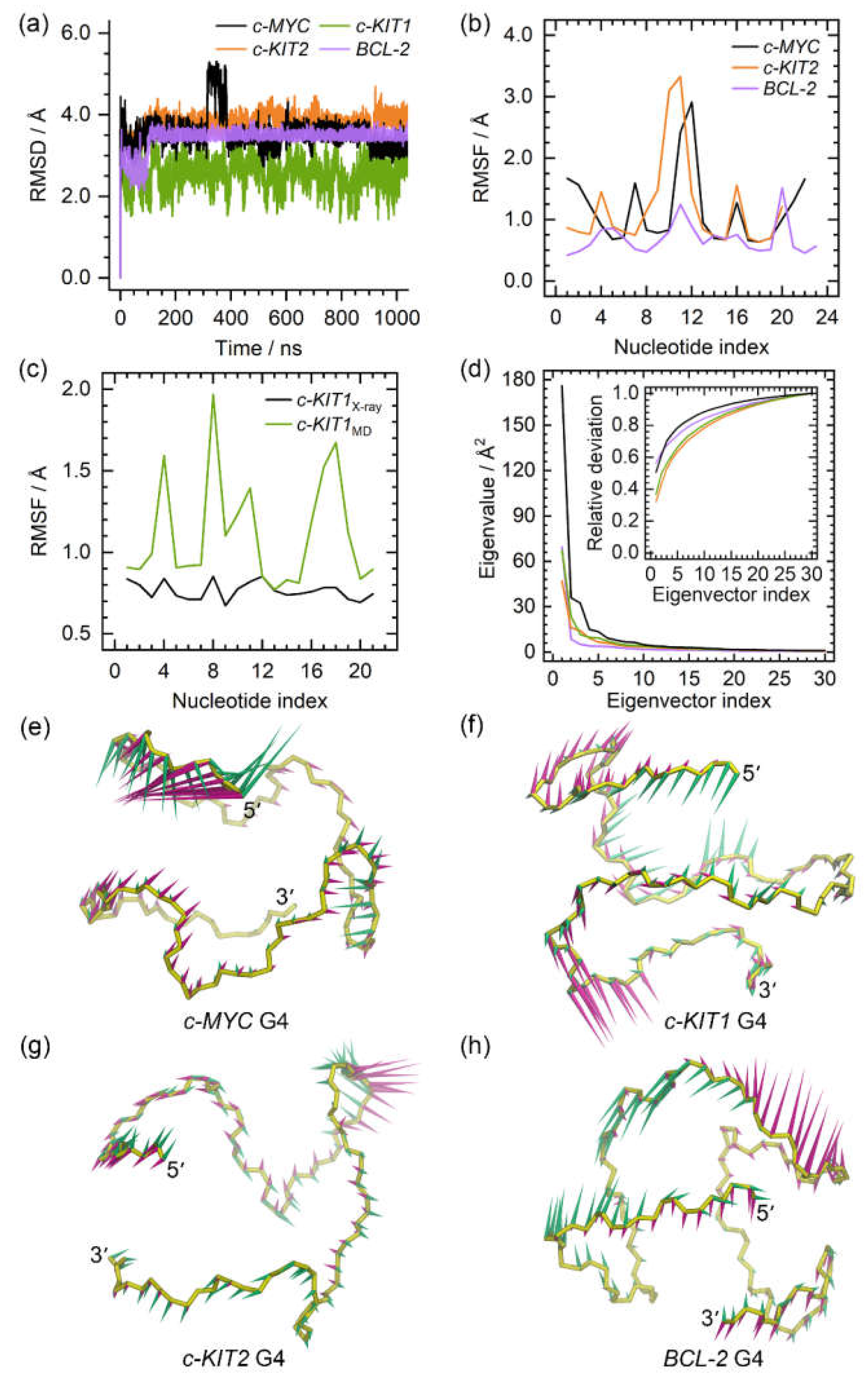
2.1. Dynamic Structural Feature of the Apo Promotor G4s
The dynamic structural features of the G4s from the promotor regions of
c-MYC,
c-KIT1,
c-KIT2, and
BCL2 were investigated in the absence of any binding factors. The features identified from MD simulations are summarized in
Figure 2. The converged root mean square deviation (RMSD) fluctuations of G4s indicated that equilibrium states were achieved (
Figure 2a). Conformationally flexible nucleotides were identified both by root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) analysis and by superimposing the equilibrated structures from MD simulations over the NMR or X-ray determined structures. In all of the G4 structures, the most flexible nucleotides were found to be located in the loop domains, as regional conformational variations were observed relative to original experimental structures (
Figure 2b,c, and
Figure 3). Specifically in the
c-MYC G4 structure, flexible nucleotides were also observed in the terminal domains (
Figure 2b and
Figure 3a). As expected, all of the guanine nucleotides that form the G-tetrad layers exhibited minimal conformational flexibility. In addition, our calculated RMSF profile for the
c-KIT G4 exhibited similar fluctuations to those determined experimentally, providing further validation of the current simulations.
PCA revealed that 42.99% to 63.13% of essential motions can be represented by the first two eigenvectors of the promotor G4s (
Figure 2d). Porcupine plots revealed that the first two eigenvectors mainly corresponded to the motions of the 5ʹ-termini of
c-MYC G4, the three loops of
c-KIT1 G4, and the second loops of the
c-KIT2 and
BCL2 G4s (
Figure 2e−h). The identified dynamic features of all G4s were consistent with the RMSF profiles and the conformational comparisons.
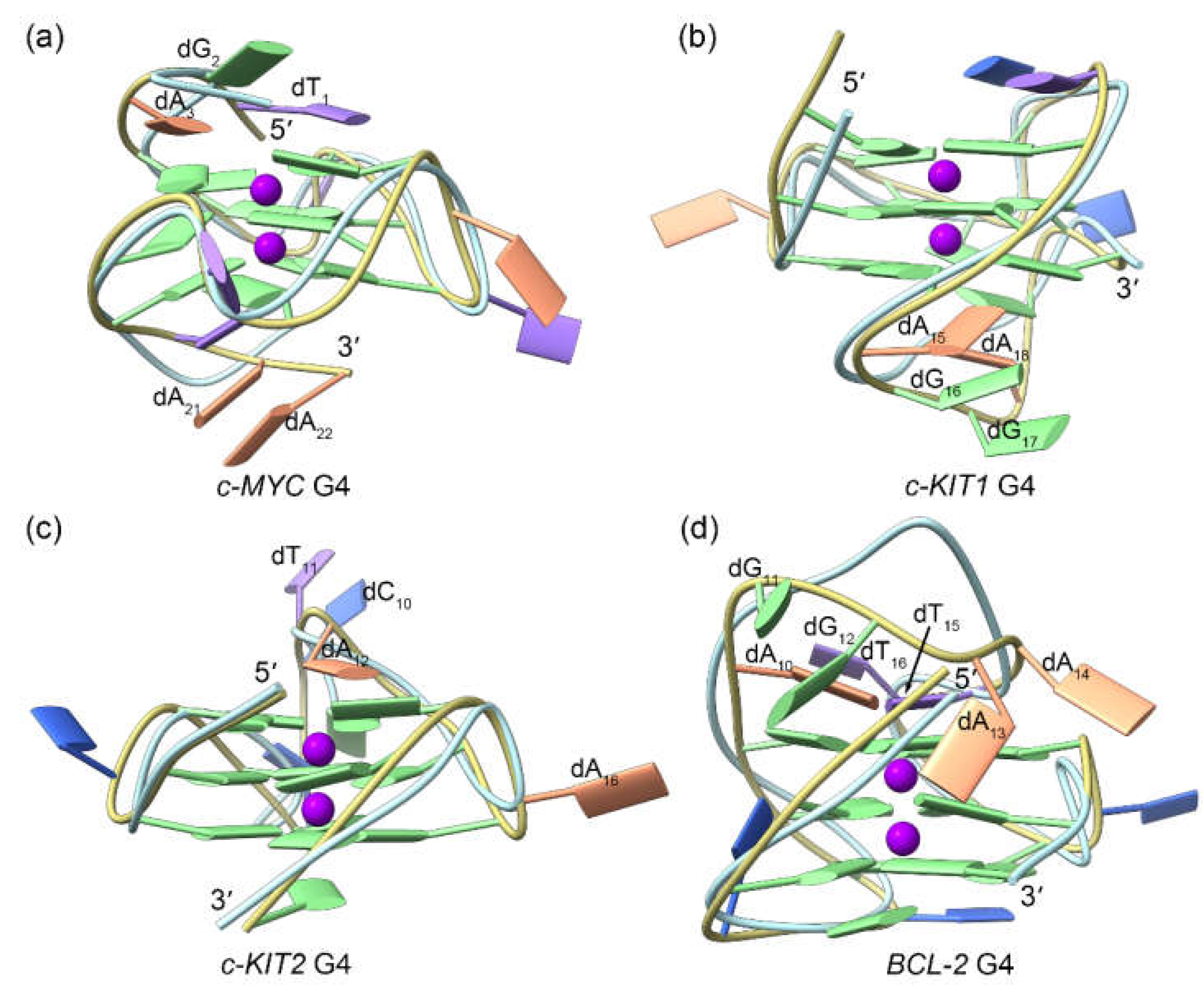
2.2. Docking-Derived Binding Mode of the Promotor G4s to the Peptides
The thiazole peptides
TH1 and
TH3 were individually docked to the MD-equilibrated structures of G4s. As shown in
Figure 4, in
c-MYC,
c-KIT1,
and c-KIT2 G4s, two binding sites were predicted for both
TH1 and
TH3, with both peptides mainly stacking to the exposed top and bottom G-tetrads of the
c-MYC and
c-KIT2 G4s while intercalating into the minor grooves of the
c-KIT1 G4 (
Figure 4a−c). Notably, the binding conformations of both peptides superimposed well in these three G4s. Conversely, due to the steric hindrance generated by the second loop to the top G-tetrad, only one molecule of peptide can bind to the
BCL2 G4, specifically at the bottom G-tetrad; in this case,
TH1 and
TH3 exhibited different orientations (
Figure 4d). Detailed information describing the interactions between G4s and the binding peptides, including intermolecular hydrogen bonds,π-π stacking interactions, and docking-evaluated binding affinities, are summarized in
Table 1.
In all four cases, TH3 was calculated to have a stronger binding affinity than was TH1; this finding is in agreement with the more potent antiproliferative activity of TH3. However, the affinity evaluation did not take into account the induced fit of the peptides when interacting with G4s. In addition, these evaluations do not deal with solvation effects precisely. Accordingly, c-KIT1 G4 was inaccurately predicted as the preferred binding target for these c-MYC-specific peptides. Therefore, we concluded that MD simulations are necessary for correctly identifying the binding feature of the G4‒peptide complexes and further evaluating the corresponding binding affinities.
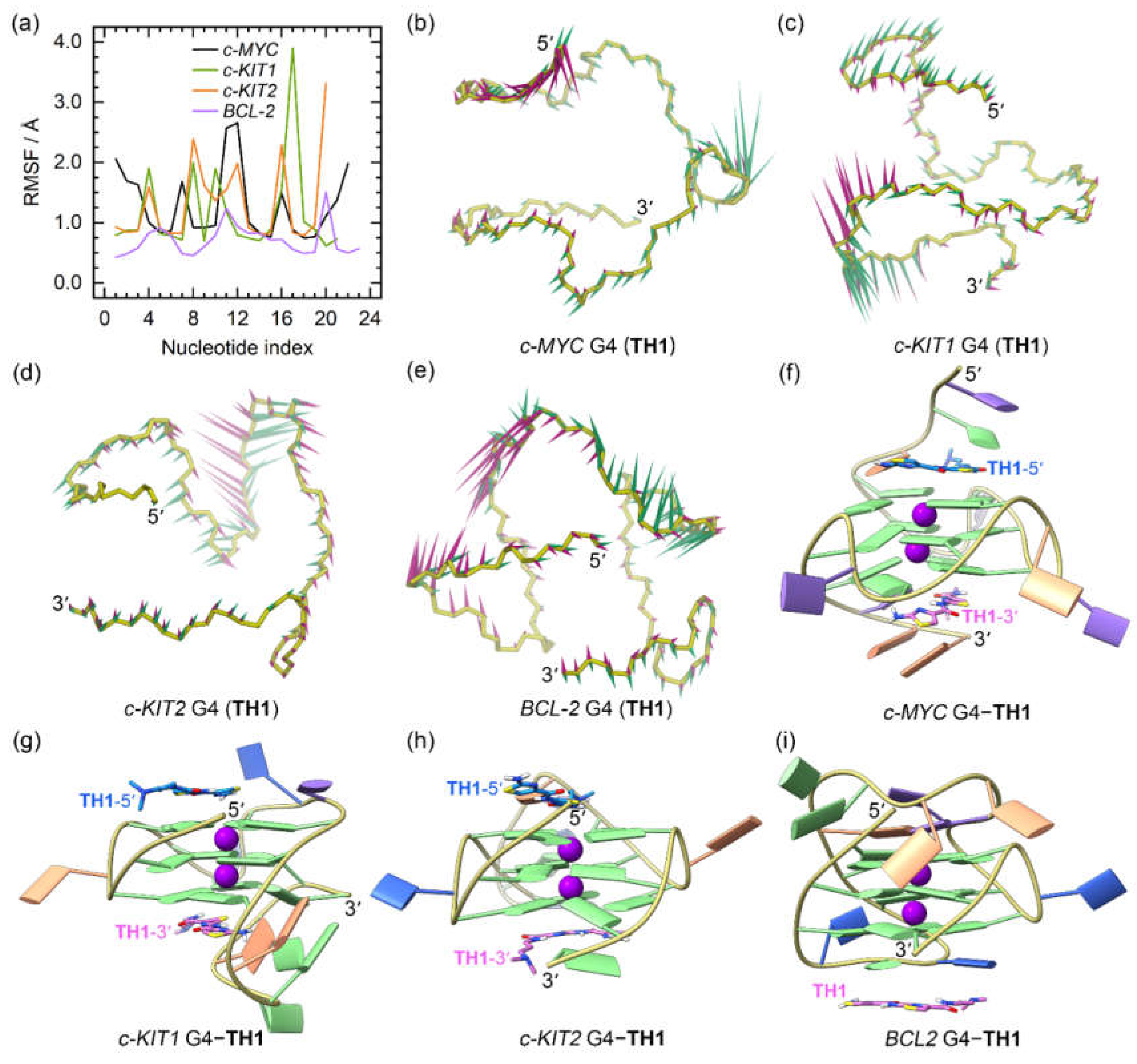
2.3. Dynamic Features of the G4‒TH1/TH3 Binding Complexes
The RMSD profiles of all the G4‒
TH1 binding complexes converged at the final MD stages (the last 300 ns), indicating that they had reached their equilibrium (
Figure S1a−d). The RMSF profiles of the
TH1-bound G4s exhibited similar patterns to those observed for apo G4s. However, the 5ʹ- and 3ʹ-termini of the
c-MYC G4 and the 3ʹ-termini of the
c-KIT2 G4 showed elevated flexibility when bound to
TH1, indicating conformational variations induced by
TH1 binding (
Figure 5a).
PCA demonstrated that 30.09% to 69.11% of the essential motions of the promotor G4s can be represented by the first two eigenvectors (
Figure S1d). Porcupine plots illustrated a correspondence of most of the motions to conformational fluctuations of the 5ʹ-termini and the second loop of the
c-MYC G4, the third loop of the
c-KIT1 G4, and the second loops of the
c-KIT2 and
BCL2 G4s (
Figure 5b−e). The equilibrated structures of the G4‒
TH1 complexes showed significant discrepancies in the
TH1 binding conformations relative to the conformations identified in docking-derived structures. As shown in
Figure 5f−i, both
TH1 molecules formed better stacking framework with the
c-MYC and
c-KIT2 G4s than that in the docking derived binding conformations. Surprisingly, the initial intercalation binding form was altered to the end-stacking mode in the
c-KIT1 G4‒
TH1 complex. In the
BCL2 G4‒
TH1 complex, instead of binding to the bottom G-tetrad,
TH1 stacked to the first loop nucleotides, demonstrating that this complex also went a drastic change in the mechanism of binding.
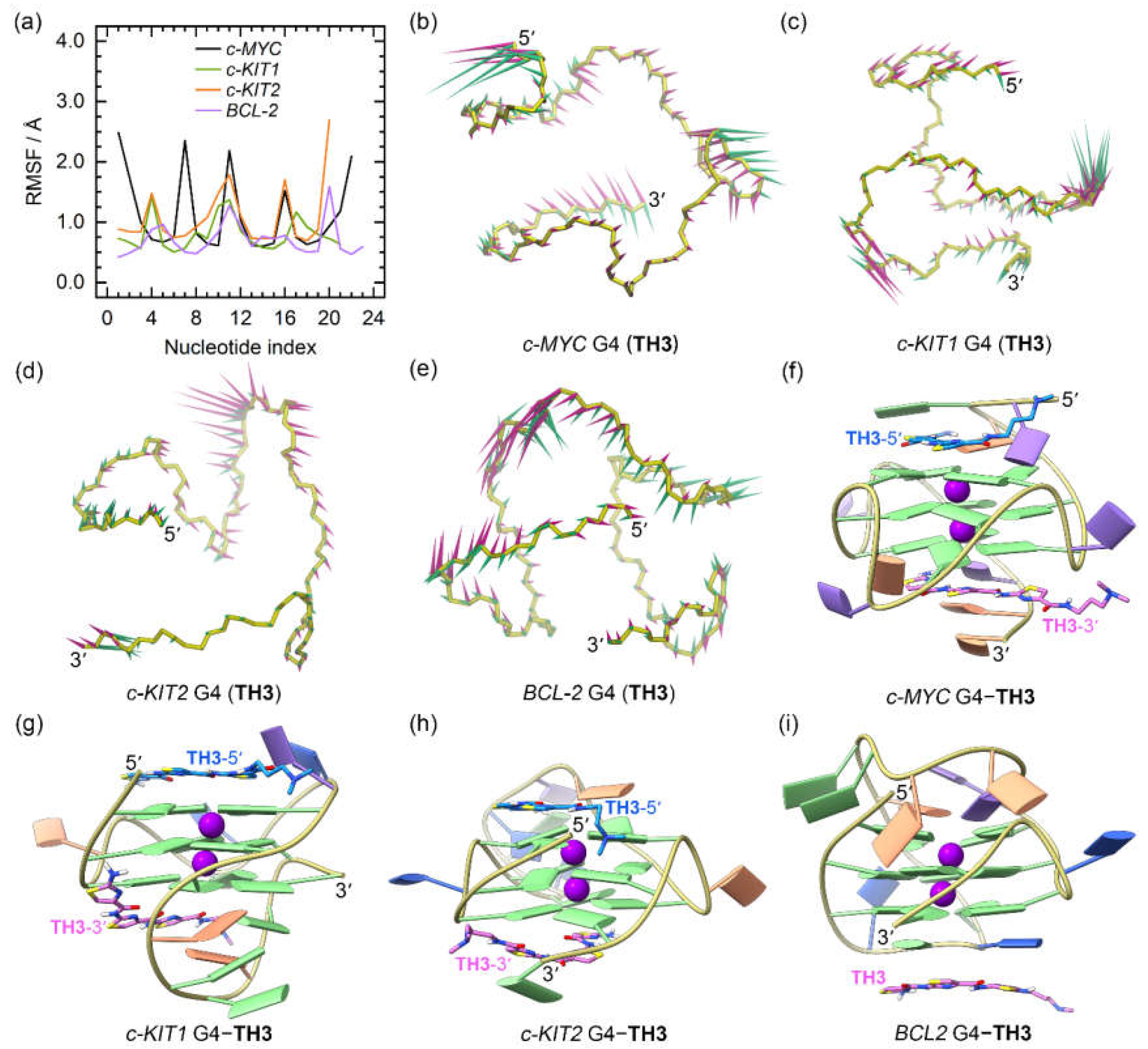
For the
TH3 bound promotor G4s, we observed more rapid convergences of the RMSD profiles with decreased values, as compared to similar analyses of the apo and the
TH1-bound structures (
Figure S2a−d). In addition, loop flexibilities were reduced as shown by the overall decreased RMSF profiles (
Figure 6a), consistent with an increased stabilizing effect of
TH3.
PCA demonstrated that 24.79% to 52.17% of the essential motions of the promotor G4s can be represented by the first two eigenvectors (
Figure S2e), which mainly corresponded to the essential motions of both the terminus and the second loop of the
c-MYC G4, the second and the third loops of the
c-KIT1 G4, and the second loops of the
c-KIT2 and
BCL2 G4s, with the motion levels apparently decreased relative to the
TH1-bound G4s (
Figure 6b−e). In the equilibrated structures, both
TH3 molecules were directly stacked to the exposed top and bottom G-tetrads of the
c-MYC,
c-KIT1, and
c-KIT2 G4s, with a single
TH3 molecule stacking to the first loop nucleotides of the
BCL2 G4 (
Figure 6f−i); these findings demonstrated that
TH1 and
TH3 share a similar mode of binding. The 2:1 binding stoichiometry of
TH3 and the
c-MYC G4 and the end-stacking binding mode were consistent with the findings from the fluorimetric titrations, NMR titrations, and the chemical shift perturbations analysis [
26].
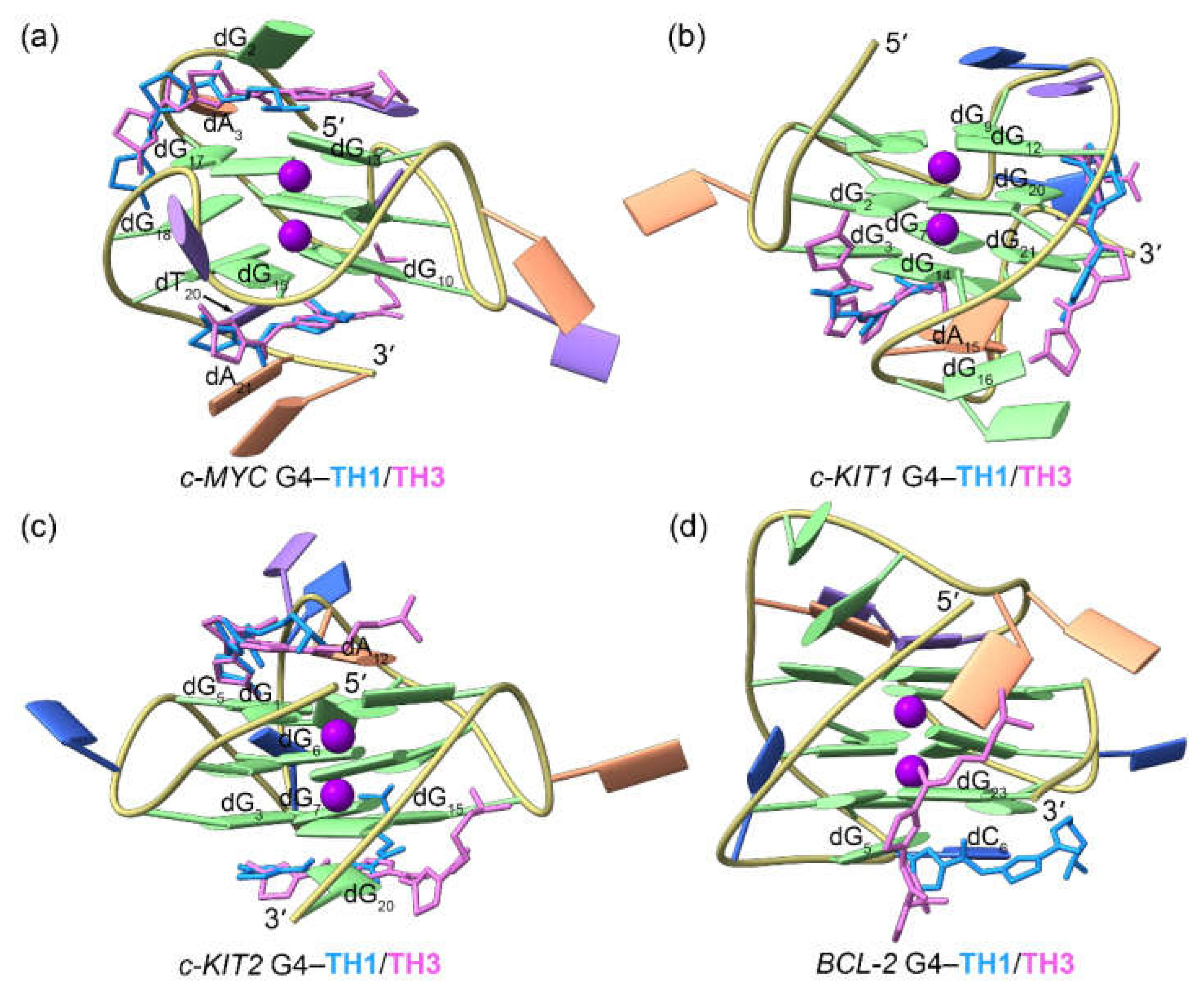
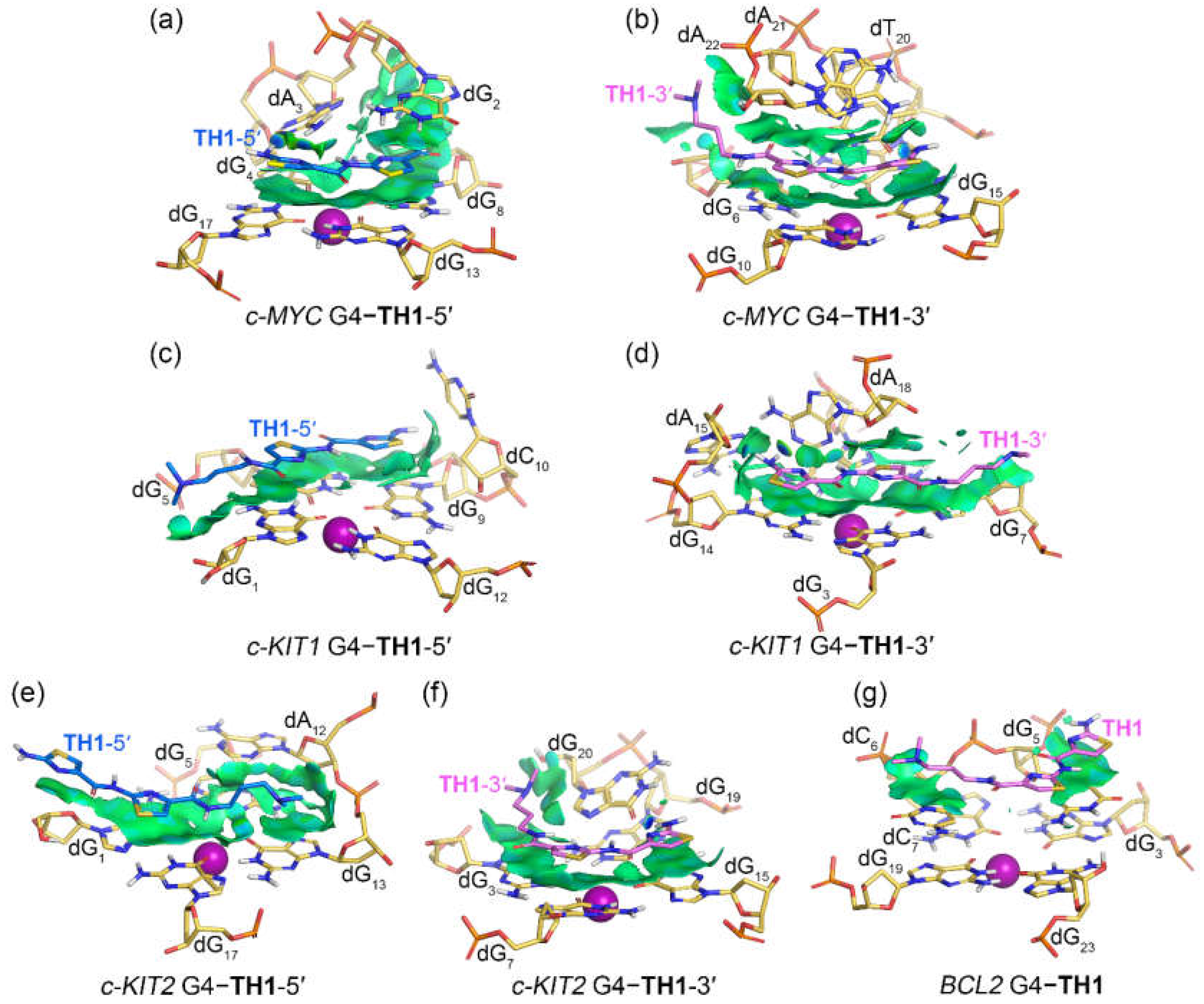
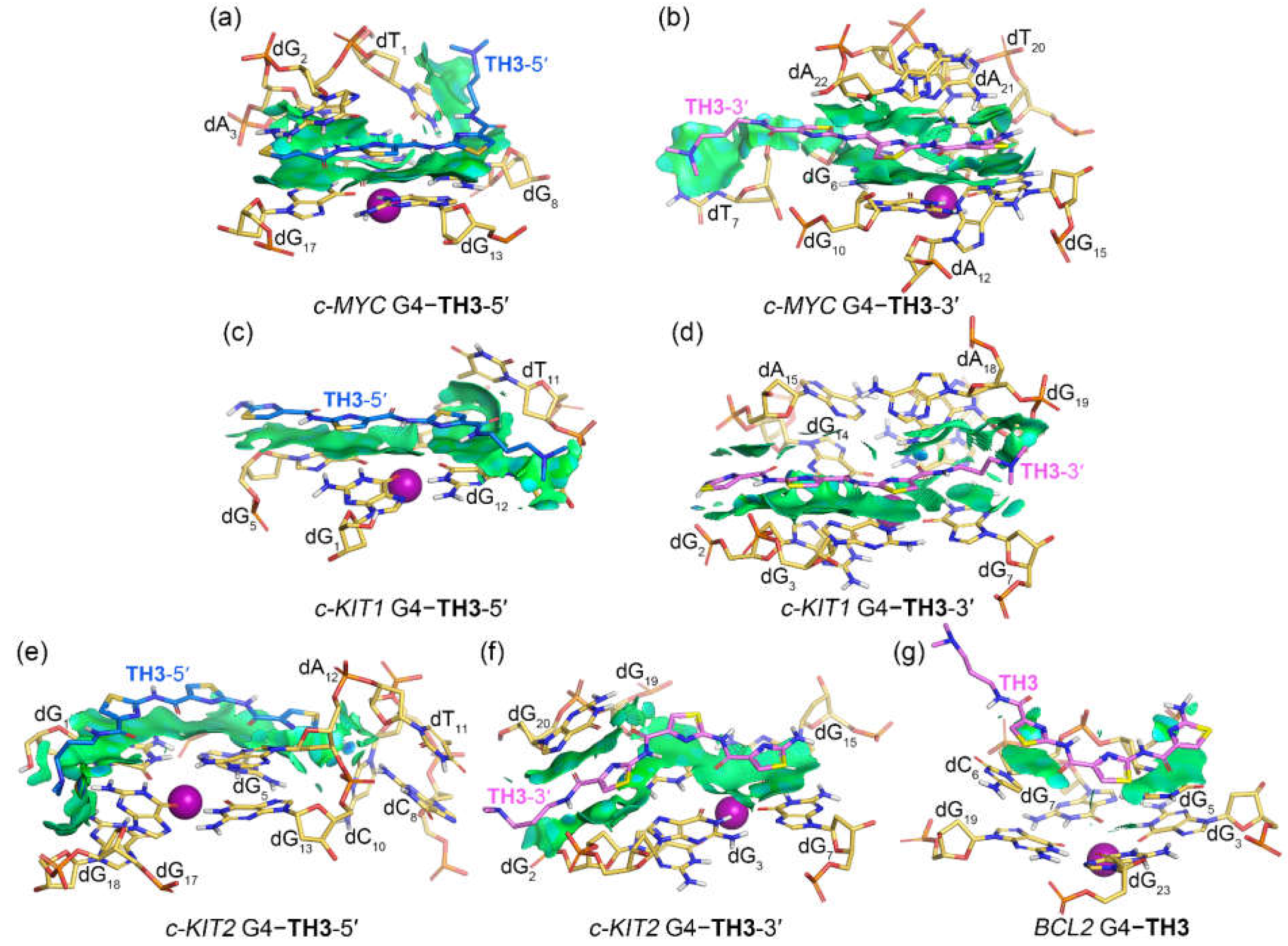
2.4. Noncovalent Interactions Mediating the Binding of G4s to TH1 and TH3
The noncovalent interactions between promotor G4s and peptides
TH1 and
TH3 were rendered as isosurfaces with NCIplot (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8). Both
TH1 and
TH3 that stacked over the top G-tetrad of the
c-MYC G4 formed extensive van der Waals (vdW) interactions with dG
8, dG
13, and dG
17.
TH1 exhibited additional vdW interactions with dG
2 and hydrogen bond interactions with dA
3, while
TH3 was found to form additional vdW interactions with dT
1 and dG2 and hydrogen bond interactions with dA
3 (
Figure 7a and
Figure 8a). For both peptides that stacked below the bottom G-tetrad of the
c-MYC G4, extensive vdW interactions with the G-tetrad nucleotides dG
6, dG
10, and dG
15 and the 3ʹ-terminal nucleotides dA
21 and dA
22 were found, with
TH3 showing additional vdW interactions with dT
7. The hydrogen bond interactions of both peptides with dT
20 are shown by the blue isosurfaces in
Figure 7b and
Figure 8b. It should be noted that both the top- and bottom-stacked
TH1 and
TH3 formed sandwich-like frameworks with the corresponding G-tetrad and terminal nucleotides, facilitating specific recognition and strong binding affinity.
In binding with the
c-KIT1 and
c-KIT2 G4s, both peptides mainly stacked to the top and bottom G-tetrads via vdW interactions without forming sandwich frameworks, except for the bottom G-tetrad stacked
TH3 that formed additional vdW interactions with dG
20 (
Figure 7c−f and
Figure 8c−f). Notably, the corresponding isosurfaces were more fragmented and less extensive compared to the isosurfaces observed in the
c-MYC G4
−TH1/TH3 complexes, indicating decreased binding specificity and affinity. For the binding with the
BCL2 G4, both
TH1 and
TH3 barely stacked to the first loop nucleotides dG
5 and dC
6 via vdW interactions, with the two localized isosurfaces correlating their weaker binding affinities.
2.5. Intermolecular and Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds
Intermolecular hydrogen bonds represent key contributions to biomolecular interactions. In the present context, we comprehensively searched for intermolecular hydrogen bonds using the criteria of bond length
3.5 Å and bond angle
120°. The typical requirement of hydrogen bond occupancy (HBO)
30% was not used so as to capture cases in which the binding peptides formed stable hydrogen bonds with G4s during late stages of MD simulations. All the intermolecular hydrogen bonds are listed in
Table 2, and the variations of distance between the hydrogen bond donor and acceptor atoms throughout the MD simulations are displayed in
Figure S3.
Overall, both
TH1 and
TH3 were found to more frequently play the role of hydrogen bond donor, while G4 nucleotides more frequently played the role of hydrogen bond acceptor. When peptides formed the sandwich-like complexes, such as
TH1 with the
c-MYC G4 and
TH3 with the
c-MYC and
c-KIT2 G4s, they showed greatly increased hydrogen bond interactions, both in the roles of hydrogen bond donors and receptors. This phenomenon was especially strong for the
c-MYC G4−
TH3 binding complex, in which all of the intermolecular hydrogen bonds exhibited over 30% occupancies, indicative of the high binding stability. Notably, an occupancy of over 30% does not necessarily mean that a hydrogen bond existed in the equilibrated structure, as relative positional changes of the ligand and receptor during late stages of the MD simulation may have led to loss of such a bond. For example, this phenomenon became apparent in analyses of the
BCL2 G4−
TH1 complex (
Figure S3j). Therefore, the distance analysis is essential to the accurate identification of hydrogen bond interactions.
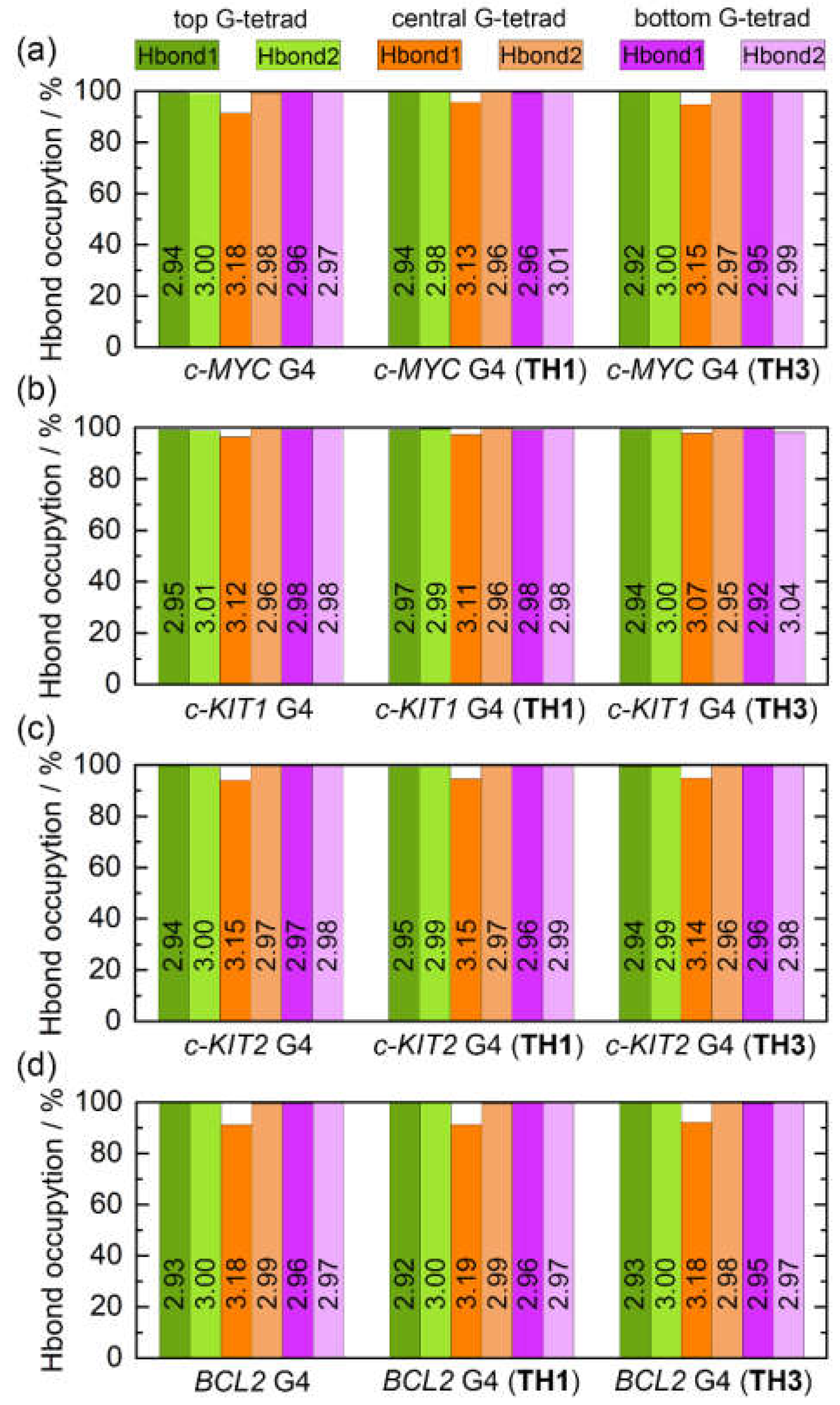
Intramolecular Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds that formed within the coplanar G-tetrad, including N1−H1···O6 (Hbond1) and N2−H21···N7 (Hbond2), were found to contribute strongly to the maintenance of the G4 structure. The state of these bonds thus may serve as a marker of G4 structural stability. The G-tetrad layer-averaged Hoogsteen HBOs and the average bond lengths for the apo and the peptide-bound G4s are summarized in
Figure 9. All of the Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds were highly stable throughout the MD simulations, as indicated by the HBOs and bond lengths (
Table S2). Interestingly, all of the exposed top and bottom G-tetrads exhibited maximum HBOs, whereas Hbond1 of the central G-tetrad exhibited decreased HBOs. Upon peptide binding, a general increasing trend of HBO was uncovered, especially for Hbond1 of the central G-tetrad. Specifically, the minimum HBOs of 91.54%, 96.45%, 94.05%, and 91.33% increased to 94.89%, 97.39%, 94.68%, and 91.36% for the
c-MYC,
c-KIT1,
c-KIT2, and BCL2 G4s, respectively (
Figure 9). Comparatively, both peptides showed stronger stabilizing effects toward the
c-MYC and
c-KIT1 G4s relative to the other promotor G4s.
2.6. Binding Free Energies between the Promotor G4s and TH1/TH3
With the ability to make good predictions on the hydration free energy for charged molecules when considering the relative solvation free energy, MM/GBSA calculations were performed to evaluate the binding affinities between the promotor G4s and
TH1 or
TH3. As summarized in
Table 3, electrostatic interactions (∆E
ele), vdW interactions (∆E
vdW), and non-polar solvation effects (∆G
SA) were all found to support the binding interactions, with vdW interactions contributing the most binding energy. In contrast, the contributions from the the polar solvation effects (∆G
GB) and entropies (T∆S) were unfavorable. In binding with every promotor G4, under the same binding position
TH3 consistently exhibited increased binding free energy relative to
TH1, consistent with the observed superiority of
TH3 in terms of antiproliferative effects.
The overall binding free energies of
TH3 followed an order of
c-MYC G4 (–71.2 kcal∙mol
-1)
c-KIT1 G4 (–53.1 kcal∙mol
-1)
c-KIT2 G4 (–45.0 kcal∙mol
-1)
BCL2 G4 (–7.1 kcal∙mol
-1), supporting its high binding specificity for the
c-MYC G4. In addition, the binding affinity order fully agrees with its stabilizing priorities accessed through FRET melting assays, providing validation of the power of MM/GBSA in ranking the relative binding affinities [
26].
TH1 showed a similar binding priority to the promotor G4s, namely
c-MYC G4 (–49.4 kcal∙mol
-1)
c-KIT1 G4 (–41.2 kcal∙mol
-1)
c-KIT2 G4 (–28.2 kcal∙mol
-1)
BCL2 G4 (–6.9 kcal∙mol
-1). Comparatively, these results demonstrate that the binding affinities were lower for
TH1; in addition,
TH3 exhibited more selective binding for the
c-MYC G4 relative to the
c-KIT1 G4 than did
TH1 (
Table 3).
It is worth noting that, the binding affinity between
TH3 and
BCL2 G4 appears to be underestimated, since the difference in melting temperatures (ΔT
m) determined in FRET melting assays is much smaller than the affinity difference. Specifically, the ΔT
m value determined for the
c-KIT2 G4 was 7.6 ℃, and the ΔT
m value determined for the
c-BCL2 G4 was 7.1 ℃. In comparison, the ΔT
m value determined for the
c-MYC4 G4 was 22.0 ℃. Similar findings also apply to
TH1. Considering the loop-stacking binding mode identified in the
BCL2 G4, we propose that under in vitro experimental conditions a second molecule of
BCL2 G4 may be recruited by the fully exposed
TH3 or
TH1, resulting in the formation of a higher-order binding complex mediated by either peptide. This complex likely promotes the binding affinity to a level similar to that observed for complexes of the peptides with
c-KIT2 G4 [
27].
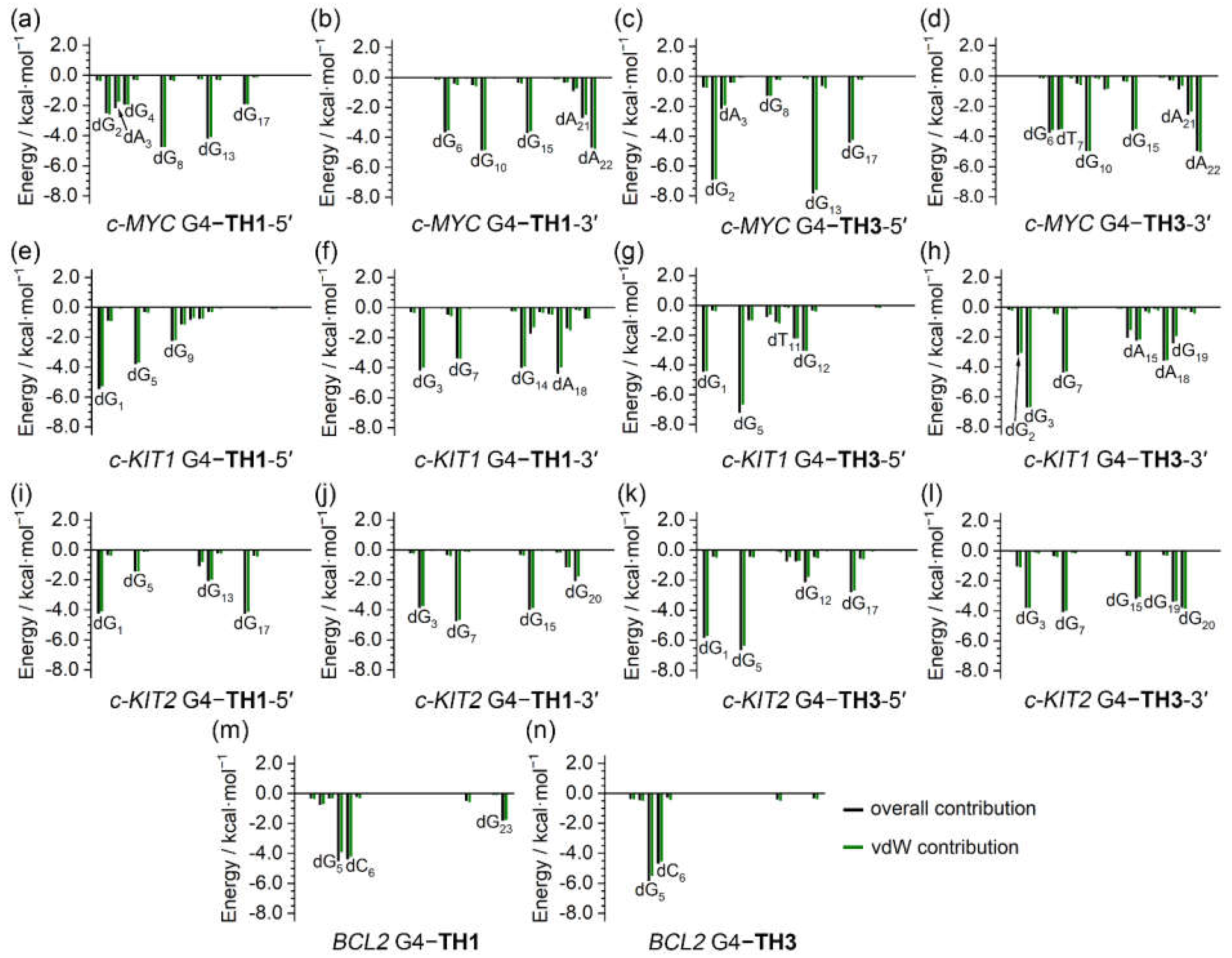
The binding free energies were further investigated to determine per-nucleotide contributions, under conditions in which entropic contributions were excluded. Intriguingly, the per-nucleotide free energy contributions calculated based on the trajectories of the last 200 ns of MD simulations were consistent with the information shown in the NCIplot, which was based on the MD-equilibrated structures. In addition, the per-nucleotide vdW contributions were essentially equal to the overall contributions in all cases, indicating the pivotal role of vdW interactions in promoting the binding of the G4s to the thiazole peptides (
Figure 10). It is noteworthy that the non-G-tetrad nucleotides that were involved in the sandwich-like binding frameworks, such as dG
2 and dA
22 of the
c-MYC G4, made significant contributions to the binding, providing valuable support for the specific binding with the
c-MYC G4.
3. Materials and Methods
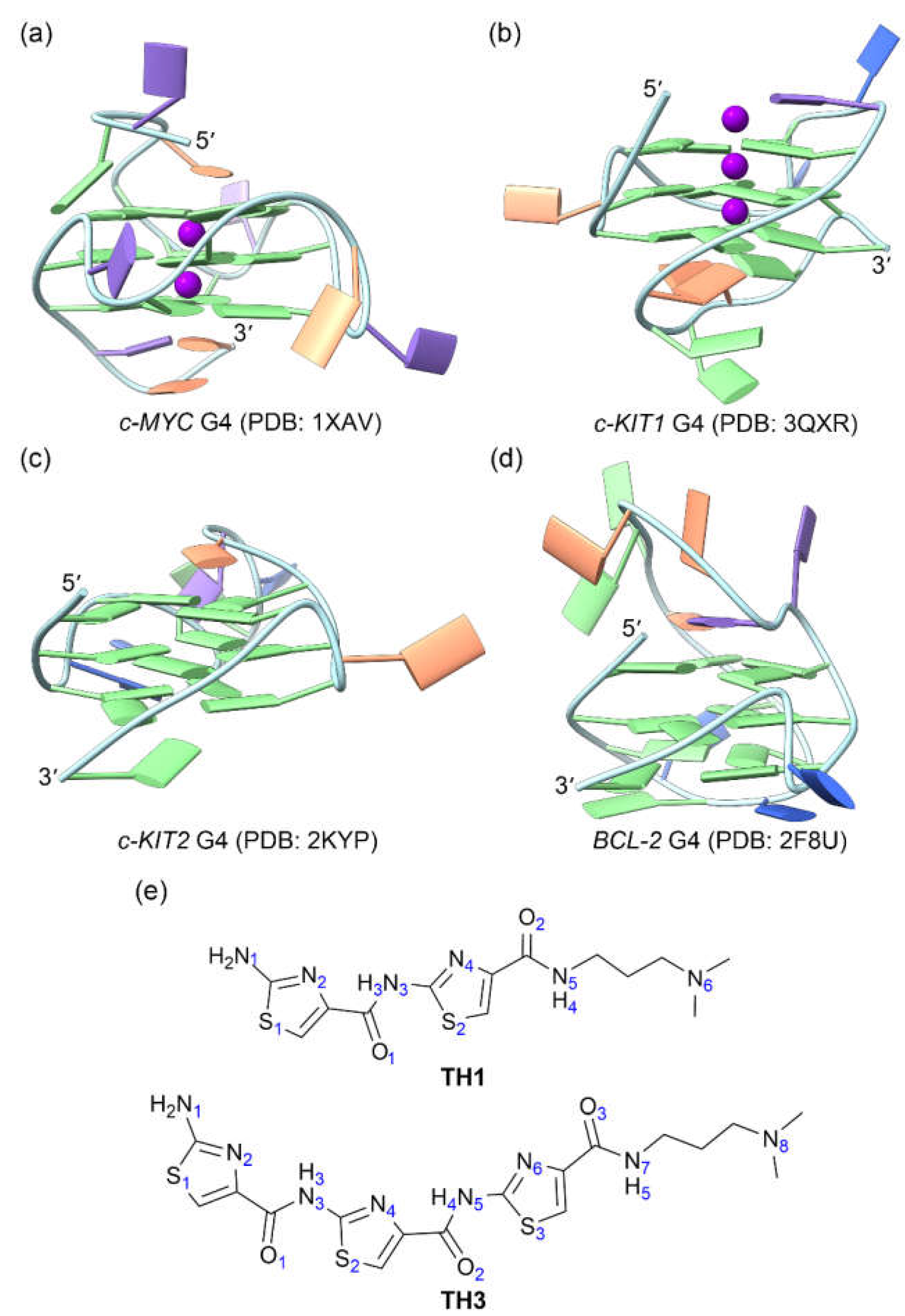
3.1. Data
The solution NMR structures of
c-MYC,
c-KIT2, and
BCL2 G4s together with the X-ray structure of
c-KIT1 G4 were retrieved from PDB data bank with the IDs of 1XAV [
18], 2KYP [
28], 2F8U [
29], and 3QXR [
30], respectively (
Figure 1a−1d). As the central potassium ions are necessary to G4 structure stability [
31,
32,
33], the models with two K
+ intercalated between the adjacent G-tetrads were generated for the
c-KIT2 and
BCL2 G4s by using the UCSF ChimeraX software (version 1.6.1) [
34]. To remain consistent with the experimental nucleotide sequence (
Table S1), the structures were edited by removing redundant terminal nucleotides. The K
+ located above the top G-tetrad in the
c-KIT1 G4 was removed due to its unstable binding [
32]. The structures of
TH1 and
TH3 were built with the GaussView software (version 6.0.16) (
Figure 1e) and were optimized through applying the density functional theory (DFT) at the level of B3LYP/6-31G(d) [
35,
36]. The atomic charges were further calculated for both compounds by using the restricted electrostatic potential (RESP) method with Gaussian 03 at the level of HF/6-31G(d) [
36].
3.2. Molecular docking
Molecular docking calculations were performed by using the AutoDock Vina 1.2.5 software [
37]. The receptors of G4s and the ligands of thiazole peptides were prepared with the AutoDockTools software (version 1.5.6) [
38]. The Gasteiger charges were computed for both receptors and ligands, with the non-polar hydrogen atoms merged. All the rotatable bonds of
TH1 and
TH3 were set flexible, while the G4s were set as rigid. In each docking calculation, a cubic box centered at the G4 geometric center comprising 90 × 90 × 90 grids with a grid spacing of 0.375 Å was used to define the possible binding region. The box was large enough to encompass every G4 structure so that no binding modes were excluded. All other parameters were set as the default. Five indepedent docking calculations with the exhaustiveness parameter of 25 were performed for each ligand in order to obtain the energetically favored and the most populated binding conformations [
39].
3.3. Molecular dynamics
Amber 22 software was used for MD simulations [
40,
41]. Each of the apo G4s and the docking-predicted binding complexes were placed at the center of a truncated octahedron box of TIP3P water molecules at a margin distance of 10.0 Å. Environmental K
+ ions were added to maintain electrical neutrality. The previously validated FF99SB force fields with parmbsc1 and χ
OL3+OL15 modifications were applied for G4 [
42,
43]. The calibrated parameter (radius 1.705 Å, well depth 0.1936829 kJ·mol
−1) and standard Amber parameter (radius 2.658 Å, well depth 0.00328 kJ·mol
−1) were used for the central and environmental K
+ ions, respectively [
27]. For
TH1 and
TH3, the second generation of general Amber force field (GAFF2) was applied [
42]. Each model was firstly energy minimized by 10000 steps steepest descent minimization with a harmonic constraint of 500 kcal mol
-1 Å
-2 imposed on the apo G4s or the complexes, followed by 10000 steps conjugated gradient minimization with no constraint. Then, the system was gradually heated from 0 to 300 K under the NVT ensemble for 500 ps, with a weak constraint of 10 kcal mol
-1 Å
-2 imposed on the apo G4s or the complexes. The model was subsequently subjected to an equilibrium simulation for 1 ns by removing all constraints. Finally, the production simulation for each model was conducted under the NPT ensemble, with the simulation time ranging from 1000 ns to 1200 ns. In all MD simulations, parameters were set according to our previous reports [
27,
44]. MD trajectories were recorded at an interval of 10 ps for the structural and energetic analyses.
3.4. Principal components analysis
PCA was performed to describe the essential motions of G4s by removing the overall translational and rotational movements from MD trajectories [
45]. Based on 10000 frames evenly extracted from the last 200 ns of MD trajectories, PCA of the G4 backbones was carried out for each model by using the CPPTRAJ module of AmberTools. The graphical summaries of essential motions along the first two eigenvectors were produced as porcupine plots by using the VMD software (version 1.9.4) [
46].
3.5. Noncovalent Interactions
NCIplot calculations were carried out with a step size of 0.10 to visualize the interacting regions between G4 and the binding peptides [
47]. The reduced gradients were rendered as an isosurface in VMD, using an isovalue of 0.3 au.
3.6. Binding free energy analysis
The binding free energies between G4 and the binding peptides were evaluated with the MM/GBSA calculations. 500 snapshots evenly extracted from the last 200 ns of MD trajectory were used for the calculation of each binding complex. The binding free energy value is equal to the free energy difference between the binding complex (G
complex) and the sum of receptor (G
rec) and ligand (G
lig) as follows:
Each item can be calculated with the equation:
where ∆E
MM is the molecular mechanical energy of the gas phase, ∆G
solv is the solvation free energy, and T∆S is the contribution of entropy. The ∆E
MM comprises contributions from electrostatic energy (∆E
ele), van der Waals (vdW) interaction energy (∆E
vdW), and internal strain energy (∆E
int) which includes bonds, angles, and dihedral energies that can be ignored in our systems:
The ∆G
solv contains contributions from a polar part (∆G
GB) and a non-polar (∆G
SA) part:
∆G
GB was estimated by the generalized Born (GB) model with the interior and exterior dielectric constants set to 4 and 80, respectively [
48,
49]. The nonpolar solvation terms were calculated according to the LCPO algorithm:
where γ and β were set to 0.0072 kcal·mol
-1·Å
-2 and 0, respectively [
50]. Therefore, the binding free energy was calculated as follows:
Based on the extracted snapshots, the entropic contribution (T∆S) was evaluated through normal mode analysis (NMA) [
27,
51].
4. Conclusions
While G4 structures represent attractive drug targets, their highly charged backbones and lack of specific binding pockets leads to critical issues regarding binding specificity. In the current work, the selective binding mechanism of the c-MYC G4-specific cell penetrating thiazole peptide TH3 was investigated through comparative studies with three other promotor G4s and with another thiazole peptide analogue. Our combined in-depth analyses revealed that in binding with the c-MYC G4 TH3 can induce the formation of structure-specific sandwich-like frameworks with both the top and bottom G-tetrads and the corresponding 5ʹ- and 3ʹ-capping nucleotides, leading to its superior binding affinity relative to the those of c-KIT1, c-KIT2, and BCL2 G4s. In addition, TH3 showed promoted specificity for c-MYC G4 relative to its analogue. Overall, our study provides pivotal insights into the selective binding mechanism of the thiazole peptide TH3, shedding new light on the design and development of drugs targeting the c-MYC G4 structure.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W. and J.L.; methodology, Y.C., Y.L. and Z.W; investigation, S.C., Q.S., Y.C. M.W. and Y.X.; formal analysis, S.C., Q.S., X.H. and H.W.; resources, L.W., J.L. and J.L; writing‒original draft preparation, S.C., Q.S. and Y.C.; writing‒review and editing, Z.W.; project administration, Z.W. and J.L; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY18H250002).
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Prevalence of quadruplexes in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 2908-2916. [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.K.; Johnston, M.; Neidle, S. Highly prevalent putative quadruplex sequence motifs in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 2901-2907. [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, J.; Kofod, M.; Nielsen, F.C. A guanosine quadruplex and two stable hairpins flank a major cleavage site in insulin-like growth factor II mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 1994, 22, 5709-5716. [CrossRef]
- Collie, G.W.; Haider, S.M.; Neidle, S.; Parkinson, G.N. A crystallographic and modelling study of a human telomeric RNA (TERRA) quadruplex. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, 5569-5580. [CrossRef]
- Seenisamy, J.; Rezler, E.M.; Powell, T.J.; Tye, D.; Gokhale, V.; Joshi, C.S.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Hurley, L.H. The dynamic character of the G-quadruplex element in the c-MYC promoter and modification by TMPyP4. J Am Chem Soc 2004, 126, 8702-8709. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Grand, C.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Hurley, L.H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99, 11593-11598. [CrossRef]
- Lattmann, S.; Stadler, M.B.; Vaughn, J.P.; Akman, S.A.; Nagamine, Y. The DEAH-box RNA helicase RHAU binds an intramolecular RNA G-quadruplex in TERC and associates with telomerase holoenzyme. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, 9390-9404. [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.L.; Armando, R.G.; Cerrudo, C.S.; Ghiringhelli, P.D.; Gomez, D.E. Telomerase as a Cancer Target. Development of new molecules. Curr Top Med Chem 2016, 16, 2432-2440. [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.T. Human telomeric G-quadruplex: structures of DNA and RNA sequences. Febs J 2010, 277, 1107-1117. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Brosh, R.M., Jr. G-quadruplex nucleic acids and human disease. Febs J 2010, 277, 3470-3488. [CrossRef]
- Eddy, J.; Maizels, N. Gene function correlates with potential for G4 DNA formation in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, 3887-3896. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.K.; Wu, Y.; Ou, T.M. RNA G-Quadruplex: The New Potential Targets for Therapy. Curr Top Med Chem 2015, 15, 1947-1956. [CrossRef]
- Buket, O.; Clement, L.; DanZhou, Y. DNA G-quadruplex and its potential as anticancer drug target. Sci China Chem 2014, 57, 1605-1614.
- Han, H.; Hurley, L.H. G-quadruplex DNA: a potential target for anti-cancer drug design. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2000, 21, 136-142. [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Hurley, L.H.; Neidle, S. Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: a novel anticancer strategy? Nat Rev Drug Discov 2011, 10, 261-275.
- Gearhart, J.; Pashos, E.E.; Prasad, M.K. Pluripotency redux--advances in stem-cell research. N Engl J Med 2007, 357, 1469-1472.
- Denis, N.; Kitzis, A.; Kruh, J.; Dautry, F.; Corcos, D. Stimulation of methotrexate resistance and dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification by c-myc. Oncogene 1991, 6, 1453-1457.
- Ambrus, A.; Chen, D.; Dai, J.; Jones, R.A.; Yang, D. Solution structure of the biologically relevant G-quadruplex element in the human c-MYC promoter. Implications for G-quadruplex stabilization. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 2048-2058. [CrossRef]
- Hatzakis, E.; Okamoto, K.; Yang, D. Thermodynamic stability and folding kinetics of the major G-quadruplex and its loop isomers formed in the nuclease hypersensitive element in the human c-Myc promoter: effect of loops and flanking segments on the stability of parallel-stranded intramolecular G-quadruplexes. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9152-9160. [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-H.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Yu, Z.-Y.; Hu, L.-N.; Ou, T.-M.; Chen, S.-B.; Huang, Z.-S.; Tan, J.-H. Discovery of a new four-leaf clover-like ligand as a potent c-MYC transcription inhibitor specifically targeting the promoter G-quadruplex. J Med Chem 2018, 61, 2447-2459. [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Guan, A.; Shen, G.; Tang, Y. Selective recognition of c-myc promoter G-quadruplex and down-regulation of oncogene c-myc transcription in human cancer cells by 3,8a-disubstituted indolizinone. Rsc Adv 2017, 7, 51965-51969. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ou, T.-M.; Hou, J.-Q.; Lu, Y.-J.; Tan, J.-H.; Gu, L.-Q.; Huang, Z.-S. 9-N-Substituted berberine derivatives: stabilization of G-quadruplex DNA and down-regulation of oncogene c-myc. Bioorg Med Chem 2008, 16, 7582-7591. [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Debnath, M.; Mandal, S.; Bessi, I.; Schwalbe, H.; Dash, J. A nucleus-imaging probe that selectively stabilizes a minor conformation of c-MYC G-quadruplex and down-regulates c-MYC transcription in human cancer cells. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 13183. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Chan, D. S.-H..; Yang, F.; Lam, H.-Y.; Yan, S.-C.; Che, C.-M.; Ma, D.-L.; Leung, C.-H. Identification of natural product fonsecin B as a stabilizing ligand of c-myc G-quadruplex DNA by high-throughput virtual screening. Chem Commun (Camb) 2010, 46, 4680-4682. [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Carver, M.; Hurley, L.H.; Yang, D. Solution structure of a 2:1 quindoline-c-MYC G-quadruplex: insights into G-quadruplex-interactive small molecule drug design. J Am Chem Soc 2011, 133, 17673-17680. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Debnath, M.; Müller, D.; Paul, R.; Das, T.; Bessi, I.; Schwalbe, H.; Dash, J. Cell penetrating thiazole peptides inhibit c-MYC expression via site-specific targeting of c-MYC G-quadruplex. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, 5355-5365. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Tian, Z.; Lou, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Hou, T.; Liu, J.-P. Insight derived from molecular dynamics simulation into the selectivity mechanism targeting c-MYC G-quadruplex. J Phys Chem B 2020, 124, 9773-9784. [CrossRef]
- Kuryavyi, V.; Phan, A.T.; Patel, D.J. Solution structures of all parallel-stranded monomeric and dimeric G-quadruplex scaffolds of the human c-kit2 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, 6757-6773. [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Chen, D.; Jones, R.A.; Hurley, L.H.; Yang, D. NMR solution structure of the major G-quadruplex structure formed in the human BCL2 promoter region. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, 5133-5144. [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Parkinson, G.N.; Reszka, A.P.; Neidle, S. Crystal structure of a c-kit promoter quadruplex reveals the structural role of metal ions and water molecules in maintaining loop conformation. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 4691-4700. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, R.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.-P. Molecular dynamics and principal components of potassium binding with human telomeric intra-molecular G-quadruplex. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 423-433. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.P. Characterization of potassium binding with human telomeres. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2015, 42, 902-909. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.P. Effects of the central potassium ions on the G-quadruplex and stabilizer binding. J Mol Graph Model 2017, 72, 168-177. [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci 2021, 30, 70-82. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Meng, T.; Qi, L.; Yan, H.; Wang, Z. Molecular insights into the selective binding mechanism targeting parallel human telomeric G-quadruplex. J Mol Graph Model 2022, 110, 108058. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, J.P. Molecular mechanism of anionic stabilizer for telomere G-quadruplex. Biophys Rep 2022, 8, 225-238.
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: new docking methods, expanded force field, and python bindings. J Chem Inf Model 2021, 61, 3891-3898. [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 2009, 30, 2785-2791. [CrossRef]
- Bhimaneni, S.; Kumar, A. Abscisic acid and aloe-emodin against NS2B-NS3A protease of Japanese encephalitis virus. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2022, 29, 8759-8766. [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M., Jr.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J Comput Chem 2005, 26, 1668-1688.
- Lee, T.S.; Allen, B.K.; Giese, T.J.; Guo, Z.; Li, P.; Lin, C.; McGee, T.D., Jr.; Pearlman, D.A.; Radak, B.K.; Tao, Y.; et al. Alchemical binding free energy calculations in AMBER20: advances and best practices for drug discovery. J Chem Inf Model 2020, 60, 5595-5623. [CrossRef]
- Machireddy, B.; Kalra, G.; Jonnalagadda, S.; Ramanujachary, K.; Wu, C. Probing the binding pathway of BRACO19 to a parallel-stranded human telomeric G-quadruplex using molecular dynamics binding simulation with AMBER DNA OL15 and ligand GAFF2 force fields. J Chem Inf Model 2017, 57, 2846-2864. [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Murillo, R.; Robertson, J.C.; Zgarbová, M.; Šponer, J.; Otyepka, M.; Jurečka, P.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd. Assessing the current state of Amber force field modifications for DNA. J Chem Theory Comput 2016, 12, 4114-4127. [CrossRef]
- Min, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Xin, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Fan, C.; Wang, Z.; et al. Crystal structure of an intramolecular mesaconyl-coenzyme a transferase from the 3-hydroxypropionic acid cycle of Roseiflexus castenholzii. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 923367. [CrossRef]
- Amadei, A.; Linssen, A.B.; Berendsen, H.J. Essential dynamics of proteins. Proteins 1993, 17, 412-425. [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 1996, 14, 33-38, 27-38. [CrossRef]
- Contreras-García, J.; Johnson, E.R.; Keinan, S.; Chaudret, R.; Piquemal, J.P.; Beratan, D.N.; Yang, W. NCIPLOT: a program for plotting non-covalent interaction regions. J Chem Theory Comput 2011, 7, 625-632.
- Onufriev, A.; Bashford, D.; Case, D.A. Exploring protein native states and large-scale conformational changes with a modified generalized born model. Proteins 2004, 55, 383-394. [CrossRef]
- Gilson, M.K.; Sharp, K.A.; Honig, B.H. Calculating the electrostatic potential of molecules in solution: Method and error assessment. J Comput Chem 1988, 9, 327-335. [CrossRef]
- Weiser, J.; Shenkin, P.S.; Still, W.C. Approximate atomic surfaces from linear combinations of pairwise overlaps (LCPO). J Comput Chem 1999, 20, 217-230.
- Hou, J.-Q.; Chen, S.-B.; Tan, J.-H.; Luo, H.-B.; Li, D.; Gu, L.-Q.; Huang, Z.-S. New insights from molecular dynamic simulation studies of the multiple binding modes of a ligand with G-quadruplex DNA. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2012, 26, 1355-1368. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The structures of oncogene promotor G4s and the cell-penetrating thiazole peptides. (a) c-MYC G4; (b) c-KIT1 G4; (c) c-KIT2 G4; (d) BCL2 G4; (e) peptides TH1 and TH3. In the G4 structures, the nucleotide bases of adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T) are colored orange, blue, green, and purple, respectively.
Figure 1.
The structures of oncogene promotor G4s and the cell-penetrating thiazole peptides. (a) c-MYC G4; (b) c-KIT1 G4; (c) c-KIT2 G4; (d) BCL2 G4; (e) peptides TH1 and TH3. In the G4 structures, the nucleotide bases of adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T) are colored orange, blue, green, and purple, respectively.
Figure 2.
The dynamic features of the apo promotor G4s. (a) the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) profiles of the apo G4s; (b) the root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF) profiles of the c-MYC, c-KIT2, and BCL2 G4s; (c) comparison of the RMSF profiles of the c-KIT1 G4 derived from X-ray experiment and MD simulation; (d) the eigenvalue profiles constructed by the first 30 eigenvectors of G4s, with the profile of the c-MYC, c-KIT1, c-KIT2, and BCL2 G4 colored black, green, orange, and purple, respectively; (e)−(f) porcupine plots of the dominant motions along the first (magenta) and the second (green) eigenvectors of the promotor G4s. The direction and size of the arrows represent the directions and extents of the principal motions of G4 backbone atoms along the corresponding eigenvector.
Figure 2.
The dynamic features of the apo promotor G4s. (a) the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) profiles of the apo G4s; (b) the root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF) profiles of the c-MYC, c-KIT2, and BCL2 G4s; (c) comparison of the RMSF profiles of the c-KIT1 G4 derived from X-ray experiment and MD simulation; (d) the eigenvalue profiles constructed by the first 30 eigenvectors of G4s, with the profile of the c-MYC, c-KIT1, c-KIT2, and BCL2 G4 colored black, green, orange, and purple, respectively; (e)−(f) porcupine plots of the dominant motions along the first (magenta) and the second (green) eigenvectors of the promotor G4s. The direction and size of the arrows represent the directions and extents of the principal motions of G4 backbone atoms along the corresponding eigenvector.
Figure 3.
Conformational comparison between the MD-equilibrated and the solution NMR/X-ray structures of the promotor G4s, with the ribbons colored khaki and light blue, respectively. For clarity, the bases in the solution NMR/X-ray structures are not shown.
Figure 3.
Conformational comparison between the MD-equilibrated and the solution NMR/X-ray structures of the promotor G4s, with the ribbons colored khaki and light blue, respectively. For clarity, the bases in the solution NMR/X-ray structures are not shown.
Figure 4.
Binding modes of the TH1/TH3 and the MD-equilibrated promotor G4s derived from molecular docking calculations. The TH1 and TH3 are colored royal blue and orchid, respectively.
Figure 4.
Binding modes of the TH1/TH3 and the MD-equilibrated promotor G4s derived from molecular docking calculations. The TH1 and TH3 are colored royal blue and orchid, respectively.
Figure 5.
The dynamic features of the promotor G4−TH1 binding complexes. (a) The RMSF profiles of the TH1 bound G4s; (b)−(e) porcupine plots of the dominant motions along the first (magenta) and the second (green) eigenvectors of the TH1 bound G4s; (f)−(i) the equilibrated conformations of the promotor G4−TH1 binding complexes. The TH1-5ʹ and TH1-3ʹ indicates the corresponding TH1 peptide stacks to the top and bottom G-tetrad, with the carbon atoms colored royal blue and orchid, respectively.
Figure 5.
The dynamic features of the promotor G4−TH1 binding complexes. (a) The RMSF profiles of the TH1 bound G4s; (b)−(e) porcupine plots of the dominant motions along the first (magenta) and the second (green) eigenvectors of the TH1 bound G4s; (f)−(i) the equilibrated conformations of the promotor G4−TH1 binding complexes. The TH1-5ʹ and TH1-3ʹ indicates the corresponding TH1 peptide stacks to the top and bottom G-tetrad, with the carbon atoms colored royal blue and orchid, respectively.
Figure 6.
The dynamic features of the promotor G4−TH3 binding complexes. (a) The RMSF profiles of the TH3 bound G4s; (b)−(e) porcupine plots of the dominant motions along the first (magenta) and the second (green) eigenvectors of the TH3 bound G4s; (f)−(i) the equilibrated conformations of the promotor G4−TH3 binding complexes. The TH3-5ʹ and TH3-3ʹ indicates the corresponding TH3 peptide stacks to the top and bottom G-tetrad, with the carbon atoms colored royal blue and orchid, respectively.
Figure 6.
The dynamic features of the promotor G4−TH3 binding complexes. (a) The RMSF profiles of the TH3 bound G4s; (b)−(e) porcupine plots of the dominant motions along the first (magenta) and the second (green) eigenvectors of the TH3 bound G4s; (f)−(i) the equilibrated conformations of the promotor G4−TH3 binding complexes. The TH3-5ʹ and TH3-3ʹ indicates the corresponding TH3 peptide stacks to the top and bottom G-tetrad, with the carbon atoms colored royal blue and orchid, respectively.
Figure 7.
Noncovalent interactions in the MD-equilibrated promotor G4‒TH1 binding complexes shown as NCI surfaces (isovalue of 0.3 au). The nucleotides that involve in the noncovalent interactions are shown in stick and are labeled.
Figure 7.
Noncovalent interactions in the MD-equilibrated promotor G4‒TH1 binding complexes shown as NCI surfaces (isovalue of 0.3 au). The nucleotides that involve in the noncovalent interactions are shown in stick and are labeled.
Figure 8.
Noncovalent interactions in the MD-equilibrated promotor G4‒TH3 binding complexes shown as NCI surfaces (isovalue of 0.3 au). The nucleotides that involve in the noncovalent interactions are shown in stick and are labeled.
Figure 8.
Noncovalent interactions in the MD-equilibrated promotor G4‒TH3 binding complexes shown as NCI surfaces (isovalue of 0.3 au). The nucleotides that involve in the noncovalent interactions are shown in stick and are labeled.
Figure 9.
Hoogsteen hydrogen-bond analysis. The hydrogen bonds of N1−H1···O6 and N2−H21···N7 are denoted as Hbond1 and Hbond2, respectively. The G-tetrad layer-averaged hydrogen-bond length are labeled on the corresponding columns.
Figure 9.
Hoogsteen hydrogen-bond analysis. The hydrogen bonds of N1−H1···O6 and N2−H21···N7 are denoted as Hbond1 and Hbond2, respectively. The G-tetrad layer-averaged hydrogen-bond length are labeled on the corresponding columns.
Figure 10.
Per-nucleotide decomposition of the binding free energy.
Figure 10.
Per-nucleotide decomposition of the binding free energy.
Table 1.
Molecular docking predicted interactions between peptides TH1/TH3 and the structures of c-MYC, c-KIT1, c-KIT2, and BCL-2 G4s.
Table 1.
Molecular docking predicted interactions between peptides TH1/TH3 and the structures of c-MYC, c-KIT1, c-KIT2, and BCL-2 G4s.
| G4 |
Peptidea
|
Hydrogen bond |
π-π stacking |
Affinityb
|
| c-MYC |
TH1-5′ |
dG2@N2−H22···O2, dG17@N2−H22···N2, |
dG17
|
−6.0 |
| dG18@N3···H1−N1 |
|
TH1-3′ |
dA21@N6−H62···O1, dG15@O3′···H1−N1 |
dG10, dG15
|
−7.4 |
|
TH3-5′ |
dA3@N6−H61···O2, dG13@N2−H21···O2,
dG17@N2−H22···N2, dG18@O4′···H1−N1 |
dG2, dG13, dG17
|
−7.5 |
|
TH3-3′ |
dG15@N2−H22···N2, dT20@N3−H3···O2, |
dG6, dG10, dG15
|
−8.0 |
| dA21@N6−H62···O1 |
| c-KIT1 |
TH1-5′ |
dG9@N2−H22···O2, dG20@N2−H22···N4
dG19@O6···H1−N1 |
|
−7.4 |
|
TH1-3′ |
dG19@N2−H22···O1 |
dG3
|
−7.5 |
|
TH3-5′ |
dG9@N2−H22···O3, dA15@N6−H62···N2,
dG16@O6···H2−N1, dG20@N2−H22···O2,
dG21@N2−H22···N4 |
|
−8.5 |
|
TH3-3′ |
dG2@OP2···H2−N1, dG3@OP2···H3−N3, |
dG3
|
−8.5 |
| dG14@N2−H22···O1, dG19@N2−H22···O3 |
| c-KIT2 |
TH1-5′ |
dG6@O4′···H2−N1, dA12@N6−H62···O2 |
|
−5.9 |
|
TH1-3′ |
dG20@N1−H1···O1, dG20@N2−H21···O1 |
dG3
|
−5.6 |
|
TH3-5′ |
dA12@N6−H61···N6, dA12@N6−H61···O3,
dA12@N6−H62···N6 |
dG1, dG5
|
−6.7 |
|
TH3-3′ |
dG20@O6···H4−N5, dG20@N1−H1···O1 |
dG7, dG15, dG20
|
−6.9 |
| BCL-2 |
TH1 |
dG5@O3′···H2−N1, dG5@N2−H22···O1,
dC6@N4−H42···N4 |
dG5, dC6
|
−6.3 |
| TH3 |
dG5@N2−H22···N2, dG5@O6···H4−N5,
dC6@O4′···H2−N1, dG23@N2−H22···N6,
dG23@N2−H22···O3 |
dG5
|
−6.8 |
Table 2.
Intermolecular hydrogen bonds formed between G4s and the binding thiazole peptides.1.
Table 2.
Intermolecular hydrogen bonds formed between G4s and the binding thiazole peptides.1.
| Model |
Acceptor |
Donor |
Ocpy. (%) |
Dist. (Å) |
Ang. (°) |
| c-MYC G4‒TH1
|
TH1-5′@N2 |
dA3@H61 |
dA3@N6 |
36.67 |
3.11 |
151.48 |
| dA3@N1 |
TH1-5′@H1 |
TH1-5′@N1 |
24.79 |
3.02 |
162.95 |
| dA3@N1 |
TH1-5′@H2 |
TH1-5′@N1 |
15.81 |
3.01 |
163.01 |
| dT20@O4 |
TH1-3′@H1 |
TH1-3′@N1 |
45.50 |
2.93 |
161.67 |
|
TH1-3′@N2 |
dA21@H62 |
dA21@N6 |
37.17 |
3.27 |
157.09 |
| dT20@O4 |
TH1-3′@H2 |
TH1-3′@N1 |
34.58 |
2.95 |
161.33 |
|
c-MYC G4‒TH3
|
TH3-5′@O2 |
dA3@H61 |
dA3@N6 |
43.21 |
3.07 |
149.62 |
|
TH3-3′@N2 |
dA21@H62 |
dA21@N6 |
32.24 |
3.27 |
157.13 |
| dT7@OP2 |
TH3-3′@H5 |
TH3-3′@N7 |
50.64 |
3.06 |
150.39 |
| dT20@O4 |
TH3-3′@H1 |
TH3-3′@N1 |
38.39 |
2.92 |
161.88 |
| dT20@O4 |
TH3-3′@H2 |
TH3-3′@N1 |
30.38 |
2.92 |
161.83 |
|
c-KIT1 G4‒TH1
|
dA15@O4′ |
TH1-3′@H1 |
TH1-3′@N1 |
35.48 |
3.00 |
155.56 |
| dA18@N1 |
TH1-3′@H2 |
TH1-3′@N1 |
34.73 |
3.05 |
157.50 |
|
c-KIT1 G4‒TH3
|
TH3-3′@O3 |
dG19@H22 |
dG19@N2 |
99.32 |
2.91 |
159.01 |
|
TH3-3′@O1 |
dG14@H22 |
dG14@N2 |
99.12 |
2.92 |
153.79 |
| dG3@OP2 |
TH3-3′@H3 |
TH3-3′@N3 |
77.86 |
3.05 |
138.60 |
|
c-KIT2 G4‒TH1
|
dG20@O6 |
TH1-3′@H1 |
TH1-3′@N1 |
39.50 |
2.93 |
161.40 |
| dG20@O6 |
TH1-3′@H2 |
TH1-3′@N1 |
31.78 |
2.93 |
161.42 |
|
c-KIT2 G4‒TH3
|
TH3-5′@O2 |
dA12@H62 |
dA12@N6 |
57.36 |
2.96 |
153.41 |
|
TH3-5′@O3 |
dA12@H61 |
dA12@N6 |
55.44 |
3.03 |
158.33 |
| dC10@O2 |
TH3-5′@H2 |
TH3-3′@N1 |
15.54 |
2.86 |
153.99 |
| dC10@O2 |
TH3-5′@H1 |
TH3-3′@N1 |
14.73 |
2.86 |
152.17 |
| dG3@OP2 |
TH3-3′@H5 |
TH3-3′@N7 |
34.43 |
3.02 |
153.99 |
|
BCL2 G4‒TH1
|
TH1@N1 |
dG5@H22 |
dG5@N2 |
45.99 |
3.09 |
156.96 |
| dC6@O5′ |
TH1@H3 |
TH1@N3 |
42.05 |
3.19 |
149.52 |
|
BCL2 G4‒TH3
|
dG5@OP2 |
TH3@H1 |
TH3@N1 |
17.04 |
2.91 |
159.19 |
| |
dG5@OP2 |
TH3@H2 |
TH3@N1 |
16.19 |
2.91 |
158.99 |
Table 3.
Binding free energies between G4s and the binding thiazole peptides.
Table 3.
Binding free energies between G4s and the binding thiazole peptides.
| G4 |
Peptide |
Energy components1
|
| ΔEele
|
ΔEvdW
|
ΔGGB
|
ΔGSA
|
ΔH |
-TΔS |
ΔGbind
|
| c-MYC |
TH1-5′ |
−2.9 ± 1.4 |
−39.0 ± 3.5 |
5.7 ± 1.1 |
−4.3 ± 0.3 |
−40.5 ± 3.5 |
20.0 ± 8.9 |
−20.5 |
|
TH1-3′ |
−1.2 ± 1.6 |
−45.5 ± 3.7 |
4.9 ± 1.2 |
−5.4 ± 0.3 |
−47.2 ± 3.7 |
18.3 ± 9.0 |
−28.9 |
|
TH3-5′ |
−2.5 ± 1.6 |
−53.9 ± 4.5 |
6.6 ± 1.4 |
−5.6 ± 0.3 |
−55.4 ± 4.3 |
20.5 ± 9.2 |
−34.9 |
|
TH3-3′ |
−4.0 ± 2.0 |
−54.0 ± 4.2 |
7.8 ± 1.6 |
−6.3 ± 0.4 |
−56.5 ± 4.4 |
20.2 ± 9.0 |
−36.3 |
| c-KIT1 |
TH1-5′ |
−1.9 ± 1.7 |
−32.3 ± 4.2 |
4.8 ± 1.6 |
−3.6 ± 0.4 |
−33.0 ± 4.2 |
17.2 ± 8.8 |
−15.8 |
|
TH1-3′ |
−7.0 ± 1.1 |
−43.7 ± 3.7 |
9.4 ± 0.9 |
−4.4 ± 0.3 |
−45.8 ± 3.6 |
20.4 ± 9.3 |
−25.4 |
|
TH3-5′ |
−1.4 ± 2.9 |
−42.4 ± 3.5 |
2.5 ± 2.4 |
−4.4 ± 0.4 |
−43.0 ± 3.6 |
21.0 ± 8.9 |
−22.0 |
|
TH3-3′ |
−4.2 ± 2.0 |
−52.0 ± 3.2 |
7.5 ± 1.5 |
−5.8 ± 0.2 |
−54.5 ± 3.1 |
23.4 ± 8.9 |
−31.1 |
| c-KIT2 |
TH1-5′ |
−2.0 ± 1.7 |
−28.6 ± 3.6 |
4.5 ± 1.4 |
−3.3 ± 0.4 |
−29.3 ± 3.6 |
18.4 ± 8.9 |
−10.9 |
|
TH1-3′ |
−0.6 ± 1.4 |
−34.6 ± 2.8 |
3.3 ± 1.2 |
−4.1 ± 0.3 |
−35.9 ± 2.8 |
18.6 ± 9.1 |
−17.3 |
|
TH3-5′ |
−3.2 ± 3.3 |
−41.7 ± 3.6 |
6.2 ± 3.0 |
−4.7 ± 0.4 |
−43.5 ± 4.0 |
21.1 ± 8.8 |
−22.4 |
|
TH3-3′ |
−2.1 ± 2.9 |
−42.7 ± 6.2 |
6.5 ± 3.0 |
−4.7 ± 1.0 |
−43.1 ± 5.2 |
20.5 ± 9.4 |
−22.6 |
| BCL-2 |
TH1 |
−9.0 ± 4.0 |
−22.4 ± 3.9 |
9.1 ± 3.3 |
−2.3 ± 0.5 |
−24.6 ± 4.5 |
17.7 ± 8.7 |
−6.9 |
| TH3 |
−1.8 ± 2.5 |
−25.6 ± 3.2 |
4.6 ± 2.2 |
−3.4 ± 0.4 |
−26.2 ± 3.4 |
19.1 ± 9.2 |
−7.1 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).